- Institute of Food Science and Technology, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Key Laboratory of Agro-Products Processing, Chinese Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing, China
Background: Corn oil, known for its high linoleic acid (LA) content, is vulnerable to isomerization during thermal processing. This results in the production of harmful trans-linoleic acid isomers (TLAs) and small amounts of beneficial conjugated linoleic isomers (CLAs).
Methods: This study examined the change in formation of TLAs and CLAs in corn oil heated to temperatures between 180°C and 240°C, and studied the kinetics of their formation, utilizing infrared spectroscopy and gas chromatography to clarify the reaction’s rate-determining steps and underlying mechanisms.
Results: The results indicated the predominant generation of three distinct TLA and CLA isomers, with their levels showing a positive correlation with both the temperature and duration of heating. Importantly, the formation of mono-TLA isomers emerged as the rate-controlling step in the isomerization process, while the presence of O2 accelerated the formation of both TLA and CLA isomers. This study provided mechanistic insights and predictive models for forming TLA and CLA isomers under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
Conclusion: These findings imply that modulating the synthesis of mono-TLA isomers could serve as an effective strategy for reducing TLA formation and enhancing the conversion of TLA to CLAs in heated corn oil, thereby establishing a theoretical framework for precisely regulating TLAs.
1 Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) has endorsed corn oil as a healthy cooking oil. Corn oil comprises approximately 80% unsaturated fatty acids, particularly containing about 49.05% linoleic acid (C18:2-9c,12c) in its total fatty acid content (He et al., 2017). However, during refining and deep-fat frying, geometric isomerization of linoleic acid in corn oil leads to increased formation of trans-linoleic acid isomers (TLAs), primarily C18:2-9t,12t, C18:2-9c,12t, and C18:2-9t,12c. Substantial TLA intake has been linked to an elevated risk of coronary heart disease and various other chronic health disorders (Ganguly and Pierce, 2012; Nestel, 2014; Guo et al., 2023). Simultaneously, position migration of σ bonds in linoleic acid of heated corn oil (He et al., 2017; Nestel, 2014; Guo et al., 2016) generates trace amounts of conjugated linoleic acid isomers (CLAs), which are beneficial to human health (Guo et al., 2016; Nirvair et al., 2007; Badawy et al., 2023). Therefore, it is crucial to elucidate the underlying relationship between TLA and CLA isomers, develop methods for precise TLA isomer control or efficient TLA-to-CLA isomer conversion, minimize the potential health risks associated with corn oil consumption, and safeguard the nutritional wellbeing of consumers.
Reaction kinetics is a fundamental approach for studying chemical reaction mechanisms by analyzing reaction rates and activation energies to elucidate the relationships between reactants and products. Studies have shown that heating temperature and time significantly affect the formation of TLA and CLA isomers in heated edible oils (Guo et al., 2016). The formation of TLAs isomers increases with temperature and time, and the reaction constants of these isomers exhibit an Arrhenius relationship with temperature (Białek et al., 2021; Guo et al., 2015). Numerous studies have confirmed the emergence of diverse CLA isomers, including C18:2-9c,11t, C18:2-10t,12c, C18:2-9t,11t, and C18:2-10t,12t, during heating of edible oils (Guo et al., 2017; Shinn et al., 2017). Our previous research identified C18:2-9t,11t and C18:2-10t,12t (t,t-CLAs) as the primary CLA isomers in heated triolein. However, the formation mechanisms of these TLA and CLA isomers and their interconversion in corn oil during heating remain unclear and require further investigation (Xie and Xia, 2019; Li et al., 2023).
The complexity of the chemical reactions in heated corn oil stems from the presence of various polyunsaturated fatty acids. When subjected to prolonged or repeated high temperatures, corn oil may undergo processes such as oxidation, isomerization, degradation, and polymerization (Li et al., 2021; Yazdi and Alemzadeh, 2017; Xiang et al., 2024). The isomerization of C18:2-9c,12c involves an intricate series of interconnected reactions (Aksoy et al., 2021; Chen and Liu, 2020). Consequently, the formation kinetics of the TLA and CLA isomers were investigated to determine the rate-controlling step and optimal heating conditions in both aerobic (O2) and anaerobic (N2) environments using infrared spectroscopy and gas chromatography. The findings of this study provide a theoretical framework for effectively controlling TLA isomers in edible oils during everyday cooking practices and optimizing the conversion of TLA isomers to CLA isomers.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Corn was sourced from the Yellow River Valley in Shandong, China. Corn oil was extracted and processed by the Xiwang Group through a series of processes, including embryo rolling, pre-pressing, alkaline refining, decolorization, dewaxing, and deodorization. The resulting corn oil met the quality standards for first-class oils specified by the national standard (GB/T 19,111–2017). The average concentrations of TLA and CLA isomers are 1.47 × 10−2 g/g, and 0.23 × 10−2 g/g respectively (He et al., 2017). C18:2 isomer standards were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Standards for linoleic acid methyl ester (LAME) mixtures (C18:2-9c,11t, C18:2-10t,12c, C18:2-9t,11t, and C18:2-10t,12t) were procured from Matreya (State College, PA, United States). Triundecanoin, used as an internal standard for GC-FID analysis, was obtained from NU-CHEK Prep. Isooctane, used as the chromatographic organic solvent, was obtained from Fisher Scientific (Fair Lawn, NJ). The heating medium consisted of silicone oil (viscosity 500 cSt) procured from the Dingye Industrial Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
2.2 Thermal processing
Aliquots of 5 g of each corn oil sample were transferred to a 20-mL micro glass ampoule. The ampoules were either purged with nitrogen gas (N2) at a flow rate of 5 mL/min for 5 min or left exposed to ambient air and then flame-sealed using an oxy-hydrogen torch. Subsequently, they were subjected to thermal treatments at 180, 210, 220, 230, and 240°C for 6, 12, 18, 36, and 42 h, respectively, in a silicone oil bath (Viscosity 500 Cst, Beijing Dingye Industry and Trade Company). The temperature fluctuations were maintained at ±1°C. Upon completion of the designated heating period, the ampoules were extracted from the silicone oil bath and allowed to equilibrate to the ambient temperature prior to further analysis.
2.3 Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters
The corn oil samples were derivatized using the technique described in our previous study (Guo et al., 2017). A 200-mg sample was accurately weighed into a sealed centrifuge tube. The sample was then combined with 2 mL of isooctane containing undecanoic acid triglycerides (serving as an internal standard at 4,000 ppm, equivalent to 8 mg). Subsequently, 0.10 mL of 2 M methanolic potassium hydroxide was introduced. The mixture was vigorously agitated for 30 s, followed by centrifugation at 4,000 revolutions per minute for 10 min. The resulting supernatant was carefully separated, and the upper layer was dehydrated using anhydrous magnesium sulfate.
2.4 Infrared spectroscopy analysis
Corn oil samples were analyzed using attenuated total reflection Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (ATR-FTIR; Tensor 37, Bruker, Germany). Prior to the sample examination, a background spectrum was acquired within the 400–4,000 cm−1 range. A 5 μL aliquot of each sample was then deposited onto the ATR crystal using a micropipette, followed by 32 scans at 4 cm−1 resolution. Sample analysis was performed immediately after oven removal. Between measurements, the ATR crystal was cleaned with acetone and isooctane. All infrared spectra were recorded in absorption mode. To mitigate issues arising from baseline shifts and peak overlaps, these spectrograms were analyzed in detail (Guo et al., 2017).
2.5 GC-FID analysis
Following methylation, samples were examined using a GC-2010 gas chromatograph (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) equipped with a CP-SIL 88 fused silica capillary column (100 m length, 0.25 mm diameter, and 0.2 mm film thickness) and a flame ionization detector. The temperature program was initiated at 60°C for 5 min, and then increased to 160°C at 25°C/min. After a 5-min incubation at 160°C, the temperature was further raised at 2°C/min to a final temperature of 220°C and maintained for 25 min. The sample injection volume was 1 mL with a 10:1 split ratio. Nitrogen (99.999%) was used as carrier gas at a flow rate of 6.3 mL/min. The detector flow rates for makeup, hydrogen, and air were set at 30, 40, and 400 mL/min, respectively. Both injector and detector temperatures were maintained at 250°C (Guo et al., 2021). Fatty acids were identified by comparing their retention times with known standards (cis-trans isomers of 2 oleic, 4 linoleic, and 8 linolenic acids), using the calculation method described by Li et al. (2013). Accurate fatty acid concentration measurements were contingent on the absence of intermolecular chemical reactions.
2.6 Formation kinetics of the isomers
Multiple reactions occur during oil heating; however, this study specifically examined the formation rate of isomerization products (TLAs and CLAs) from linoleic acid when heated in O2 and N2 environments. The isomer formation rate can be expressed using the following general Equation 1:
Where C represents the heat-induced isomerization products, k denotes the formation rate of isomerization C, and n indicates the order of formation with respect to C.
Equation 1 can be integrated over a specified concentration range and time period as shown in Equation 2.
where C0 and Ct represent the concentrations of C at time 0 and t, respectively.
This integral is valid when n ≥ 2. For a zero-order reaction, becomes Equation 3,
When n = 1, the result is Equation 4,
In first-order reactions, the rate is proportional to the isomerization concentration in corn oil, and ln (Ct/C0) is proportional to the reaction duration. In this study, the reaction order was determined using graphical correlations.
The isomerization of C18:2-9c,12c in corn oil to TLA and CLA isomers can be analyzed by examining the relationship between isomer concentration and time. The Arrhenius equation describes the relationship between the reaction rate and temperature Equation 5 is shown below.
Where A pre-exponential factor, R is the ideal gas constant, and Ea is the activation energy.
Determining k for isomerization at a minimum of three different temperatures allows for Ea calculation from the slope of the plot between ln k and 1/T.
Using Ea, a mathematical model (Equation 6) relating the isomer concentrations to heating temperature and time can be constructed as follows:
This integral was applied for n ≥ 2. For zero-order reactions, the mathematical model (Equation 7) is transformed as follows,
When n = 1, the result is
namely:
2.7 Statistical analysis
All experiments were performed in triplicate using a completely randomized design. Data visualization was conducted using the SigmaPlot software (version 12.0; Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, United States).
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Infrared spectral analysis of TLA and CLA isomers
The infrared spectra of unheated and heated corn oil were analyzed using ATR-FTIR (Figure 1). The spectrum revealed absorption peaks ranging from 3,008 cm−1 to 723 cm−1, indicative of the presence of various functional groups in the corn oil triglyceride components. Notably, the prominent absorption peaks observed at 2,923 cm−1, 2,854 cm−1, 1,743 cm−1, 1,160 cm−1 and 723 cm−1 can be attributed to the symmetric stretching vibration of the hydrocarbon chain, antisymmetric stretching vibration, Fermi vibration of the carbonyl group, C-O stretching bending vibration, and planar rocking vibration of the methylene groups, respectively.
Upon high-temperature heating, significant changes were observed in the corn oil spectra, particularly at 966 cm−1, which represented the C-H groups out-of-plane deformation absorption. Corn oil heated at 220°C for 12 h exhibited a significantly higher absorption at 966 cm−1 (approximately a one-fold increase in peak area) than unheated corn oil (Figure 1), confirming the formation of trans fatty acids during high-temperature heating. The intensity of the 966 cm−1 absorption peak in corn oil increased proportionally with heating time and temperature. The absorption intensity at 966 cm−1 was higher in the presence of oxygen (O2) than in nitrogen (N2) at the same temperature and heating duration, suggesting that O2 accelerated the formation of trans double bonds. In the presence of O2, the cis double bond of UFAs undergoes a hydrogen abstraction at the allyl or diallyl position and forms corresponding cis double bond radicals, which are thermodynamically unstable, immediately converting into peroxyl radicals (Rc-O-O·) in the subsequent oxidative process to accelerate and induce isomerization reaction. A new finding reported by that Rc-O-O-H is a very important intermediate, and the cleavage of O-O bond (160.97 kJ/mol) in Rc-O-O-H is the rate-controlling step during the cis/trans isomerization (Guo et al., 2023). Notably, ATR-FTIR analysis can only detect the total concentration of trans fatty acids, and cannot distinguish between mono- and di-trans isomers. Christy (2009) demonstrated that linoleic acid can be isomerized to conjugated linoleic acids (CLAs) upon heating at 250°C, with absorption peaks at 987 cm−1 and 946 cm−1. However, no corresponding peaks were detected in the ATR-FTIR spectra of corn oil heated at 220°C, implying that the amount of CLAs formed in corn oil under these conditions was likely below the detection threshold of ATR-FTIR.
3.2 GC analysis of TLA and CLA isomers
As shown in Figure 2, the TFA and CLA isomers were observed by heating corn oil under high temperature conditions. The TFAs in corn oil include trans oleic acid (C18:1-9t), trans linoleic acids (C18:2-9c,12t, C18:2-9t,12c, C18:2-9t,12t), and trans linolenic acids (C18:3-9c,12c,15t, C18:3-9c,12t,15c, C18:3-9t,12c,15c, C18:3-9t,12t,15c, and C18:3-9t,12c,15t). The concentration of C18:1-9t increased with both heating temperature and duration. The levels of C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c produced during the heating of corn oil were nearly equivalent and exceeded the amount of C18:2-9t,12t, suggesting that C18:2-9c,12c isomerize more readily to single-trans isomers and exhibit a lower tendency to form double-trans isomers under the applied heating conditions. A similar trend was observed in the isomerization of linolenic acid. The concentrations of C18:3-9c,12t,15t, C18:3-9c,12c,15t, and C18:3-9c,12t,15c in corn oil heated for 24 h were significantly lower than those heated for 12 h at both 220°C and 240°C. This decrease can be attributed to the conversion or degradation of these trans-linolenic acid isomers at higher temperatures and longer heating durations. The above results indicated that the double bonds of UFAs during the heating process first isomerize to give rise to mono-trans isomers, then to double-trans isomers, and finally to multi-trans isomers.
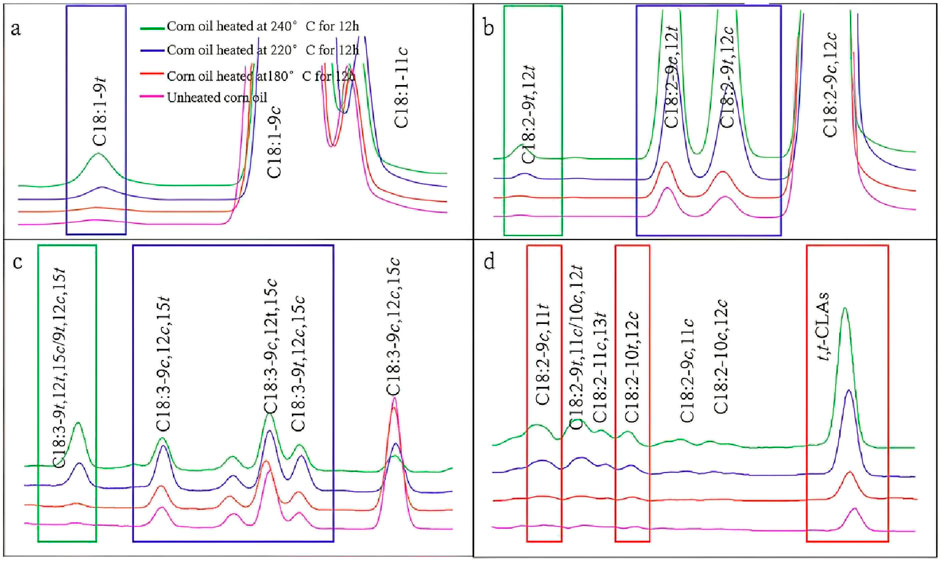
Figure 2. (a-d) Gas chromatogram of unheated corn oil heated at 180, 220, and 240°C for 12 h in corn oil.
The initial formation of CLAs was characterized by t,t-CLAs, indicating a radical-mediated isomerization pathway, followed by the emergence of C18:2-9c,11t and C18:2-10t,12c through extended heating and cooling. As the temperature continued to rise, additional CLA isomers (C18:2-9t,11c/10c,12t, C18:2-11c,13t, C18:2-9c,11c, and C18:2-10c,12c) appeared in extremely low amounts (<0.5% total CLA). These findings align with those of previous studies on CLAs isomerization (Li et al., 2013). The diversity and abundance of these isomers increased in response to elevated heating temperatures and prolonged exposure, supporting the results obtained by ATR-FTIR. However, the quantitative analysis of C18:2-9t,11c/10c,12t, C18:2-11c,13t, C18:2-9c,11c, and C18:2-10c,12c proved challenging due to their low concentrations.
Thus, this study was primarily focused on the formation kinetics of TLAs (C18:2-9c,12t, C18:2-9t,12c, and C18:2-9t,12t) and CLAs (t,t-CLAs, C18:2-9c,11t, and C18:2-10t,12c) isomerized from linoleic acid in corn oil to further elucidate the mechanisms and key controlling steps of the isomerization process.
3.3 Kinetics for the formation of TLA isomers
The relationships between ln (Ct/C0) and heating duration for C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c under N2 and O2 atmospheres are shown in Figures 3a,b. The linear correlations observed indicated that the thermally induced isomerization reactions followed first-order kinetics concerning C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c concentrations. The rate constants (k) derived from the slopes of the first-order plots at 180, 210, 220, 230, and 240°C were 0.0062 and 0.0065 h−1, 0.0204 and 0.0206 h−1, 0.0534 and 0.0536 h−1, 0.0976 and 0.0980 h−1, and 0.1002 and 0.1007 h−1, respectively, for C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c formation (Table 1). In the presence of O2, the k values at the same temperatures were 0.0099 and 0.0101 h−1; 0.0531 and 0.0533 h−1; 0.0573 and 0.0577 h−1; 0.0996 and 0.0999 h−1; and 0.1103 and 0.1111 h−1, respectively (Table 1), significantly exceeding those under N2. These findings suggest comparable formation rates for C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c, which increased with temperature and O2 presence.
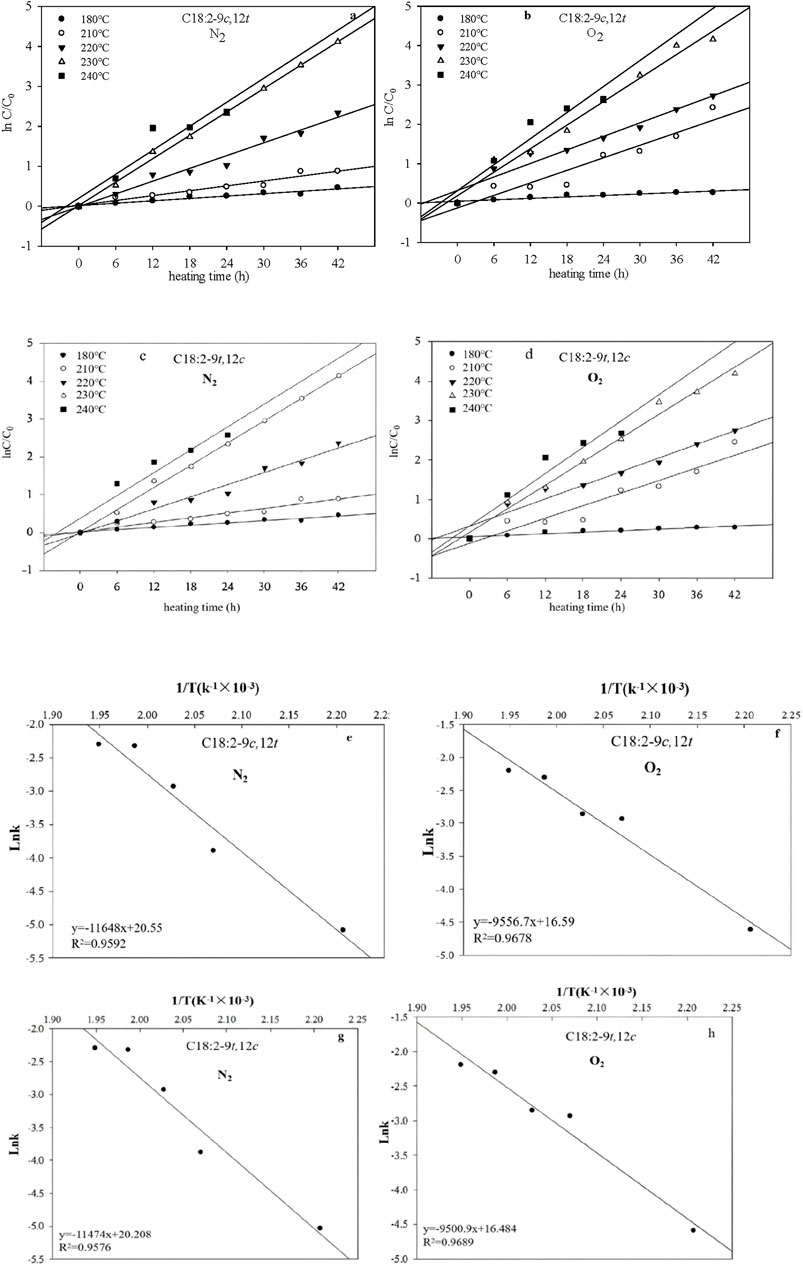
Figure 3. Plots showing the correlation between ln (Ct/C0) and time for the C18:2-9c,12t in the presence of N2 (a) and O2 (b), and the C18:2-9t,12c in the presence of N2 (c) and O2 (d), and the relationship between lnk and 1/T for the C18:2-9c,12t in the presence of N2 (e) and O2 (f), and the C18:2-9t,12c in the presence of N2 (g) and O2 (h) at different temperatures.
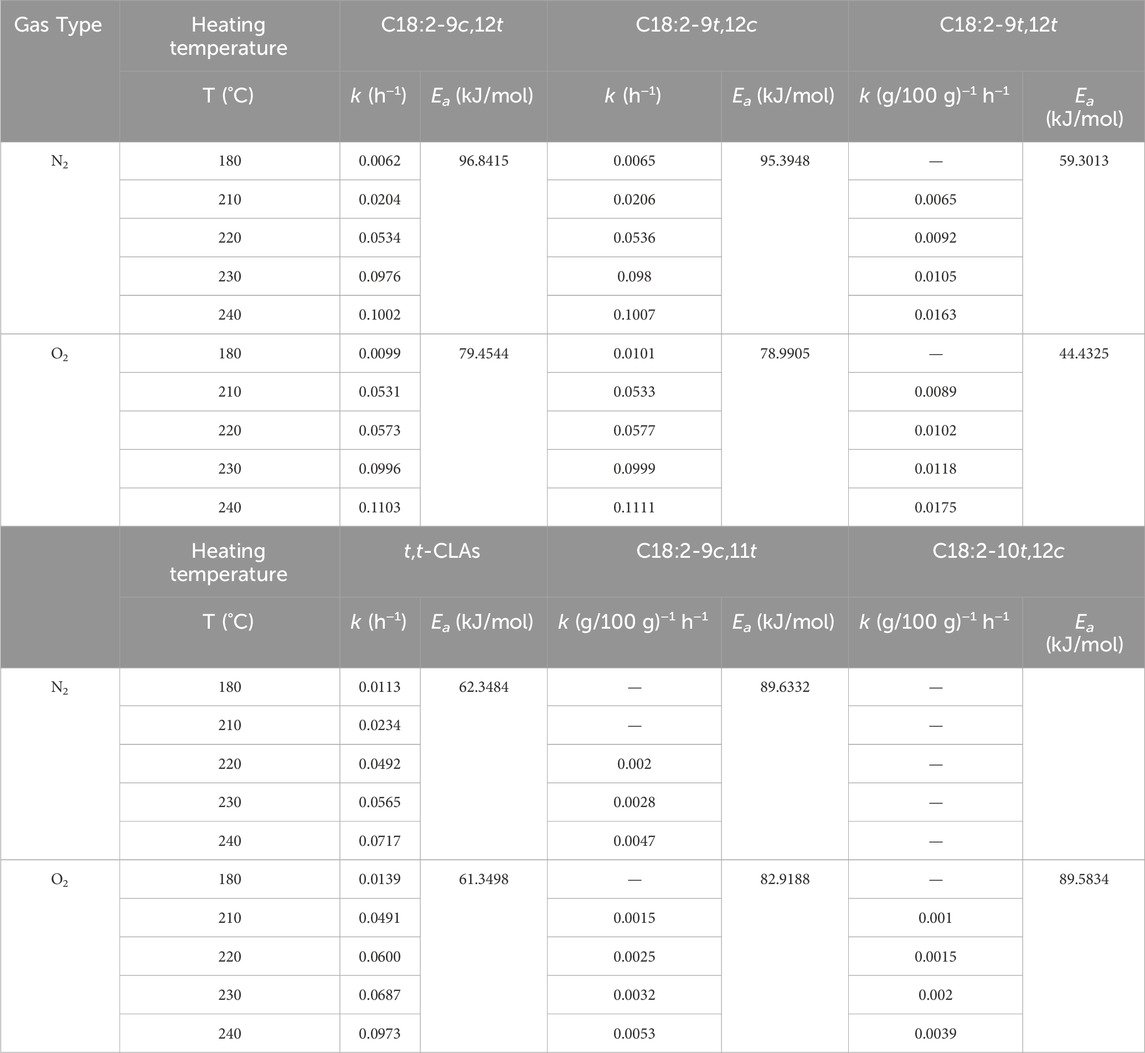
Table 1. Kinetic parameters for (1) formation of C18:2-9c,12t; (2) formation of C18:2-9t,12c; (3) formation of C18:2-9t,12t; (4) formation of t,t-CLAs; (5) formation of C18:2-9c,11t; and (6) formation of C18:2-10t,12c.
The Ea values for C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c isomer formation were 96.8415 and 95.3948 kJ/mol and 79.4544 kJ/mol under N2 and 78.9905 kJ/mol under O2, respectively. These values indicate a reduction in Ea in the presence of O2 compared with that in N2. Notably, the Ea values for C18:2-9c,12t were nearly identical to those for C18:2-9t,12c, suggesting that the energy required for thermal formation of C18:2-9c,12t in corn oil was comparable to that of C18:2-9t,12c. By incorporating k and Ea into the first-order kinetic model (Equation 8), the concentrations of C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c isomers in corn oils at various temperatures and heating times were successfully predicted (Table 2).
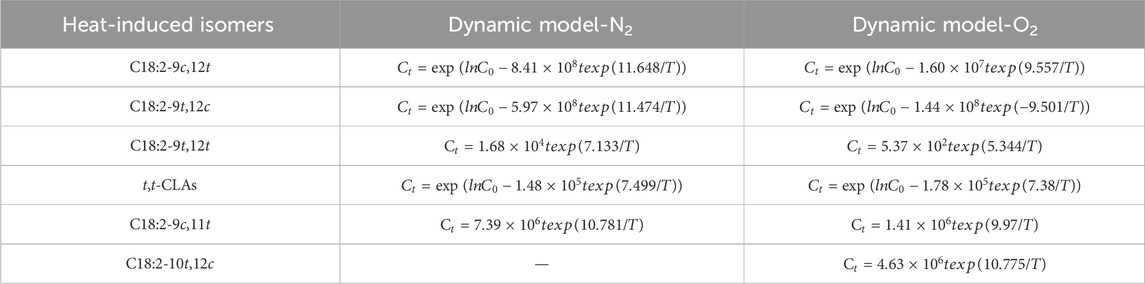
Table 2. Dynamic model of heat-induced isomers for concentration, heating temperature, and heating time in the presence of N2 and O2.
At 180°C, C18:2-9t,12t was not formed in the heated corn oil. It emerged when corn oil was heated to 210°C for 24 h or at 220°C and 230°C for 6 h under N2. O2 presence accelerated C18:2-9t,12t isomer. Linear correlations between Ct and heating time for C18:2-9t,12t indicated zeroth-order formation reactions under both N2 and O2 (Figure 4). The k values for C18:2-9t,12t formation increased with increasing temperature under both atmospheres, with higher values observed in O2 than in N2 at equivalent temperatures (Figure 4; Table 1).
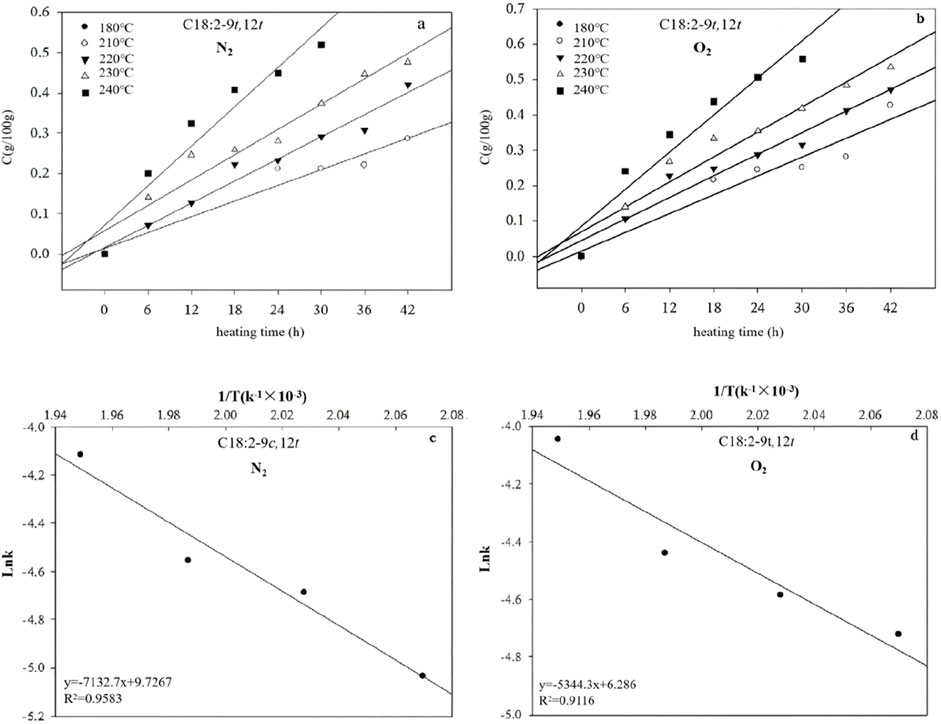
Figure 4. Plots showing the correlation between Ct and time for the C18:2-9t,12t in the presence of N2 (a) and O2 (b), and the relationship between lnk and 1/T in the presence of N2 (c) and O2 (d) at different temperatures.
The activation energy (Ea) for a zeroth-order reaction can be determined using data from a graph correlating lnk and T−1 (Figure 4). The analysis revealed that the Ea values for C18:2-9t,12t formation were higher in the presence of N2 (59.3013 kJ/mol) than in the presence of O2 (44.4325 kJ/mol) (Table 1). This observation indicates that thermodynamic processes will likely dominate C18:2-9t,12t production. Owing to the superior thermodynamic stability of the t,t conformation relative to the c,t/t,c conformations, the intermediate isomers C18:2-9c,12t and C18:2-9t,12c were predominantly transformed into the more stable C18:2-9t,12t. The reaction temperature primarily influenced these transformations. Furthermore, the zero-order mathematical model (formula 8) was employed, utilizing k and Ea data, to estimate C18:2-9t,12t isomer concentrations in corn oils subjected to various temperatures and heating durations (Table 2).
3.4 Kinetics for the formation of CLA isomers
Figure 5 shows that the t, t-CLA isomer formation follows a first-order reaction in the heating system in the presence of N2 and O2. Notably, the reaction order remains unchanged with increasing temperature. The k for t,t-CLA formation at 180, 210, 220, 230, and 240°C were 0.0113 and 0.0139 h−1, 0.0234 and 0.0491 h−1, 0.0492 and 0.0600 h−1, 0.0565 and 0.0687 h−1, 0.0717 and 0.0973 h−1, respectively, under N2 and O2 atmospheres (Table 1). The k value was higher in the presence of O2 than in N2, indicating that O2 facilitated the formation of t,t-CLA isomers. Additionally, Ea for the formation of t,t-CLAs was lower in the presence of O2 (61.3498 kJ/mol) than in N2 (62.3484 kJ/mol), suggesting that O2 accelerates the isomerization process. These trends are consistent with the formation of TLA isomers.
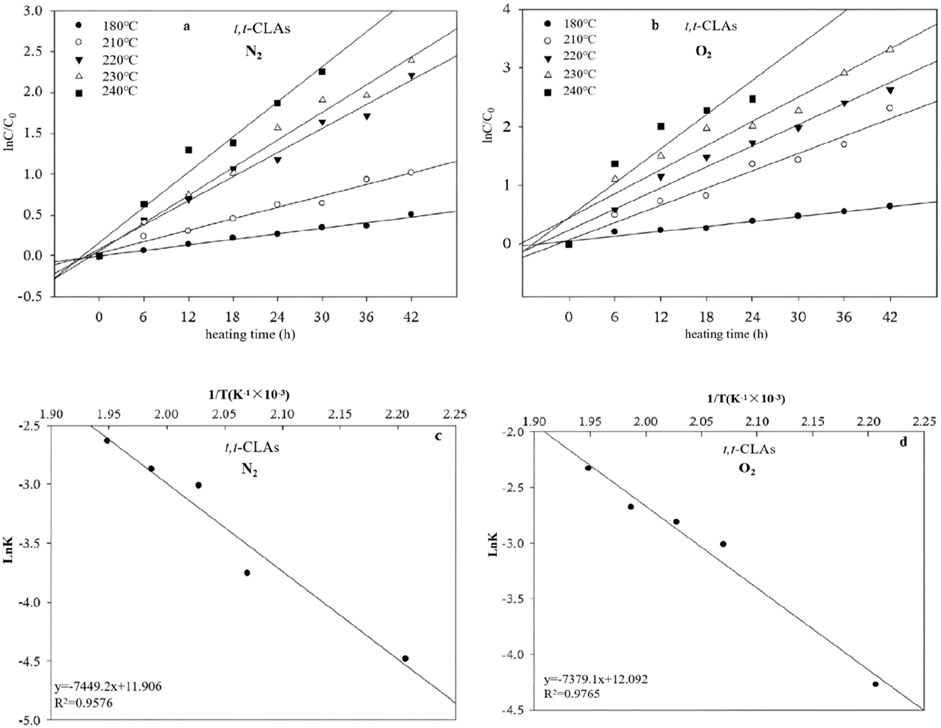
Figure 5. Plots showing the correlation between ln (Ct/C0) and time for the t,t-CLAs in the presence of N2 (a) and O2 (b), and the relationship between lnk and 1/T in the presence of N2 (c) and O2 (d) at different temperatures.
In the presence of N2, the formation of C18:2-9c,11t was not observed at 180°C and 210°C and only appeared at 220°C after 18 h. Similarly, C18:2-10t,12c could not be detected until heating to 220°C for 30 h, rendering its rate constant incalculable. In O2, neither C18:2-9c,11t nor C18:2-10t,12c were formed at 180°C, emerging at 210°C for 24 h and 30 h, respectively. The concentrations of C18:2-9c,11t, and C18:2-10t,12c exhibited linear relationships with heating time and temperature, indicative of zero-order reactions (Figure 6). The k values increased with increasing temperature, and were higher in O2 than in N2 (Table 1). Table 1 shows that t,t-CLAs have lower Ea values for isomerization than C18:2-9c,11t and C18:2-10t,12c (Table 1), indicating that t,t-CLAs have lower activation energies for isomerization than C18:2-9c,11t and C18:2-10t,12c. This observation explains why t,t-CLAs are formed first, followed by the generation of C18:2-9c,11t, C18:2-10t,12c, and other isomers. Furthermore, mathematical models relating the concentration, heating temperature, and time of t,t-CLAs, C18:2-9c,11t, and C18:2-10t,12c were derived (Table 2).
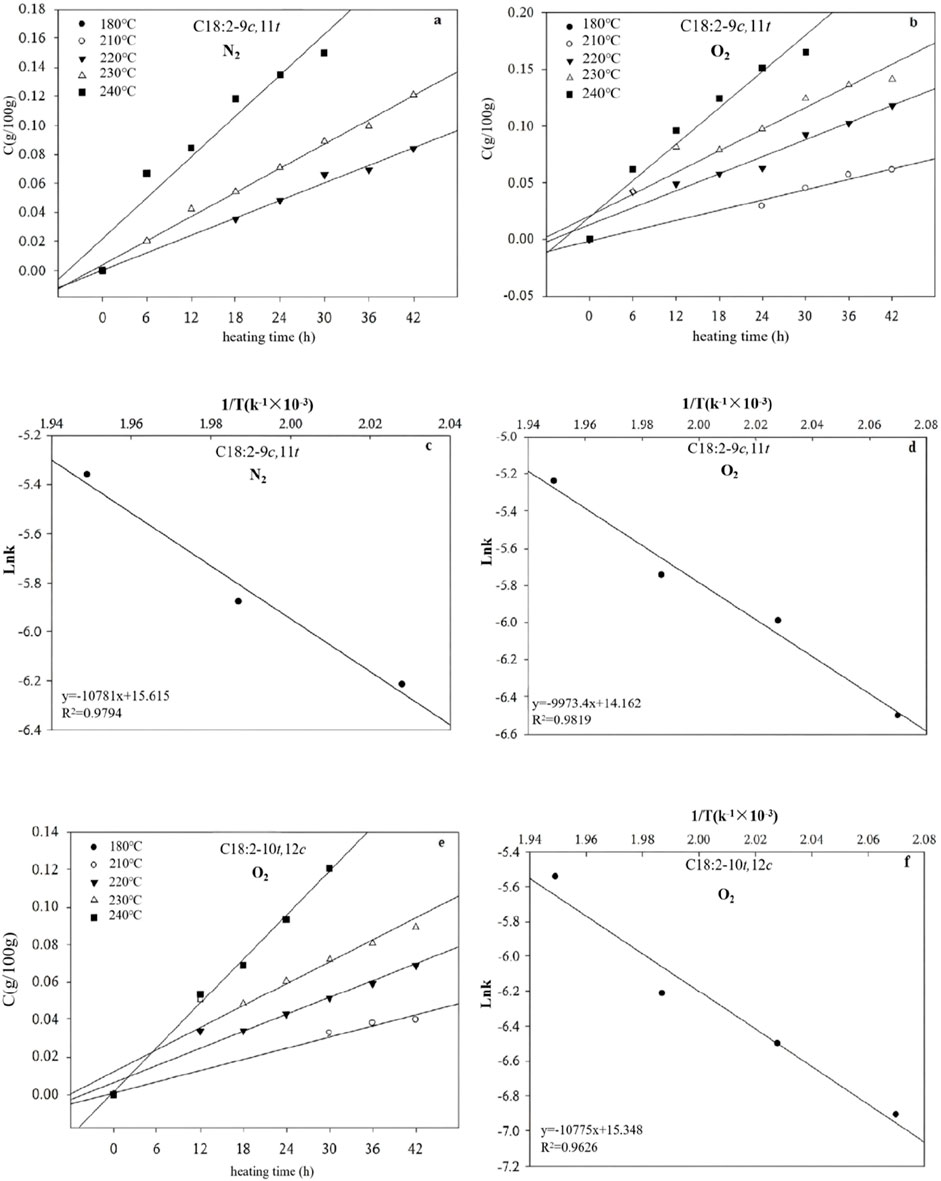
Figure 6. Plots showing the correlation between ln (Ct/C0) and time for C18:2-9c,11t in the presence of N2 (a) and O2 (b), C18:2-10t,12c in the presence (e) of O2, and the relationship between ln k and 1/T for C18:2-9c,11t in the presence of N2 (c) and O2 (d), and C18:2-10t,12c in the presence (f) of O2 at different temperatures.
These results demonstrate that linoleic acid in corn oil undergoes isomerization during thermal processing, initially forming equal amounts of mono-TLA isomers, which are then transformed into double-TLA isomers. Concurrently, t,t-CLAs are generated, followed by mono-CLA and cis-CLA isomers, as the temperature increases. The k and Ea values for the formation of mono-TLA isomers were significantly higher than those for double-TLA isomers, suggesting that mono-TLA isomer formation is rate-limiting. Thus, the inhibition of mono-TLA isomer formation can effectively reduce the production of TLAs. For CLAs formation, the t,t-CLAs showed lower k and Ea values than mono-TLA isomers but higher values than double-TLA isomers, suggesting that t,t-CLAs primarily isomerize from mono-TLA isomers and that promoting the conversion of mono-TLA isomers to t,t-CLAs may offer a promising strategy for mitigating TLAs formation. Previous studies showed that the formation of these TFA isomers in plant oil followed the free radical isomerization and proton transfer isomerization mechanisms, via the oxidation-induced isomerization, hydrogen extraction isomerization, direct isomerization, and proton transfer isomerization pathways [4]. These isomerization pathways well explain the formation and distribution of each TFA isomers at different reaction conditions.
4 Conclusion
The UFAs in corn oil undergoes a series of transformations during the thermal processing. It first isomerized to the mono-trans isomers, and then isomerized to double-trans isomers, finally isomerized to multi-trans isomers. This process generates t,t-CLAs, and their associated isomers during the thermal processing. Kinetic analysis revealed that the formation of mono-TLA isomers was the rate-controlling step in the isomerization process, the presence of O2 accelerated the formation of these TLA and CLA isomers. In addition, the mechanisms and prediction models governing the formation of TLA and CLA isomers in the presence of N2 and O2 are elucidated and constructed. These findings suggest that inhibiting the formation of mono-TLA isomers could be an effective strategy to reduce TLAs in heated corn oil, whereas promoting the transformation of TLAs to CLAs offers a promising alternative approach for TLAs mitigation.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YH: Writing – original draft. FH: Writing – review and editing. ML: Data curation, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Software, Writing – review and editing. XH: Methodology, Writing – review and editing. HH: Project administration, Writing – review and editing. FG: Project administration, Writing – review and editing. QW: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. QG: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Special National Key Research and Development Plan (2024YFD2100301), the Natural Science Foundation of China (32472474), and the National Peanut Industry Technology System (CARS-13-13).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aksoy, A. S., and Taşan, M. (2021). Effect of chemical refining steps on the some micro and macro element content and quality parameters in corn oil. Turk. J. Agric. For. 9 (6), 982–990. doi:10.24925/turjaf.v9i6.982-990.3919
Badawy, S., Liu, Y., Guo, M., Liu, Z., Xie, C., Marwan, M. A., et al. (2023). Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) as functional food: is it beneficial or not? Food Res. Int. 172, 113158. doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113158
Białek, M., Białek, A., Ruszczyńska, A., Bulska, E., Zaworski, K., and Czauderna, M. (2021). Evaluation of the influence of diet supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid isomers on elemental composition in the cardio-oncological nutritional programming rat’ model. J. Trace Elem. Med. Bio. 68, 126816. doi:10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126816
Chen, J. P., and Liu, H. B. (2020). Nutritional indices for assessing fatty acids: a mini-review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (16), 5695. doi:10.3390/ijms21165695
Christy, A. A. (2009). Thermally induced isomerization of trilinolein and trilinoelaidin at 250 degrees C: analysis of products by gas chromatography and infrared spectroscopy. Lipids 44 (12), 1105–1112. doi:10.1007/s11745-009-3363-x
Ganguly, R., and Pierce, G. N. (2012). Trans fat involvement in cardiovascular disease. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 56, 1090–1096. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201100700
Guo, Q., Ha, Y. M., Li, Q. P., Jin, J., Deng, Z. X., Li, Y. F., et al. (2015). Impact of additives on thermally-induced trans isomers in 9c,12c linoleic acid triacylglycerol. Food Chem. 174, 299–305. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.11.063
Guo, Q., Jiang, F., Deng, Z. X., Li, Q. P., Jin, J., Ha, Y. M., et al. (2017). Reaction pathway mechanism of thermally induced isomerization of 9,12-linoleic acid triacylglycerol. J. Sci. Food Agric. 97 (6), 1861–1867. doi:10.1002/jsfa.7988
Guo, Q., Li, T., Qu, Y., Liang, M., Ha, Y. M., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). New research development on trans fatty acids in food: biological effects, analytical methods, formation mechanism, and mitigating measures. Prog. Lipid Res. 89, 101199. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101199
Guo, Q., Li, T., Qu, Y., Wang, X. P., Liu, L., Liu, H. Z., et al. (2021). Action of phytosterols on thermally induced trans fatty acids in peanut oil. Food Chem. 344, 128637. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128637
Guo, Q., Wang, F., He, F., Ha, Y. M., Li, Q. P., Jin, J., et al. (2016). The impact of technical cashew nut shell liquid on thermally-induced trans isomers in edible oils. J. Food Sci. Tech. Mys. 53 (3), 1487–1495. doi:10.1007/s13197-015-2147-y
He, F., Guo, Q., Gu, F. Y., Ha, Y. M., Ning, J. J., Gao, P. P., et al. (2017). Principal component analysis of fatty acids and their isomers in eleven brands of corn oil. Mod. Food. Sci. Tech. 33 (02), 190–196. doi:10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2017.2.029
Li, A., Yuan, B. F., Li, W. M., Wang, F., and Ha, Y. M. (2013). Thermally induced isomerization of linoleic acid in soybean oil. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 166, 55–60. doi:10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2012.12.003
Li, T., Guo, Q., Qu, Y., Li, Y. J., Liu, H. Z., Liu, L., et al. (2021). Solubility and physicochemical properties of resveratrol in peanut oil. Food Chem. 368, 130687. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130687
Li, T., Guo, Q., Qu, Y., Liu, H. Z., Liu, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023). Inhibition mechanism of trans-resveratrol on thermally induced trans fatty acids in peanut oil. Food Chem. 406, 134863. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.134863
Nestel, P. (2014). Trans fatty acids: are its cardiovascular risks fully appreciated? Clin. Ther. 36 (3), 315–321. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2014.01.020
Nirvair, S. K., Hubbard, N. E., and Erickson, K. L. (2007). Conjugated linoleic acid isomers and cancer. J. Nutr. 137 (12), 2599–2607. doi:10.1093/jn/137.12.2599
Shinn, S. E., Ruan, C. M., and Proctor, A. (2017). Strategies for producing and incorporating conjugated linoleic acid-rich oils in foods. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Trans. 8 (1), 181–204. doi:10.1146/annurev-food-030216-025703
Xiang, F., Ding, C. X., Wang, M., Hu, H., Ma, X. J., Xu, X. B., et al. (2024). Vegetable oils: classification, quality analysis, nutritional value, and lipidomics applications. Food Chem. 439, 138059. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.138059
Xie, X. B., and Xia, Y. (2019). Analysis of conjugated fatty acid isomers by the paternò-büchi reaction and trapped ion mobility mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 91 (11), 7173–7180. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00374
Keywords: corn oil, linoleic acid, isomerization, kinetics, gas chromatography, infrared spectroscopy
Citation: Hu Y, He F, Liang M, Li Z, Huang X, Hu H, Gu F, Wang Q and Guo Q (2025) Formation kinetic study of thermally induced trans and conjugated linoleic acids in corn oil. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 5:1552638. doi: 10.3389/frfst.2025.1552638
Received: 28 December 2024; Accepted: 17 June 2025;
Published: 24 September 2025.
Edited by:
Elena Bartkiene, Lithuanian University of Health Sciences, LithuaniaReviewed by:
Vassilis Athanasiadis, University of Thessaly, GreeceDjiazet Steve, UMR7274 Laboratoire Réactions et Génie des Procédés (LRGP), France
Copyright © 2025 Hu, He, Liang, Li, Huang, Hu, Gu, Wang and Guo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qin Guo, Z3VvcWluMjAxMHlsQDE2My5jb20=
 Yumeng Hu
Yumeng Hu Fan He
Fan He Qiang Wang
Qiang Wang