Abstract
Background:
Nature-based interventions are emerging as an alternative to therapeutic approaches aimed to reduce and prevent mental and physical ailments. However, little is known of the types of interventions available to use by healthcare professionals. This systematic review of reviews aimed to classify and categorise different types of Nature-Based Interventions (NBIs) which currently exist under different names and approaches. The second aim of our review was to explore the mediating and moderating factors impacting NBI effectiveness.
Methods:
The systematic review used the narrative synthesis approach following the PRISMA guidelines, using the following databases: Academic Search Complete, APA PsycInfo, CINAHL, MEDLINE, and included only peer-reviewed review articles in English which explored Nature Based Interventions (NBIs), excluding animal-based interventions. The quality review was conducted using AMSTAR-2.
Results:
The review included a total of 61 reviews of NBIs, covering 13 different categories of NBIs: nature-based interventions, horticulture, nature exposure, green exercise, wilderness and adventure therapy, forest therapy, blue space interventions, care farming, nature play, nature-based education, environmental volunteerism, immersive nature experiences, and caring for country. Furthermore, 11 moderating and mediating factors influencing NBI effectiveness were identified: social, physical activity, age, nature connectedness, duration and frequency, gender, symptom severity, environment type, participant motivation and preference, challenge confrontation, and autonomy, responsibility, and skill and knowledge acquisition.
Conclusion:
The current review found a wide variety of NBIs, showcasing the many different options available to individuals and healthcare professionals offering accessible and cost-effective NBIs. Moreover, the moderating and mediating factors identified in our review will help future researchers, healthcare professionals, and practitioners consider these factors when evaluating the effectiveness of NBIs.
Systematic review registration:
PROSPERO (https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42023491598), identifier (CRD42023491598).
1 Introduction
Nature-based interventions (NBIs) are activities, programmes, or strategies which aim to improve a person’s mental and physical health by involvement in a nature-based experience (Shanahan et al., 2019). Among many other benefits, NBIs offer cost-effective ways of improving peoples’ physical and mental health and wellbeing (Hinde et al., 2021; Pretty and Barton, 2020). These cost-effective interventions are especially crucial for a world tackling increasing healthcare costs (OECD, 2024).
A wide variety of NBIs exist under different names, approaches, and target populations, many of which overlap. NBIs can refer to interventions which are both outdoors (Struthers et al., 2024) and indoors (Yeo et al., 2020), natural or virtual (Wen et al., 2024). In one specific example, forest therapy, forest bathing, or shinrin-yoku refer to immersing yourself within the forest using our five core senses (Wen et al., 2019). On the other hand, research on forest bathing using virtual reality is in development (Masters et al., 2024), although the use of all our five core senses in virtual reality is still severely limited. As such, this nomenclature calls into question whether virtual forest bathing is closer to watching videos of nature (Mauldin et al., 2025) than it is to forest bathing in a real forest. As such, there is a clear need for categorising different nature-based interventions.
Moreover, factors such as nature connectedness (Rosa et al., 2023), physical activity (Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022), or intervention duration (Yeo et al., 2020) may influence NBI effectiveness, yet they are sparsely controlled for or reported in individual NBI studies. A review on nature prescribing even found that evaluations of nature prescribing programmes was lacking (Kondo et al., 2020). Awareness of factors associated with NBIs and subsequent reporting on those factors in studies would facilitate comparisons between different studies. A more comprehensive synthesis of these factors would thus improve our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of NBIs and allow future studies, reviews, and meta-analyses to account for these factors and even aid in evaluating nature prescribing programmes.
Lastly, NBIs should offer individuals a range of options to choose from so that individuals can choose the NBI which works best for their surrounding environment and personal preferences. Some individuals may not be able to access green space, while others might not have access to a clean blue space. Personalisation is a well-known and effective strategy of improving therapy outcomes (Nye et al., 2023), and providing a wide spectrum of NBI options would be especially valuable for nature prescriptions, potentially improving patients’ engagement and health outcomes.
Taking things together, the research questions of this review are two-fold: Firstly, what are the different types and categories of NBIs? Secondly, what are the moderating and mediating factors associated with NBIs? By answering these two questions, we aim to clarify the NBI literature and provide a pathway towards improving research on NBIs and personalising NBIs according to individual preferences.
2 Methods
This review followed the PRISMA 2020 review guidelines (Page et al., 2021) and was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42023491598) ahead of the review.
2.1 Search strategy and inclusion and exclusion criteria
Electronic databases (MEDLINE, Academic Search Complete, APA PsycInfo, CINAHL Ultimate) and grey literature (Google Scholar, Semantic Scholar) were searched in February 2024 and further electronic databases (CINAHL Ultimate, MEDLINE, CINAHL Plus with Full Text, APA PsycInfo) were subsequently searched in January 2025. The January 2025 search was restricted to peer-reviewed systematic reviews in English and excluded animal-based interventions. The detailed list of keywords can be found below and the PICO framework can be found in Table 1.
Table 1
| Population | Intervention | Control | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusive of healthy and clinical populations | Nature-based interventions, excluding animal-based interventions | Any controls considered, including reviews considering studies with no controls | Any outcomes assessed |
PICO framework for this review.
2.1.1 Keywords
-
Nature-Based Interventions: blue gym* OR care farm* OR care-farm* OR eco therap* OR ecotherap* OR eco-therap* OR environmental volunteer* OR farm therap* OR farm-therap* OR forest bath* OR forest therap* OR forest* therap* OR forest-bath* OR garden prescr* OR garden therap* OR green care OR green exercise OR green gym* OR green prescri* OR healing garden* OR horticultural therap* OR horticulture therap* OR nature assisted therap* OR nature based rehabilitation OR nature intervention* OR nature play OR nature prescri* OR nature rehabilitation OR nature therap* OR nature view* OR nature-assisted therapy OR nature-based OR nature-based intervention* OR nature-based rehabilitation OR nature-based* OR NBI* OR outdoor exercise OR park prescri* OR rehabilitation garden* OR shinrin yoku OR social farm* OR social horticult* OR therap* farm* OR therap* garden* OR therap* horticult* OR wild play OR wilderness therap* OR wilderness-therap*.
-
NOT: narrow band imaging.
-
Reviews: review* OR systematic review*.
The search was restricted to only systematic reviews of the literature. As this review of reviews is focused on what types of NBIs exist, there were also no restrictions in terms of the types of outcomes.
2.2 Screening and extraction
References were downloaded from the databases and uploaded to Rayyan for de-duplication and screening. Review screening and selection were conducted by two researchers whereas data extraction was conducted by the main author. Disagreements over the inclusion and exclusion of reviews during review screening and selection were resolved in regular meetings and agreed upon by both researchers.
2.3 Quality review
The quality review was conducted by the main author using the online checklist version of the AMSTAR-2 (Shea et al., 2017), which categorises systematic review quality according to the number of critical and non-critical flaws and weaknesses. The quality review identified 3 high quality reviews, 13 moderate quality reviews, 18 low quality reviews, and 27 critically low quality reviews. There was an overall improvement in review quality over time. All reviews were considered for exploring the different types of NBIs as the review quality does not impact the type of NBI it explored. Moreover, this approach is appropriate especially for exploring less common NBIs which might be underrepresented in the literature. Regarding the moderating and mediating factors, only moderate and high quality reviews were considered to include only factors with strong supporting evidence.
2.4 Data synthesis
The review used the narrative synthesis approach (Popay et al., 2006) to best describe and summarise the findings of our review.
3 Results
The details of the literature search and screening process can be found in Figure 1.
Figure 1
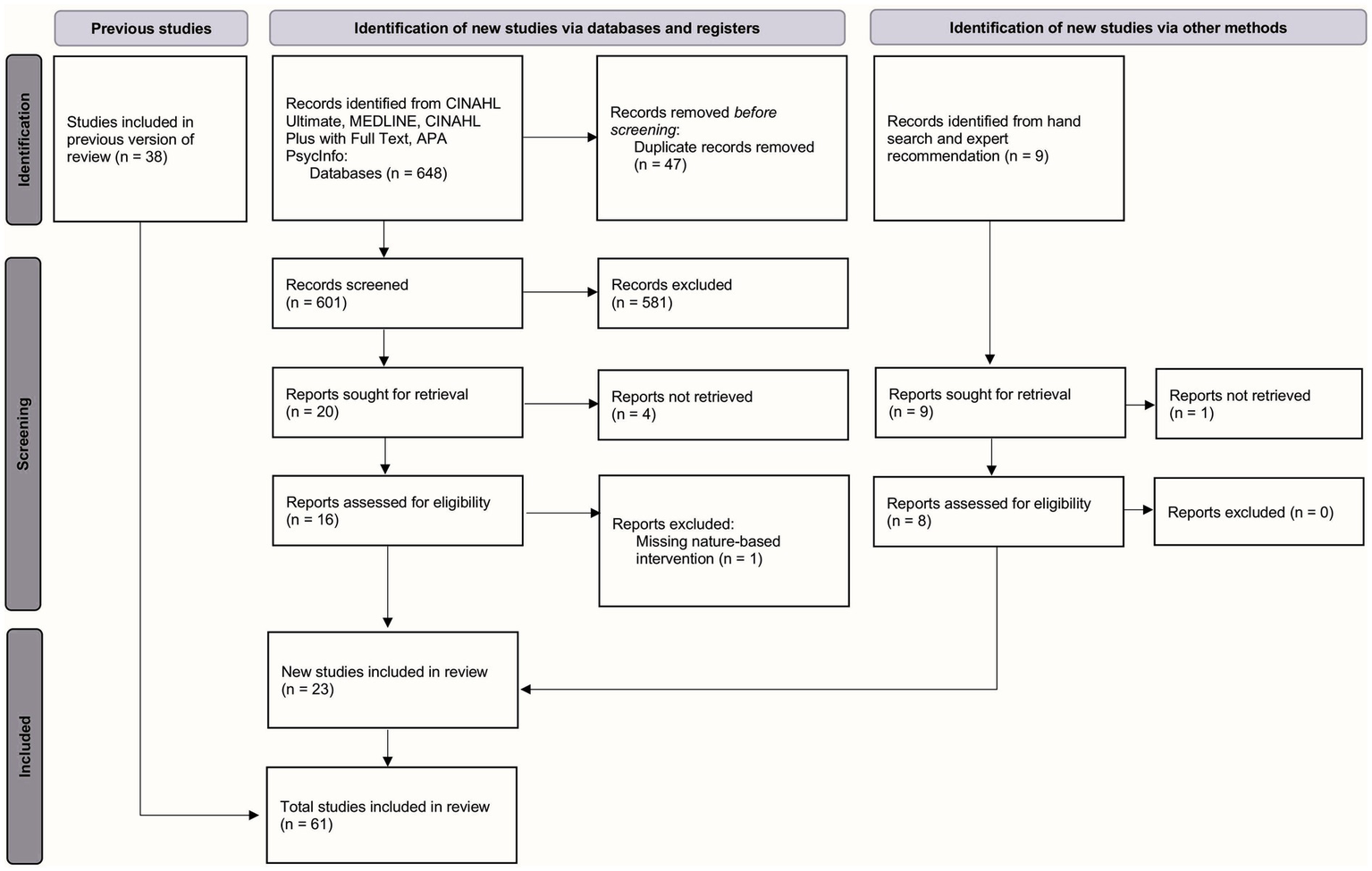
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram of the systematic review process.
3.1 Data extraction
The results of the data extraction can be found in Supplementary Table 1. The table contains the following information from the studies included in the review: Review, Population, Intervention, Control, Outcome, Moderating/Mediating Factors, and Conflict of Interest and Funding.
3.2 NBI types
The types of NBIs in the literature were identified and grouped according to thematic and conceptual similarities. Sixteen reviews reviewed horticultural interventions (Annerstedt and Währborg, 2011; Atchison et al., 2024; Bikomeye et al., 2022; Genter et al., 2015; Giang et al., 2024; Kondo et al., 2018; Lee et al., 2024; Lu et al., 2019; Mmako et al., 2020; Rueff and Reese, 2023; Trøstrup et al., 2019; Walker-Mao et al., 2024; Wang M. et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2022; Yun et al., 2024; Zhao et al., 2022), twelve reviews on nature exposure and nature viewing (Bikomeye et al., 2022; Corazon et al., 2019; Djernis et al., 2019; Fan and Baharum, 2024; Kondo et al., 2018; Paredes-Céspedes et al., 2024; Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022; Walker-Mao et al., 2024; Wang Y. et al., 2024; Wen et al., 2024; Yeo et al., 2020; Zhao et al., 2022), ten reviews on green exercise (Bikomeye et al., 2022; Coventry et al., 2021; Fraser et al., 2020; Kondo et al., 2018; Ma et al., 2023; Mmako et al., 2020; Paredes-Céspedes et al., 2024; Picton et al., 2020; Rueff and Reese, 2023; Struthers et al., 2024), ten reviews on Wilderness/Adventure Therapy (Annerstedt and Währborg, 2011; Bettmann et al., 2016; Bowen and Neill, 2013; Fatima et al., 2022; Gillis et al., 2016; Kraft and Cornelius-White, 2020; Pomfret et al., 2023; Rosa et al., 2023; Rueff and Reese, 2023; Shanahan et al., 2009), ten reviews on forest bathing (Bikomeye et al., 2022; Caponnetto et al., 2022; Fatima et al., 2022; Kamioka et al., 2012; Kotera et al., 2022; Lee et al., 2017; Quan et al., 2020; Rueff and Reese, 2023; Siah et al., 2023; Wen et al., 2019), five on NBIs (Fatima et al., 2022; Gritzka et al., 2020; Obeng et al., 2023; Taylor et al., 2022; Trøstrup et al., 2019), four on blue space interventions (Britton et al., 2020; Carneiro et al., 2024; Guntur et al., 2023; Overbury et al., 2023), four on nature-assisted therapy (Annerstedt and Währborg, 2011; Kotera et al., 2022; Rueff and Reese, 2023; Smith et al., 2024), three on ecotherapy (Caddick and Smith, 2014; Fatima et al., 2022; Rueff and Reese, 2023), two on farming (Cano-Verdugo et al., 2024; Gorman and Cacciatore, 2017), two on nature play (Dankiw et al., 2020; Johnstone et al., 2022), two on nature-based education (Ly and Vella-Brodrick, 2024; Miller et al., 2021), one on environmental volunteerism (Chen et al., 2022), one on immersive nature experiences (Mygind et al., 2019), and one about caring for country (Fatima et al., 2022).
3.2.1 Nature-based interventions/eco-therapy/nature-assisted therapy
NBIs can be understood as an overall umbrella term for any of the types of NBIs in this review. Similarly, eco-therapy can also be used as an overarching term for both active (exercise, gardening) and passive (nature exposure) nature-based techniques and practices. Nature-Assisted Therapy can also be understood as a broad term covering such practices, with the aim of recovering a patient’s health using interventions involving plants, natural materials, or outdoor environments (Annerstedt and Währborg, 2011).
3.2.2 Horticulture/horticultural therapy
Horticulture-based interventions are the most common type of interventions appearing in the reviews of this review. The activities in these interventions mainly involve gardening and other forms of taking care of plants (Tu, 2022).
3.2.3 Nature exposure/nature viewing
Nature exposure interventions typically involve exposure to outdoor nature, but can also include interventions using simulated nature indoors (Yeo et al., 2020). It is important to differentiate between outdoor nature exposure interventions and green exercise and wilderness therapy as nature exposure and nature viewing interventions should be more passive and at most include a light level of activity, as physical activity can have effects beyond nature exposure itself (Corazon et al., 2019; Kondo et al., 2018). For example, one review claimed forest therapy to involve nature viewing (Kondo et al., 2018).
3.2.4 Green exercise
Green exercise interventions consist of engaging in physical activity, such as walking or running, in nature (Bikomeye et al., 2022). These interventions are different from wilderness/adventure therapy in that although they do involve physical activity, their focus is not on overcoming challenges.
3.2.5 Wilderness/adventure therapy
The key features of Wilderness/Adventure Therapy Programmes usually involve some form of more complex, longer-term outdoor exercise activities hiking, trekking, and camping from 2 weeks to as long as 3 months (Bettmann et al., 2016). Likewise, the core of adventure interventions involves a certain form of risk in nature, such as camping, backpacking, or skiing. As such, these interventions can encompass both wilderness and adventure intervention programmes (Rosa et al., 2023).
3.2.6 Forest bathing/forest therapy
Forest bathing, also called shinrin-yoku, is a practice involving conscious and mindful immersion in the forest through all five senses. Forest therapy is related to forest bathing in the sense that it is a clinical application of forest bathing with a focus on specific physical and mental health difficulties (Caponnetto et al., 2022).
3.2.7 Blue space interventions
Most of the other NBIs mentioned cover green spaces, but blue spaces are just as viable for NBIs. Blue spaces can be defined as all visible, outdoor, natural surface waters with the potential to promote human health and wellbeing (Britton et al., 2020). As such, as of right now, all interventions involving blue spaces would be under the umbrella term Blue Space Interventions, and such interventions may include surfing (Carneiro et al., 2024), scuba diving (Guntur et al., 2023), or outdoor swimming (Overbury et al., 2023). Although there is some overlap between blue and green spaces, some reviews argue that blue spaces can offer original benefits which might be inaccessible in green spaces alone (Britton et al., 2020).
3.2.8 Care farming
Care farming involves the use of farms and agricultural landscapes for promoting mental and physical health through regular farming activities (Gorman and Cacciatore, 2017).
3.2.9 Nature play
Nature play interventions are nature-based, unstructured interventions aimed at children which allow them to play in environments containing natural elements such as gardens, forests, ponds, water, mud, plants, or rocks (Dankiw et al., 2020).
3.2.10 Nature-based education
Nature-Based Education or Nature-Based Learning is an approach in education which utilises the natural environment to facilitate learning (Miller et al., 2021). Such activities can include simply using a natural area as an outdoor classroom to actively using the natural environment in classes.
3.2.11 Environmental volunteerism
Environmental volunteerism involves activities such as tidying trails, soil preparation, tree planting, or recycling (Chen et al., 2022) and whereas most of the aforementioned interventions used nature in some way to improve mental and physical health, environmental volunteerism gives back to nature and Earth to improve our health.
3.2.12 Immersive nature experiences
Also called “friluftsliv,” this Scandinavian tradition covers a wider range of interventions: outdoor life, outdoor recreation and education, or adventure recreation and education, with an emphasis on achieving closeness to nature (Mygind et al., 2019).
3.2.13 Caring for country
Caring for Country is less of an intervention and more of a tradition for Indigenous Australians. It involves spending time in the country, revegetation, harvesting, protecting sacred areas and threatened species, or controlling fires, weeds, or feral animals (Fatima et al., 2022). These activities express the deeply interconnected relationship between the people and the country, from which both the people and the country benefit. These activities may resemble environmental volunteerism, as perhaps environmental volunteerism is a way for our modern population to try to reconnect and care for their country again.
3.2.14 Active and passive interventions and focus on nature
Two types of interventions have emerged from the analysis. The first type explored the level of activity required for participants to engage with NBIs. Active interventions were characterised by the participants’ direct physical, behavioural, or cognitive engagement. These interventions included such activities as movement, decision-making, skill-building, or overcoming challenges that require sustained and intentional participation. In contrast, passive interventions referred to experiences in which individuals receive the benefits of nature with minimal physical or mental effort. These were less demanding and included such activities as simply being present in a natural environment, viewing nature, or engaging in undirected relaxation outdoors. The terms Nature-Based Interventions and Blue Space Interventions were excluded as they cover a wide range of interventions including both passive and active ones, making them unfit for this distinction. For more details on this active and passive distinction for each NBI please see Table 2.
Table 2
| NBI type | Passive/Active | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Horticultural therapy | Active | Involves gardening and plant care, thus requires physical engagement |
| Nature exposure/viewing | Passive | Requires minimal engagement as it involves sitting or walking slowly while observing nature |
| Green exercise | Active | Involves physical activity in nature, such as walking, running and other intentional movement |
| Wilderness/Adventure therapy | Active | Includes extended, challenges outdoors requiring intense participant involvement |
| Forest bathing | Passive | The focus is on mindful presence and sensory immersion so it can involve slow movement, but it does not require intense physical engagement |
| Care farming | Active | Engages participants in farm work, thus requires physical engagement |
| Nature play | Active | Involves unstructured physical and imaginative activity in nature |
| Nature-based education | Active | Includes learning through doing in a natural setting, thus it could be physically, cognitively and emotionally engaging |
| Environmental volunteerism | Active | Involves physically demanding activities, such as planting or cleaning |
| Immersive nature experiences | Both | Includes recreation and education outdoors and can involve either passive or active recreation |
| Caring for country | Active | Involves culturally-driven practices that include interaction with land and environment |
Passive and active type of NBIs with a rationale for inclusion.
The second type of NBI that has emerged refers to whether nature was a primary or secondary focus. In NBIs that viewed nature as a primary focus, nature was the central therapeutic or educational agent, and the benefits of NBIs could be easily linked to nature. These NBIs included activities such as forest bathing, where the primary focus is on connecting with nature, or horticultural therapy, which focuses on attending to nature. On the other hand, in NBIs that viewed nature as a secondary focus, nature played a supportive or contextual role. These NBIs included outdoor classrooms, where the learning experience was the primary focus or green exercise, where physical activity is the primary focus of an activity, and nature is the context within which it is conducted. Similarly to the previous table, the terms Nature-Based Interventions and Blue Space Interventions were excluded as they cover a wide range of interventions. For more details on this primary and secondary distinction for each NBI please see Table 3.
Table 3
| NBI type | Nature as a primary or secondary focus | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Horticultural therapy | Primary | Involves noticing the beauty of nature and creating it |
| Nature exposure/viewing | Primary | Nature is the main reason for engaging in this activity |
| Green exercise | Secondary | Physical activity is the primary reason |
| Wilderness/Adventure therapy | Secondary | Challenges are the main reason for this activity |
| Forest bathing | Primary | Nature is the therapeutic agent and the activity helps individuals connect with nature |
| Care farming | Secondary | Farming is the main focus |
| Nature play | Secondary | Play is the main focus and nature is contextual |
| Nature-based education | Secondary | Education is the main focus |
| Environmental volunteerism | Secondary | Volunteerism is the main focus |
| Immersive nature experiences | Primary | Nature is the primary focus of the experience, its beauty and engagement with it |
| Caring for country | Secondary | It is about the relationship with the land and restoring it |
NBIs where nature is seen as a primary or secondary focus.
3.3 NBI moderating/mediating factors
The review identified multiple possible moderating/mediating factors potentially impacting the effectiveness of a given NBI. Of the 16 high quality and moderate quality reviews, only 7 found significant moderating/mediating factors. These factors were: social (Overbury et al., 2023; Rosa et al., 2023; Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022; Yeo et al., 2020), physical activity (Overbury et al., 2023; Rosa et al., 2023; Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022), age (Ly and Vella-Brodrick, 2024; Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022), nature connectedness (Overbury et al., 2023; Rosa et al., 2023), duration and frequency (Lee et al., 2024; Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022; Wang M. et al., 2024; Wang Y. et al., 2024; Yeo et al., 2020), gender (Ly and Vella-Brodrick, 2024), symptom severity (Lee et al., 2024), environment type (Wang M. et al., 2024), participant motivation (Rosa et al., 2023), challenge confrontation (Rosa et al., 2023), dementia (Yeo et al., 2020), skill/knowledge acquisition (Yeo et al., 2020), and autonomy/responsibility (Yeo et al., 2020).
3.3.1 Social
The social factor appeared in four out of five reviews discussing the moderating/mediating factors. In one study, a two-year exposure to a schoolyard improved children’s social well-being (Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022). However, social interaction was also an important aspect of NBIs for older adults (Yeo et al., 2020). Moreover, positive social interactions may improve hopelessness and feeling bad about oneself in depression (Rosa et al., 2023).
3.3.2 Physical activity
Many of the NBIs in this review involve some form of physical activity, which may be another factor in terms of many of the benefits of NBIs (Rosa et al., 2023; Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022), as physical activity and the outdoors are inherently linked.
3.3.3 Age
In one review, nature exposure did not seem to have the same effects on school children aged 7–12 when compared to middle or high school students (Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022). Another review found mixed effects of age in relation to mental, physical, and social wellbeing (Ly and Vella-Brodrick, 2024).
3.3.4 Nature connectedness
As some NBIs can strengthen a participant’s nature connectedness (Rosa et al., 2023), or in the case of blue space interventions, water connectedness (Overbury et al., 2023), a person’s nature connectedness might impact how responsive they are to a given NBI.
3.3.5 Duration and frequency
In studies with older adults, a larger proportion of the studies which lasted more than 5 weeks (7 out of 9) reported significant findings compared to the proportion of studies lasting 5 weeks or less (3 out of 9) (Yeo et al., 2020). Another review also reported the benefits of NBIs on attentional functioning in children in the short term, while the benefits of long-term NBIs were difficult to assess (Vella-Brodrick and Gilowska, 2022). As the former review focused on older adults and the latter on children and cognitive benefits, the efficiency of short-term vs. long-term NBIs is difficult to disentangle. As for frequency, horticultural interventions of 2 or more in frequency were more beneficial (Wang et al., 2024).
3.3.6 Gender
One review found differences between the effects of gender on physical activity between boys and girls at school (Ly and Vella-Brodrick, 2024), where although boys were found to have more physical activity overall, it was girls’ physical activity which benefited most from NBIs.
3.3.7 Symptom severity
One review on horticultural therapy and individuals with schizophrenia (Lee et al., 2024) found that symptom severity was important, as the effect sizes were larger for those with moderate severity compared to those with mild severity.
3.3.8 Environment type
A review on horticultural therapy in older patients with dementia (Wang M. et al., 2024) found outdoor interventions to have a larger effect size than indoor interventions.
3.3.9 Participant motivation and preference
One review highlights the importance of participant motivation and preference on the effectiveness of NBIs (Rosa et al., 2023). The more the participants are motivated to participate in the intervention, and the more the intervention aligns with the participants’ preferences, the less likely they may be to drop out of the intervention.
3.3.10 Challenge confrontation
Overcoming a challenge, which is an aspect present in some adventure therapies, has been found to be an effective way of improving the symptoms of depression by potentially improving the participants’ self-confidence and resilience (Rosa et al., 2023).
3.3.11 Autonomy, responsibility and skill and knowledge acquisition
NBIs which involved providing older adults with autonomy, responsibility, and some form of skill or knowledge acquisition, were more likely to be effective (Yeo et al., 2020). Another review shares a similar view, noting that the satisfaction of needs such as autonomy, competence, and relatedness might partly explain the mental health benefits of NBIs (Rosa et al., 2023). As such, an improved perception of autonomy through NBIs might improve their effectiveness. The acquisition of new knowledge and skills in older adults can thus not only improve the effectiveness of NBIs but also improve their lives.
4 Discussion
The aim of this systematic review of reviews was two-fold: Map out what types of NBIs exist and find out what moderating or mediating factors might be impacting their effectiveness. The review found a wide spectrum of NBIs discussed in the literature and multiple factors potentially impacting their effectiveness.
Our findings show a wide spectrum of NBIs offering unique mechanisms for improving peoples’ mental, physical, and social wellbeing, combined with a combination of multiple core factors influencing their effectiveness. The benefits of these interventions are well-established in the literature covered in our review, and our analysis highlights the need to tailor interventions to individual characteristics. For example, while horticultural therapy is frequently employed due to its robust evidence base for mental health improvements (Tu, 2022), interventions like environmental volunteerism, though primarily focused on older adults (Chen et al., 2022), also benefit younger populations (McDougle et al., 2011). This underscores the need for identifying the right person-intervention fit in future research.
The correct person-intervention fit may relate to the type of interventions used. The current review identified two types of interventions, i.e., those that are passive vs. active and interventions where nature is a primary focus vs. a secondary focus. These distinctions are important for several reasons. First, they help clarify the mechanisms of change, making it more effective to apply behavioural change models. For example, one of the most prevalent models is the COM-B model of change (Michie et al., 2011), which consists of three elements: capability (skill-building, support in knowing NBIs), opportunity (accessibility of green spaces and tools), and motivation (goal-setting, habit-formation). The opportunity aspect of COM-B may be especially relevant to nature-based interventions and urban planning, as better access to and improved quality of green and blue spaces are associated with improved physical and mental health benefits (Ekkel and de Vries, 2017).
Passive interventions may be particularly suitable for those who have low capability or limited access to quality nature. Active NBIs offer greater physical and psychological benefits but require more motivation to engage. Similarly, NBIs that have nature as a secondary focus might be easier to implement than those less familiar or comfortable with engaging with NBIs. Primary NBIs, on the other hand, require a stronger alignment across all three components of the COM-B model, but may also result in deeper nature-connectedness. Thus, distinguishing between the different types of interventions can be useful in clarifying the mechanisms for change. Subsequently, they will help tailor interventions to individuals’ needs, improving the impact and sustainability of NBIs. Further research needs to explore the differences in the impact of these interventions through a meta-analysis and establish in what situations and with whom they would be most effective.
4.1 NBI factors
The factors impacting NBI effectiveness are a complex, interconnected matrix of characteristics of given NBIs and people participating in them. As such, it is essential to consider that these factors influence not only NBI effectiveness but also each other. Identifying similarities and inconsistencies between these factors can help researchers and practitioners design NBI approaches that maximise the impact of nature on their wellbeing.
4.1.1 Social
This overall pattern of the importance of the social aspects of NBIs is difficult to ignore. NBIs can not only bring people together, but also improve people’s social skills (Bloomfield, 2017). As such, social NBIs might be effective at combating increasing loneliness (Buecker et al., 2021), and implementing group NBIs might bring about greater benefits than individual ones.
4.1.2 Physical activity
Nature can not only make it easier for people to achieve sufficient levels of physical activity, it can also enhance the amount and intensity of the physical activity itself (Gladwell et al., 2013). Researchers exploring NBIs involving physical activity should account for the benefits of physical activity and ensure the benefits are not purely based on the physical activity involved in the NBI. Similarly, practitioners may find it useful to account for patients’ physical ability when choosing appropriate NBIs and recommending NBIs involving physical activity when suitable.
4.1.3 Age
The reviews included in our review cover all age ranges from children to older adults, and as such, NBIs appear to be appropriate for individuals of any age. However, age remains a factor (Shanahan et al., 2019), as not all NBIs are equally appropriate for all ages. For example, more physically intensive NBIs such as weeks or months-long hikes might be too difficult, if not detrimental, to older adults. Future research should thus take into consideration the differences in the effectiveness of NBIs between major age groups and throughout childhood and adolescence. In addition, practitioners may want to take age into account especially in combination with the physical requirements of an NBI.
4.1.4 Nature connectedness
Nature connectedness can change how individuals interact with nature (Martin et al., 2020). For example, blue space interventions such as swimming claim to involve more immersion in nature (Overbury et al., 2023) than green space interventions, as you are surrounded and within the water. The question is whether this complete connectedness of being within nature changes peoples’ nature connectedness differently than just looking at nature on a screen such as in nature viewing. Future studies may not only explore an individual’s nature connectedness before the study, they may also explore how a person’s nature connectedness changes throughout the different types of NBIs.
4.1.5 Duration and frequency
NBIs may last anywhere from a few minutes, hours, to weeks or months. As such, it is essential to narrow down the minimum efficient “dose” of NBIs (Wilkie and Davinson, 2021) in terms of both duration and frequency. Future research should thus explore experiment duration and frequency as an essential variable to determine NBI efficiency. Ascertaining the minimum effective dose of NBIs would be of special benefit to healthcare professionals and practitioners.
4.1.6 Symptom severity
Symptom severity has been found to be an important factor, which aligns with other mental health literature, for example, with depression severity and antidepressant effects (Fournier et al., 2010), with patients with increased severity seeing more benefit from antidepressants. As such, NBIs might be especially beneficial for people with more severe mental health symptomology.
4.1.7 Environment type
Outdoor interventions have been found to be more effective than indoor ones, aligning with previous literature on exercise and how people find outdoor exercise to be more enjoyable than indoor exercise (Noseworthy et al., 2023). Healthcare practitioners and clinicians should thus consider outdoor NBIs before indoor ones.
4.1.8 Participant motivation and preference
Treatment preference is associated with decreased rates of dropping out of treatments (Windle et al., 2020). Developing personalised NBIs and ensuring they are interventions people want to do themselves would thus increase the likelihood of them participating in the intervention and not dropping out.
4.1.9 Challenge confrontation
Research shows confronting a challenge may lead to improvements in depression symptoms after NBIs (Rosa et al., 2023), however, this factor might have broader applicability. Improvements in peoples’ self-confidence and resilience might apply to non-depressed individuals as well (Liu et al., 2020). As such, when considering patients with impaired self-confidence, resilience, or depression, NBIs involving challenge confrontation might prove beneficial.
4.1.10 Autonomy, responsibility and skill and knowledge acquisition
Autonomy refers to the extent to which a person can live an independent life and is often decreased in older adults (Sánchez-García et al., 2019). Learning new skills and knowledge is not just a way for older adults to spend time, it can also be a way for them to chase subjects and skills they did not have time to invest in during their life (Narushima, 2008), providing countless benefits. NBIs which improve a person’s autonomy and skills may thus be especially beneficial for older adults.
4.2 Strengths and limitations
One of the strengths of this review is that it covered a wide range of NBIs with different names and methodologies. Moreover, the review also identified less common NBIs such as environmental volunteerism, caring for country, and multiple blue space interventions. A limitation of this review is that it did not cover NBIs utilising animals, such as animal-assisted therapies (Kamioka et al., 2014). Another limitation of the review is that it only included peer-reviewed systematic reviews in English, potentially missing out on less common or newly researched NBIs and factors impacting them, and NBIs from different settings and non-English-speaking countries. Furthermore, as only 16 of the 61 reviews were of high enough quality to be considered for the mediating/moderating factor analysis, and only 7 of the reviews explored such factors, the current review might have missed out on some factors only included in the lower quality reviews. As this is a review of reviews and not a review of NBI studies, the review might have missed out on NBIs which have not been reviewed yet. For example, stargazing would certainly fall into the category of NBIs (Bell et al., 2014), however, due to limited literature on the benefits of stargazing and a lack of reviews including it, it wasn’t possible to include it in our review.
5 Conclusion
Our review set out to explore what types of NBIs exist and what factors may impact their effectiveness. The review found a wide variety of NBIs under different umbrella terms and names and attempted to differentiate between the found NBIs in a systematic way based on their features. Although the review found 13 different types of NBIs, it is essential to note that most of these NBIs overlap in terms of their features and aims. In terms of factors, this review found a spectrum of factors potentially impacting NBI efficacy. Future research can not only utilise the NBI terms categorised in this review, it can also consider the factors found in this review when researching and applying NBIs to improve people’s mental and physical health and overall wellbeing. Furthermore, healthcare professionals and policymakers may benefit from the findings of the review by considering the wide spectrum of NBIs available in order to bring personalised and cost-effective treatments into healthcare.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
BK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. JO'K: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JB: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This publication has been developed within the framework of the Interreg North-West Europe 2021-2027 project ‘Forest4Youth’ (project code NWE0400643), co-funded by the European Union.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1625294/full#supplementary-material
References
1
Annerstedt M. Währborg P. (2011). Nature-assisted therapy: systematic review of controlled and observational studies. Scand. J. Public Health39, 371–388. doi: 10.1177/1403494810396400
2
Atchison K. Hoang P. M. Merrikh D. Chang C. Watt J. A. Hofmeister M. et al . (2024). Treatments for depression for older adults living in long-term care: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc.26:105435. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2024.105435
3
Bell R. Irvine K. N. Wilson C. Warber S. L. (2014). Dark nature: exploring potential benefits of nocturnal nature-based interaction for human and environmental health. Eur. J. Ecopsychol.5, 1–15. Available at: https://ecopsychology-journal.eu/v5/EJE%20v5_Bell%20et%20al.pdf
4
Bettmann J. E. Gillis H. L. Speelman E. A. Parry K. J. Case J. M. (2016). A meta-analysis of wilderness therapy outcomes for private pay clients. J. Child Fam. Stud.25, 2659–2673. doi: 10.1007/s10826-016-0439-0
5
Bikomeye J. C. Balza J. S. Kwarteng J. L. Beyer A. M. Beyer K. M. M. (2022). The impact of greenspace or nature-based interventions on cardiovascular health or cancer-related outcomes: a systematic review of experimental studies. PLoS One17:e0276517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276517
6
Bloomfield D. (2017). What makes nature-based interventions for mental health successful?BJPsych Int.14, 82–85. doi: 10.1192/s2056474000002063
7
Bowen D. J. Neill J. T. (2013). A Meta-analysis of adventure therapy outcomes and moderators. Open Psychol. J.6, 28–53. doi: 10.2174/1874350120130802001
8
Britton E. Kindermann G. Domegan C. Carlin C. (2020). Blue care: a systematic review of blue space interventions for health and wellbeing. Health Promot. Int.35, 50–69. doi: 10.1093/heapro/day103
9
Buecker S. Mund M. Chwastek S. Sostmann M. Luhmann M. (2021). Is loneliness in emerging adults increasing over time? A preregistered cross-temporal meta-analysis and systematic review. Psychol. Bull.147, 787–805. doi: 10.1037/bul0000332
10
Caddick N. Smith B. (2014). The impact of sport and physical activity on the well-being of combat veterans: a systematic review. Psychol. Sport Exerc.15, 9–18. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2013.09.011
11
Cano-Verdugo G. Flores-García B. D. Núñez-Rocha G. M. Ávila-Ortíz M. N. Nakagoshi-Cepeda M. A. A. (2024). Impact of urban farming on health: a systematic review. J. Public Health46, e500–e509. doi: 10.1093/pubmed/fdae056
12
Caponnetto P. Inguscio L. Triscari S. Casu M. Ferrante A. Cocuzza D. et al . (2022). New perspectives in psychopathology and psychological well-being by using forest therapy: a systematic review. Open Psychol. J.15:1–9. doi: 10.2174/18743501-v15-e220922-2021-ht3-1755-1
13
Carneiro L. Clemente F. M. Claudino J. G. Ferreira J. Ramirez-Campillo R. Afonso J. (2024). Surf therapy for people with mental health disorders: a systematic review of randomized and non-randomized controlled trials. BMC Complement. Med. Ther.24:376. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04674-0
14
Chen P.-W. Chen L.-K. Huang H.-K. Loh C.-H. (2022). Productive aging by environmental volunteerism: a systematic review. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr.98, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.archger.2021.104563
15
Corazon S. S. Sidenius U. Poulsen D. V. Gramkow M. C. Stigsdotter U. K. (2019). Psycho-physiological stress recovery in outdoor nature-based interventions: a systematic review of the past eight years of research. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health16:1711. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16101711
16
Coventry P. A. Brown J. V. E. Pervin J. Brabyn S. Pateman R. Breedvelt J. et al . (2021). Nature-based outdoor activities for mental and physical health: systematic review and meta-analysis. SSM Popul. Health16:100934. doi: 10.1016/j.ssmph.2021.100934
17
Dankiw K. A. Tsiros M. D. Baldock K. L. Kumar S. (2020). The impacts of unstructured nature play on health in early childhood development: a systematic review. PLoS One15:e0229006. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229006
18
Djernis D. Lerstrup I. Poulsen D. Stigsdotter U. Dahlgaard J. O’Toole M. (2019). A systematic review and Meta-analysis of nature-based mindfulness: effects of moving mindfulness training into an outdoor natural setting. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health16:3202. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16173202
19
Ekkel E. D. de Vries S. (2017). Nearby green space and human health: evaluating accessibility metrics. Landsc. Urban Plan.157, 214–220. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.06.008
20
Fan L. Baharum M. R. (2024). The effects of digital nature and actual nature on stress reduction: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Internet Interv.38:100772. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2024.100772
21
Fatima Y. Liu Y. Cleary A. Dean J. Smith V. King S. et al . (2022). Connecting the health of country with the health of people: application of ‘caring for country’ in improving the social and emotional well-being of indigenous people in Australia and New Zealand. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac.31:100648. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2022.100648
22
Fournier J. C. DeRubeis R. J. Hollon S. D. Dimidjian S. Amsterdam J. D. Shelton R. C. et al . (2010). Antidepressant drug effects and depression severity: a patient-level meta-analysis. JAMA303, 47–53. doi: 10.1001/jama.2009.1943
23
Fraser M. Polson R. Munoz S.-A. MacRury S. (2020). Psychological effects of outdoor activity in type 2 diabetes: a review. Health Promot. Int.35, 841–851. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daz064
24
Genter C. Roberts A. Richardson J. Sheaff M. (2015). The contribution of allotment gardening to health and wellbeing: a systematic review of the literature. Br. J. Occup. Ther.78, 593–605. doi: 10.1177/0308022615599408
25
Giang T. A. Cheng J. Y. Kwok H. Y. F. Hay G. M. S. Koh J. E. J. Johandi F. et al . (2024). Effectiveness of horticultural therapy in older adults without dementia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc.25:105296. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2024.105296
26
Gillis H. L. Speelman E. Linville N. Bailey E. Kalle A. Oglesbee N. et al . (2016). Meta-analysis of treatment outcomes measured by the Y-OQ and Y-OQ-SR comparing wilderness and non-wilderness treatment programs. Child Youth Care Forum45, 851–863. doi: 10.1007/s10566-016-9360-3
27
Gladwell V. F. Brown D. K. Wood C. Sandercock G. R. Barton J. L. (2013). The great outdoors: how a green exercise environment can benefit all. Extrem. Physiol. Med.2:3. doi: 10.1186/2046-7648-2-3
28
Gorman R. Cacciatore J. (2017). Cultivating our humanity: a systematic review of care farming & traumatic grief. Health Place47, 12–21. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2017.06.006
29
Gritzka S. MacIntyre T. E. Dörfel D. Baker-Blanc J. L. Calogiuri G. (2020). The effects of workplace nature-based interventions on the mental health and well-being of employees: a systematic review. Front. Psych.11:323. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00323
30
Guntur G. Solikhin M. N. Fauzi F. Shahril M. I. B. Salimin N. B. (2023). The benefits of scuba diving for people with physical disabilities: a systematic review of the literature. Jurnal Keolahragaan11:Article 1. doi: 10.21831/jk.v11i1.60136
31
Hinde S. Bojke L. Coventry P. (2021). The cost effectiveness of Ecotherapy as a healthcare intervention, separating the Wood from the trees. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health18:11599. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111599
32
Johnstone A. McCrorie P. Cordovil R. Fjørtoft I. Iivonen S. Jidovtseff B. et al . (2022). Nature-based early childhood education and children’s physical activity, sedentary behavior, motor competence, and other physical health outcomes: a mixed-methods systematic review. J. Phys. Act. Health19, 456–472. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2021-0760
33
Kamioka H. Okada S. Tsutani K. Park H. Okuizumi H. Handa S. et al . (2014). Effectiveness of animal-assisted therapy: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med.22, 371–390. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2013.12.016
34
Kamioka H. Tsutani K. Mutoh Y. Honda T. Shiozawa N. Okada S. et al . (2012). A systematic review of randomized controlled trials on curative and health enhancement effects of forest therapy. Psychol. Res. Behav. Manag.5, 85–95. doi: 10.2147/prbm.s32402
35
Kondo M. C. Jacoby S. F. South E. C. (2018). Does spending time outdoors reduce stress? A review of real-time stress response to outdoor environments. Health Place51, 136–150. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2018.03.001
36
Kondo M. C. Oyekanmi K. O. Gibson A. South E. C. Bocarro J. Hipp J. A. (2020). Nature prescriptions for health: a review of evidence and research opportunities. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health17:4213. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17124213
37
Kotera Y. Richardson M. Sheffield D. (2022). Effects of Shinrin-Yoku (Forest bathing) and nature therapy on mental health: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Int. J. Ment. Heal. Addict.20, 337–361. doi: 10.1007/s11469-020-00363-4
38
Kraft M. Cornelius-White J. (2020). Adolescent experiences in wilderness therapy: a systematic review of qualitative studies. J. Creat. Ment. Health15, 343–352. doi: 10.1080/15401383.2019.1696259
39
Lee Y.-W. Chen T.-T. Hsu C.-W. Chen M.-D. Lin P.-Y. Huang Y.-C. et al . (2024). Efficacy of horticultural therapy on positive, negative, and affective symptoms in individuals with schizophrenia: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Healthcare12:2104. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12212104
40
Lee I. Choi H. Bang K.-S. Kim S. Song M. Lee B. (2017). Effects of Forest therapy on depressive symptoms among adults: a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health14:321. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14030321
41
Liu J. J. W. Ein N. Gervasio J. Battaion M. Reed M. Vickers K. (2020). Comprehensive meta-analysis of resilience interventions. Clin. Psychol. Rev.82:101919. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2020.101919
42
Lu L.-C. Lan S.-H. Hsieh Y.-P. Yen Y.-Y. Chen J.-C. Lan S.-J. (2019). Horticultural therapy in patients with dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Dement.35:1533317519883498. doi: 10.1177/1533317519883498
43
Ly V. Vella-Brodrick D. A. (2024). Effects of school-led greenspace interventions on mental, physical and social wellbeing in children and adolescents: a systematic review. Educ. Psychol. Rev.36:133. doi: 10.1007/s10648-024-09963-1
44
Ma J. Lin P. Williams J. (2023). Effectiveness of nature-based walking interventions in improving mental health in adults: a systematic review. Curr. Psychol.43, 9521–9539. doi: 10.1007/s12144-023-05112-z
45
Martin L. White M. P. Hunt A. Richardson M. Pahl S. Burt J. (2020). Nature contact, nature connectedness and associations with health, wellbeing and pro-environmental behaviours. J. Environ. Psychol.68:101389. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp.2020.101389
46
Masters R. Nicoly J. Gaddy V. Interrante V. Ortega F. (2024). The impact of nature realism on the restorative quality of virtual reality forest bathing. ACM Trans. Appl. Percept.22:3:1-3:18. doi: 10.1145/3670406
47
Mauldin R. L. Highfill M. C. Schuman D. Henderson S. Anderson A. (2025). Viewing nature-focused livestreams and subjective well-being: a scoping review. Ecopsychology17, 42–54. doi: 10.1089/eco.2024.0007K
48
McDougle L. M. Greenspan I. Handy F. (2011). Generation green: understanding the motivations and mechanisms influencing young adults’ environmental volunteering. Int. J. Nonprofit Volunt. Sect. Mark.16, 325–341. doi: 10.1002/nvsm.431
49
Michie S. van Stralen M. M. West R. (2011). The behaviour change wheel: a new method for characterising and designing behaviour change interventions. Implement. Sci.6:42. doi: 10.1186/1748-5908-6-42
50
Miller N. C. Kumar S. Pearce K. L. Baldock K. L. (2021). The outcomes of nature-based learning for primary school aged children: a systematic review of quantitative research. Environ. Educ. Res.27, 1115–1140. doi: 10.1080/13504622.2021.1921117
51
Mmako N. J. Courtney-Pratt H. Marsh P. (2020). Green spaces, dementia and a meaningful life in the community: a mixed studies review. Health Place63:102344. doi: 10.1016/j.healthplace.2020.102344
52
Mygind L. Kjeldsted E. Hartmeyer R. D. Mygind E. Bølling M. Bentsen P. (2019). Immersive nature-experiences as health promotion interventions for healthy, vulnerable, and sick populations? A systematic review and appraisal of controlled studies. Front. Psychol.10:943. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00943
53
Narushima M. (2008). More than nickels and dimes: the health benefits of a community-based lifelong learning programme for older adults. Int. J. Lifelong Educ.27, 673–692. doi: 10.1080/02601370802408332
54
Noseworthy M. Peddie L. Buckler E. J. Park F. Pham M. Pratt S. et al . (2023). The effects of outdoor versus indoor exercise on psychological health, physical health, and physical activity behaviour: a systematic review of longitudinal trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health20:1669. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031669
55
Nye A. Delgadillo J. Barkham M. (2023). Efficacy of personalized psychological interventions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol.91, 389–397. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000820
56
Obeng J. K. Kangas K. Stamm I. Tolvanen A. (2023). Promoting sustainable well-being through nature-based interventions for young people in precarious situations: implications for social work. A systematic review. J. Happiness Stud.24, 2881–2911. doi: 10.1007/s10902-023-00683-x
57
OECD (2024). Fiscal sustainability of health systems: How to finance more resilient health systems when money is tight?Paris: OECD Publishing. doi: 10.1787/880f3195-en
58
Overbury K. Conroy B. W. Marks E. (2023). Swimming in nature: a scoping review of the mental health and wellbeing benefits of open water swimming. J. Environ. Psychol.90:102073. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp.2023.102073
59
Page M. J. McKenzie J. E. Bossuyt P. M. Boutron I. Hoffmann T. C. Mulrow C. D. et al . (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
60
Paredes-Céspedes D. M. Vélez N. Parada-López A. Toloza-Pérez Y. G. Téllez E. M. Portilla C. et al . (2024). The effects of nature exposure therapies on stress, depression, and anxiety levels: a systematic review. European journal of investigation in health. Psychol. Educ.14, 609–622. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe14030040
61
Picton C. Fernandez R. Moxham L. Patterson C. F. (2020). Experiences of outdoor nature-based therapeutic recreation programs for persons with a mental illness: a qualitative systematic review. JBI Evid. Synth.18, 1820–1869. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-d-19-00263
62
Pomfret G. Sand M. May C. (2023). Conceptualising the power of outdoor adventure activities for subjective well-being: a systematic literature review. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour.42, 100641–100610. doi: 10.1016/j.jort.2023.100641
63
Popay J. Roberts H. Sowden A. Petticrew M. Arai L. Rodgers M. et al . (2006). Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews: A product from the ESRC Methods Programme. Lancaster University. doi: 10.13140/2.1.1018.4643
64
Pretty J. Barton J. (2020). Nature-based interventions and mind–body interventions: saving public health costs whilst increasing life satisfaction and happiness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health17:7769. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17217769
65
Quan N. G. Lohman M. C. Resciniti N. V. Friedman D. B. (2020). A systematic review of interventions for loneliness among older adults living in long-term care facilities. Aging Ment. Health24, 1945–1955. doi: 10.1080/13607863.2019.1673311
66
Rosa C. D. Chaves T. S. Collado S. Larson L. R. Profice C. C. (2023). The effect of nature-based adventure interventions on depression: a systematic review. Environ. Behav.55, 140–174. doi: 10.1177/00139165231174615
67
Rueff M. Reese G. (2023). Depression and anxiety: a systematic review on comparing ecotherapy with cognitive behavioral therapy. J. Environ. Psychol.90, 102097–102018. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp.2023.102097
68
Sánchez-García S. García-Peña C. Ramírez-García E. Moreno-Tamayo K. Cantú-Quintanilla G. R. (2019). Decreased autonomy in community-dwelling older adults. Clin. Interv. Aging14, 2041–2053. doi: 10.2147/cia.s225479
69
Shanahan D. F. Astell–Burt T. Barber E. A. Brymer E. Cox D. T. C. Dean J. et al . (2019). Nature-based interventions for improving health and wellbeing: the purpose, the people and the outcomes. Sports7:141. doi: 10.3390/sports7060141
70
Shanahan L. McAllister L. Curtin M. (2009). Wilderness adventure therapy and cognitive rehabilitation: joining forces for youth with TBI. Brain Inj.23, 1054–1064. doi: 10.3109/02699050903421115
71
Shea B. J. Reeves B. C. Wells G. Thuku M. Hamel C. Moran J. et al . (2017). AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ358:j4008. doi: 10.1136/bmj.j4008
72
Siah C. J. R. Goh Y. S. Lee J. Poon S. N. Ow Yong J. Q. Y. Tam W. W. (2023). The effects of forest bathing on psychological well-being: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Ment. Health Nurs.32, 1038–1054. doi: 10.1111/inm.13131
73
Smith F. Howie L. Malsingh J. O’Mant A. Shakespeare S. Tunney K. (2024). Effects of nature-based mindfulness on pain and wellbeing for adults with persistent pain: a systematic literature review. Phys. Ther. Rev.29, 101–116. doi: 10.1080/10833196.2024.2367814
74
Struthers N. A. Guluzade N. A. Zecevic A. A. Walton D. M. Gunz A. (2024). Nature-based interventions for physical health conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res.258:119421. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.119421
75
Taylor E. M. Robertson N. Lightfoot C. J. Smith A. C. Jones C. R. (2022). Nature-based interventions for psychological wellbeing in long-term conditions: a systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health19:3214. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063214
76
Trøstrup C. H. Christiansen A. B. Stølen K. S. Nielsen P. K. Stelter R. (2019). The effect of nature exposure on the mental health of patients: a systematic review. Qual. Life Res.28, 1695–1703. doi: 10.1007/s11136-019-02125-9
77
Tu H. (2022). Effect of horticultural therapy on mental health: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs.29, 603–615. doi: 10.1111/jpm.12818
78
Vella-Brodrick D. A. Gilowska K. (2022). Effects of nature (greenspace) on cognitive functioning in school children and adolescents: a systematic review. Educ. Psychol. Rev.34, 1217–1254. doi: 10.1007/s10648-022-09658-5
79
Walker-Mao C. Sachs A. L. Walls Wilson J. Wrigley J. Litt J. S. Farewell C. V. et al . (2024). Systematic review of nature-based interventions for perinatal depression, anxiety, and loneliness. Matern. Child Health J.28, 1886–1896. doi: 10.1007/s10995-024-03989-1
80
Wang M. Qian Y. Yu X. Xing Y. (2024). Effectiveness of horticultural therapy in older patients with dementia: a meta-analysis systemic review. J. Clin. Nurs.33, 4543–4553. doi: 10.1111/jocn.17444
81
Wang Y. Timms F. Li J. Yu H. (2024). Benefits of nature-based intervention in combating the impact of urbanization on psychopathology in industrialized societies. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry37, 202–211. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000937
82
Wang Z. Zhang Y. Lu S. Tan L. Guo W. Lown M. et al . (2022). Horticultural therapy for general health in the older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One17:e0263598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263598
83
Wen Y. Shen X. Shen Y. (2024). Improving immersive experiences in virtual natural setting for public health and environmental design: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One19:e0297986. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297986
84
Wen Y. Yan Q. Pan Y. Gu X. Liu Y. (2019). Medical empirical research on forest bathing (Shinrin-yoku): a systematic review. Environ. Health Prev. Med.24:70. doi: 10.1186/s12199-019-0822-8
85
Wilkie S. Davinson N. (2021). Prevalence and effectiveness of nature-based interventions to impact adult health-related behaviours and outcomes: a scoping review. Landsc. Urban Plan.214:104166. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2021.104166
86
Windle E. Tee H. Sabitova A. Jovanovic N. Priebe S. Carr C. (2020). Association of Patient Treatment Preference with Dropout and Clinical Outcomes in adult psychosocial mental health interventions: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry77, 294–302. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2019.3750
87
Yeo N. L. Elliott L. R. Bethel A. White M. P. Dean S. G. Garside R. (2020). Indoor nature interventions for health and wellbeing of older adults in residential settings: a systematic review. The Gerontologist60, e184–e199. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnz019
88
Yun J. Yao W. Meng T. Mu Z. (2024). Effects of horticultural therapy on health in the elderly: a review and meta-analysis. J. Public Health32, 1905–1931. doi: 10.1007/s10389-023-01938-w
89
Zhao Y. Liu Y. Wang Z. (2022). Effectiveness of horticultural therapy in people with dementia: a quantitative systematic review. J. Clin. Nurs.31, 1983–1997. doi: 10.1111/jocn.15204
Summary
Keywords
nature-based interventions, green space interventions, blue space interventions, horticulture, forest bathing, nature
Citation
Kaleta B, Campbell S, O’Keeffe J and Burke J (2025) Nature-based interventions: a systematic review of reviews. Front. Psychol. 16:1625294. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1625294
Received
08 May 2025
Accepted
22 July 2025
Published
08 August 2025
Volume
16 - 2025
Edited by
Birgitta Dresp-Langley, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), France
Reviewed by
Justin Lawson, Deakin Univeristy, Australia
Dahlia Stott, Drexel University, United States
Dorothy Schmalz, The University of Utah, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Kaleta, Campbell, O’Keeffe and Burke.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Branislav Kaleta, branislavkaleta@rcsi.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.