- 1Department of Sports and Health, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou, China
- 2Department of Graduation, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou, China
- 3Department of Linguistics and Modern Languages, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Sha Tin, China
This study investigated smartphone use characteristics including the purpose of smartphone use (i.e., leisure, learning, or work) and situational smartphone use (i.e., sitting, standing, or moving about) in Chinese adolescents. Moreover, it tested the moderating role of self-control in the link between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use. A total of 947 adolescents completed measures of the purpose of their smartphone use, situational smartphone use, sedentary behavior, self-control, time on smartphone, and smartphone addiction. Results showed that the majority of smartphone use was for leisure and learning, and 90.9% of adolescents reported typically sitting as they used the smartphone. Problematic smartphone use was positively correlated with sedentary behavior and negatively correlated with self-control. Moreover, the relationship between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use was moderated by self-control, in that the negative correlation was stronger for adolescents with low self-control and weaker for those with high self-control. These results contribute to the understanding of when sedentary behavior is associated with problematic smartphone use. Several limitations and implications are discussed in this study.
Introduction
With the development of internet-based smart devices, the prevalence of smartphone use has steadily increased worldwide, including in China. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of China (2019) announced that more than 1.57 billion Chinese people had their own mobile phones in 2018. Although the smartphone brings conveniences to people’s digital lifestyle, many problematic smartphone usages have also emerged among younger people, including in Chinese adolescents (Liu et al., 2017, 2018a). With its special features of convenience, immediacy, and affordability, today’s smartphone allows people to call, receive and send messages, surf the internet, play mobile games, and update social networking sites (e.g., Facebook and WeChat) almost anywhere and anytime. Historically, these activities were defined as sedentary behaviors (Rosenberg et al., 2010). More importantly, a consistent body of literature showed that more than 80% of people reported typically sitting when using their device (Barkley and Lepp, 2016; Long et al., 2016; Lee et al., 2017; Fennell et al., 2019), and such inactive behaviors are linked to numerous comorbidities including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and metabolic syndrome (Owen et al., 2010). Due to the prevalence of smartphone usage and the access it provides to sedentary behaviors, it is important to expand our understanding of the behavioral health implications potentially related to smartphone use. This study considers the relationship between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use and tests the moderating role of self-control in the relationship between those variables.
Sedentary Behavior and Problematic Smartphone Use
An excessive amount of sedentary behavior in adolescents is a growing problem in China (Lu et al., 2017). Although many factors may affect sedentary behavior, the association of smartphone use with sedentary behavior and leisure time is well demonstrated, much as sedentary behavior has been linked with traditional forms of screen-based activities (e.g., watching television, playing video games, and surfing the internet). For example, 70% of college students and 81% of adults reported using their smartphone for leisure purposes (Barkley and Lepp, 2016; Fennell et al., 2019). Prior research has also found that sedentary behaviors are strong predictors of smartphone usage time in college students as well as adults aged 18–80, indicating that excessive smartphone use may increase sedentary behaviors and distract from physical activity (Barkley and Lepp, 2016; Fennell et al., 2019). Furthermore, after controlling for other factors linked to physical quality (e.g., gender, percentage of body fat, and self-efficacy for exercise), excessive smartphone use can ultimately result in reduced cardiorespiratory fitness levels among college students (Lepp et al., 2013).
Prior studies have focused mainly on college students or adults. However, little is known about the relationship between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use in adolescents. Adolescence represents a critical transitional stage of development, during which personal lifestyle choices and behavior patterns are established. Clearly, more studies are required to explore smartphone use characteristics as well as the relationship between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use in adolescents.
Self-Control as a Moderator
Self-control, defined as the ability to volitionally control or override inner desires and external temptations in order to achieve long-term goals (Tangney et al., 2004), is an important dispositional trait for generating adaptive personal and social responses. High self-control is positively associated with desirable life outcomes, including better physical and mental health, higher academic performance, and more wealth (Tangney et al., 2004; Moffitt et al., 2011). In contrast, a deficit in self-control is positively associated with undesirable outcomes or social problems, such as binge eating, aggression, depression, and addiction (Denson et al., 2011; Özdemir et al., 2014; Pearson et al., 2018). Problematic smartphone use is generally described as an addictive behavior or incapacity to control cravings to use smartphones (Walsh et al., 2010; Liu et al., 2018b). According to self-regulation theory, addictive behaviors primarily result from failures of self-regulation. Poor self-control might limit an individual’s ability to reduce cravings and restrain addiction (Köpetz et al., 2013; Gökçearslan et al., 2016). This lack of self-control is intrinsically linked to problematic smartphone use. Indeed, a consistent body of research has shown that low levels of self-control not only predict high-frequency usage of smartphones (Wilmer and Chein, 2016; Berger et al., 2018) but also link to smartphone addiction such as withdrawal symptoms, mood changes and cyberspace-oriented relationship (Gökçearslan et al., 2016; Jiang and Zhao, 2016; Yun et al., 2016; Berger et al., 2018).
Self-control is also correlated with sedentary behavior. For example, preliminary evidence showed that lower inhibition-control was directly or indirectly associated with sedentary behavior (Hoang et al., 2013). In modern life, although individuals often plan and intend to exercise, they do not always transform their intentions into actual exercise behavior. According to behavioral economics theory, sedentary behavior can be perceived as an easy, “low-cost” activity with immediate reinforcements, such as fun and entertainment, whereas physical activity can be viewed as a “high-cost” commitment, requiring effort and few immediate reinforcements (Epstein, 1998). Thus, Martin Ginis and Bray (2010) suggested that the capacity to block out sedentary behavior and promote physical activity requires self-control.
With in-depth study, self-control not only negatively correlated with personal and social problems, but also played an important, protective moderator role in the relationship between negative factors and their outcomes. Cooper et al. (2017) found that self-control could buffer the correlation between school burnout and emotional dysregulation. Furthermore, Liu et al. (2018b) found that the direct association between mindfulness and poor sleep quality and the indirect association through rumination were both moderated by self-control among adolescents. These two associations are stronger for those with low self-control and weaker for those with high self-control.
To the best of our knowledge, it remains unclear how sedentary behavior and self-control interact to affect problematic smartphone use. To fill these gaps, it is worth constructing a moderation model to test the moderating variable of self-control in the association between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use. The moderation model would contribute to understanding of how self-control protects individuals from problematic smartphone use.
Hypotheses
This study aims to investigate smartphone use characteristics and explore the relationship between sedentary behavior, self-control and problematic smartphone use in Chinese adolescents. Specifically, we hypothesized the following in a sample of adolescents.
Hypothesis 1: Because a smartphone provides a variety of leisure (e.g., videos and game) and learning (e.g., English materials) applications, the majority of smartphone use will be for leisure and learning purposes in Chinese adolescents.
Hypothesis 2: Because the smartphone makes it easier to access traditionally sedentary and screen-based activities, smartphone use will occur primarily while sitting.
Hypothesis 3: Because smartphone use primarily occurs while sitting, the sedentary behavior will be positively related to problematic smartphone behaviors.
Hypothesis 4: Because prior researches have indicated that self-control plays an important protective role, the relationship between sedentary behaviors and problematic smartphone use was moderated by self-control.
Materials and Methods
Participants and Data Collection
We used a descriptive transversal design study which was approved by the Human Experimental Ethics Board of Author’s University (Reference number: 2018LCLL-007). With a convenient sampling method, we recruited students from two junior high schools (grade 7 to grade 9) and two senior high schools (grade 10 to grade 12) in the Guangdong province in southern China. In each target school, we randomly chose two or three classes in each grade. Prior to investigation, the parents or guardians of participants were well-informed and their written consent was obtained. A total of 969 Chinese target students were invited to voluntarily participate in the anonymous paper-and-pencil questionnaires survey, which was conducted in classrooms by well-trained college students. All participants completed our survey, but 22 participants were excluded because of missing data on the main variables. Overall, 947 adolescents in the sample were employed, the mean age was 14.13 (SD = 1.79) ranging from 11 to 18 years. There were 489 male students with an average age of 14.13 (SD = 1.71) and 458 female students with an average age of 14.12 (SD = 1.89).
Measurements
Smartphone Use Characteristics
The study evaluated basic demographics (e.g., age, gender, grade, and smartphone ownership), purpose of smartphone use, and situational smartphone use. Regarding purpose of smartphone use, participants were asked to indicate “what percentage of the time the smartphone is used for the following purposes: leisure, learning, work.” The list of items was designed to ensure that the sum of the three responses totaled 100% (Lepp et al., 2014). The situational smartphone use was assessed with three fixed choice items: “When I am using my smartphone, I am most often: (a) sitting, (b) standing, or (c) moving about.”
Sedentary Behavior
Sedentary behavior (i.e., sitting) was assessed with two items from the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) (Craig et al., 2003; Bauman et al., 2009). Participants reported the average number of minutes of each week day (or each weekend day) they spent sitting. Weekly sedentary behavior was calculated using the following equation: weekly sedentary behavior = [(5 × minutes of sitting per week day) + (2 × minutes of sitting per weekend day)]/7.
Self-Control
We used the China short form of the trait self-control scale (SCS) (Tan, 2008) revised from the original version by Tangney et al. (2004), including a scale of 19 items. The SCS measures five aspects of self-control abilities:(1) deliberate and non-impulsive action, (2) healthy habits, (3) resistance to temptation, (4) work ethic, and (5) moderation in seeking diversions. Participants assessed each item on a five-point scale from 1 (not at all like me) to 5 (very much like me). Higher scores on this scale indicate a stronger capability for self-control.
Problematic Smartphone Use
Two questionnaires were selected to assess the problematic smartphone use, including time on smartphone use and smartphone addiction scale.
Time on smartphone was assessed with two items using a method followed by Lepp et al. (2014). Participants were asked to estimate their average time spent (in minutes) on their smartphone for each weekday and each weekend day. This self-report measure is associated with objectivity and other self-reported measures of smartphone use, which were applied in previous studies (Barkley and Lepp, 2016; Fennell et al., 2019). Weekly smartphone use was calculated using the following equation: weekly smartphone use = [(5 × minutes of smartphone use per week day) + (2 × minutes of smartphone use per weekend day)]/7.
Smartphone addiction was assessed by the ten-item Smartphone Addiction Scale-Short Version (SAC-SV) for adolescents (Kwon et al., 2013). The scale was translated by independent researchers using the parallel translation method. Any disagreement was resolved by discussion or, if required, by consulting a third author. Participants assessed each item on a six-point scale: 1 (fully disagree) to 6 (fully agree). The total scores ranged from 10 to 60. Kwon et al. (2013) suggested cut-off points per gender (boys 31 and girls 33) to classify the smartphone addiction group (SAG) or non-smartphone addiction group (non-SAG).
Statistical Analysis
All data analysis was performed using SPSS 23.0. A p-value of 0.05 indicated statistical significance. We first computed descriptive statistics for the whole sample, and then compared differences between SAG and non-SAG with continuous variables using independent t-test and categorical variables using χ2. Additionally, we used a Pearson correlation analysis to assess the association between sedentary behavior, physical activity, self-control, smartphone use, and smartphone addiction. Finally, we performed moderation analyses using Hayes (2013) bootstrapping Process for SPSS (Model 1) to examine whether the sedentary behavior effect on time of smartphone use and smartphone addiction were moderated by self-control. All continuous variables were standardized and the interaction terms were computed based on standardized scores. The bootstrapping method produced 95% bias-corrected confidence intervals of these effects from 5000 resamples of the data (Hayes, 2013).
Results
Descriptive Statistics and Comparative Analysis
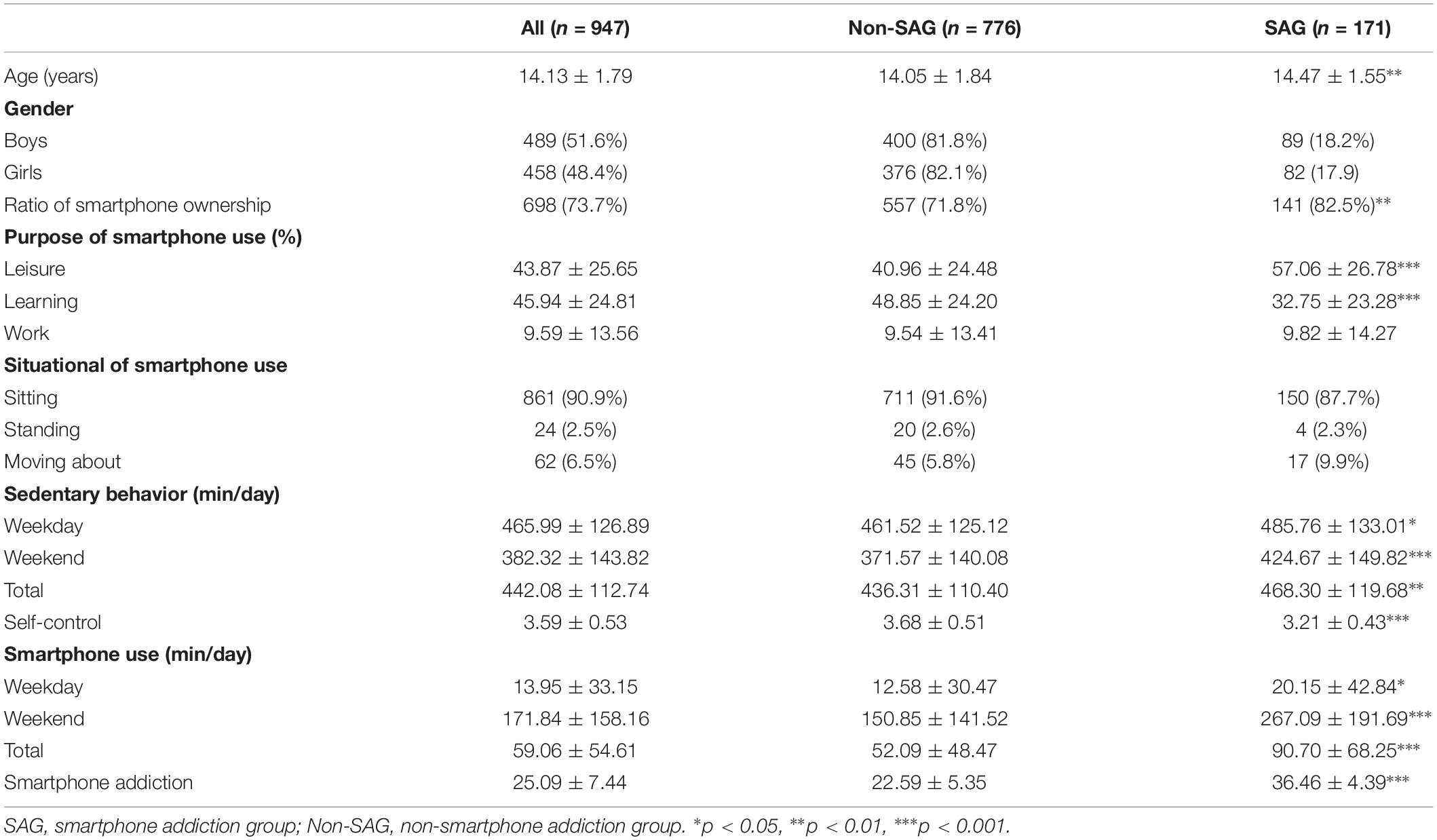
Based on of results of previous studies (Kwon et al., 2013; Lopez-Fernandez, 2017), the scoring 32 was selected as the cut-off to identify smartphone addiction because there was no significant difference between gender in SAS-SV scores (t = 0.69, p = 0.49). Table 1 presented the socio-demographic and smartphone use characteristics between those with and without SA.
A total of 947 adolescent subjects participated in this study; 698 of the participants (73.7%) owned a smartphone with 776 of them in the non-SAG (81.9%) and 171 in the SAG (18.1%). When these two groups were compared, there were no significant differences in their genders; however, the age was significantly greater in the SAG (t = 2.76, p = 0.006), and the proportion of smartphone ownership was also significantly higher in the SAG (χ2 = 8.24; p = 0.004).
Regarding purpose of smartphone use, on average, participants categorized 43.87% of their smartphone use as leisure, 45.94% as learning, and 9.59% as work. On close inspection, the SAG had significantly greater smartphone use as leisure (t = 7.92, p < 0.001), but lower smartphone use as learning (t = -7.65, p < 0.001) compared with the non-SAG. In this sample, 90.9, 2.5, and 6.5% of participants reported that they are most likely sitting down, standing and moving, respectively, while using their smartphone. However, there was no significant difference in usage preferences between SAG and non-SAG regarding these three postures (χ2 = 0.014, p = 0.906).
The mean daily sitting was 442.08 (SD = 112.74) min/day. The mean self-control score was 3.59 (SD = 0.53) units. When these two groups were compared, the SAG showed significantly higher sedentary behavior on weekdays (t = 2.26, p = 0.024) and weekends (t = 4.43, p < 0.001), as well as higher overall minutes being sedentary (t = 3.38, p < 0.001). They also showed significantly lower self-control than the non-SAG (t = 11.17, p < 0.001).
Regarding daily smartphone use, mean smartphone use time in weekdays, weekends, and total minutes was 13.95 (SD = 33.15), 171.84 (SD = 158.16), and 59.06 (SD = 54.61) min/day, respectively. The SAG had significantly greater smartphone use weekdays (t = 2.71; p = 0.007), weekends (t = 9.07; p < 0.001), and for total minutes of use (t = 8.69; p = 0.005).
Correlation Analyses
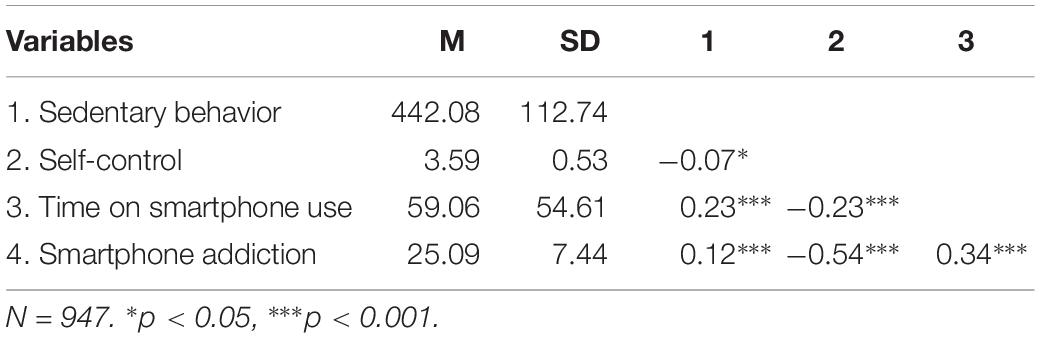
The descriptive statistics and correlation matrix are presented in Table 2. Sedentary behavior was positively correlated with time on smartphone use (p < 0.001) and smartphone addiction (p < 0.001), and negatively correlated with self-control (p < 0.05). Self-control was negatively associated with time on smartphone use (p < 0.001) and smartphone addiction (p < 0.001).
Testing for the Moderation Model
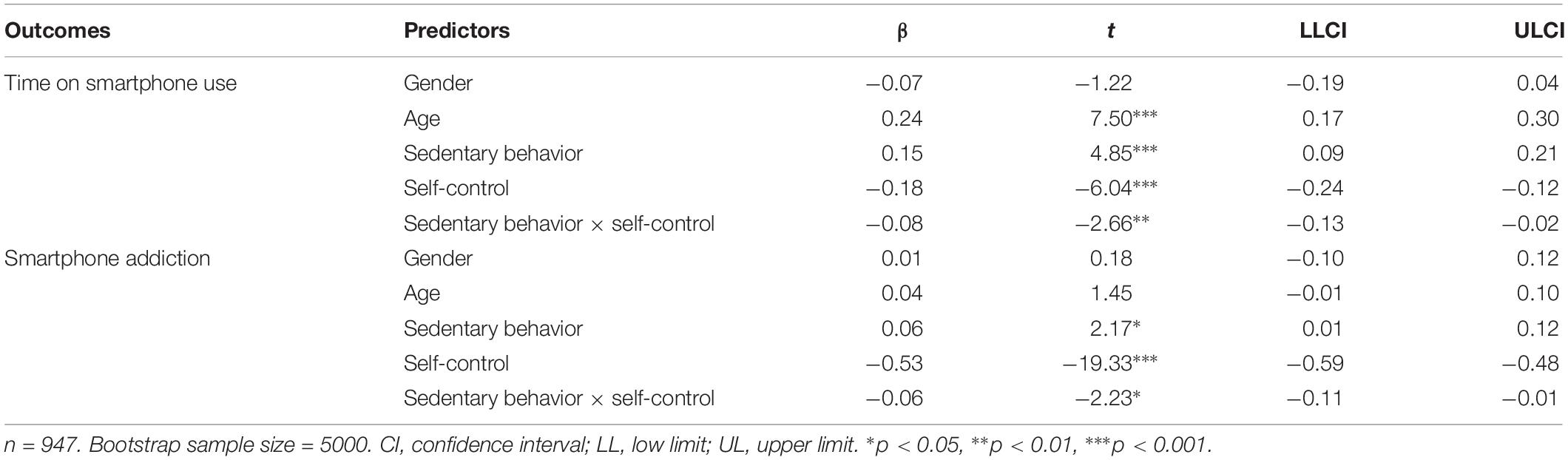
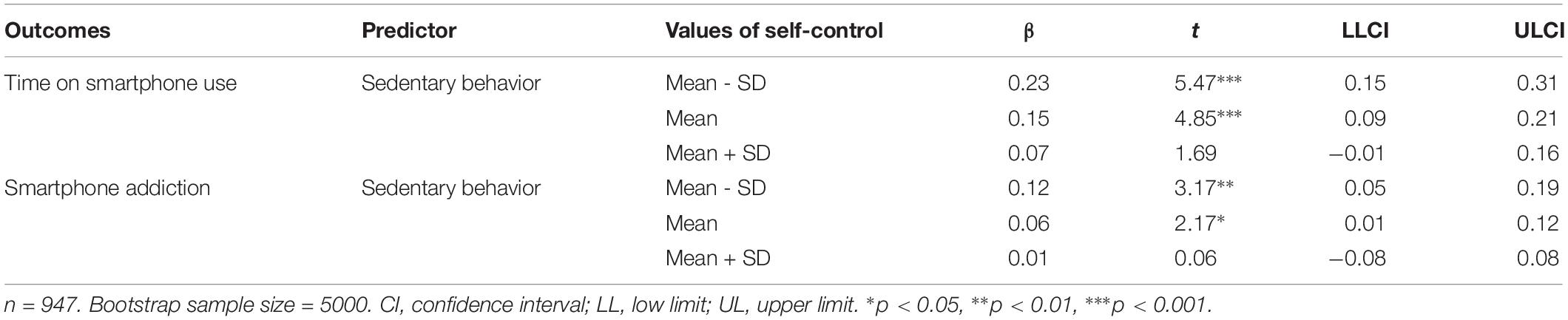
The main results of moderation analysis generated by Hayes (2013) SPSS macro PROCESS are presented in Table 3. Regarding time on smartphone use, after controlling for gender and age, sedentary behavior was positively correlated with time on smartphone use (β = 0.15, p < 0.001); self-control was negatively correlated with time on smartphone use (β = −0.18, p < 0.001); and the interaction of sedentary behavior and self-control was negatively correlated with time on smartphone use (β = −0.08, p < 0.01). Namely, self-control moderated the association between sedentary behavior and time on smartphone use. To better understand the moderating effect of self-control, the plot of the relation between sedentary behavior and time on smartphone use at two levels of self-control (1 SD below the mean and 1 SD above the mean) was described in Figure 1. As can be seen from Figure 1 and the conditional effects analysis in Table 4, for individuals with low self-control (1 SD below the mean), sedentary behavior was positively associated with time on smartphone use (β = 0.23, p < 0.001), while this association (β = 0.07, p > 0.05) was not significant for individuals with high self-control (1 SD above the mean).
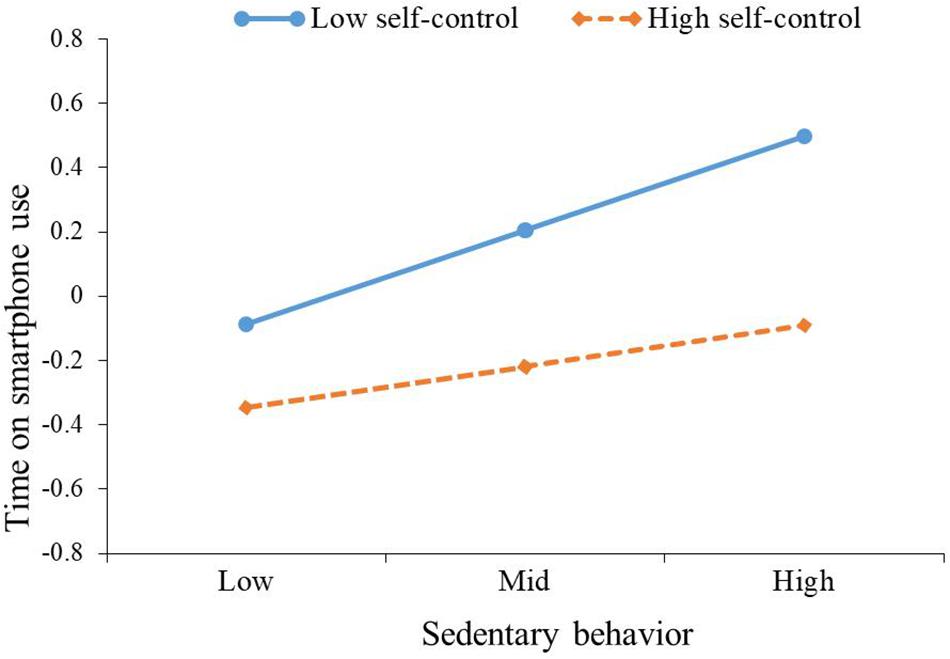
Figure 1. The plot of the relationship between sedentary behavior and time on smartphone use at two levels of self-control.
As can be seen from the moderation model for predicting smartphone addiction, after controlling for gender and age, sedentary behavior was positively correlated with smartphone addiction (β = 0.06, p < 0.05), while the interaction of sedentary behavior and self-control was negatively correlated with smartphone addiction (β = −0.06, p < 0.05). In other words, self-control moderated the association between sedentary behavior and smartphone addiction. The plot of the relation between sedentary behavior and smartphone addiction at two levels of self-control (1 SD below the mean and 1 SD above the mean) was described in Figure 2. As can be seen from Figure 2 and the conditional effects analysis in Table 4, for individuals with low self-control (1 SD below the mean), sedentary behavior was positively associated with smartphone addiction (β = 0.12, p < 0.01), while this association (β = 0.01, p > 0.05) was not significant for individuals with high self-control (1 SD above the mean).
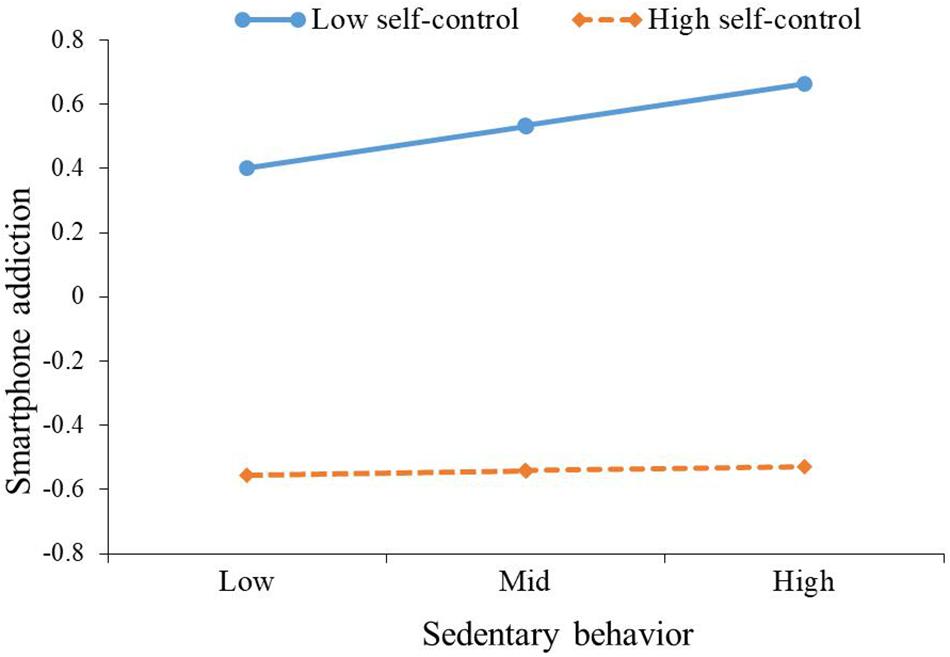
Figure 2. The plot of the relationship between sedentary behavior and smartphone addiction at two levels of self-control.
Discussion
A descriptive transversal design was carried out to investigate smartphone use characteristics in this study, including the purpose of smartphone use (i.e., leisure, learning, or work) and situational smartphone use (i.e., sitting, standing, or moving about). Furthermore, this study examined the moderating role of self-control between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use in Chinese adolescents. In the current study, the proportion of adolescents who own a smartphone is 73.7% among Chinese adolescents. They spend more time on their smartphone on weekends because of the heavy learning tasks and explicit prohibition in school on smartphone use at weekday (Gao et al., 2014). The prevalence of potential smartphone addiction was 18.1%, similar to the range reported in the Kwon et al. (2013) for Korean adolescents (16.6% in boys, 26.6% in girls).
In this study, participants reported that, on average, 43.87% of their smartphone use was for leisure, 45.94% for learning, and 9.59% for work, indicating the percentage of total daily smartphone use devoted to leisure and learning was similar in adolescents. Thus, Hypothesis 1 was supported. These results are inconsistent with previous studies that have shown the majority of smartphone use was for leisure in college students (70–88% use for leisure) (Lepp et al., 2013, 2017; Barkley and Lepp, 2016) and adults (61% use for leisure) (Fennell et al., 2019). However, the purpose of smartphone use was significantly different between SAG and non-SAG, namely, the SAG had greater smartphone use for leisure, while the non-SAG had greater smartphone use for learning. These results combined with previous logistic regression analysis results showed that levels of smartphone addiction were reduced when smartphones were used for learning (Lee et al., 2017), suggesting that parents and teachers should provide guidance for adolescents about specific functions of smartphone use, such as learning or searching for information to reduce smartphone addiction.
Regarding situational use, 90.9% of all adolescents reported using the smartphone primarily while sitting. This is very similar to previous research in samples of college students (87%) and adults (81%) (Barkley and Lepp, 2016; Fennell et al., 2019). It seems that smartphones, despite their portability and mobility, are primarily sedentary devices for all individuals regardless of age. So Hypothesis 2 was verified.
Congruent with previous studies (Barkley and Lepp, 2016; Fennell et al., 2019), our finding showed that sedentary behavior was negatively correlated with use time on smartphones, suggesting that individuals who allocated more time for daily sitting use smartphones for greater periods. But beyond the time on smartphone use of previous studies, our results demonstrated that sedentary behavior was also negatively associated with smartphone addiction, indicating that our findings more comprehensively revealed the relationships between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use. Thus, Hypothesis 3 was supported. In addition, prior studies have identified sedentary behavior as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease (Katzmarzyk et al., 2009; Carter et al., 2017), which is worrisome as individuals with smartphone addiction spent more time on sedentary behavior and are at greater risk for cardiovascular disease than those without smartphone addiction.
Unlike sedentary behavior, the results of relationship between physical activity and problematic smartphone use were inconsistent in prior studies. For example, some researchers found there was no direct relationship between volume of daily physical activity and time on smartphone use (Barkley and Lepp, 2016; Fennell et al., 2019), while Kim et al. (2015) revealed that average number of walking steps per day negatively correlated with smartphone addiction. Other researches demonstrated that using the smartphone for texting during treadmill exercise may reduce participation in vigorous intensity exercise (Rebold et al., 2016), while using the smartphone for listening to music has been shown to increase exercise intensity (Rebold et al., 2015), suggesting the relationship between physical activity and smartphone depending on the aspect of smartphone functions. Based on the results from previous studies, we speculate that smartphone use may increase sedentary behavior by using traditional forms of screen-based apps while simultaneously prompt physical activity by using health related apps.
Novel to our study was our demonstration that not only the relationships between sedentary behavior and time spent on smartphone use but also between sedentary behavior and smartphone addiction were moderated by self-control. These two associations were stronger for individuals with low self-control than for those with high self-control. Therefore, Hypothesis 4 was verified, which indicates the sense of moderation of self-control in the relationship between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use. These findings are consistent with recent theorizing on the trait of self-control (de Ridder et al., 2012; Hofmann et al., 2014b) and prior studies (Cooper et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2018b) indicating the protective role of self-control. Individuals who are high in self-control are more likely to reduce problematic smartphone use even though their sedentary behavior is at a high level. Presumably, these individuals have developed a good coping strategy and self-control capacities that help them to avoid using the smartphone when they are sitting. In contrast, smartphone use among persons who are low in self-control seems to be more strongly influenced by sedentary behavior. An explanation could be that these individuals’ attention was generally hijacked by the smartphone, which leads individuals to respond immediately to smartphone signals when they are sitting (Berger et al., 2018).
Limitations and Implications
Several limitations of the present study are noteworthy. First, due to the cross-sectional survey design in this study, causal relationships between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use should be interpreted with great caution. Future research may adopt longitudinal or experimental study models to strictly identify the causal relationships among these variables. Second, due to social desirability and other biases, the self-report method might inflate shared method variance and restrict the validity of the data. Future research using objective methods (such as ActiGraph accelerometers and smartphone apps) to assess the sedentary behavior and smartphone use may be necessary to address this. Third, self-control can be subdivided into trait self-control and state self-control; however, only the trait self-control was considered in our study, potentially limiting the utilization of the present study. Future research should try to investigate both state and trait self-control.
Despite the above limitations, the results of this study contribute to an expanding of the scope of interventions geared toward preventing problematic smartphone use in adolescents. Our data show that sedentary behavior was negatively correlated with problematic smartphone use. Although we cannot determine causal relationships between sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use, reducing sedentary behavior is undoubtedly beneficial for alleviating problematic smartphone use. In fact, China’s government has enacted a “National Teenagers’ Sunny Sports Program” with the goal of having students do 1 h of exercise every day to promote physical activity and reduce sedentary behaviors. We speculate that such a program is not only useful in the field of physical fitness but also in curbing excessive or problematic smartphone use. Other interventions could target adolescents with low self-control by raising their awareness of their tendency to problematic smartphone use and launching evidence-based public health programs for improving self-control levels. Fortunately, promising results have been found in prior research on self-control training (Hofmann et al., 2014a; Friese et al., 2017). One big advantage of such trainings may be the high domain-general capacity; training in self-control in one field may lead to broad improvements in other fields over time. For example, Zou et al. (2016) have found that participating in 5 weeks of aerobic exercise (physical self-control) can increase self-control after ego-depletion in terms of pain tolerance. These pieces of evidence give reason to assume that adolescents low in self-control could benefit from exercise training, leading them to reduced problematic smartphone use.
Conclusion
This study has found that the majority of smartphone use was for leisure and learning, which was positively associated with sedentary behavior in Chinese adolescents. Furthermore, results of this study provided evidence that self-control exerts a moderating role on the impact of sedentary behavior on adolescents with problematic smartphone use. In other words, strengthening self-control may be effective in helping adolescents with sedentary behavior to limit their problematic smartphone use. The current study expands the pediatric literature on sedentary behavior and problematic smartphone use during the potentially critical developmental period of adolescence and points to the need to launch evidence-based exercise interventions and self-control training for adolescents at risk for problematic smartphone use.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated for this study are available on request to the corresponding author.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Human Experimental Ethics Board of Guangzhou Sports University. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
M-QX, LL, and MH contributed to the conception and design of the study. Z-RW and JL organized the database. M-QX and LL analyzed the data. M-QX and Z-RW wrote the first draft of the manuscript. MH and ZX contributed to the manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Social Science Foundation of China (grant number 18BTY055).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Barkley, J. E., and Lepp, A. (2016). Mobile phone use among college students is a sedentary leisure behavior which may interfere with exercise. Comput. Human Behav. 56, 29–33. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.11.001
Bauman, A., Bull, F., Chey, T., Craig, C. L., Ainsworth, B. E., Sallis, J. F., et al. (2009). The international prevalence study on physical activity: results from 20 countries. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 6:21. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-6-21
Berger, S., Wyss, A. M., and Knoch, D. (2018). Low self-control capacity is associated with immediate responses to smartphone signals. Comput. Human Behav. 86, 45–51. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2018.04.031
Carter, S., Hartman, Y., Holder, S., Thijssen, D. H., and Hopkins, N. D. (2017). Sedentary behavior and cardiovascular disease risk: mediating mechanisms. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 45, 80–86. doi: 10.1249/jes.0000000000000106
Cooper, A. N., Seibert, G. S., May, R. W., Fitzgerald, M. C., and Fincham, F. D. (2017). School burnout and intimate partner violence: the role of self-control. Pers. Individ. Dif. 112, 18–25. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.02.047
Craig, C. L., Marshall, A. L., Sjöström, M., Bauman, A. E., Booth, M. L., Ainsworth, B. E., et al. (2003). International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 35, 1381–1395. doi: 10.1249/01.mss.0000078924.61453.fb
de Ridder, D. T. D., Lensvelt-Mulders, G., Finkenauer, C., Stok, F. M., and Baumeister, R. F. (2012). Taking stock of self-control: a meta-analysis of how trait self-control relates to a wide range of behaviors. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 16, 76–99. doi: 10.1177/1088868311418749
Denson, T. F., Capper, M. M., Oaten, M., Friese, M., and Schofield, T. P. (2011). Self-control training decreases aggression in response to provocation in aggressive individuals. J. Res. Pers. 45, 252–256. doi: 10.1016/j.jrp.2011.02.001
Epstein, L. H. (1998). Integrating theoretical approaches to promote physical activity. Am. J. Prev. Med. 15, 257–265. doi: 10.1016/s0749-3797(98)00083-x
Fennell, C., Barkley, J. E., and Lepp, A. (2019). The relationship between cell phone use, physical activity, and sedentary behavior in adults aged 18–80. Comput. Human Behav. 90, 53–59. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2018.08.044
Friese, M., Frankenbach, J., Job, V., and Loschelder, D. D. (2017). Does self-control training improve self-control? A meta-analysis. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 12, 1077–1099. doi: 10.1177/1745691617697076
Gao, Q., Yan, Z., Zhao, C., Pan, Y., and Mo, L. (2014). To ban or not to ban: differences in mobile phone policies at elementary, middle, and high schools. Comput. Human Behav. 38, 25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.05.011
Gökçearslan, S̨, Mumcu, F. K., Has̨laman, T., and Çevik, Y. D. (2016). Modelling smartphone addiction: the role of smartphone usage, self-regulation, general self-efficacy and cyberloafing in university students. Comput. Human Behav. 63, 639–649. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.091
Hayes, A. F. (2013). Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach. New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Hoang, T., Koyama, A., Barnes, D., Sidney, S., Jacobs, D., Zhu, N., et al. (2013). Long-term patterns of low physical activity and cognitive function in mid-life: the CARDIA study. Alzheimers Dement. 9(Suppl. 4), 134–135. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.2468
Hofmann, W., Adriaanse, M., Vohs, K. D., and Baumeister, R. F. (2014a). Dieting and the self-control of eating in everyday environments: an experience sampling study. Br. J. Health Psychol. 19, 523–539. doi: 10.1111/bjhp.12053
Hofmann, W., Luhmann, M., Fisher, R. R., Vohs, K. D., and Baumeister, R. F. (2014b). Yes, but are they happy? Effects of trait self-control on affective well-being and life satisfaction. J. Pers. 82, 265–277. doi: 10.1111/jopy.12050
Jiang, Z., and Zhao, X. (2016). Self-control and problematic mobile phone use in Chinese college students: the mediating role of mobile phone use patterns. BMC Psychiatry 16:416. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-1131-z
Katzmarzyk, P. T., Church, T. S., Craig, C. L., and Bouchard, C. (2009). Sitting time and mortality from all causes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 41, 998–1005. doi: 10.1249/mss.0b013e3181930355
Kim, S.-E., Kim, J.-W., and Jee, Y.-S. (2015). Relationship between smartphone addiction and physical activity in Chinese international students in Korea. J. Behav. Addict. 4, 200–205. doi: 10.1556/2006.4.2015.028
Köpetz, C. E., Lejuez, C. W., Wiers, R. W., and Kruglanski, A. W. (2013). Motivation and self-regulation in addiction: a call for convergence. Pers. Psychol. Sci. 8, 3–24. doi: 10.1177/1745691612457575
Kwon, M., Kim, D.-J., Cho, H., and Yang, S. (2013). The smartphone addiction scale: development and validation of a short version for adolescents. PLoS One 8:e83558. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083558
Lee, H., Kim, J. W., and Choi, T. Y. (2017). Risk ractors for smartphone addiction in Korean adolescents: smartphone use patterns. J. Korean Med. Sci. 32, 1674–1679. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2017.32.10.1674
Lepp, A., Barkley, J. E., and Karpinski, A. C. (2014). The relationship between cell phone use, academic performance, anxiety, and satisfaction with life in college students. Comput. Human Behav. 31, 343–350. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2013.10.049
Lepp, A., Barkley, J. E., and Li, J. (2017). Motivations and experiential outcomes associated with leisure time cell phone use: results from two independent studies. Leis. Sci. 39, 144–162. doi: 10.1080/01490400.2016.1160807
Lepp, A., Barkley, J. E., Sanders, G. J., Rebold, M., and Gates, P. (2013). The relationship between cell phone use, physical and sedentary activity, and cardiorespiratory fitness in a sample of U.S. college students. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 10:79. doi: 10.1186/1479-5868-10-79
Liu, Q.-Q., Zhang, D.-J., Yang, X.-J., Zhang, C.-Y., Fan, C.-Y., and Zhou, Z.-K. (2018a). Perceived stress and mobile phone addiction in Chinese adolescents: a moderated mediation model. Comput. Human Behav. 87, 247–253. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2018.06.006
Liu, Q.-Q., Zhou, Z.-K., Yang, X.-J., Kong, F.-C., Sun, X.-J., and Fan, C.-Y. (2018b). Mindfulness and sleep quality in adolescents: analysis of rumination as a mediator and self-control as a moderator. Pers. Individ. Dif. 122, 171–176. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2017.10.031
Liu, Q.-Q., Zhou, Z.-K., Yang, X.-J., Kong, F.-C., Niu, G.-F., and Fan, C.-Y. (2017). Mobile phone addiction and sleep quality among Chinese adolescents: a moderated mediation model. Comput. Human Behav. 72, 108–114. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2017.02.042
Long, J., Liu, T.-Q., Liao, Y.-H., Qi, C., He, H.-Y., Chen, S.-B., et al. (2016). Prevalence and correlates of problematic smartphone use in a large random sample of Chinese undergraduates. BMC Psychiatry 16:408. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-1083-1083
Lopez-Fernandez, O. (2017). Short version of the smartphone addiction scale adapted to Spanish and French: towards a cross-cultural research in problematic mobile phone use. Addict. Behav. 64, 275–280. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.11.013
Lu, C., Stolk, R. P., Sauer, P. J. J., Sijtsma, A., Wiersma, R., Huang, G., et al. (2017). Factors of physical activity among Chinese children and adolescents: a systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 14, 36. doi: 10.1186/s12966-017-0486-y
Martin Ginis, K. A., and Bray, S. R. (2010). Application of the limited strength model of self-regulation to understanding exercise effort, planning and adherence. Psychol. Health 25, 1147–1160. doi: 10.1080/08870440903111696
Moffitt, T. E., Arseneault, L., Belsky, D., Dickson, N., Hancox, R. J., Harrington, H., et al. (2011). A gradient of childhood self-control predicts health, wealth, and public safety. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 2693–2698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010076108
Owen, N., Healy, G. N., Matthews, C. E., and Dunstan, D. W. (2010). Too much sitting: the population health science of sedentary behavior. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 38, 105–113. doi: 10.1097/JES.0b013e3181e373a2
Özdemir, Y., Kuzucu, Y., and Ak, S̨ (2014). Depression, loneliness and Internet addiction: how important is low self-control? Comput. Human Behav. 34, 284–290. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.02.009
Pearson, C. M., Mason, T. B., Cao, L., Goldschmidt, A. B., Lavender, J. M., Crosby, R. D., et al. (2018). A test of a state-based, self-control theory of binge eating in adults with obesity. Eat. Disord. 26, 26–38. doi: 10.1080/10640266.2018.1418358
Rebold, M. J., Lepp, A., Sanders, G. J., and Barkley, J. E. (2015). The impact of cell phone use on the intensity and liking of a bout of treadmill exercise. PLoS One 10:e0125029. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125029
Rebold, M. J., Sheehan, T., Dirlam, M., Maldonado, T., and O’Donnell, D. (2016). The impact of cell phone texting on the amount of time spent exercising at different intensities. Comput. Human Behav. 55, 167–171. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.09.005
Rosenberg, D. E., Norman, G. J., Wagner, N., Patrick, K., Calfas, K. J., and Sallis, J. F. (2010). Reliability and validity of the sedentary behavior questionnaire (SBQ) for adults. J. Phys. Act. Health 7, 697–705. doi: 10.1123/jpah.7.6.697
Tan, S. H. (2008). Revision of self-dontrol scale for Chinese college students. Chin. J. Clin. Psychol. 16, 468–470.
Tangney, J. P., Baumeister, R. F., and Boone, A. L. (2004). High self-control predicts good adjustment, less pathology, better grades, and interpersonal success. J. Pers. 72, 271–324. doi: 10.1111/j.0022-3506.2004.00263.x
Walsh, S. P., White, K. M., and Young, R. M. (2010). Needing to connect: the effect of self and others on young people’s involvement with their mobile phones. Aust. J. Psychol. 62, 194–203. doi: 10.1080/00049530903567229
Wilmer, H. H., and Chein, J. M. (2016). Mobile technology habits: patterns of association among device usage, intertemporal preference, impulse control, and reward sensitivity. Psychon. Bull. Rev. 23, 1607–1614. doi: 10.3758/s13423-016-1011-z
Yun, I., Kim, S.-G., and Kwon, S. (2016). Low self-control among South Korean adolescents: a test of Gottfredson and Hirschi’s generality hypothesis. Int. J. Offender Ther. Comp. Criminol. 60, 1185–1208. doi: 10.1177/0306624x15574683
Keywords: sedentary behavior, problematic smartphone use, self-control, adolescents, exercise interventions
Citation: Xiang M-Q, Lin L, Wang Z-R, Li J, Xu Z and Hu M (2020) Sedentary Behavior and Problematic Smartphone Use in Chinese Adolescents: The Moderating Role of Self-Control. Front. Psychol. 10:3032. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.03032
Received: 03 September 2019; Accepted: 20 December 2019;
Published: 21 January 2020.
Edited by:
Henriette van Praag, Florida Atlantic University, United StatesReviewed by:
Rosa Magallon, University of Zaragoza, SpainAurelio Olmedilla, University of Murcia, Spain
Copyright © 2020 Xiang, Lin, Wang, Li, Xu and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Hu, d2hvb21pbkBhbGl5dW4uY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Ming-Qiang Xiang
Ming-Qiang Xiang Long Lin1†
Long Lin1† Zi-Rong Wang
Zi-Rong Wang Jin Li
Jin Li Zebo Xu
Zebo Xu