- 1College of Instrumentation & Electrical Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun, China
- 2Department of Technical, Sinotest Equipment Co., Ltd., Changchun, China
- 3Department of research and development, Jingwei Hirain Co., Ltd., Changchun, China
- 4Development of Large-Scale models, Changchun UP Optotech Co., Ltd., Changchun, China
Effective natural gas leakage detection is of great significance in terms of economy, environment and safety. Due to the irregular shape and ambiguous boundary of the gas, traditional motion detection algorithms are difficult to adapt to the changes in the gas movement state with the environment, resulting in an increased probability of false alarms. To address this issue, this paper proposes a gas plume-constrained YOLOv11 model based on infrared imaging detection technology, named YPCN (YOLO-Plume Classification Network). A new backbone feature extraction network, MobileNetV4, is selected to replace the original backbone network, and SPD-Conv is introduced in the segmentation head network. This network effectively reduces model complexity and enhances inference speed while maintaining detection accuracy. Additionally, a gas plume model is introduced as a key physical constraint condition in the loss function to enhance the model’s accuracy, segmentation precision, and generalization ability in handling gas plume tasks. Moreover, this paper constructs a gas leakage dataset consisting of 13,109 frames, covering different distances, sizes, and backgrounds. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves an F1-score of 88.97% and an IoU of 89.74%, improving upon the baseline by 7.37% and 7.59%, respectively, with a detection accuracy reaching 99.78%.
1 Introduction
As a fossil fuel primarily composed of methane, natural gas occupies a significant position in the global energy system and is extensively utilized in power generation [1], industrial manufacturing [2], transportation [3], and residential application [4]. Compared to coal and oil, natural gas exhibits higher combustion efficiency and lower pollutant emissions, making it a critical component in national strategies aimed at optimizing energy structures [5]. However, despite its advantages in terms of cleanliness and efficiency, the inherent physicochemical properties of natural gas pose considerable safety and environmental risks. Natural gas leaks not only contribute to the intensification of the greenhouse effect but also present significant safety hazards [6]. When leaked gas accumulates in an enclosed environment and reaches the lower explosive limit (LEL) [7], the presence of an ignition source may lead to combustion or even explosion, thereby posing severe threats to human life and property. The development of gas leakage detection technologies capable of promptly identifying leakage points is therefore essential for mitigating these risks. Consequently, there exists a pressing need for the advancement of high-precision gas leakage detection systems.
A substantial amount of research has been conducted to achieve leakage detection tasks with different objectives. Semiconductor [8], electrochemical [9], and catalytic combustion sensors [10] are primarily used to detect gas concentrations at specific locations. However, their detection range is relatively limited, making it challenging to cover large areas. Additionally, these sensors typically require direct contact with or close proximity to monitoring points, imposing significant constraints on installation flexibility. To enhance the accuracy of gas leakage detection, sensor arrays are often employed, leveraging the collaborative operation of multiple sensors to improve spatial coverage and detection precision [11–13]. However, this approach not only increases equipment costs and maintenance complexity but also suffers from issues such as sensor aging and signal drift. In contrast, laser remote sensing technology [14] enables line-of-sight measurement of columnar gas concentrations, thereby extending the detection range to some extent. Nevertheless, these sensors still struggle to effectively monitor complex environments, and their accuracy is highly susceptible to environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and wind speed. In addition to the above techniques, various laser spectroscopic sensing methods have been successfully applied for the accurate identification of combustion products and gas components. These include wavelength modulation spectroscopy with direct absorption calibration [15], self-calibrated 2f/1f wavelength modulation spectroscopy [16], photoacoustic spectroscopy [17, 18], and quartz-enhanced laser spectroscopy [19, 20]. While these techniques demonstrate excellent sensitivity and selectivity in controlled environments, they are often limited by instrumentation complexity and spatial constraints in large-scale field applications. Consequently, developing a gas leakage detection method that balances detection accuracy, coverage area, and environmental adaptability remains a critical research challenge.
Unlike traditional gas leakage detection technologies, detection methods based on the infrared absorption characteristics of gases enable non-contact measurement. Optical gas imaging (OGI)-based area source detection facilitates long-range dynamic remote sensing, allowing for the visualization of gas plumes, which has now become a mainstream approach in gas leakage detection [21–25]. Compared with point detection techniques, infrared imaging methods offer greater spatial awareness and real-time visualization of gas dispersion, making them highly suitable for complex and large-scale environments. However, existing OGI techniques primarily rely on the subjective judgment of inspection personnel, as current equipment lacks the capability for automatic detection. Consequently, achieving intelligent gas leak detection has emerged as a critical issue that urgently requires resolution.
The emergence of deep learning-based approaches has significantly advanced object detection. Nevertheless, gas leakage target recognition based on infrared imaging detection technology still presents considerable challenges. The primary difficulties include: (1) the absence of a fixed morphology and well-defined boundaries; (2) the partial transparency of gases in the visual spectrum, making detection highly susceptible to complex background interference; and (3) the presence of visually similar disturbances that can be misclassified as gas plumes. Wang et al. (2020) [26] constructed the first methane leakage video image dataset, GasVid, and proposed a CNN-based methane plume detection method, achieving detection accuracy exceeding 95% across different leakage scales and imaging distances. Similarly, Yan et al. (2024) [27] introduced improvements to the backbone network of DeepLabV3+, with experimental results demonstrating an accuracy of 86.24% and an Intersection over Union (IoU) of 84.23%. However, these methods rely on datasets with relatively simple backgrounds. When disturbances resembling gas motion patterns and edge characteristics appear, the extracted features of these disturbances may closely align with those of the gas plumes, leading to a higher false detection rate. Such false detections can trigger unnecessary emergency responses in industrial facilities, potentially resulting in significant economic losses.
This study proposes a YOLOv11 model with gas plume constraints based on OGI technology to address the aforementioned challenges. In comparison with existing literature, the key contributions of this study are as follows: (a) Development of an infrared camera-based natural gas imaging system and implementation of industrial field tests for gas leakage detection. (b) Proposal of a YOLOv11 model with gas plume constraints, incorporating the lightweight MobileNetV4 to reduce parameter complexity and enhance computational efficiency. By integrating a gas plume model into the network loss function as a physical constraint, the proposed model effectively learns prior knowledge of gas plume behavior during training, thereby improving the accuracy of gas leakage detection, segmentation precision, and model generalization capability. The remainder of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the structure of the mid-infrared spectroscopic imaging system. Section 3 presents the model improvement methods. Section 4 describes the model training environment. Section 5 shows the experimental results. Finally, Section 6 provides the conclusion and future perspectives.
2 Principle and system composition
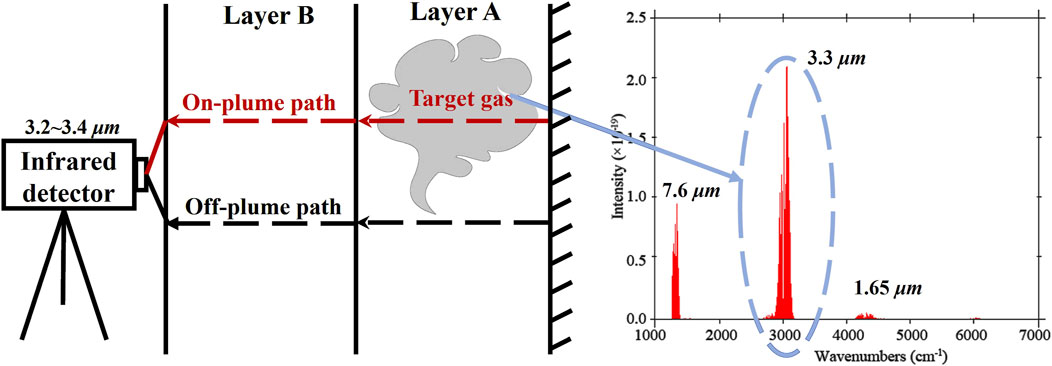
As shown in Figure 1, OGI technology visualizes otherwise invisible gases by measuring the difference in infrared radiation intensity between the background and the leaking gas [25]. The primary component of natural gas is methane, whose molecular characteristic absorption peak appears at a wavelength of 3,021 cm-1 (3.31 μm) [28]. Therefore, OGI technology for detecting natural gas leaks typically employs a narrow-band pass filter in the 3.2–3.4 μm range, which covers the absorption features of alkane gases such as methane, butane, and others, enabling their effective detection. This makes OGI an ideal technology for detecting natural gas leaks.
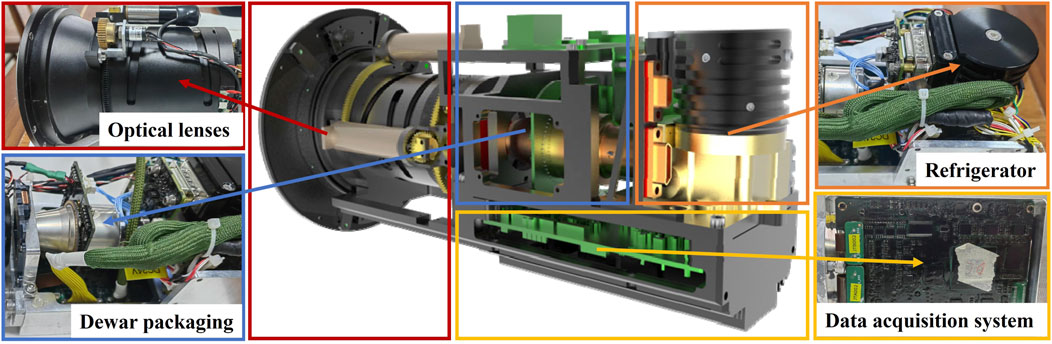
To achieve precise imaging of natural gas within a narrow spectral range, an infrared imaging detection system based on a HgCdTe infrared detector is proposed. The system structure is shown in Figure 2. The core components include an infrared optical lens, an infrared focal plane detector Dewar assembly, an integrated Stirling cooler, and a high-speed acquisition board. All modules are encapsulated within a high-strength explosion-proof casing made of 316 stainless steel to meet the stringent explosion-proof requirements of the oil and gas industry, ensuring long-term stable operation in complex industrial environments.
The infrared radiation emitted from the leaking gas is collected and focused by an optical system with a focal length ranging from 50 to 200 mm. The focused radiation then passes through a narrowband filter, which has a transmission spectrum range of 3.2∼3.4 μm. Subsequently, the filtered signal is imaged onto a HgCdTe infrared detector, featuring a resolution of 320 × 256 pixels, a noise equivalent temperature difference (NETD) less than 25 mK, and a frame rate of 25 Hz. The resulting 14-bit digital infrared image undergoes non-uniformity correction processing, after which a black-and-white video image output is generated.
3 Methods
YOLOv11 is a single-stage object detection model, with its algorithm framework primarily divided into three components: the backbone network (Backbone), the bottleneck network (Neck), and the detection layer (Output) [29].
The Backbone network consists of standard convolution modules (Conv), C3K2 modules, a Spatial Pyramid Pooling Structure (SPPS), and C2PSA modules. Among these, the C3K2 module is a crucial feature extraction component in the YOLOv11 model, designed as an improvement over the traditional C3 module. By integrating variable convolution kernels and a channel separation strategy, it enhances feature extraction capabilities, making it particularly suitable for complex scenarios and deep-level feature extraction tasks. The C2PSA module, designed to further enhance feature extraction, combines the Cross Stage Partial (CSP) structure with the Pyramid Squeeze Attention (PSA) mechanism, thereby improving multi-scale feature extraction capabilities.
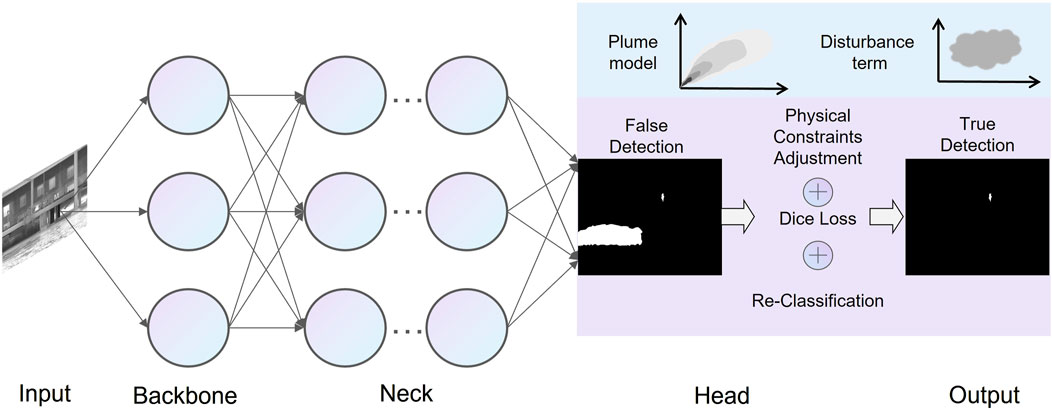
Although the existing YOLOv11n model has achieved certain success in detection accuracy, its backbone network and segmentation head module still have room for optimization in terms of parameter quantity and computational complexity. In this paper, we propose an improved strategy based on YOLOv11: adopting the lightweight MobileNetV4 as the backbone feature extraction network and introducing SPD-Conv (Spatial Pyramid Decomposition Convolution) into the segmentation head module. This approach significantly reduces the number of model parameters and GFLOPs while enhancing inference speed, all without sacrificing detection accuracy. Additionally, the Dice loss function is employed in the loss function design, with a gas plume model incorporated as a key physical constraint. The YPCN model is an optimized variant based on the YOLOv11 framework, specifically designed for natural gas leak detection tasks. The algorithm process is illustrated in Figure 3.
3.1 Lightweight backbone network
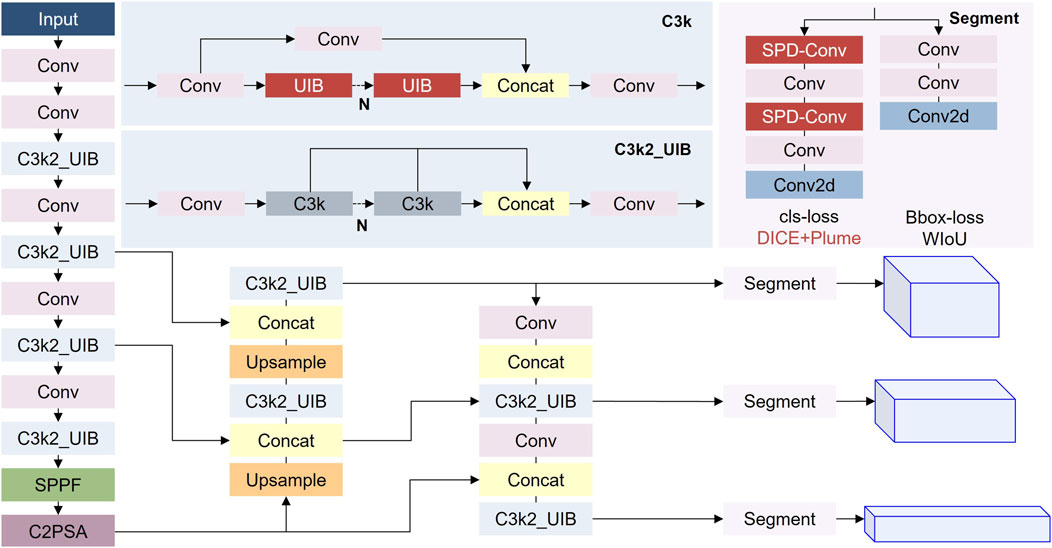
Although YOLOv11 has demonstrated outstanding performance in object detection tasks, there is still room for optimization in its network design for gas leak detection in infrared images. The improved network structure diagram is shown in Figure 4.
In convolutional neural network (CNN) architectures, a notable performance degradation occurs when processing low-resolution images and small objects. This issue primarily stems from the use of stride convolutions and pooling layers, which lead to the loss of fine-grained information. While stacking numerous residual structures increases network depth and enhances accuracy, it also complicates model deployment on edge devices. To address this challenge, this study replaces YOLOv11’s primary feature extraction network with MobileNetV4.
MobileNetV4 [30] introduces the Unified Inverted Bottleneck (UIB) module and Neural Architecture Search (NAS) technology. By combining the inverted residual structure and depth wise separable convolution, it optimizes computational efficiency and feature extraction capabilities. The UIB module reduces computational overhead while maintaining high performance, and NAS automatically searches for the optimal architecture to enhance accuracy and efficiency. The combination of the two enables MobileNetV4 to run efficiently on resource-constrained devices and automatically adjust the network architecture based on the hardware platform to achieve a balance between performance and efficiency. The specific operation for replacing the backbone is to substitute the parts corresponding to the 80 × 80, 40 × 40, and 20 × 20 scales in the YOLOv11 backbone with the corresponding feature maps of 80 × 80 × 64, 40 × 40 × 128, and 20 × 20 × 256 channels in the MobileNetV4 backbone.
In practical applications, the gases in diffusion often exhibit low contrast and blurred edges. Traditional convolution operations often fail to capture these low-contrast and blurred-edge tiny features due to insufficient local receptive fields, resulting in poor segmentation effects. Therefore, on the basis of the original network architecture, a dedicated segmentation head for tiny objects is added, and some traditional convolution layers are replaced with SPD-Conv layers. This segmentation head adopts a multi-scale feature fusion strategy, integrating feature maps from different levels to enable the tiny smoke regions to obtain richer context information, thereby improving the overall segmentation result’s coherence and accuracy.
3.2 Loss function
In this paper, a novel constraint module is developed by leveraging the distinctive characteristics of the plume. This module is integrated into the YOLOv11 object detection framework, thereby enhancing both the accuracy and robustness of the detection system. The diffusion behavior of leaking gas exhibits unique dynamic physical characteristics, especially under fixed source conditions, where its diffusion pattern shows distinct jet diffusion features. This diffusion pattern can be effectively described using the Gaussian plume model, providing a new theoretical basis for distinguishing between leaked gas and interfering objects in target detection tasks.
The dispersion of the leaking gas can be characterized using the Gaussian plume model, which primarily focuses on the concentration distribution of the gas as it disperses from the point source. In a three-dimensional context, this concentration distribution is mathematically represented in Equation 1 below.
where parameters
The Gaussian plume model is simplified to a weighting formula, as shown in Equation 2, in the context of segmentation tasks.
The segmentation loss is formulated based on the Dice Loss, while the initial pixel-wise loss function is defined in Equation 3 below:
After incorporating Gaussian plume weights, the Dice Loss is reformulated as shown in Equation 4.
4 Experiment related work
4.1 Dataset production
The dataset utilized for pre-training in this study was generated using a butane gas tank and captured by a custom-developed refrigerated mid-infrared camera. While our primary application targets methane plume detection, the dataset used for training predominantly consists of butane-based infrared imagery. This decision was made due to practical constraints: controlled methane plume datasets with adequate annotations are limited, whereas butane offers safer and more accessible experimental conditions. Although butane and methane exhibit different infrared absorption spectra, our model does not rely solely on gas-specific spectral features. Instead, it is designed to learn plume morphology, motion patterns, and spatial-temporal cues that are common across various hydrocarbon gases. Deep learning models trained on one gas can generalize to others when trained to detect structural and behavioral signatures rather than spectral fingerprints.
During the experiment, four video recordings were obtained, each with an average duration of 5 minutes. A total of 13,109 still images were extracted from these videos for model training purposes. A partial visualization of the pre-training dataset is presented in Figure 5.
Using the open-source image annotation tool Labelme, individual instances of leaking gas in the dataset were labeled with the tag “gasleak,” while the rest of the image was considered as “background.” The annotation information was saved in a JSON file corresponding to the image name, and then converted into the required TXT file format for model training via a TXT file conversion process. The dataset was divided into training, validation, and test sets in an 8:1:1 ratio for neural network model training and validation. A total of 13,109 individual instances of leaking gas were annotated in the dataset. The number of leaking gas instances exhibited significant variation across different images. Some images contained gas leak areas as small as 99 pixels, while others had gas leak areas as large as 14,133 pixels. This variation highlights the diversity of the dataset, which is of great significance for model learning. Not only does it provide rich feature information for the model, but it also allows the model to learn and adapt to various conditions in complex environments, thereby enhancing the model’s generalization and robustness.
4.2 Data pre-processing
The image data collected by the infrared camera has a size of 320 × 256. To facilitate subsequent input into the deep learning network for training, the size needs to be adjusted to 640 × 640. The traditional Letterbox method has the advantage of maintaining the original aspect ratio of the image and avoiding distortion caused by scaling or cropping. However, when the detection head of the model is affected by an irregular background, the filled area may impact performance. Since the blank area is usually filled with black (RGB: [0, 0, 0]), it may interfere with tasks such as object detection, especially on the boundaries. Particularly for infrared data, the black background may have a negative impact on the model’s learning process. Additionally, for small objects (such as gas leaks in infrared images), it may lead to the dilution or submersion of object information.
This paper adopts the WarpAffine method for image data preprocessing. WarpAffine is an affine transformation method that can directly map the image to the target size without additional padding. By direct mapping, the introduction of padding areas at the image edges is avoided, thereby reducing the invalid information caused by padding. Precise affine transformation can adjust the size while preserving the image structure, thus ensuring the complete retention of the edge information of the leaked gas. Affine transformation can be accelerated by hardware, enabling efficient preprocessing under the premise of real-time performance.
4.3 Model training ablation
In this experiment, the following hardware environment was used: the GPU is a NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080ti, the CPU is an Intel i9-14900 k processor, and the memory size is 16 GB. The software environment includes the Windows 11 operating system, Python 3.9, CUDA 11.8, and PyTorch 2.0.0. All training was performed without loading pre-trained weights, and conducted under consistent experimental conditions to ensure fairness. Model performance was validated on a held-out test set. The input image resolution was set to 640 × 640 pixels. Training was conducted for 500 epochs with a batch size of 32. The model was optimized using the SGD optimizer with an initial learning rate of 0.01 and a weight decay of 0.0005. A cyclical learning rate scheduler based on the cosine annealing strategy was applied to encourage stable convergence. To enhance generalization and robustness, the following data augmentation techniques were used during training: random horizontal and vertical flips, random cropping, Gaussian noise injection, and brightness/contrast adjustments.
5 Experiment and results
5.1 Experimental environment
The field test was carried out on 22 October 2024 in Lanjia Town, Kuancheng District, Changchun City, Jilin Province. The cameras were tested according to different distances, backgrounds, and from a variety of angles. The visible and corresponding infrared images of the test scene are shown in Figure 6.
5.2 Evaluation metrics
The evaluation metrics used in this paper include Precision, Recall rate (Recall), F1 score (F1), Intersection over Union (IoU) the number of parameters (Params), and Frames Per Second (FPS) [31]. Among these, Precision and Recall rate are used as basic metrics, while the F1 score and MAP, which are calculated based on Precision and Recall, are used as the final evaluation indicators to measure the model’s recognition accuracy. GFLOPS is used to measure the complexity of the model or algorithm, and PARAMS represents the size of the model. Generally, the smaller the parameters and GFLOPS, the less computational power the model requires, resulting in lower hardware performance requirements, making it easier to deploy the model on low-end devices. Precision, as defined in Equation 5, is the ratio of true positive samples predicted by the model to the total number of predicted positive samples. Recall, shown in Equation 6, quantifies the proportion of true positives among all actual positive instances. The F1 score, given in Equation 7, combines Precision and Recall through their harmonic mean, providing a balanced assessment of model performance. Finally, the Intersection over Union (IoU), defined in Equation 8, evaluates the overlap between the predicted and ground truth segments, and is commonly used in segmentation tasks.
5.3 Ablation experiments
In this outdoor experiment, a total of six sets of video image data were collected, covering various scenarios with different backgrounds and leakage scales. Specifically, it encompasses large and small gas leakage scenes with the sky as the background, large and small leakage scenarios under complex backgrounds in close-range conditions, and large and small leakage scenarios under complex backgrounds in long-range conditions. The average duration of each video was 3 min, and a total of 9,632 static images were acquired, among which 1,665 were images of no leakage scenes.
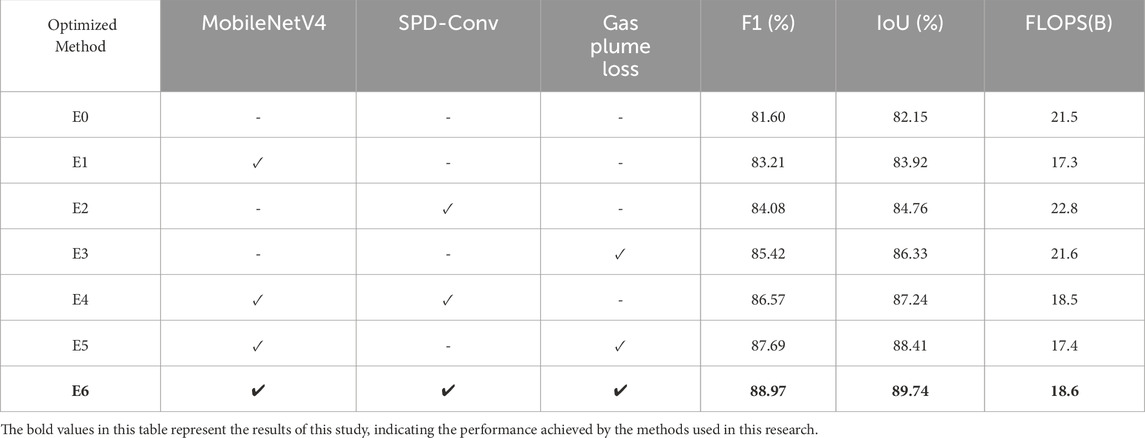
Table 1 presents the results of the ablation study conducted to systematically evaluate the individual and combined effects of the three proposed optimization modules: MobileNetV4, SPD-Conv, and the gas plume loss function. The baseline model, E0, corresponds to the original YOLOv11 framework without any architectural modifications. Configurations E1 through E5 represent intermediate variants in which one or two modules were added incrementally, while E6 represents the complete model that integrates all three enhancements.
The results clearly demonstrate that each module contributes positively to model performance. Introducing MobileNetV4 alone (E1) improves the F1-score from 81.60% to 83.21% and IoU from 82.15% to 83.92%, while significantly reducing FLOPs from 21.5B to 17.3B, highlighting its lightweight yet effective design. Adding SPD-Conv in isolation (E2) boosts the F1-score to 84.08% and IoU to 84.76%, albeit at a computational cost, increasing FLOPs to 22.8B. The gas plume loss function, which leverages a physics-informed constraint derived from the Gaussian plume model, yields a substantial improvement in segmentation accuracy (F1 = 85.42%, IoU = 86.33%) with only a marginal increase in FLOPs (21.6B).
Combinations of modules in E4 and E5 further improve performance, suggesting that the modules are complementary rather than redundant. Notably, the fully integrated model E6 achieves the best overall results, with an F1-score of 88.97% and an IoU of 89.74%, surpassing the baseline by 7.37% and 7.59%, respectively. Moreover, E6 maintains a relatively low computational cost (18.6B FLOPs), thanks to the efficiency introduced by the MobileNetV4 backbone, which offsets the added complexity from SPD-Conv and the loss constraint.
This ablation study validates the design rationale of the proposed YPCN architecture and underscores the synergistic benefits of the combined modules in enhancing both detection performance and computational efficiency for real-time infrared gas leak detection applications.
5.4 Comparative experiments
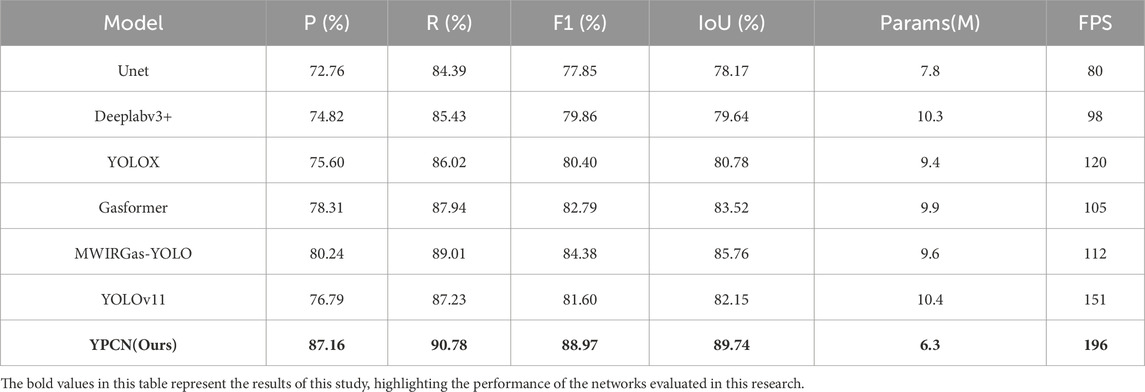
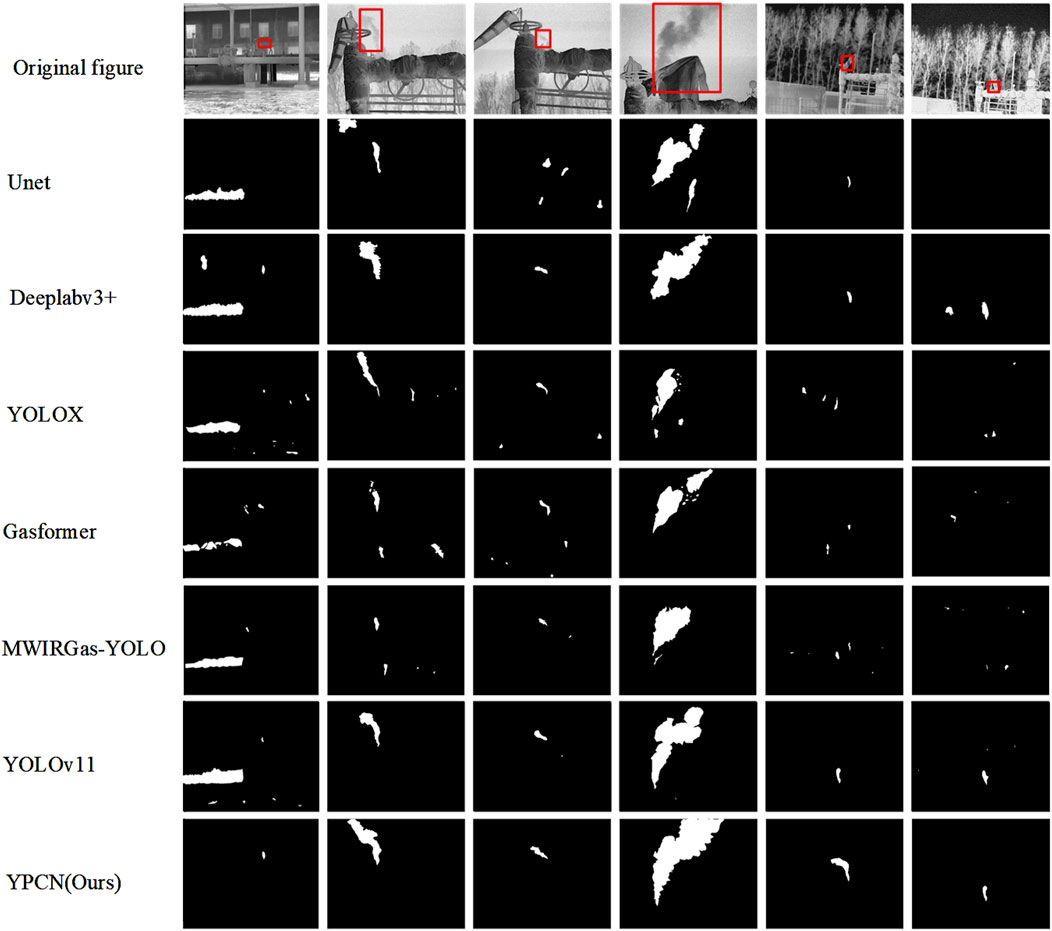
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the proposed YPCN model, we conducted comparative experiments against six widely used segmentation and detection methods, namely, Unet [32], Deeplabv3+ [33], YOLOX [34], Gasformer [35], MWIRGas-YOLO [36], and YOLOv11 [37]. The quantitative results are summarized in Table 2, while the qualitative outputs are presented in Figure 7.
In terms of precision, recall, F1-score, and IoU, the proposed YPCN achieves the highest scores across all evaluation metrics, with values of 87.16%, 90.78%, 88.97%, and 89.74%, respectively. Compared with the original YOLOv11, YPCN improves F1 by 7.37% and IoU by 7.59%, which demonstrates a substantial performance gain. Even when compared to more advanced models such as Gasformer and MWIRGas-YOLO, YPCN exhibits superior balance between accuracy and model efficiency.
Furthermore, YPCN is the most lightweight model among all competitors, with only 6.3M parameters, significantly smaller than Deeplabv3+ (10.3M) and YOLOv11 (10.4M). In terms of real-time performance, YPCN also leads with an impressive 196 FPS, making it highly suitable for deployment in industrial safety systems where low latency is critical.
The qualitative comparisons in Figure 7 further corroborate the quantitative findings. Traditional methods such as Unet and Deeplabv3+ often fail to segment complete gas plumes, particularly under complex backgrounds or with small, low-contrast leaks. While YOLOX and Gasformer capture plume shapes more effectively, they still suffer from over-segmentation and misclassification in noisy scenes. The proposed YPCN produces consistently accurate and complete segmentation masks, even in challenging long-range or weak-signal scenarios. Its superior boundary refinement and suppression of background interference are attributed to the integration of physical priors via the gas plume loss function and the optimized network design.
Collectively, the results in Table 2 and Figure 7 highlight that YPCN not only surpasses existing models in detection accuracy, but also offers clear advantages in computational efficiency and robustness, making it a strong candidate for practical gas leak monitoring applications. The proposed network surpasses the other three models across all evaluation metrics, achieving a detection accuracy of 99.78%. In contrast, the highest accuracy reported in existing literature is 95% [26].
6 Conclusion and future perspectives
Based on the passive imaging technology of cryogenic infrared detectors, this paper proposes a deep learning-based gas semantic segmentation method based on the YOLOv11 model. Firstly, MobileNetV4 is used to replace the original backbone network, and the SPD-Conv module is introduced into the segmentation head to reduce the model parameters and complexity. In addition, the gas plume model is introduced as a key physical constraint condition in the loss function to improve the accuracy, segmentation precision and generalization ability of the model in processing gas plume tasks. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves an F1 score of 88.97% and an IoU of 89.74%, with a detection accuracy of up to 99.78%, demonstrating clear superiority over existing methods. These results demonstrate the potential of the proposed model for deployment in real-time industrial safety monitoring systems. To assess the applicability of the algorithm, we conducted a preliminary evaluation on a small test set of methane plume data (details in Section Ⅴ). The model achieved comparable performance, suggesting that features learned from butane can transfer effectively to methane in terms of plume localization. Nonetheless, we acknowledge the limitations of this approach. Butane and methane differ in their infrared absorption spectra, emissivity, and thermal contrast—factors that can impact plume visibility in IR imaging. We address this limitation in our future work by planning to incorporate mixed-gas and methane-specific datasets for fine-tuning. In the future, we will further optimize the network model to improve its accuracy and make it better applied to the task of natural gas leakage detection.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to am56aG91MjJAbWFpbHMuamx1LmVkdS5jbg==.
Author contributions
JZ: Writing – original draft, Methodology. YL: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. YZ: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. HH: Software, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Software, Writing – review and editing. FS: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. CC: Project administration, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by the National Key R&D Program of China under Grant 2024YFC2814303, in part by the Science and Technology Department of Jilin Province of China under Grant 20220203016SF and Grant 20240304195SF, in part by the Industrial Technology Research and Development Project of Jilin Provincial Development and Reform Com-mission under Grant 2024C007-5.
Conflict of interest
Author YZ was employed by Sinotest Equipment Co., Ltd. Author HH was employed by Jingwei Hirain Co., Ltd. Author ZL was employed by Changchun UP Optotech Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Alabdulwahab A, Abusorrah A, Zhang X, Shahidehpour M. Coordination of interdependent natural gas and electricity infrastructures for firming the variability of wind energy in stochastic day-ahead scheduling. IEEE Trans Sustain Energ (2015) 6:606–15. doi:10.1109/TSTE.2015.2399855
2. Li Y, Zou Y, Tan Y, Cao Y, Liu X, Shahidehpour M, et al. Optimal stochastic operation of integrated low-carbon electric power, natural gas, and heat delivery system. IEEE Trans Sustain Energ (2018) 9:273–83. doi:10.1109/TSTE.2017.2728098
3. Khan MI, Yasmin T, Shakoor A. Technical overview of compressed natural gas (CNG) as a transportation fuel. Renew Sustain Energ Rev (2015) 51:785–97. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.06.053
4. Liu G, Dong X, Jiang Q, Dong C, Li J. Natural gas consumption of urban households in China and corresponding influencing factors. Energy Policy (2018) 122:17–26. doi:10.1016/j.enpol.2018.07.016
5. Zou C, Lin M, Ma F, Liu H, Yang Z, Zhang G, et al. Development, challenges and strategies of natural gas industry under carbon neutral target in China. Petrol Explor Dev (2024) 51:476–97. doi:10.1016/S1876-3804(24)60038-8
6. Ravikumar AP, Wang J, McGuire M, Bell CS, Zimmerle D, Brandt AR. Good versus Good Enough? Empirical tests of methane leak detection sensitivity of a commercial infrared camera. Environ Sci Technol (2018) 52:2368–74. doi:10.1021/acs.est.7b04945
7. Prakash N, Ramachandran A, Varma R, Chen J, Mazzoleni C, Du K. Near-infrared incoherent broadband cavity enhanced absorption spectroscopy (NIR-IBBCEAS) for detection and quantification of natural gas components. Analyst (2018) 143(14):3284–91. doi:10.1039/c8an00819a
8. Krishna KG, Parne S, Pothukanuri N, Kathirvelu V, Gandi S, Joshi D. Nanostructured metal oxide semiconductor-based gas sensors: a comprehensive review. Sens Actuators A Phys (2022) 341:113578. doi:10.1016/j.sna.2022.113578
9. Baranwal J, Barse B, Gatto G, Broncova G, Kumar A. Electrochemical sensors and their applications: a review. Chemosensors (2022) 10:363. doi:10.3390/chemosensors10090363
10. Su JC, Cao LH, Li L, Wei J, Li GN, Yuan YY. Highly sensitive methane catalytic combustion micro-sensor based on mesoporous structure and nanocatalyst. Nanoscale (2013) 5:9720–5. doi:10.1039/c3nr02916f
11. Lee H, Lee D, Lee J, Shin D. Efficient gas leak simulation surrogate modeling and super resolution for gas detector placement optimization. Comput Chem Eng (2023) 181:108508. doi:10.1016/j.compchemeng.2023.108508
12. Cho J, Kim H, Gebreselassie AL, Shin D. Deep neural network and random forest classifier for source tracking of chemical leaks using fence monitoring data. J Loss Prevent Process Ind (2018) 56:548–58. doi:10.1016/j.jlp.2018.01.011
13. Zhang XQ, Shi JH, Huang XY, Xiao F, Yang M, Huang JW, et al. Towards deep probabilistic graph neural network for natural gas leak detection and localization without labeled anomaly data. Expert Syst Appl (2023) 231:120542. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120542
14. Gong WH, Hu J, Wang ZW, Wei YB, Li YF, Zhang TT, et al. Recent advances in laser gas sensors for applications to safety monitoring in intelligent coal mines. Front Phys (2022) 10:1058475. doi:10.3389/fphy.2022.1058475
15. Li JS, Deng H, Sun J, Yu BL, Fischer H. Simultaneous atmospheric CO, N2O and H2O detection using a single quantum cascade laser sensor based on dual-spectroscopy techniques. Sens Actuators B Chem (2016) 231:723–32. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2016.03.089
16. Liu NW, Xu LG, Li JS. Self-calibrated wavelength modulation spectroscopy based on 2f/1f amplitude and integral area for trace gas sensing. Opt Quant Electron (2023) 55(1):22–11. doi:10.1007/s11082-022-04174-w
17. Xu SY, Wang QY, Zhu Z, Wang JL, Zou X, Li ZG, et al. Photoacoustic spectroscopy based on vertical cruciform multi-stepped photoacoustic cell achieving ppb-level acetylene detection. Sens Actuators B Chem (2024) 418:136313. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2024.136313
18. Huang Q, Wei Y, Li JS. Simultaneous detection of multiple gases using multi-resonance photoacoustic spectroscopy. Sensors Actuators B Chem (2022) 369:132234. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2022.132234
19. Xu L, Zhou S, Liu N, Zhang M, Liang J, Li JS. Multigas sensing technique based on quartz crystal tuning fork-enhanced laser spectroscopy. Anal Chem (2020) 92(20):14153–63. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.0c03233
20. Xu L, Liu K, Liang J, Li JS, Zhou S. Micro-quartz crystal tuning fork-based photodetector array for trace gas detection. Anal Chem (2023) 95(17):6955–61. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.3c00318
21. Wang Q, Sun YL, Pan XT, Xing MW, Zhao Y. Optical gas imaging for accurate leakage source measurement based on optical flow analysis. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas (2025) 74:1–8. doi:10.1109/TIM.2025.3529059
22. Murphy B, Cahill R, McCaul C, Buggy D. Optical gas imaging of carbon dioxide at tracheal extubation: a novel technique for visualising exhaled breath. Br J Anaesth (2021) 126:E77–8. doi:10.1016/j.bja.2020.11.016
23. Wang Q, Sun YL, Jing YX, Pan XT, Xing MW. YOLOGAS: an intelligent gas leakage source detection method based on optical gas imaging. IEEE Sens J (2024) 24:35621–7. doi:10.1109/JSEN.2024.3437200
24. An JY, Shin HJ, Yang M, Park DY, Yang J, Kim HJ. Non-contact diagnosis of sleep breathing disorders using infrared optical gas imaging: a prospective observational study. Sci Rep (2022) 12:21052. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-25637-w
25. Olbrycht R, Kaluza M. Optical gas imaging with uncooled thermal imaging camera—impact of warm filters and elevated background temperature. IEEE Trans Ind Electron (2020) 67:9824–32. doi:10.1109/TIE.2019.2956412
26. Wang JF, Tchapmi LP, Ravikumar AP, McGuire M, Bell CS, Zimmerle D, et al. Machine vision for natural gas methane emissions detection using an infrared camera. Appl Energ (2020) 257:113998. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.113998
27. Yan M, Li Z, Dong Z, Liun YM, Chen LY, Wu XS, et al. Gas leak real-time detection and volume flow quantification based on infrared imaging and advanced algorithms. IEEE Access (2025) 13:7284–92. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3525764
28. Ye WL, Zheng CT, Yu X, Song ZW, Wang YD. Performances of a mid-infrared CH4 detection device using an optimized asymmetric ellipse gas-cell. Microw Opt Technol Lett (2011) 53:2327–30. doi:10.1002/mop.26282
29. Wan DH, Lu RS, Shen SY, Xu T, Lang XL, Ren ZJ. Mixed local channel attention for object detection. Eng Appl Artif Intell (2023) 123:106442. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2023.106442
30. Qin DF, Leichner C, Delakis M, Fornoni M, Luo SX, Yang F, et al. MobileNetV4: universal models for the mobile ecosystem. Computer Vis - ECCV 2024, Pt XL (2024) 15098:78–96. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-73661-2_5
31. Wang LY, Zhang GX, Wang WJ, Chen JY, Jiang XY, Yuan H, et al. A defect detection method for industrial aluminum sheet surface based on improved YOLOv8 algorithm. Front Phys (2024) 12:1419998. doi:10.3389/fphy.2024.1419998
32. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI); October 05-09 2015; Munich, Germany (2015). p. 234–41. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
33. Chen LCE, Zhu YK, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: V Ferrari, M Hebert, C Sminchisescu, and Y Weiss, editors. Computer vision - eccv 2018. Cham: Springer (2018). p. 833–51. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-01234-2_49
34. Fan JZ, Zhou J, Zhao Q, Luo D, Chen W. Broadband infrared imaging for enhanced gas leak detection. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Photonics, Optics and Laser Technology - Volume 1: PHOTOPTICS. SciTePress (2025). p. 102–8. doi:10.5220/0013152300003902
35. Sarker TTS, Embaby MG, Ahmed KR, AbuGhazaleh A. Gasformer: A transformer-based architecture for segmenting methane emissions from livestock in optical gas imaging. In: Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). IEEE (2024). p. 5489–97. doi:10.1109/CVPR46437.2024.00542
36. Xu SW, Wang X, Sun QY, Dong KJ. MWIRGas-YOLO: gas leakage detection based on mid-wave infrared imaging. Sensors (2024) 24(13):4345. doi:10.3390/s24134345
Keywords: natural gas leakage, mid-infrared spectrum, combustible gas cloud imaging, plume classification network, YOLO
Citation: Zhou J, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Hu H, Leng Z, Sun F and Chen C (2025) High-accuracy combustible gas cloud imaging system using YOLO-plume classification network. Front. Phys. 13:1603047. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1603047
Received: 31 March 2025; Accepted: 04 June 2025;
Published: 19 June 2025.
Edited by:
Jingsong Li, Anhui University, ChinaReviewed by:
Qiaoyun Wang, Northeastern University, ChinaToqi Tahamid Sarker, Southern Illinois University Carbondale, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Liu, Zhang, Hu, Leng, Sun and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Sun, c3VuZmVuZ0BqbHUuZWR1LmNu; Chen Chen, Y2NoZW5Aamx1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Jiani Zhou1
Jiani Zhou1 Chen Chen
Chen Chen