- 1School of Fine Arts, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing, China
- 2School of Design, Jiangnan University, Wuxi, China
Given the escalating global concern regarding food waste, food packaging emerges as a critical area for intervention. Existing research, however, predominantly concentrates on consumer attitudes, offering limited insight into the role of food packaging in mitigating food waste. To address this gap, this study employs the BRT model, incorporating the variable of behavioral rationality into traditional theory and integrating values as a preceding variable. It integrates consumer values, behavioral rationality, attitudes, and behavioral intentions to explore the influence mechanism of food packaging on consumer behavior, explaining behavioral intentions through supporting/rejecting reasons. The study investigates how visual attributes, functionality, environmental sustainability, and social attributes within supporting reasons positively influence consumers' attitudes and behavioral intentions to reject food waste. Conversely, it investigates how information overload, functional deficiencies, inappropriate sizing, and high cognitive load within rejection reasons negatively impact these attitudes and intentions. By dissecting the positive and negative impacts of food packaging attributes on consumer attitudes and behavioral intentions across supporting and rejecting reasons, this research aims to identify key design factors for food packaging. This will fill existing research gaps, provide a theoretical foundation for food packaging design, and encourage consumers to adopt positive behaviors that reduce food waste. The findings indicate that: (1) consumer values significantly influence different behavioral attitudes; (2) supporting reasons related to food packaging positively impact the rejection of food waste behavior, while rejecting reasons have the opposite effect; (3) both positive and negative reasons significantly influence consumer attitudes and behavioral intentions, highlighting the need to optimize design elements in food packaging to positively influence consumer behavior; (4) packaging design factors have a more significant impact on intentions to conserve food than consumer attitudes themselves. This study extends the Behavioral Reasoning Theory (BRT) to understand food packaging's influence on consumer behavior, addressing contextual factors within BRT. Furthermore, it provides a scientific basis for food companies to optimize packaging design, which has practical implications for mitigating global food waste.
Introduction
Food is a fundamental condition for human survival and an essential guarantee for the development of human society. However, the phenomenon of food waste is increasingly prevalent in our rapidly developing modern society. Food waste, as a significant and practical issue of global concern, has a considerable impact on food security and supply (Campoy-Muñoz et al., 2021). It is a widespread issue worldwide, with its definition evolving alongside the complexities of the food supply chain (Parfitt et al., 2010). According to estimates by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), approximately one-quarter to one-third of food produced globally is wasted (Bellemare et al., 2017), with variations across different countries and regions. In developed areas, consumer-level food waste constitutes the largest proportion (Heng and House, 2022), while in developing regions, post-harvest losses are more significant (Parfitt et al., 2010). Due to conflicts in certain countries and regions, global food production is projected to decline in 2024, while the number of people suffering from hunger continues to rise, exceeding 860 million, posing a severe threat to global food security (Moffat, 1992). The FAO reports that the world is facing the most severe food crisis in 50 years (Wu et al., 2014). Consequently, the increasingly dire food crisis has led countries worldwide to recognize the importance of food security, attempting to alleviate and improve the issue of food waste through various methods (Boliko, 2019). Food waste is one of the critical causes of the food crisis, referring to food that is still usable but is lost at the retail or sales level due to consumer behavior, such as purchasing excessive amounts of food, discarding food before it is consumed (Zeineddine et al., 2021), or rejecting food that does not meet aesthetic standards (Bauer et al., 2023). These behaviors are often intentional acts of food waste (Dusoruth and Peterson, 2020). The severity of food waste behavior is particularly pronounced in countries and regions with high levels of urbanization, including China (Han et al., 2020). The extent of China's food waste is alarming, with approximately 26.3% of the food produced for residential consumption wasted or lost each year. The food loss rate across the entire supply chain stands at 19.0% ± 5.8%, with the consumer segment being the largest source of waste, accounting for 7.3% ± 4.8% (Liu et al., 2013). The total estimated loss and waste amount to 422.56 million tons, representing about 22.37% of total food production (Jia et al., 2022), with wasteful practices continuing to rise (Zhang et al., 2022).
The causes of food waste are multifaceted, encompassing consumer behavior, food packaging design, and supply chain management (dos Santos et al., 2022). Food packaging, in particular, emerges as a significant driver of food waste, with research indicating that improvements in packaging design can mitigate this issue (Chan, 2022). As an indispensable component of the food supply chain, food packaging's primary functions are to extend shelf life and ensure food safety through physical protection, chemical barriers, microbial inhibition, and information dissemination (Salgado et al., 2021). Studies reveal that in developing countries, the volume of food waste attributable to packaging issues surpasses the quantity of food produced annually (Mao et al., 2008). Food packaging has consistently addressed the challenge of extending food longevity through more effective methods (Nair et al., 2023), aiming to mitigate food waste at its source rather than managing it through waste disposal strategies (Stangherlin and De Barcellos, 2018). This underscores the potential of food packaging design to influence and potentially reduce food waste behaviors. Therefore, investigating the mechanisms through which food packaging design impacts consumer behavior in reducing food waste is essential, as it can enhance the effectiveness of food packaging. Conversely, it can effectively mitigate environmental pollution (Versino et al., 2023). Furthermore, sustained guidance and influence can positively impact consumer behavior (Chu et al., 2020), thereby fostering the advancement of sustainable consumption (Coussy et al., 2013). It is acknowledged that consumers' perceptions and requirements regarding packaging vary across different regions, reflecting cultural and societal disparities, economic constraints (Zeng, 2021), and limitations imposed by infrastructure and environmental technologies in certain developing nations. Considering the overall trends in food packaging design, research into food packaging design holds significant importance in reducing food waste behaviors; however, the specific implementation strategies and packaging improvements must be adapted to account for environmental variations (Du Rietz Dahlström and Kremel, 2023). Consequently, through the strategic design of packaging elements, it is feasible to diminish food waste, lessen environmental impacts, and promote sustainable consumption practices.
This study aims to dissect the mechanisms through which food packaging influences consumer food waste behavior, identifying key design elements that encourage waste reduction. These elements include functional design aspects (e.g., preservation technologies, portion sizes; Yokokawa et al., 2019; Obersteiner et al., 2021), visual design (e.g., color schemes, graphic elements; Wang, 2013; Marques da Rosa et al., 2018), and informational design (e.g., consumption guidelines, environmental prompts; Lindh and Olsson, 2016; d'Astous and Labrecque, 2021). Through empirical research and longitudinal tracking, the study seeks to clarify the role of food packaging design in fostering thrifty consumer habits and promoting sustainable consumption models. The findings will provide actionable recommendations for businesses to optimize food packaging design and for governments to formulate relevant policies, thereby mitigating food waste at its source and contributing to global food security. The significance of this research is underscored by its multifaceted benefits. From a food safety perspective, reducing consumer-level food waste through packaging design enhances food resource utilization, alleviates the imbalance between food supply and demand, and strengthens national and global food security, thus safeguarding fundamental human needs (Barone and Aschemann-Witzel, 2022). Environmentally, food waste and packaging waste are intertwined, exacerbating resource depletion and environmental pollution. Inappropriate food packaging not only leads to material waste but also poses long-term hazards to ecosystems, such as soil and water bodies, due to its poor biodegradability (Georgakoudis et al., 2023). Scientific packaging design can extend food shelf life and reduce excessive packaging, thereby promoting ecologically sustainable development (Bakkaloglu and Arici, 2019). Economically, reducing food waste can lower production costs for businesses and improve economic efficiency (Martin-Rios et al., 2022). Socioculturally, food packaging, as a frequently encountered medium in daily life, can subtly integrate concepts such as food conservation and eco-friendly consumption through clever design, thereby guiding the public to develop healthy and civilized consumption habits. This, in turn, fosters a societal ethos of valuing food and embracing green living, contributing to the construction of a resource-efficient and environmentally friendly society (Suwandi et al., 2023).
Food packaging design must meet market demands while catering to consumers' desire for aesthetic enjoyment (Zhang, 2016). It can reflect the principles of fun and practicality, enhancing the consumption experience while highlighting the inherent value of the food itself (Biswas Majee et al., 2025). Therefore, conveying the concept of food conservation through packaging design can effectively influence consumer behavior regarding food. Relevant data shows that over 80% of consumers are willing to pay for environmentally friendly packaging (Ling et al., 2021). Consumers' recognition of green design and concepts in food packaging encourages enterprises and governments to prioritize this area, evident in the multifunctionality, sustainability, and recyclability of food packaging (Lindh and Olsson, 2016). Food packaging design can extend food safety and the lifespan of packaging (Pereira de Abreu et al., 2012), reflecting the ideals of conservation and environmental protection in both food and packaging (Opara and Mditshwa, 2013). Thus, education and the promotion of green ideas in food packaging design are particularly crucial (Xiao-b, 2014).
The research findings offer multifaceted contributions to practical applications. At the corporate level, identifying the factors influencing consumer food waste behavior through food packaging design enables businesses to reduce excessive packaging costs, develop lightweight and multifunctional packaging to minimize waste, and enhance market competitiveness. For consumers, incorporating designs that promote conservation and environmental awareness on packaging encourages rational consumption, fosters food-saving habits, and improves the consumer experience. Within the food packaging industry, the research provides a basis for establishing green packaging standards, driving the industry toward sustainability and multifunctionality. In terms of policy-making, the results offer data support for government implementation of green packaging incentive policies and regulation of excessive packaging, as well as providing a reference for integrating conservation and environmental concepts into social publicity and education policies. To elucidate the mechanism by which food packaging factors influence consumer behavior, we employ the Behavioral Reasoning Theory (BRT) to explain the motivations underlying consumers' rejection of food waste, predicting behavior through intention (Unal et al., 2024). We supplement this with the inclusion of consumer context, which allows for a more comprehensive consideration of various influencing factors in the actual purchase and consumption process. In the context of food packaging, considering specific factors in packaging design enables an accurate analysis of consumer behavioral intentions under specific packaging factor backgrounds, addressing the limitations of existing research that focuses on internal consumer factors while neglecting the contextual influence of external factors (Popovic et al., 2019). Specifically, BRT, by incorporating reasoning variables, compensates for the shortcomings of traditional behavioral theories (TPB), providing a more comprehensive explanation of behavioral intentions (Wirama and Wirama, 2024). Simultaneously, incorporating consumer context into the research scope makes the results more relevant to real-life consumption scenarios, where different packaging design factors have varying impacts on consumer behavior. This consideration of contextual factors aids in packaging design that better serves consumers' actual purchasing behavior. Utilizing BRT, we analyze the influence paths on consumers' rejection of food waste behavior through multi-level and multi-dimensional approaches. The study employs a two-stage modeling approach based on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) to systematically analyze the second-order constructs of “Reasons for” and “Reasons against” (Xu et al., 2024). Specifically, in the first stage, path analysis is conducted on the observed variables corresponding to each first-order construct using the PLS-SEM algorithm, thereby obtaining latent variable information for the first-order constructs, which effectively refines and represents the core information contained within them. In the second stage, the latent variable information of the first-order constructs obtained in the first stage is used as measurement indicators for the second-order constructs, constructing a measurement model for the second-order constructs, thus realizing the modeling process from specific constructs.
Literature review
Behavior reasoning theory
According to Behavior Reasoning Theory (BRT), the rationality of behavior or the reasons behind actions is a more direct and critical factor influencing decision-making than traditional psychological variables such as values and attitudes (Westaby, 2005). Most scholars have conducted extensive and in-depth research on green low-carbon psychology and behavior using the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), Theory of Reasoned Action (TRA), and Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB; Liu et al., 2017). These traditional models of green consumption have received substantial empirical support for the relationship between attitude and behavioral intention; however, they often overlook the rationality of behavior. Traditional theoretical models, predicated on the “rational consumer” assumption, posit that consumers engage in cost-benefit analyses to maximize utility, thereby illustrating the limitations of rational models in the study of user behavior (Jackson, 2005). Concurrently, consumer decision-making in related fields is often influenced by factors such as social norms, moral cognition, and status quo bias (Abhyankar, 2022). Furthermore, traditional models overlook the impact of contextual factors, such as habitual consumption and aesthetic preferences, thereby neglecting the rationalization of human behavior (Temizkan, 2022). Consequently, traditional theories struggle to explain the non-linear relationships between variables; for instance, the influence of attitudes on behavior may exhibit threshold effects due to the influence of other factors, which the traditional linear structures of models like TPB fail to capture (Velnampy and Achchuthan, 2016). The rationality of consumer behavior transcends the traditional rational assumptions, emphasizing the decision-making processes of consumers under conditions of bounded rationality, including the cognitive rationality of information acquisition and processing (Estrada, 2010), as well as contextual and habitual factors in decision-making (Kevin et al., 2024). Moreover, in the specific context of food packaging, numerous studies have explored the impact of factors such as the promotion of purchase intention through eco-friendly packaging and consumer preferences for recyclable and biodegradable materials (Kevin et al., 2024), as well as moderating factors like price and social influence (Chopde, 2024). Integrating these factors into the model is essential, highlighting the advantages of BRT in analyzing the interactions between variables. To investigate the impact of food packaging factors on consumer behavioral rationality, this study incorporates behavioral rationality into the traditional theoretical model. The BRT model offers unique advantages in analyzing behavioral rationality. Consequently, the BRT model is employed to analyze the underlying mechanisms of consumers' environmental behavioral intentions. Furthermore, values significantly influence consumers, exerting a long-term and fundamental effect. Traditional theoretical models, when discussing behavioral intentions, often focus on attitudes, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control, yet overlook values as an antecedent variable. Therefore, this research integrates values into the discussion to examine how food packaging influences subsequent consumer attitudes, behavioral rationality, and behavioral intentions (Claudy and Peterson, 2013). Methodologically, this paper utilizes BRT to organically integrate consumer values, behavioral rationality, attitudes, and behavioral intentions, thereby exploring the intrinsic mechanisms of food packaging's impact on consumer behavior. Explaining consumer behavioral intentions through supporting/rejecting reasons is crucial, with values serving to predict behavioral rationality, attitudes, and behavioral intentions (Sahu et al., 2020).
Building upon the preceding discussion, this study centers on elucidating the mechanism by which food packaging influences consumers' behaviors in rejecting food waste. The research methodology is as follows: Grounded in the Behavior Reasoning Theory (BRT), with the incorporation of consumer context as a supplementary element, thereby addressing the limitations of traditional theories in overlooking external factors. This approach employs “reason for” and “reason against” variables to interpret behavioral motivations. Furthermore, it integrates specific aspects of food packaging, including functionality, visual design, and informational design, to construct a multi-dimensional influence pathway. The aim is to investigate their specific impacts on consumers' behavioral intentions and their actions in rejecting food waste.
Food packaging design factors
Food packaging design factors represent a multidimensional and interdisciplinary field. It encompasses visual design, material science, environmental impacts, and consumer behavior. Multiple factors influence consumers' purchasing decisions. These include, but are not limited to, the packaging's visual attributes (Marques da Rosa et al., 2018; Ahmadi et al., 2013), functional properties (Yokokawa et al., 2019; Obersteiner et al., 2021), environmental attributes (Lindh and Olsson, 2016; d'Astous and Labrecque, 2021), and social connotations (Wang, 2013). The visual attributes of packaging, such as its color and shape, significantly impact consumers' product preferences and their impressions of a product's taste and health benefits (Marques da Rosa et al., 2018). Many elements of packaging design affect consumer behavior, including aspects such as its informational content, content protection, identification, smart features, geometric shape, eco-friendliness, durability, and color (Konstantoglou et al., 2020). The environmental attributes of food packaging include the use of recyclable materials, reduced resource consumption, and minimized environmental pollution (Wang and Sun, 2010). Meanwhile, the functional attributes of food packaging, including its durability, shelf-life extension capabilities, and controlled release technologies, are crucial in maintaining food quality and safety (Shima Jafarzadeh et al., 2023). Thus, food packaging designs contribute to consumers' confidence, ensuring that the materials do not contaminate or migrate to the food, as well as preventing physical damage (Helanto et al., 2019). Moreover, the eco-friendliness of food packaging influences not only purchasing intentions but also environmental intentions. In addition, consumers' awareness and understanding of eco-friendly packaging impact their purchasing decisions. Consumers' awareness and knowledge of eco-friendly packaging vary across different countries and regions. For instance, South African consumers possess limited knowledge about eco-friendly packaging and exhibit fewer environmentally friendly behaviors related to packaging (Scott and Vigar-Ellis, 2014). In Ghana, research also indicates that although consumers' awareness of environmental issues positively and significantly impacts their green purchasing decisions, the effect of green packaging itself on consumers' purchasing decisions is not significant (Rokka and Uusitalo, 2008). This finding suggests that consumers' sociodemographic characteristics can influence their awareness, behavior, and expectations regarding the environmental sustainability of food packaging. Factors such as their gender, age, and educational level affect consumers' perceptions and behaviors regarding the environmental sustainability of food packaging (Chirilli et al., 2022). To encourage consumers to adopt more sustainable food practices, packaging designers must consider visual attributes, functional properties, environmental characteristics, and social significance, while also ensuring that this information effectively reaches consumers. Additionally, they must account for cross-cultural differences and individual consumer traits to develop personalized and effective packaging design strategies (Lindh and Olsson, 2016; Borgman et al., 2018).
Meanwhile, poor packaging design negatively affects consumers' purchasing decisions, perceptions, and behaviors, which indirectly influences their food-saving habits. Excessive marketing claims on packaging, such as health and nutrition assertions, can mislead consumers, causing food to appear healthier than it actually is, leading to over-purchasing (Obersteiner et al., 2021). Furthermore, misleading information on packaging designs can cause consumers to develop misconceptions, resulting in food waste behaviors (Chandon, 2013; Cairo, 2015). Improper packaging sizes or difficult-to-open packages may prevent consumers from correctly storing or using their food, ultimately leading to premature spoilage and disposal (Boyce et al., 2008). Unreasonable packaging sizes can lead to consumer misunderstandings regarding the product capacity. If a container's shape is particularly large, it may be perceived as containing more of the product, even if the actual capacity is small (Valerie Folkes, 2004). The packaging dimensions can significantly impact consumers' perceptions of the product capacity; these may involve its volume, weight, and overall impressions, thus affecting consumers' perceptions of the amount of food purchased and contributing to food waste (Ordabayeva, 2013). Additionally, poorly functional packaging designs can increase food waste and exacerbate environmental issues (Konstantoglou et al., 2020). The functionality of packaging is often inadequate, failing to protect its contents and extend the shelf life of food, which consequently contributes to consumers' food waste behaviors (Ploom et al., 2020). Consumers' perceptions of the risks associated with packaging influence their decisions regarding food waste, where health consciousness and environmental awareness emerge as key factors. Poorly functional packaging tends to exacerbate food waste (Zeng, 2021). Research indicates that consumers' perceptions of the risks of packaging directly affect their food waste behaviors (Zeng, 2021). A lack of awareness among consumers regarding packaging design often results in misunderstandings about food's freshness and shelf life, leading to food waste (Obersteiner et al., 2021). Insufficient consumer awareness of food packaging safety can result in the neglect of both safety and environmental considerations while selecting packaging, further contributing to food waste (Kang and Wang, 2021). Overly complex or difficult-to-understand information on packaging diminishes consumers' engagement and attentiveness to this information, adversely affecting their purchasing decisions and food consumption and thus causing food waste (Mruk-Tomczak et al., 2019).
Consumer waste behavior: factors associated with packaged food
The factors influencing consumer behavior regarding packaged food waste are multifaceted, with packaging design playing a crucial role in encouraging proper food consumption, waste reduction, and effective sorting and recycling of both food and packaging waste. As a critical intermediary between production and consumption, packaging design characteristics significantly influence consumer purchasing decisions. Furthermore, they indirectly affect the extent of food waste through storage practices and usage frequency. Research indicates that 60% of consumers try new products due to their packaging (Uddin et al., 2022), highlighting the impact of packaging design on consumer purchasing behavior. Packaging features also exert influence; studies show that visual and sensory cues affect consumer decision-making. For instance, red-orange is associated with “sweetness,” while blue-green suggests “health,” and angular designs enhance a modern aesthetic (Marques da Rosa et al., 2018). Transparent packaging enhances product authenticity, thereby influencing consumer visual experiences (Simmonds et al., 2017). Packaging quality is another significant factor in consumer decision-making. While some packaging utilizes recyclable materials, the cost often includes a premium (Zeng and Durif, 2019). Storage behavior is also linked to packaging quality; large-capacity packaging can lead to food waste and over-purchasing, while smaller packaging, though convenient, increases packaging costs, also incurring a premium (Wikström et al., 2019). Resealable packaging extends shelf life post-opening, reducing waste from spoilage, but it also increases packaging costs, again with a premium (Nemat et al., 2020a). This underscores that both the visual aspects and quality of packaging are critical factors influencing consumer decision-making. Consequently, visual attributes and packaging quality serve as communication channels, thereby encouraging consumers to conserve food and properly categorize food packaging waste (Nemat et al., 2020b). The functional and educational aspects of food packaging design, which can extend food shelf life and diminish food waste, are also critical determinants of consumer behavior (Almli et al., 2018).
Consumers' perceptions of and attitudes toward packaging largely determine whether they will reduce their food waste. In this context, consumers are unlikely to prioritize food packaging or reductions in food waste as the primary motivation in their purchasing decisions (Kapoor and Kumar, 2019). At the same time, consumers' inadequate knowledge about optimized packaging affects their ability to use these packages correctly at home (Obersteiner et al., 2021). Additionally, consumers' perceptions of green packaging also influence their decisions regarding food waste (Zeng, 2021). However, an insufficient understanding of the environmental impacts of food packaging may lead to choices that inadvertently negate consumers' eco-friendly intentions (Lindh and Olsson, 2016). The functionality of packaging plays a significant role in reducing food waste, as the functional information provided on food packaging can greatly impact consumers' choices regarding optimized packaging (Almli et al., 2018). Although the information conveyed through packaging design holds tremendous potential to reduce food waste, consumers still seldom pay proper attention to such information (Rokka and Uusitalo, 2008). Perceptions regarding packaging also reflect consumers' age, gender, and educational levels, as older consumers may generate more food waste (Hazuchova et al., 2020). Furthermore, consumers' perceptions and strategies regarding imperfect or secondary foods are essential in reducing food waste (Varese et al., 2022). Consumers' perceptions and behaviors play a crucial role in minimizing food waste. Additionally, consumers' awareness and actions regarding food waste issues are vital in achieving societal sustainability (Norton et al., 2022).
Research hypotheses and models
Research hypothesis
Values and consumer support and rejection reasons for food waste refusal
Values, representing stable psychological dispositions formed in daily life, shape an individual's perception of themselves and the world (Kesberg and Keller, 2018). Consumer values influence attitudes and behavioral intentions toward food packaging (Kumar et al., 2023). Drawing on Schwartz's dimensions of values, consumer values can be understood as openness to food packaging (Przymuszała et al., 2024). Research on attitudes and behavioral intentions toward food packaging highlights understanding and acceptance (Li et al., 2020). For instance, consumers' environmental values (environmental cognition acceptance) can influence their intention to purchase environmentally friendly packaging (Jha et al., 2023). Therefore, this study uses “consumer acceptance of food packaging” to represent consumer values, defined as an individual's willingness to engage with and understand new concepts. Acceptance is reflected in consumers' willingness to embrace and acknowledge novel packaging materials (e.g., bio-based materials, biodegradable plastics) and design concepts (e.g., circular packaging, environmental intentions). Research indicates that consumer inclusivity indirectly influences sustainable decision-making behaviors by affecting their environmental attitudes (Zhao et al., 2024). Food packaging, a persistent topic in the food industry, has packaging design factors that can satisfy consumers' food experience through protection and recommendation, especially in functional design, environmental concepts, and visual experience (Sumi and Swathilakshmi, 2023; Un-Noor et al., 2017). Consequently, for consumers with a high degree of openness to new things, excellent food packaging aligns with their values. Consumer acceptance of food packaging is both a manifestation of values and a behavioral driver, with its core being the construction of a trust bond between consumers and packaging through design innovation, information transparency, and cultural adaptation (d'Astous and Labrecque, 2021). Concurrently, decision theory (Fishburn, 1991) and attribution theory (Asanakutlu and Sahin, 2014) further affirm that values influence the reasons consumers support or reject specific behaviors. Thus, the development of behavioral rationality is not independent of beliefs and values; rather, values serve as the foundational basis for behavioral rationality (Henshel, 1971). Therefore, within the context of research on the rejection of food waste, this study posits that consumers' values (The acceptance of food packaging) impact their justifications for supporting or rejecting consumer behaviors that mitigate food waste. Based on this, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H1: Consumer values (The acceptance of food packaging) positively influence their support for reasons to refuse food waste.
H2: Consumer values (The acceptance of food packaging) negatively influence their rejection of reasons to refuse food waste.
Values and consumer attitudes toward food waste rejection
Research indicates that values are not only direct factors in the formation of attitudes but also serve as significant mechanisms that indirectly influence attitudes by providing reasons for support or rejection (Kristiansen and Zanna, 1988). Consequently, when consumers' values align with the values represented in food packaging, they are more likely to develop a positive attitude toward the product (Venkatesh and Davis, 2000), and at this juncture, behavioral justifications may not be activated (Afroz et al., 2015). In such cases, consumers tend to pursue psychological shortcuts and simplify personal information processing (Ju, 2015). Consumers who are more inclined to accept high-quality food packaging are the first to experience the design of food packaging, enjoy the food, and reject food waste, indicating their open-mindedness toward the rejection of food waste (Hinnüber et al., 2019). This value system encourages a positive attitude toward certain behaviors (Davis, 1989). Consumer attitudes toward the rejection of food waste may be formed through either intermediary or direct pathways. Therefore, when consumers develop their attitudes toward food waste rejection through direct pathways, values can influence attitudes without the need for behavioral rationalization (Afroz et al., 2015). Conversely, when attitudes are formed through intermediary pathways, values will influence attitudes indirectly via behavioral rationalization (Chaturvedi et al., 2023). Based on this, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H3: Consumers' values (inclusivity toward food packaging) positively influence their attitudes toward rejecting food waste.
Consumer support, opposition, and attitudes toward food waste rejection
Behavioral rationality refers to the specific justifications individuals employ to defend their expected behaviors, which are regarded as critical antecedent variables influencing attitudes and behavioral intentions (Chatzisarantis and Biddle, 1998). When individuals rationalize their anticipated actions, they often experience comfort, which, in turn, fosters a positive attitude toward those actions (Jones and Wirtz, 2006). Food packaging, as a significant factor facilitating consumer purchases and consumption of food, encourages consumer support for food waste rejection for several reasons, such as visual attributes in packaging design (Marques da Rosa et al., 2018; Ahmadi et al., 2013), functional attributes (Yokokawa et al., 2019; Obersteiner et al., 2021), environmental attributes (Lindh and Olsson, 2016; d'Astous and Labrecque, 2021) and social cognition (Wang, 2013). Conversely, there are also reasons for rejection, including over-information (Chandon, 2013; Cairo, 2015), regional cognitive disparities (Zeng, 2021; Obersteiner et al., 2021), and low functionality (Boyce et al., 2008; Ploom et al., 2020). These supportive and oppositional reasons further influence consumers' positive or negative attitudes toward rejecting food waste. Based on this, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H4: Consumers' supportive reasons for rejecting food waste positively affect their attitudes toward food conservation.
H5: Consumers' oppositional reasons for rejecting food waste negatively affect their attitudes toward food conservation.
Consumer support, rejection, and intentions regarding food waste behavior
Behavioral rationality possesses corrective and defensive mechanisms (Przeworski and Vreeland, 2002), yet prior theoretical models of behavior have not explained this aspect. Social psychology theories demonstrate that these mechanisms aid individuals in enhancing or preserving self-worth, allowing rationality to transcend attitudes in explaining behavioral occurrences (Malle, 1999). In other words, individuals feel more comfortable when they have justifications for correcting and defending their actions, even if their attitudes do not entirely align with their behavioral intentions. Consumers maintain a positive attitude toward green practices, but irrational packaging design creates a gap between green attitudes and behaviors. Consequently, this paper posits the following hypotheses:
H6: The reasons consumers support food waste rejection positively influence their behavior toward rejecting food waste.
H7: The reasons consumers oppose food waste rejection negatively influence their behavior toward rejecting food waste.
Consumer attitudes and behavioral intentions regarding food waste rejection
Although consumers may hold a positive attitude toward eco-friendly food, actual actions often experience the impact of the “value-action gap,” which refers to recognizing a problem without taking action (Zhuo et al., 2022). Research indicates that environmentally conscious consumers are more likely to take steps to reduce food waste (Chen, 2019). Specifically, feelings of responsibility and self-efficacy are crucial psychological factors that activate personal norms and further influence the intention to reduce food waste (Wang et al., 2022). Attitudes also directly and positively impact behavioral intentions. A study in West Sumatra found that attitudes significantly and positively influenced households' intentions to reduce food waste, which in turn strongly affected actual food waste behavior (Guchi and Syafrizal, 2022). Other research suggests that while consumers may be aware of the food waste issue, this awareness does not always translate into action, a phenomenon termed the “value-action gap” (Neff et al., 2015). Accordingly, this paper hypothesizes:
H8: Consumers' attitudes toward food waste rejection positively influence their intentions to engage in food waste rejection behavior.
Theoretical model
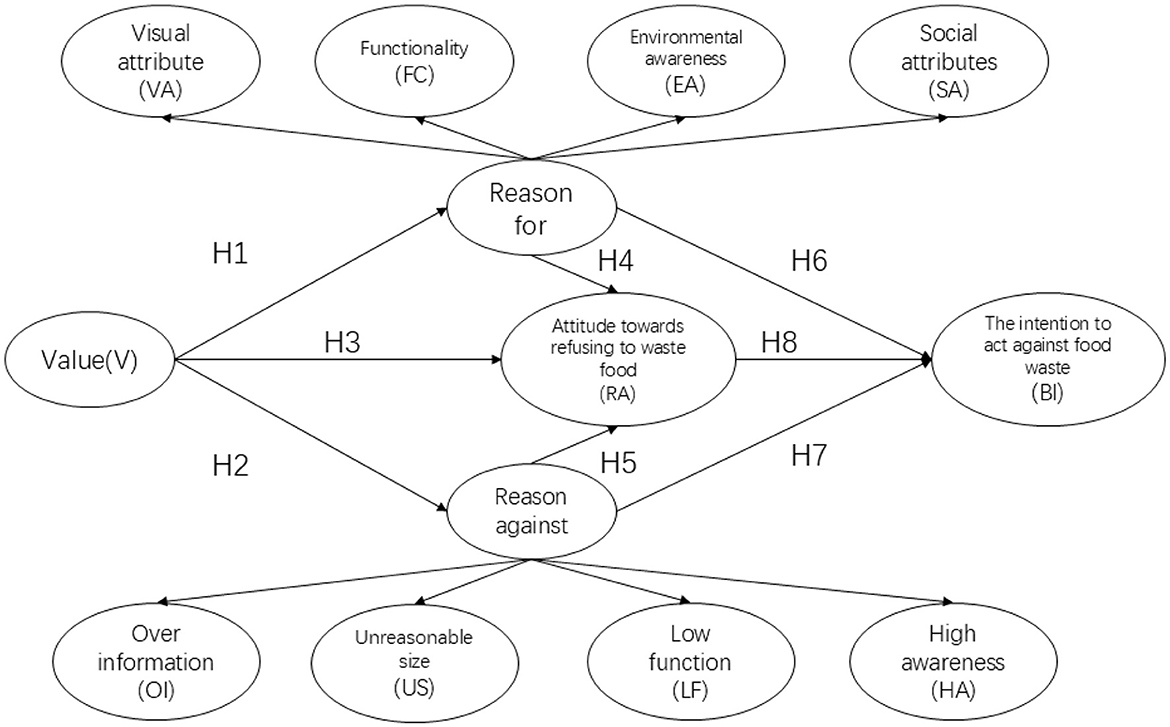
Based on the analysis above, we construct the following theoretical model, as shown in Figure 1.
Questionnaire design
This study examines the influence of food packaging factors on consumer food waste reduction across eight categories, drawing on previous research and literature. Based on this foundation, a survey was designed to assess how various food packaging design elements and consumer values impact their support for or rejection of food waste. The aim is to validate the mechanisms and effects of food packaging design factors on consumers' cognitive attitudes and behavioral intentions.
From the perspective of cognitive attitudes, consumers' values—The acceptance of food packaging—affect their attitudes toward rejecting food waste, exhibiting both positive and negative influences. This is adapted from the viewpoints of Chan and Xiao regarding values (Chan, 2022; Xiao-b, 2014; V1–V3). Additionally, the eight types of food packaging design factors are analyzed for their impact on consumers' cognitive attitudes toward rejecting food waste, referencing the visual factors in food packaging design as studied by Wang (2013) and Marques da Rosa et al. (2018; VA1–VA3), functional attributes (Yokokawa et al., 2019; Obersteiner et al., 2021; FC1–FC3), environmental awareness factors (Lindh and Olsson, 2016; d'Astous and Labrecque, 2021; EA1–EA3), and social factors (Wang, 2013; SA1–SA3). These four dimensions are measured for their positive impact on consumers' rejection of wasteful behaviors.
Furthermore, regarding the negative impact of food packaging design factors on consumers' attitudes toward rejecting food waste, it includes four dimensions. Zeng believes that excessive marketing information, health information, and nutritional information in food packaging design can lead to consumer food waste behavior and affect food conservation (Zeng, 2021; OI1–OI3). Ploom and Pentus believe that Unreasonable size in food packaging design can lead to food waste behavior among consumers due to unreasonable packaging size, difficulty in opening, and size that is not easy to carry and store, thereby affecting food conservation (Ploom et al., 2020; US1–US3). Chandon believes that low functionality in food packaging design can lead to food waste behavior among consumers due to the inability to protect food, short shelf life, and unfavorable transportation, thereby affecting food conservation (Chandon, 2013; LF1–LF3). Obersteiner and Cociancig et al. believe that the differences in other social and cultural levels lead to High awareness of environmental protection in food packaging design. The phenomenon of protection leads to food freshness cognitive bias, shelf life cognitive bias and other information bias, which lead to food waste behavior and affect the item design of food conservation (Obersteiner et al., 2021; Ploom et al., 2020; HA1–HA3).
On the perspective of rejecting food waste, according to Kunda and Zhuo, Ren et al., it is believed that behavioral rationality can enhance individual awareness and self-worth, promote the generation of positive attitudes toward food conservation and environmental protection, but attitudes may not necessarily translate into action intentions (Zhuo et al., 2022; Kunda, 1990). On this perspective, item design is carried out to reduce food waste, protect the environment, reflect personal morality, and demonstrate the willingness to take practical actions for Attitude toward reusing to waste food (Neff et al., 2015; Fornell and Larcker, 1981; RA1–RA3).
From the perspective of behavioral intention, Wang, Li, Guchi and Anon's research on behavioral intention, including the influence of self-belonging and self-efficacy and attitude on behavior (Wang et al., 2022; Guchi and Syafrizal, 2022). This dimension examines the personal intention to act against food waste, the sense of self belonging and self-efficacy of behavior, and the implementation of specific behaviors (Neff et al., 2015; Gelman, 2006; BI1–BI3).
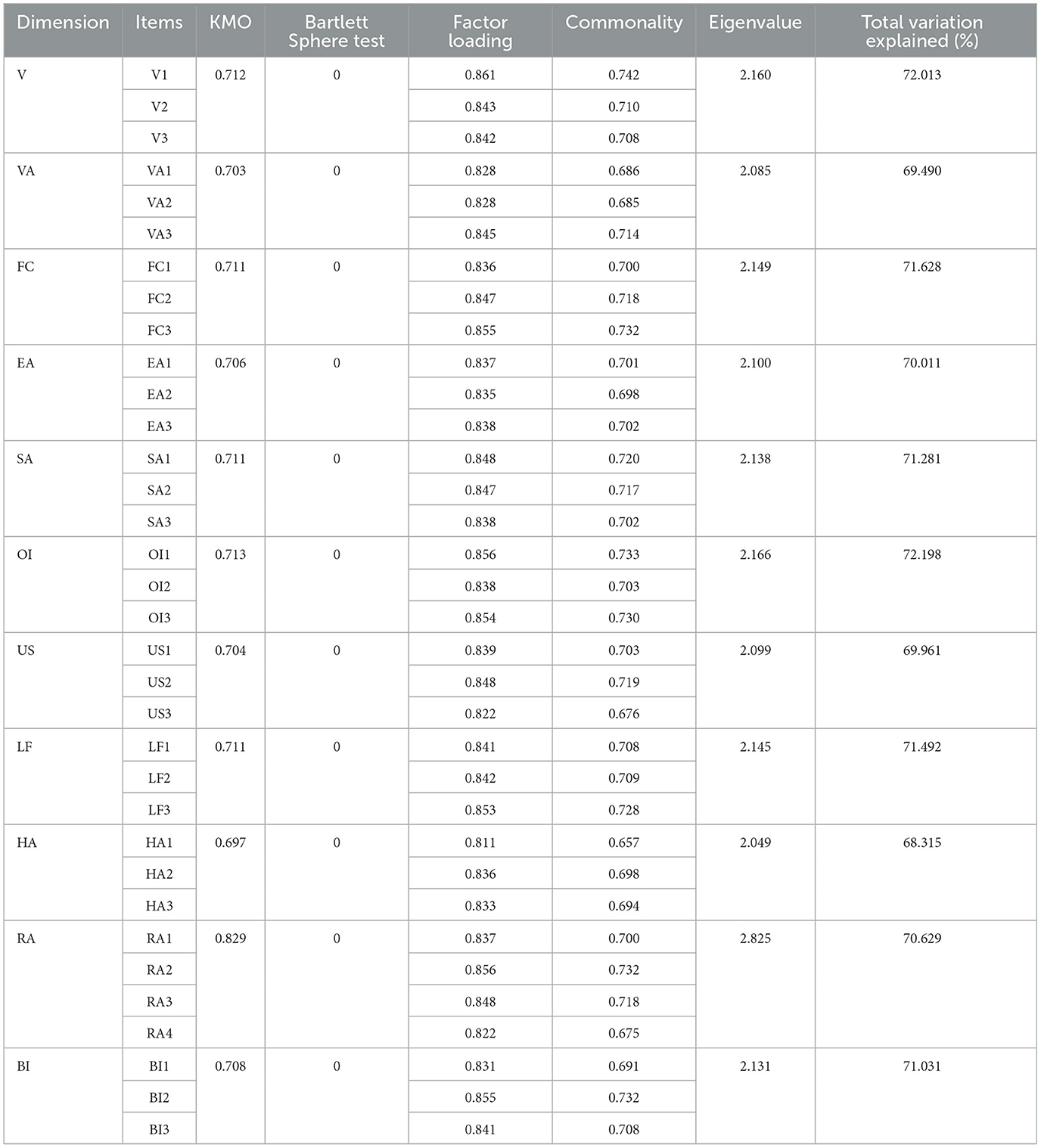
Based on the above analysis, the items for questionnaire design are shown in Table 1.
Informed consent
To facilitate data collection, an online questionnaire survey method was selected. Given the geographically dispersed consumer distribution discussed earlier, an online survey approach was deemed more appropriate than offline methods. Consequently, all respondents were recruited through the Wenjuanxing online platform. Furthermore, this study received ethical approval from the School of Fine Arts, Nanjing Normal University. An online informed consent form was presented prior to the commencement of the survey. Due to the online nature of participation, all participants provided their consent verbally. Respondents were directed to the survey questionnaire only after confirming their informed consent by selecting the “agree” option. Participants who selected the “disagree” option were excluded from the survey. This approach ensured the collection of authentic and comprehensive consumer survey data. All respondents were consumers who had purchased or used food packaging. Moreover, this study adhered to the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the School of Fine Arts, Nanjing Normal University (ID: NO. NNU SFA-E-2024-002, June 19, 2024). All participants provided informed consent, and their privacy was strictly protected. Personal information was kept confidential throughout the study. Participants were informed of their voluntary participation and their right to withdraw at any time. All respondents were adults, with no minors included.
Empirical research
Sample demographic characteristics
Data collection for this study utilized an online questionnaire format, distributed via online platforms to a broad demographic to ensure the sample's representativeness and mitigate regional biases, thereby enhancing the validity of the collected data. The survey was conducted between July and September 2024, utilizing the “Wenjuanxing” data survey platform to collect a total of 562 samples. After eliminating invalid samples, 513 valid samples were ultimately obtained, resulting in an effective rate of 91.3%. The reasons for sample exclusion were three-fold: (1) Duplicate submissions from the same IP address were consolidated, with only one retained as a valid sample; (2) Surveys completed in an excessively short timeframe were deemed invalid; (3) Samples containing sequences of repeated numerical entries were excluded. All items were assessed using a Likert scale, with scores ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly agree). Prior to participation, an online informed consent form was presented. Given the online nature of the survey, verbal consent was obtained from all respondents. Furthermore, participants were required to confirm their comprehension of the informed consent and indicate their agreement by selecting an affirmative option to access the questionnaire. At the same time, the respondents could only participate in the questionnaire survey once and could not participate in the questionnaire repeatedly, which ensured the accuracy of the questionnaire survey. Non-agreement resulted in the termination of the survey. This study did not involve minors, as they are considered to lack full behavioral capacity due to their developmental stage.
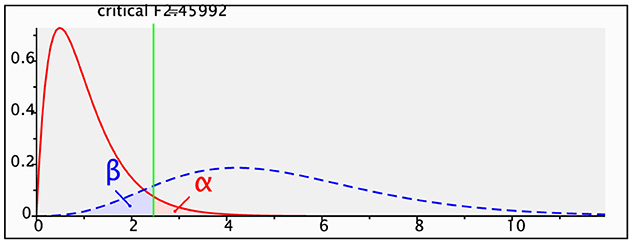
The questionnaire comprised 34 items, yielding 513 valid responses. Statistical power analysis, conducted using G*Power, was performed for a linear multiple regression model, specifically focusing on the R2 deviation in a fixed model. As illustrated in Figure 2, the input parameters included an effect size f2 of 0.15, a significance level (α error probability) of 0.05, and a desired statistical power (1-β error probability) of 0.90, representing a 90% probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. Consequently, under these parameters, G*Power calculated a required total sample size of 108. This sample size ensures sufficient statistical power to detect effects within the model, given the specified effect size and significance level. The actual statistical power was 0.9013736, slightly exceeding the target of 0.90, indicating that the sample size meets the study design requirements and supports the reliability of the findings. Given the effective sample size of 513, which substantially surpasses the minimum requirement of 108, the sample size is deemed adequate for the study.
Therefore, the data analysis proceeded based on this standard, primarily utilizing SPSS 22.0 and Smart-PLS 4.1 software. Descriptive statistical analysis of the sample demographic variables is presented in Table 2.
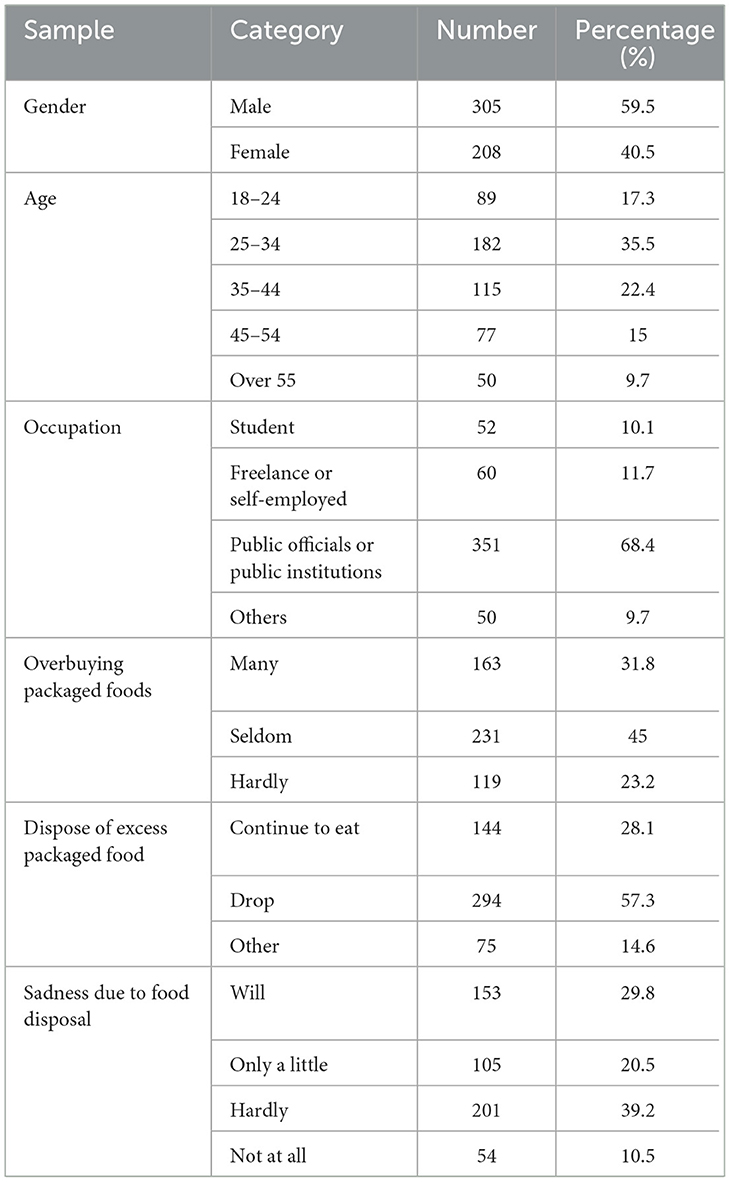
The survey encompassed 513 questionnaires, with sample regions strategically selected across 19 provinces, including Jiangsu, Fujian, Sichuan, Shandong, Anhui, Zhejiang, Hunan, Jiangxi, Hubei, Heilongjiang, and Guangdong, thereby demonstrating the comprehensiveness of the sample collection. Nevertheless, regional disparities in economic development influenced the distribution of consumers who had utilized or experienced food packaging. Notably, a significant proportion of respondents hailed from economically advanced regions such as Jiangsu, Fujian, Guangdong, and Zhejiang, indicating a heightened level of attention toward food packaging in more developed areas, thus validating the authenticity of the sample collection. The online survey participation comprised a slightly higher number of male respondents compared to female respondents, with the age distribution predominantly skewed toward young and middle-aged individuals. In terms of the occupational distribution, government workers and public institution staff accounted for the largest proportion, followed by freelancers and students, and other occupations accounted for approximately 10%. At the same time, according to the questionnaire, the proportion of respondents who overbought packaged food was as high as 86.8%, of which 31.8% of these respondents often overbought packaged food. When faced with a large amount of excess packaged food, 57.3% of respondents stated that they would directly discard it, and only 28.1% were willing to continue to eat it. Meanwhile, 71.9% of the 513 respondents would throw food away or use it for other purposes, and 49.7% did not feel sad or upset about food waste. This means that nearly half of the respondents were indifferent to food waste. In summary, the proportion of the sample that responded to each part of the questionnaire was reasonable, meeting the requirements of the research. According to the data on the respondents' activities related to buying packaged food, dealing with excessive packaged food, and discarding packaged food, it is necessary to study the influence of food packaging design factors on consumers' behavior in terms of rejecting food waste.
Reliability and validity analysis
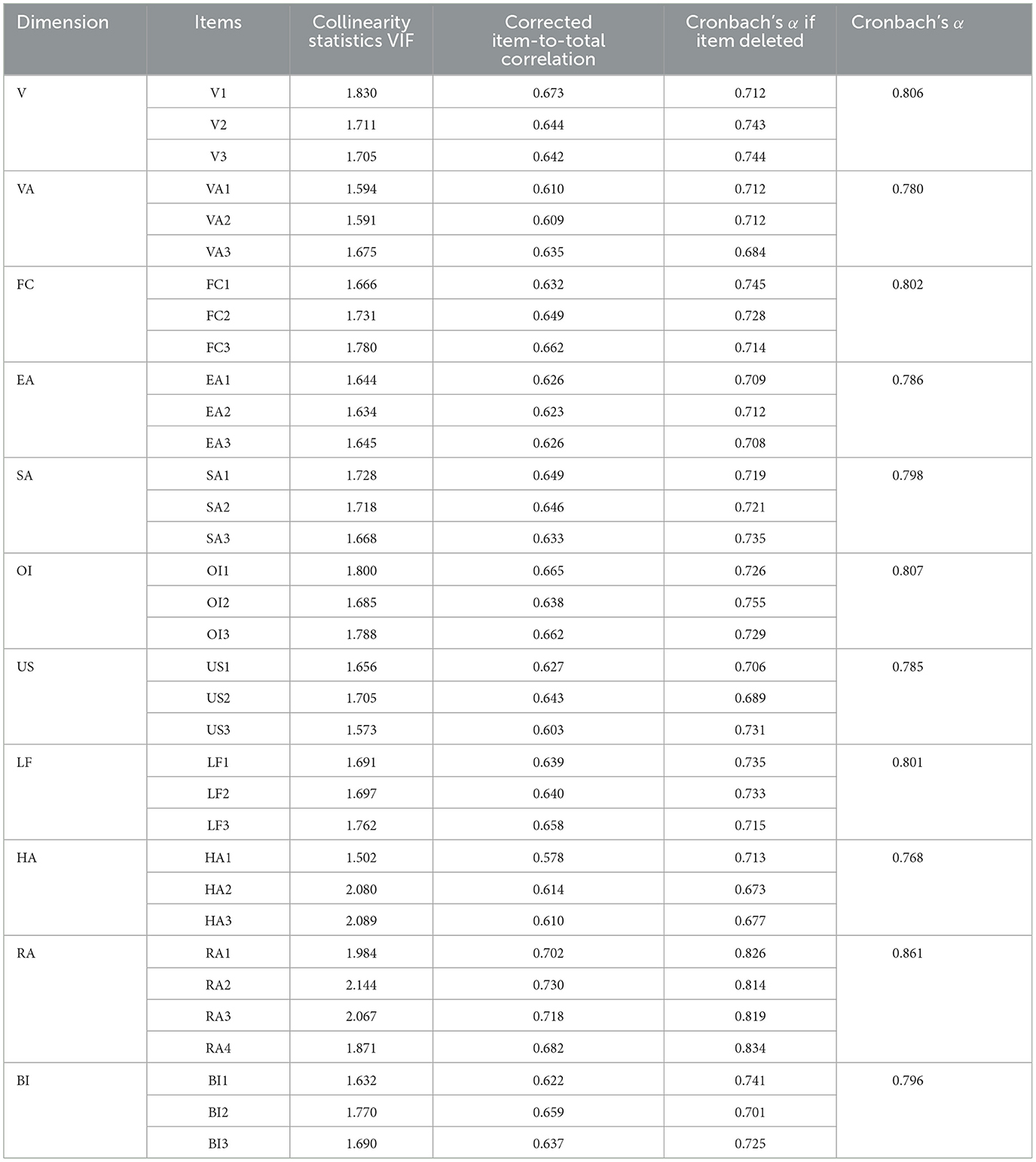
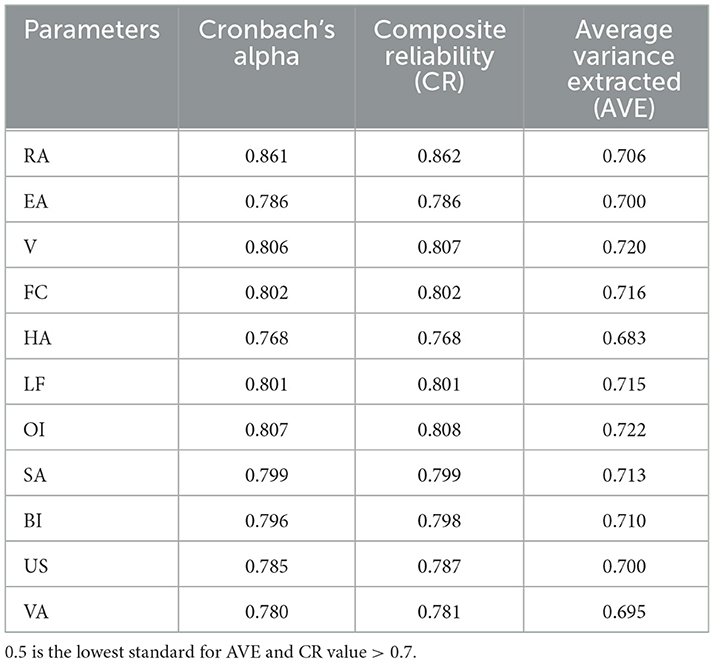
Reliability refers to the consistency or stability of measurement results. Research indicates that a Cronbach's α value between 0.7 and 0.9 is generally considered to reflect good internal consistency (Oviedo and Campo-Arias, 2005). The Cronbach's α values for each measurement variable, calculated using SPSS 22.0, were all greater than 0.7, while the overall Cronbach's α for the questionnaire exceeded 0.6 (Yin and Wei, 2012; Chan and Idris, 2017). The total correlations after item deletion were all above 0.5 (Yin and Wei, 2012), indicating that the constructs in this study possess good reliability. The variance inflation factor (VIF) serves as a metric for assessing multicollinearity among independent variables, quantifying the extent to which each predictor variable is linearly explained by others. A higher VIF value indicates a more severe multicollinearity issue (Willis and Perlack, 1978). Research suggests that a VIF exceeding 5 suggests the presence of some degree of multicollinearity within the measurement scale (Alhamami et al., 2024); ideally, the VIF should be below 3.3 (Bria et al., 2021). At this level, the correlation between predictor variables is low, resulting in more stable regression estimates, which is conducive to constructing robust analytical models. As shown in Table 3, the VIF values for all variables are below 3.3, indicating the absence of multicollinearity issues. Overall, the Cronbach's alpha coefficient (a reliability indicator) and the VIF values (a multicollinearity indicator) in Table 3 collectively demonstrate that the measurement scale used in this study has good reliability and does not exhibit multicollinearity issues, thus supporting the construction of a stable and reliable analytical model.
Utilizing SPSS 22.0, the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure and Bartlett's test of sphericity were conducted. Relevant studies indicate that the KMO value serves as an indicator of the suitability of data for factor analysis, with a KMO value greater than 0.7 generally considered acceptable for this purpose (Campos et al., 2013; Yordanova and Krastev, 2018; Sara et al., 2020). Furthermore, a significance level of less than 0.05 in Bartlett's test suggests that the covariance matrix of the variables is not an identity matrix, indicating significant correlations among the variables, thus making them suitable for factor analysis (Wu and Wong, 2003; Dyer and Keating, 1980). As shown in Table 4, the KMO values for the variables ranged from 0.704 to 0.829, all exceeding the threshold of 0.7, and the significance of Bartlett's test was less than 0.05, confirming that all variables passed the Bartlett's test of sphericity. This establishes a solid foundation for the factor analysis of the data. Consequently, principal component analysis was employed for the factor analysis of the variables, revealing that each variable could extract a factor with an eigenvalue greater than 1, and the cumulative variance contribution of all variables exceeded 50%. This indicates that the factors identified in this study provide a robust explanation for the variables analyzed (Feng, 2012). Additionally, the commonalities for all items were greater than 0.5 (Liang and Khan, 2024), and the factor loadings were all above 0.6 (Elias et al., 2020), which are within reasonable limits. In summary, this study concludes that the survey results exhibit strong unidimensionality, indicating that there is no issue of common method bias in the data, as illustrated in Table 4.
When Cronbach's α and composite reliability exceed the 0.7 threshold, the scale is deemed acceptable, as indicated in Table 3, suggesting that the scale demonstrates satisfactory reliability. Validity analysis was conducted using Smart-PLS4.1, with validity assessed through Average Variance Extracted (AVE) and Composite Reliability (CR) values. As presented in Table 5, the CR values range from 0.768 to 0.862, and the AVE values range from 0.683 to 0.722. According to Fornell et al., both CR and AVE values are critical for assessing convergent validity, with CR values needing to be greater than 0.7, and 0.5 being the minimum acceptable AVE value (Fornell and Larcker, 1981; Churchill, 1979). The results in Table 5 indicate that all AVE values surpass the 0.5 threshold, and all CR values exceed the 0.7 threshold, confirming that all variables exhibit robust convergent validity.
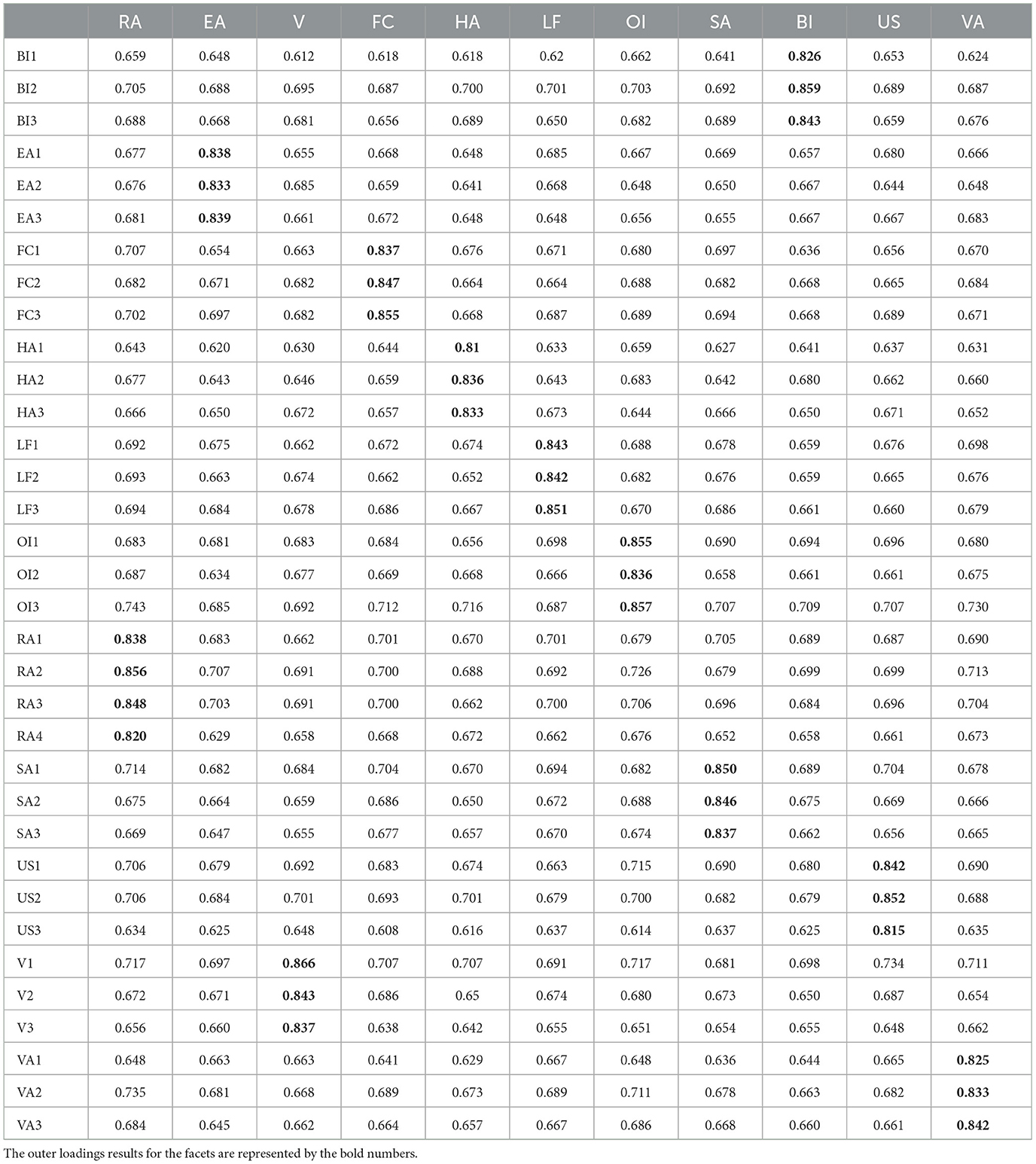
As shown in Table 6, the outer loadings derived from the indicators of each construct in this study exceed the results of each additional construct's cross-loadings. It is noteworthy that cross-loadings are commonly employed as a preliminary step in assessing the discriminant validity of indicators (Leguina, 2015). Therefore, as indicated in Table 6, all variables demonstrate good discriminant validity.
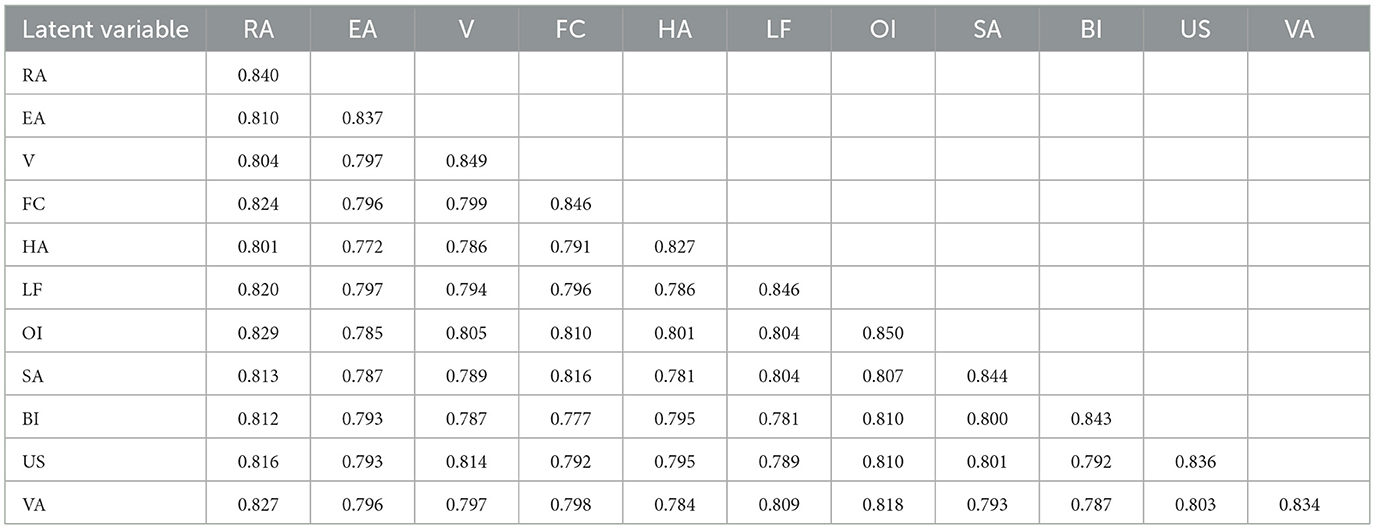
The Heterotrait-Monotrait Ratio (HTMT) is an index used to assess the discriminant validity of variables within a structural equation model. HTMT values below 0.85 are generally considered to indicate that the variables exhibit satisfactory discriminant validity (Henseler et al., 2015). It is essential to evaluate these metrics to mitigate potential multicollinearity issues arising from highly correlated constructs. The results indicate that all HTMT scores are within acceptable limits ( ≤ 0.85), with values ranging from 0.528 to 0.825 (Table 7). Therefore, it can be concluded that there is sufficient evidence to support the model's satisfactory discriminant validity in this study.
Discriminant validity refers to the differences among various latent variables. According to Fornell's recommendations, this can be verified by comparing the correlation coefficients between latent variables with the square root of the Average Variance Extracted (AVE). If the square root of the AVE is greater than the correlation coefficients of the variables, it indicates that the scale possesses good discriminant validity (Fornell and Larcker, 1981). As shown in Table 7, the square roots of the AVE for the latent variables are all greater than the correlation coefficients among the latent variables. Therefore, significant correlations exist among the main variables of this study, namely V, BI, EA, FC, HA, LF, OI, RA, SA, US, and VA, and the square roots of the AVE exceed the correlation coefficients between the variables. Moreover, the correlations of the exogenous structures are all less than 0.85 (Gelman, 2006), indicating good discriminant validity. According to Table 8, the square roots of the AVE for the latent variables are greater than the correlation coefficients among the latent variables, and the correlations of the exogenous structures are all less than 0.85. Thus, it can be concluded that all variables exhibit good discriminant validity.
Model testing
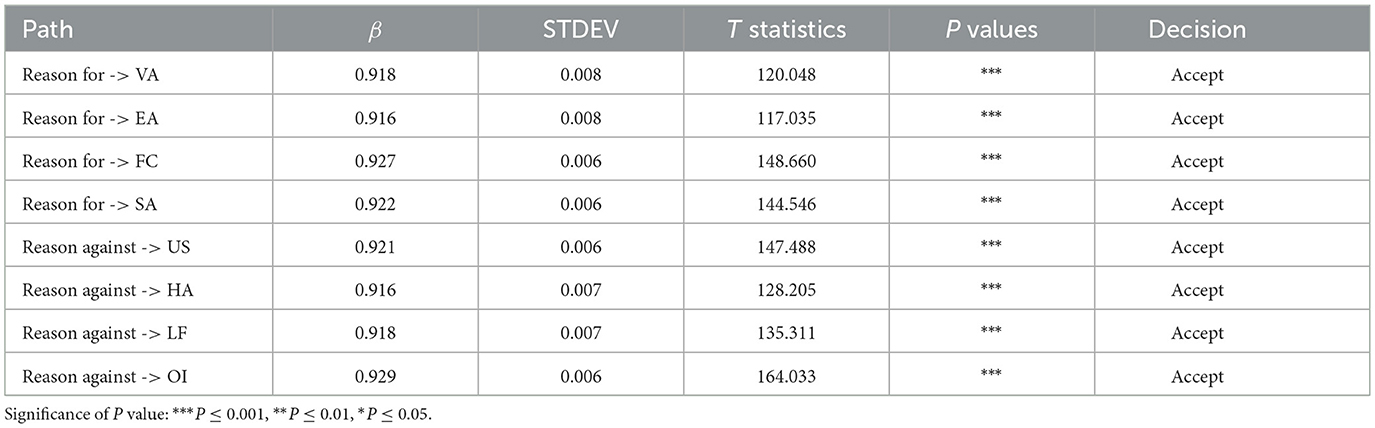
SRMR is one of the commonly used fit indices in Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to evaluate the degree of fit between the model and the data. A smaller SRMR value indicates a better fit of the model to the data. Related research shows that SRMR performs well in handling ordered factor analysis models, particularly when data distribution is abnormal; in such cases, the testing results of SRMR are more reliable. An SRMR value less than 0.08 indicates a very high fit of the model to the data (Ximénez et al., 2022). Furthermore, an NFI greater than 0.8 reflects a high fit of the model; the closer the value is to 1, the stronger the model fit, signifying that the model can accurately capture the structures and relationships within the data (Gowen et al., 2011). As shown in Table 9, the SRMR value of 0.058 is below the threshold of 0.08, indicating a good model fit. Additionally, the NFI value of 0.964 is greater than 0.8, indicating a high model fit.
Path hypothesis analysis
Finally, the hypotheses were tested using PLS-SEM, and path coefficients were calculated by employing the Bootstrap method with 5,000 resamples, as shown in Table 10. The P-values for the second-order model hypotheses were all found to be less than 0.05, indicating statistical significance. Therefore, the second-order model hypotheses were validated. As presented in Table 8, the statistical results demonstrate that all eight second-order model path relationships are significant, indicating that visual attributes, social attributes, environmental attributes, and functional attributes serve as positive reasons for consumers to reject food waste, while excessive information, low functionality, unreasonable sizes, and overly high cognitive load are identified as negative reasons for consumers' rejection of food waste.
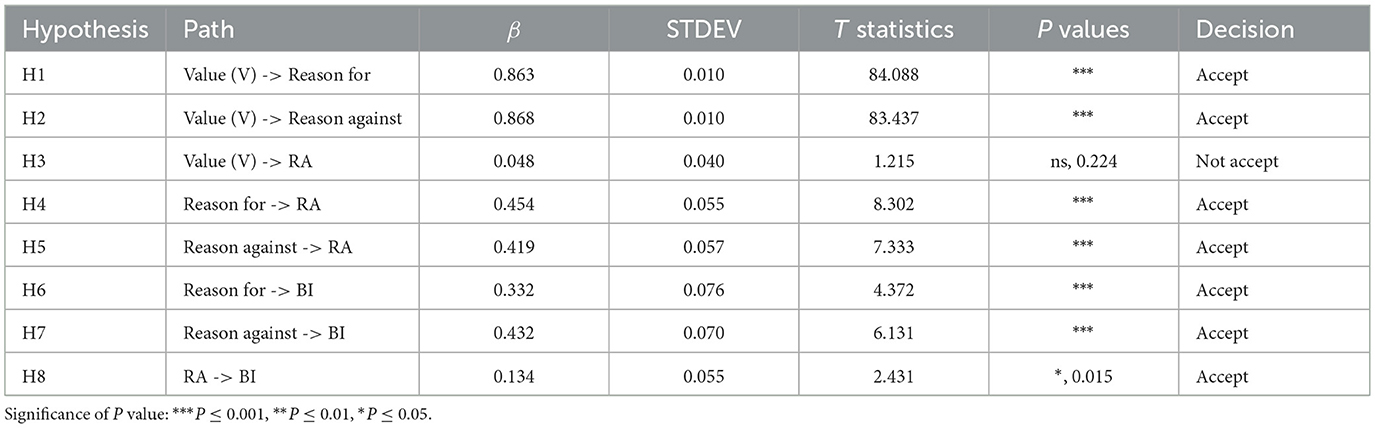
The analysis of the path coefficients from Table 11 indicates that values (The acceptance of food packaging) significantly influence the reasons for support (T = 84.088, P < 0.01) and the reasons for rejection (T = 83.473, P < 0.01), thereby providing support for hypotheses H1 and H2. However, the results regarding attitudes toward food conservation (T = 1.215, P > 0.01) are not significant, leading to the rejection of hypothesis H3. Furthermore, the reasons for support significantly affect attitudes toward rejecting food waste (T = 8.302, P < 0.01) and the behavioral intention to reject food waste (T = 4.372, P < 0.01), confirming hypotheses H4 and H6. Similarly, the reasons for rejection significantly influence consumers' attitudes toward rejecting food waste (T = 7.333, P < 0.01) and their behavioral intention to reject food waste (T = 6.131, P < 0.01), thus supporting hypotheses H5 and H7. Lastly, consumers' attitudes toward rejecting food waste significantly impact their behavioral intention to reject food waste (T = 1.758, P < 0.05), confirming hypothesis H8.
The results of hypothesis testing are shown in the above table, as shown in Figure 3.
Discussion
This study employs the Behavior Reasoning Theory (BRT) as its foundation, incorporating consumer context to elucidate behavioral motivations through the variables of “reason for” and “reason against.” By integrating specific elements of food packaging, including its functionality, visual design, and informational aspects, this research delves into the correlation between food packaging factors and consumers' rejection of food waste. Furthermore, it explores consumers' attitudes toward food waste reduction and their behavioral intentions to conserve food. The subsequent discussion will unfold in accordance with the research model's structural sequence, integrating the validation of hypotheses and the presentation of results derived from the structural equation model. Key findings of this research are as follows:
Regarding the second-order model, the study confirms that visual, functional, environmental, and social attributes of food packaging design positively influence consumers' attitudes toward rejecting food waste. Conversely, excessive information, inappropriate dimensions, low functionality, and high cognitive load in food packaging design significantly and negatively impact consumers' attitudes toward rejecting food waste. From a data perspective, among the positive attributes, functional attributes (FC; T: 148.66, P < 0.01) exhibit a more significant influence on attitudes toward rejecting food waste than the other three attributes. Social attributes (SA; T: 144.546, P < 0.01) follow, demonstrating a more significant impact than visual attributes (VA; T: 120.048, P < 0.01) and environmental attributes (EA; T: 117.035, P < 0.01). This conclusion aligns with the findings of Aschemann-Witzel et al. 92015), Chen and Jai (2018), and Kim et al. (2020), indicating that consumers prioritize the functional and social attributes of food packaging. Among the negative attributes, excessive information (OI; T: 164.033, P < 0.01) has the most substantial impact on consumers' food waste behavior, representing the most significant factor contributing to food waste. This is followed by inappropriate dimensions (US; T: 147.488, P < 0.01) and low functionality (LF; T: 135.311, P < 0.01), with inappropriate dimensions showing greater significance than low functionality. The factor of high information cognitive load (HA; T: 128.205, P < 0.01) exhibits slightly lower significance. The significant negative impact of information overload on consumers aligns with Hunteret al.'s (2024) findings. Furthermore, the significance of information overload and unreasonable package size exceeding that of low functionality corroborates Chandon's (2013) assertions. Overall, the detrimental aspects of food packaging exert a more significant influence on consumers than the beneficial aspects. The T-values for rejection reasons are consistently higher than those for supporting reasons, indicating a lower tolerance among consumers for food packaging. Inferior food packaging has a more pronounced effect on consumers' attitudes and behaviors regarding food waste. While superior food packaging can alter consumer attitudes and behaviors toward rejecting food waste, its impact is less substantial than the detrimental effects of poor packaging. Consequently, research on the influence of food packaging factors on consumer attitudes and behaviors reveals that negative factors have a greater impact than positive factors, highlighting the more prominent harm caused by inferior packaging.
Regarding hypothesis validation, the confirmation of H1 and H2 indicates that consumer values, specifically their perception of food packaging inclusivity, significantly influence both supporting and refuting arguments. This suggests that superior food packaging design substantially impacts consumers' rationale for supporting food conservation, while inferior packaging significantly affects their reasons for rejecting such practices. This demonstrates that food packaging design directly influences consumers' justifications for either supporting or rejecting behaviors related to food waste. Conversely, the rejection of H3 implies that consumers in the context of food packaging cannot solely rely on their values to form attitudes against food waste; they also require information derived from food packaging design elements. This finding diverges from Isabel Schäufele's assertion that consumer values, such as health and environmental consciousness, directly influence purchasing attitudes and intentions, highlighting the differential impact of consumer values on attitudes toward various behavioral intentions (Schäufele and Janssen, 2021). This observation underscores that while consumer values significantly affect justifications related to food packaging, they do not directly influence attitudes against food waste, and their impact varies across different behavioral intentions.
The validation of hypotheses H4 and H6 confirms that the four second-order models within food packaging exert a significant positive influence on consumers' supporting reasons, attitudes toward rejecting waste, and behavioral intentions. The significance of this influence is more pronounced on attitudes than on behavioral intentions, indicating that food packaging is more effective in shaping consumers' attitudes toward rejecting food waste. Hypotheses H5 and H7 are also validated, demonstrating that the four second-order models in food packaging have a significant negative impact on consumers' rejection reasons, attitudes toward food conservation, and behavioral intentions. The significance of this negative impact is nearly equivalent on both attitudes and behavioral intentions, suggesting that poor food packaging design has a comparable detrimental effect on consumers' attitudes and behavioral intentions. A comparative analysis reveals that the significance of supporting reasons on attitudes (T: 8.302) is greater than that of rejection reasons on attitudes (T: 7.333), implying that superior food packaging design is more likely to foster positive consumer attitudes. Furthermore, the significance of supporting reasons on behavioral intentions (T: 4.372) is less than that of rejection reasons on attitudes (T: 6.131), indicating that inferior food packaging has a more substantial negative impact on consumers' waste-averse behaviors than superior packaging has a positive impact. Finally, the validation of H8 confirms the significant influence of attitudes on behavioral intentions. While both food packaging design factors and attitudes significantly affect behavior, consistent with the findings of Jeżewska-Zychowicz and Jeznach (2015) and Govindappa and Radha (2013), which suggest that packaging factors and consumer attitudes interact to influence consumer behavior, this study further reveals that the significance of attitudes toward rejecting food waste on food conservation behavior is considerably less than the significance of supporting/rejection reasons on food conservation behavior. This suggests that consumers are more readily influenced by food packaging factors in their waste-averse behaviors. Based on the conclusions drawn from hypotheses H4 to H8, consumer values significantly influence the reasons for supporting or rejecting food packaging. However, they do not directly impact attitudes toward rejecting food waste, and their effects on different behavioral intention attitudes vary. This suggests that, within the context of food packaging, the objective characteristics of the packaging itself exert a greater influence on consumers' behavioral intentions than their subjective attitudes.
Theoretical contributions and practical implications
This study examines the hypothesized relationships between structural paths and the validation of model-based path relationships regarding consumers' attitudes and behavioral intentions to reject food waste, influenced by food packaging design factors. The research aims to simulate consumers' intentions to conserve food by integrating food packaging design elements with consumers' rejection of food waste and cognitive attitudes. The validation indicates that the quality of food packaging design factors directly impacts consumers' reasons for support and rejection, thereby affecting their attitudes and experiences related to food, ultimately influencing their stance against food waste and hindering their behavioral intentions to reject it.
Theoretical contributions
Through empirical analysis, this study reconfirms the influence of consumer values and food packaging design elements on consumer emotions, clarifying their crucial roles in shaping consumers' conservation attitudes and behavioral intentions, thereby further enriching and refining the theoretical framework of the relationship between consumer behavior and food packaging design. Simultaneously, a novel theoretical model is innovatively constructed to deeply explore the relationship paths between food packaging design elements and consumers' attitudes and behavioral intentions toward rejecting food waste, providing a new perspective and research direction for the theoretical development in the field of food packaging design, which has significant reference value for the theoretical research of food packaging design. Furthermore, the research not only analyzes the impact of food packaging design elements and consumer values on consumers' supporting/rejecting reasons, attitudes, and behavioral intentions but, more importantly, builds a theoretical framework for future analysis of food packaging design guiding consumer behavioral intentions, which is conducive to the in-depth development of subsequent related research in this field.
Practical contributions
The research findings offer valuable insights for the advancement of design elements in food packaging, encompassing visual appeal, functionality, environmental sustainability, and social impact. These insights assist designers in understanding the roles of various elements in influencing consumer attitudes and behavioral intentions, thereby facilitating the optimization of food packaging design. Furthermore, the research outcomes delineate key priorities for the future development of food packaging, emphasizing the importance of enhancing consumers' attitudes and behavioral intentions toward food conservation. This directs designers to prioritize the strategic application and integration of packaging design elements, tailoring designs to the specific attributes of different food products. This approach aims to capture consumer attention and encourage food-saving behaviors. The study also identifies unfavorable aspects of food packaging design from the consumer's perspective, offering recommendations to mitigate these issues. This contributes to a more positive consumer experience, strengthens the perceived value of food conservation, and ultimately fosters the formation of intentions to conserve food. In addition, the research underscores the significance of innovative food packaging design, encouraging designers to leverage design effects and objectives to reshape consumer perceptions of food waste. This, in turn, promotes the adoption and practice of food-saving behaviors among consumers, providing direct guidance for food packaging design practices.
Consequently, this study has yielded significant findings at both theoretical and practical levels. Theoretically, it addresses research gaps, refines the existing theoretical framework, and establishes a robust foundation for future academic investigations. Practically, it offers clear guidance and actionable strategies for the food packaging design industry, assisting the sector in promoting consumer behaviors conducive to food conservation through optimized packaging design. The research outcomes hold immediate practical significance and provide substantial support and positive direction for the future advancement of food packaging design, both in terms of theoretical research and practical innovation, thereby contributing to the evolution of the food packaging field toward greater scientific rigor and enhanced efficiency.
Conclusions and suggestions
Conclusions
This study delves into the correlation between consumer values and food packaging design elements, with a specific focus on their impact on consumers' value attitudes and behavioral intentions regarding food waste reduction. Positive food packaging factors encompass visual appeal, functional utility, environmental sustainability, and social significance. Conversely, negative factors include information overload, diminished functionality, inappropriate sizing, and elevated cognitive costs. By integrating these factors, a comprehensive research model was constructed, effectively capturing the behavioral shifts experienced by consumers after interacting with food packaging. This model offers significant guidance for the advancement of food packaging design.
Empirical data validation robustly demonstrates a significant association between food packaging design elements and consumers' attitudes and behavioral intentions. Notably, consumers exhibit a high degree of endorsement for the conservation and environmental principles embodied in food packaging design, coupled with a sustained intention to act accordingly. This finding not only elucidates consumers' value preferences in food packaging selection but also provides direction for the future development of food packaging design.
The findings of this study offer significant insights and practical value for packaging designers. They can leverage these results to gain a deeper understanding of consumer needs and expectations, enabling more precise articulation of design concepts. This approach ensures that food packaging effectively addresses consumer requirements on a functional level while also resonating with their values. By optimizing food packaging design, we anticipate fostering a positive consumer attitude and behavior toward reducing food waste, thereby contributing to resource conservation and environmental protection. Future research should build upon these findings, exploring how food packaging design can further influence consumer behavior and how innovation in this area can be achieved across diverse cultural contexts.
Future research suggestions
The present study acknowledges certain limitations inherent in its methodology. The primary reliance on online questionnaires for data collection, while facilitating rapid and large-scale information gathering, introduces potential biases in sample representativeness. Specifically, the demographic profile of online survey respondents may skew toward younger age groups, leading to an underrepresentation of both adolescent and elderly populations. Adolescents, as the future drivers of societal change, are a critical demographic for cultivating food conservation awareness, given their formative consumption patterns. Simultaneously, the burgeoning elderly population in China, influenced by established habits and potentially slower adoption of new concepts, warrants significant attention in consumer behavior research.
To address these limitations, future research should adopt a mixed-methods approach. Quantitatively, this could involve optimizing online questionnaire distribution channels, collaborating with schools and community centers to target specific demographics, and expanding the sample size of adolescent and elderly participants. Furthermore, incorporating offline surveys, such as paper-based questionnaires administered in senior activity centers and schools, would enhance sample diversity. Qualitatively, in-depth exploration of the underlying motivations and behavioral drivers related to food conservation among adolescents and the elderly is essential. For instance, in-depth interviews and discussions can be employed to ascertain the conservation education they received within their familial and scholastic environments, as well as the influence of peer groups on their food conservation attitudes. For the elderly demographic, an exploration of traditional life experiences and memories of material scarcity can illuminate how these factors have shaped their current consumption habits and the underlying reasons for their resistance to emerging conservation concepts. Furthermore, organizing discussions on food conservation topics among adolescents and senior citizens from diverse age groups and backgrounds can facilitate the observation of idea exchange and consensus-building within these groups, thereby yielding richer and more profound insights.
Integrating large-scale data statistical analysis from quantitative research with the in-depth insights from qualitative research allows for a comprehensive understanding of the overall trends and disparities in food conservation awareness and behavior across different groups at a macro level. Simultaneously, it enables an in-depth analysis of the complex psychological and social factors underlying individual behaviors at a micro level. This comprehensive approach provides a more complete and thorough understanding of the research subjects, offering a more robust theoretical and data foundation for refining related research, thereby enhancing the practical guidance value and social significance of the research findings.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.28908881.v2.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Review Committee of the School of Fine Arts, Nanjing Normal University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JM: Investigation, Data curation, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology. LZ: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. CY: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abhyankar, A. (2022). Behavioural economics towards better decision making. J. Glob. Econ. 16, 1–10. doi: 10.1956/jge.v16i2.648
Afroz, R., Rahman, A., Masud, M. M., Akhtar, R., and Duasa, J. B. (2015). How individual values and attitude influence consumers' purchase intention of electric vehicles—some insights from Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. Environ. Urban. ASIA 6, 193–211. doi: 10.1177/0975425315589160
Ahmadi, G., Bahrami, H. R., and Ahani, M. (2013). An investigation of visual components of packaging on food consumer behavior. Business Econ. Res. 3:1. doi: 10.5296/ber.v3i2.3799
Alhamami, M., Alduais, A., Qasem, F., and Alasmari, M. (2024). Psychometric features of the arabic version of the children's communication checklist (CCC2). J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 17, 3247–3264. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S462462
Almli, V. L., Gaarder, M. Ã., Kvalvã, M., and Pettersen, G. (2018). “Communicating packaging functionality for food waste reduction influences consumer choices,” in The 21st IAPRI World Conference on Packaging (Stakkevollan: DEStech Publications, Inc.), 250–257. doi: 10.12783/iapri2018/24394
Asanakutlu, T., and Sahin, T. K. (2014). An empirical investigation of attiribution for success and failure. Res. J. Business Manage. 1, 191–203.
Aschemann-Witzel, J., De Hooge, I., Amani, P., Bech-Larsen, T., and Oostindjer, M. (2015). Consumer-related food waste: causes and potential for action. Sustainability 7, 6457–6477. doi: 10.3390/su7066457
Bakkaloglu, Z., and Arici, M. (2019). Farkli Çözücülerle Propolis Ekstraksiyonunun Toplam Fenolik Içerigi, Antioksidan Kapasite ve Antimikrobiyal Aktivite Üzerine Etkileri. Akademik Gida 17, 538–545. doi: 10.24323/akademik-gida.667272
Barone, A. M., and Aschemann-Witzel, J. (2022). Food handling practices and expiration dates: consumers' perception of smart labels. Food Control 133:108615. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2021.108615
Bauer, A.-S., Dörnyei, K. R., and Krauter, V. (2023). Consumer complaints about food packaging. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 7:1047451. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2023.1047451
Bellemare, M. F., Çakir, M., Peterson, H. H., and Novak, L. (2017). On the measurement of food waste. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 99, 1148–1158. doi: 10.1093/ajae/aax034
Biswas Majee, S., Avlani, D., Kumar, A., and Bera, R. (2025). Harnessing nanotheranostics for the management of breast and ovarian cancer. Acad. Nano Sci. Mater. Technol. 2, 1–15. doi: 10.20935/AcadNano7563
Boliko, M. C. (2019). FAO and the situation of food security and nutrition in the world. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 65, S4–S8. doi: 10.3177/jnsv.65.S4
Borgman, I., Mulder-Nijkamp, M., and de Koeijer, B. (2018). The influence of packaging design features on consumers' purchasing and recycling behaviour. Essay (Master), University of Twente, Enschede, Netherlands. doi: 10.12783/iapri2018/24397
Boyce, J., Broz, C. C., and Binkley, M. (2008). Consumer perspectives: take-out packaging and food safety. Br. Food J. 110, 819–828. doi: 10.1108/00070700810893340
Bria, M., Djakfar, L., and Wicaksono, A. (2021). The impacts of mediating the work environment on the mode choice in work trips. Open Eng. 11, 592–605. doi: 10.1515/eng-2021-0058
Cairo, E. R. (2015). Consumers may be misled despite the list of ingredients being displayed on the packaging of a foodstuff. Eur. J. Risk Regul. 6, 454–457. doi: 10.1017/S1867299X00004955
Campos, J. A. D. B., Bonafé, F. S. S., Dovigo, L. N., and Marôco, J. (2013). Avaliação psicométrica da escala de atitudes em relação à estatística. Revista Brasileira de Biometria 31, 327–337.
Campoy-Muñoz, P., Cardenete, M. A., and Delgado, M. D. C. (2021). Food losses and waste: a needed assessment for future policies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:11856. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111586
Chan, L. L., and Idris, N. (2017). Validity and reliability of the instrument using exploratory factor analysis and Cronbach's alpha. Int. J. Acad. Res. Business Soc. Sci. 7, 400–410. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v7-i10/3387
Chan, R. B. Y. (2022). A review of packaging-related studies in the context of household food waste: drivers, solutions and avenues for future research. Packag. Technol. Sci. 35, 3–51. doi: 10.1002/pts.2611
Chandon, P. (2013). How package design and packaged-based marketing claims lead to overeating. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 35, 7–31. doi: 10.1093/aepp/pps028
Chaturvedi, P., Kulshreshtha, K., Tripathi, V., and Agnihotri, D. (2023). Exploring consumers' motives for electric vehicle adoption: bridging the attitude–behavior gap. Benchmark. Int. J. 30, 4174–4192. doi: 10.1108/BIJ-10-2021-0618
Chatzisarantis, N. L. D., and Biddle, S. J. H. (1998). Functional significance of psychological variables that are included in the Theory of Planned Behaviour: a Self-Determination Theory approach to the study of attitudes, subjective norms, perceptions of control and intentions. Eur. J. Soc. Psychol. 28, 303–322. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-0992(199805/06)28:3<303::AID-EJSP853>3.0.CO;2-6
Chen, H. S. (2019). Environmental concerns and food consumption: what drives consumers' actions to reduce food waste? J. Int. Food Agribusiness Market. 31, 273–292. doi: 10.1080/08974438.2018.1520179
Chen, H. S., and Jai, T.-M. (2018). Waste less, enjoy more: forming a messaging campaign and reducing food waste in restaurants. J. Qual. Assurance Hospital. Tourism 19, 495–520. doi: 10.1080/1528008X.2018.1483282
Chirilli, C., Molino, M., and Torri, L. (2022). Consumers' awareness, behavior and expectations for food packaging environmental sustainability: influence of socio-demographic characteristics. Foods 11:2388. doi: 10.3390/foods11162388
Chopde, S. (2024). Sustainable packaging and its impact on consumer behaviour. Int. J. Multidiscipl. Res. 6, 1–8. doi: 10.36948/ijfmr.2024.v06i04.26010
Chu, W., Williams, H., Verghese, K., Wever, R., and Glad, W. (2020). Tensions and opportunities: an activity theory perspective on date and storage label design through a literature review and co-creation sessions. Sustainability 12:1162. doi: 10.3390/su12031162
Churchill, G. A. A. (1979). Paradigm for developing better measures of marketing constructs. J. Market. Res. 16, 64–73. doi: 10.1177/002224377901600110
Claudy, M. C., and Peterson, M. (2013). Understanding the attitude-behavior gap for renewable energy systems using behavioral reasoning theory. J. Macromarket. 33, 273–287. doi: 10.1177/0276146713481605
Coussy, H., Guillard, V., Guillaume, C., and Gontard, N. (2013). Role of packaging in the smorgasbord of action for sustainable food consumption. Agro-food-Indus. Hi Tech 24, 15–19.
d'Astous, A., and Labrecque, J. (2021). The impact of responsible food packaging perceptions on naturalness and healthiness inferences, and consumer buying intentions. Foods 10:2366. doi: 10.3390/foods10102366
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q. 13, 319–340. doi: 10.2307/249008
dos Santos, J. I. A. S., da Silveira, D. S., da Costa, M. F., and Duarte, R. B. (2022). Consumer behaviour in relation to food waste: a systematic literature review. Br. Food J. 124, 4420–4439. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-09-2021-1075
Du Rietz Dahlström, S., and Kremel, A. (2023). Consumer behavior as a challenge and opportunity for circular food packaging—a systematic literature review. Circular Econ. Sustain. 4, 1–26. doi: 10.1007/s43615-023-00290-1
Dusoruth, V., and Peterson, H. H. (2020). Food waste tendencies: behavioral response to cosmetic deterioration of food. PLoS ONE 15:e0233287. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233287
Dyer, D. D., and Keating, J. P. (1980). On the determination of critical values for Bartlett's test. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 75, 313–319. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1980.10477468
Elias, S., Veerapandiyan, A., Sundram, L. K., and Ismail, N. (2020). Exploring the items for measuring e-Procurement usage construct: an exploratory factor analysis. Int. J. Acad. Res. Business Soc. Sci. 10, 758–772. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v10-i12/8164
Estrada, F. (2010). Economics and rationality of organizations: an approach to the work of Herbert A. Simon. SSRN Electron. J. 21811, 1–16. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.1583199
Feng, X. (2012). Reliability and validity of new general self-efficacy scale (NGSSE). J. Mudanjiang Normal Univ. Philos. Soc. Ed. 4, 127–129. doi: 10.13815/j.cnki.jmtc(pss).2012.04.042
Fishburn, P. C. (1991). Decision theory: the next 100 years? Econ. J. 101, 27–32. doi: 10.2307/2233833
Fornell, C., and Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Market. Res. 18, 39–50. doi: 10.1177/002224378101800104
Gelman, A. (2006). The difference between “significant” and “not significant” is not itself statistically significant. Am. Stat. 60, 328–331. doi: 10.1198/000313006X152649
Georgakoudis, E. D. P., Georgia, G., and Tipi, N. S. (2023). The packaging redesign issue – space exploitation and environmental benefits. Manage. Environ. Q. 34, 1–20. doi: 10.1108/MEQ-08-2021-0195
Govindappa, R., and Radha, D. S. (2013). Consumerss attitude and purchasing intentions towards packaged foods: review of literature. SSRN Electron. J. 1–6. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.2340351
Gowen, A. A., Downey, G., Esquerre, C., and O'Donnell, C. P. (2011). Preventing over-fitting in PLS calibration models of near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy data using regression coefficients. J. Chemometr. 25, 375–381. doi: 10.1002/cem.1349
Guchi, A. R., and Syafrizal, A. (2022). The effect of attitude, subjective norm, perceived behaviour control on intention to reduce food waste and food waste behaviour. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. 12, 329–338. doi: 10.29322/IJSRP.12.05.2022.p12540
Han, X., Hu, C., and Lin, L. (2020). A study on the impact of China's urbanization on the quantity of municipal solid waste produced. Waste Manage. Res. 38, 184–192. doi: 10.1177/0734242X19886912
Hazuchova, N., Antosova, I., and Stavkova, J. (2020). Food wastage as a display of consumer behaviour. J. Competitive. 12:51. doi: 10.7441/joc.2020.02.04
Helanto, K., Matikainen, L., Talj, R., and Rojas, O. (2019). Bio-based polymers for sustainable packaging and biobarriers: a critical review. BioResources 14, 4902–4951. doi: 10.15376/biores.14.2.Helanto
Heng, Y., and House, L. (2022). Consumers' perceptions and behavior toward food waste across countries. Int. Food Agribusiness Manage. Rev. 25, 197–210. doi: 10.22434/IFAMR2020.0198
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., and Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Market. Sci. 43, 115–135. doi: 10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Henshel, A. M. (1971). The relationship between values and behavior: a developmental hypothesis. Child Dev. 42, 1997–2007. doi: 10.2307/1127602
Hinnüber, F., Szarucki, M., and Szopik-Depczyńska, K. (2019). The effects of a first-time experience on the evaluation of battery electric vehicles by potential consumers. Sustainability 11:7034. doi: 10.3390/su11247034
Hunter, G. L., Taylor, S. A., and Kallen, P. H. (2024). Shoppers' susceptibility to information overload: scale development and validation. J. Market. Theory Pract. 32, 94–113. doi: 10.1080/10696679.2022.2121287
Jackson, T. (2005). Motivating sustainable consumption: a review of evidence on consumer behaviour and behavioural change. Sustain. Dev. Res. Netw. 29, 30–40.
Jeżewska-Zychowicz, M., and Jeznach, M. (2015). Consumers' behaviours related to packaging and their attitudes towards environment. J. Agribusiness Rural Dev. 37, 457–447. doi: 10.17306/JARD.2015.47
Jha, S., Paliwal, M., and Sengupta, S. (2023). Influence of cause-related packaging on high cultural capital consumers' purchase intention toward snacking products – use of consumption value theory. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plann. 18, 2207–2211. doi: 10.18280/ijsdp.180725
Jia, L., Zhang, J., and Qiao, G. (2022). Scale and environmental impacts of food loss and waste in china—a material flow analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 20:460. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010460
Jones, S. M., and Wirtz, J. G. (2006). How does the comforting process work? An empirical test of an appraisal-based model of comforting. Hum. Commun. Res. 32, 217–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2958.2006.00274.x
Ju, X. (2015). Consumers' variety seeking: from an information perspective. Int. Business Res. 8, 42–53. doi: 10.5539/ibr.v8n3p42
Kang, J., and Wang, D. (2021). Date analysis of consumers' purchase intention based on the safety of food plastic packaging materialst. J. Phys. Confer. Ser. 1955:012036. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1955/1/012036
Kapoor, S., and Kumar, N. (2019). Does packaging influence purchase decisions of food products? A study of young consumers of India. Acad. Market. Stud. J. 23, 1–16.
Kesberg, R., and Keller, J. (2018). The relation between human values and perceived situation characteristics in everyday life. Front. Psychol. 9:1676. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01676
Kevin, A., Budiman, F., Putra, H., Suhargo, T., and Prasetyawati, T. (2024). Intention to buy products with environmentally friendly packaging in Jakarta, Indonesia. J. Syntax Admiration 5, 1790–1803. doi: 10.46799/jsa.v5i5.1164
Kim, M. J., Hall, C. M., and Kim, D.-K. (2020). Predicting environmentally friendly eating out behavior by value-attitude-behavior theory: does being vegetarian reduce food waste? J. Sustain. Tourism 28, 797–815. doi: 10.1080/09669582.2019.1705461
Konstantoglou, A., Folinas, D., and Fotiadis, T. (2020). Investigating food packaging elements from a consumer's perspective. Foods 9:1097. doi: 10.3390/foods9081097
Kristiansen, C. M., and Zanna, M. P. (1988). Justifying attitudes by appealing to values: a functional perspective. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 27, 247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8309.1988.tb00826.x
Kumar, T., Kiran, B., and Babu, N. (2023). Deciphering customer perceived value a comparative study using Holbrook's Typology across Brands in Visakhapatnam. J. Adv. Zool. 44, 1565–1578. doi: 10.17762/jaz.v44iS-3.1909
Kunda, Z. (1990). The case for motivated reasoning. Psychol. Bull. 108, 480–498. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.108.3.480
Leguina, A. (2015). A primer on partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Int. J. Res. Method Educ. 38, 220–221. doi: 10.1080/1743727X.2015.1005806
Li, T., Lloyd, K., Birch, E., Wu, X., Mirosa, M., Liao, X., et al. (2020). A quantitative survey of consumer perceptions of smart food packaging in China. Food Sci. Nutr. 8, 3977–3988. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.1563
Liang, L. H., and Khan, M. N. A. A. (2024). Exploring items for measuring the sales and service tax (SST) compliance constructs using exploratory factor analysis (EFA) procedure. Int. J. Acad. Res. Business Soc. Sci. 14, 1312–1325. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v14-i1/20544
Lindh, H., and Olsson, A, Williams, H. (2016). Consumer perceptions of food packaging: contributing to or counteracting environmentally sustainable development? Packag. Technol. Sci. 29, 3–23. doi: 10.1002/pts.2184
Ling, G. M., Tiep, H. S., Fern, Y. S., and Lun, T. W. (2021). Factors influencing consumers' purchase behaviour towards green packaged products. RSF Confer. Ser. Business Manage. Soc. Sci. 1, 52–56. doi: 10.31098/bmss.v1i1.254
Liu, J., Lundqvist, J., and Weinberg, J. (2013). Food losses and waste in China and their implication for water and land. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47, 10137–10144. doi: 10.1021/es401426b
Liu, Y., Segev, S., and Villar, M. E. (2017). Comparing two mechanisms for green consumption: cognitive-affect behavior vs theory of reasoned action. J. Consum. Market. 34, 442–454. doi: 10.1108/JCM-01-2016-1688
Malle, B. F. (1999). How people explain behavior: a new theoretical framework. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 3, 23–48. doi: 10.1207/s15327957pspr0301_2
Mao, X.-Q., Zheng, S.-I., Yu, L.-J., Jiang, Z.-B., and Chen, J.-P. (2008). Comparative study of management system of plastic food-packaging materials worldwide. Packag. Eng. 29, 42–46+52.
Marques da Rosa, V., Spence, C., and Tonetto, L. M. (2018). Influences of visual attributes of food packaging on consumer preference and associations with taste and healthiness. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 43, 210–217. doi: 10.1111/ijcs.12500
Martin-Rios, C., Rogenhofer, J., and Alvarado, M. (2022). The true cost of food waste: tackling the managerial challenges of the food supply chain. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 131, 190–195. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.12.005
Moffat, A. S. (1992). Does global change threaten the world food supply? Science 256, 1140–1141. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1140
Mruk-Tomczak, D., Jerzyk, E., and Wawrzynkiewicz, N. (2019). Consumer engagement and the perception of packaging information. Olsztyn Econ. J. 14, 195–207. doi: 10.31648/oej.3971
Nair, S. S., Trafiałek, J., and Kolanowski, W. (2023). Edible packaging: a technological update for the sustainable future of the food industry. Appl. Sci. 13:8234. doi: 10.3390/app13148234
Neff, R. A., Spiker, M. L., and Truant, P. L. (2015). Wasted food: US consumers' reported awareness, attitudes, and behaviors. PLoS ONE 10:e0127881. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0127881
Nemat, B., Razzaghi, M., Bolton, K., and Rousta, K. (2020a). The potential of food packaging attributes to influence consumers' decisions to sort waste. Sustainability 12:2234. doi: 10.3390/su12062234
Nemat, B., Razzaghi, M., Bolton, K., and Rousta, K. (2020b). The influence of food packaging on consumers sorting behavior. J. Coast. Zone Manag. 23:4.
Norton, V., Waters, C., Oloyede, O. O., and Lignou, S. (2022). Exploring consumers' understanding and perception of sustainable food packaging in the UK. Foods 11:3424. doi: 10.3390/foods11213424
Obersteiner, G., Cociancig, M., Luck, S., and Mayerhofer, J. (2021). Impact of optimized packaging on food waste prevention potential among consumers. Sustainability 13:4209. doi: 10.3390/su13084209
Opara, U. L., and Mditshwa, A. (2013). A review on the role of packaging in securing food system: adding value to food products and reducing losses and waste. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 8, 2621–2630. doi: 10.5897/AJAR2013.6931
Ordabayeva, N. (2013). Predicting and managing consumers' package size impressions. J. Market. Consum. Res. 77, 123–137. doi: 10.1509/jm.12.0228
Oviedo, H. C., and Campo-Arias, A. (2005). Metodología de investigación y lectura crítica de estudios Aproximación al uso del coeficiente alfa. Rev. Colomb. Psiquiatr. 34, 572–580.
Parfitt, J., Barthel, M., and Macnaughton, S. (2010). Food waste within food supply chains: quantification and potential for change to 2050. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 365, 3065–3081. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2010.0126
Pereira de Abreu, D.A., Cruz, J. M., and Losada, P. P. (2012). Active and intelligent packaging for the food industry. Food Rev. Int. 28, 146–187. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2011.595022
Ploom, K., Pentus, K., Kuusik, A., and Varblane, U. (2020). The effect of culture on the perception of product packaging: a multimethod cross-cultural study. J. Int. Consum. Market. 32, 163–177. doi: 10.1080/08961530.2019.1660752
Popovic, I., Bossink, B. A. G., and van der Sijde, P. C. (2019). Factors influencing consumers' decision to purchase food in environmentally friendly packaging: what do we know and where do we go from here? Sustainability 11:7197. doi: 10.3390/su11247197
Przeworski, A., and Vreeland, J. R. (2002). A statistical model of bilateral cooperation. Polit. Anal. 10, 101–112. doi: 10.1093/pan/10.2.101
Przymuszała, P., Turalska, M., Zielińska-Tomczak, Ł., Chmielewski, A., Cerbin-Koczorowska, M., Marciniak, R., et al. (2024). Theory of planned behavior as a theoretical framework for exploring nursing students' intentions for interprofessional collaboration: a qualitative study. SAGE Open 14, 1–15. doi: 10.1177/21582440241284472
Rokka, J., and Uusitalo, L. (2008). Preference for green packaging in consumer product choices–do consumers care? Int. J. Consum. Stud. 32, 516–525. doi: 10.1111/j.1470-6431.2008.00710.x
Sahu, A. K., Padhy, R. K., and Dhir, A. (2020). Envisioning the future of behavioral decision-making: a systematic literature review of behavioral reasoning theory. Austral. Market. J. 28, 145–159. doi: 10.1016/j.ausmj.2020.05.001
Salgado, P. R., Di Giorgio, L., Musso, Y. S., and Mauri, A. N. (2021). Recent developments in smart food packaging focused on biobased and biodegradable polymers. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 5:630393. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2021.630393
Sara, K., Witi, F. L., and Mude, A. (2020). The readiness analysis of blended learning in flores university. Jurnal ilmu pengetahuan teknologi komputer 6, 137–142. doi: 10.33480/JITK.V6I1.1392
Schäufele, I., and Janssen, M. (2021). How and why does the attitude-behavior gap differ between product categories of sustainable food? Analysis of organic food purchases based on household panel data. Front. Psychol. 12:595636. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.595636
Scott, L., and Vigar-Ellis, D. (2014). Consumer understanding, perceptions and behaviours with regard to environmentally friendly packaging in a developing nation. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 38, 642–649. doi: 10.1111/ijcs.12136
Shima Jafarzadeh, M. F., Amjadi, S., Kouzegaran, V. J., Almasi, H., Garavand, F., and Zargar, M. (2023). Plant protein-based nanocomposite films: a review on the used nanomaterials, characteristics, and food packaging applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 63, 9667–9693. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2070721
Simmonds, G., Woods, A., and Spence, C. (2017). ‘Show me the goods': assessing the effectiveness of transparent packaging vs. product imagery on product evaluation. Food Qual. Prefer. 63, 18–27. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2017.07.015
Stangherlin, I. C., and De Barcellos, M. D. (2018). Drivers and barriers to food waste reduction. Br. Food J. 120, 2364–2387. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-12-2017-0726
Sumi, M., and Swathilakshmi, P. R. (2023). A detailed analysis of electric vehicle technology advancements and future prospects. Int. J. Res. Appl. Sci. Eng. Technol. 11, 1003–1010. doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2023.50247
Suwandi, H., Bakrie, N., Vianney, A., and Hendriana, E. (2023). Drivers of young consumers' willingness to reduce food waste and buy intelligent packaging. Mix J. Ilmiah Manajemen 13:320. doi: 10.22441/jurnal_mix.2023.v13i2.005
Temizkan, V. (2022). Investigating the effect of consumers environmental values on green buying behavior. Business Econ. Res. J. 13, 505–521. doi: 10.20409/berj.2022.386
Uddin, M., Humaira, B., and Rouf, M. (2022). The impact of packaging on consumer buying decision: an application on consumer goods. J. Sci. Technol. 20, 76–81. doi: 10.59125/JST.20209
Unal, U., Bagci, R., and Taşçioglu, M. (2024). The perfect combination to win the competition: bringing sustainability and customer experience together. Business Strategy Environ. 33, 1–19. doi: 10.1002/bse.3728
Un-Noor, F., Padmanaban, S., Mihet-Popa, L., Mollah, M. N., and Hossain, E. A. (2017). Comprehensive study of key electric vehicle (EV) components, technologies, challenges, impacts, and future direction of development. Energies 10:1217. doi: 10.3390/en10081217
Valerie Folkes, S. M. (2004). The effect of package shape on consumers' judgments of product volume: attention as a mental contaminant. J. Consum. Res. 31, 390–401. doi: 10.1086/422117
Varese, E., Cesarani, M. C., and Wojnarowska, M. (2022). Consumers' perception of suboptimal food: strategies to reduce food waste. Br. Food J. 125, 361–378. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-07-2021-0809
Velnampy, T., and Achchuthan, S. (2016). Integrated model for understanding and enhancing green purchase behavioral intention: directions for future research. J. Sociol. Res. 7, 105–122. doi: 10.5296/jsr.v7i1.9541
Venkatesh, V., and Davis, F. D. A. (2000). Theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: four longitudinal field studies. Manage. Sci. 46, 186–204. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.46.2.186.11926
Versino, F., Ortega, F., Monroy, Y., Rivero, S., López, O. V., García, M. A., et al. (2023). Sustainable and bio-based food packaging: a review on past and current design innovations. Foods 12:1057. doi: 10.3390/foods12051057
Wang, D., and Sun, C. (2010). “Food packaging and design in view of environmental protection,” in 2010 International Conference on Management and Service Science (Wuhan), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ICMSS.2010.5577153
Wang, E. S. (2013). The influence of visual packaging design on perceived food product quality, value, and brand preference. Int. J. Retail Distrib. Manage. 41, 805–816. doi: 10.1108/IJRDM-12-2012-0113
Wang, J., Li, M., Li, S., and Chen, K. (2022). Understanding consumers' food waste reduction behavior—a study based on extended norm activation theory. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:4187. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19074187
Westaby, J. D. (2005). Behavioral reasoning theory: identifying new linkages underlying intentions and behavior. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 98, 97–120. doi: 10.1016/j.obhdp.2005.07.003
Wikström, F., Williams, H., Trischler, J., and Rowe, Z. (2019). The importance of packaging functions for food waste of different products in households. Sustainability 11:2641. doi: 10.3390/su11092641
Willis, C. E., and Perlack, R. D. (1978). Multicollinearity: effects, symptoms, and remedies. J. Northeastern Agric. Econ. Council 7, 55–61. doi: 10.1017/S0163548400001989
Wirama, I. G. K. A., and Wirama, D. G. (2024). Behavioural reasoning theory perspectives: hospitality accounting system adoption. J. Akuntansi 28, 438–456. doi: 10.24912/ja.v28i3.2151
Wu, J., and Wong, A. C. M. (2003). A note on determining the p -value of Bartlett's test of homogeneity of variances. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 32, 91–101. doi: 10.1081/STA-120017801
Wu, S.H., Ho, C. T., Nah, S. L., and Chau, C. F. (2014). Global hunger: a challenge to agricultural, food, and nutritional sciences. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 54, 151–162. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2011.578764
Xiao-b, H. J. (2014). The study on green packaging in the perspective of the food safety. Food Res. Dev. 35, 160–162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2014.18.041
Ximénez, C., Maydeu-Olivares, A., Shi, D., and Revuelta, J. (2022). Assessing cutoff values of SEM fit indices: advantages of the unbiased SRMR Index and its cutoff criterion based on communality. Struct. Eq. Model. Multidiscipl. J. 29, 368–380. doi: 10.1080/10705511.2021.1992596
Xu, Y., He, D., and Fan, M. (2024). Antecedent research on cross-border E-commerce consumer purchase decision-making: the moderating role of platform-recommended advertisement characteristics. Heliyon 10:e37627. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37627
Yin, Z. J., and Wei, H. (2012). Analysis on reliability and validity of resident's satisfaction survey for community health services of Guangzhou. Chin. J. Public Health Manage. 28, 244–246. doi: 10.19568/j.cnki.23-1318.2012.02.072
Yokokawa, N., Kikuchi-Uehara, E., Amasawa, E., Sugiyama, H., and Hirao, M. (2019). Environmental analysis of packaging-derived changes in food production and consumer behavior. J. Indus. Ecol. 23, 1253–1263. doi: 10.1111/jiec.12918
Yordanova, B., and Krastev, L. (2018). Factorial Structure and Differential Features of Aesthetic Preferences. Psychol. Thought 11, 112–121. doi: 10.5964/psyct.v11i2.300
Zeineddine, M., Kharroubi, S., Chalak, A., and Hassan, H. (2021). Post-consumer food waste generation while dining out: a close-up view. PLoS ONE 16:e0251947. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251947
Zeng, T. (2021). Impacts of consumers' perceived risks in eco-design packaging on food wastage behaviors. Br. Food J. 124, 2512–2532. doi: 10.1108/BFJ-05-2021-0603
Zeng, T., and Durif, F. (2019). The influence of consumers' perceived risks towards eco-design packaging upon the purchasing decision process: an exploratory study. Sustainability 11:6131. doi: 10.3390/su11216131
Zhang, K., Li, F., Li, H., and Yin, C. (2022). Sustainable management of food waste during COVID-19 pandemic: insights into irrational food hoarding among Chinese citizens. Foods 11:4049. doi: 10.3390/foods11244049
Zhang, Y. (2016). The application and psychology of color in food packaging design. Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 9, 687–690. doi: 10.19026/ajfst.10.2216
Zhao, A. L., Dermody, J., Koenig-Lewis, N., and Hanmer-Lloyd, S. (2024). Cultivating sustainable consumption: the role of harmonious cultural values and pro-environmental self-identity. J. Consum. Behav. 23, 1014–1031. doi: 10.1002/cb.2261
Keywords: sustainable consumption, food packaging, food wastage, behavioral intention, BRT
Citation: Mu J, Zhou L and Yang C (2025) Research on the influence mechanism of food packaging on consumers' behavioral intention to refuse food waste based on behavioral reasoning theory. Front. Psychol. 16:1630861. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1630861
Received: 19 May 2025; Accepted: 01 September 2025;
Published: 24 September 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Biraglia, University of Leeds, United KingdomReviewed by:
Iza Gigauri, University of Georgia, GeorgiaEvelyn Hendriana, BINUS Business School Doctor of Research in Management, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Mu, Zhou and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juncheng Mu, MjExNjAxMDA5QG5qbnUuZWR1LmNu
 Juncheng Mu
Juncheng Mu Linglin Zhou
Linglin Zhou Chun Yang
Chun Yang