- 1School of Computer Science, Guangdong University of Education, Guangzhou, China
- 2School of Electronic Science and Engineering, South China Normal University, Foshan, China
- 3School of Information Engineering, Guangzhou Panyu Polytechnic, Guangzhou, China
The rise of user-generated content on social media is making memes a prevalent medium for expression. However, some memes convey offensive information toward individuals or groups on particular aspects. Detecting such harmful content is essential to mitigate potential conflicts and harm. This paper proposes a retrieval-augmented prompting network (RAPN) for hateful meme detection. The proposed model utilizes a retrieval-augmented selector to identify semantically relevant prompting examples from diverse sources, enhancing the selection to better match the inference instances. Based on the prompting framework, attention networks are employed to extract critical features from input instance and examples. By applying contrastive learning to label and feature spaces, the model is capable of learning more discriminative information for classification. Comprehensive evaluations on benchmark datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms the baseline methods. Thereby, the proposed model has strong evidence of high accuracy on the task of hateful meme classification.
1 Introduction
Advances in the internet era have significantly boosted the widespread popularity of user-generated social media information. People on social networks are constantly encouraged to express their opinions to a global audience, which generates a massive volume of content on virtually anything [1]. A meme is representative content which conveys underlying meaning in a subtle and implicit manner. Typically, a meme is the combination of text and image. Despite their appealing, funny, and dramatic graphics along with confusing, amusing, and caustic sentences, memes can be implicitly offensive [2]. As an example, the image paired with the text, in Figure 1 ©Getty Images signifies racial discrimination toward Muslims. Current publications report that various potentially dangerous textual or visual content carry subjective hatred, including aggression, insults, and disparagement [3]. The spread of such hateful memes harms not just the individuals and groups attacked but also deliberately instigates violent conflict [4]. As one of the largest social media platforms, Facebook removed 9.6 million pieces of offensive or misleading content in the first quarter of 2020. In such a data-saturated social network, manually reviewing and preventing all forms of hate speech seems impractical. Therefore, the requirement for automatically detecting hateful memes is firmly emphasized.

Figure 1. Example of a hateful meme. Sourced from https://www.drivendata.org/competitions/64/hateful-memes/. ©Getty Images.
The task of hateful meme detection (HMD) thus arises. A great deal of effort is expended on deep learning-based multimodal data analysis. In this process, a meme is classified as hateful or non-hateful. A primary reason for is that both textual and visual information, together with the relationship between them, need to be processed to identify the hateful tendency [5, 6]. Cutting-edge outcomes are obtained by prompting pretrained language models (PLMs), which focus more on learning ability from given samples rather than integrating multimodal interaction strategies [7]. In these methods, the meme text, extracted image captions, and pretrained masked language models are concatenated for harmful meme detection [8]. Remarkably, the approach of Pro-Cap PromptHate has an impressive average accuracy of 91.03 on the real-world dataset HarM, substantially outperforming state-of-the-art multimodal-specific models [9]. As a result, prompt-based learning gives rise to new opportunities to enhance HMD performance.
According to the United Nations Strategy and Plan of Action on Hate Speech, a hateful meme involves offensive contents concerning religion, ethnicity, nationality, race, color, descent, gender, or other identity factors [10]. With such a definition, each meme can be further categorized into an aspect following a binary classification. In this context, a comprehensive understanding of memes is attained, which in turn paves a way of improving HMD methods. While restricted to hateful meme datasets, the categorization of hateful memes can be performed using retrieval augmented schemes. That is, based on pre-training with more-related samples, a model tends to be more effectively prompted in its detection. In the context of natural language processing (NLP), retrieval augmentation is a technique that enhances the capability of a given model by integrating it with external knowledge sources [11]. Intrinsic knowledge and retrieved information are combined, based on which the basic model is refined to be more accurate and reliable. Following this idea, retrieval augmented methods can further be employed in providing higher-quality content, especially during the inference stage [12]. HMD is a task where the literature highlights not just the learning of multimodal hatefulness but also reasoning with external knowledge [13–16].
To address HMD challenges, a retrieval-augmented prompting network (RAPN) is proposed here. Given memes, including the inference instance and the examples, are initially converted to unimodal form using ClipCap [17] and encoded via a fine-tuned BLIP-2 [18]. With the structure of the attention network, critical features for detection are effectively extracted. Furthermore, supervised contrastive learning is applied to distinguish the correlation and difference among diversified meme categories within example batches. Motivated by the paradigm of retrieval augmentation, an example selection strategy is established. Random examples are selected to preserve sample diversity during training while the most similar hate and non-hate examples are captured as inference instances during the test. The three contributions of this study are as follows.
First, retrieval-augmented selection is devised to capture the prompting examples from extending sources. Thus, the most relevant samples for the inference instance are taken as examples during testing, which effectively improves the model’s learning ability. Second, in line with the framework of prompt-based methods, both label-based and feature-based contrastive learning strategies are applied for model optimization. Specifically, feature-based contrastive learning, which aims to learn critical information from memes of the same aspects, substantially enhances the classification accuracy. Third, experiments on benchmark datasets indicate that our model is capable of detecting the given memes in the prompting framework. The proposed model produces results considerably better than the baseline methods.
The rest of this study is organized as follows. In Section 2, we review the related work of hateful meme detection and retrieval-augmented methods. The proposed RAPN is described in detail in Section 3. In Section 4, we evaluate our model on hateful meme detection experiments and discuss the results. Concluding remarks are presented in Section 5.
2 Related work
2.1 Hateful meme detection approaches
Progress in HMD tasks is driven by the generation of hateful meme datasets [6, 19, 20]. Since memes generally possess multimodality, most ongoing studies tend to address HMD through multimodal classification [6, 18, 21]. Both intramodal information and intermodal integration are employed to detect whether the image–text pair takes on a hateful meaning or not [22]. In this context, Zhang et al. devised a complementary visual and linguistic network, which leverages contextual-level and sensitive object-level information to make hateful meme predictions [23]. Pramanick et al. developed a novel multimodal deep neural network that systematically analyzes the local and global perspective of input memes [5]. With the application of background knowledge, Kiran et al. effectively fused the semantic understanding from both modalities [24]. Wu et al. proposed an enhanced multimodal fusion framework for HMD on a brain-inspired framework. This architecture jointly combines the main semantics and the subtle metaphors behind memes, which mitigates cognitive biases against HMD [3].
More recently, prompting PLMs benefits both unimodal [25] and multimodal [26] tasks to a certain extent. Cao et al. designed simple prompts and provided in-context examples to exploit the implicit knowledge in a pretrained RoBERTa language model for HMD [7]. Furthermore, a frozen pretrained vision-language model (PVLM) was utilized to generate captions with critical information which facilitates detection without increasing computational costs [9]. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets provide strong evidence for the effectiveness of prompting approaches.
2.2 Retrieval-augmented strategies
Retrieval-based methods show their superiority in a range of NLP tasks. By retrieving relevant information from more knowledge sources, these methods improve model performance and support the subsequent generation process [27]. For an input query, relevant documents or passages are fetched from a large corpus. The retrieved information is then combined with the original input to form an augmented content. On the task of semantic parsing, Pasupat et al. controlled the behavior of parsers via retrieval and augmentation processes across domains [28]. Zhang et al. applied the retrieval strategy to align knowledge base labels with input contexts for distantly supervised information extraction [29]. With respect to large language models (LLMs), Ren et al. investigated the impacts of retrieval augmentation on pen-domain question answering, which reduces hallucination and improves accuracy in perceiving factual knowledge boundary [30]. For low-resource settings, Seo et al. proposed a retrieval-augmented data augmentation framework that trains data through retrieval, boosting model performance on domain-specific tasks [31]. In these applications, information of greater relevance is retrieved from a broader source, which facilitates the model’s robustness regarding infrequent data points [32].
3 Methodology
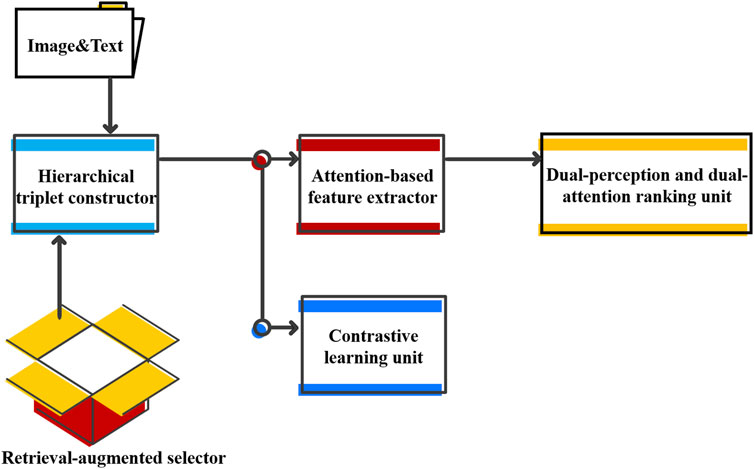
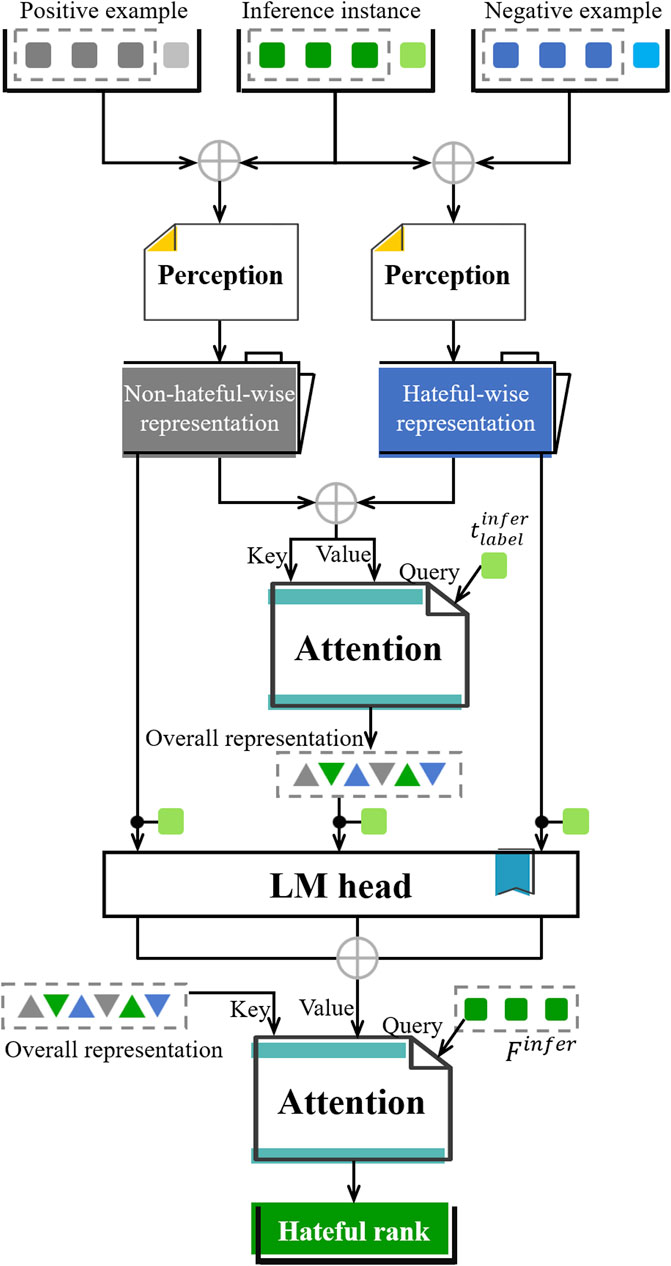
Figure 2 presents the framework of RAPN. HMD is initially performed on the basis of a PVLM with prompts, referred to as a “hierarchical triplet constructor.” Each prompt is constructed as a triple sequence of memes, with each meme being a triple textual sequence as well. Specifically, a retrieval-augmented module is devised to retrieve the most similar examples to construct the prompt during testing. Then, a textual encoder is employed for deriving embeddings. Both a feature extractor and a ranking unit are established on attention mechanism. Key features are extracted and used to classify the inference instance as either “hateful” or “non-hateful.” Contrastive learning within a training batch is implemented to enhance the classification accuracy. More details about each component are described in the following sections.
3.1 Hierarchical triplet constructor
For an input meme with

Figure 3. Example of a meme triplet. Meme sourced from https://www.drivendata.org/competitions/64/hateful-memes/. ©Getty Images.
Conforming with the prompt template, a non-hateful and a hateful meme are concatenated following the inference instance sequentially, given as a positive and a negative example, respectively (Figure 4). As long as each meme is a triplet, a hierarchical triplet in textual form is constructed. To facilitate processing, each triplet sequence is established within fixed positions. The text and caption of the triplet are concatenated and arranged into one sequence segment with the category label into the other (Figure 5). Every sequence is constrained to its predefined length. If the length is not reached, it is padded; otherwise, it is truncated. Given the pivotal role of inference instances in classification, the length of inference instance is extended, whereas that of examples is reduced. The inference instance sequence

Figure 4. Example of a hierarchical triplet in prompt template. Memes sourced from https://www.drivendata.org/competitions/64/hateful-memes/. ©Getty Images.
Similarly, the sequences of positive
3.2 Retrieval-augmented selector
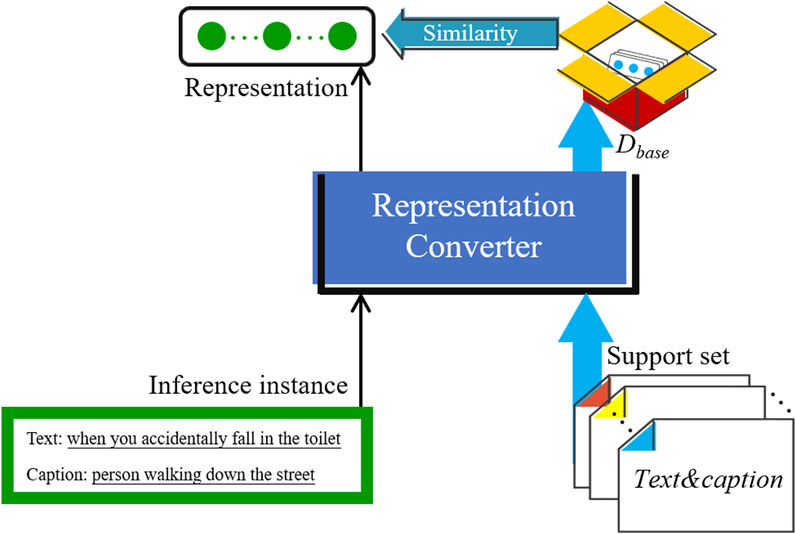
The equations should be inserted in editable format from the equation editor. All figures and tables should be cited in the main text as “Figure 1”, “Table 1”, and so forth. The purpose of retrieval-augmented selection is to capture the most relevant sample of the inference instance as a prompting example. Thus, the quality of prompts can be improved to benefit the model’s learning. A two-stage sample selecting approach is thus proposed: in the training stage, we take a random selection to enhance example diversity; in the test stage, we use vector retrieval to select relevant prompt examples based on similarity. The schematic of retrieval augmented example selection is shown in Figure 6.
A pre-trained Jina [33] model is employed as the vector converter to obtain a relevant sample from the support set. In line with the aforementioned meme triplet, the text and image caption are concatenated to obtain its vector:
where
All of the sample vectors can be derived using (Equation 3), and they are further stored in the retrieval database
where
3.3 Attention-based feature extractor
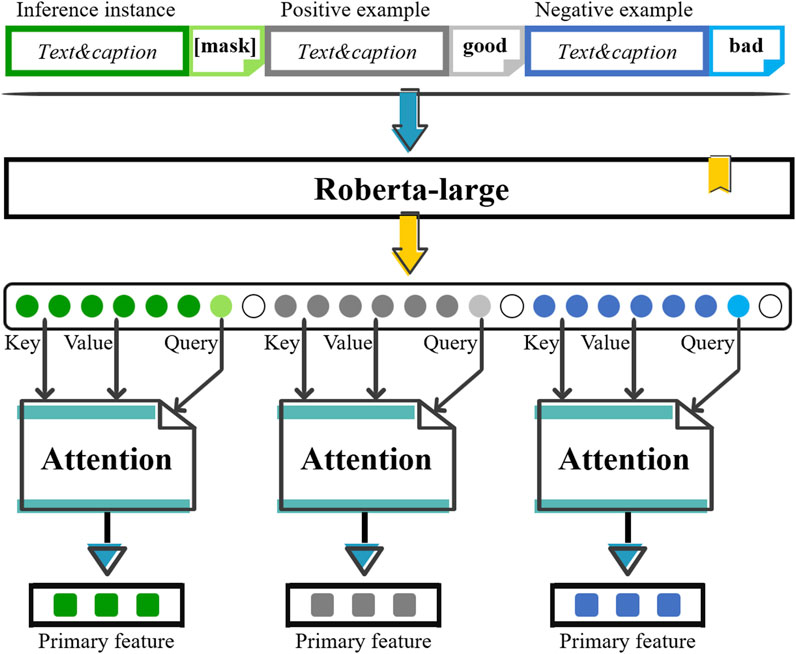
The primary feature, from the text and image caption, is obtained by feeding the hierarchical textual triplet into an attention-based feature extractor. The architecture of feature extraction is exhibited in Figure 7. A pre-trained Roberta-large model is applied to convert the prompt sequences into embeddings via Equations 5–8:
where
The embeddings are then sent to the attention network. For the inference instance, the label embedding
where
3.4 Dual-perception and dual-attention ranking unit
Tables should be inserted at the end of the manuscript. In order to predict the category label of the inference instance, the interaction between the label embedding and primary feature is performed in the dual-perception and dual-attention ranking unit (Figure 8). In the context of prompting, since the label is a prediction target, a greater weight is assigned during ranking.
For each sequence, the label token can be extracted from its label embedding, which is further integrated with the primary feature. Then, the integration of inference instance is respectively paired with those of examples, which are respectively fed into two perception networks to derive the hateful- and the non-hateful-wise representations (Equations 10, 11).
where
The learning of the relation between inference instance and both examples is thus carried out. Each perception outcome contains either the hateful feature or the non-hateful feature. Both outcomes are combined and sent to the attention mechanism to obtain overall representation of the prompt. Specifically, the fused outcome is used as key and value, while the label embedding of the inference instance is the query, as presented in Equation 12:
Based on the attention mechanism, both the hateful- and non-hateful-wise representation can be perceived by using the label token and further fused into the overall presentation.
Subsequently, a linear classifier LMhead is taken to predict three scores upon the representations via Equations 13–15:
where
Lastly, an attention network is established, allowing the adaptive selection of hateful proportions. The query is the primary of the inference instance, the key is the overall representation, and the value is the concatenation of the three scores from LMhead. The final rank
3.5 Contrastive learning unit
The meme classification result is determined by the ranking on hateful and non-hateful scores, with model training guided by cross-entropy loss. To further enhance learning the relationship between hateful and non-hateful information in the inference instance, contrastive learning strategies are proposed to facilitate training processes.
3.5.1 Label-based contrastive learning
There is clearly a certain distinction in the masked label between hateful and non-hateful inference instances. Label features are grouped by category in the vector space, with intra-category clustered and inter-category separated. Label prediction is performed using the masked category extracted from the prompt. In this way, contrastive learning on a category label can benefit the learning of hateful and non-hateful information.
Compared with the masked label, the label of the same category forms positive samples, while those of the different category are negative samples within a batch. Based on contrastive learning, discriminative categories are taken by pulling positive samples closer and pushing negative samples farther apart. The loss function of label-based contrastive learning is given in Equation 17:
where
3.5.2 Feature-based contrastive learning
Like label-based contrastive learning, contrastive learning on primary features is also conducted during training. In the case of an inference instance of the actual category “hateful,” its mask token lies closer to the example of bad token and farther to that of good token in the feature space. Specifically, the inference instance label token
where
According to Equation 19, the total training loss of RAPN combines
where
4 Experiments
4.1 Dataset
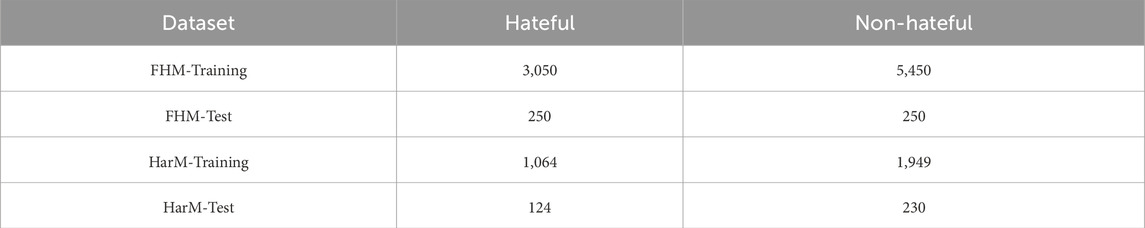
Experiments were performed on two public datasets: Facebook Hate Memes (FHM) [6] and Harmful Memes (HarM) [5]. The FHM dataset is developed by Facebook to support a crowdsourced initiative on multimodal HMD. HarM includes real-world COVID-19 memes from Twitter, which are labeled as highly harmful, partially harmful, and harmless. Consistent with prior research [7], we adopt a binary classification scheme by merging highly harmful and partially harmful memes into a single “hateful” label. We augment the image with entity information and racial characteristics using external tools (Google Vision Web Entity Detection API) and the pretrained FairFace classifier [34]. Table 1 presents the statistics for both datasets.
4.2 Experimental setting
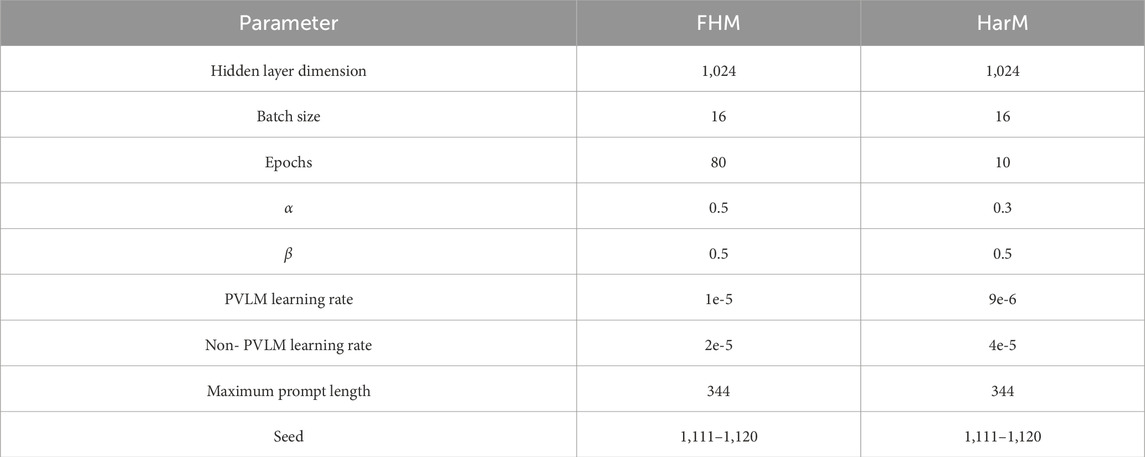
The pretrained RoBERTa-large is employed with its hidden layer dimension set to 1,024. To preserve the performance of the pretrained language model during training, a hierarchical learning rate strategy is applied with a smaller learning rate for the pretrained model and a larger learning rate for other layers. The model settings are detailed in Table 2.
4.3 Baselines
To comprehensively evaluate the performance of the proposed model, the following baselines are taken for comparison.
Unimodal methods:
Text-Bert: a text-only approach based on fine-tuned BERT [35] model on hateful meme text classification.
Image-Region: an image-only method that processes hateful meme images using Faster R-CNN [36] and ResNet-152 [37], then sends the representations to a classifier.
Multimodal methods:
Late Fusion [38]: a model that extracts visual features and textual features using ResNet-152 and BERT, with simple fusion followed by linear classification.
MMBT-Region [39]: a supervised multimodal approach using bit-transformation on image-region features.
ViLBERT CC [40]: a multimodal model that is pretrained on the Conceptual Captions dataset.
Visual BERT COCO [41]: a vision-language model that is pretrained on the COCO dataset.
MOMENTA [5]: a multimodal deep neural network that analyzes global and local information from a given meme while incorporating contextual background.
LLM:
DeepSeek V3: untrained DeepSeek V3 is employed via its application programming interface (API).
Prompt-based Methods:
PromptHate [7]: a prompt-based method that converts images into textual descriptions, concatenates them with text, and constructs sequences. The sequences are fine-tuned with Roberta and fed into a linear layer for classification.
Pro-Cap [9]: based on PromptHate zero-shot, VQA is employed to ask BLIP-2 questions, which improves the image-caption quality and the classification performance.
4.4 Main results
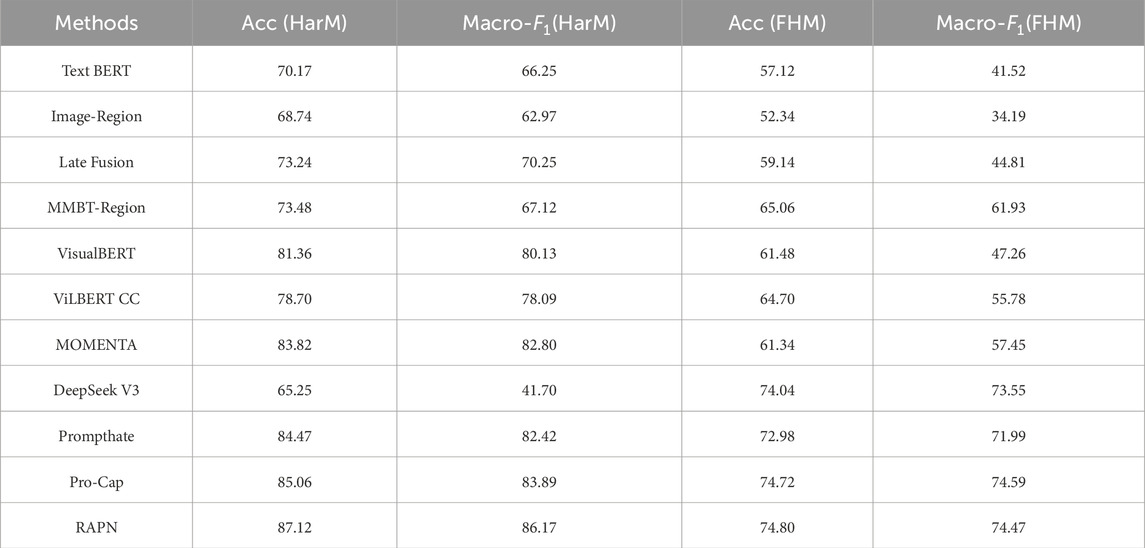
In this experiment, we adopted accuracy and macro-F1 as evaluation metrics to assess the working performance. Table 3 compares the results of baseline methods with the proposed model on the HarM and FHM datasets, with all metrics averaged over ten independent runs. Of all methods, RAPN consistently outperforms the baselines in both evaluation settings.
Multimodal approaches are clearly better alternatives than single-modality methods in HMD tasks. With respect to multimodal models, Late Fusion and MMBT-Region are of inferior performance due to the absence of model pretraining. In contrast, both VisualBERT-COCO and ViLBERT-CC benefit from additional pretraining on external multimodal corpora. Moreover, MOMENTA enhances classification by jointly modeling both global and local information in memes through a fine-grained analysis paradigm. Apparently, there is a considerable gap between the performance on HarM and FHM of multimodal models. A possible explanation is that samples from FHM tend to suffer from missing modalities, such as blurry text or low-quality images, resulting in significant performance decline. One can also see a sub-optimal outcome of DeepSeek V3 on both datasets. Without model fine-tuning, LLMs fall short in HMD because the labeling largely relates to human subjectivity and requires domain-specific historical knowledge.
Experimental results show that prompt-based baselines achieve comparable results across both datasets. By converting the multimodal HMD into NLP tasks, prompts are established to guide the models in classification and leverage the implicit knowledge by adopting a masked language modeling training objective for HMD. Compared to Pro-Cap, our model achieves increments of 2.6% and 0.08% on HarM and FHM, respectively. Thus, the effectiveness of prompting is further highlighted. By introducing attention-based feature extraction and retrieval augmented strategy, more relevant examples with similar aspects are selected for prompting in testing while key features from given memes are captured. In this way, the relationship between inference instance and prompting examples within feature space is determined. With learning of hateful and non-hateful information from examples, it is reasonable to expect more precise features and thus better performance.
4.5 Ablation study
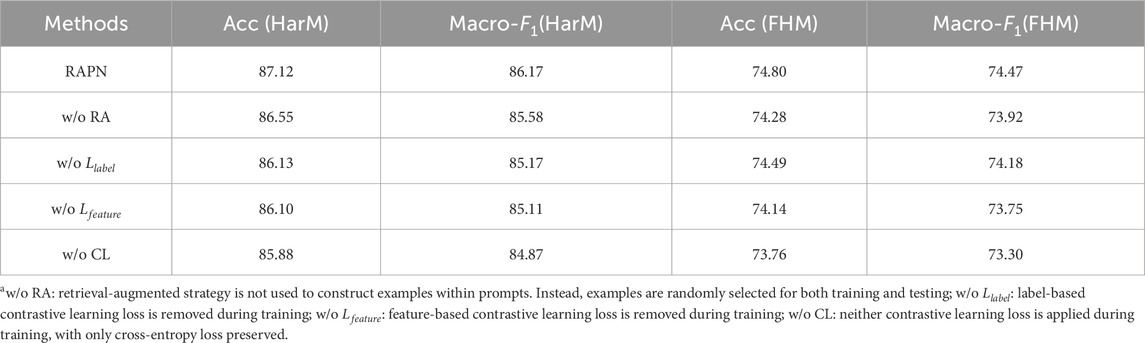
In order to determine the importance of components in RAPN, an ablation study was conducted (Table 4). Based on the structure of RAPN, four components are sequentially removed.
According to Table 4, the retrieval-augmented strategy does make a contribution to HMD. The retrieval process identifies semantically similar samples from example sets based on the inference instance. More relevant examples of the inference instance are thus selected for classification. Moreover, the ablating of
4.6 Visualization
To intuitively demonstrate the impact of the contrastive learning scheme on model learning, the t-SNE visualization on the HarM test set is conducted [42]. As presented in Figure 9, most green and red dots form distinct clusters. This result validates the proposed model’s capability of learning discriminative features based on contrastive learning strategies. Specifically, the featured-based contrastive learning benefits from learning from category labels with the same aspects. Clearly, the specific category label of an inference instance is close to its corresponding positive/negative tokens within the feature space, demonstrating the effectiveness of our contrastive learning unit.
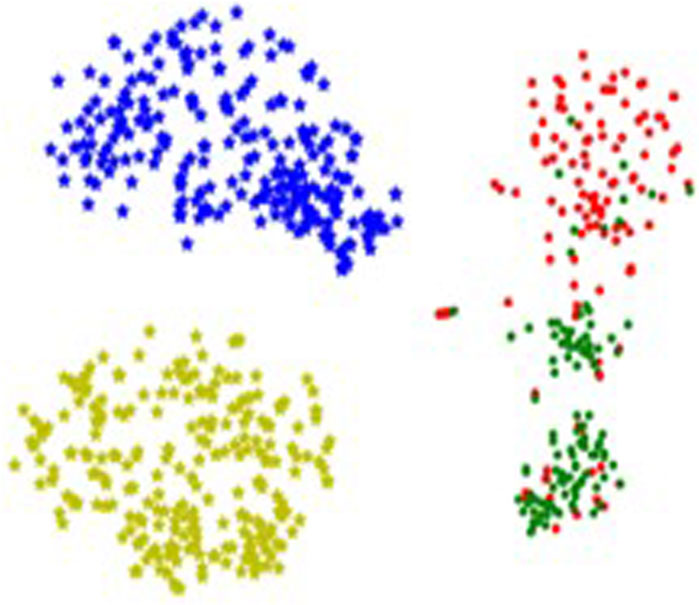
Figure 9. Visualization of label tokens. * Green dots: label tokens of non-hateful inference instances. Red dots: label tokens of hatful inference instances. Yellow stars: label tokens of positive examples. Blue stars: label tokens of negative examples.
5 Conclusion
This study proposes a retrieval-augmented prompting network (RAPN) on the task of HMD. In the proposed model, a retrieval-augmented selector is built to capture semantically similar prompting examples from a wide-range of sources, thus enhancing the prompt relevance toward the inference instance. Based on the attention mechanism, valuable features from both inference instance and examples are extracted, and these are further used to determine the hateful score. Contrastive learning on category label and feature is employed during training, further promoting the ability to distinguish hateful and non-hateful memes. Experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model. Experimental results reveal that our model is the best alternative compared with baselines. In the future, we will consider further improving the model’s generalizability across diverse datasets and cultural contexts by using LLMs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
QK: writing – original draft, formal analysis, writing – review and editing, investigation, methodology, conceptualization, and validation. YL: validation, methodology, conceptualization, investigation, writing – review and editing, and writing – original draft. JL: validation, conceptualization, methodology, writing – original draft, writing – review and editing, and investigation. XL: writing – review and editing, writing – original draft, investigation, and validation. RZ: supervision, resources, writing – review and editing, visualization, project administration, and conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research is a project supported by Guangzhou Science and Technology Plan Project (202102080394), the Research Platform and Project of Guangdong Provincial Department of Education under grant number 2024KQNCX141, and the Science and Technology Projects of Guangzhou under grant number 2025A04J4163.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the reviewers and editors of Frontiers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Schouten K, Frasincar F. Survey on aspect-level sentiment analysis. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng (2016) 28:813–30. doi:10.1109/tkde.2015.2485209
2. Kapil P, Ekbal A. A transformer based multi task learning approach to multimodal hate speech detection. Nat Lang Process.J (2025) 11:100133. doi:10.1016/j.nlp.2025.100133
3. Wu F, Gao B, Pan X, Li L, Ma Y, Liu S, et al. Fuser: an enhanced multimodal fusion framework with congruent reinforced perceptron for hateful memes detection. Inf Process Manag (2024) 61:103772–25. doi:10.1016/j.ipm.2024.103772
4. Saha P, Das M, Mathew B, Mukherjee A. Hate speech: detection, mitigation and beyond. In: Proceedings of the Sixteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (2023). p. 1232–5.
5. Pramanick S, Sharma S, Dimitrov D, Akhtar MS, Nakov P, Chakraborty T. MOMENTA: a multimodal framework for detecting harmful memes and their targets. Findings Assoc Comput Linguistics: EMNLP (2021) 2021:4439–55. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2109.05184
6. Kiela D, Firooz H, Mohan A, Goswami V, Singh A, Ringshia P, et al. The hateful memes challenge: detecting hate speech in multimodal memes. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst (2020) 33:2611–24. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2005.04790
7. Cao R, Lee RKW, Lee RKW, Chong WH. Prompting for multimodal hateful meme classification. In: Pro-cap: leveraging a frozen vision-language model for hateful meme detection. Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: Association for Computational Linguistics. arXiv preprint arXiv:2302.04156 (2023).
8. Ji J, Ren W, Naseem U. Identifying creative harmful memes via prompt-based approach. In: Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023 (2023). p. 3868–72.
9. Cao R, Hee MS, Kuek A, Chong WH, Lee RKW, Jiang J. Pro-cap: leveraging a frozen vision-language model for hateful meme detection. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM) (2023). p. 5244–52.
10. Guterres A. United Nations strategy and plan of action on hate speech. New York, NY: United Nations Digital Library (2019). Available online at: https://www.un.org/en/hate-speech/un-strategy-and-plan-of-action-on-hate-speech.
11. He H, Zhang H, Roth D (2022). Rethinking with retrieval: faithful large language model inference. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.00303.
12. Divekar A, Durrett G (2024). SYNTHESIZRR: generating diverse datasets with retrieval augmentation, 19200, 27. doi:10.18653/v1/2024.emnlp-main.1071
13. Radford A, Kim JW, Hallacy C, Ramesh A, Goh G, Agarwal S, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, 139 (2021). p. 8748–63.
14. Liang X, Huang Y, Liu W, Zhu H, Liang Z, Chen L. TRICAN: multi-modal hateful memes detection with triplet-relation information cross-attention network. In: Proceedings of the 2022 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (2022). p. 1–8. doi:10.1109/ijcnn55064.2022.9892164
15. Kumar GK, Nandakumar K. Hate-CLIPper: multimodal hateful meme classification based on cross-modal interaction of CLIP features. In: Proceedings of the second workshop on NLP for positive impact (2022). p. 171–83.
16. Sharma S, Kulkarni A, Suresh T, Mathur H, Nakov P, Akhtar MS, et al. Characterizing the entities in harmful memes: who is the hero, the villain, the victim? In: Proceedings of the 17th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (2023). p. 2149–63.
17. Mokady R, Hertz A, Bermano AH (2021). CLIPCap: CLIP prefix for image captioning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.09734.
18. Li J, Li D, Savarese S, Hoi SCH (2023). BLIP-2: bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. arXiv preprint. arXiv:2301.12597.
19. Suryawanshi S, Chakravarthi BR, Arcan M, Buitelaar P. Multimodal meme dataset (MultiOFF) for identifying offensive content in image and text. In: Proceedings of the second workshop on trolling, aggression and cyberbullying (2020). p. 32–41.
20. Gomez R, Gibert J, Gómez L, Karatzas D. Exploring hate speech detection in multimodal publications. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (2020). p. 1459–67.
21. Hossain E, Hoque MM, Hossain MA. An inter-modal attention framework for multimodal offense detection. Lect Notes Netw Syst (2023) 569:853–62. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-19958-5_81
22. Hermida PCQ, Santos EM. Detecting hate speech in memes: a review. Artif Intell Rev (2023) 56:12833–51. doi:10.1007/s10462-023-10459-7
23. Zhang W, Liu G, Li Z, Zhu F (2020). Hateful memes detection via complementary visual and linguistic networks. arXiv:2012.04977.
24. Kiran A, Shetty M, Shukla S, Kerenalli V, Das B. Getting around the semantics challenge in hateful memes. Lect Notes Data Eng Commun Technol (2022) 142:341–51. doi:10.1007/978-981-19-3391-2_26
25. Gao T, Fisch A, Chen D. Making pre-trained language models better few-shot learners. In: Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (2021). p. 3816–30.
26. Zeng A, Wong A, Welker S, Choromanski K, Tombari F, Purohit A, et al. Socratic models: composing zero-shot multimodal reasoning with language. In: Proceedings of the 36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2022). p. 00598. arXiv:2204.
27. Luo M, Gokhale T, Varshney N, Yang Y, Baral C. Retrieval augmented modeling. Synth Lect Comput Vis (2025) 135–57. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-57816-8_5
28. Pasupat P, Zhang Y, Guu K, Lee L (2022). Controllable semantic parsing via exemplar retrieval. arXiv:2110.08458v2.
29. Zhang Y, Fei H, Li P. End-to-End distantly supervised information extraction with retrieval augmentation. In: Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (2022). p. 2449–55. doi:10.1145/3477495.3531876
30. Ren R, Wang Y, Qu Y, Dai Y, Huang S, Zhao WX, et al. Investigating the factual knowledge boundary of large language models with retrieval augmentation. In: Proceedings of the 38th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (2024). arXiv:2307.11019v3.
31. Seo M, Baek J, Thorne J, Hwang SJ. Retrieval-augmented data augmentation for low-resource domain tasks. In: Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2024). arXiv:2402.13482v1.
32. Yu G, Liu L, Jiang H, Shi S, Ao X. Making better use of training corpus: retrieval-based aspect sentiment triplet extraction via label interpolation. In: Proceedings of the 61st annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (2023). p. 4914–27.
33. Günther M, Ong J, Mohr I, Abualhaija S, van Berkel N, Bogdan R, et al. Jina embeddings 2: 8192-token general-purpose text embeddings for long documents. In: Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (2023). arXiv:2305.08322.
34. Kärkkäinen K, Joo J. FairFace: face attribute dataset for balanced race, gender, and age for bias measurement and mitigation. In: Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (2021). p. 1547–57.
35. Devlin J, Chang M, Lee K, Toutanova K. BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (2019). p. 4171–86.
36. Ren S, He K, Girshick RB, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell (2017) 39:1137–49. doi:10.1109/tpami.2016.2577031
37. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2016). p. 770–8.
38. Pramanick S, Dimitrov D, Mukherjee R, Sharma S, Akhtar MS, Nakov P, et al. Detecting harmful memes and their targets. Findings Assoc Comput Linguistics: ACL/IJCNLP 2021 (2021) 2783–96. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2110.00413
39. Kiela D, Bhooshan S, Firooz H, Testuggine D, Perez E. Supervised multimodal bitransformers for classifying images and text. In: Proceedings of the ViGIL workshop at NeurIPS 2019 (2019).
40. Lu J, Batra D, Parikh D, Lee S. ViLBERT: pretraining task-agnostic visiolinguistic representations for vision-and-language tasks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst (2019) 32:13–23. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1908.02265
41. Li LH, Yatskar M, Yin D, Hsieh C-J, Chang K-W (2019). VisualBERT: a simple and performant baseline for vision and language. arXiv preprint arXiv:1908.03557. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2108.01301
Keywords: hateful meme detection, prompt, retrieval-augmented strategy, attention mechanism, contrastive learning
Citation: Kuang Q, Lin Y, Liu J, Lai X and Zhong R (2025) A retrieval-augmented prompting network for hateful meme detection. Front. Phys. 13:1614267. doi: 10.3389/fphy.2025.1614267
Received: 18 April 2025; Accepted: 28 May 2025;
Published: 04 July 2025.
Edited by:
Jiazhong Lu, Chengdu University of Information Technology, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Kuang, Lin, Liu, Lai and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Runlu Zhong, emhvbmdydW5sdUAxMjYuY29t
 Qiuhua Kuang1
Qiuhua Kuang1 Runlu Zhong
Runlu Zhong