- Department of Materials Engineering, Sao Carlos School of Engineering, University of Sao Paulo, Sao Carlos, Brazil
This study investigates the degradation behavior of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) rigid packaging with and without an antibacterial additive composed of silver nanoparticles (Ag) supported on silica-ceramic base. The objective was to evaluate the influence of the additive on packaging properties and degradation under soil burial, natural environmental aging, and accelerated aging conditions. The additive, already known to extend the shelf life of pasteurized milk from 7 to 15 days, showed no effect on the mechanical properties, such as Young’s modulus (E), maximum tensile stress (σm), and elongation at break (ɛb), or thermal stability of HDPE in the initial state. No significant degradation occurred under soil burial within the evaluated period. However, susceptibility to degradation was observed after 10 months of natural aging and 12 days of accelerated aging, mainly though reductions in tensile strength and elongation at break. Under natural aging, samples containing the antibacterial additive showed greater loss in deformation at break (99.8%) then neat HDPE (96.0%). Thermal analysis confirmed the deterioration of HDPE after exposure to degradation tests, but the presence of Ag nanoparticles partially preserved polymer stability against UV radiation. These findings indicate that while the antibacterial additive does not hinder HDPE performance during use, it influences its long-term degradation profile, with implications for both product functionality and environmental persistence.
1 Introduction
Silver nanoparticles, also known as nanosilver, are recognized for their antibacterial properties, and this characteristic has highlighted this material as one of the most commonly used engineered nanomaterial (Sotiriou and Pratsinis, 2011; Bruna et al., 2021). The use of this material meets the requirements for various applications such as antibacterial coatings for medical devices, food packaging, water and air filters, among others (Bruna et al., 2021; Dheyab et al., 2025; Guo et al., 2013). Silver nanoparticles with sizes between 10 and 100 nm exhibited antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Additionally, silver nanoparticles are more reactive than the silver ions and are capable of crossing the microbial cell wall, leading to its dysfunction (Anjali Das et al., 2020).
The combination of nanotechnology with polymer science and engineering has generated important solutions for the food packaging sector, for example, by enhancing properties such as flexibility, gas, moisture, and light barrier, and greater thermal stability (Hoque et al., 2024; Rao et al., 2024). In addition of these, the antimicrobial characteristic is one of the properties of great interest in the development of food packaging, to promote the increased shelf life of stored food. In this regard, the use of nanoscale metals such as silver has been extensively explored. Silver is a material recognized for its antibacterial properties, and when at the nanoscale, its germicidal potential becomes more notable (Morones-Ramirez et al., 2005; Jo et al., 2018; Oliani et al., 2017; Fauziyah et al., 2020). Silver nanoparticles are widely recognized for their strong antimicrobial activity against various foodborne pathogens and are relatively cost-effective compared to other nanomaterials. These qualities make them attractive for use in biodegradable food packaging. However, excessive or uncontrolled use may pose health risks due to potential nanoparticle migration into food. Therefore, evaluating their toxicity is essential alongside their application. Regulatory agencies have established concentration limits, which are important references for research and development in food technology (Rao et al., 2024). In a recent study, Mulla et al. (2024) developed sustainable food packaging incorporating thyme essential oil, which exhibited suitable mechanical properties and effective antimicrobial activity. The packaging significantly delayed microbial growth and texture deterioration in milk cake samples, extending their shelf life by over 10 days when using 20 wt% thyme oil.
A crucial stage in the development of polymeric materials, which cannot be overlooked, is the degradation of these materials pre- and/or post-consumption. It is also essential to evaluate the degradation process in different situations, including those outside controlled laboratory parameters, in order to approximate real-world scenarios of improper disposal. This helps in understanding the environmental impact these materials can cause and in evaluating mitigation or containment measures for these effects.
Most polyolefins, such as polyethylene, are sensitive to degradation caused by the combined action of ultraviolet (UV) radiation and the presence of oxygen (Grigoriadou et al., 2018). This situation can be further exacerbated by favorable conditions of heat, humidity, and the presence of other atmospheric impurities (Baum, 1974). The energy required to initiate the degradation process, which causes the braking of chemical bonds in this context, comes from the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun, whose energy is associated with its wavelength; the shorter the wavelength, the higher the associated energy, with wavelengths between 280 and 400 nm being the most critical (Grigoriadou et al., 2018; Baum, 1974).
For an ideally perfect molecular structure of high-density polyethylene (HDPE), composed solely of hydrocarbons with no instaurations, the initiation of degradation due to UV radiation would potentially be more complex. However, it is observed that during its production, the polymer undergoes oxidation at various levels, leading to the productions of functional groups such as carbonyl, hydroxyl, and unsaturation’s. Such groups, including also the residues of transition metals used in catalysis during polymerization, are more sensitive to UV radiation and, consequently, can be considered potential initiators of material degradation. Due to the presence of these degradation facilitators, the use of stabilizing agents is a common practice in order to prolong the lifespan of these materials. The resulting chain reactions cause both crosslinking and chain scission of the polymer, leading to the reorientation of macromolecular chains. This significantly reduces the material’s mechanical performances (Baum, 1974).
Biodegradation is considered the process by which the material is consumed by microbiological agents such as fungi and bacteria, leading to changes in its properties. Biodegradation is limited for polymeric materials such as HDPE due to their high molecular weight and hydrophobic nature, contrasting with hydrophilic surfaces of most microorganisms (Restrepo-Flórez et al., 2014). There is a lack of understanding regarding the mechanisms by which polyethylene biodegradation occurs, despite evidence of its occurrence. However, it is considered that colonization by biofilm is the initial stage of this process. Microorganisms like Comamonas testosteroni, Bacillus firmus, and Paenibacillus macquariensis have shown remarkable ability to degrade HDPE, leading to biofilm formation, surface deterioration, and alterations in functional groups (Newrick et al., 2025).
Similar to others methods, biodegradation is facilitated by combined action with other abiotic means of material deterioration, contributing to the reduction of polymer’s molecular weight and oxidation, transforming hydrocarbons into components that can be consumed by microorganisms, such as carboxylic acid (Restrepo-Flórez et al., 2014).
The HDPE packaging evaluated in this study promotes a considerable and desirable increase in the shelf life of pasteurized milk from 7 to 15 days. This increase is due to the incorporation of an antibacterial component formed by silver nanoparticles supported on a silica ceramic base into the polymer matrix. While this additive effectively hinders biofilm formation and reduces bacterial growth (FAPESP, 2015), its influence on the degradation behavior and physical-chemical properties of the packaging remains unknown. It is important to note that the production process, the incorporation method, and the content of the additive used are protected by industrial confidentiality and are therefore excluded from the discussion of this study. Given that HDPE is inherently resistant to biodegradation, strategies that integrate antimicrobial performance with end-of-life considerations are particularly relevant. Therefore, this study aims to evaluate the degradation of HDPE and HDPE + silver nanoparticles packaging under three different conditions: composted burial soil, natural environmental aging, and accelerate aging–through mass variation, tensile testing, and thermogravimetric analysis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
The samples were obtained from rigid high-density polyethylene (HDPE) milk packaging. Packaging was produced both with (labeled HDPE + Ag sample) and without (labeled HDPE sample) the addition of an antibacterial additive consisting of silver nanoparticles supported on silica (FAPESP, 2015). Due to confidentiality agreements concerning the additive formulation and processing method, only general information can be provided: the silver particles are in the 10–20 nm range and incorporated at a concentration of less than 1% by weight. Both types of packaging were manufactured using the blow molding process and supplied by the agricultural company Agrindus S.A. producer of milk and dairy products.
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Degradation by soil burial
The soil burial degradation assay was conducted in accordance with ASTM G160-12 - Standard Practice for Evaluating Microbial Susceptibility of Nonmetallic Materials by Laboratory Soil Burial (ASTM International, 2012). In this assay, the simulation involves the condition in which the material is discarded as buried, undergoing degradation caused by the action of microorganisms. The methodology essentially involves measuring the mass loss of the samples before and after the burial periods. A total of 20 specimens of each sample type were cut from the packaging, in a square shape of 50 × 50 mm and a thickness of 1.5 mm, buried, and collected after a period of 20 months. Composted soil, characterized by high organic matter content, was used for the burial tests. To ensure control of temperature at 30 oC ± 2 oC and the relative humidity between 85% and 95% of the system, as stipulated by the standard, the assay was conducted in a controlled tropical chamber. The temperature and relative humidity of the system were controlled daily using a thermo-hygrometer.
2.2.2 Degradation by natural environmental aging
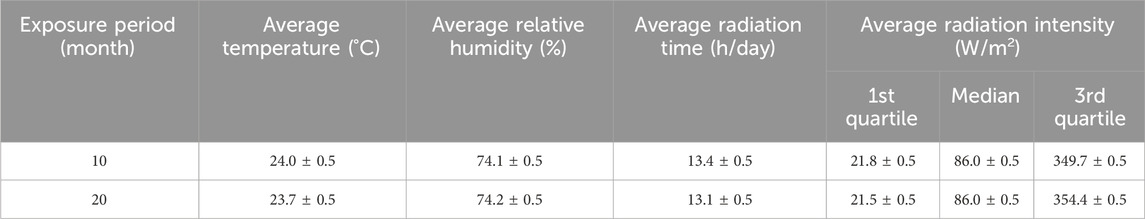
The degradation assay through natural environmental aging was conducted following the criteria established in ASTM D1435-13 - Standard Practice for Outdoor Weathering of Plastics (ASTM International, 2013). In this assay, the samples are exposed to environmental climatic conditions, promoting material degradation through various means, particularly photo-oxidation. The exposure panel with 80 test specimens was oriented north at a 45-degree angle relative to the ground. The exposure took place in the city of Sao Carlos, in the state of Sao Paulo, Brazil, with geographical coordinates: latitude 21°59′54.3″South and longitude 47°55′39.7″West, at an elevation of 841 m (Sanvezzo et al., 2021). The exposure occurred during 20 months and the meteorological conditions information was collected from the database of the Environmental Comfort Laboratory Meteorological Station (LCA) (Institute of Architecture and Urbanism and University of São Paulo, 2023) of the Institute of Architecture and Urbanism of the University of Sao Paulo. The measurements were taken at 30-min intervals, and the parameters analyzed were: temperature, relative humidity, average radiation time, and radiation intensity with a spectrum band measured between 400 and 1,100 nm. Sample collection for property evaluation occurred after exposure periods of 10 and 20 months. Table 1 shows the meteorological information obtained from the LCA laboratory, for each exposure period of the environmental aging degradation assay.
The radiation values, which correspond to the average of the recorded energy flux density, for the samples exposed to natural environmental aging degradation were presented in relation to the 1st, 2nd (median), and 3rd quartiles for the period in which any incidence of radiation with wavelengths between 400 and 1,100 nm was recorded. The maximum radiation value recorded for both periods was 700 W/m2.
2.2.3 Degradation by accelerated aging
The accelerated aging test was conducted in accordance with ASTM G154-16 - Standard Practice for Operating Fluorescent Ultraviolet (UV) Lamp Apparatus for Exposure of Nonmetallic Materials (ASTM International, 2016) standard in a UVA radiation equipment (Sanvezzo et al., 2021). In this assay, cycles of UVA radiation are simulated to accelerate the degradation of the material. Sample exposure followed cycle of 4 of the referenced standards with 8 h of radiation at 70 oC and 4 h of water condensation at 50 oC, using a UVA fluorescent lamp with typical irradiance of 1.55 W/m2 and an approximate wavelength of 340 nm. Samples were collected at 5 different periods after exposure. Table 2 shows the exposure time, radiation time, and condensation time to with the samples were subjected for the different exposure periods.
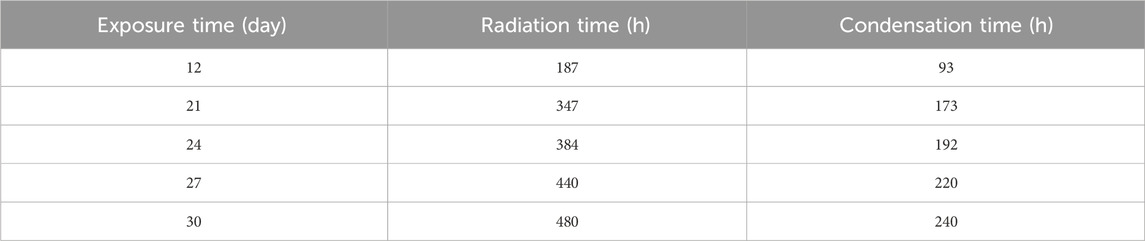
Table 2. Exposure time, radiation time, and condensation time of the accelerated aging degradation assay.
2.2.4 Mechanical tensile test
The mechanical tensile test was conducted in accordance with ASTM D638-14 - Standard Test Method for Tensile Properties of Plastics (ASTM International, 2014). The equipment used was the EMIC DL3000 universal testing machine. Ten test specimens with Type IV geometry and dimensions were tested for each sample type. The tests were conducted at a crosshead speed of 5 mm/min. Secant modulus (at 0.01 strain), maximum tensile stress, and elongation at break were calculated.
2.2.5 Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
The thermal stability of the samples was evaluated through TGA analysis performed using a TGA Pyris 1 instrument, employing inert nitrogen gas atmosphere at a flow rate of 20.0 mL/min. The heating rate was set at 10 °C/min, with a temperature range from 30 °C to 600 °C. Three samples of each material were randomly collected from the test specimens.
2.2.6 Statistical analysis
Data from the mechanical and thermal analyses were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) using IMB SPSS software (version 25). Values are expressed as a mean ± standard deviation. Different superscript letters in the same column indicate significant differences according to one-way ANOVA followed Tukey’s at a 95% confidence level (p < 0.05).
3 Results and discussions
3.1 Degradation by soil burial
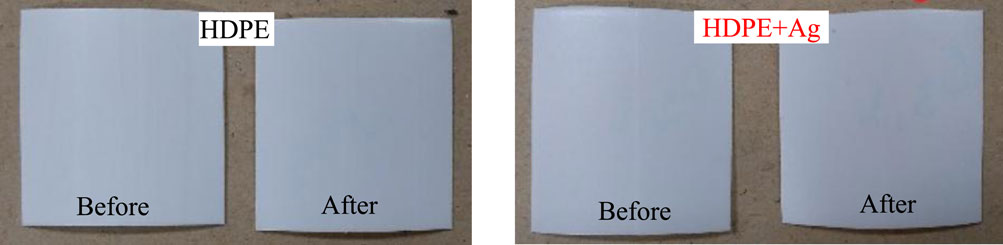
The samples with and without the incorporation of the antibacterial additive exposed to the simulated burial soil test were collected after a period of 20 months. All 20 test specimens evaluated, without exception, showed no significant mass variation or any physical or visual alterations such as changes in color, brightness, or roughness. Figure 1 shows examples of the test specimens before and after burial of the HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples.
HDPE is widely known for being highly resistant to change or decomposition and inert material, make it very difficult to degrade by chemical or biological processes in the environment even after being buried for several years as landfill. Ghatge et al. (2020) reported that a polyethylene sheet exhibited only an insignificant weight loss and minor degradation when kept in moist soil for 12–32 years.
3.2 Degradation by natural environmental aging
All test specimens, both HDPE and HDPE + Ag, showed no significant mass variation or visible changes in color, brightness, or roughness after 20 months of degradation by natural environmental aging. However, it is well known from the literature (Wang et al., 2025; Singh and Sharma, 2008) that UV radiation can break C–H and C–C bonds in HDPE, generating free radicals and leading to the loss of hydrogen atom from the polymer chains, which results in the formation of vinyl groups.
3.2.1 Mechanical properties
Table 3 summarizes the average Young’s modulus (E), maximum tensile stress (σm), and elongation at break (ɛb) values calculated for the samples with and without the incorporation of the antibacterial additive in relation to the exposure time to the natural environmental aging degradation test.
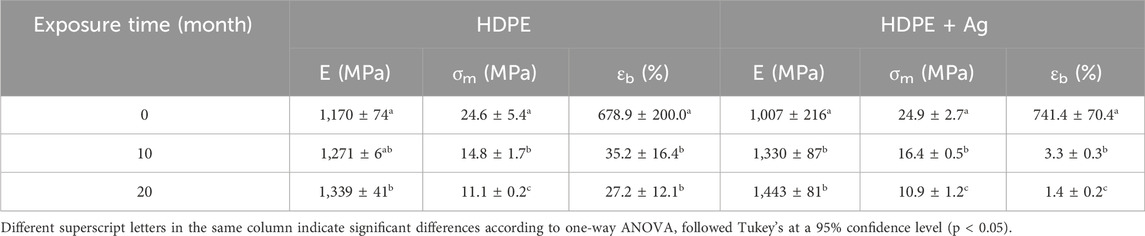
Table 3. Average Young’s modulus (E), maximum tensile stress (σm), and elongation at break (ɛb) of HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples in relation to the exposure time to the natural environmental aging degradation test.
The effect of Ag nanoparticles addition on the mechanical properties of the HDPE matrix can be evaluated by comparing the results of Young’s modulus, maximum tensile stress, and elongation at break of the unexposed (0 months) HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples. The results do not show a noteworthy difference between the values, then the addition of Ag nanoparticles neither improved nor worsened the mechanical properties of HDPE.
The results of the tensile test show that for both HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples, considering the standard deviation of the measurements, there is no significant difference in the Young’s modulus values between the unexposed samples (0 months) and the samples exposed during 10 and 20 months to the natural environmental aging degradation test. Although the average values of the elastic modulus show a slight increase with the exposure time to environmental aging degradation for both HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples, it is not possible to assent that this is a trend of the material since these values fall within the standard deviation of each sample.
Regarding the maximum tensile stress (σm) and elongation at break (ɛb), both HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples showed a considerable decrease in the average σm and ɛ values with the increased exposure time during the natural environmental aging degradation test (Table 3). The HDPE sample shows a 54.9% and 96.0% reduction in tensile stress and percentage of elongation, respectively. The HDPE + Ag sample displayed a 56.2% and 99.8% reduction in tensile stress and percentage of elongation, respectively. These reductions indicate the advancement of materials photodegradation, which involves processes that result in both chain scission reactions and crosslinking due to the environmental aging degradation test, thus affecting the mechanical performance of the materials. The greater decrease in σm and ɛb for HDPE + Ag sample compared to HDPE sample is most likely due to the presence of numerous interfaces and reactive groups introduced by the addition of the nanoparticles, which can serve as sites for accelerated oxidation during photodegradation (Grigoriadou et al., 2018).
The greater loss in rupture deformation observed for HDPE + Ag samples may be attributed to the presence of silver nanoparticles. While their concentration is relatively low and cannot be disclosed, they may influence local stress distribution in the polymer matrix, resulting in subtle changes in mechanical behavior under aging conditions.
The lack of significant differences in the initial mechanical properties between HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples can be attributed to the low concentration of Ag nanoparticles (<1 wt%), which is sufficient to impart surface antimicrobial activity but insufficient to significantly alter the bulk mechanical behavior of the polymer. The antimicrobial effect is primarily driven by surface interaction, including ion release and contact-killing mechanisms, whereas mechanical reinforcement typically requires higher nanoparticle loadings or stronger interfacial bonding with the polymer matrix. While higher concentrations or alternative dispersion strategies could be potentially affecting the mechanical performance, in this study the additive concentration was defined according to industrial application constraints, balancing antimicrobial effectiveness with processability. This highlights the dual role of the additive: effective antimicrobial performance during use, with limited impact on initial mechanical properties, but a measurable influence on long-term degradation behavior under environmental exposure.
3.2.2 Thermal properties
The thermal stability of the studied samples was evaluated by TGA analysis. Table 4 summarizes the initial temperature of mass loss (Ti), the maximum mass loss temperature (Tmax), and the final temperature of mass loss (Tf) values calculated for the HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples in relation to the exposure time to the natural environmental aging degradation test.
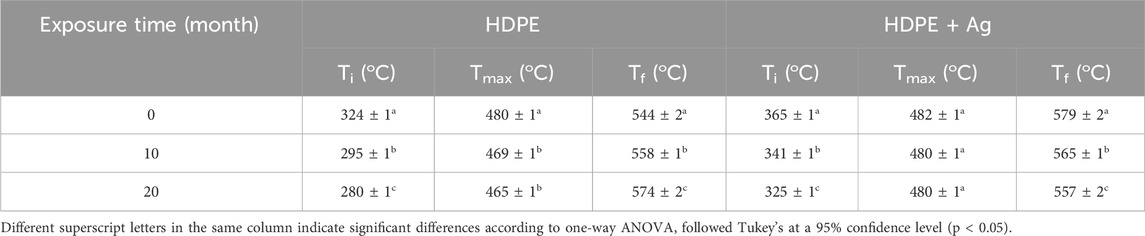
Table 4. Initial temperature of mass loss (Ti), maximum mass loss temperature (Tmax), and final temperature of mass loss (Tf) of HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples in relation to the exposure time to the natural environmental aging degradation test.
All samples, under all environmental degradation conditions, show only one mass loss in the TG curve and consequently a single peak in the DTG curve, corresponding to the thermal decomposition of the polymer.
The results indicate that the presence of the antibacterial additive increases the thermal stability of the polymer, regardless of exposure to the degradation test. The unexposed HDPE + Ag sample (0 months) exhibits an initial temperature of mass loss (Ti) and a maximum mass loss temperature (Tmax) that are 41 oC and 2 oC higher, respectively, compared to the HDPE sample.
The increase exposure time to the environmental degradation test significantly reduces the thermal stability of both HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples. The HDPE sample shows a reduction in thermal stability of 44 oC in Ti and 15 oC in Tm after exposure to the natural degradation test for 20 months, compared to the unexposed sample. The HDPE + Ag sample shows a reduction of 40 oC in Ti and 2 oC in Tm compared to the unexposed sample for the same exposure time.
3.3 Degradation by accelerated aging
All HDPE and HDPE + Ag test specimens showed no significant mass variation, nevertheless the samples exhibited visible yellowing in color and a loss of brightness after 30 days degradation by the accelerated aging test.
3.3.1 Mechanical properties
Table 5 summarizes the average Young’s modulus (E), maximum tensile stress (σm), and elongation at break (ɛb) values calculated for the HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples in relation to the exposure time to the accelerated aging degradation test.
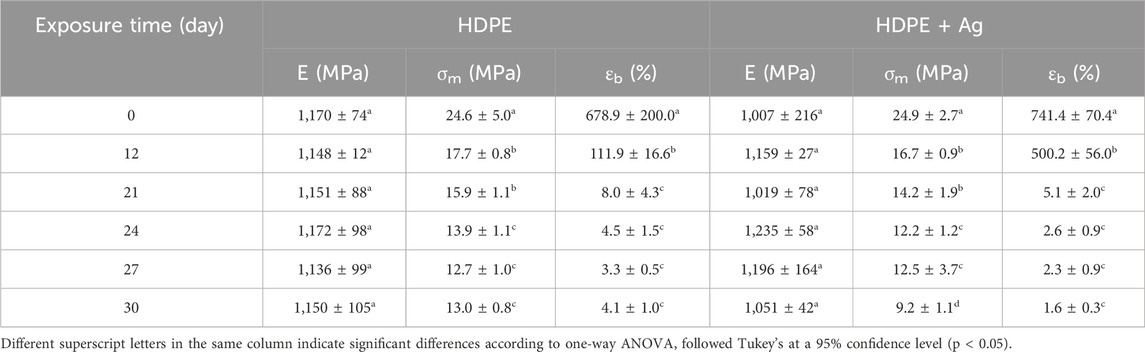
Table 5. Average Young’s modulus (E), maximum tensile stress (σm), and elongation at break (ɛb) of HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples in relation to the exposure time to the accelerated aging degradation test.
A similar trend was observed for the mechanical properties of the samples exposed to accelerated aging compared to those exposed to natural environmental aging. This suggests that the incorporation of silver nanoparticles did not significantly influence the mechanical performance of the polymer.
The results show no significant difference in the Young’s modulus values between the unexposed samples and the exposed samples, but there was a considerable decrease in the average σm and ɛ values with increased exposure time during the accelerated aging degradation test. The HDPE sample exhibits a 51.6% and 99.5% reduction in tensile stress and percentage of elongation, respectively. The HDPE + Ag sample showed a 63.1% and 99.8% reduction in tensile stress and percentage of elongation, respectively, Table 5, indicating the photodegradation advancement. Additionally, the results show no considerable influence of the addition of Ag nanoparticles on the mechanical properties of the samples exposed to accelerated aging.
Studies (Fairbrother et al., 2019; Hsueh et al., 2020) evaluated the changes in performance of HDPE films after degradation by natural environmental aging and accelerated aging. The results showed that HDPE films become brittle, with higher temperatures and more intense UV radiation accelerating the reduction in elongation at break. Other studies (Ainali et al., 2021; Carrasco et al., 2001; Grigoriadou et al., 2011) have shown that exposure to UV radiation leads to a non-monotonic response in the tensile strength of HDPE, characterized by an initial increase followed by a decline, whereas the elastic modulus demonstrates a more intricate dependence on aging time.
3.3.2 Thermal properties
To assess the impact of accelerated aging on the thermal stability of the studied samples, the samples exposed for 12 and 30 days in degradation tests were analyzed using TGA. Table 6 summarizes the initial temperature of mass loss (Ti), the maximum mass loss temperature (Tmax), and the final temperature of mass loss (Tf) values obtained for the HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples in relation to the exposure time to the accelerated aging degradation test.
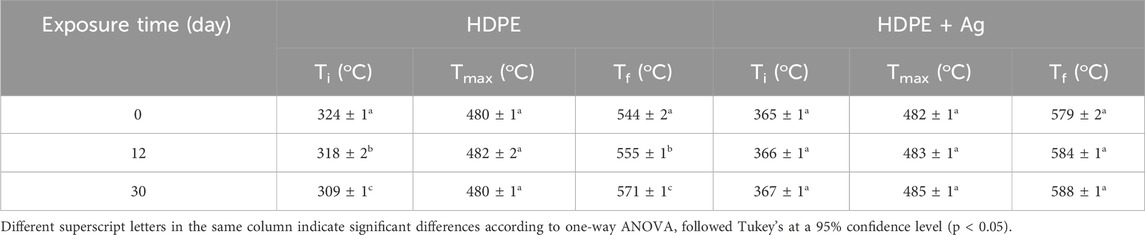
Table 6. Initial temperature of mass loss (Ti), maximum mass loss temperature (Tmax), and final temperature of mass loss (Tf) of HDPE and HDPE + Ag samples in relation to the exposure time to the accelerated aging degradation test.
TGA results displayed that the presence of Ag nanoparticles increases the thermal stability of the polymer during UV exposure, nonetheless of the exposure time to the accelerated aging test. The HDPE + Ag sample displayed a slight increase in thermal stability, showing a moderate increase in all three temperatures (Ti, Tmax and Tf), which is clear evidence that Ag nanoparticles stabilize the HDPE against UV exposure. However, the HDPE sample showed a decrease in thermal stability with the increase in exposure time to the accelerated aging degradation test. The HDPE sample exhibits a reduction in the initial temperature of mass loss of 15 oC after 30 days of exposure to accelerated aging when compared to the unexposed sample.
In summary, the results show that the additive does not affect the initial mechanical or thermal performance of HDPE, but it alters the degradation pathways during natural and accelerated aging. Specifically, we highlight the trade-off between antimicrobial effectiveness and degradation behavior: the presence of Ag nanoparticles partially stabilizes the polymer against UV radiation but, at the same time, leads to a greater loss of elongation at break under environmental exposure. This dual role of the additive–preserving antimicrobial activity during use while modifying long-term degradation–offers new insights into the design of active packaging systems, where both product functionality and environmental persistence must be considered.
4 Conclusion
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the degradation of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) rigid packaging with and without the incorporation of an antibacterial additive, composed of silver nanoparticles supported on a silica-ceramic base, through three different degradation tests. The presence of silver nanoparticles as an antibacterial additive in the HDPE packaging increased the shelf life of pasteurized milk from 7 to 15 days, however, the influence of this additive on packaging properties and degradation is unknown. Polyethylene is a polymer that exhibits excellent stability against biodegradation processes, as ascertained by soil burial test, where the samples showed no degradation, primarily due to the short exposure time tested. The incorporation of antibacterial additive did not affect the mechanical properties, such as Young’s modulus (E), maximum tensile stress (σm), and elongation at break (ɛb), nor did it alter the thermal stability of HDPE. The samples proved to be more susceptible to degradation from exposure to both natural environmental and accelerated aging processes, as evidenced primarily by the decrease in mechanical properties such as maximum tensile stress and rupture deformation. Additionally, it was observed that the loss of these properties occurred independently of the presence of the additive. However, for samples exposed to natural environmental aging, those containing additive showed a greater loss of rupture deformation. The elastic modulus exhibits more complex exposure-time-dependent behavior. The deterioration of the material after exposure to degradation tests was also confirmed by the loss of thermal stability of the HDPE sample without the Ag nanoparticles. Such a phenomenon was also observed to a lesser extend for the sample with the incorporation of Ag nanoparticles, which maintained the thermal stability of the polymer closer to that of the unexposed sample, evidencing that the additive also stabilizes the HDPE against UV exposure.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
CP: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Validation, Methodology. MB: Visualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Data curation, Supervision, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors thank Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) Brazil - finance code 001 and 88887.887751/2023-0 and Programa Unificado de Bolsas (PUB) da Pro-Reitoria de Graduação - for the financial support.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Prof. E. M. S. Sanchez for the accelerated aging tests, Agrindus S.A. company for the packaging donation, and R. G. Pereira for all the assistance in the laboratories.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ainali, N. M., Bikiaris, D. N., and Lambropoulou, D. A. (2021). Aging effects on low-and high-density polyethylene, polypropylene and polystyrene under UV irradiation: an insight into decomposition mechanism by Py-GC/MS for microplastic analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 158, 105207. doi:10.1016/j.jaap.2021.105207
Anjali Das, C. G., Ganesh Kumar, V., Stalin, D. T., Karthick, V., Govindaraju, K., Mary, J. J., et al. (2020). Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles (biosynthesis): a short review on recent advances. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 27, 101593. doi:10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101593
ASTM International (2012). Astm G160-12: standard practice for evaluating microbial susceptibility of nonmetallic materials by laboratory soil burial. West Conshohocken (PA): ASTM International.
ASTM International (2013). ASTM D1435-13: standard practice for outdoor weathering of plastics. West Conshohocken (PA): ASTM International.
ASTM International (2014). ASTM D638-14: standard test method for tensile properties of plastics. West Conshohocken (PA): ASTM International.
ASTM International (2016). ASTM G154-16: standard practice for operating fluorescent ultraviolet (UV) lamp apparatus for exposure of nonmetallic materials. West Conshohocken (PA): ASTM International.
Baum, B. (1974). The weathering degradation of polyolefins. Polym. Eng. & Sci. 14 (3), 206–211. doi:10.1002/pen.760140309
Bruna, T., Maldonado-Bravo, F., Jara, P., and Caro, N. (2021). Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (13), 7202. doi:10.3390/ijms22137202
Carrasco, F., Pagès, P., Pascual, S., and Colom, X. (2001). Artificial aging of high-density polyethylene by ultraviolet irradiation. Eur. Polym. J. 37, 1457–1464. doi:10.1016/S0014-3057(00)00251-2
Dheyab, M. A., Aziz, A. A., Nowfal, S. H., Braim, F. S., Abdullah, W., Kasasbeh, W. H. M., et al. (2025). Sustainable green synthesis of silver nanoparticles for safer biomedical application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 13, 115998. doi:10.1016/j.jece.2025.115998
Fairbrother, A., Hsueh, H.-C., Kim, J. H., Jacobs, D., Perry, L., Goodwin, D., et al. (2019). Temperature and light intensity effects on photodegradation of high-density polyethylene. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 165, 153–160. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.05.002
Fapesp, A. (2015). Brazilian company doubles shelf life of pasteurized fresh milk. Available online at: https://agencia.fapesp.br/brazilian-company-doubles-shelf-life-of-pasteurized-fresh-milk/21432.
Fauziyah, S., Salihi, A., and Benjakul, S. (2020). Effect of silver nanoparticles on growth and acid production by Streptococcus thermophilus in milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 73 (4), 701–708. doi:10.1111/1471-0307.12686
Ghatge, S., Yang, Y., Ahn, J.-H., and Hur, H.-G. (2020). Biodegradation of polyethylene: a brief review. Appl. Biol. Chem. 63, 27. doi:10.1186/s13765-020-00511-3
Grigoriadou, I., Paraskevopoulos, K. M., Chrissafis, K., Pavlidou, E., Stamkopoulos, T.-G., and Bikiaris, D. (2011). Effect of different nanoparticles on HDPE UV stability. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 96, 151–163. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2010.10.001
Grigoriadou, I., Pavlidou, E., Paraskevopoulos, K. M., Terzopoulou, Z., and Bikiaris, D. N. (2018). Comparative study of the photochemical stability of HDPE/Ag composites. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 153, 23–36. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.04.016
Guo, L., Yuan, W., Lu, Z., and Li, C. M. (2013). Polymer/nanosilver composite coatings for antibacterial applications. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 439, 69–83. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2012.12.029
Hoque, M., Sengar, A. S., Kerry, J. P., and Pathania, S. (2024). “Chapter Ten - application of nanotechnology in food packaging,” in Biodegradable and edible food packaging. Editors K. Bashir, K. Jan, S. Jan, A. L. Khan, and D. J. Mcclements (Academic Press), 303–344. doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-95624-6.00010-2
Hsueh, H. C., Kim, J. H., Orski, S., Fairbrother, A., Jacobs, D., Perry, L., et al. (2020). Micro and macroscopic mechanical behaviors of high-density polyethylene under UV irradiation and temperature. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 174, 109098. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2020.109098
Institute of Architecture and Urbanism, University of São Paulo (2023). Meteorological station system. Sao Carlos (SP): Institute of Architecture and Urbanism (IAU). Available online at: https://sistemas.iau.usp.br/eMeteorologica.
Jo, Y., Garcia, C. V., Ko, S., Lee, W., Shin, G. H., Choi, J. C., et al. (2018). Characterization and antibacterial properties of nanosilver-applied polyethylene and polypropylene composite films for food packagingapplications. Food Biosci. 23, 83–90. doi:10.1016/j.fbio.2018.03.008
Morones-Ramirez, J. R., Elechiguerra, J. L., Camacho, A., Holt, K., Koiri, J. B., Tapia, J., et al. (2005). The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 16 (10), 2346–2353. doi:10.1088/0957-4484/16/10/059
Mulla, M. F. Z., Ahmed, J., Vahora, A., Pathania, S., and Rashed, M. S. (2024). Characterization of biopolymers based antibacterial films enriched with thyme essential oil and their application for milk cake preservation. Front. Food. Sci. Technol. 4, 1356582. doi:10.3389/frfst.2024.1356582
Newrick, B. A., Valdés, D., Laca, A., Laca, A., and Díaz, M. (2025). Enhanced biodegradation of high-density polyethylene microplastics: study of bacterial efficiency and process parameters. J. Hazard. Mater. 485, 136822. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.136822
Oliani, W. L., Parra, D. F., Komatsu, L. G. H., Lincopan, N., Rangari, V. K., and Lugao, A. B. (2017). Fabrication of polypropylene/silver nanocomposites for biocidal applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 75, 845–853. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2017.02.109
Rao, M. M. V., Mohammad, N., Banerjee, S., and Khanna, P. K. (2024). Synthesis and food packaging application of silver nano-particles: a review. Hybrid. Adv. 6, 100230. doi:10.1016/j.hybadv.2024.100230
Restrepo-Flórez, J. M., Bassi, A., and Thompson, M. R. (2014). Microbial degradation and deterioration of polyethylene - a review. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 88, 83–90. doi:10.1016/j.ibiod.2013.12.014
Sanvezzo, P. B., Negreiros, F. P. C., and Branciforti, M. C. (2021). Degradation of polypropylene and jute fiber-reinforced composites exposed to natural and accelerated aging: mechanical properties and wettability. Chemistry 3, 1392–1400. doi:10.3390/chemistry3040100
Singh, B., and Sharma, N. (2008). Mechanistic implications of plastic degradation. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 93, 561–584. doi:10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2007.11.008
Sotiriou, G. A., and Pratsinis, S. E. (2011). Engineering nanosilver as an antibacterial, biosensor and bioimaging material. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 1 (1), 3–10. doi:10.1016/j.coche.2011.07.001
Keywords: high-density polyethylene, silver nanoparticles, shelf life, pasteurized milk, soil burialdegradation, natural environmental aging, accelerated aging
Citation: Pena CAP and Branciforti MC (2025) Degradation study of extended-shelf-life pasteurized milk packaging under different aging conditions. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 5:1620402. doi: 10.3389/frfst.2025.1620402
Received: 29 April 2025; Accepted: 17 September 2025;
Published: 02 October 2025.
Edited by:
Marya Raji, Moroccan Foundation for Advanced Science, Innovation and Research, MoroccoReviewed by:
Mehraj Fatema Z. Mulla, Teagasc - Irish Agriculture and Food Development Authority, IrelandKhadija El Bourakadi, Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University, Morocco
Copyright © 2025 Pena and Branciforti. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Marcia Cristina Branciforti, bWFyY2lhY2JAc2MudXNwLmJy
 Carlos Alberto Pinheiro Pena
Carlos Alberto Pinheiro Pena Marcia Cristina Branciforti
Marcia Cristina Branciforti