- 1Department of Nursing, Leshan Vocational and Technical College, Leshan, China
- 2Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 3Mianyang Central Hospital, School of Medicine, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Mianyang, Sichuan, China
Objective: This study aims to systematically evaluate the efficacy of mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) for children diagnosed with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and their parents.
Methods: A comprehensive search of PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, PsycINFO and ERIC was conducted to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) published up to December 31, 2024, that assessed the effects of MBIs on children with ASD and their parents. Two independent reviewers screened studies, extracted relevant data, and assessed the quality of the included literature. A meta-analysis was performed using standardized mean differences (SMDs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results: A total of 12 RCTs involving 643 participants were included. The meta-analysis showed that MBIs significantly reduced parental stress [SMD = −0.69, 95% CI (−1.36, −0.02), p = 0.04], improved parental mindfulness awareness [SMD = 3.08, 95% CI (0.26, 5.90), p = 0.03], and alleviated anxiety, depression, and stress in parents [SMD = −0.57, 95% CI (−1.09, −0.06), p = 0.03]. Additionally, MBIs significantly improved social responsiveness in children with autism [SMD = −0.35, 95% CI (−0.66, −0.04), p = 0.03]. However, no statistically significant differences were observed between the MBI and control groups in reducing problematic behaviors in children [SMD = −0.45, 95% CI (−0.90, 0.00), p = 0.05], improving children’s emotional and behavioral difficulties [SMD = −0.23, 95% CI (−0.66, 0.19), p = 0.28], or enhancing parental psychological resilience [SMD = 0.85, 95% CI (−1.96, 3.66), p = 0.55].
Conclusion: This meta-analysis demonstrates that MBIs significantly reduce parental stress, alleviate anxiety, depression, and stress, and enhance mindfulness awareness in parents of children with autism. Furthermore, MBIs were found to significantly improve social responsiveness in children with autism. However, their effects on children’s emotional and behavioral challenges and parental psychological resilience remain inconclusive.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42023424059.
1 Introduction
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition characterized by deficits in social interaction, communication, and the presence of restricted and repetitive behaviors—features commonly described as the “Kanner triad” (Botelho et al., 2024; Lord et al., 2018). Symptoms typically emerge in early childhood. A recent global systematic review estimates that ASD affects approximately 1–2% of the world’s population, accounting for over 60 million individuals worldwide (Zeidan et al., 2022). Although ASD is more commonly diagnosed in males (male-to-female ratio of approximately 4:1), emerging research highlights potential diagnostic biases and gender-based phenotypic variability. Specifically, females with ASD often present with internalizing symptoms and employ stronger social camouflage strategies, contributing to underrecognition or delayed diagnoses (Lai et al., 2015; Schuck et al., 2019).
For many parents, receiving an ASD diagnosis for their child represents a profound psychological shift. Initial reactions commonly include denial, confusion, guilt, and grief, which are often part of a broader emotional process known as “diagnosis resolution” (Sher-Censor and Shahar-Lahav, 2022). These emotional responses can be shaped by cultural and contextual factors. In non-Western settings, such as Iran, parents report heightened stigma and emotional isolation following diagnosis (Sharifi et al., 2025). In atypical developmental contexts, like those involving hearing parents of oral deaf children, early relational disruptions may complicate parents’ understanding of their child’s emotional and mental states (Lecciso et al., 2013).
While a range of therapeutic approaches is available to address ASD’s core symptoms—including applied behavior analysis (ABA), cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), speech and language therapy, and developmental social-pragmatic interventions—most demand intensive parental involvement (Vismara and Rogers, 2010; Wood et al., 2020). However, these interventions often overlook the emotional well-being of caregivers, a factor now recognized as critical to treatment adherence, family functioning, and child developmental outcomes.
Mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs), which integrate elements of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR), acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT), and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), have gained attention as supportive strategies for families of children with ASD (Boyd et al., 2018; Schwartzman et al., 2022). For parents, MBIs offer tools to reduce stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms while fostering emotion regulation and parenting self-efficacy. For children, particularly those with high emotional reactivity, modified MBIs may improve emotional awareness and social responsiveness (Kemeny et al., 2012; Ridderinkhof et al., 2018).
Although several systematic reviews have evaluated the effectiveness of MBIs, most have targeted either parents or children in isolation, without examining interrelated outcomes within family systems. For instance, Chua and Shorey (2022) and Suvarna et al. (2024) reported the efficacy of mindfulness- and ACT-based interventions in improving parental well-being but did not assess child-related outcomes. Other reviews (Borquist-Conlon et al., 2019; Li et al., 2023; Scherer et al., 2019) lacked recent randomized controlled trials (RCTs) or failed to adopt a dyadic focus. Therefore, the present study aims to update and extend existing evidence by including recent RCTs and concurrently evaluating the impact of MBIs on both children with autism and their parents. This dual focus offers a more integrated understanding of the familial impact of MBIs, thereby filling a critical gap in current literature.
2 Method
This systematic review was registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) under registration number CRD42023424059.
2.1 Literature search methodology
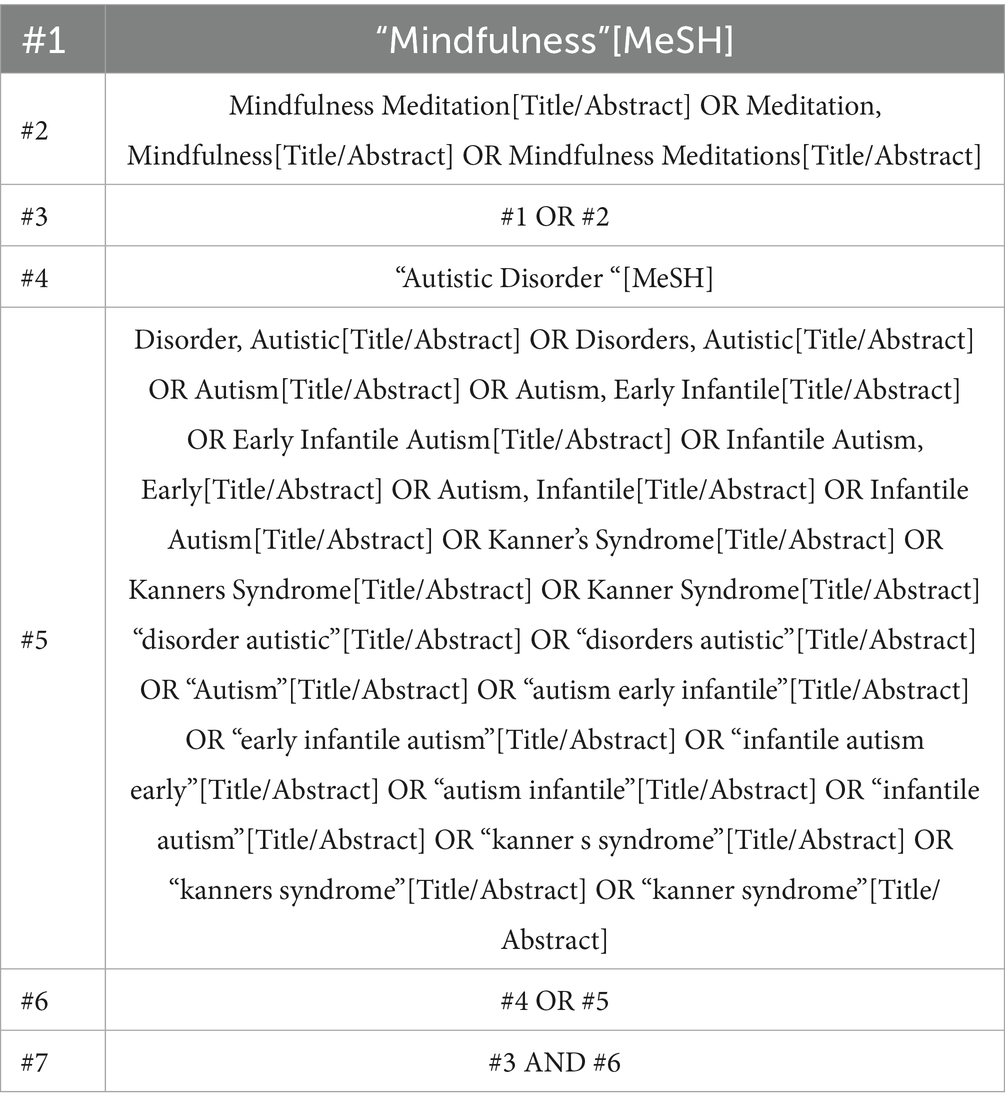
A systematic search was conducted across six databases—PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, The Cochrane Library, PsycINFO and ERIC—for relevant studies published up to December 31, 2024. Gray literature, including dissertations, preprints, and trial registries such as ClinicalTrials.gov, was not included in this review. This may introduce a risk of publication bias, which is acknowledged as a limitation. To ensure comprehensive retrieval, broad search terms were used, focusing on the generic terms for “Autistic Disorder “and “Mindfulness.” The search strategy is detailed in Table 1 (using PubMed as an example).
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion and exclusion criteria for studies were based on the PRISMA statement and the “PICOS” framework, as follows: Population: Children diagnosed with autism and their parents; Intervention: Mindfulness-based therapy; Comparison: Control groups that did not receive any mindfulness intervention or placebo treatment; Outcomes: Psychological, emotional, and behavioral effects on children with autism and their parents; Study Design: Randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Studies were excluded if they involved duplicate content or were non-randomized controlled trials (non-RCTs), including letters, animal studies, protocols, conference abstracts, and case reports. Additionally, studies were excluded if the intervention was not rooted in mindfulness-based practices.
2.3 Risk of bias and data extraction
The Cochrane Collaboration’s Risk of Bias tool was used to assess the risk of bias (Higgins et al., 2011). The following factors were considered to determine whether a study had a low, uncertain, or high risk of bias: random sequence generation and allocation concealment (selection bias); blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias); blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias); incomplete outcome data (attrition bias); selective reporting (reporting bias); and other potential biases. Two reviewers independently assessed and verified the quality of the included studies. In cases of disagreement, a third evaluation was conducted by the authors.
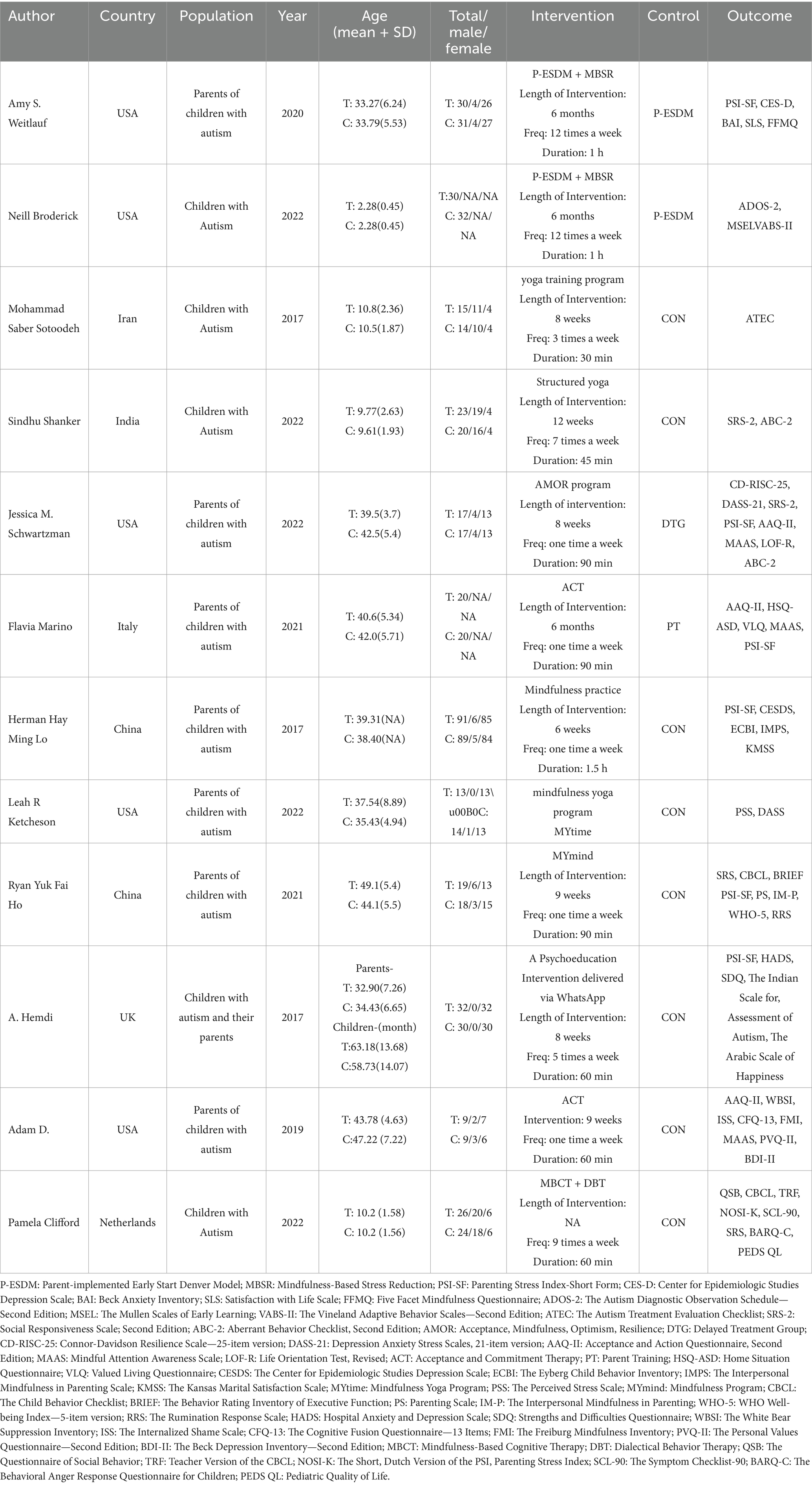
Two authors independently extracted the relevant data, which included the following: sample size, sex, and age of both experimental and control groups; first author; country of origin; year of publication; sample size; experimental intervention procedures and follow-up duration; control groups; and results.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using Review Manager version 5.4. Continuous variables were reported as mean difference (MD) or standardized mean difference (SMD), accompanied by 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Categorical data were expressed as relative risk (RR) with corresponding 95% CIs. A two-tailed test was applied to assess heterogeneity. A fixed-effects model was employed when p > 0.05 and I2 < 50%, indicating the absence of significant heterogeneity across studies. In cases of substantial heterogeneity (p < 0.05, I2 > 50%), a random-effects model was applied to estimate the cumulative effect size. Differences with p < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Literature search results
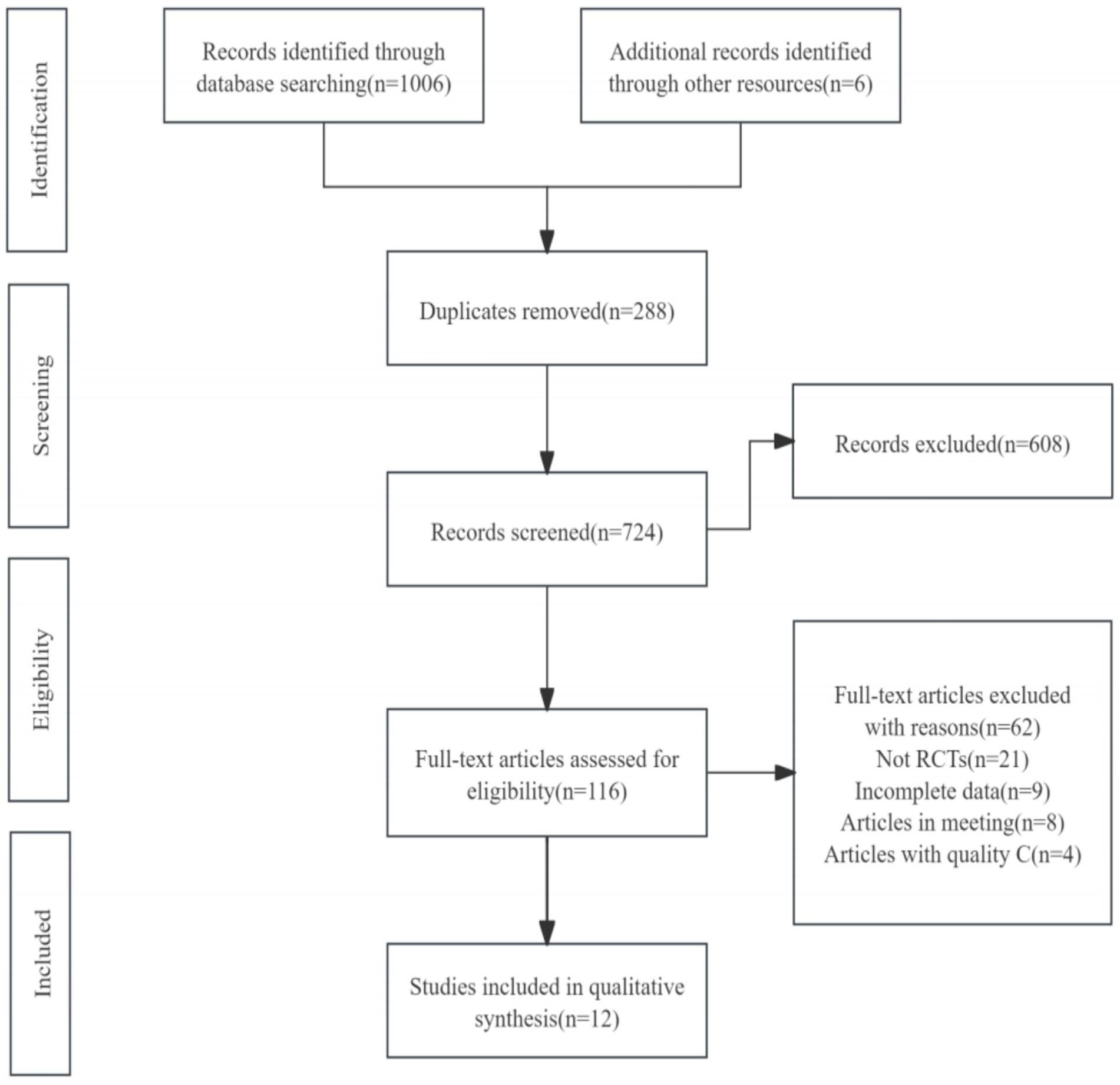
A total of 12 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were included in this review, selected from 1,012 potentially eligible studies identified in the initial literature search. After removing duplicates, screening titles and abstracts, and reviewing full texts, studies that did not meet the inclusion criteria were excluded. The PRISMA flowchart illustrating the study selection process is presented in Figure 1. The detailed information of the included studies is provided in Table 2.
3.2 Risk for bias
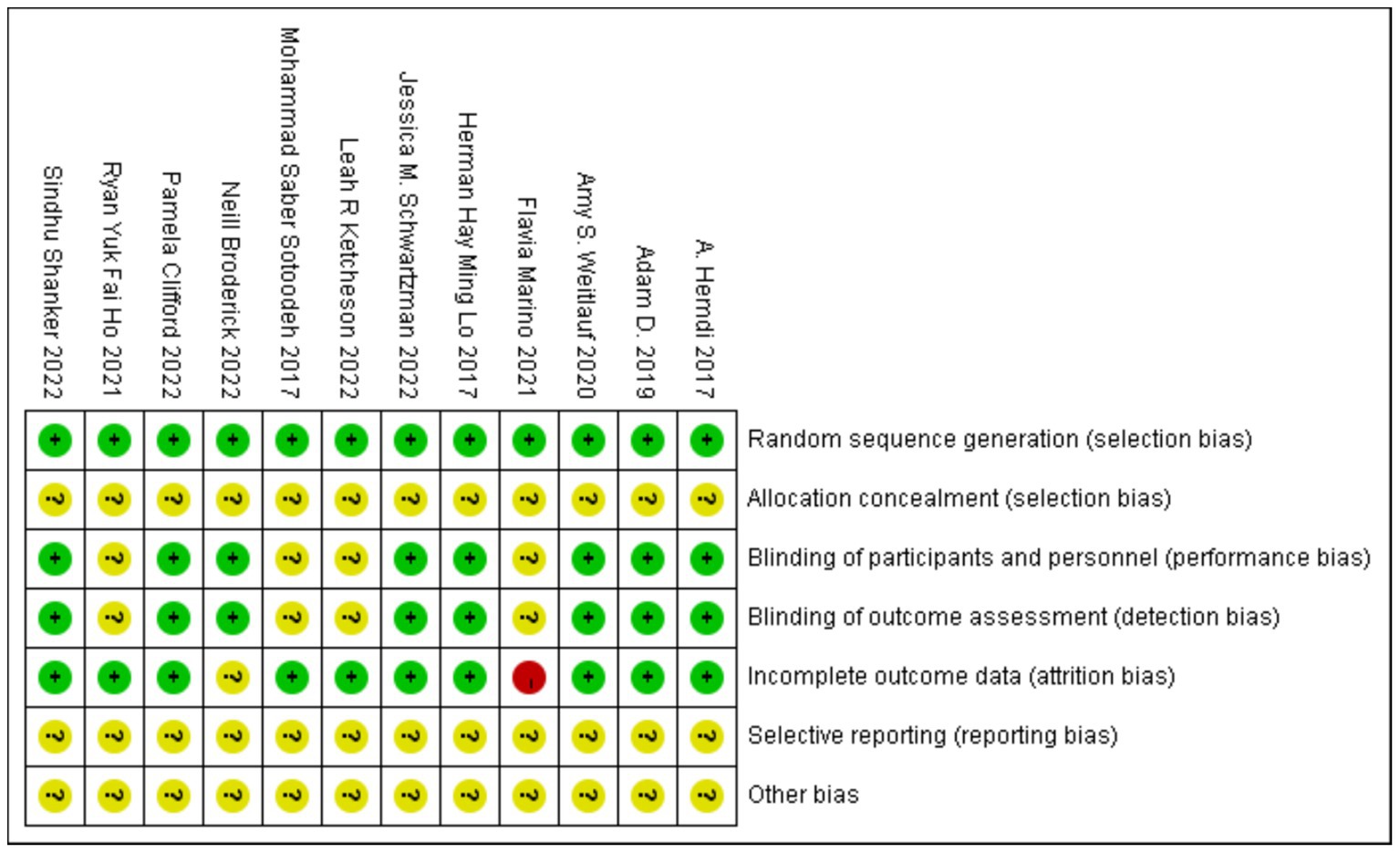
The included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) showed no significant baseline differences between the experimental and control groups. None of the 12 studies reported allocation concealment in their descriptions of the random sequence generation process. Eight studies documented the blinding of both participants and outcome assessors. One study reported a missing population and provided detailed handling of data for the disenrolled participants, whereas another study also had a missing population but did not describe how the data were managed. None of the 12 studies explicitly acknowledged any other sources of bias. Overall, the quality of the included studies was relatively reliable, although certain limitations were present. Specific risk assessment results are shown in Figure 2.
3.3 Meta analysis
3.3.1 Effect of MBIs on parental stress in children with autism
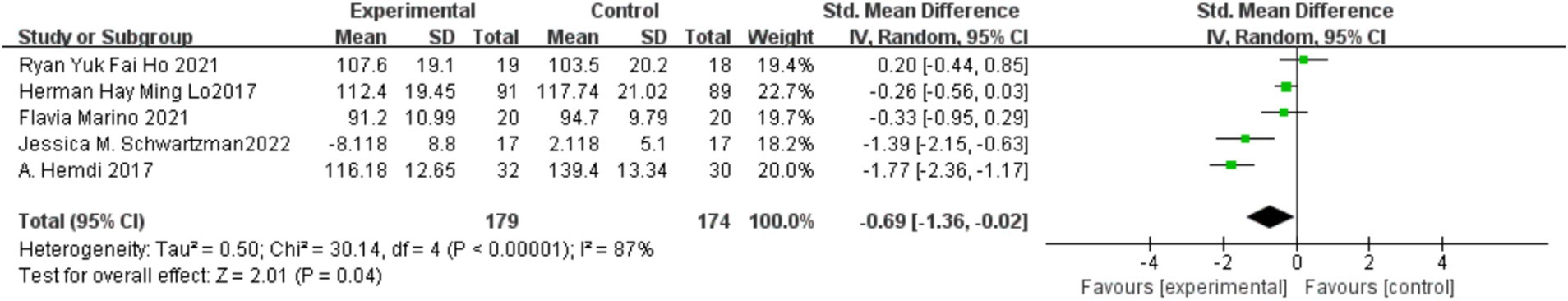
Five studies (Hemdi and Daley, 2017; Ho et al., 2021; Marino et al., 2021; Schwartzman et al., 2022) reported on the impact of MBIs on parental stress in children diagnosed with autism, with a total of 179 participants in the experimental group and 174 in the control group. Considerable heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2 = 87%, p < 0.00001), so a random-effects model was applied. Since the measurement methods differed across studies, standardized mean differences (SMD) were used for the meta-analysis. The results indicated that the MBI intervention significantly reduced parental stress in parents of children with autism [SMD = −0.69, 95% CI (−1.36, −0.02), p = 0.04]. The details are presented in Figure 3.
3.3.2 Effect of MBIs on parental psychological resilience in children with autism
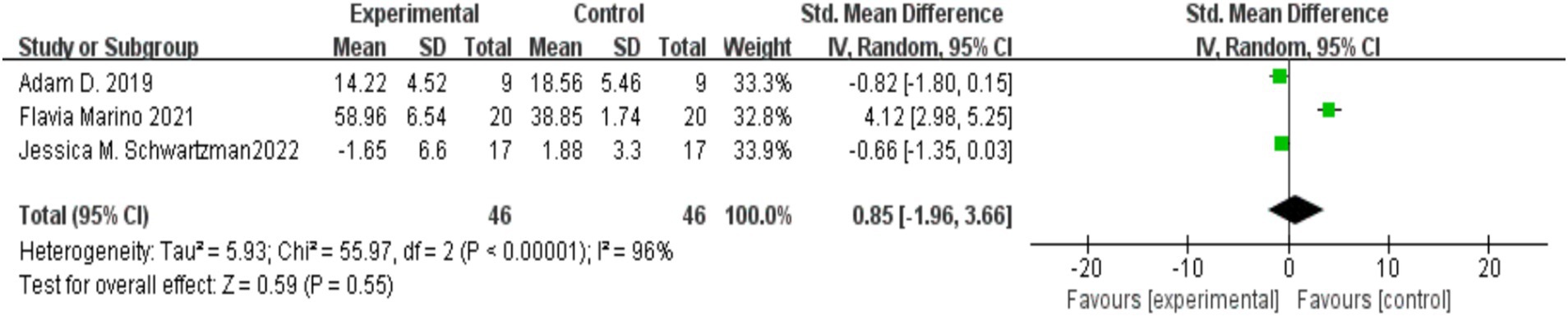
Three studies (Hahs et al., 2018; Marino et al., 2021; Schwartzman et al., 2022) reported on the impact of MBIs on the psychological resilience of parents of children with autism, with a total of 46 participants in both the experimental and control groups. Considerable heterogeneity was observed among the studies (I2 = 96%, p < 0.00001), so a random-effects model was applied. Since the measurement methods differed across studies, standardized mean differences (SMD) were used for the meta-analysis. The results indicated that the MBI intervention had no significant effect on the psychological resilience of parents of children with autism [SMD = 0.85, 95% CI (−1.96, 3.66), p = 0.55]. The details are presented in Figure 4.
3.3.3 Impact of MBIs on the daily consciousness state of parents of children with autism
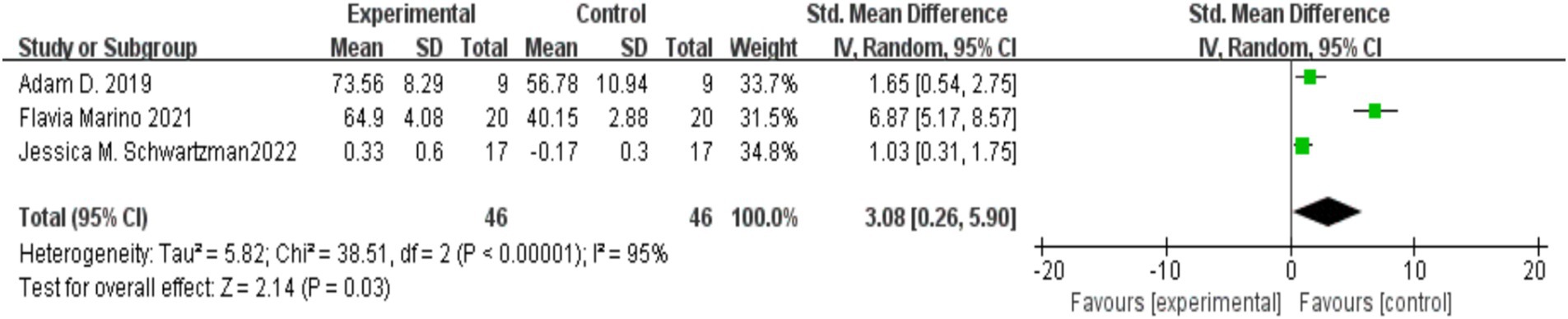
Three studies (Hahs et al., 2018; Marino et al., 2021; Schwartzman et al., 2022) investigated the effect of MBIs on the daily state of consciousness in parents of children with autism, with 46 participants in both the experimental and control groups. Significant heterogeneity was found across the studies (I2 = 95%, p < 0.00001), prompting the use of a random-effects model. The meta-analysis revealed that parents in the MBI group had significantly higher levels of consciousness than those in the control group [SMD = 3.08, 95% CI (0.26, 5.90), p = 0.03]. The results are illustrated in Figure 5.
3.3.4 Effects of MBIs on anxiety, depression, and stress in parents of children with autism
Two studies (Ketcheson et al., 2022; Schwartzman et al., 2022) reported the effects of MBIs on anxiety, depression, and stress in parents of children with autism, involving 30 participants in the experimental group and 31 in the control group. No significant heterogeneity was observed between the studies (I2 = 0%, p = 0.42), so a fixed-effects model was applied. The results showed that the MBI group exhibited significantly lower levels of anxiety, depression, and stress compared to the control group [SMD = −0.57, 95% CI (−1.09, −0.06), p = 0.03]. The details are shown in Figure 6.
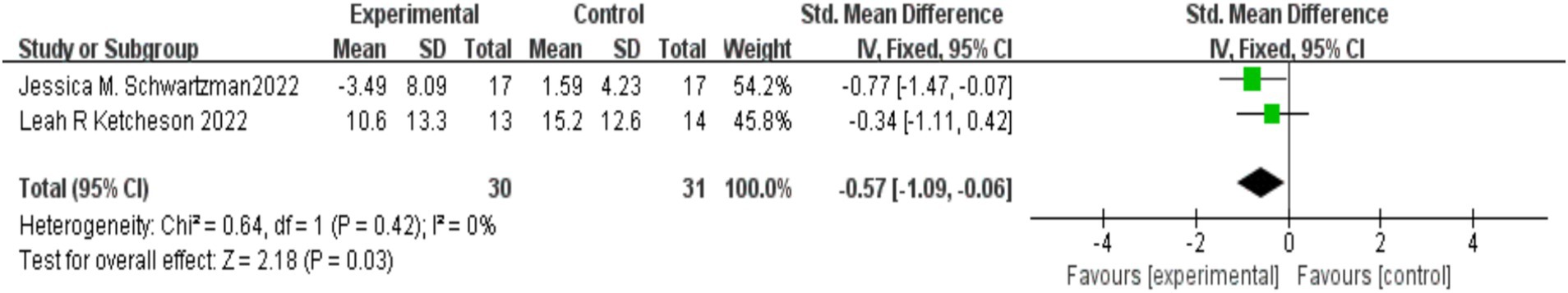
Figure 6. Effect of mindfulness-based interventions on anxiety, depression, and stress in parents of children with autism.
3.3.5 Effects of MBIs on the social responsiveness of children with autism
Four studies (Clifford et al., 2022; Ho et al., 2021; Schwartzman et al., 2022; Shanker and Pradhan, 2023) examined the impact of MBIs on the social responsiveness of children with autism, with 85 participants in the experimental group and 79 in the control group. No significant heterogeneity was observed between the studies (I2 = 0%, p = 0.45), and a fixed-effects model was applied. The meta-analysis revealed that MBIs significantly enhanced the social responsiveness of children with autism, with the difference between the groups being statistically significant [SMD = −0.35, 95% CI (−0.66, −0.04), p = 0.03]. The results are presented in Figure 7.
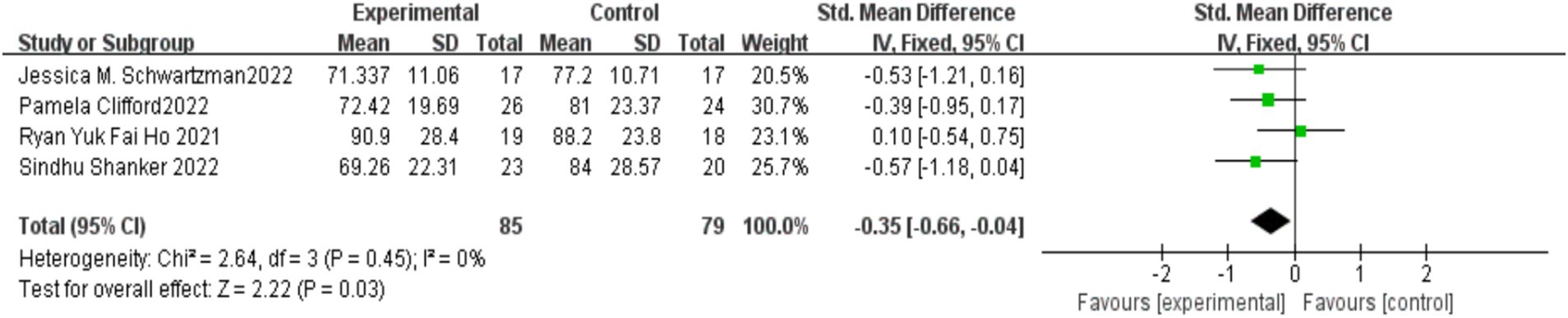
Figure 7. Effect of mindfulness-based interventions on social responsiveness in children with autism.
3.3.6 Effects of MBIs on problematic behaviors in children with autism
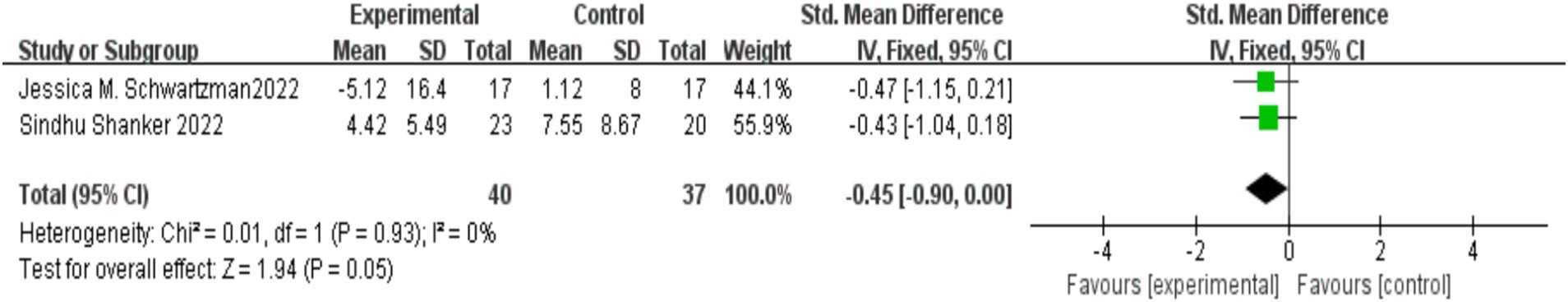
Two studies (Schwartzman et al., 2022; Shanker and Pradhan, 2023; Ho et al., 2021) examined the effects of MBIs on problematic behaviors in children with autism, with 40 participants in the experimental group and 37 in the control group. No significant heterogeneity was found between the studies (I2 = 0%, p = 0.93), and a fixed-effects model was applied for the meta-analysis. The results indicated that there was no statistically significant difference between the mindfulness-based psychological intervention group and the control group [SMD = −0.45, 95% CI (−0.90, 0.00), p = 0.05]. The findings are illustrated in Figure 8.
3.3.7 Effects of MBIs on emotional and behavioral problems in children with autism
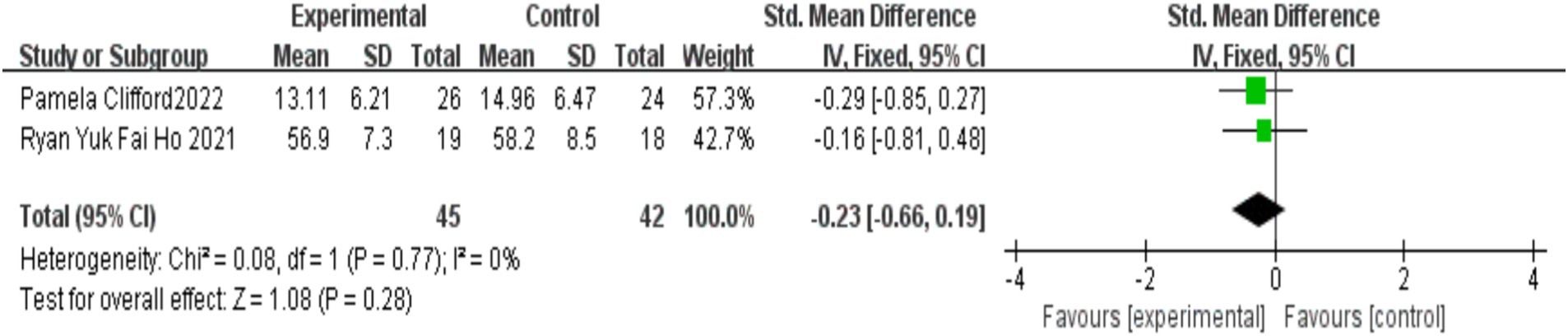
Two studies (Clifford et al., 2022; Ho et al., 2021) assessed the effects of MBIs on emotional and behavioral issues in children with autism, with 45 participants in the experimental group and 42 in the control group. No significant heterogeneity was observed between the studies (I2 = 0%, p = 0.77). Meta-analysis using a fixed-effects model indicated that the difference in the improvement of emotional and behavioral problems between the MBI group and the control group was not statistically significant [SMD = −0.23, 95% CI (−0.66, 0.19), p = 0.28]. The detailed results are presented in Figure 9.
3.4 Publication bias and sensitivity analysis
Visual inspection of funnel plots suggested approximate symmetry indicating low risk of publication bias for primary outcomes. However, we acknowledge that funnel plot interpretation is limited when few studies are included (<10 per outcome) and heterogeneity is high. Sensitivity analyses using the leave-one-out method confirmed that summary estimates for significant outcomes (e.g., parental stress, social responsiveness) remained robust and directionally consistent (all p < 0.05). Nevertheless, substantial heterogeneity persisted (I2 > 85%) even after sequentially removing individual studies, particularly for parental resilience and stress outcomes.
We attempted subgroup analyses to explore sources of heterogeneity (e.g., intervention duration, ASD severity), but insufficient reporting in original studies precluded meaningful stratification—only 4/12 studies specified ASD severity levels, and intervention durations varied widely (6 weeks to 6 months).
4 Discussion
This meta-analysis synthesized the results of 12 RCTs involving 643 children with autism and their parents, evaluating the impact of MBIs. The findings suggest that MBIs are a promising therapeutic tool, with significant positive effects on both the emotional well-being of parents and the behavioral outcomes of children with autism. Specifically, MBIs significantly reduced parental stress and anxiety, improved emotional regulation, and enhanced the social responsiveness of children. These results align with previous studies, such as those by Singh et al. (2019), which also highlighted the positive effects of mindfulness practices on stress reduction and emotional well-being in parents. By incorporating mindfulness practices into daily routines, parents reported enhanced emotional regulation, which likely facilitated more effective caregiving and improved family dynamics. This result aligns with Weitlauf et al. (2020), who demonstrated that MBIs help reduce parental distress and foster resilience in the face of caregiving challenges.
Mindfulness-based interventions offer parents effective strategies for managing stress and regulating emotions. Engaging in mindfulness exercises enables parents to become more aware of their emotional responses and stress levels, fostering better coping mechanisms. This aligns with findings by Aydin (2023), who demonstrated that mindfulness practices help parents not only acknowledge but also accept their emotions, thus preventing negative emotions like anxiety and despair from overwhelming them. Moreover, mindfulness exercises promote self-reflection, enabling parents to apply positive emotion regulation strategies and reduce stress while interacting with their children with autism (Mo et al., 2024).
One key observation in this study is that MBIs significantly enhance parents’ daily awareness. The increased mindfulness allows parents to better focus on their present emotional state and interactions with their children, improving their ability to understand and respond to their children’s needs. This heightened consciousness, in turn, leads to more effective communication and improved emotional bonding (Chua and Shorey, 2022). Thus, mindfulness interventions do not only reduce stress but also improve the overall quality of parent–child interactions.
Regarding children, the results indicate that MBIs can lead to improvements in emotional regulation and social behavior. The differential effects observed—where MBIs improve social responsiveness but not broader emotional or behavioral issues—may be attributed to the nature of mindfulness training, which emphasizes present-moment awareness and interpersonal attunement, directly benefiting social skills but less effective in altering entrenched emotional or behavioral patterns. This aligns with the dual-process theory of ASD (Ridderinkhof et al., 2021), where top-down cognitive control (targeted by MBIs) improves social attention, whereas bottom-up limbic dysregulation requires more intensive intervention. Children who participated in the mindfulness interventions showed notable improvements in social responsiveness and reduced stereotypical behaviors, which is consistent with findings from previous studies examining mindfulness interventions for children with ASD (Ridderinkhof et al., 2021). The improvement in social engagement is particularly important given that children with ASD often struggle with social communication and emotional regulation. The results suggest that mindfulness, particularly when adapted for children, may provide a useful tool in addressing these core deficits of ASD.
However, the effectiveness of MBIs varied depending on several factors, including the age of the child and the severity of their symptoms. Younger children, due to developmental limitations in attention span and emotional regulation, may have more difficulty engaging in traditional mindfulness practices. Older children, on the other hand, might benefit more significantly from the intervention due to their greater ability to focus and regulate their emotions (Borquist-Conlon et al., 2019; Tao et al., 2021). This age-dependent variability in intervention outcomes suggests that modifications to mindfulness practices may be necessary to optimize their effectiveness for different age groups.
Furthermore, it is important to note that the duration of the intervention and the specific mindfulness techniques used could have influenced the observed outcomes. Several studies have suggested that longer-duration mindfulness programs may yield better results, especially in improving behavioral outcomes in children (Xie et al., 2022). Our findings indicate that children who underwent longer mindfulness interventions experienced more substantial improvements in social and emotional domains. Therefore, further research is needed to determine the optimal duration and structure of mindfulness interventions for children with ASD.
While the results are promising, several limitations should be considered. It is noteworthy that all included studies were conducted in Western or Asian countries, raising concerns about cultural generalizability. Cultural norms fundamentally shape parenting practices and emotional expression—key mechanisms through which MBIs operate (Kirmayer, 2015)—potentially moderating intervention efficacy. Future research must therefore prioritize underrepresented regions (e.g., Africa, Latin America) and examine cultural adaptations of MBIs. First, the majority of studies included in this review were of moderate methodological quality, and many lacked long-term follow-up data. As a result, it is unclear whether the observed improvements in children’s behavior and parents’ well-being are sustained over time. Additionally, the lack of consistency in intervention delivery across studies—such as variations in the number of sessions, the intensity of the intervention, and the experience of the facilitators—makes it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the most effective approach. Future research should aim to standardize these intervention parameters to better understand their impact. Third, the variation in intervention duration and intensity (ranging from 6-week to 6-month programs) may explain inconsistencies in findings. Unfortunately, due to reporting limitations, we could not formally assess this through subgroup analysis. Future studies should systematically examine dosage-response relationships.
In conclusion, the findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis support the use of mindfulness-based interventions as a promising approach for improving the emotional well-being of parents and the behavioral outcomes of children with ASD. However, further research is needed to examine the long-term effects of these interventions, as well as to explore how variables such as age, intervention duration, and severity of ASD symptoms influence the outcomes of mindfulness interventions. By optimizing the delivery of MBIs and understanding their underlying mechanisms, it is possible to enhance the therapeutic potential of these interventions in both children with ASD and their families.
This systematic review highlights the potential benefits of MBIs for children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and their parents. While these findings are promising, two critical considerations warrant emphasis: First, methodological limitations in the extant literature—particularly the frequent absence of allocation concealment and blinding in included RCTs—may contribute to overestimation of intervention effects, necessitating cautious interpretation of current evidence. Second, the broader field of MBIs for ASD remains developmental; though recent studies have expanded applications to high-functioning subgroups and diverse cultural contexts (Boyd et al., 2022; Zeidan et al., 2022), substantial knowledge gaps persist regarding intervention refinement, cultural adaptation, and long-term efficacy. These limitations collectively underscore the imperative for more rigorously designed trials that address methodological weaknesses while advancing context-specific implementation frameworks.
5 Conclusion
This systematic review and meta-analysis provides robust evidence that MBIs are effective in alleviating parental stress, anxiety, and depressive symptoms, while significantly enhancing mindfulness awareness among parents of children with autism. Furthermore, MBIs have demonstrated a moderate but meaningful impact on improving social responsiveness in children with ASD, suggesting their potential to address core social–emotional challenges. Clinically, MBIs may serve as an effective adjunctive therapy for reducing caregiver burden in ASD families, potentially enhancing adherence to developmental interventions and improving overall family functioning.
However, the analysis also revealed non-significant effects on reducing children’s problematic behaviors, improving emotional and behavioral difficulties, and enhancing parental psychological resilience. The parental resilience outcome exemplifies how meta-analytical imprecision (CI width >2 SDs) can mask clinically relevant signals. While statistically inconclusive, the point estimate (SMD = 0.85) aligns with qualitative reports of improved coping. Future trials require ≥80% power to detect resilience changes—our calculations suggest 150 participants/arm for SMD = 0.4. These inconclusive findings highlight the variability in outcomes, which may be influenced by factors such as child age, symptom severity, intervention type, and duration. Importantly, most included studies were of moderate methodological quality and lacked long-term follow-up, limiting the generalizability and sustainability of observed benefits. Moreover, the heterogeneity in delivery formats and assessment tools presents challenges in determining standardized best practices.
Future research should prioritize high-quality, longitudinal RCTs that incorporate dyadic designs, consider cultural and developmental adaptations, and explore synergistic effects with other evidence-based interventions. By optimizing the structure and personalization of MBIs, researchers and clinicians may better support the mental health of both children with ASD and their caregivers, contributing to more holistic and family-centered care strategies.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
QP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. JJ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. HA: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. CZ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aydin, A. (2023). Examining the mediating role of mindful parenting: a study on the relationship between parental emotion regulation difficulties and problem behaviors of children with ASD. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 53, 1873–1883. doi: 10.1007/s10803-022-05455-9
Borquist-Conlon, D. S., Maynard, B. R., Brendel, K. E., and Farina, A. S. J. (2019). Mindfulness-based interventions for youth with anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Res. Soc. Work. Pract. 29, 195–205. doi: 10.1177/1049731516684961
Botelho, R. M., Silva, A. L. M., and Borbely, A. U. (2024). The autism Spectrum disorder and its possible origins in pregnancy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 21:244. doi: 10.3390/ijerph21030244
Boyd, J. E., Lanius, R. A., and McKinnon, M. C. (2018). Mindfulness-based treatments for posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of the treatment literature and neurobiological evidence. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 43, 7–25. doi: 10.1503/jpn.170021
Boyd, N., and Alexander, D. G. (2022). An online mindfulness intervention for medical students in South Africa: A randomised controlled trial. S. Afr. J. Psychiatr. 28:1840.
Chua, J. Y. X., and Shorey, S. (2022). The effect of mindfulness-based and acceptance commitment therapy-based interventions to improve the mental well-being among parents of children with developmental disabilities: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 52, 2770–2783. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-04893-1
Clifford, P., Gevers, C., Jonkman, K. M., Boer, F., and Begeer, S. (2022). The effectiveness of an attention-based intervention for school-aged autistic children with anger regulating problems: a randomized controlled trial. Autism Res. 15, 1971–1984. doi: 10.1002/aur.2800
Hahs, A. D., Dixon, M. R., and Paliliunas, D. (2018). Randomized controlled trial of a brief acceptance and commitment training for parents of individuals diagnosed with autism spectrum disorders. J. Contextual Behav. Sci. 154–159. doi: 10.1016/j.jcbs.2018.03.002
Hemdi, A., and Daley, D. (2017). The effectiveness of a psychoeducation intervention delivered via WhatsApp for mothers of children with autism Spectrum disorder (ASD) in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: a randomized controlled trial. Child Care Health Dev. 43, 933–941. doi: 10.1111/cch.12520
Higgins, J. P. T., Altman, D. G., Gøtzsche, P. C., Jüni, P., Moher, D., Oxman, A. D., et al. (2011). The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
Ho, R. Y. F., Zhang, D., Chan, S. K. C., Gao, T. T., Lee, E. K. P., Lo, H. H. M., et al. (2021). Brief report: mindfulness training for Chinese adolescents with autism spectrum disorder and their parents in Hong Kong. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 51, 4147–4159. doi: 10.1007/s10803-020-04729-4
Kemeny, M. E., Foltz, C., Cavanagh, J. F., Cullen, M., Giese-Davis, J., Jennings, P., et al. (2012). Contemplative/emotion training reduces negative emotional behavior and promotes prosocial responses. Emotion 12, 338–350. doi: 10.1037/a0026118
Ketcheson, L. R., Wengrovius, C. M., Staples, K. L., and Miodrag, N. (2022). MYTime: a mindfulness and yoga program to promote health outcomes in parents of children with autism Spectrum disorder. Glob Adv. Health Med. 11:2164957x221110154. doi: 10.1177/2164957x221110154
Lai, M. C., Lombardo, M. V., Auyeung, B., Chakrabarti, B., and Baron-Cohen, S. (2015). Sex/gender differences and autism: setting the scene for future research. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 54, 11–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2014.10.003
Lecciso, F., Petrocchi, S., and Marchetti, A. (2013). Hearing mothers and oral deaf children: an atypical relational context for theory of mind. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 28, 903–922. doi: 10.1007/s10212-012-0146-1
Li, S., Chen, Z., Yong, Y., Xie, J., and Li, Y. (2023). Effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy-based interventions for improving the psychological health of parents of children with special health care needs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Compr. Psychiatry 127:152426. doi: 10.1016/j.comppsych.2023.152426
Lord, C., Elsabbagh, M., Baird, G., and Veenstra-Vanderweele, J. (2018). Autism spectrum disorder. Lancet 392, 508–520. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(18)31129-2
Marino, F., Failla, C., Chilà, P., Minutoli, R., Puglisi, A., Arnao, A. A., et al. (2021). The effect of acceptance and commitment therapy for improving psychological well-being in parents of individuals with autism spectrum disorders: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Sci. 11:880. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11070880
Mo, S., Bu, F., Bao, S., and Yu, Z. (2024). Comparison of effects of interventions to promote the mental health of parents of children with autism: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 114:102508. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2024.102508
Ridderinkhof, A., de Bruin, E. I., Blom, R., and Bögels, S. M. (2018). Mindfulness-based program for children with autism Spectrum disorder and their parents: direct and long-term improvements. Mindfulness (N Y) 9, 773–791. doi: 10.1007/s12671-017-0815-x
Ridderinkhof, A., Elmose, M., de Bruin, E. I., Blom, R., Salem-Guirgis, S., Weiss, J. A., et al. (2021). A person-centered approach in investigating a mindfulness-based program for adolescents with autism spectrum disorder. Mindfulness 12, 2394–2414. doi: 10.1007/s12671-021-01668-8
Scherer, N., Verhey, I., and Kuper, H. (2019). Depression and anxiety in parents of children with intellectual and developmental disabilities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 14:e0219888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219888
Schuck, R. K., Flores, R. E., and Fung, L. K. (2019). Brief report: sex/gender differences in symptomology and camouflaging in adults with autism Spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 49, 2597–2604. doi: 10.1007/s10803-019-03998-y
Schwartzman, J. M., Millan, M. E., Uljarevic, M., and Gengoux, G. W. (2022). Resilience intervention for parents of children with autism: findings from a randomized controlled trial of the AMOR method. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 52, 738–757. doi: 10.1007/s10803-021-04977-y
Shanker, S., and Pradhan, B. (2023). Effect of yoga on the social responsiveness and problem behaviors of children with ASD in special schools: a randomized controlled trial. Explore (N.Y.) 19, 594–599. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2022.12.004
Sharifi, H., Norouzi, G., and Ashori, M. (2025). Lived experiences of mothers of children with mild intellectual disabilities: a phenomenological study. J. Intellect. Disabil. 15:17446295251321043. doi: 10.1177/17446295251321043
Sher-Censor, E., and Shahar-Lahav, R. (2022). Parents’ resolution of their child’s diagnosis: a scoping review. Attach Hum. Dev. 24, 580–604. doi: 10.1080/14616734.2022.2034899
Singh, N. N., Lancioni, G. E., Karazsia, B. T., Myers, R. E., Hwang, Y. S., and Anālayo, B. (2019). Effects of mindfulness-based positive behavior support (MBPBS) training are equally beneficial for mothers and their children with autism Spectrum disorder or with intellectual disabilities. Front. Psychol. 10:385. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00385
Suvarna, V., Farrell, L., Adams, D., Emerson, L. M., and Paynter, J. (2024). Parenting practices and externalizing behaviors in autistic children: a systematic literature review. Clin. Child. Fam. Psychol. Rev. 27, 235–256. doi: 10.1007/s10567-024-00467-6
Tao, S., Li, J., Zhang, M., Zheng, P., Lau, E. Y. H., Sun, J., et al. (2021). The effects of mindfulness-based interventions on child and adolescent aggression: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mindfulness 12, 1301–1315. doi: 10.1007/s12671-020-01570-9
Vismara, L. A., and Rogers, S. J. (2010). Behavioral treatments in autism spectrum disorder: what do we know? Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 6, 447–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131151
Weitlauf, A. S., Broderick, N., Stainbrook, J. A., Taylor, J. L., Herrington, C. G., Nicholson, A. G., et al. (2020). Mindfulness-based stress reduction for parents implementing early intervention for autism: an RCT. Pediatrics 145, S81–S92. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-1895K
Wood, J. J., Kendall, P. C., Wood, K. S., Kerns, C. M., Seltzer, M., Small, B. J., et al. (2020). Cognitive behavioral treatments for anxiety in children with autism spectrum disorder: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatr. 77, 474–483. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.4160
Xie, S., Gong, C., Lu, J., Li, H., Wu, D., Chi, X., et al. (2022). Enhancing Chinese preschoolers’ executive function via mindfulness training: an fNIRS study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 16:961797. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.961797
Keywords: mindfulness-based therapies, autism spectrum disorder, systematic review, meta-analysis, parent–child intervention, intervention efficacy author country population year age
Citation: Peng Q, Dong Y, Jin J, Ao H, Zhang C and Ma Y (2025) The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions for children with autism and their parents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 16:1526001. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1526001
Edited by:
Miao Cao, Fudan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Annalisa Levante, University of Salento, ItalyYuehua Xu, Beijing Normal University, China
Yun Tang, Yunnan Normal University, China
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Dong, Jin, Ao, Zhang and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yanfei Ma, bWF5YW5mZWkwODE2QDE2My5jb20=
 Qiyan Peng
Qiyan Peng Yujie Dong
Yujie Dong Jie Jin
Jie Jin Huan Ao
Huan Ao Chi Zhang
Chi Zhang Yanfei Ma
Yanfei Ma