Abstract
Bacteria have developed increasing resistance to currently used antimicrobial agents. New classes of antimicrobial drugs are urgently required to fight drug-resistant pathogens. Here, we designed and synthesized a series of calix[4]arene derivatives as antibacterial agents by biomimicking the structural properties and biological functions of antibacterial peptides. After introducing cationic hydrophilic moieties and preliminary structural optimization, we obtained a lead compound (16) that exhibited excellent antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, low toxicity toward mammalian cells and poor hemolytic activity. The antibacterial mechanism studies showed that compound 16 can destroy bacterial cell membrane directly, leading to bacterial death and a low tendency to develop bacterial resistance.
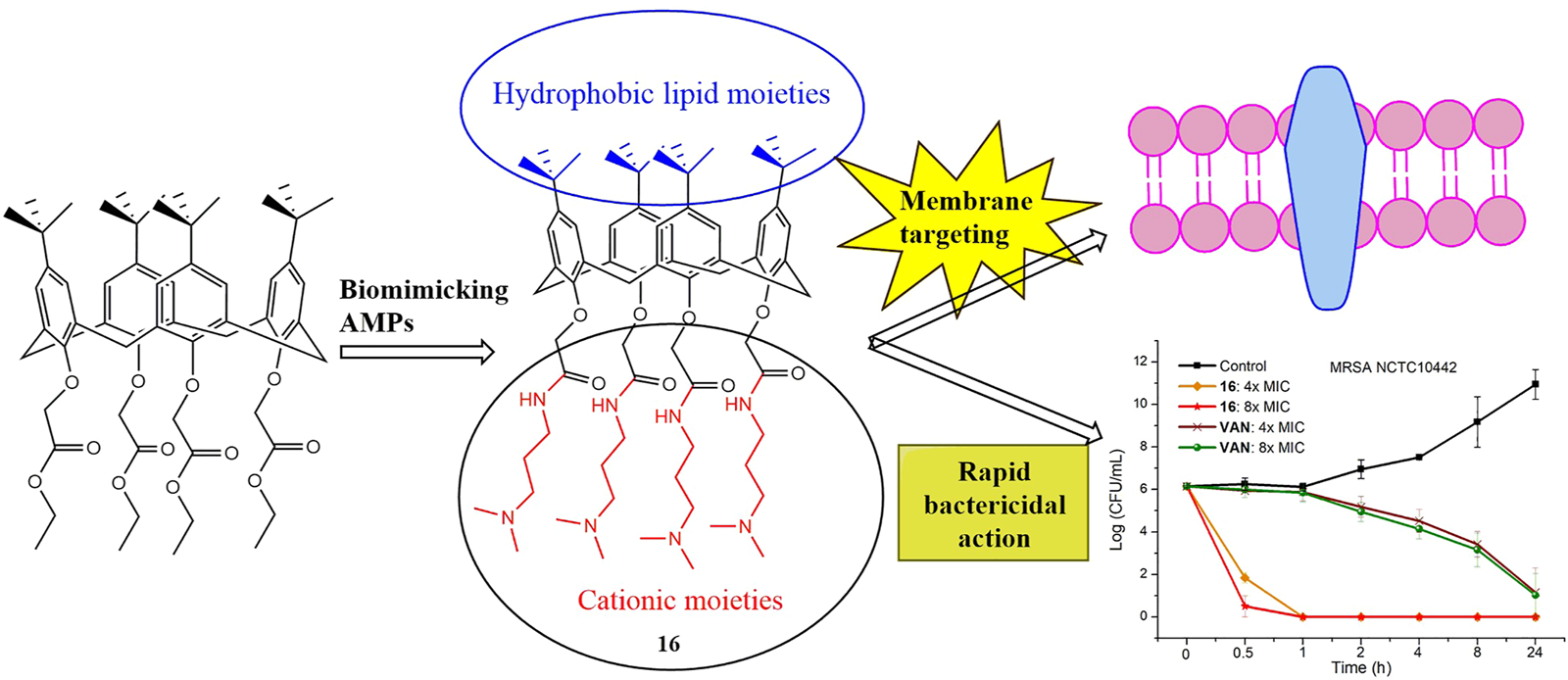
Graphical Abstract
Introduction
The development of multi-drug resistant bacteria and the decrease in the discovery of new antibiotics pose a major threat to public health in the 21st century (Lyddiard et al., 2016; Woolhouse et al., 2016; Monserrat-Martinez et al., 2019). In addition, due to the rapid development of antimicrobial resistance, short medication cycle, and low profits of antimicrobial agents, many pharmaceutical companies have greatly reduced their investment in the development of antimicrobial agents, which could slow the discovery of new antibiotics (Livermore, 2011; Rogers et al., 2012). The ESKAPE pathogens, including Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter spp., are spreading and becoming more resistant to many commonly used antibacterial agents (Rice, 2008). Currently, most newly approved antibiotics are likely to develop rapid resistance as most of them belong to known classes of antibiotics, based on the molecular scaffolds of traditional antibiotics (Molchanova et al., 2017). In 2017, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a priority list of drug-resistant pathogens to guide the development of new antibiotics and warned that there was a serious lack of new antibiotics to treat the growing number of drug-resistant infections (Kmietowicz, 2017). Antimicrobial resistance causes increases in mortality, morbidity, length of hospitalization and cost of healthcare (Maragakis et al., 2008). If effective measures are not taken to combat antibiotic resistance, we will return to the “pre-antibiotic era,” and most surgical procedures will not be safe to implement.
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), also known as host defense peptides, exist in various life forms from microorganisms to humans. Most of them are positively charged and possess broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacteria, viruses and fungi (Koh et al., 2015; Lázár et al., 2018; Arbour et al., 2020; Thapa et al., 2020). Compared with conventional antibiotics, AMPs have several obvious advantages, such as rapid bactericidal action (Li et al., 2017), immunomodulatory activity (Jenssen et al., 2006), synergistic effects with antibacterial agents (Zasloff, 2002), and low probability of developing bacterial resistance (Wimley and Hristova, 2011). However, the progress in the clinical application of AMPs has been hindered by the sensitivity to proteolytic enzymes, poor in vivo efficacy and poor pharmacokinetic properties (Adessi and Soto, 2002; Marr et al., 2006; Costa et al., 2019). Small peptidomimetics that mimic the chemical structure and biological function of AMPs can avoid most of the defects of AMPs (Hickey et al., 2015; Nizalapur et al., 2017). Several small peptidomimetics have shown great application potential, such as Brilacitine and LTX-109 that have successfully entered or completed Phase II clinical trials (Isaksson et al., 2011; Mensa et al., 2014; Kowalski et al., 2016; Kuppusamy et al., 2019).
Calixarene derivatives have been found to contain various biological activities, such as antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal and anticancer activities (Yousaf et al., 2015; Nasuhi Pur, 2016). In addition, they do not display obvious cytotoxicity and immunogenicity (Ma and Zhao, 2015; Pur, 2021). Due to their versatility, low cost and unique three-dimensional structures, calixarene could serve as an ideal molecular scaffold for the design and optimization of drug molecules (Hanna et al., 2003; Mokhtari and Pourabdollah, 2013). Calix[4]arene derivatives have attracted special attention owing to the cheap and easy availability, unique structural characteristics and easy modification (Naseer et al., 2017; Bono et al., 2018). The functionalized basket cavity of calix[4]arene is suitable for small ions and neutral molecules, and calix[4]arene can provide excellent conditions for the incorporation of other moieties via the hydroxyl groups (Naseer et al., 2017). The antitumor agent calix[4]arene compound OTX008 that targets human galectin-1 is being evaluated in phase I clinical trial, indicating that calixarene has great potential as a molecular skeleton of drugs (Läppchen et al., 2015). However, to our knowledge, there are no other calixarene-based drugs have entered clinical trials at present (Nimse and Kim 2013). As reported, calixarene derivatives have great potential as antibacterial agents and could avoid cross-resistance with existing antibacterial agents due to their different molecular structures from existing antibacterial agents (Shurpik et al., 2020).
In this work, by biomimicking AMPs, we designed and synthesized a series of calix[4]arene derivatives as membrane-active antibacterial agents. The most promising compound 16 showed potent antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). No bacterial resistance was observed for compound 16 in the laboratory simulation of the drug resistance study. The commercial reagents 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene, and tetraethyl 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-O,O′,O″,O‴-tetraacetate were used as the starting materials, and then cationic moieties were introduced to the calix[4]arene scaffold to form cationic amphiphilic structures. The introduced cationic moieties are beneficial to identify bacterial cells, which can promote the interaction between cationic calix[4]arene compounds and negatively charged bacterial membranes via electrostatic action, while the hydrophobic tert-butyl groups can facilitate the insertion of calix[4]arene compounds into bacterial phospholipid bilayer membranes, leading to the change in the permeability of bacterial cell membranes and the death of bacteria. The difference in cell membrane composition between eukaryotes and bacteria is very conducive to improving the selectivity of cationic amphiphilic calix[4]arene derivatives. Bacterial membranes are rich in anionic lipids (Malmsten, 2014), while the membrane surfaces of eukaryotes mainly contain zwitterionic phospholipids including phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, and sphingomyelin (Pasupuleti et al., 2012). After a series of structural modifications, the cationic hydrophilic moieties of calix[4]arene derivatives were fine-tuned to obtain potent antibacterial agents with good antibacterial activity and low toxicity. Finally, the time-kill kinetics, drug resistance development, in vitro cytotoxicity toward mammalian cells, and the antibacterial mechanism were studied. These findings suggest that this design strategy for calix[4]arene-based AMPs mimics is very conducive to developing new antibacterial agents to fight drug-resistant bacteria.
Results and Discussion
Design and Synthesis of Calix[4]arene-Based Antibacterial Derivatives
The synthetic routes for synthesizing various amphiphilic calix[4]arene analogs are shown in Schemes 1, 2. The starting material 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene was treated with epibromohydrine together with K2CO3 to yield intermediate compound 2. Compounds 3–12 were then obtained by the treatment of compound 2 with corresponding amines. Polyamine compounds often become polycations at physiological pH and then exert their biological activity. The Nitrogen atoms containing lone pairs of electrons in polyamines are easily protonated to be positively charged. Compound 3 was coupled with iodomethane to afford compound 13. The starting materials tetraethyl 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-O,O′,O″,O‴-tetraacetate was hydrolyzed by LiOH to produce compound 15. Then the acid 15 was reacted with 3-dimethylaminopropylamine in the presence of 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride (DMTMM) to provide compound 16. In fact, we initially planned to design and synthesize a four-arm modified intermediate epoxy compound 2a (Scheme 3), and then 2a reacted with the corresponding amines to prepare a series of amphiphilic cationic four-arm modified calixarene derivatives as antibacterial compounds (Scheme 3). We tried many different conditions, but failed to synthesize 2a. All synthesized compounds were characterized by H NMR, C NMR, and HRMS.
SCHEME 1
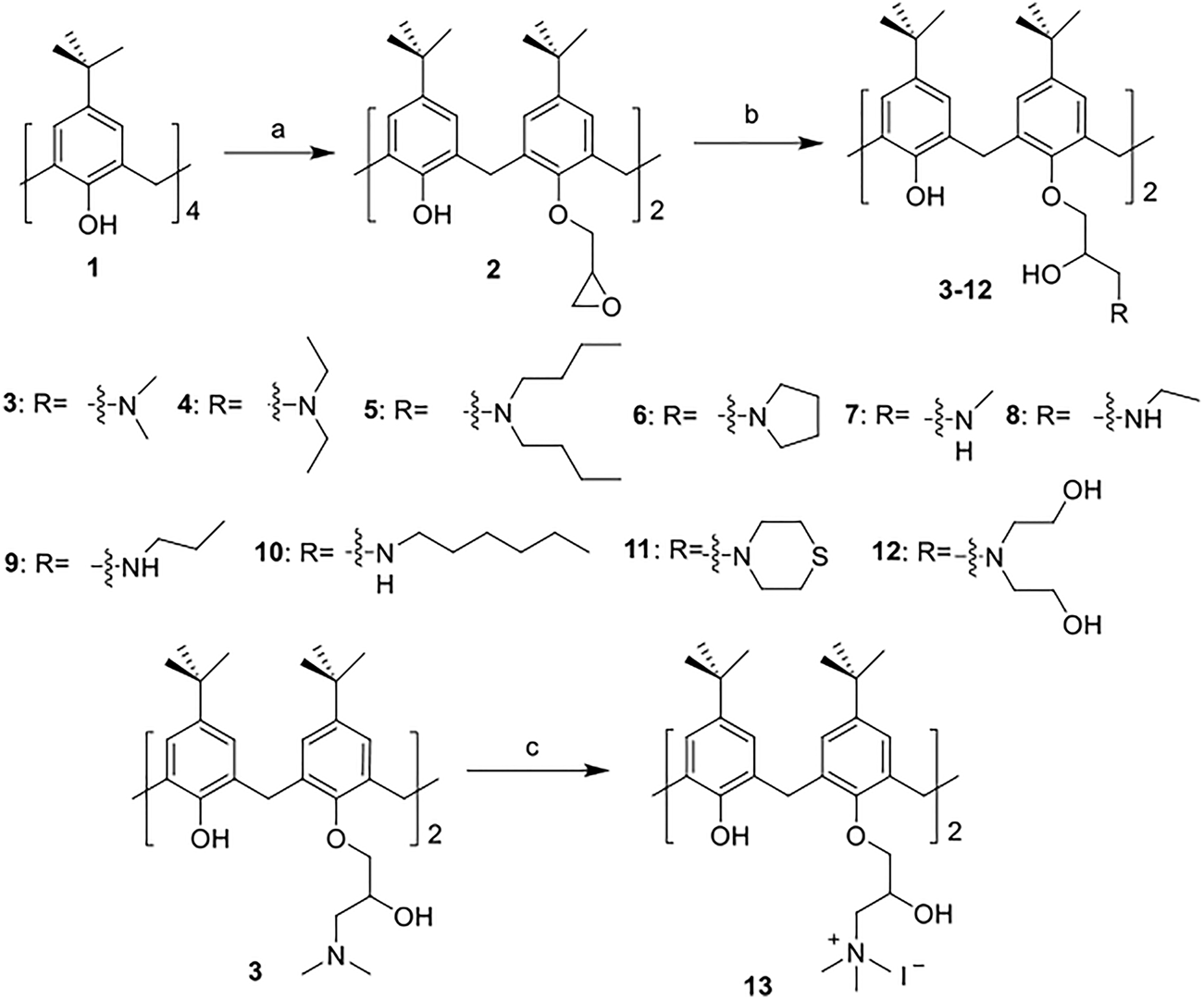
Synthesis of cationic amphiphilic calix[4]arene derivatives 2–13. Reagents and conditions: (a) epibromohydrin, KI, K2CO3, acetonitrile, 85°C, reflux, 10–12 h (b) corresponding amines, CH3OH, 65°C, reflux, 3 h. (c) Iodomethane, CH3OH, room temperature (RT), overnight.
SCHEME 2
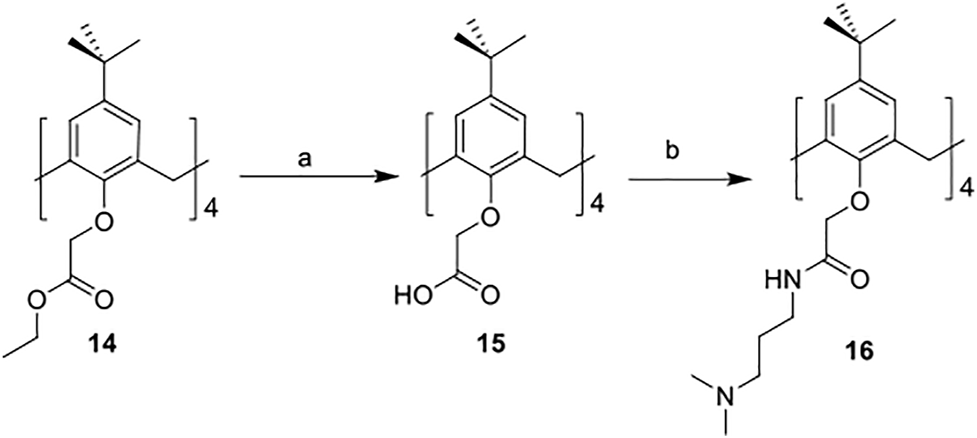
Synthesis of cationic amphiphilic calix[4]arene derivatives 15–16. Reagents and conditions: (a) LiOH, THF/water, RT, 1.5 h (b) 3-dimethylaminopropylamine, DMTMM, DIPEA, DMF, RT, 12 h.
SCHEME 3
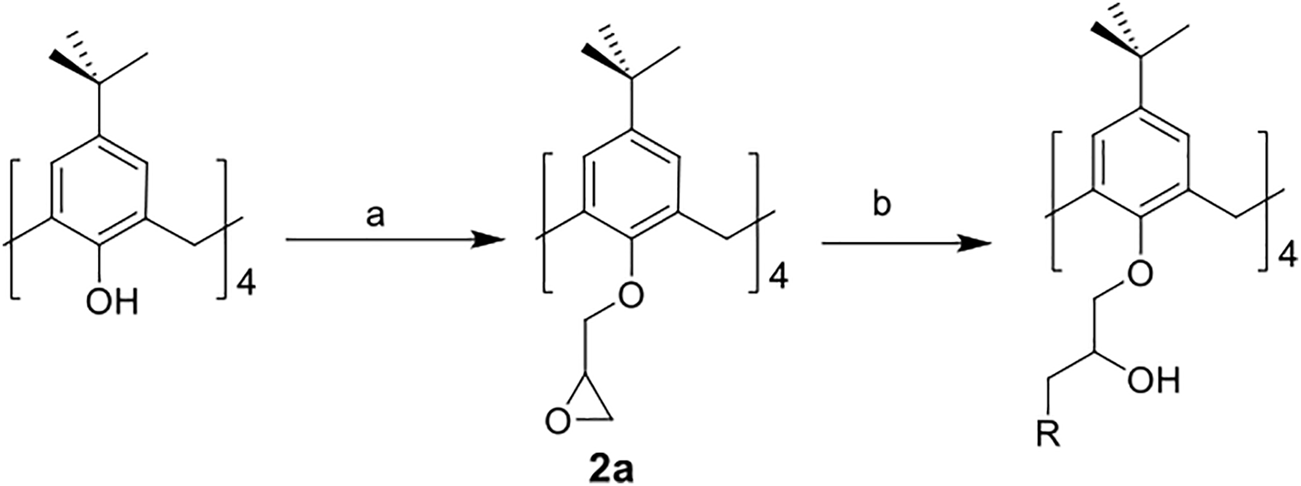
Synthesis of calix[4]arene derivative 2a. Reagents and conditions: (a) epibromohydrin, KI, K2CO3 or potassium tert-butoxide, acetonitrile, 85°C, reflux. (b) corresponding amines, CH3OH, 65°C, reflux.
In Vitro Antibacterial and Hemolytic Activity
The in vitro antibacterial activity of the calix[4]arene derivatives was evaluated against three Gram-positive bacteria, including S. aureus ATCC29213, MRSA NCTC10442 and MRSA N315. The in vitro antibacterial activity was assessed by minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). The HC50 value (concentration of compounds required to lyse 50% of rabbit red blood cells) was used to evaluate the hemolytic activity of the synthesized compounds toward rabbit red blood cells (Table 1).
TABLE 1
| Compound | MIC, µg/ml (µM) | HC50, µg/ml (µM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus ATCC29213 | MRSA N315 | MRSA NCTC10442 | ||
| 1 | >50 (>77) | >50 (>77) | >50 (>77) | >200 (>308) |
| 2 | >50 (>66) | >50 (>66) | >50 (>66) | >200 (>263) |
| 3 | 13 (15) | 13 (15) | 13 (15) | >200 (>235) |
| 4 | 25 (28) | 13 (14) | 25 (28) | >200 (>220) |
| 5 | >50 (>49) | >50 (>49) | >50 (>49) | >200 (>196) |
| 6 | 50 (55) | 50 (55) | >50 (>55) | >200 (>221) |
| 7 | 4.7 ± 2 (5.7 ± 2) | 1.6 (1.9) | 3.1 (3.8) | 151 ± 5 (183 ± 6) |
| 8 | 1.6 (1.8) | 1.2 ± 0.4 (1.4 ± 0.5) | 1.6 (1.8) | 123 ± 8 (144 ± 9) |
| 9 | 2.3 ± 0.8 (2.6 ± 0.9) | 2.3 ± 0.8 (2.6 ± 0.9) | 4.7 ± 2 (5.3 ± 2) | 191 ± 2 (217 ± 3) |
| 10 | >50 (>52) | >50 (>52) | >50 (>52) | >200 (>208) |
| 11 | >50 (>52) | >50 (>52) | >50 (>52) | >200 (>207) |
| 12 | >50 (>52) | >50 (>52) | >50 (>52) | >200 (>206) |
| 13 | 3.1 (2.8) | 3.1 (2.8) | 3.1 (2.8) | 16 ± 1 (14 ± 1) |
| 14 | >50 (>50) | >50 (>50) | >50 (>50) | >200 (>201) |
| 16 | 1.6 (1.3) | 1.6 (1.3) | 3.1 (2.6) | >200 (>164) |
| vancomycin | 0.78 (0.50) | 1.6 (1.1) | 1.6 (1.1) | NDa |
In vitro anti-Gram-positive bacterial activities and hemolytic activities of calix[4]arene derivatives 1–16.
Not determined.
To investigate the effects of different secondary amine substituents on the antibacterial and hemolytic activities of the calix[4]arene derivatives, compounds 7–10 were synthesized. Compounds 7–9 displayed good antibacterial activities against Gram-positive bacterial strains tested (MICs = 1.2–4.7 μg/ml) and weak hemolytic activity, with HC50 values in the range of 123–191 μg/ml. However, n-hexylamine-coupled compound 10, a more hydrophobic compound, showed very poor antibacterial activity (MICs > 50 μg/ml) and very poor hemolytic activities (HC50 > 200 μg/ml). The anti-Gram-positive bacterial activities of these compounds are determined by the hydrophobic side chains connected to positive charge centers. These results suggested that the secondary amine substituents with short hydrophobic side chains can greatly improve the antibacterial activity of calix[4]arene derivatives, and also slightly increase the hemolytic activity of calix[4]arene derivatives.
Next, compounds 3–6, 11–12, and 16 were used to explore the effects of different types of tertiary amine substitutions on the hemolytic and antibacterial activity of amphiphilic calix[4]arene derivatives. Dimethylamine-coupled compound 3 and diethylamine-coupled compound 4 showed moderate antibacterial activity (MICs = 13–25 μg/ml). However, dibutylamine-coupled compound 5 did not display any antibacterial activities even at the highest tested concentration of 50 μg/ml. This result indicated that tertiary amine substituted calix[4]arene derivatives with long alkyl side chains would lead to a significant decrease or even loss in biological activity. When introducing pyrrolidine (6), very weak antibacterial activity was observed (MICs ≥ 50 μg/ml). 3-Dimethylaminopropylamine-containing compound 16 with four-arm functionalization displayed enhanced antibacterial activity, with MICs in the range of 1.6–3.1 μg/ml. Compound 16 was also used to investigate the effect of four-arm modification and two-arm modification on the biological activity of amphiphilic cationic calixarene derivatives. We found that the membrane selectivity of four-arm modified compound 16 was higher than that of two-arm modified calixarene derivatives. Owing to the low pKa value of the introduced cationic group, compound 11 containing thiomorpholine (pKa of free thiomorpholine = 9.0) (Jones et al., 2017), and compound 12 containing diethanolamine (pKa of free diethanolamine = 8.9) (Singh et al., 2011), exhibited very poor antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria (MICs > 50 μg/ml). It manifested that the amine substituents with low pKa value were harmful to the antibacterial activity of calix[4]arene derivatives. No hemolytic activity (HC50 > 200 μg/ml) was observed for these eight compounds, suggesting that tertiary amine substitutions had little effect on the hemolytic activity of calix[4]arene derivatives. Tertiary amine 3 was reacted with iodomethane to yield quaternary ammonium salt 13 that was used to investigate the effect of quaternary ammonium salt substitution on the antibacterial and hemolytic activities of amphiphilic calix[4]arene derivatives. Compared with the precursor compound 3, both the activity against Gram-positive bacteria and the hemolytic activity of compound 13 increased obviously, with MICs of 3.1 μg/ml and HC50 of 16 ± 1 μg/ml. These results suggested that quaternary ammonium salt substitutions had a significant effect on the antibacterial activity and hemolytic activity of calix[4]arene derivatives.
From the preliminary structure-activity relationship (SAR) study of amphiphilic calix[4]arene derivatives, we found that several structural parameters have significant effects on the antibacterial and hemolytic activities, including the types of amine substituents, the length of the carbon chain connected to the positive charge center and the pKa value of the cationic group. The introduction of amine groups with long hydrophobic side chains would lead to the loss in antibacterial activity of calix[4]arene compounds (MIC > 50 μg/ml). In addition, poor antibacterial activity was observed when low pKa amine groups were incorporated. 3-Dimethylaminopropylamine coupled compound 16 displayed excellent anti-Gram-positive bacterial activity (MICs = 1.6–3.1 μg/ml) and very weak hemolytic activity (HC50 > 200 μg/ml). The cationic moieties play an important role in the interaction with negatively charged bacterial membranes. The incorporation of cationic groups enables the cationic calix[4]arene derivatives to act on negatively charged bacterial cell membranes through electrostatic interaction, which is helpful for calix[4]arene derivatives to distinguish bacterial cell membranes from mammalian cell membranes. Among all the synthesized compounds, only compound 16 with four-arm tertiary amines functionalized showed excellent antimicrobial activity and very poor hemolytic activity.
Time-Kill Kinetics
To investigate the bactericidal performance of calix[4]arene derivatives, we determined the time-kill kinetics curves of compound 16 against MRSA NCTC10442 at different concentrations (4× and 8× MIC). As shown in Figure 1, compound 16 reduced 4.3 and 5.6 log bacteria (killing > 99.99% of MRSA NCTC10442) within 0.5 h at 4× and 8× MIC, respectively, indicating that compound 16 exhibited rapid bactericidal activity. In contrast, the commercial vancomycin only achieved 1.6 and 2.0 log bacterial reductions within 4 h at 4× and 8× MIC, respectively. These findings indicated that compound 16 showed rapid bactericidal action that will help to reduce the treatment time of bacterial infection and the probability of developing bacterial resistance.
FIGURE 1
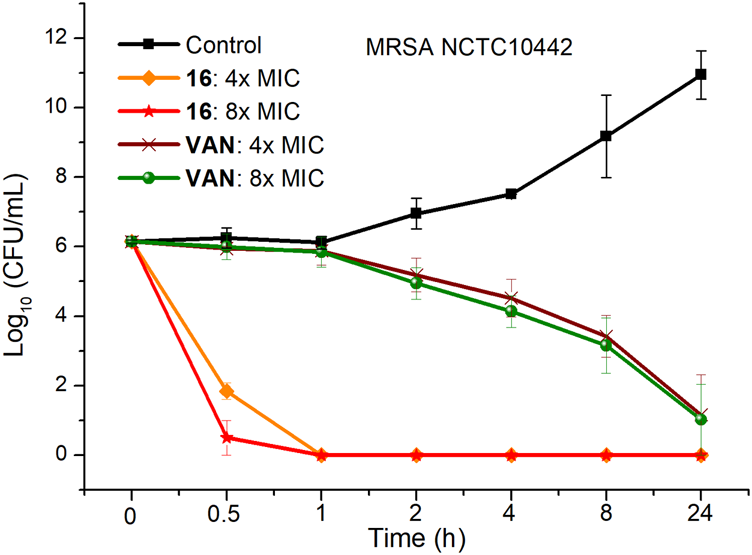
Time-kill kinetics of compound 16 and vancomycin against MRSA NCTC10442.
Resistance Development Study
The ability to overcome bacterial resistance has become an important criterion to evaluate a new antibacterial drug (Gajdács, 2019). The rapid development of bacterial resistance to antimicrobials is a major threat to public health in the 21st century (Walsh, 2000; O’Neill, 2008; Piddock, 2012). The membrane-targeting antibacterial agents can effectively avoid or slow down the development of bacterial resistance. To evaluate the tendency of bacterial resistance of compound 16, a laboratory simulation study on the drug resistance of compound 16 was carried out. In the presence of a sublethal concentration of compound 16 or norfloxacin, S. aureus ATCC29213 was consecutively passaged for 19 days. As shown in Figure 2, after 19 passages, no more than a 4-fold increase in the MIC values was observed for compound 16. In contrast, the MIC value of norfloxacin was increased by 32-fold after 17 passages, indicating that norfloxacin could rapidly induce bacterial resistance. The reason may be that the bacterial membrane is a conservative component in the evolution of bacterial cells and determines the phenotype, it is difficult for bacteria to keep alive with great changes in the composition of the cell membranes (Zasloff, 2002; Yeaman and Yount, 2003). These results demonstrated that compound 16 has obvious advantages over conventional antibacterial drugs, and can avoid the occurrence of developing bacterial resistance.
FIGURE 2
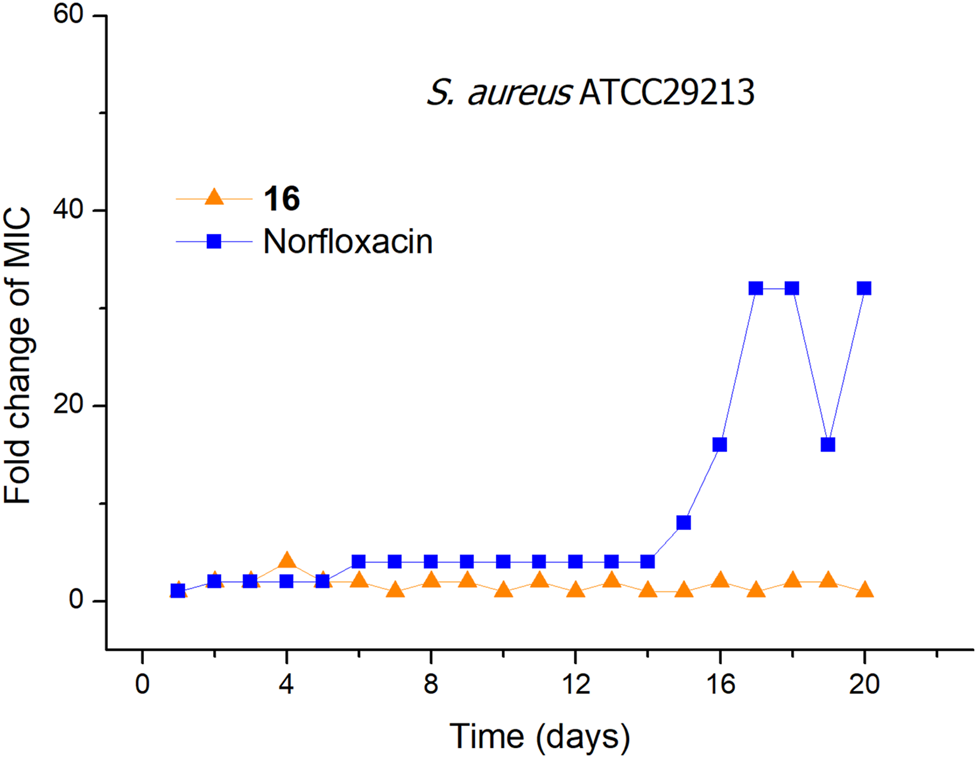
Bacterial resistance studies of compound 16 and norfloxacin against S. aureus ATCC29213.
Antibacterial Mechanism Studies
The rapid bactericidal action of compound 16 may be based on the membrane-active mode of action. To verify this hypothesis, SYTOX Green dye was used to study the effect of compound 16 on the bacterial cell membrane. SYTOX Green is a green nucleic acid dye that can easily penetrate the damaged bacterial cell membrane but cannot penetrate the living cell membrane with a complete membrane structure (Roth et al., 1997; Thakur et al., 2015). After binding with intracellular nucleic acid, its fluorescence intensity will be significantly enhanced. As shown in Figure 3, when MRSA NCTC10442 were treated with compound 16 at four different concentrations (1×, 2×, 4× and 8× MIC), the fluorescence intensity increased notably. The results indicated that compound 16 could increase the permeability of Gram-positive bacterial cell membrane, and then destroy the integrity of bacterial cell membranes, causing the leakage of the cellular contents and bacterial cell death.
FIGURE 3
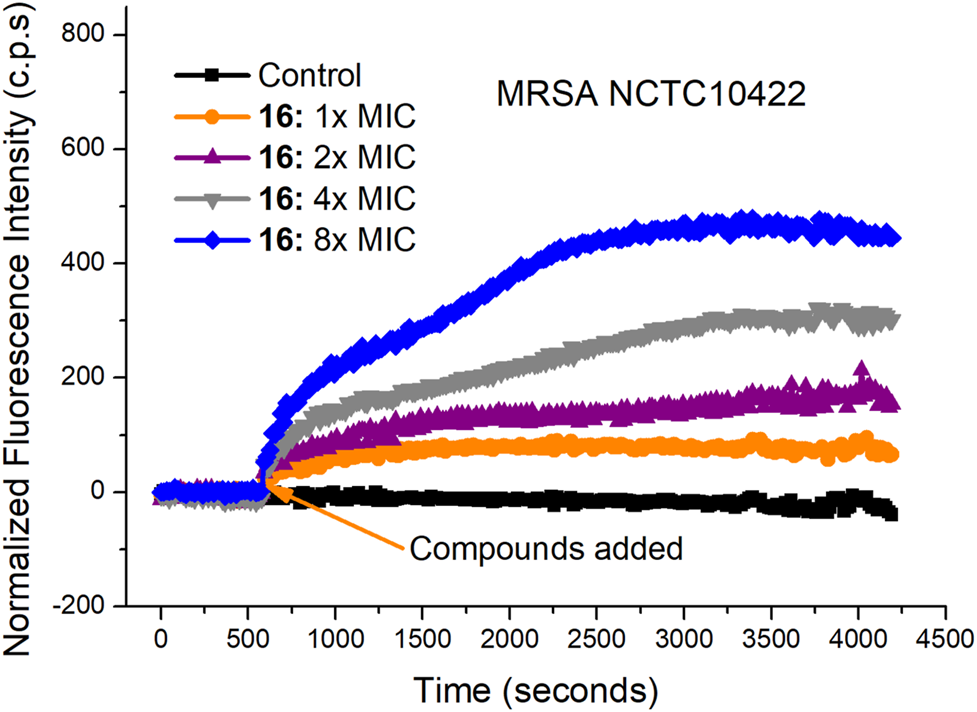
Cytoplasmic membrane permeabilization of compounds 16 against MRSA NCTC10442.
The interaction between compound 16 and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) which was one of the main components of Gram-positive bacteria was also explored. The binding affinity between compound 16 and LTA was determined using the BODIPY-TR-cadaverine displacement assay. The fluorescence intensity of the probe was quenched when it was bound to LTA (Swain et al., 2019). When the probe is replaced by compound 16 and dissolved in solution, the fluorescence will be significantly enhanced. As shown in Figure 4, a proper amount of BODIPY-TR-cadaverine (30 ± 5%) was replaced by 1× MIC compound 16 from LTA. And compound 16 can replace a considerable amount of BODIPY-TR-cadaverine from LTA at 16× MIC (67 ± 2%), indicating that compound 16 could interact with LTA on the bacterial surface via a concentration-dependent manner.
FIGURE 4
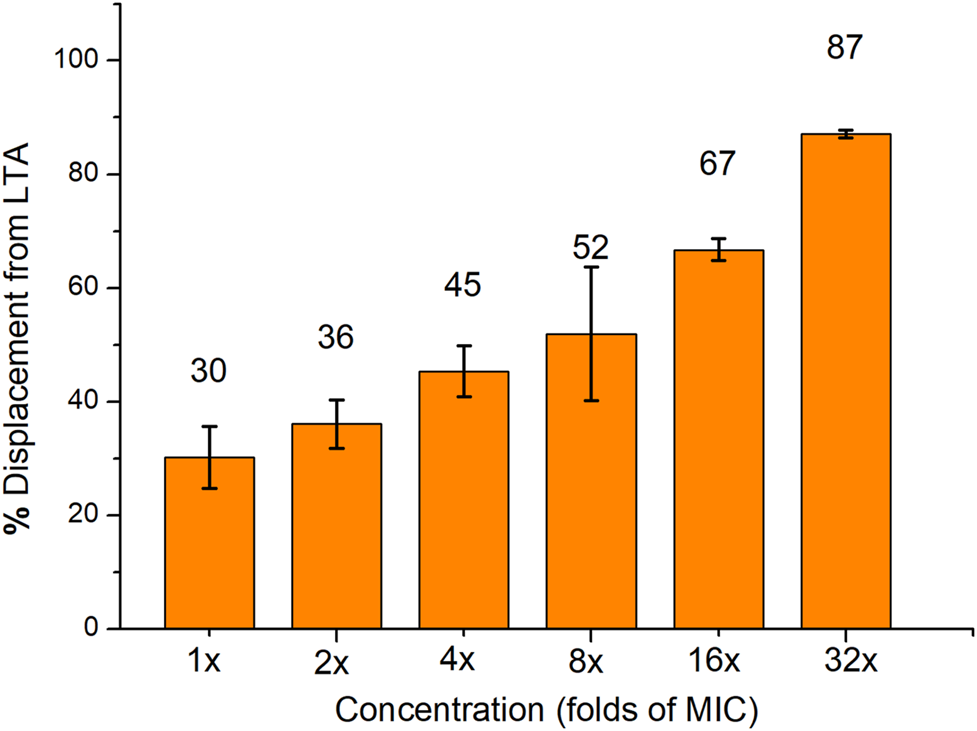
The displacement of BODIPY-TR-cadaverine from LTA was caused by compound 16. Data are presented as the average value of two independent experiments.
In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation
An important parameter in the development of antimicrobial drugs is their ability to selectively act on microbial cells rather than mammalian cells. CCK-8 assay was used to evaluate the in vitro cytotoxicity of compound 16 toward mammalian cells (mouse fibroblast NCTC clone 929). As shown in Figure 5, compound 16 showed very low cytotoxicity toward mouse fibroblast NCTC clone 929 cells at the concentration of ≤ 25 μg/ml (8–16× MIC). 72 ± 6% viability of mouse fibroblasts was observed for compound 16 at 25 μg/ml. In general, when considering the low MIC values of compound 16 against Gram-positive bacterial strains, these cytotoxicity results are very encouraging.
FIGURE 5
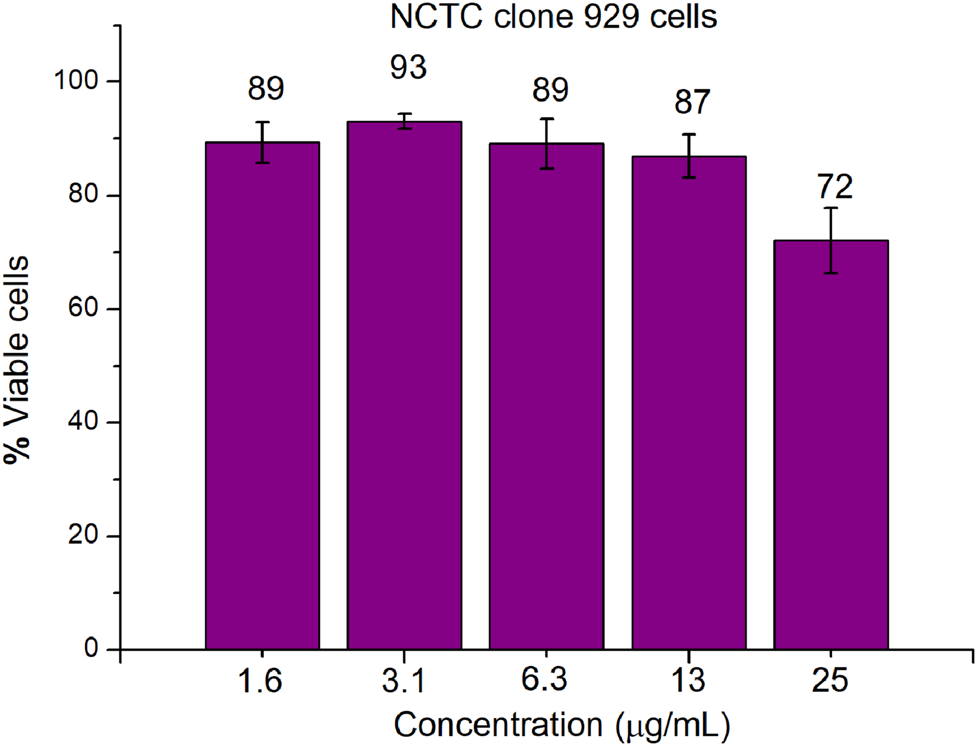
Cytotoxicity of compound 16 against mouse NCTC clone 929 cells using CCK-8 assays.
Conclusion
In summary, we have designed and synthesized a series of calix[4]arene-based antibacterial agents, and have evaluated the in vitro antibacterial and hemolytic activity of these synthesized compounds. The incorporation of different cationic groups can effectively improve the antibacterial activity of calix[4]arene derivatives. The most promising compound 16 showed excellent activity against all tested Gram-positive bacterial strains. The antibacterial mechanism studies have shown that compound 16 could destroy the integrity of Gram-positive bacteria, causing the leakage of cell contents and leading to bacterial cell deaths. Membrane active mode of action and rapid bactericidal ability can effectively reduce the probability of bacterial drug resistance. In general, we have synthesized a class of calix[4]arene derivatives as membrane-active antibacterial agents, which provided a new design idea for the development of new membrane-active antibacterial agents.
Materials and Methods
Chemistry
All chemicals and solvents were purchased from commercial suppliers and used directly without further purification. 4-Tert-butylcalix[4]arene, and tetraethyl 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-O,O′,O″,O‴-tetraacetate were purchased from Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. The completion of all reactions was monitored by thin-layer chromatography (Merck silica gel 60 F254). 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on the JEOL 400 MHz spectrometer operating at frequencies of 400 and 100 MHz, respectively. Chemical shifts (δ) are given in ppm, and coupling constants (J) are given in Hz. HRMS spectra were recorded on a Thermo DFS mass spectrometer. The final products were purified by preparative high-performance liquid chromatography on an Agilent 1260 Integrated system (C18 column, YMC-Pack, 20 mm × 150 mm, 5 µm), using methanol and distilled water (both containing 0.1% formic acid) as the gradient elution.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(oxiran-2-ylmethoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (2)
4-Tert-butylcalix[4]arene (200 mg, 0.31 mmol) was dissolved in anhydrous acetonitrile by ultrasonic, and then epibromohydrin (202 μl, 2.5 mmol), potassium iodide (20 mg, 0.12 mmol) and potassium carbonate (170 mg, 1.2 mmol) were added. The reaction mixture was refluxed at 85°C overnight. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was diluted with ethyl acetate and washed twice with water. The organic phase was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was purified by silica gel chromatography (petroleum ether: ethyl acetate, 4:1, v:v) to give compound 2 as a white solid (141 mg, 70%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.18–7.09 (m, 2H), 7.08–7.03 (m, 4H), 6.81 (s, 4H), 4.37–4.21 (m, 6H), 4.10–4.03 (m, 2H), 3.55 (s, 2H), 3.37–3.28 (m, 4H), 3.11–2.89 (m, 4H), 1.30–1.26 (m, 18H), 1.02–0.92 (m, 18H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.55, 150.50, 149.56, 149.52, 147.25 (2×C), 141.64, 141.61, 141.58, 132.78, 132.66, 132.62, 132.48, 127.93, 127.79, 127.73, 127.64, 125.80, 125.71, 125.59, 125.22, 125.19, 125.15, 125.10, 76.04, 75.75, 60.47, 50.28, 44.77, 44.73, 34.02, 34.01, 33.89 (2×C), 31.75 (6×CH3), 31.62 (2×CH2), 31.59 (2×CH2), 31.07 (6×CH3). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C50H65O6 [M + H]+ 761.4781, found 761.4762.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(3-(dimethylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (3)
To a solution of 2 (38 mg, 0.050 mmol) in methanol (5.0 ml), dimethylamine (1.0 ml) was added, and the reaction mixture was refluxed at 65°C for 3 h. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was directly distilled under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified by HPLC to give compound 3 as a white solid (22 mg, 59%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.19–7.11 (m, 8H), 4.61–4.37 (m, 2H), 4.35–4.24 (m, 4H), 4.23–4.08 (m, 3H), 4.06–3.92 (m, 2H), 3.65–3.36 (m, 6H), 3.22–3.13 (m, 1H), 2.82 (s, 12H), 1.23 (s, 18H), 1.14–1.10 (m, 18H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 149.93, 149.88, 149.04, 148.89, 147.85, 147.71, 142.57, 142.51, 132.80, 132.64, 132.56, 132.47, 127.84, 127.81, 127.79, 127.43, 126.24, 125.96, 125.82, 125.62, 125.49, 125.45, 125.36, 100.00, 78.36, 78.29, 66.13, 65.73, 61.26, 61.17, 44.62 (2×CH3), 44.55 (2×CH3), 34.16, 34.10, 33.95 (2×C), 31.72 (2×CH2), 31.71 (2×CH2), 31.10 (6×CH3), 31.07 (6×CH3). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C54H79N2O6 [M + H]+ 851.5938, found 851.5923.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(3-(diethylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (4)
Compound 4 was prepared from 2 (37 mg, 0.049 mmol) and diethylamine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a white solid (28 mg, 75%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.20 (s, 1H), 7.82–7.72 (m, 1H), 7.10–6.99 (m, 4H), 6.98–6.89 (m, 2H), 6.88 (s, 2H), 4.55–3.87 (m, 10H), 3.45–3.30 (m, 6H), 2.94–2.76 (m, 12H), 1.27–1.24 (m, 18H), 1.18–1.12 (m, 12H), 1.07 (s, 9H), 1.02 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.15, 150.00, 149.96, 149.32, 149.20, 147.64, 147.50, 142.44, 142.39, 142.30, 132.52, 132.41, 132.35, 132.26, 128.03, 127.88, 127.86, 127.66, 126.10, 125.86, 125.73, 125.52, 125.39, 125.33, 78.83, 78.60, 66.10, 65.81, 56.32, 55.95, 47.96 (2×CH2), 47.94 (2×CH2), 34.08, 34.04, 33.96 (2×C), 31.75 (2×CH2), 31.73 (2×CH2), 31.07 (6×CH3), 31.04 (6×CH3), 9.76 (2×CH3), 9.55 (2×CH3). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C58H87N2O6 [M + H]+ 907.6564, found 907.6556.
15,35,55,75-tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(3-(dibutylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52--diol (5)
Compound 5 was prepared from 2 (39 mg, 0.051 mmol) and di-n-butylamine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a brown solid (27 mg, 70%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.21 (s, 1H), 7.77–7.66 (m, 1H), 7.09–7.00 (m, 4H), 6.99–6.86 (m, 4H), 4.59–4.52 (m, 2H), 4.50–3.88 (m, 10H), 3.46–3.26 (m, 4H), 3.05–2.82 (m, 4H), 2.80–2.65 (m, 8H), 1.64–1.46 (m, 8H), 1.39–1.30 (m, 8H), 1.29–1.24 (m, 18H), 1.08 (s, 9H), 1.02 (s, 9H), 0.92 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 12H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.23, 149.93, 149.77, 149.48, 149.21, 147.77, 147.47, 142.55, 142.34, 142.17, 133.25, 132.88, 132.80, 132.70, 128.21, 127.87, 127.74, 127.50, 126.42, 125.92, 125.77, 125.69, 125.47, 125.39, 79.76, 79.28, 67.54, 67.06, 57.38, 56.59, 54.38 (2×CH2), 54.30 (2×CH2), 34.20, 34.12, 33.95, 33.93, 32.51, 32.04, 31.94, 31.74, 31.72 (3×CH3), 31.68 (3×CH3), 31.18 (3×CH3), 31.13 (3×CH3), 28.36 (2×CH2), 28.17 (2×CH2), 20.61 (2×CH2), 20.58 (2×CH2), 14.08 (2×CH3), 14.04 (2×CH3). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C66H103N2O6 [M + H]+ 1,019.7816, found 1,019.7791.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(2-hydroxy-3-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)propoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (6)
Compound 6 was prepared from 2 (35 mg, 0.046 mmol) and tetrahydropyrrole (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a white solid (27 mg, 78%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.59 (s, 1H), 7.41–7.35 (m, 1H), 7.08–6.97 (m, 4H), 6.89–6.76 (m, 4H), 5.78 (br, 4H), 4.64–4.51 (m, 2H), 4.28–3.74 (m, 8H), 3.46–3.15 (m, 16H), 2.11–1.99 (m, 8H), 1.29–1.24 (m, 18H), 1.00 (s, 9H), 0.97 (s, 9H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.10, 150.05, 149.96, 149.14, 149.10, 147.67, 147.64, 142.51, 142.36, 132.69, 132.54, 132.51, 132.36, 127.88, 127.79, 127.76, 127.46, 126.16, 125.94, 125.88, 125.73, 125.50, 125.38, 125.26, 78.64, 78.31, 66.68, 66.44, 59.41, 59.11, 54.88 (2×CH2), 54.82 (2×CH2), 34.11, 34.08, 33.95, 33.94, 31.99, 31.76 (2×CH2), 31.72 (6×CH3), 31.58, 31.08 (3×CH3), 31.06 (3×CH3), 23.31 (4×CH2). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C58H83N2O6 [M + H]+ 903.6251, found 903.6240.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(2-hydroxy-3-(methylamino)propoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (7)
Compound 7 was prepared from 2 (35 mg, 0.046 mmol) and methylamine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a brown solid (18 mg, 51%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.64 (s, 1H), 8.08 (s, 1H), 7.08–7.00 (m, 4H), 6.98–6.90 (m, 4H), 5.62 (s, 4H), 4.60 (d, J = 19.3 Hz, 2H), 4.30–4.06 (m, 6H), 3.99–3.77 (m, 2H), 3.49–3.20 (m, 8H), 2.75 (d, J = 5.5 Hz, 6H), 1.23 (s, 18H), 1.07 (s, 18H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 149.87, 149.82, 149.68, 148.73, 148.56, 148.11, 147.97, 142.76, 142.55, 133.12, 133.01, 132.85, 132.67, 127.68, 127.60, 127.30, 127.08, 126.39, 126.15, 126.08, 125.91, 125.79, 125.64, 125.51, 78.42, 78.04, 66.75, 66.16, 52.82, 52.51, 34.24, 34.22, 33.95, 33.94, 33.89, 33.78, 32.24, 32.07, 32.02, 31.78, 31.69 (3×CH3), 31.67 (3×CH3), 31.16 (3×CH3), 31.14 (3×CH3). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C52H75N2O6 [M + H]+ 823.5625, found 823.5591.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72--bis(3-(ethylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (8)
Compound 8 was prepared from 2 (37 mg, 0.048 mmol) and ethylamine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a white solid (22 mg, 58%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.64 (s, 1H), 8.53 (s, 1H), 7.07–6.96 (m, 8H), 5.80 (br, 4H), 4.81–4.65 (m, 2H), 4.41–4.10 (m, 6H), 3.95–3.80 (m, 2H), 3.47–3.02 (m, 12H), 1.44–1.34 (m, 6H), 1.26–1.18 (m, 18H), 1.16–1.06 (m, 18H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 149.99, 149.61, 149.47, 148.73, 148.52, 148.30, 148.07, 142.84, 142.48, 142.38, 133.57, 133.50, 133.21, 133.08, 127.82, 127.14, 127.07, 126.64, 126.18, 125.95, 125.85, 125.74, 125.62, 125.50, 78.23, 77.89, 67.08, 66.87, 50.50, 49.89, 43.60, 43.35, 34.32, 34.29, 33.94, 33.91, 32.65, 32.31, 32.22, 31.99, 31.67, 31.65, 31.63 (3×CH3), 31.23 (3×CH3), 31.21 (3×CH3), 29.78, 11.59, 11.46. HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C54H79N2O6 [M + H]+ 851.5938, found 851.5928.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(2-hydroxy-3-(propylamino)propoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (9)
Compound 9 was prepared from 2 (35 mg, 0.046 mmol) and N-propylamine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a white solid (26 mg, 74%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.64 (s, 1H), 8.55 (s, 1H), 7.07–7.03 (m, 2H), 7.03–7.00 (m, 4H), 7.00–6.96 (m, 2H), 4.83–4.64 (m, 2H), 4.41–4.10 (m, 6H), 3.94–3.77 (m, 2H), 3.47–3.09 (m, 8H), 3.03–2.87 (m, 4H), 1.92–1.76 (m, 4H), 1.25–1.20 (m, 18H), 1.16–1.11 (m, 18H), 1.01 (t, J = 7.4 Hz, 6H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.04, 149.65, 149.54, 148.77, 148.59, 148.25, 148.04, 142.76, 142.44, 142.34, 133.56, 133.27, 133.14, 127.82, 127.78, 127.16, 127.11, 126.60, 126.18, 125.92, 125.86, 125.72, 125.60, 125.50, 78.23, 77.94, 67.01, 66.89, 50.91, 50.36, 50.27, 50.04, 34.32, 34.29, 33.93, 33.91, 32.66, 32.31, 32.24, 32.01, 31.67, 31.65, 31.64 (3×CH3), 31.23 (3×CH3), 31.22 (3×CH3), 29.78, 19.79, 19.63, 11.42, 11.41. HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C56H83N2O6 [M + H]+ 879.6251, found 879.6237.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(3-(hexylamino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (10)
Compound 10 was prepared from 2 (47 mg, 0.062 mmol) and n-hexylamine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3 and purified by HPLC to give compound 10 as a brown solid (25 mg, 53%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.63–8.60 (m, 2H), 7.07–6.96 (m, 8H), 4.96–4.66 (m, 3H), 4.40–4.04 (m, 7H), 3.88–3.78 (m, 2H), 3.51–2.84 (m, 14H), 1.91–1.68 (m, 4H), 1.40–1.28 (m, 12H), 1.22 (s, 18H), 1.14 (s, 18H), 0.90–0.86 (m, 6H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 149.56, 149.47, 148.75, 148.55, 148.29, 148.06, 142.79, 142.44, 133.66, 133.58, 133.31, 133.15, 127.83, 127.10, 127.04, 126.66, 126.19, 126.17, 125.96, 125.83, 125.75, 125.61, 125.49, 100.00, 78.19, 77.84, 67.03, 66.81, 50.84, 50.17, 48.84, 48.47, 34.32, 34.30, 33.93, 33.92, 33.90, 32.71, 32.35, 32.25, 32.01, 31.66, 31.62 (3×CH3), 31.38, 31.36, 31.24 (3×CH3), 31.22 (3×CH3), 31.00, 26.61, 26.58, 26.18, 26.00, 22.54, 22.52, 14.04 (2×CH3). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C62H95N2O6 [M + H]+ 963.7190, found 963.7176.
15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-bis(2-hydroxy-3-thiomorpholinopropoxy)-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (11)
Compound 11 was prepared from 2 (44 mg, 0.058 mmol) and thiomorpholine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a white solid (27 mg, 61%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.76 (s, 1H), 8.33–8.23 (m, 1H), 7.09–6.95 (m, 8H), 4.58–3.89 (m, 10H), 3.49–3.28 (m, 4H), 2.94–2.84 (m, 8H), 2.78–2.60 (m, 12H), 1.26–1.21 (m, 18H), 1.16–1.08 (m, 18H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 149.93, 149.66, 149.50, 149.17, 148.93, 148.08, 147.82, 142.76, 142.59, 142.53, 133.72, 133.21, 133.20, 128.18, 127.76, 127.59, 127.29, 126.64, 126.12, 125.96, 125.78, 125.65, 125.61, 125.52, 79.63, 78.95, 68.06, 67.67, 61.13, 60.88, 55.78 (2×CH2), 55.73 (2×CH2), 34.31, 34.25, 33.95, 33.94, 32.88, 32.34, 32.19, 32.02, 31.69, 31.67, 31.64 (6×CH3), 31.25 (3×CH3), 31.21 (3×CH3), 28.19, 28.16. HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C58H84N2O6S2 [M + 2H]2+ 484.2880, found 484.2874.
32,72-Bis(3-(bis(2-hydroxyethyl)amino)-2-hydroxypropoxy)-15,35,55,75-tetra-tert-butyl-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diol (12)
Compound 12 was prepared from 2 (49 mg, 0.064 mmol) and diethanolamine (1.0 ml), following the procedure used to prepare 3. The product was obtained as a white solid (29 mg, 59%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 8.54–7.85 (m, 2H), 7.09–6.98 (m, 4H), 6.97–6.81 (m, 4H), 4.95 (s, 10H), 4.58 (s, 2H), 4.38–4.16 (m, 4H), 4.04–3.65 (m, 10H), 3.44–3.26 (m, 4H), 3.18–3.04 (m, 4H), 3.00–2.54 (m, 6H), 1.26–1.19 (m, 18H), 1.11–1.00 (m, 18H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ 150.05, 149.58, 149.37, 149.14, 147.85, 147.73, 147.70, 142.72, 133.39, 133.26, 133.09, 132.82, 128.42, 128.13, 127.62, 127.42, 126.69, 126.26, 126.03, 125.85, 125.77, 125.43, 78.89, 78.28, 68.45, 67.74, 59.01 (2×CH2), 58.73 (2×CH2), 57.99 (2×CH2), 57.67 (2×CH2), 34.23, 34.21, 33.92, 33.91, 33.89, 32.84, 32.51, 32.20, 31.68 (3×CH3), 31.63 (3×CH3), 31.20 (3×CH3), 31.18 (3×CH3). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C58H88N2O10 [M + 2H]2+ 486.3214, found 486.3207.
3,3′-((15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-32,72-dihydroxy-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,52-diyl)bis(oxy))bis(2-hydroxy-N,N,N-trimethylpropan-1-aminium) Iodide (13)
A mixture of compound 3 (54 mg, 0.063 mmol) and methyl iodide (1.0 ml) was dissolved in methanol and was stirred overnight at room temperature. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was directly concentrated under reduced pressure. Then the crude product was purified by HPLC to provide compound 13 as a white solid (26 mg, 48%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 7.28–7.14 (m, 6H), 7.06–7.02 (m, 2H), 4.56–3.90 (m, 12H), 3.85–3.78 (m, 2H), 3.69–3.45 (m, 8H), 3.45–3.34 (m, 14H), 1.29 (s, 12H), 1.22 (s, 6H), 1.19 (s, 6H), 1.06–1.03 (m, 12H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ 150.75, 150.70, 150.66, 150.56, 149.38, 149.34, 144.05, 144.00, 143.98, 134.08, 134.03, 133.97, 129.47, 129.43, 129.34, 129.20, 127.33, 127.16, 127.07, 126.93, 126.55, 126.45, 126.36, 126.34, 79.44, 79.39, 69.62, 69.50, 66.77 (2×CH3), 65.25 (2×CH2), 55.23 (2×CH3), 43.20 (2×CH3), 35.01, 35.00, 34.76, 32.46, 32.32, 32.06 (3×CH3), 31.54 (3×CH3), 31.25, 30.25, 24.40, 24.15, 14.47, 11.44. HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C56H84I2N2O6 [M − 2I]2+ 440.3159, found 440.3152.
2,2′,2″,2‴-((15,35,55,75-Tetra-tert-butyl-1,3,5,7(1,3)-tetrabenzenacyclooctaphane-12,32,52,72-tetrayl)tetrakis(oxy))tetrakis(N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)acetamide) (16)
Tetraethyl 4-tert-butylcalix[4]arene-O,O′,O″,O‴-tetraacetate (100 mg, 0.10 mmol) was dissolved in tetrahydrofuran, and then lithium hydroxide (48 mg, 2.0 mmol) dissolved in water (2.0 ml) was added. After the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1.5 h, acetic acid was added to adjust its acidity, then the mixture was diluted with n-butanol and washed twice with water. The organic phase was concentrated under reduced pressure to give crude product 15, which was directly used for the next step without further purification. Subsequently, 15 was dissolved in DMF (5.0 ml), and then 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride (223 mg, 0.81 mmol), DIPEA (0.27 ml, 1.6 mmol) and 3-(dimethylamino)-1-propylamine (203 μl, 0.016 mmol) were added. After stirring overnight at room temperature, the reactant mixture was diluted with n-butanol and washed twice with water. The organic phase was concentrated under reduced pressure, and the crude product was purified by HPLC to yield compound 16 as a brown solid (12 mg, 12%). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3OD) δ 6.92 (s, 8H), 4.85–4.78 (m, 8H), 4.61 (s, 8H), 3.39 (t, J = 6.8 Hz, 8H), 2.91–2.77 (m, 8H), 2.72–2.58 (m, 24H), 1.99–1.84 (m, 8H), 1.11 (s, 36H). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CD3OD) δ 172.09 (4×C), 134.96 (4×C), 134.94 (4×C), 134.88 (4×C), 134.82 (4×C), 127.15 (8×CH), 75.44 (4×CH2), 56.71 (4×CH2), 43.75 (8×CH3), 37.42 (4×CH2), 34.98 (4×CH, 4×CH2), 31.85 (12×CH3), 26.37 (4×CH2). HRMS (ESI+): calculated for C72H114N8O8 [M + 2H]2+ 609.4374, found 609.4359.
Antibacterial Activity Evaluation
MIC values were determined by the broth microdilution method according to the guidelines established by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Bacterial cells were prepared on Mueller-Hinton agar (MHA) plates at 37°C for 24 h and adjusted to approximately 1.0 × 106 CFU/ml. Compounds were dissolved in DMSO and water to prepare stock solution, and then diluted to the required concentration in Mueller-Hinton Broth (MHB) medium. The bacterial suspension (100 μl) was added to each well of the 96-well plate and mixed with an equal volume of the two-fold serial dilutions of the compounds (100 μl), then the 96-well plates were incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The MIC values were determined by measuring OD600 and visual inspection. Compared with the negative control group, the MIC value was determined as the lowest sample concentration without bacterial growth. All reported MIC values have been determined repeatedly.
Hemolytic Activity Evaluation
Fresh rabbit red blood cells (RBCs) were washed three times with PBS, centrifuged at 2,500 rpm for 3 min, and then diluted with PBS to prepare 8% (v/v) suspension. The compounds were dissolved in DMSO (final DMSO concentration of ≤ 0.50%) or PBS, and then diluted with PBS. Two-fold serial dilutions of compounds (100 μl) were incubated for 1 h at 37°C with 100 μl of RBC suspension (∼5.0×108 cells/ml) in a 96-well plate. Then, the mixture was centrifuged at 2,500 rpm for 5 min, 100 μl supernatant was transferred into a 96-well plate and measured the absorbance at 576 nm using BioTek multi-detector microplate reader. RBCs treated with PBS were used as a negative control, and RBCs treated with 2.0% Triton X-100 solution were used as a positive control. The hemolysis percentage was calculated by the following formula: % hemolysis = [(Abssample − Absnegative control)/(Abspositive control − Absnegative control)] × 100. All values have been determined at least twice independently with biologically replicates.
Cytotoxicity Assay
Mouse NCTC clone 929 cells (∼2.0 × 104 cells/well) were incubated in a 96-well plate, and treated with different concentrations of compound 16 at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 24 h. Then, 10 μl of CCK-8 reagent was added to each well and incubated at 37°C with 5.0% CO2 for 1 h. The absorbance at 450 nm was detected by BioTek multi-detector microplate reader, and the cell viability was calculated by the ratio of OD450 value of compound-treated cells to OD450 value of untreated cells. The experiments were carried out at least twice with biologically replicates.
SYTOX Green Assay
Bacteria were cultured on MHA plates overnight, then the bacterial cells were washed twice with PBS buffer (10 mM, pH = 7.2) and resuspended in PBS. The absorbance of the suspension at 600 nm was adjusted to 0.20. After mixing with 0.30 μM SYTOX Green, the suspension was cultured in dark. The change of fluorescence intensity was monitored by the BioTek multi-detector microplate reader (excitation wavelength: 504 nm, emission wavelength: 523 nm). After the fluorescence signal was stable, compound 16 dissolved in DMSO was immediately added to the SYTOX Green-treated bacterial suspension, and the change of fluorescence intensity was recorded for about 1 h. All experiments were conducted at least twice with biologically replicates.
BODIPY™-TR-Cadaverine Displacement Assay
BODIPY™-TR-cadaverine replacement test was used to determine the binding affinity between compound 16 and lipoteichoic acid (LTA). BODIPY™-TR-cadaverine was purchased from ThermoFisher, LTA from S. aureus was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. When the probe binds to LTA, the fluorescence intensity of the probe is quenched. The fluorescence will be significantly enhanced when the probe is replaced and re-dissolved in solution. BODIPY™-TR-cadaverine (final concentration of 5.0 μM) and LTA (final concentration of 10 μg/ml) were mixed in the 24 well plates with Tris buffer (50 mM, pH = 7.4). After 15 min, compound 16 (1×, 2×, 4×, 8×, 16× and 32× MIC) dissolved in DMSO was added, and then the mixture was placed in the dark for 30 min at room temperature. Finally, the fluorescence intensity (excitation wavelength 580 nm, emission wavelength 620 nm) was measured using a Biotek multiple detector microplate reader. These experiments were performed at least twice with biological replications. The percentage of displacement from LTA was obtained according to the following formula: % displacement from LTA = [(Fsample − F0)/(Fmax − F0)] × 100. F0 is the fluorescence intensity of the probe with LTA, and Fmax is the fluorescence intensity of the probe without LTA and compound 16.
Time-Kill Study
Bacterial cells were incubated on MHA plates at 37°C for 24 h, and then adjusted to approximately 1.0 × 106 CFU/ml. The bacterial suspensions were treated with compound 16 at different concentrations (4× and 8× MIC) and were incubated at 37°C. Then, the culture samples (100 μl) were respectively taken from the mixture at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8 and 24 h and were serially diluted 10-fold in PBS. The dilutions were plated onto MHA plates and incubated at 37°C for 24 h, then the bacterial colonies were counted. The experiments were repeated at least twice and with biological replicates.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
SF, Y-YD, SML, and SPL conceived and designed the experiments. SML and SPL coordinated the whole study. The experiments were carried out by SF, HZL, HXL, JL, RZ, and YC. Y-YD, SF, and SML analyzed the data. The manuscript was written through contributions from all authors. All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21907019), the Talent Fund for High-Level University Construction of Guangzhou (B195002009029 and B195002009030), Educational Commission of Guangdong Province (2019KQNCX118), Medical Scientific Research Foundation of Guangdong Province (A2020396), College Student Laboratory Opening Project of Guangzhou Medical University (01-408-2102053), and High-level University Construction Fund of Guangdong Province (06-410-2107207; 06-410-2107286).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1
Abd HamidS.M BunnoriN.AdekunleI. A.AliY. (2015). Applications of Calixarenes in Cancer Chemotherapy: Facts and Perspectives. Dddt9, 2831–2838. 10.2147/DDDT.S83213
2
AdessiC.SotoC. (2002). Converting a Peptide into a Drug: Strategies to Improve Stability and Bioavailability. Cmc9, 963–978. 10.2174/0929867024606731
3
ArbourC. A.MendozaL. G.StockdillJ. L. (2020). Recent Advances in the Synthesis of C-Terminally Modified Peptides. Org. Biomol. Chem.18, 7253–7272. 10.1039/d0ob01417f
4
BonoN.PennettaC.SganappaA.GiupponiE.SansoneF.VolonterioA.et al (2018). Design and Synthesis of Biologically Active Cationic Amphiphiles Built on the Calix[4]arene Scaffold. Int. J. Pharmaceutics549, 436–445. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.08.020
5
CostaF.TeixeiraC.GomesP.MartinsM. C. L. (2019). Clinical Application of AMPs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.1117, 281–298. 10.1007/978-981-13-3588-4_15
6
GajdácsM. (2019). The Concept of an Ideal Antibiotic: Implications for Drug Design. Molecules24, 892. 10.3390/molecules24050892
7
HannaT. A.LiuL.Angeles-BozaA. M.KouX.GutscheC. D.EjsmontK.et al (2003). Synthesis, Structures, and Conformational Characteristics of Calixarene Monoanions and Dianions. J. Am. Chem. Soc.125, 6228–6238. 10.1021/ja0289797
8
HickeyS. M.AshtonT. D.KhosaS. K.RobsonR. N.WhiteJ. M.LiJ.et al (2015). Synthesis and Evaluation of Cationic Norbornanes as Peptidomimetic Antibacterial Agents. Org. Biomol. Chem.13, 6225–6241. 10.1039/c5ob00621j
9
IsakssonJ.BrandsdalB. O.EngqvistM.FlatenG. E.SvendsenJ. S. M.StensenW. (2011). A Synthetic Antimicrobial Peptidomimetic (LTX 109): Stereochemical Impact on Membrane Disruption. J. Med. Chem.54, 5786–5795. 10.1021/jm200450h
10
JenssenH.HamillP.HancockR. E. W. (2006). Peptide Antimicrobial Agents. Clin. Microbiol. Rev.19, 491–511. 10.1128/CMR.00056-05
11
JonesM. R.MathieuE.DyragerC.FaissnerS.VaillancourtZ.KorshavnK. J.et al (2017). Multi-target-directed Phenol-Triazole Ligands as Therapeutic Agents for Alzheimer's Disease. Chem. Sci.8, 5636–5643. 10.1039/c7sc01269a
12
KmietowiczZ. (2017). Few Novel Antibiotics in the Pipeline, WHO Warns. Bmj358, j4339. 10.1136/bmj.j4339
13
KohJ.-J.LinH.CarolineV.ChewY. S.PangL. M.AungT. T.et al (2015). N-lipidated Peptide Dimers: Effective Antibacterial Agents against Gram-Negative Pathogens through Lipopolysaccharide Permeabilization. J. Med. Chem.58, 6533–6548. 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.5b00628
14
KowalskiR. P.RomanowskiE. G.YatesK. A.MahF. S. (2016). An Independent Evaluation of a Novel Peptide Mimetic, Brilacidin (PMX30063), for Ocular Anti-infective. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther.32, 23–27. 10.1089/jop.2015.0098
15
KuppusamyR.WillcoxM.BlackD. S.KumarN. (2019). Short Cationic Peptidomimetic Antimicrobials. Antibiotics8, 44. 10.3390/antibiotics8020044
16
LäppchenT.DingsR. P. M.RossinR.SimonJ. F.VisserT. J.BakkerM.et al (2015). Novel Analogs of Antitumor Agent Calixarene 0118: Synthesis, Cytotoxicity, Click Labeling with 2-[18F]fluoroethylazide, and In Vivo Evaluation. Eur. J. Med. Chem.89, 279–295. 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.048
17
LázárV.MartinsA.SpohnR.DarukaL.GrézalG.FeketeG.et al (2018). Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Show Widespread Collateral Sensitivity to Antimicrobial Peptides. Nat. Microbiol.3, 718–731. 10.1038/s41564-018-0164-0
18
LiJ.KohJ.-J.LiuS.LakshminarayananR.VermaC. S.BeuermanR. W. (2017). Membrane Active Antimicrobial Peptides: Translating Mechanistic Insights to Design. Front. Neurosci.11, 73. 10.3389/fnins.2017.00073
19
LivermoreD. M.BlaserM.CarrsO.CassellG.FishmanN.GuidosR.et al (2011). Discovery Research: the Scientific Challenge of Finding New Antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother.66, 1941–1944. 10.1093/jac/dkr262
20
LyddiardD.JonesG. L.GreatrexB. W. (2016). Keeping it Simple: Lessons from the Golden Era of Antibiotic Discovery. FEMS Microbiol. Lett.363, fnw084. 10.1093/femsle/fnw084
21
MaX.ZhaoY. (2015). Biomedical Applications of Supramolecular Systems Based on Host-Guest Interactions. Chem. Rev.115, 7794–7839. 10.1021/cr500392w
22
MalmstenM. (2014). Antimicrobial Peptides. Upsala J. Med. Sci.119, 199–204. 10.3109/03009734.2014.899278
23
MaragakisL. L.PerencevichE. N.CosgroveS. E. (2008). Clinical and Economic Burden of Antimicrobial Resistance. Expert Rev. Anti-infective Ther.6, 751–763. 10.1586/14787210.6.5.751
24
MarrA.GooderhamW.HancockR. (2006). Antibacterial Peptides for Therapeutic Use: Obstacles and Realistic Outlook. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol.6, 468–472. 10.1016/j.coph.2006.04.006
25
MensaB.HowellG. L.ScottR.DeGradoW. F. (2014). Comparative Mechanistic Studies of Brilacidin, Daptomycin, and the Antimicrobial Peptide LL16. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.58, 5136–5145. 10.1128/AAC.02955-14
26
MokhtariB.PourabdollahK. (2013). Applications of Nano-Baskets in Drug Development: High Solubility and Low Toxicity. Drug Chem. Toxicol.36, 119–132. 10.3109/01480545.2011.653490
27
MolchanovaN.HansenP.FranzykH. (2017). Advances in Development of Antimicrobial Peptidomimetics as Potential Drugs. Molecules22, 1430. 10.3390/molecules22091430
28
Monserrat-MartinezA.GambinY.SiereckiE. (2019). Thinking outside the Bug: Molecular Targets and Strategies to Overcome Antibiotic Resistance. Ijms20, 1255. 10.3390/ijms20061255
29
NaseerM. M.AhmedM.HameedS. (2017). Functionalized Calix[4]arenes as Potential Therapeutic Agents. Chem. Biol. Drug Des.89, 243–256. 10.1111/cbdd.12818
30
Nasuhi PurF. (2016). Calixdrugs: Calixarene-Based Clusters of Established Therapeutic Drug Agents. Mol. Divers.20, 781–787. 10.1007/s11030-016-9667-x
31
NimseS. B.KimT. (2013). Biological Applications of Functionalized Calixarenes. Chem. Soc. Rev.42, 366–386. 10.1039/c2cs35233h
32
NizalapurS.KimyonO.YeeE.HoK.BerryT.ManefieldM.et al (2017). Amphipathic Guanidine-Embedded Glyoxamide-Based Peptidomimetics as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Biofilm Disruptors. Org. Biomol. Chem.15, 2033–2051. 10.1039/c7ob00053g
33
O'NeillA. (2008). New Antibacterial Agents for Treating Infections Caused by Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs17, 297–302. 10.1517/13543784.17.3.297
34
PasupuletiM.SchmidtchenA.MalmstenM. (2012). Antimicrobial Peptides: Key Components of the Innate Immune System. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol.32, 143–171. 10.3109/07388551.2011.594423
35
PiddockL. J. (2012). The Crisis of No New Antibiotics-What Is the Way Forward?Lancet Infect. Dis.12, 249–253. 10.1016/S1473-3099(11)70316-4
36
PurF. N. (2021). Calix[4]API-s: Fully Functionalized Calix[4]arene-Based Facial Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Mol. Divers.25, 1247–1258. 10.1007/s11030-020-10042-0
37
RiceL. B. (2008). Federal Funding for the Study of Antimicrobial Resistance in Nosocomial Pathogens: No ESKAPE. J. Infect. Dis.197, 1079–1081. 10.1086/533452
38
RogersG. B.CarrollM. P.BruceK. D. (2012). Enhancing the Utility of Existing Antibiotics by Targeting Bacterial Behaviour?Br. J. Pharmacol.165, 845–857. 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01643.x
39
RothB. L.PootM.YueS. T.MillardP. J. (1997). Bacterial Viability and Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing with SYTOX Green Nucleic Acid Stain. Appl. Environ. Microbiol.63, 2421–2431. 10.1128/aem.63.6.2421-2431.1997
40
ShurpikD. N.PadnyaP. L.StoikovIICraggP. J. (2020). Antimicrobial Activity of Calixarenes and Related Macrocycles. Molecules25, 5145. 10.3390/molecules25215145
41
SinghP.van SwaaijW. P. M.BrilmanD. W. F. (2011). Kinetics Study of Carbon Dioxide Absorption in Aqueous Solutions of 1,6-hexamethyldiamine (HMDA) and 1,6-hexamethyldiamine, N,N′ Di-methyl (HMDA, N,N′). Chem. Eng. Sci.66, 4521–4532. 10.1016/j.ces.2011.06.008
42
SwainJ.El KhouryM.FlamentA.DezanetC.BriéeF.Van Der SmissenP.et al (2019). Antimicrobial Activity of Amphiphilic Neamine Derivatives: Understanding the Mechanism of Action on Gram-Positive Bacteria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (Bba) - Biomembranes1861, 182998. 10.1016/j.bbamem.2019.05.020
43
ThakurS.CattoniD. I.NöllmannM. (2015). The Fluorescence Properties and Binding Mechanism of SYTOX Green, a Bright, Low Photo-Damage DNA Intercalating Agent. Eur. Biophys. J.44, 337–348. 10.1007/s00249-015-1027-8
44
ThapaR. K.DiepD. B.TønnesenH. H. (2020). Topical Antimicrobial Peptide Formulations for Wound Healing: Current Developments and Future Prospects. Acta Biomater.103, 52–67. 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.12.025
45
WalshC. (2000). Molecular Mechanisms that Confer Antibacterial Drug Resistance. Nature406, 775–781. 10.1038/35021219
46
WimleyW. C.HristovaK. (2011). Antimicrobial Peptides: Successes, Challenges and Unanswered Questions. J. Membr. Biol239, 27–34. 10.1007/s00232-011-9343-0
47
WoolhouseM.WaughC.PerryM. R.NairH. (2016). Global Disease burden Due to Antibiotic Resistance - State of the Evidence. J. Glob. Health6, 010306. 10.7189/jogh.06.010306
48
YeamanM. R.YountN. Y. (2003). Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Peptide Action and Resistance. Pharmacol. Rev.55, 27–55. 10.1124/pr.55.1.2
49
ZasloffM. (2002). Antimicrobial Peptides of Multicellular Organisms. Nature415, 389–395. 10.1038/415389a
Summary
Keywords
antimicrobial agents, Calix[4]arene derivatives, membrane-active, peptidomimetics, bacterial resistance, gram-positive bacteria
Citation
Fang S, Dang Y-Y, Li H, Li H, Liu J, Zhong R, Chen Y, Liu S and Lin S (2022) Membrane-Active Antibacterial Agents Based on Calix[4]arene Derivatives: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Front. Chem. 10:816741. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.816741
Received
17 November 2021
Accepted
07 January 2022
Published
08 February 2022
Volume
10 - 2022
Edited by
Wenshe Ray Liu, Texas A&M University, United States
Reviewed by
Margherita De Rosa, University of Salerno, Italy
Lorenzo Stella, University of Rome Tor Vergata, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2022 Fang, Dang, Li, Li, Liu, Zhong, Chen, Liu and Lin.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shouping Liu, liushouping2018@163.com; Shuimu Lin, linshuimu020@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
This article was submitted to Chemical Biology, a section of the journal Frontiers in Chemistry
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.