- 1School of Information Engineering (School of Big Data), Xuzhou University of Technology, Xuzhou, China
- 2School of Medical Imaging, Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou, China
Multimodal medical Image fusion (MMIF) has received widespread attention due to its promising application in clinical diagnostics and treatment. Due to the inherent limitations of fusion algorithms, the quality of obtained medical fused images (MFI) varies significantly. An objective evaluation of MMIF can quantify the visual quality differences in fused images and facilitate the rapid development of advanced MMIF techniques, thereby enhancing fused image quality. However, rare research has been dedicated to the MMIF objective evaluation. In this study, we present a multi-scale aware attention network for MMIF quality evaluation. Specifically, we employ a Multi-scale Transform structure that simultaneously processes these multi-scale images using an ImageNet pre-trained ResNet34. Subsequently, we incorporate an online class activation mapping mechanism to focus visual attention on the lesion region, enhancing representative discrepancy features closely associated with MFI quality. Finally, we aggregate these enhanced features and map them to the quality difference. Due to the lack of dataset for the objective evaluation task, we collect 129 pairs of source images from public datasets, namely, the Whole Brain Atlas, and construct a MMIF quality database containing 1,290 medical fused images generated using MMIF algorithms. Each fused image was annotated with a subjective quality score by experienced radiologists. Experimental results demonstrate that our method produces a satisfactory consistent with subjective perception, superior to the state-of-the-art quality evaluation methods. The source images dataset is publicly available at: http://www.med.harvard.edu/AANLIB/home.html.
1 Introduction
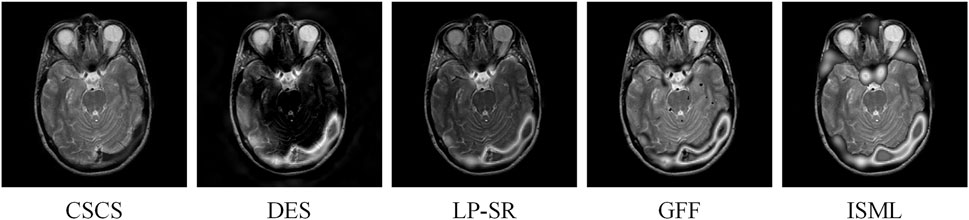
Multimodal medical image fusion (MMIF) is increasingly common in clinical diagnostics. MMIF algorithms aim to generate high-quality fused images from multimodal input images [1–3]. However, most existing MMIF algorithms struggle to achieve optimal fusion due to inherent model limitations. Even worse, instead of promoting, fused image quality declined during the fusion process, even increasing the risk of misdiagnosis. Figure 1 illustrates fusion results from different MMIF algorithms, where the first four images exhibit lower quality compared to the last one, with the first image being the worst. As observed, low-quality fused images fail to convey the critical information of the original images, contradicting the very purpose of image fusion. Conversely, high-quality fused images provide clinicians with more reliable information, enhancing diagnostic confidence and decision-making. Hence, it is natural to consider how to achieve a fairer evaluation of these fused images.
In previous work, researchers generally compare the fusion results using both subjective and objective assessments [4–8]. Subjective quality evaluation refers to the visual judgment of image quality by human observers based on perceptual impressions, typically using scoring or ranking methods to quantify visual performance [9]. While this approach closely reflects clinical perception, it is labor-intensive and not scalable for large volumes of medical data. To address this limitation, objective quality assessment methods have been extensively developed to automatically evaluate fused images through computational models and algorithms [10–16]. These methods avoid human bias and enable large-scale assessment by quantifying image quality using well-defined criteria. Generally, objective evaluation methods can be classified into full-reference, reduced-reference, and no-reference approaches [17–19]. Since no ground-truth fused images exist, the no-reference approach is the most suitable for this task. This approach is not only more theoretically realistic but also exhibits higher applicability in clinical settings, as physicians are the ultimate beneficiaries of quality evaluation, the results of image quality assessment can vary depending on the scenario (e.g., the presence or absence of lesion regions in the image), leading to potential instability. No reference evaluation algorithms are roughly divided into hand-crafted metrics and deep learning-based metrics. For instance, Yang et al. [11] gauged structural similarity information of fused images. Qu et al. [15] used mutual information to measure fused images. Tang et al. [17] adopted non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) and pulse coupled neural network (PCNN) for medical fusion image evaluation. However, these studies are limited in their ability to effectively capture hand-crafted features. To alleviate this limitation, deep learning-based metrics have been reported for MMIF quality assessment. Tian et al. [20] exploited a generative adversarial network (GAN) to implement objective evaluation of MMFI. However, such models often face criticism for being “black-box” approaches, making it difficult to gain sufficient trust from radiologists.
In this study, we construct a medical image fusion quality dataset and utilize it to evaluate the performance of the proposed MS-ANN model for MMIF quality assessment. We first conduct multi-scale transform to capture different scale information of fused images. Meanwhile, input these multi-scale images to fine-tuned ImageNet pre-trained ResNet34. Then, we utilize an online class activation mapping mechanism (CAM) to capture visualization attention to the lesion regions, such operation is highly related to radiologists making decisions. Finally, by aggregating the multi-scale streams to complement each other, we obtain richer, enhanced discrepancy features that are subsequently mapped to the quality differences of the fused images.
The key contributions of the proposed MS-AAN are summarized as follows.
(1) Given the limited research on objective evaluation for MMIF, we propose a no-reference fused image quality assessment method based on a multi-scale aware attention network, termed MS-AAN. MS-AAN not only automatically predicts the quality of fused images but also enhances model interpretability.
(2) To characterize quality discrepancies in fused images, we capture and aggregate multi-scale features by utilizing multi-scale transformer and ImageNet pre-trained ResNet34. Such multi-scale streams complement each other and can obtain plentiful details of quality discrepancy-related cues.
(3) To locate lesion clews and enhance feature representation, we propose a CAM attention network, which can pay attention to the lesion regions via generating localization heat maps. It is highly related to radiologists making decisions. In this way, our MS-AAN earns the trust of radiologists.
2 Related work
2.1 Objective evaluation of multimodal medical image fusion
Multimodal medical image fusion (MMIF) plays an important role in clinical diagnostics and treatment. For radiologists, high-quality fused images can enhance diagnostic confidence and aid in follow-up treatment planning. Plenty of MMIF quality evaluation algorithms have been reported. For instance, Xydeas et al. [10] used gradient information from source images to evaluate fused images. Yang et al. [11] gauged structure similarity information of fused images. Li et al. [12] adopted edge information from the source image to the fused image for objective assessment. Zhao et al. [13] proposed phase congruency to evaluate fused images. Zheng et al. [14] designed perceptual evaluation via a ratio of spatial frequency error. Qu et al. [15] used mutual information to measure fused images. Liu et al. [16] adopted entropy for fused image objective assessment. Tang et al. [17] adopted non-subsampled contourlet transform and pulse coupled neural network for medical fusion image evaluation. However, these handcrafted methods often lack the ability to effectively capture complex representation features. As a result, deep learning-based metrics for MMIF evaluation have attracted much attention. Tian et al. [20] introduced a generative adversarial network to implement MMIF evaluation. Wang et al. [21] proposed a no-reference image quality assessment framework that incorporates an adaptive graph attention module to enhance both local and contextual information. Liu et al. [9] developed a CNN-based multi-focus image fusion quality assessment model using hierarchical semantic features to better capture focus-level details. Additionally, Yue et al. [18] introduced a pyramid-based framework for assessing the quality of retinal images, which improves robustness to various types of distortions commonly found in clinical data. However, such studies often face challenges in addressing the “black-box” nature of the model. This limits the ability to sufficient trust from radiologists. Despite the growing interest in MMIF evaluation, few studies have focused on objective evaluation, and there is a lack of high-quality fused images. As a result, no reference metric demonstrates significant practical value for this task.
2.2 Multi-scale aware network
In recent years, multi-scale transform has achieved progress in the field of multimodal medical image fusion [22, 23], especially non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) has displayed tremendous results [24, 25]. Specifically, Huang et al. [25] proposed SPECT and CT image fusion based on NSCT and PCNN. Yin et al. [24] used NSCT and PCNN for medical image fusion. Tang et al. [17] proposed a medical fusion image evaluation method based on NSCT and PCNN. Therefore, the combination of NSCT and PCNN has been proven to be a highly effective strategy for MMIF and MMIF quality evaluation. Inspired by this, can we replace PCNN with deep learning? Recent advancements in pre-trained CNNs on ImageNet have demonstrated their ability to extract richer features [26–28]. Motivated by the above fact, we employ a simple yet effective approach by combining NSCT with a pre-trained CNN to capture richer multi-scale feature representations.
2.3 CAM attention mechanism
Recent years have witnessed that the CAM is an effective tool for model interpretability. Zhou et al. used CAM to locate class-relevant objects [29]. Subsequently, gradient-weighted CAM was further extended to obtain better localization [30]. Ouyang et al. adopted gradient-weighted CAM to learn chest X-ray abnormality localization [31]. Tang et al. utilized an online CAM mechanism to concentrate on thyroid nodule localization, improving the model interpretability [32]. Thus, in this paper, we further extend the CAM attention mechanism to guide the network in focusing on lesion regions, enhancing the representative discriminative features, which ensures alignment with radiologists’ decision-making.
3 Methods
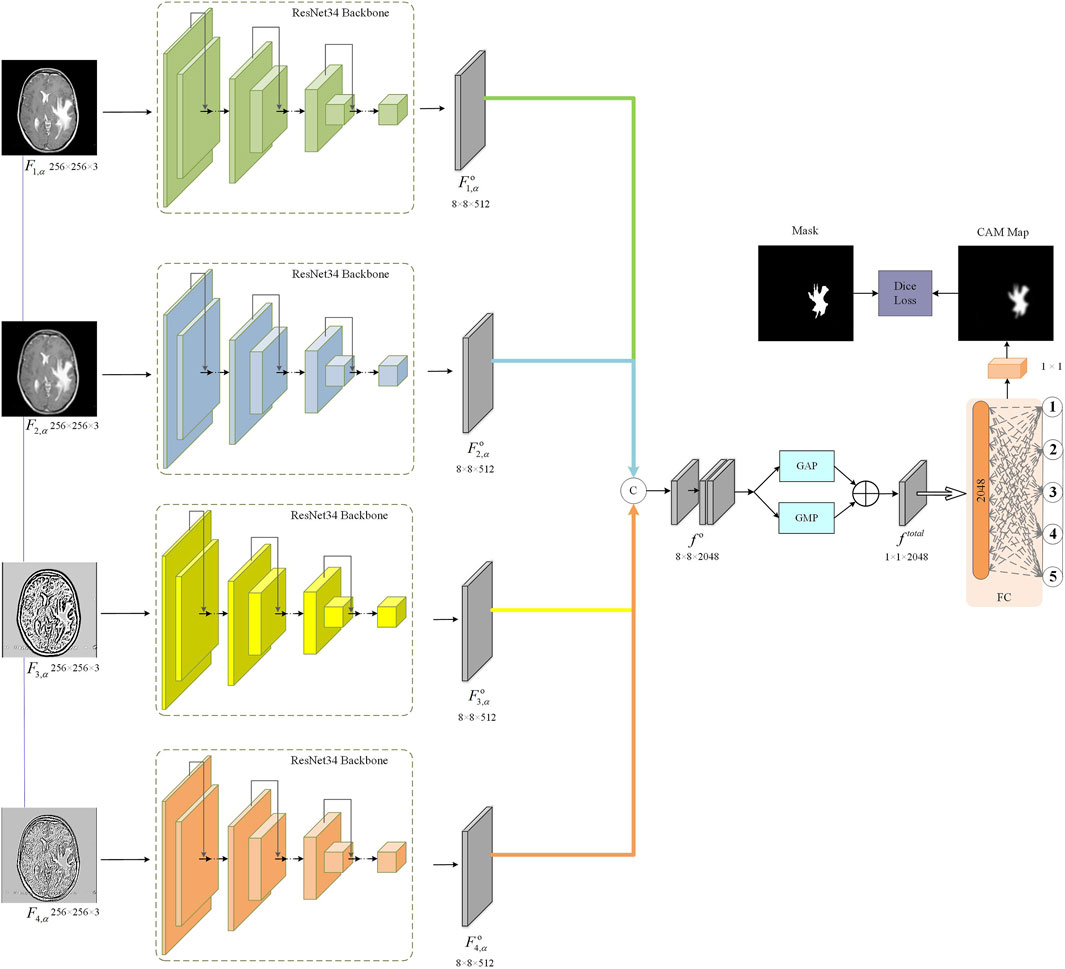
The proposed MS-ANN model is designed to comprehensively capture perceptual quality information from multimodal fused medical images. Its architecture comprises three main components: a multi-scale transform module, an ImageNet pre-trained ResNet34 backbone, and a CAM attention mechanism, as illustrated in Figure 2. First, we construct a multi-scale stream network with NSCT by down-sampling the input fused images to generate representations at four different scales. Each scale is processed by four ResNet34 backbone, which is selected for its efficiency and strong feature representation ability. Using a pre-trained model also facilitates robust learning with limited data. To enhance model interpretability and ensure the network emphasizes diagnostically relevant regions, we incorporate a CAM-based attention mechanism after feature extraction. Finally, the attention-refined features from all scales are concatenated and mapped to a quality score through fully connected layers.
3.1 Multi-scale aware neural network
We adopt the NSCT to perform multi-scale and multi-directional decomposition on the medical fused image. NSCT is a shift-invariant extension of the contourlet transform that enables rich representation of image features across different scales and directions, which is particularly beneficial for medical image analysis. Specifically, the medical fused image F is transformed into multiple sub-band
Where
Where
3.2 Aggregation of multi-scale feature
Considering the advantages of multi-scale transform, we aggregate the output features of multi-scale streams for MMIF quality evaluation. Firstly, we perform concatenate operations on four multi-scale stages, as shown in Equation 3:
where
Where
3.3 CAM attention mechanism
To capture quality discrepancy features of lesion region from the whole medical fused images, we introduce the CAM attention mechanism. Specifically, we generate the attention feature map
Where
Where
Where
3.4 Total loss function
As observe in Figure 2, total loss function of our MS-ANN, comprise of attention
4 Experiments
4.1 Dataset
In this study, we perform medical fused data for appraising the developed MS-ANN in MMIF quality assessment. Specifically, we collect 129 pairs of source images from public datasets, i.e., Whole Brain Atlas, which include CT and MR, MR-T1 and MR-T2, MR-T2 and PET, MR-T2 and SPECT, as shown in Figure 3. The selected images span a wide range of anatomical structures and clinical conditions (e.g., tumors, lesions, and degenerative changes), ensuring that the dataset is both diverse and representative of real-world clinical fusion scenarios. We then apply ten representative state-of-the-art MMIF algorithms [16, 24, 33–40], resulting in a total of 1,290 fused images. This dataset construction process is consistent with our previous work, where more technical details of the fusion methods can be found [20, 41]. For subjective quality assessment, each fused image is annotated with a Mean Opinion Score (MOS) ranging from 1 (lowest quality) to 5 (highest quality), as independently rated by two experienced radiologists. To ensure the reliability and consistency of the subjective assessment, a senior radiologist further reviewed and validated the assigned scores.
To rigorously evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed MS-ANN, we adopt four widely recognized quantitative assessment metrics [42, 43]: Pearson’s Linear Correlation Coefficient (PLCC), Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient (SRCC), Kendall’s Rank Correlation Coefficient (KRCC), and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE). These metrics are designed to measure the alignment between the predicted quality scores generated by the model and the ground-truth MOS provided by expert radiologists. Specifically, PLCC, SRCC, and KRCC are used to evaluate the consistency between the predicted quality scores and the ground-truth MOS, with higher values indicating better consistency with human perception. RMSE measures the absolute prediction error, where lower values represent better performance. These metrics are widely used in the field and ensure comparability with previous IQA studies [9, 18, 19, 21, 44].
4.2 Performance comparison
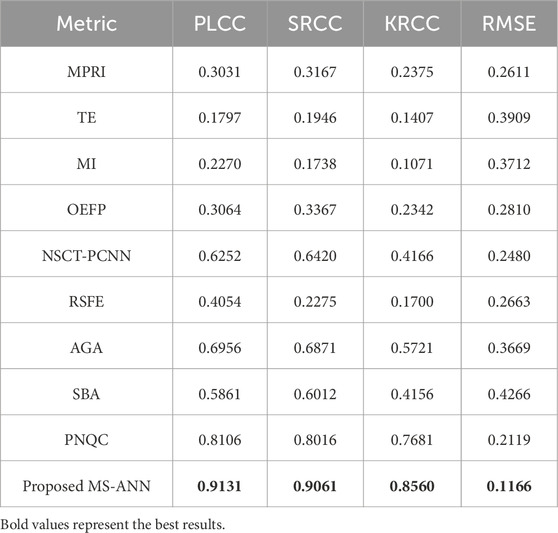
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed MS-ANN, we compare it with six mainstream methods, including multiple pseudo reference images-based quality metric (MPRI) [44], Tsallis entropy-based quality metric (TE) [45], mutual information-based quality metric (MI) [46], the objective evaluation of fusion performance (OEFP) [10], the ratio of spatial frequency error-based quality metric (RSFE) [14], the NSCT-PCNN-based quality metric (NSCT-PCNN) [17], the adaptive graph attention (AGA) for blind image quality assessment method [21], statistically based approach (SBA) for multi-focus image fusion quality assessment [9], and pyramid networks with quality-aware contrast loss (PNQC) for retinal image quality assessment [18]. Among these metrics, higher values of MPRI, TE, MI, OEFP, NSCT-PCNN, AGA, SBA, and PNQC indicate better quality, whereas lower values of RSFE denote better quality.
We compute the PLCC, SRCC, KRCC and RMSE values of six mainstream methods and MS-ANN, as shown in Table 1. The highest scores are highlighted in bold. Based on Table 1, our MS-ANN achieves the best performance, significantly outperforming the six competing models. Specifically, compared to the second-ranked RIQA, our proposed method improves PLCC from 0.8106 to 0.9131, SRCC from 0.8016 to 0.9061, KRCC from 0.7681 to 0.8560, while declining RMSE 0.2119 from to 0.1166.
4.3 Ablation study
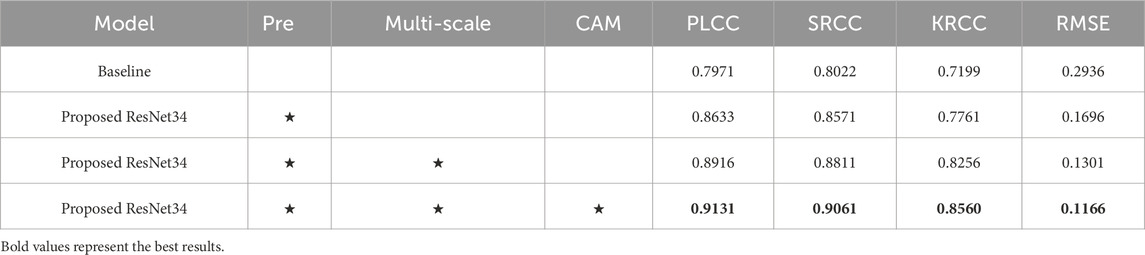
We conduct ablation studies to discuss the contribution of each important part of the MS-ANN. We first train each component independently on the medical fused dataset and then jointly optimize all components of MS-ANN. The results are presented in Table 2.
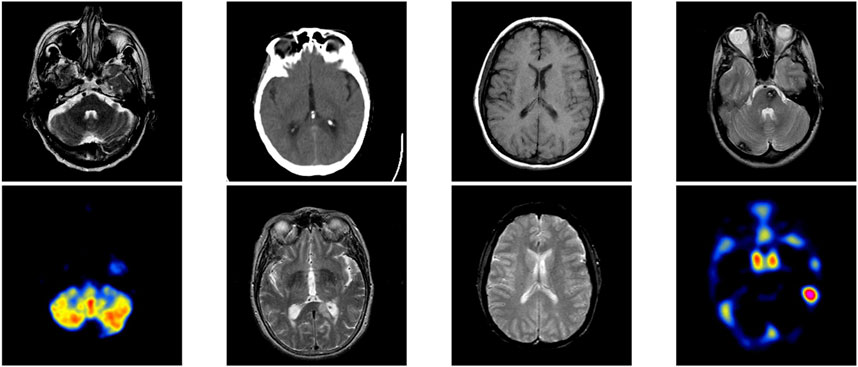
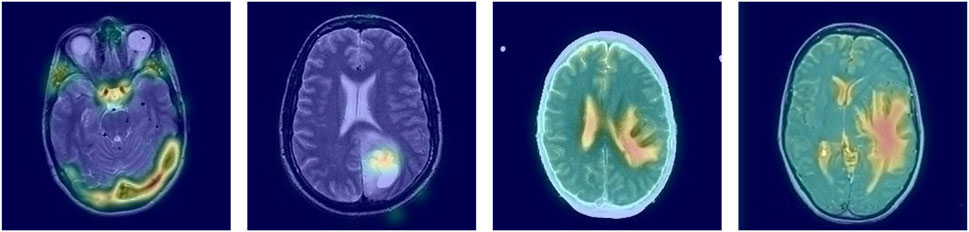
First, the baseline model refers to ResNet34 without ImageNet pre-training, achieving a PLCC of 0.7971, SRCC of 0.8022, KRCC of 0.7199, and RMSE of 0.2936. Second, we apply a pre-training strategy to enhance the ability to capture features. As shown in the second row of Table 2, performance significantly improves, with PLCC increasing from 0.7971 to 0.8633, SRCC from 0.8022 to 0.8571, and KRCC from 0.7199 to 0.7761, while RMSE decreases from 0.2936 to 0.1696. These results demonstrate that the ImageNet pre-trained model outperforms the baseline model without pre-training. This improvement may be attributed to the effective use of pre-trained knowledge, which helps mitigate the challenge of limited training data. Third, we further introduce NSCT to capture more multi-scale features. With the addition of multi-scale transform, the results show noticeable improvements when comparing baseline + Pre and baseline + Pre + multi-scale: PLCC increases by 2.83% (0.8633 vs. 0.8916), SRCC by 2.40% (0.8571 vs. 0.8811), and KRCC by 4.95% (0.7761 vs. 0.8256), while RMSE decreases by 3.95% (0.1696 vs. 0.1301). Moreover, we integrate the CAM mechanism to guide the model’s attention toward lesion regions, thereby enhancing both feature representation and interpretability. As shown in Table 2, the proposed MS-ANN (Baseline + Pre + multi-scale + CAM) achieves superior performance compared to the variant without CAM (Baseline + Pre + multi-scale). Specifically, PLCC increases from 0.8916 to 0.9131, SRCC from 0.8811 to 0.9061, KRCC from 0.8256 to 0.8560, and RMSE decreases from 0.1301 to 0.1166. These improvements demonstrate that CAM significantly enhances the model’s ability to capture quality-related features. More importantly, the lesion-focused attention maps provide intuitive visual explanations, which can assist radiologists in verifying model predictions and build greater confidence in clinical use. As shown in Figure 4, the CAM-based heatmaps illustrate the model’s ability to concentrate on diagnostically relevant regions, offering visual support for the model’s quantitative superiority.
4.4 External validation
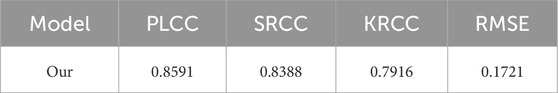
To further validate the generalization ability of our MS-ANN, we conduct an external independent evaluation using the multimodal medical image fusion database [17]. It is important to note that the performance metrics reported in Table 3 differ from those in Table 2 because they are obtained under different evaluation settings. Specifically, Table 2 reports results from ablation studies conducted on the training dataset to analyze the contribution of each model component, whereas Table 3 presents results from a separate external dataset. As shown in Table 3, our model achieves promising performance, with a PLCC of 0.8591, SRCC of 0.8388, KRCC of 0.7916, and RMSE of 0.1721. These results demonstrate the robustness and effectiveness of MS-ANN in assessing multimodal medical image fusion quality across different datasets.
5 Conclusion
In this paper, we develop a quality evaluation metric for multimodal medical image fusion, called no reference multi-scale aware attention network (MS-ANN). Specifically, we first apply a multi-scale transform to extract different scale information from fused images and feed these transformed images into an ImageNet pre-trained ResNet34. This multi-scale strategy enables complementary feature extraction, capturing rich details relevant to quality assessment. Then, we propose a CAM attention network, which captures visualization attention to the lesion regions to facilitate model interpretability. Finally, we employ a concatenation operation to refine quality discrepancy features and map them to the quality differences in multimodal fusion images. However, the dataset used in this study exhibits an imbalance between MRI-PET and MRI-SPECT image pairs, with MRI-SPECT images being more prevalent. Moreover, the diversity of medical conditions and anatomical regions is somewhat limited, which may affect the model’s generalization to other clinical settings or imaging modalities. In future work, we aim to address these limitations by expanding the dataset to cover a broader range of organs and clinical conditions, thereby improving the robustness and generalization capability of the proposed MS-ANN model. Additionally, while our study adopts widely accepted statistical metrics to evaluate image quality prediction, it is important to recognize the potential influence of MMIF quality on downstream clinical tasks such as diagnosis accuracy or treatment decisions. High-quality fused images can provide clearer lesion boundaries, improved structural detail, and more reliable functional information, which are crucial in radiological assessment and therapy planning. In future work, we intend to design user studies or integrate radiologist-in-the-loop evaluations to measure the actual diagnostic utility of images rated by our model. Such assessments would offer a more comprehensive validation of the model’s clinical value and help bridge the gap between objective image quality assessment and practical medical outcomes. Despite these limitations, the proposed MS-ANN shows strong consistency with subjective perception, offering potential to facilitate clinical diagnosis and guide the development of advanced multimodal medical image fusion techniques.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
CT: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft. JZ: Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. LT: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Xu Zhou Science and technology Program, China (KC22466) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (82001912).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Birkfellner W, Figl M, Furtado H, Renner A, Hatamikia S, Hummel J. Multi-modality imaging: a software fusion and image-guided therapy perspective. Front Phys (2018) 6:66. doi:10.3389/fphy.2018.00066
2. Azam MA, Khan KB, Salahuddin S, Rehman E, Khan SA, Khan MA A review on multimodal medical image fusion: compendious analysis of medical modalities, multimodal databases, fusion techniques and quality metrics. Comput Biol Med (2022) 144:105253. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105253
3. Zhou T, Cheng Q, Lu H, Li Q, Zhang X, Qiu S. Deep learning methods for medical image fusion: a review. Comput Biol Med (2023) 160:106959. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106959
4. Cheng S, Liu R, He Y, Fan X, Luo Z. Blind image deblurring via hybrid deep priors modeling. Neurocomputing (2020) 387:334–45. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2020.01.004
5. Shao W-Z, Lin Y-Z, Liu Y-Y, Wang L-Q, Ge Q, Bao B-K, et al. Gradient-based discriminative modeling for blind image deblurring. Neurocomputing (2020) 413:305–27. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2020.06.093
6. Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process (2004) 13:600–12. doi:10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
7. Shen L, Chen X, Pan Z, Fan K, Li F, Lei J. No-reference stereoscopic image quality assessment based on global and local content characteristics. Neurocomputing (2021) 424:132–42. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2020.10.024
8. Ma K, Liu W, Zhang K, Duanmu Z, Wang Z, Zuo W. End-to-End blind image quality assessment using deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Image Process (2018) 27:1202–13. doi:10.1109/TIP.2017.2774045
9. Liu Y, Qi Z, Cheng J, Chen X. Rethinking the effectiveness of objective evaluation metrics in multi-focus image fusion: a statistic-based approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (2024) 46:5806–19. doi:10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3367905
10. Xydeas CS, Petrović V. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electron Lett (2000) 36:308–9. doi:10.1049/el:20000267
11. Yang C, Zhang J-Q, Wang X-R, Liu X. A novel similarity based quality metric for image fusion. Inf Fusion (2008) 9:156–60. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2006.09.001
12. Li S, Kwok JT, Wang Y. Combination of images with diverse focuses using the spatial frequency. Inf Fusion (2001) 2:169–76. doi:10.1016/S1566-2535(01)00038-0
13. Zhao J, Laganiere R, Liu Z. Performance assessment of combinative pixel-level image fusion based on an absolute feature measurement. Int J Innovat Comput Inf Control (2006) 3. doi:10.1109/ICICIC.2006.296
14. Zheng Y, Essock EA, Hansen BC, Haun AM. A new metric based on extended spatial frequency and its application to DWT based fusion algorithms. Inf Fusion (2007) 8:177–92. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2005.04.003
15. Qu G, Zhang D, Yan P. Information measure for performance of image fusion. Electron Lett (2002) 38:313–5. doi:10.1049/el:20020212
16. Liu Y, Liu S, Wang Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf Fusion (2015) 24:147–64. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2014.09.004
17. Tang L, Tian C, Li L, Hu B, Yu W, Xu K. Perceptual quality assessment for multimodal medical image fusion. Signal Process Image Commun (2020) 85:115852. doi:10.1016/j.image.2020.115852
18. Yue G, Zhang S, Zhou T, Jiang B, Liu W, Wang T. Pyramid network with quality-aware contrastive loss for retinal image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Med Imaging (2025) 44:1416–31. doi:10.1109/TMI.2024.3501405
19. Guo Y, Hu M, Min X, Wang Y, Dai M, Zhai G, et al. Blind image quality assessment for pathological microscopic image under screen and immersion scenarios. IEEE Trans Med Imaging (2023) 42:3295–306. doi:10.1109/TMI.2023.3282387
20. Tian C, Zhang L. G2NPAN: GAN-guided nuance perceptual attention network for multimodal medical fusion image quality assessment. Front Neurosci (2024) 18:1415679. doi:10.3389/fnins.2024.1415679
21. Wang H, Liu J, Tan H, Lou J, Liu X, Zhou W, et al. Blind image quality assessment via adaptive graph attention. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol (2024) 34:10299–309. doi:10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3405789
22. Duan H, Wang W, Xing L, Xie B, Zhang Q, Zhang Y. Identifying geological structures in the Pamir region using non-subsampled shearlet transform and gravity gradient tensor. Geophys J Int (2025) 240:2125–43. doi:10.1093/gji/ggaf036
23. Ma J, Chen Y, Chen L, Tang Z. Dual-attention pyramid transformer network for no-reference image quality assessment. Expert Syst Appl (2024) 257:125008. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125008
24. Yin M, Liu X, Liu Y, Chen X. Medical image fusion with parameter-adaptive pulse coupled neural network in nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas (2019) 68:49–64. doi:10.1109/TIM.2018.2838778
25. Huang C, Tian G, Lan Y, Peng Y, Ng EYK, Hao Y, et al. A new pulse coupled neural network (PCNN) for brain medical image fusion empowered by shuffled frog leaping algorithm. Front Neurosci (2019) 13:210. doi:10.3389/fnins.2019.00210
26. Norouzi M, Hosseini SH, Khoshnevisan M, Moshiri B. Applications of pre-trained CNN models and data fusion techniques in Unity3D for connected vehicles. Appl Intell (2025) 55:390. doi:10.1007/s10489-024-06213-3
27. Swamy MR, P V, Rajendran V. Deep learning approaches for online signature authentication: a comparative study of pre-trained CNN models. Eng Res Express (2025) 7:015230. doi:10.1088/2631-8695/ada86d
28. Arnia F, Saddami K, Roslidar R, Muharar R, Munadi K. Towards accurate diabetic foot ulcer image classification: leveraging CNN pre-trained features and extreme learning machine. Smart Health (2024) 33:100502. doi:10.1016/j.smhl.2024.100502
29. Zhou B, Khosla A, Lapedriza A, Oliva A, Torralba A. Learning deep features for discriminative localization. In: 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV: IEEE (2016). p. 2921–9. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2016.319
30. Selvaraju RR, Cogswell M, Das A, Vedantam R, Parikh D, Batra D. Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. Venice: IEEE: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision ICCV (2017). p. 618–26. doi:10.1109/ICCV.2017.74
31. Ouyang X, Karanam S, Wu Z, Chen T, Huo J, Zhou XS, et al. Learning hierarchical attention for weakly-supervised chest X-ray abnormality localization and diagnosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging (2021) 40:2698–710. doi:10.1109/TMI.2020.3042773
32. Tang L, Tian C, Yang H, Cui Z, Hui Y, Xu K, et al. TS-DSANN: texture and shape focused dual-stream attention neural network for benign-malignant diagnosis of thyroid nodules in ultrasound images. Med Image Anal (2023) 89:102905. doi:10.1016/j.media.2023.102905
33. Min X, Zhai G, Gu K, Yang X, Guan X. Objective quality evaluation of dehazed images. IEEE Trans Intell Transport Syst (2019) 20:2879–92. doi:10.1109/TITS.2018.2868771
34. Liu Y, Chen X, Ward RK, Jane Wang Z. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation. IEEE Signal Process Lett (2016) 23:1882–6. doi:10.1109/LSP.2016.2618776
35. Das S, Kundu MK. NSCT-based multimodal medical image fusion using pulse-coupled neural network and modified spatial frequency. Med Biol Eng Comput (2012) 50:1105–14. doi:10.1007/s11517-012-0943-3
36. Li S, Kang X, Hu J. Image fusion with guided filtering. IEEE Trans Image Process (2013) 22:2864–75. doi:10.1109/TIP.2013.2244222
37. Shen R, Cheng I, Basu A. Cross-scale coefficient selection for volumetric medical image fusion. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng (2013) 60:1069–79. doi:10.1109/TBME.2012.2211017
38. Du J, Li W, Xiao B, Nawaz Q. Union Laplacian pyramid with multiple features for medical image fusion. Neurocomputing (2016) 194:326–39. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2016.02.047
39. Tang L, Tian C, Xu K. Exploiting quality-guided adaptive optimization for fusing multimodal medical images. IEEE Access (2019) 7:96048–59. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2926833
40. Das S, Kundu MK. A neuro-fuzzy approach for medical image fusion. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng (2013) 60:3347–53. doi:10.1109/TBME.2013.2282461
41. Tang L, Hui Y, Yang H, Zhao Y, Tian C. Medical image fusion quality assessment based on conditional generative adversarial network. Front Neurosci (2022) 16:986153. doi:10.3389/fnins.2022.986153
42. Hu B, Wang S, Gao X, Li L, Gan J, Nie X. Reduced-reference image deblurring quality assessment based on multi-scale feature enhancement and aggregation. Neurocomputing (2023) 547:126378. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2023.126378
43. Sim K, Yang J, Lu W, Gao X. Blind stereoscopic image quality evaluator based on binocular semantic and quality channels. IEEE Trans Multimedia (2022) 24:1389–98. doi:10.1109/TMM.2021.3064240
44. Min X, Zhai G, Gu K, Liu Y, Yang X. Blind image quality estimation via distortion aggravation. IEEE Trans Broadcast (2018) 64:508–17. doi:10.1109/TBC.2018.2816783
45. Sholehkerdar A, Tavakoli J, Liu Z. In-depth analysis of Tsallis entropy-based measures for image fusion quality assessment. Opt Eng (2019) 58:1. doi:10.1117/1.OE.58.3.033102
Keywords: multimodal medical image fusion, objective evaluation, multi-scale transform, class activation mapping mechanism, region of interest
Citation: Tian C, Zhang J and Tang L (2025) Perceptual objective evaluation for multimodal medical image fusion. Front. Phys. 13:1588508. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1588508
Received: 06 March 2025; Accepted: 13 May 2025;
Published: 26 May 2025.
Edited by:
Zhiqin Zhu, Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Tian, Zhang and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lu Tang, eHp0YW5nbHVAeHpobXUuZWR1LmNu
 Chuangeng Tian
Chuangeng Tian Juyuan Zhang1
Juyuan Zhang1 Lu Tang
Lu Tang