Shape-shifting worm blob model could inspire future robot swarms
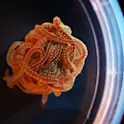
By Mischa Dijkstra, Frontiers science writer ‘Blob’ of Lumbriculus variegatus blackworms. The half-circle to the right is the edge of a petri dish. Image credit: Harry Tuazon Lumbriculus variegatus blackworms can aggregate into ‘blobs’ capable of collective movement. Researchers observed blackworms to model the behavior of individual worms, as well as the formation and movement of blobs. They showed that effective collective movement can only emerge when there is a balance between ‘clinginess’ and independent movement. These results may serve as a model to study other systems with emergent properties, such as nets of biopolymers. Blackworms (Lumbriculus variegatus) are distant relatives of rainworms, measuring up to 10 cm long. They live in shallow marshes, ponds, and swamps in Europe and North America, where they feed on microorganisms and debris. To protect themselves from drought, blackworms can aggregate as entangled, shape-shifting ‘blobs’ composed of a few to hundreds of individuals. Just like swarms of bees, rafts of fire ants, or flocks of starlings, blackworm blobs can show ‘intelligent’ collective movement. Now, scientists show that effective collective movement can only emerge in blackworm blobs when conditions are just right – in particular, when there is a balance between the activity and ‘clinginess’ […]