- 1School of Physical Education, Shandong University, Jinan, China
- 2Department of Physical Education, Liaoning Institute of Science and Engineering, Jinzhou, China
- 3School of Physical Education, Ludong University, Yantai, China
- 4School of Economics and Management, Wuhan Sports University, Wuhan, China
Introduction: Social support is widely recognized as a key determinant of athletes’ mental health; however, inconsistencies remain regarding the strength and source-specific effects of this relationship. This meta-analysis systematically quantifies the association between social support and mental health outcomes in athletes and examines variations by support source.
Methods: A systematic search was conducted across multiple databases to identify relevant studies. Random-effects models were used to calculate pooled effect sizes expressed as correlation coefficients (r). Subgroup analyses compared the associations of family and friends’ support versus team-based support with mental health indicators.
Results: Forty studies encompassing 14,462 athletes were included. Overall social support correlated positively with well-being (r = 0.31) and negatively with anxiety (r = −0.22), depression (r = −0.27), and stress (r = −0.25). Notably, support from family and friends showed a significantly stronger negative association with depressive symptoms than team-based support.
Discussion: In conclusion, social support plays a vital role in enhancing athletes’ mental health, particularly through close interpersonal relationships. These findings underscore the importance of integrating diverse sources of social support in interventions aimed at improving psychological well-being in athletes.
Introduction
It is widely recognized that regular participation in sport is associated with improved mental health and enhanced psychological well-being (Mahindru et al., 2023). However, while sport participation may serve as a protective factor, athletes are concurrently exposed to a constellation of stressors in their pursuit of competitive excellence (Daley et al., 2023). These include excessive training demands, dense competition schedules, intense media scrutiny, and the psychological burden of injury-related career uncertainty (Haugen, 2022). Such cumulative pressures have been consistently linked to elevated levels of depression and anxiety, threatening both performance and overall well-being. Recognizing these risks, recent research has increasingly focused on athletes’ mental health, emphasizing the prevalence and impact of psychological disorders across competitive levels and prompting growing interest in psychosocial resources, particularly social support, as potential buffers against psychological distress (Küttel and Larsen, 2020; Stevens et al., 2024).
Social support has long been recognized as a critical factor in mitigating the adverse psychological effects of stress and enhancing psychological resilience (Bedaso et al., 2021; Zhou and Cheng, 2022; Stevens et al., 2024). For athletes, who often operate in high-pressure environments characterized by intense physical training, performance expectations, limited recovery time, and public scrutiny, social support plays a particularly vital role in preserving mental health (Nuetzel, 2023; Simons and Bird, 2023). In addition to the physical and emotional challenges inherent in competitive sport, athletes may also experience prolonged time away from family, fear of underperformance, and conflicts between personal and athletic identities, all of which increase their reliance on external support (Stevens et al., 2024). Social support is typically provided by key figures in an athlete’s immediate environment, including family members, friends, coaches, and teammates. These individuals help shape both the perception and availability of support, which are essential in responding to psychological stressors. The stress-buffering model (Cohen and Wills, 1985) provides a widely accepted theoretical explanation for how social support influences mental health outcomes. This model suggests that social support reduces the negative psychological impact of stress by facilitating emotional regulation, fostering adaptive coping strategies, and diminishing the perceived severity of stressful experiences. Within the context of sport, this framework has been used to explain how supportive interpersonal relationships may protect athletes from anxiety, emotional exhaustion, and other mental health challenges (Delfin et al., 2024; Hartley et al., 2023). Complementing this view, the dual continuum model of mental health (Keyes, 2002) emphasizes that mental health is not merely the absence of psychopathology, but also the presence of positive psychological functioning. From this perspective, social support not only helps reduce negative symptoms such as anxiety and depression but also contributes to enhanced psychological flourishing and well-being.
Although numerous studies have underscored the potential positive effects of social support on athletes’ mental health, including reduced anxiety and depression as well as enhanced well-being, the empirical findings remain inconsistent. Some studies report significant associations between higher levels of social support and better mental health outcomes (DeFreese and Smith, 2014; Hagiwara et al., 2017, 2021; Simons and Bird, 2023), whereas others find weak or non-significant associations (Price and Weiss, 2000). This inconsistency may stem from differences in how social support is conceptualized and measured across studies, particularly in relation to the sources of support (e.g., family, coaches, teammates). The role of these sources may vary, with some providing more meaningful psychological benefits than others depending on the context.
Furthermore, individual factors such as gender and athlete level can moderate the effectiveness of social support. Female athletes may face unique psychological challenges, such as societal gender expectations and role conflicts, which could shape their use of social support (Cnen et al., 2021). On the other hand, male athletes may be less likely to seek support due to cultural norms around emotional expression. Additionally, elite athletes often experience higher performance pressures and career uncertainties, which may lead to more specialized support needs compared to recreational athletes (Kuok et al., 2021; Reardon, 2021). However, further research is required to better understand how these factors interact with social support and affect mental health outcomes.
Despite existing studies, no comprehensive meta-analysis has yet quantified the relationship between social support and mental health in athletes or explored how individual factors such as gender and athlete level, as well as different sources of support, influence this relationship. This study aims to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess the strength and direction of this association and examine potential variations based on support sources. By synthesizing existing evidence, this study seeks to clarify inconsistencies in the current literature and provide a robust empirical foundation for future intervention strategies.
Methods
Search strategy and study selection
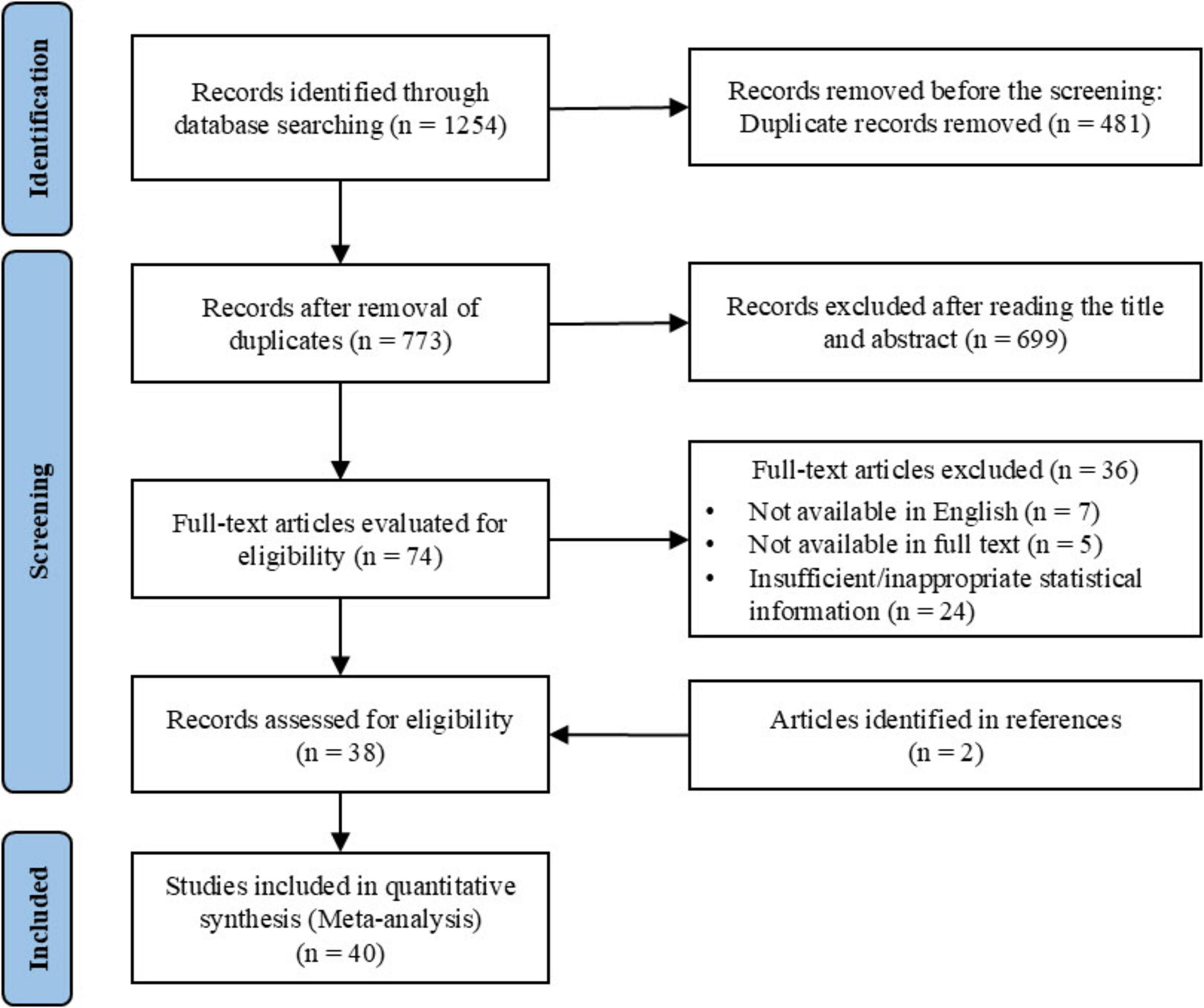
This systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines (Page et al., 2021) and were prospectively registered in the PROSPERO database (registration number: CRD420251054013). A comprehensive literature search was performed across four electronic databases (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and SPORTDiscus) for studies published up to May 20, 2025. Predefined combinations of keywords and Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) were applied, including: (“social support” OR “social identity” OR “social network” OR “family support” OR “friend support” OR “peer support” OR “coach support”) AND (“mental health” OR “wellbeing” OR “anxiety” OR “depress” OR “stress”) AND (“athlete” OR “player”). Detailed search strategies for each database are presented in Supplementary File 1. After the removal of duplicates, titles and abstracts were screened for relevance, followed by full-text assessment based on predefined eligibility criteria. Figure 1 illustrates the study selection process, detailing the stages of screening and inclusion based on the predefined eligibility criteria. Two reviewers independently conducted the screening process, with any disagreements resolved by consultation with a third reviewer.
Eligibility criteria
Studies were included if they met the following criteria: (a) published in peer-reviewed journals; (b) involved healthy athletes as participants; (c) examined the association between social support and mental health outcomes, including wellbeing, anxiety, depression, or stress; and (d) employed validated instruments to assess both social support and mental health variables. Studies were excluded if they met any of the following conditions: (a) focused on non-athletes or clinical populations (e.g., patients with mental health disorders); (b) did not report on social support or mental health outcomes; (c) did not provide sufficient data to calculate effect sizes.
Methodological quality assessment and risk of bias
The methodological quality of the included studies was appraised using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) adapted for cross-sectional designs, which assesses study quality across three domains: selection of participants, comparability of study groups, and ascertainment of the outcome. The maximum attainable score is 9. To ensure methodological rigor, only studies scoring greater than 5 points were included in the meta-analysis. Quality assessment was conducted independently by two reviewers, and any discrepancies were resolved through discussion or consultation with a third reviewer. Risk of publication bias was examined through visual inspection of funnel plots and statistically assessed using Egger’s regression test.
Data Extraction
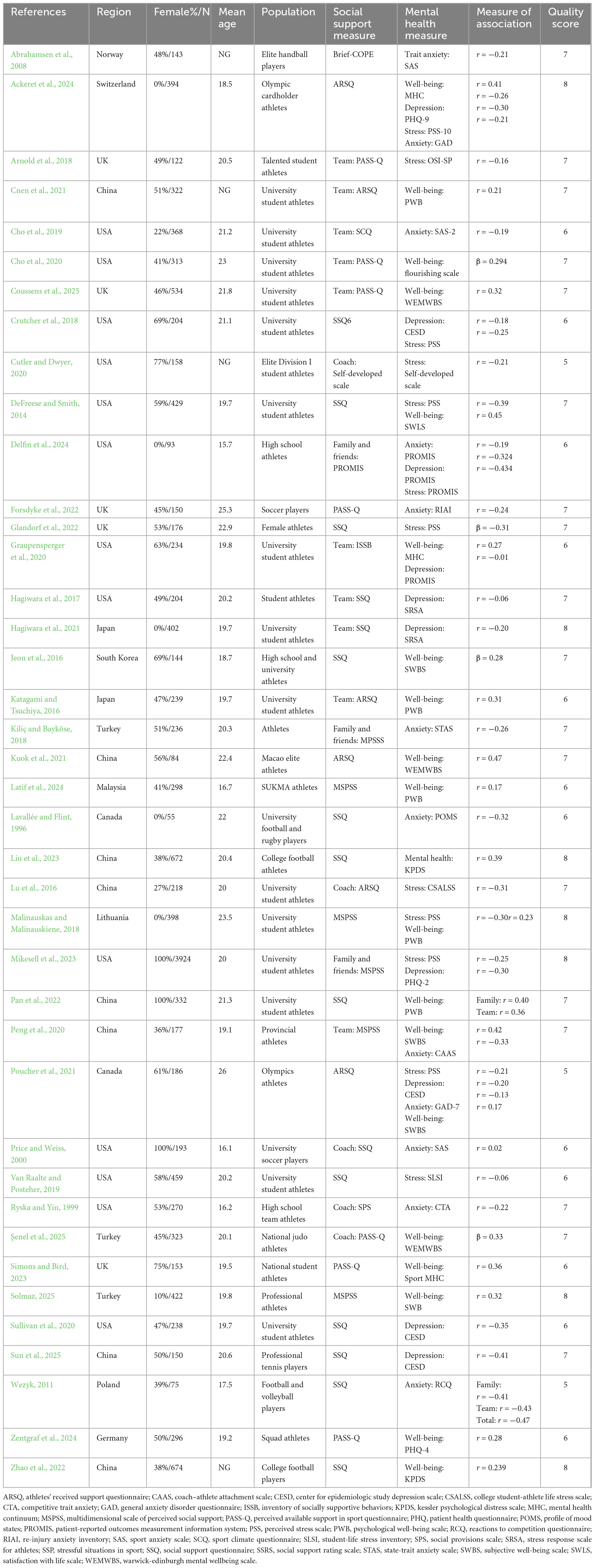
Mental health outcomes reported across the included studies were categorized into four domains: wellbeing (e.g., assessed using the Psychological Well-Being Scale), anxiety (e.g., Sport Anxiety Scale), depression (e.g., Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale), and stress (e.g., Perceived Stress Scale). The primary data extracted included measures of association between social support and each mental health outcome, specifically Pearson’s correlation coefficients (r) or standardized regression coefficients (β). In addition, relevant demographic and study-level characteristics were recorded, including participants’ age, gender (female %), athlete level, geographic region, and the instruments used to assess social support and mental health variables. A summary of the extracted data is presented in Table 1.
Statistical analyses
All meta-analyses were conducted using the metagen function from the meta package in R (version 4.3.0). Correlation coefficients (r) were used as the primary effect size. For studies reporting standardized regression coefficients (β), values were converted to r using the following formula:
Where λ was set to 1 if β was positive and 0 if negative (Peterson and Brown, 2005). To stabilize variance and improve the precision of pooled estimates, Fisher’s z-transformation was applied to all r values prior to analysis (Lei et al., 2018), with back-transformation performed to facilitate interpretation. A random-effects model was employed to account for heterogeneity across studies. I2 statistics were used to assess heterogeneity, with values ≥50% indicating substantial heterogeneity across studies. Effect sizes were interpreted as small (r < 0.30), moderate (0.30 ≤ r < 0.50), or large (r ≥ 0.50), with statistical significance defined as p < 0.05.
Subgroup meta-analyses were conducted to examine the associations between social support and mental health outcomes across three categories: (1) overall social support, (2) support from sport team members (e.g., teammates and coaches), and (3) support from family and friends. Additionally, moderation analyses were conducted to assess the moderating role of gender and athlete level in the strength and direction of the relationships between social support and mental health. Gender composition was defined by the proportion of female participants in each study, grouped into three categories: ≤40%, 40%–60%, and ≥60%. Athlete level was divided into professional (e.g., Olympic, national, and provincial level athletes) and amateur groups (e.g., student athletes and participants in campus or amateur competitions).
Results
Study selection and characteristics
A total of 1,254 studies were initially identified through keyword searches. After eliminating duplicates, 773 articles remained for further screening. Title and abstract review resulted in 74 studies, which were then evaluated for full-text eligibility. Based on the eligibility criteria, 38 studies were selected for inclusion. Additionally, two more studies were identified through reference list reviews, bringing the total number of studies included in the meta-analysis to 40. The full screening process is shown in Figure 1.
Table 1 summarizes the key characteristics of the studies included in the meta-analysis. The majority of the studies included a mixed-gender sample, with participants aged 16–26 years, and most studies reporting an average age between 18 and 23 years. Participants were categorized into professional athletes (e.g., Olympic, elite, national-level) and non-professional athletes (e.g., university and high school athletes). The most commonly used social support measures were the Social Support Questionnaire and the Perceived Athlete Social Support Questionnaire. Mental health outcomes were assessed using a variety of scales, with common measures for anxiety (e.g., Sport Anxiety Scale, Generalized Anxiety Disorder), depression (e.g., Center for Epidemiologic Study Depression Scale, Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System), stress (e.g., Perceived Stress Scale), and well-being (e.g., Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale).
Methodological quality assessment and risk of bias
The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using the NOS for cross-sectional studies. Of the 40 studies, 17 were rated as moderate quality (5–6 points), while 23 were rated as high quality (7–8 points), indicating an overall moderate to high methodological quality. A detailed NOS evaluation is provided in Supplementary File 2. The funnel plot indicated a generally symmetrical distribution, suggesting no significant bias (Supplementary File 3). Egger’s test for publication bias revealed no significant bias in the meta-analysis examining the relationship between overall social support and well-being (t = −0.21, b = −0.49, p = 0.83). Due to the small number of studies (fewer than 10) included in the other meta-analyses, Egger’s test was not applicable for those analyses.
Meta-analysis results
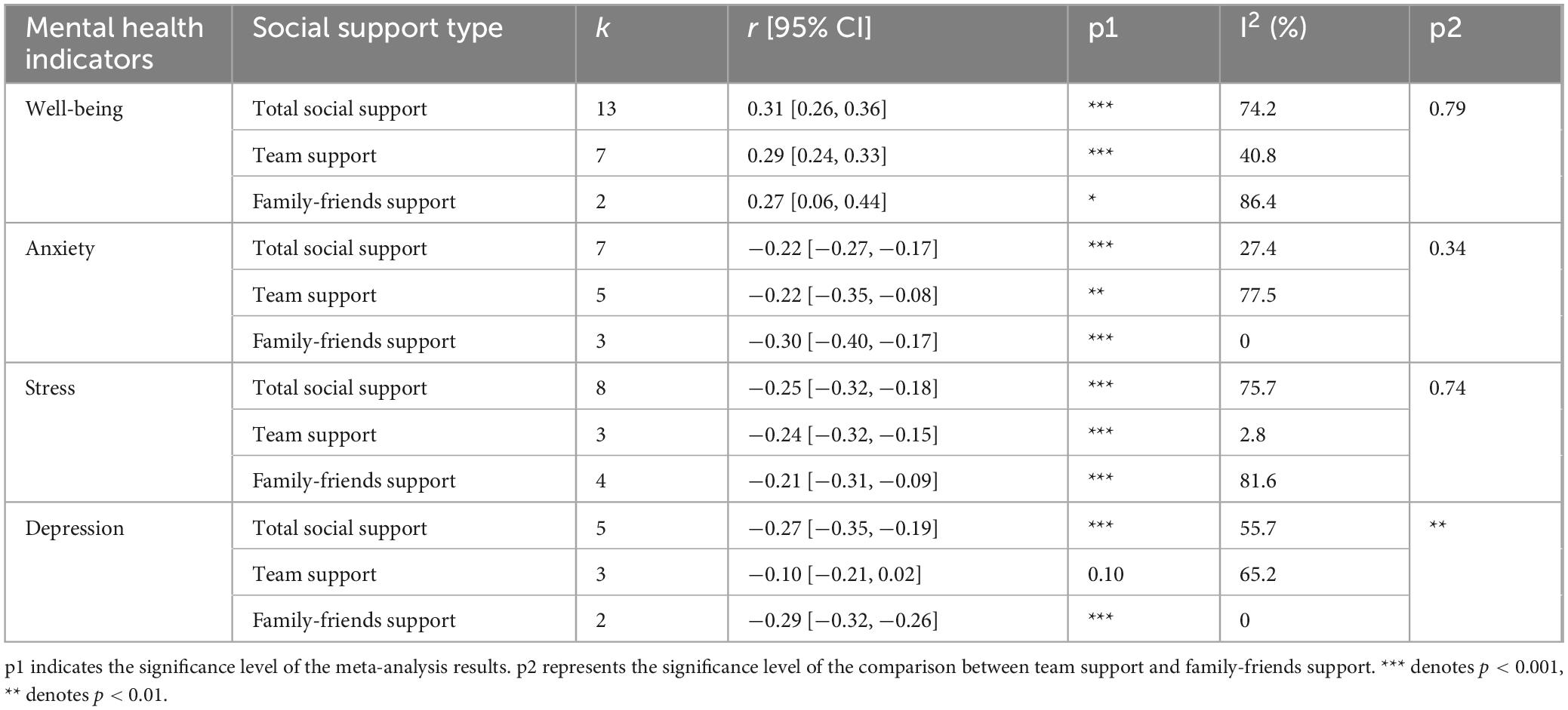
13 studies, involving a total of 4,482 participants, examined the relationship between total social support and well-being, revealing a significant moderate effect (r = 0.31, 95% CI [0.26, 0.36], p < 0.001). Seven studies, with 1,273 participants, assessed the relationship between overall social support and anxiety, demonstrating a significant small negative effect (r = −0.22, 95% CI [−0.27, −0.17], p < 0.001). Eight studies, comprising 2,404 participants, explored the relationship between overall social support and stress, showing a significant small negative effect (r = −0.25, 95% CI [−0.32, −0.18], p < 0.001). Finally, five studies involving 1,172 participants examined the link between overall social support and depression, revealing a significant small negative effect (r = −0.27, 95% CI [−0.35, −0.19], p < 0.001). Detailed forest plots visualizing the meta-analytic findings can be found in Supplementary File 4.
Subgroup analysis revealed no significant differences in the relationships between team support and well-being, and between family-friends support and well-being. Similarly, no significant differences were found in the relationships between team support, family-friends support, and anxiety or stress. However, a significant difference was observed in the relationship between social support and depression (p < 0.01), with family-friends support showing a stronger negative association with depression. The detailed meta-analysis and subgroup analysis results are provided in Table 2. Furthermore, moderation analyses revealed no significant moderating effects of gender composition or athlete level on the relationships between overall social support and various mental health outcomes, including wellbeing, anxiety, and stress (see Supplementary File 5).
Discussion
This meta-analysis shows a significant positive relationship between social support and well-being in athletes, along with a negative relationship between social support and anxiety, stress, and depression. Family-friends support was found to have a stronger negative relationship with depression compared to team support. Furthermore, moderation analyses revealed that gender and athlete level did not significantly moderate these relationships. These findings underscore the important role of social support in the mental health of athletes, particularly in reducing anxiety, stress, and depression, with consistent findings across different genders and athlete levels.
The findings of this meta-analysis align with previous research in both general and clinical populations, which highlight social support as a crucial buffering mechanism for mitigating psychological stress (Bedaso et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2018; Zhou and Cheng, 2022). It has been well-established in the literature that social support enhances resilience, alleviates the negative impacts of stress, and improves emotional regulation (Acoba, 2024). However, the context for athletes is distinctly different. Athletes not only face the typical psychological challenges of daily life but also deal with sport-specific stressors such as performance pressure, competition anxiety, and the psychological consequences of injuries (Stevens et al., 2024). These factors make athletes’ mental health particularly vulnerable, especially in high-competition environments, where the need for psychological support becomes even more critical (Küttel and Larsen, 2020).
Our study indicates a stronger association between support from family and friends and the reduction of depressive symptoms compared to support from coaches or teammates. This finding underscores the unique role of intimate and stable relationships in addressing mental health challenges. The support from family and friends often extends beyond the athletic domain and provides stable emotional regulation resources that are essential for managing persistent negative emotions (Lisinskiene and Lochbaum, 2022; Mira et al., 2023). In contrast, team support tends to focus on performance and goal achievement (González-García et al., 2022), and while it positively impacts overall well-being, anxiety, and stress, its direct emotional support for mental health is likely weaker. These results suggest that targeted psychological health interventions should not only focus on strengthening team dynamics but should also prioritize personal and familial support networks to address emotional and psychological needs more effectively.
Our meta-analysis found no significant moderating effects of gender or athlete level on the relationship between social support and mental health outcomes. This suggests that, within the scope of this study, the association between social support and mental health outcomes (e.g., wellbeing, anxiety, and stress) remains consistent across both genders and athlete levels. However, the lack of significant moderation may be due to the limited sample sizes and study heterogeneity, which could have reduced statistical power. Future research with larger, more homogeneous samples could provide clearer insights into the potential moderating roles of these factors.
Several limitations of this meta-analysis warrant cautious interpretation of the findings. First, substantial heterogeneity was observed across studies, which may be partly attributed to differences in sample characteristics, sport types, and the instruments used to assess social support and mental health outcomes. Additionally, the limited number of studies available for certain psychological outcomes (e.g., anxiety and depression) may have reduced the stability and generalizability of the pooled estimates. Finally, the heterogeneity of assessment tools across studies compromised the comparability of findings and hindered the examination of instrument-specific effects. Future research should utilize standardized and validated instruments to improve measurement consistency, and report disaggregated data to facilitate subgroup analyses.
Conclusion
This meta-analysis demonstrates that social support is crucial in enhancing athletes’ mental health by improving well-being and reducing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and stress. Notably, support from family and friends has a stronger association with alleviating depressive symptoms compared to team-based support, emphasizing the value of intimate, stable relationships. These findings emphasize the importance of incorporating multiple sources of social support in mental health strategies for athletes to effectively address their psychological needs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
JL: Data curation, Conceptualization, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Software. RD: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Resources, Software. XW: Methodology, Data curation, Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. LL: Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1642886/full#supplementary-material
References
Abrahamsen, F., Roberts, G., Pensgaard, A., and Ronglan, L. (2008). Perceived ability and social support as mediators of achievement motivation and performance anxiety. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 18, 810–821. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2007.00707.x
Ackeret, N., Röthlin, P., and Horvath, S. (2024). Factors contributing to elite athletes’ mental health in the junior-to-senior transition: A mixed methods study. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 73:102645. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2024.102645
Acoba, E. F. (2024). Social support and mental health: the mediating role of perceived stress. Front. Psychol. 15:1330720. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1330720
Arnold, R., Edwards, T., and Rees, T. (2018). Organizational stressors, social support, and implications for subjective performance in high-level sport. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 39, 204–212. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2018.08.010
Bedaso, A., Adams, J., Peng, W., and Sibbritt, D. (2021). The relationship between social support and mental health problems during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Reproductive Health 18, 1–23. doi: 10.1186/s12978-021-01209-5
Cho, H., Yi Tan, H., and Lee, E. (2020). Importance of perceived teammate support as a predictor of student-athletes’ positive emotions and subjective well-being. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coaching 15, 364–374. doi: 10.1177/1747954120919720
Cho, S., Choi, H., and Kim, Y. (2019). The relationship between perceived coaching behaviors, competitive trait anxiety, and athlete burnout: A cross-sectional study. Int. J Environ. Res. Public Health 16:1424. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16081424
Cnen, T.-W., Chiu, Y.-C., and Hsu, Y. (2021). Perception of social support provided by coaches, optimism/pessimism, and psychological well-being: Gender differences and mediating effect models. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 16, 272–280. doi: 10.1177/1747954120968649
Cohen, S., and Wills, T. A. (1985). Stress, social support, and the buffering hypothesis. Psychol. Bull. 98:310. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.98.2.310
Coussens, A. H., Stone, M. J., and Donachie, T. C. (2025). Coach–athlete relationships, self-confidence, and psychological wellbeing: The role of perceived and received coach support. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 25:e12226. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12226
Crutcher, B., Moran, R. N., and Covassin, T. (2018). Examining the relationship between social support satisfaction and perceived stress and depression in athletic training students. Athletic Training Educ. J. 13, 168–174. doi: 10.4085/1302168
Cutler, B. A., and Dwyer, B. (2020). Student-athlete perceptions of stress, support, and seeking mental health services. J. Issues Intercollegiate Athletics 13:16. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5245(05)80031-8
Daley, M. M., Shoop, J., and Christino, M. A. (2023). Mental health in the specialized athlete. Curr Rev Musculoskeletal Med. 16, 410–418. doi: 10.1007/s12178-023-09851-1
DeFreese, J. D., and Smith, A. L. (2014). Athlete social support, negative social interactions, and psychological health across a competitive sport season. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 36, 619–630. doi: 10.1123/jsep.2014-0040
Delfin, D., Wallace, J., Baez, S., Karr, J. E., Terry, D. P., Hibbler, T., et al. (2024). Social support, stress, and mental health: examining the stress-buffering hypothesis in adolescent football athletes. J. Athletic Training 59, 499–505. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-0324.23
Forsdyke, D., Madigan, D., Gledhill, A., and Smith, A. (2022). Perceived social support, reinjury anxiety, and psychological readiness to return to sport in soccer players. J. Sport Rehabil. 31, 749–755. doi: 10.1123/jsr.2021-0181
Glandorf, H. L., Coffee, P., and Madigan, D. J. (2022). Team identification and athlete burnout: Testing longitudinal serial mediation via perceived support and stress. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 63:102292. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2022.102292
González-García, H., Martinent, G., and Nicolas, M. (2022). Relationships between coach’s leadership, group cohesion, affective states, sport satisfaction and goal attainment in competitive settings. Int. J. Sports Sci. Coach. 17, 244–253. doi: 10.1177/17479541211053229
Graupensperger, S., Benson, A. J., Kilmer, J. R., and Evans, M. B. (2020). Social (un) distancing: Teammate interactions, athletic identity, and mental health of student-athletes during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Adolesc. Health 67, 662–670. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2020.08.001
Hagiwara, G., Iwatsuki, T., Isogai, H., van Raalte, J. L., and Brewer, B. W. (2017). Relationships among sports helplessness, depression, and social support in American college student-athletes. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 17:753. doi: 10.7752/jpes.2017.02114
Hagiwara, G., Tsunokawa, T., Iwatsuki, T., Shimozono, H., and Kawazura, T. (2021). Relationships among student-athletes’ identity, mental health, and social support in Japanese student-athletes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:7032. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18137032
Hartley, C., Hartley, C., and Coffee, P. (2023). “The influence of social support on athletes,” in: Social Psychology in Sport, eds L. Davis, R. Keegan, and S. Jowett. (Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics).
Haugen, E. (2022). Athlete mental health & psychological impact of sport injury. Operative Techniques Sports Med. 30:150898. doi: 10.1016/j.otsm.2022.150898
Jeon, H., Lee, K., and Kwon, S. (2016). Investigation of the structural relationships between social support, self-compassion, and subjective well-being in Korean elite student athletes. Psychol. Rep. 119, 39–54. doi: 10.1177/0033294116658226
Katagami, E., and Tsuchiya, H. (2016). Effects of social support on athletes’ psychological well-being: The correlations among received support, perceived support, and personality. Psychology 7:1741. doi: 10.4236/psych.2016.713163
Keyes, C. L. (2002). The mental health continuum: From languishing to flourishing in life. J. Health Soc. Behav. 43, 207–222. doi: 10.2307/3090197
Kiliç, T., and Bayköse, N. (2018). The mediator role of family support in relation between continuous anxiety and mental toughness in athletes. Turkish Online J. Educ. Technol. 17, 769–773.
Kuok, A. C., Chio, D. K., and Pun, A. C. (2021). Elite athletes’ mental well-being and life satisfaction: a study of elite athletes’ resilience and social support from an Asian unrecognised National Olympic Committee. Health Psychol. Rep. 10, 302–312. doi: 10.5114/hpr.2021.107073
Küttel, A., and Larsen, C. H. (2020). Risk and protective factors for mental health in elite athletes: A scoping review. Int. Rev. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 13, 231–265. doi: 10.1080/1750984X.2019.1689574
Latif, R. A., Majeed, H. A., Tumijan, W., Tajri, A. A., Rajli, M. A., Hidayat, Y., et al. (2024). Enhancing athletic well-being: Unravelling the impact of social support. Information Manag. Bus. Rev. 16, 248–256. doi: 10.22610/imbr.v16i3(I).3796
Lavallée, L., and Flint, F. (1996). The relationship of stress, competitive anxiety, mood state, and social support to athletic injury. J. Athletic Training 31, 296–299.
Lei, H., Cui, Y., and Zhou, W. (2018). Relationships between student engagement and academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Soc. Behav. Pers. Int. J. 46, 517–528. doi: 10.2224/sbp.7054
Lisinskiene, A., and Lochbaum, M. (2022). The coach–athlete–parent relationship: The importance of the sex, sport type, and family composition. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:4821. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19084821
Liu, Z., Zhao, X., Zhao, L., and Zhang, L. (2023). Relationship between perceived social support and mental health among Chinese college football athletes: A moderated mediation model. BMC Psychol. 11:329. doi: 10.1186/s40359-023-01357-2
Lu, F. J., Lee, W. P., Chang, Y.-K., Chou, C.-C., Hsu, Y.-W., Lin, J.-H., et al. (2016). Interaction of athletes’ resilience and coaches’ social support on the stress-burnout relationship: A conjunctive moderation perspective. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 22, 202–209. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2015.08.005
Mahindru, A., Patil, P., and Agrawal, V. (2023). Role of physical activity on mental health and well-being: A review. Cureus 15:e33475. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33475
Malinauskas, D. R., and Malinauskiene, V. (2018). The mediation effect of perceived social support and perceived stress on the relationship between emotional intelligence and psychological wellbeing in male athletes. J. Hum. Kinetics 65, 291–303. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2018-0017
Mikesell, M., Petrie, T. A., Chu, T. L. A., and Moore, E. W. G. (2023). The relationship of resilience, self-compassion, and social support to psychological distress in women collegiate athletes during COVID-19. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 45, 224–233. doi: 10.1123/jsep.2022-0262
Mira, T., Jacinto, M., Costa, A. M., Monteiro, D., Diz, S., Matos, R., et al. (2023). Exploring the relationship between social support, resilience, and subjective well-being in athletes of adapted sport. Front. Psychol. 14:1266654. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1266654
Nuetzel, B. (2023). Coping strategies for handling stress and providing mental health in elite athletes: A systematic review. Front. Sports Act. Living 5:1265783. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2023.1265783
Page, M. J., Mckenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. bmj 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
Pan, H.-W., Huang, W.-Y., and Wu, C.-E. (2022). Research on the relationships among the gender consciousness, social support, and wellbeing in Taiwan college female athletes. SAGE Open 12:21582440221097895. doi: 10.1177/21582440221097895
Peng, J., Zhang, J., Zhao, L., Fang, P., and Shao, Y. (2020). Coach–athlete attachment and the subjective well-being of athletes: A multiple-mediation model analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:4675. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17134675
Peterson, R. A., and Brown, S. P. (2005). On the use of beta coefficients in meta-analysis. J. Appl. Psychol. 90, 175–181. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.90.1.175
Poucher, Z., Tamminen, K., Sabiston, C., Cairney, J., and Kerr, G. (2021). Prevalence of symptoms of common mental disorders among elite Canadian athletes. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 57:102018. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2021.102018
Price, M. S., and Weiss, M. R. (2000). Relationships among coach burnout, coach behaviors, and athletes’ psychological responses. Sport Psychol. 14, 391–409. doi: 10.1123/tsp.14.4.391
Reardon, C. L. (2021). The mental health of athletes: Recreational to elite. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 20, 631–637. doi: 10.1249/JSR.0000000000000916
Ryska, T. A., and Yin, Z. (1999). Testing the buffering hypothesis: Perceptions of coach support and pre-competitive anxiety among male and female high school athletes. Curr. Psychol. 18, 381–393. doi: 10.1007/s12144-999-1011-5
Şenel, E., Küttel, A., Adiloğullari, İ, and Jowett, S. (2025). Psychological predictors of mental well-being in Judo athletes: Exploring the impacts of the coach-athlete relationship, social support, and psychological safety. Psychol. Sport Exerc. 79:102850. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2025.102850
Simons, E. E., and Bird, M. D. (2023). Coach-athlete relationship, social support, and sport-related psychological well-being in National collegiate athletic association division I student-athletes. J. Study Sports Athletes Educ. 17, 191–210. doi: 10.1080/19357397.2022.2060703
Solmaz, S. (2025). Enhancing subjective well-being in young professional athletes: The role of self-esteem and perceived social support in moderating neuroticism. SAGE Open 15:21582440251323673. doi: 10.1177/21582440251323673
Stevens, M., Cruwys, T., Olive, L., and Rice, S. (2024). Understanding and improving athlete mental health: A social identity approach. Sports Med. 54, 837–853. doi: 10.1007/s40279-024-01996-4
Sullivan, M., Moore, M., Blom, L. C., and Slater, G. (2020). Relationship between social support and depressive symptoms in collegiate student athletes. J. Study Sports Athletes Educ. 14, 192–209. doi: 10.1080/19357397.2020.1768034
Sun, R., Li, T., Li, M., and Meng, L. (2025). The effects of tennis on depressive symptoms and pro-social behaviors in university students: The mediating role of appreciative social support. Front. Psychol. 16:1428977. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1428977
Van Raalte, L. J., and Posteher, K. A. (2019). Examining social support, self-efficacy, stress, and performance, in US Division I collegiate student-athletes’ academic and athletic lives. J. Study Sports Athletes Educ. 13, 75–96. doi: 10.1080/19357397.2019.1635419
Wang, J., Mann, F., Lloyd-Evans, B., Ma, R., and Johnson, S. (2018). Associations between loneliness and perceived social support and outcomes of mental health problems: A systematic review. BMC Psychiatry 18:156. doi: 10.1186/s12888-018-1736-5
Wezyk, A. (2011). Relationships between competitive anxiety, social support and self-handicapping in youth Sport. Biomed. Hum. Kinetics 3, 72–77. doi: 10.2478/v10101-011-0016-3
Zentgraf, K., Musculus, L., Reichert, L., Will, L., Roffler, A., Hacker, S., et al. (2024). Advocating individual-based profiles of elite athletes to capture the multifactorial nature of elite sports performance. Sci. Rep. 14:26351. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76977-8
Zhao, L., Liu, Z., and Zhang, L. (2022). The effect of the perceived social support on mental health of Chinese college soccer players during the COVID-19 lockdown: The chain mediating role of athlete burnout and hopelessness. Front. Psychol. 13:1001020. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1001020
Keywords: social support, mental health, wellbeing, anxiety, depression, stress
Citation: Luo J, Du R, Wang X and Luo L (2025) The relationship between social support and mental health in athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Psychol. 16:1642886. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1642886
Received: 07 June 2025; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 03 September 2025.
Edited by:
Pedro Forte, Higher Institute of Educational Sciences of the Douro, PortugalReviewed by:
Artan R. Kryeziu, University of Pristina, AlbaniaRozita Abdul Latif, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Luo, Du, Wang and Luo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaolin Wang, d3hsMjMyNDEyQDE2My5jb20=; Liang Luo, MjAyNDEwMkB3aHN1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Jianing Luo1
Jianing Luo1 Xiaolin Wang
Xiaolin Wang