- 1 Department of Psychology, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA
- 2 Department of Psychology, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA
An object can be categorized at different levels of abstraction: as natural or man-made, animal or plant, bird or dog, or as a Northern Cardinal or Pyrrhuloxia. There has been growing interest in understanding how quickly categorizations at different levels are made and how the timing of those perceptual decisions changes with experience. We specifically contrast two perspectives on the timing of object categorization at different levels of abstraction. By one account, the relative timing implies a relative timing of stages of visual processing that are tied to particular levels of object categorization: Fast categorizations are fast because they precede other categorizations within the visual processing hierarchy. By another account, the relative timing reflects when perceptual features are available over time and the quality of perceptual evidence used to drive a perceptual decision process: Fast simply means fast, it does not mean first. Understanding the short-term and long-term temporal dynamics of object categorizations is key to developing computational models of visual object recognition. We briefly review a number of models of object categorization and outline how they explain the timing of visual object categorization at different levels of abstraction.
Introduction
At a glance, we can detect an object in the environment, recognize it as an object we have seen before, categorize it as an animal or as a bird, or, if we are an expert, identify it as a male Indigo Bunting in winter plumage. What is the timing of visual object categorizations at different levels of abstraction, and how does that timing constrain theories of visual object categorization?
We begin this article by reviewing a body of empirical work that suggests that object categorization first occurs at a particular entry level, typically an intermediate, or basic level, of the conceptual hierarchy, before categorizations at more subordinate or superordinate levels can be made. According to this view, basic-level categorization is a relatively early stage within the visual processing hierarchy. We contrast this view with a number of computational models of object categorization that propose no stage-like mechanism. We close by reviewing a body of more recent empirical work that investigates the timing of object categorization without invoking stage-like mechanisms.
The Basic Level of Categorization
The seminal work of Rosch and colleagues was among the first to ask whether particular kinds of object categorizations are made more quickly than others. With what is now a widely used speeded category verification task, participants were first shown a category label (e.g., “animal” or “bird” or “Northern Cardinal”), were then shown a picture containing an object, and were asked to verify whether the object was a member of the labeled category. Rosch et al. (1976) found that participants were fastest to verify object categories at an intermediate level (e.g., bird vs. other animals) than at more superordinate levels (e.g., animal vs. vehicle) or subordinate levels (e.g., Northern Cardinal vs. other birds). Rosch and colleagues termed this intermediate level of abstraction the basic level.
According to Rosch and colleagues, the basic level carves nature at its joints. Categorizations at the basic level are fastest because they are the most natural way to divide up the world into different categories. Many features are shared among members of the same basic-level category and fewer features are shared between members of different basic-level categories. By contrast, members of different subordinate categories share many features with members of similar subordinate categories (e.g., American Robins and Barn Swallows all have feathers, beaks, wings, and other features that are common to all birds) and members of the same superordinate category generally share relatively fewer features (e.g., relatively fewer visible features are common to all animals). In other words, basic-level categories are the highest intermediate level of a category hierarchy where objects share similar shapes. The relative balance of intra-class and inter-class shape variability has been a strong theoretical component of many descriptions of the basic-level advantage since the initial reports of Rosch and colleagues, and will be a point we return to again later in this review.
The Entry Level of Categorization
Jolicoeur et al. (1984) referred to the fastest level of categorization as the entry level. For many category members, the basic level is the entry level, whereby “basic-level (categorization) occurs first and is followed, some time later, by subordinate-level identification” (Jolicoeur et al., 1984, p. 270). But, Jolicoeur and colleagues also observed that atypical members of basic-level categories could be categorized faster at the subordinate level (e.g., penguin) than the basic level (e.g., bird). While the basic level may commonly be the entry level, that is not always the case. So whereas the basic level is defined ontologically and structurally as the highest intermediate level where objects share similar shapes, the entry level is defined behaviorally as the fastest level of categorization within a hierarchy.
Both the term “entry level” and its description implies a particular kind of object recognition process: The entry level is the level at which perceptual information first makes contact with stored representations and knowledge about objects. By this view, most objects are categorized first at the basic level (the entry level) before being categorized at more subordinate or superordinate levels (Figure 1A). Categorizations at subordinate and superordinate levels follow according to a temporal hierarchy of processing stages. Basic-level categorization is not simply faster than more subordinate or superordinate categorizations. Basic-level categorization is faster because basic-level categorization occurs before processing of more subordinate or superordinate categorizations can even begin – it is fastest because that stage of processing is a prerequisite for further stages of categorization.
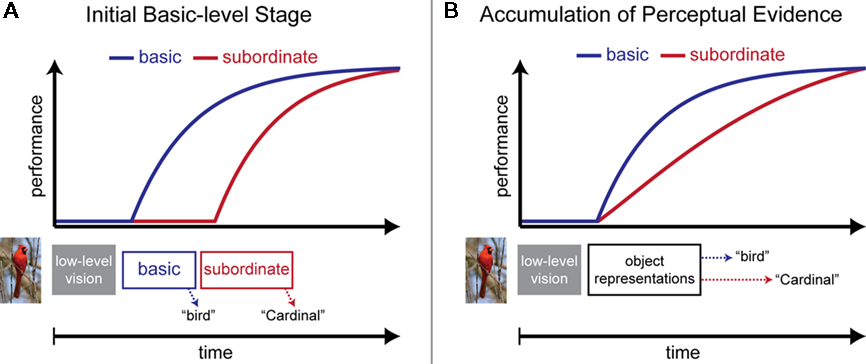
Figure 1. Illustration of two competing accounts of the basic-level advantage in object categorization. Top panels illustrate the time course for basic-level (blue) and subordinate-level (red) categorization as a function of processing time. Bottom panels illustrate proposed categorization mechanisms over time. (A) Initial Basic-level Stage. After low-level visual processing, an initial stage of processing determines an object’s basic-level category. After this initial basic-level stage has completed, a subsequent stage determines the subordinate-level category. The basic-level advantage is observed because the basic-level stage happens first, as reflected by the early onset of its time course. (B) Accumulation of Perceptual Evidence. An alternative account does not invoke stages of processing for different categorization decisions. Categorization is determined by an accumulation of perceptual evidence over time. This account predicts no difference in the onset of the time course functions. The basic-level advantage is observed because basic-level categories engender a more rapid accumulation of perceptual evidence over time.
The timing of object categorization is not simply based on the statistical structure of object categories, but can be affected by a perceiver’s experience and knowledge. Unlike novices, an expert bird watcher can categorize a picture at the subordinate level, identifying it as an Indigo Bunting, as quickly and accurately as they can categorize it at the basic level, as a bird (Tanaka and Taylor, 1991; Johnson and Mervis, 1997). Tanaka and Taylor characterized this expertise effect as an entry-level shift (Figure 2A). One possible explanation for this result is that, for experts, perceptual information can make direct contact with subordinate category knowledge, whereas novices must first access the basic level.
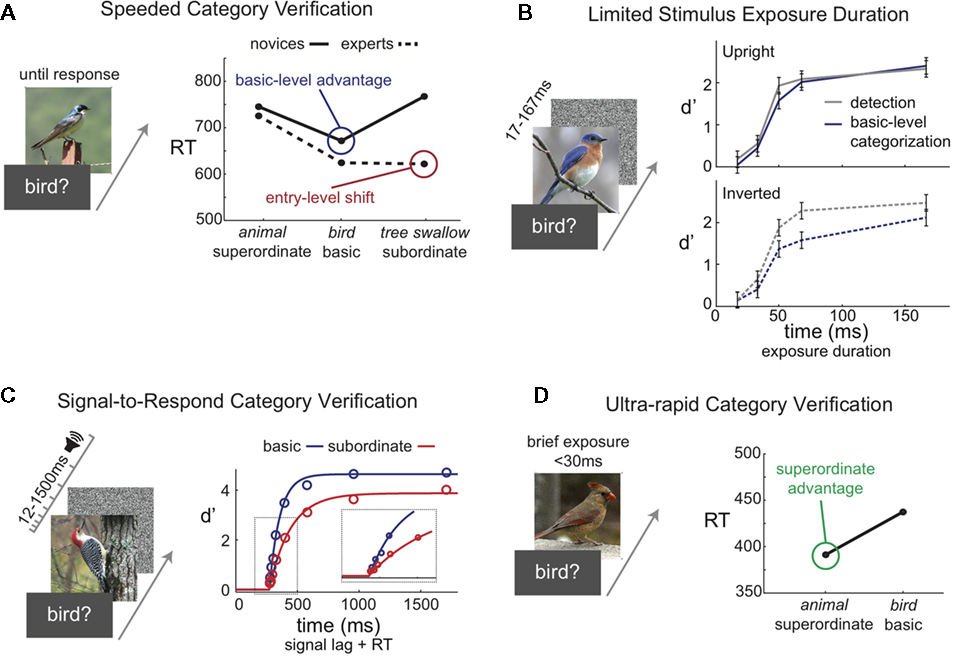
Figure 2. Data from four common paradigms used to investigate the timing of visual object categorization. (A) Speeded Category Verification Task. On each trial, a superordinate, basic, or subordinate category label is presented followed by a pictured object. Participants verify whether the object is a member of the labeled category. The graph illustrates mean reaction times for categorization by novices (solid line) and experts (dotted line). Novices show a basic-level advantage. Experts show an entry-level shift, where subordinate categorizations are as fast as basic-level categorizations. Data from Tanaka and Taylor (1991). (B) Limited Exposure Duration. The time course of categorization is investigated by systematically varying the exposure duration of a masked stimulus. The top plot shows equivalent performance with upright objects for object detection (gray) and basic-level categorization (blue) for exposure durations ranging from 17 to 167 ms. In the bottom plot, these time courses are dissociated when the stimulus images are inverted, with basic-level categorization worse than object detection. Data from Mack et al. (2008). (C) Signal-to-Respond. The time course of categorization is investigated by systematically varying the time to respond. The STR paradigm asks participants to verify categories at different levels of abstraction, but responses must be made when a response signal is presented. Timing between the onset of the image and presentation of the response signal systematically maps out how categorization evolves over time. Performance for basic (blue) and subordinate (red) categorization is plotted as a function of reaction time plus response signal lag (open circles represent behavioral results and solid lines are fits of a shifted exponential curve). Critically, there is no difference in the onset of performance for these categorizations. The inset plots a zoomed in view of where the time courses first rise above-chance performance. Data from Mack et al. (2009). (D) Ultra-rapid Category Verification. Ultra-rapid categorization typically involves very brief stimulus exposures (<30 ms) and a go/no-go response to a target category at a superordinate or basic level. The graph illustrates the superordinate-level advantage for mean reaction times observed in ultra-rapid categorization. Data from Macé et al. (2009).
Detecting, Categorizing, and Identifying Objects
This view that basic-level categorization is literally an entry level, a stage of visual processing that precedes stages of categorization at other levels, was suggested by Grill-Spector and Kanwisher (2005). They conducted a series of speeded category verification experiments that included simple object detection as well as basic-level categorization and subordinate-level identification. On some trials, participants would verify whether any object was present or not, while on other trials they would verify a basic-level category (e.g., bird), or verify a subordinate-level identity (e.g., Blue Jay). As a measure of the time course of these decisions, they systematically manipulated the exposure duration of the images. Examining accuracy as a function of exposure duration, they observed equivalent time courses for object detection and basic-level categorization that were both significantly faster than the time course for subordinate-level identification (Figure 2B).
Grill-Spector and Kanwisher explained the equivalent timing of object detection and basic-level categorization by proposing that the very same perceptual mechanism both segments objects from the background and categorizes them at the basic level. Subordinate-level identification and superordinate-level categorization only take place at a subsequent stage of processing, as suggested by a literal interpretation of the entry level of categorization. This tight coupling between object detection and categorization was supported by another experiment by Grill-Spector and Kanwisher (2005) where participants performed both object detection and categorization on the same trial with limited exposure duration. Their proposed mechanistic coupling of detection and categorization was supported by an observed behavioral coupling, whereby successful object detection on a given trial depended on the success of categorization on that same trial and vice-versa.
Based on these empirical results, the notion that basic-level categorization precedes more subordinate and superordinate levels of categorization certainly appears intuitive and compelling. The perceptual system is carving a visual image at its joints, extracting objects and their basic-level categorizations. Certain kinds of experience and expertise can further tune the visual system to initially extract objects at more subordinate levels of abstraction. However, this idea is quite provocative, in that many models of object recognition propose no such initial stage of categorization (see Palmeri and Cottrell, 2009, for a recent review).
Categorization and Identification in Models of Object Recognition
According to many computational models, categorization and identification are perceptual decisions made at the same, relatively late stage of visual processing. These models propose no sequential stages where objects are first categorized at the basic level and only later processed at more subordinate or superordinate levels. Certain kinds of perceptual decisions may be more difficult or take longer than others because of similarity, experience, and other factors, but the added time is not because some decisions follow other decisions structurally within the visual processing hierarchy (Palmeri et al., 2004; Mack et al., 2009; Figure 1B).
For example, one canonical model of visual object recognition (Riesenhuber and Poggio, 2000; Serre et al., 2007) assumes a hierarchy of visual processing that begins with low-level features and conjunctions of features, moves on to view-based representations and object representations, which are then mapped to known categories and identities of objects (Figure 3A). Basic-level categorization and subordinate-level identification are instantiated within the same output layer of the model. Similarly, Cottrell and colleagues (e.g., Joyce and Cottrell, 2004; Figure 3B) have proposed a hierarchy of visual processing that begins with Gabor filtering, goes through a stage of principal components analysis (PCA), and then a neural network mapping PCA representations onto known categories and identities of objects. Neither model has a basic-level categorization stage within the visual processing hierarchy.
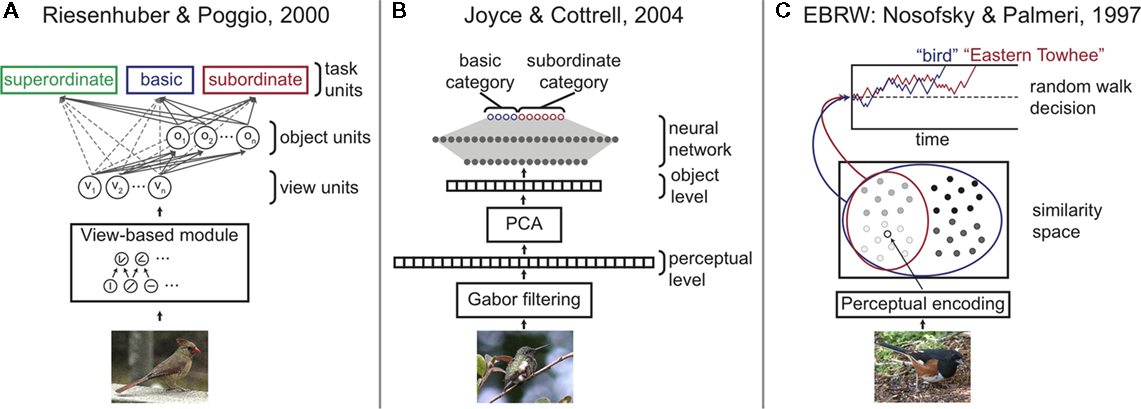
Figure 3. Illustration of three computational models of visual object categorization. (A) Riesenhuber and Poggio’s (2000) model assumes a hierarchy of visual processing that begins with encoding of low-level features and feature conjunctions, moves on to view-based representations and object representations, which are then mapped to task units representing different levels of categorization. (B) Cottrell and colleagues’ model of object recognition proposes a hierarchy of visual processing of Gabor filtering, principal components analysis (PCA), and then a neural network mapping PCA representations onto known categories of objects (e.g., Joyce and Cottrell, 2004). (C) Nosofsky and Palmeri’s (1997) exemplar-based random walk (EBRW) model proposes that the perceptual representation of an object activates similar stored object representations in memory providing incremental and noisy evidence toward a categorization decision. A decision is made once the random walk accumulation of perceptual evidence reaches a threshold. In all three computational models, decisions about category or identity are at a late decision stage of the visual processing hierarchy.
Exemplar-based models (e.g., Nosofsky, 1986; Kruschke, 1992; Nosofsky and Kruschke, 1992) also account well for object recognition, categorization, and identification. These models assume an initial stage of perceptual processing that creates a multidimensional perceptual representation of a viewed object. This object representation activates stored object representations in memory according to their similarity to the viewed object, with perceptual dimensions more diagnostic of the particular category or identity decision receiving greater weight than non-diagnostic dimensions. These stored exemplar objects are associated with known categories or identities through weights learned by Hebbian or error-driven learning rules, depending on the particular model.
So neither the exemplar models nor many extant object recognition models propose a stage of categorization that precedes identification. In fact, if anything, in all of these models representations of object identities, in the form of individual object representations, precede representations of object categories. Yet they can readily account for basic-level advantages in category learning (e.g., Palmeri, 1999a; Joyce and Cottrell, 2004).
Exemplar-based models have been extended to account for the time course of object categorization. For example, according to the exemplar-based random walk model (EBRW; Nosofsky and Palmeri, 1997; Palmeri, 1997; Figure 3C), as an object activates similar stored object representations in memory, incremental evidence is provided for competing categorizations. The incremental evidence is noisy, so it needs to be accumulated over time. As the name implies, EBRW assumes a random walk process, where evidence favoring one category pushes the accumulated evidence in one direction while evidence in favor of the other category pushes it in the opposite direction. A categorization decision is made when the accumulated evidence reaches a response threshold. Analogous mechanisms readily allow for more than two alternative categorizations (Palmeri, 1997). EBRW is a member of a family of stochastic accumulator models (Ratcliff and Smith, 2004). So it inherits the success of these models in accounting for things like the shape of response time distributions and speed-accuracy tradeoffs. These models also provide compelling accounts of the neural processes engaged in perceptual decision making (e.g., Perrett et al., 1998; Gold and Shadlen, 2007; Purcell et al., 2010).
Exemplar-based random walk is unique among stochastic accumulator models as the first to provide a theory suggesting that the dynamic evidence accumulation in categorization is an outcome of similarity to exemplar objects. The model accounts for details of response times observed during categorization tasks. With some relatively simple assumptions about how experience with objects strengthens their representations, thereby influencing the rate of evidence accumulation, the model accounts for speedups in response times over learning (Nosofsky and Palmeri, 1997; Palmeri, 1997, 1999b). Key to the present article, the model can also account for the entry-level shift with experience, predicting faster categorization at the basic level for novices but equal categorization at the basic and subordinate level for experts (Mack et al., 2007).
Lamberts (1995, 2000) recognized that perceptual processing takes variable amounts of time. Particularly salient perceptual dimensions might be processed more quickly than less salient perceptual dimensions, resulting in a multidimensional perceptual representation of a viewed object that develops over time. His model accounts for situations where salient object dimensions dominate more rapid categorizations, but diagnostic, even if less salient, dimensions dominate more deliberative categorizations (Lamberts, 1998; see also Cohen and Nosofsky, 2003). For example, coarse object shape or color might be available quickly and dominate categorizations under speeded conditions, but finer perceptual details that take more time to become available, yet are more diagnostic of category, are used during unspeeded categorizations. This coarse-to-fine temporal dynamic is consistent with several lines of cognitive neuroscience research (e.g., see Fabre-Thorpe, this issue).
In all of the models we reviewed, decisions about category or identity are instantiated at an output layer of the hierarchy. Some decisions take more time to make because they require a longer accumulation of noisier evidence, not because the stage of processing that drives those decisions follows other stages and their decisions. Under rapid conditions, salient perceptual information may be available more quickly, which could cause decisions that only require salient perceptual information to be made quickly, but that does not mean that those decisions precede other decisions in the processing hierarchy.
This view of categorization as a relatively late perceptual decision process, not a stage of visual processing, is also consistent with emerging brain imaging data (e.g., Jiang et al., 2007) showing that activation of object-sensitive areas in inferotemporal cortex (IT) reflects object representations, not explicit category membership, which is instead reflected in activation of prefrontal cortex. This does not mean that top-down factors, such as attention to diagnostic dimensions (e.g., see Palmeri and Gauthier, 2004), or perceptual learning (e.g., see Goldstone, 1998), cannot influence how perceptual representations are instantiated in IT (Folstein et al., 2010). It does imply that categorization is not a stage of processing in the ventral visual processing stream.
If there truly is a basic-level stage of visual processing – as suggested by some characterization of the entry-level phenomena – this would seriously challenge these computational models. We now review more recent empirical work that challenges the stage-like view of categorization.
Uncoupling the Timing of Object Detection and Categorization
If there exists an initial stage of visual processing that both detects and segments objects from the background and categorizes them at the basic level, then manipulations that affect categorization should also affect detection in the very same manner. Counter to this prediction, Mack et al. (2008) showed that stimulus inversion and image degradation impaired basic-level categorization but not object detection (Figure 2B). In these experiments, the time course of object detection was uncoupled from that of object categorization. This timing difference suggests that detection and basic-level categorization are not the same visual process.
The timing of object categorizations in any experiment depends not only on the within-category similarity of a particular target category, but also on what contrast categories are used in the experiment (D’Lauro et al., 2008; Macé et al., 2009). Consider a speeded category verification experiment where half the items are dogs and the other half are cars. While both dog and car are themselves basic-level categories, the contrast within the experiment between dogs and cars vary across vastly different superordinate-level categories. This means that on some trials, a participant verifies a picture of a dog as a dog, but on other trials denies that a picture of a car is a dog, which is an easy perceptual decision to make. Consider instead an experiment where half the test items are dogs and the other half are cats. Now both are basic-level categories and the contrast between them is within the same superordinate-level category. Bowers and Jones (2008) showed that categorization using a distant between-category contrast (e.g., dog vs. bus) was as fast as object detection, as observed by Grill-Spector and Kanwisher (2005). But categorization with a more similar between-category contrast (e.g., dog vs. cat) was significantly slower than object detection. Even though participants had the same basic-level category as a target (dog) in each case, the speed of the categorization was affected by the ontological distance of the contrast category (see also Macé et al., 2009). With a true basic level contrast, basic-level categorization is significantly slower than object detection, which does not suggest a common visual process for detecting and categorizing objects.
Similarly, Mack and Palmeri (2010) noted that Grill-Spector and Kanwisher used people vs. cars as the two categories in their experiment attempting to demonstrate a behavioral coupling between object detection decisions and basic-level categorization decisions. While by themselves these are basic-level categories, their contrast within the experiment spans different superordinate-level categories. Indeed, Mack and Palmeri showed that when categorizations instead involved a contrast within the same superordinate-level category (e.g., dog vs. bird) there was no evidence for a strong behavioral coupling of detection and categorization within the same trial. Instead, objects were often successfully detected without being successfully categorized (see also de la Rosa et al., 2011).
In all of these experiments, the timing of object detection and basic-level categorization were easily dissociated. If object detection and basic-level categorization take place at the same stage of visual processing, then image manipulations within a trial or manipulations of the contrast category across trials should affect detection and categorization similarly. They did not. Instead, this recent work is consistent with the assumptions made by the object categorization models reviewed earlier, where detecting, categorizing, or identifying objects are perceptual decisions based on an accumulation of perceptual evidence. Some decisions may be made more quickly than others. But the relative timing of those decisions need not imply a commensurate timing of the stages of visual processing (Palmeri et al., 2004).
The Time Course of the Basic-Level Advantage
While it is clear that the timing of basic-level categorization is not linked to the timing of object detection, what about the timing of basic-level and subordinate-level categorization? For non-experts, basic-level categorization is faster. Does basic-level categorization precede subordinate-level categorization or is it simply faster? Again, does fastest mean first?
Mack et al. (2009) contrasted the time course of basic- and subordinate-level categorization using a well-known signal-to-respond (STR) procedure. This procedure is similar to a speeded category verification task, but includes an explicit STR at a particular point in time. The signal is presented systematically at different delays after a stimulus appears in order to map out how categorization performance evolves over time. Exposure duration is constant. STR limits the amount of time to make a decision.
Data from an STR procedure can be characterized by the onset, growth rate, and asymptote of categorization performance as a function of time. Of key interest for Mack et al. (2009) was the onset, which indicates the time when above-chance categorizations are possible. If basic-level categorization occurs first, then the onset of subordinate-level categorization should be significantly delayed relative to the onset of basic-level categorization, as illustrated in Figure 1A. In other words, there should be a window of time when only above-chance basic-level categorization is possible. However, Mack et al. (2009)observed equivalent onsets in the time course of basic- and subordinate-level categorization (Figure 2C). The STR curves only differed in growth rate and asymptote. Basic-level categorizations may be made faster than subordinate-level categorizations, but a basic-level stage of visual processing does not precede categorization at other levels.
Ultra-Rapid Object Categorization
A parallel line of research over the past decade has characterized the timing of object categorization using an ultra-rapid categorization task (e.g., Thorpe et al., 1996; Fabre-Thorpe et al., 2001; VanRullen and Thorpe, 2001; Macé et al., 2009). A typical ultra-rapid experiment asks participants to verify the category of objects in images that are presented very briefly (<30 ms). Most use a go/no-go task with objects from one target category (the “go”) intermixed with objects from distractor categories (the “no-go”). For example, “animal” might be the target category and participants press a key (“go”) only when an animal is detected in the briefly presented images.
In this task, not only are the image exposures ultra-rapid, but responses are ultra-rapid as well. Accurate manual responses verifying object category are made as quickly as 250 ms after the stimulus appears (VanRullen and Thorpe, 2001). Accurate saccade responses are even faster, within 150 ms (Kirchner and Thorpe, 2006; Bacon-Macé et al., 2007). ERP measures also show a divergence in target vs. non-target waveforms at frontal electrode sites only 150 ms after stimulus onset (Thorpe et al., 1996).
What’s striking with respect to the other work we have reviewed so far is that ultra-rapid categorization tasks show ultra-rapid categorization at the superordinate level. It is abstract categories, like animals or vehicles, that are so rapidly detected in images. Indeed, the speed of ultra-rapid categorization led to the speculation that superordinate categorization represents the category to which the visual system has the fastest access (Thorpe et al., 1996; Fabre-Thorpe et al., 2001), leaving little room for even faster basic-level categorization (VanRullen and Thorpe, 2001). In fact, in ultra-rapid categorization tasks, superordinate-level categorization is significantly faster and more accurate than basic-level categorization (Macé et al., 2009; see Figure 2D).
One interpretation of the findings from ultra-rapid categorization is akin to the interpretation of the basic-level advantage from speeded category verification that we reviewed at the outset of this article. An initial stage of superordinate-level categorization precedes categorization at other levels. An object’s superordinate category is determined first and guides subsequent categorizations at more specific levels in the conceptual hierarchy (Thorpe et al., 1996). Of course, this proposal cannot be reconciled with the directly opposite proposal that an initial stage of basic-level categorization precedes categorization at other levels (Grill-Spector and Kanwisher, 2005).
An alternative interpretation is that the timing of visual perceptual processing can systematically affect the timing of object categorization. Because ultra-rapid categorization severely limits exposure duration, it limits the amount of perceptual processing of an image that can occur. With limited exposure, it is likely that only relatively coarse and potentially salient visual properties of an image are encoded (Lamberts and Freeman, 1999). This means that the perceptual information available early in the time course of encoding may favor an object’s superordinate-level category (Rogers and Patterson, 2007; Macé et al., 2009; Fabre-Thorpe, under review). Additional exposure would be necessary to encode more detailed features required for fast and accurate basic- or subordinate-level categorization. That said, it is clear that one important direction for future research on the timing of object categorization is to reconcile the classic finding of a basic-level advantage observed during speeded category verification with the superordinate-level advantage observed during ultra-rapid categorization, and to provide an explanation within a single theoretical framework (Mack and Palmeri, 2011).
Summary
In this article, we outlined two diverging theoretical perspectives on how the visual system categorizes objects. According to one, the relative timing of object categorization implies a relative timing of stages of visual processing: An early stage of visual processing both detects and categorizes objects at the basic level before categorizations at more subordinate or superordinate levels can occur. According to the other, the relative timing of object categorization reflects the timing of the availability of perceptual features and the quality of perceptual evidence used to drive a perceptual decision process: Certain categorizations can be made more quickly than others, but that is not because those categorizations occur before others in the visual processing hierarchy.
On the surface, the finding from speeded category verification that basic-level categorization is faster than either superordinate- or subordinate-level categorization, or the finding from ultra-rapid categorization that superordinate-level categorization is faster than either basic- or subordinate-level categorization, seems consistent with stages of visual processing. But while stages of processing are sufficient to account for the relative timing, they are not necessary.
Indeed, computational models have little difficulty accounting for relative timing differences without invoking stages of processing (e.g., Palmeri and Gauthier, 2004; Mack et al., 2007; Palmeri and Tarr, 2008; Palmeri and Cottrell, 2009). Many computational models assume a visual processing hierarchy with perceptual decisions regarding recognition, categorization, or identification near the end of the network. Moreover, it is difficult to imagine a coherent stages of processing account where basic-level categorization occurs first under some task conditions but superordinate-level categorization occurs first under other task conditions.
We also reviewed empirical evidence that is inconsistent with the stages of processing account. Grill-Spector and Kanwisher (2005) observed a coupling of object detection and basic-level categorization. These were uncoupled in a series of published papers that followed (Bowers and Jones, 2008; Mack et al., 2008; Mack and Palmeri, 2010; de la Rosa et al., 2011). Furthermore, detailed examination of the time course of basic- and subordinate-level categorization does not indicate stages either (Mack et al., 2009).
While a clearer picture is emerging about the timing of visual object categorization, there are still unanswered questions. Chief among these is fully understanding how the relative timing of object categorizations can vary so considerably under speeded category verification vs. ultra-rapid categorization paradigms. We are beginning to make empirical progress in understanding these differences (Mack and Palmeri, 2011), but a theoretical account still needs to be established. In addition, there is clear evidence that the timing of object categorization changes with experience (Tanaka and Taylor, 1991), but more work is needed to unravel the precise time course of categorization by experts and novices in order to understand how the timing of these perceptual decisions varies with expertise, and how experience impacts the representations and processes underlying object categorization.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Temporal Dynamics of Learning Center, NSF SBE-0542013, and a Grant from the James S. McDonnell Foundation. Bird images courtesy of Ken Thomas (http://www.KenThomas.us).
References
Bacon-Macé, N., Kirchner, H., Fabre-Thorpe, M., and Thorpe, S. J. (2007). Effects of task requirements on rapid natural scene processing: from common sensory encoding to distinct decisional mechanisms. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 33, 1013–1026.
Bowers, J. S., and Jones, K. W. (2008). Detecting objects is easier than categorizing them. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 61, 552–557.
Cohen, A. L., and Nosofsky, R. M. (2003). An extension of the exemplar-based random-walk model to separable-dimension stimuli. J. Math. Psychol. 47, 150–165.
de la Rosa, S., Choudhery, R. N., and Chatziastros, A. (2011). Visual object detection, categorization, and identification tasks are associated with different time courses and sensitivities. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 37, 38–47.
D’Lauro, C., Tanaka, J. W., and Curran, T. (2008). The preferred level of face categorization depends on discriminability. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 15, 623–629.
Fabre-Thorpe, M., Delorme, A., Marlot, C., and Thorpe, S. J. (2001). A limit to the speed of processing in ultra-rapid visual categorisation of novel natural scenes. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 13, 171–180.
Folstein, J. R., Palmeri, T. J., and Gauthier, I. (2010). Category learning stretches diagnostic shape dimensions in human visual cortex. Paper Presented at the Society for Neuroscience Conference, San Diego, CA.
Gold, J. I., and Shadlen, M. N. (2007). The neural basis of decision making. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 30, 535–574.
Grill-Spector, K., and Kanwisher, N. (2005). Visual recognition: as soon as you know it is there, you know what it is. Psychol. Sci. 16, 152–160.
Jiang, X., Bradley, E., Rini, R. A., Zeffiro, T., Vanmeter, J., and Riesenhuber, M. (2007). Categorization training results in shape- and category-selective human neural plasticity. Neuron 53, 891–903.
Johnson, K. E., and Mervis, C. B. (1997). Effects of varying levels of expertise on the basic level of categorization. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 126, 248–277.
Jolicoeur, P., Gluck, M. A., and Kosslyn, S. M. (1984). Pictures and names: making the connection. Cogn. Psychol. 16, 243–275.
Joyce, C., and Cottrell, G. W. (2004). “Solving the visual expertise mystery,” in Connectionist Models of Cognition and Perception II: Proceedings of the Eighth Neural Computation and Psychology Workshop, eds H. Bowman, and C. Labiouse (London: World Scientific).
Kirchner, H., and Thorpe, S. J. (2006). Ultra-rapid object detection with saccadic eye movements: visual processing speed revisited. Vision Res. 46, 1762–1776.
Kruschke, J. K. (1992). ALCOVE: an exemplar-based connectionist model of category learning. Psychol. Rev. 99, 22–44.
Lamberts, K. (1998). The time course of categorization. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 24, 695–711.
Lamberts, K. (2000). Information-accumulation theory of speeded categorization. Psychol. Rev. 107, 227–260.
Lamberts, K., and Freeman, R. P. J. (1999). Categorization of briefly presented objects. Psychol. Res. 62, 107–117.
Macé, M. J.-M., Joubert, O. R., Nespoulous, J.-L., and Fabre-Thorpe, M. (2009). Time-course of visual categorizations: you spot the animal faster than the bird. PLoS ONE 4, e5927.
Mack, M. L., Gauthier, I., Sadr, J., and Palmeri, T. J. (2008). Object detection and basic level categorization: sometimes you know it is there before you know what it is. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 15, 28–35.
Mack, M. L., and Palmeri, T. J. (2010). Decoupling object detection and categorization. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 36, 1067–1079.
Mack, M. L., and Palmeri, T. J. (2011). Unraveling ultra-rapid categorization. Paper to be Given at the 11th Annual meeting of the Vision Science Society, Naples, FL.
Mack, M. L., Wong, A. C.-N., Gauthier, I., Tanaka, J. W., and Palmeri, T. J. (2007). “Unraveling the time course of perceptual categorization: does fastest mean first?” in Proceedings of the 29th Annual Cognitive Science Society, eds D. S. McNamara, and J. G. Trafton (Austin, TX: Cognitive Science Society), 1253–1258.
Mack, M. L., Wong, A. C.-N., Gauthier, I., Tanaka, J. W., and Palmeri, T. J. (2009). Time-course of visual object categorization: fastest does not necessarily mean first. Vision Res. 49, 1961–1968.
Nosofsky, R. M. (1986). Attention, similarity, and the identification-categorization relationship. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 115, 39–57.
Nosofsky, R. M., and Kruschke, J. K. (1992). Investigations of an exemplar-based connectionist model of category learning. Psychol. Learn. Motiv. 28, 207–250.
Nosofsky, R. M., and Palmeri, T. J. (1997). An exemplar-based random walk model of speeded classification. Psychol. Rev. 104, 266–300.
Palmeri, T. J. (1997). Exemplar similarity and the development of automaticity. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 23, 324–354.
Palmeri, T. J. (1999a). Learning hierarchically structured categories: a comparison of category learning models. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 6, 495–503.
Palmeri, T. J. (1999b). Theories of automaticity and the power law of practice. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 25, 543–551.
Palmeri, T. J., and Cottrell, G. (2009). “Modeling perceptual expertise,” in Perceptual Expertise: Bridging Brain and Behavior, eds D. Bub, M. Tarr, and I. Gauthier (New York, NY: Oxford University Press), 197–244.
Palmeri, T. J., and Gauthier, I. (2004). Visual object understanding. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 291–303.
Palmeri, T. J., and Tarr, M. J. (2008). “Object recognition and long-term visual memory for objects,” in Visual Memory, eds S. Luck, and A. Hollingsworth (Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press), 163–207.
Palmeri, T. J., Wong, A. C.-N., and Gauthier, I. (2004). Computational approaches to the development of perceptual expertise. Trends Cogn. Sci. (Regul. Ed.) 8, 378–386.
Perrett, D. I., Oram, M. W., and Ashbridge, E. (1998). Evidence accumulation in cell populations responsive to faces: an account of generalisation of recognition without mental transformations. Cognition 67, 111–145.
Purcell, B. A., Heitz, R. P., Cohen, J. Y., Schall, J. D., Logan, G. D., and Palmeri, T. J. (2010). Neurally-constrained modeling of perceptual decision making. Psychol. Rev. 117, 1113–1143.
Ratcliff, R., and Smith, P. L. (2004). A comparison of sequential sampling models for two-choice reaction time. Psychol. Rev. 111, 333–367.
Riesenhuber, M., and Poggio, T. (2000). Models of object recognition. Nat. Neurosci. 3(Suppl.), 1199–1204.
Rogers, T. T., and Patterson, K. (2007). Object categorization: reversals and explanations of the basic-level advantage. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 136, 451–469.
Rosch, E., Mervis, C. B., Gray, W. D., Johnson, D. M., and Boyes-Braem, P. (1976). Basic objects in natural categories. Cogn. Psychol. 8, 382–439.
Serre, T., Oliva, A., and Poggio, T. (2007). A feedforward architecture accounts for rapid categorization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 6424–6429.
Tanaka, J. W., and Taylor, M. (1991). Object categories and expertise: is the basic level in the eye of the beholder? Cogn. Psychol. 23, 457–482.
Thorpe, S., Fize, D., and Marlot, M. (1996). Speed of processing in the human visual system. Nature 381, 520–522.
Keywords: object recognition, object categorization, time course, temporal dynamics, computational modeling, reaction times
Citation: Mack ML and Palmeri TJ (2011) The timing of visual object categorization. Front. Psychology 2:165. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2011.00165
Received: 02 March 2011; Accepted: 01 July 2011;
Published online: 15 July 2011.
Edited by:
Rufin VanRullen, Centre de Recherche Cerveau et Cognition, FranceReviewed by:
Timothée Masquelier, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, SpainMichèle Fabre-Thorpe, Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique, France
Copyright: © 2011 Mack and Palmeri. This is an open-access article subject to a non-exclusive license between the authors and Frontiers Media SA, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in other forums, provided the original authors and source are credited and other Frontiers conditions are complied with.
*Correspondence: Michael L. Mack, Department of Psychology, The University of Texas at Austin, 1 University Station A8000, Austin, TX 78712, USA. e-mail:bWFjay5taWNoYWVsQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==

