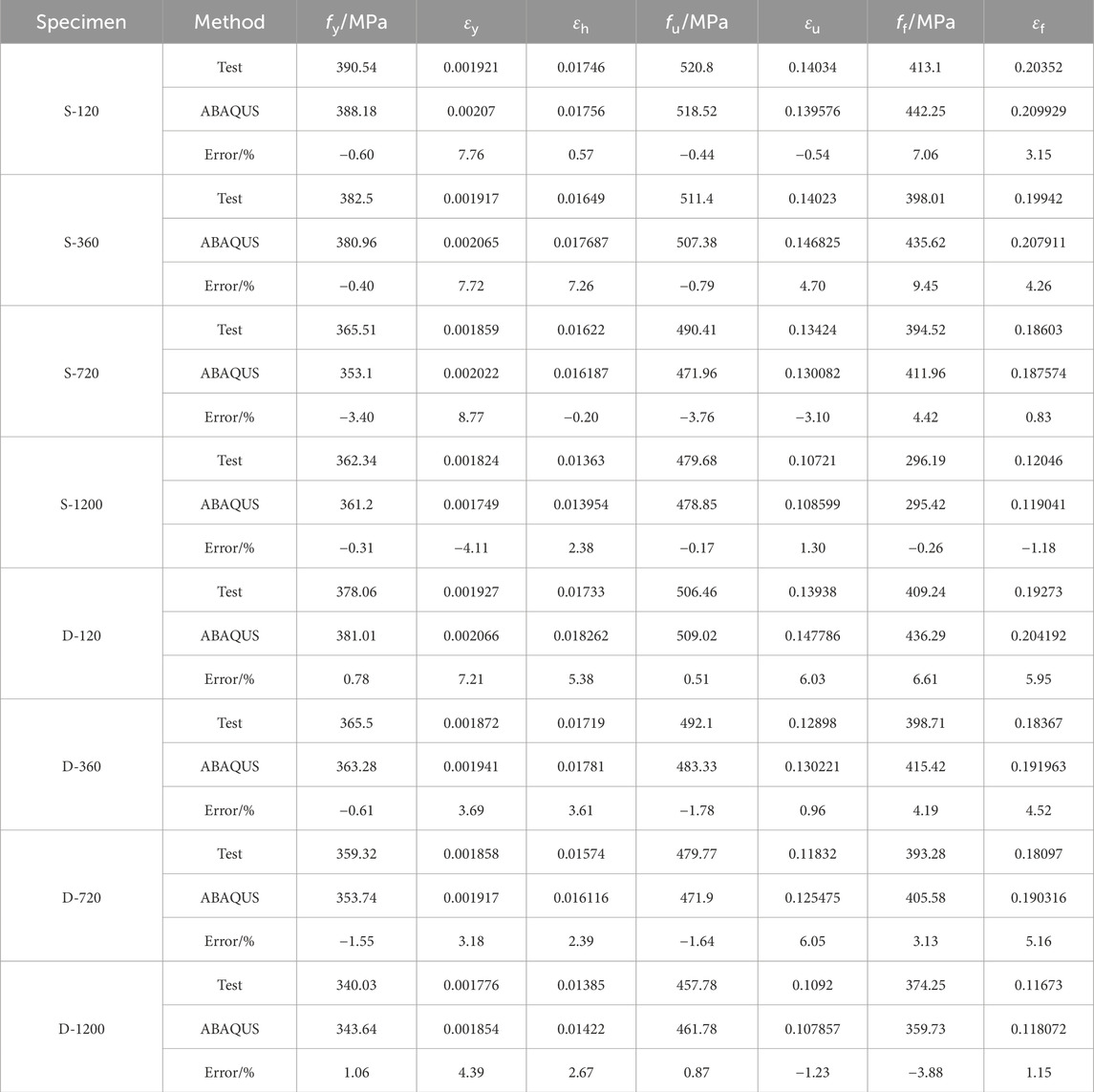
- 1School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Hubei University of Arts and Science, Xiangyang, China
- 2School of Civil Engineering, Chang’an University, Xi’an, China
This study simplifies the uniaxial tensile stress-strain curve of weathering steel and establishes degradation expressions for key mechanical properties, including elastic modulus, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, fracture strength, and their corresponding strains, under single-side and double-sided corrosion, using mass loss rate and average corrosion depth as variables. Based on prior research, mathematical fitting was applied to the hardening and necking segments of the curve. Two constitutive models for SPA-H weathering steel under coupled corrosion were proposed, incorporating mass loss rate or average corrosion depth as the damage parameter. The models were validated against experimental data from this study, existing literature, and finite element simulations. Error analysis showed that the model based on average corrosion depth achieved higher accuracy than that based on mass loss rate. Reliability analysis further confirmed that both models are applicable when the design partial safety factor is ≥1.0. Moreover, a novel finite element method was developed by integrating the uniform corrosion approach with the equivalent material property method. Implemented in ABAQUS, this method effectively reproduced the uniaxial tensile behavior of all corroded specimens, demonstrating its feasibility and potential for engineering applications.
1 Introduction
Corrosion is a global issue that has been continuously addressed but remains unresolved and is a significant challenge that humanity must overcome on the path to a sustainable society (Bender et al., 2022). Corrosion causes an annual direct economic loss of up to US$276 billion in the United States, accounting for 3.1% of its gross domestic product (GDP) (Bender et al., 2022). Similar studies conducted in countries such as China, Japan, the United Kingdom, and Venezuela have reported comparable or even higher cost estimates, leading to a projected global direct economic loss from corrosion exceeding US$1.8 trillion annually (Bender et al., 2022). Corrosion poses a significant challenge to the sustainable development of steel structures. In China, protective coatings are the primary but costly method of corrosion control. A 2002 survey reported that coatings accounted for 75.63% (151.84 billion RMB) of the total direct corrosion cost, with an estimated 75 billion RMB spent in the construction sector alone (Hou et al., 2017). By 2014, the cost had risen sharply to 703.78 billion RMB (Ma et al., 2021), highlighting the heavy financial burden. In contrast, weathering steel offers a more sustainable alternative, with advantages such as durability, low maintenance, cost-efficiency, aesthetic appeal, and design flexibility (https://luxunique.co.uk/benefits-of-cortensteel/?srsltid=AfmBOorrBTGesA22lTFiVgewNm5paXiRPHKPktfgO8riEmlrIfUkKvVt).
Weathering steel, also known as Corten steel in America (Raja et al., 2021), Q355NH steel in China (GB50017, 2017), and SPA-H steel in Japan (JIS, 2010), is widely used in bridges (Krivy et al., 2016), buildings (Hopkin et al., 2018), towers (Křivý et al., 2022), and other outdoor infrastructure, such as outdoor sculptures (Mabry, 2016) and other landscapes (Shi, 2019). The mechanical strength of these three typical structural weathering steels is very similar, but there are still certain differences in their chemical compositions, which affect their corrosion resistance (Wang et al., 2013; Xin-liang et al., 2012). The steel’s ability to form a protective rust layer in response to atmospheric conditions is key to its longevity and minimal maintenance requirements. However, this protective mechanism is influenced by various environmental factors, including the coupling of process-induced and atmospheric corrosion (Morcillo et al., 2013; Morcillo et al., 2019). Unfortunately, current research focused on the corrosion of weathering steel under a single atmospheric or specific chemical environment (Han et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2019).
Developing constitutive models for structural steels, considering the material behavior after corrosion, is crucial for accurately predicting their mechanical behavior under different environments, optimizing structural design, and ensuring structural safety. Research on the constitutive model of ordinary carbon or alloy steel has been relatively thorough (Kim et al., 2013; Kweon et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2022), but there is limited study on weathering steel after corrosion (Han et al., 2024). Existing studies focused on constitutive models under a single corrosion environment (Han et al., 2024; Guo et al., 2019; Guo et al., 2024; Jiang et al., 2024; Nie et al., 2019) without addressing dual or multiple corrosion coupling. As a result, current models fail to fully account for the cumulative effects of numerous corrosion factors, leading to inaccuracies in predicting the mechanical properties of materials in complex corrosive environments and thus failing to meet the needs of practical engineering applications.
As mentioned, weathering steel is widely used in outdoor sculptures and landscape structures, with SPA-H being the primary material in China. Initially imported from Japan, domestic production now fully complies with JIS G 3125 (JIS, 2010). Studies confirmed its excellent corrosion resistance (Wang et al., 2013). For aesthetic and artistic purposes, to enhance texture and creative effects and achieve the desired surface color effect of weathering steel, weathering steel typically undergoes chemical solution corrosion (CSC) in the shortest possible time after rust removal. According to the construction process, the anti-corrosion layer formed on the weathering steel surface must be removed before CSC, followed by short-term chemical corrosion and long-term atmospheric corrosion (AC). This makes the study of the mechanical performance degradation and constitutive model of SPA-H weathering steel under the continuous effects of CSC and subsequent AC highly valuable. Developing a constitutive model for SPA-H weathering steel subjected to coupled corrosion is necessary to analyze complexly shaped weathering steel structures using numerical methods and better assess their load-bearing capacity. The author investigated the corrosion behavior and mechanical performance degradation of SPA-H weathering steel under the coupled effects of CSC and AC simulated by copper-accelerated acetic acid-salt spray testing (CASS) (Lu et al., 2024) but did not address its constitutive model. Based on the previous research (Lu et al., 2024), this paper develops a novel constitutive model for weathering steel under the coupled effects of CSC and CASS using mathematical regression methods. It validates the model’s reliability through tests and an innovative finite element analysis method.
2 Brief overview of coupled corrosion experiments and results
2.1 Coupled corrosion experiments
Ref. (Lu et al., 2024). described the entire coupled corrosion experiment process and the surface morphology of the corroded specimens. Therefore, this paper only briefly overviews the corrosion experiment.
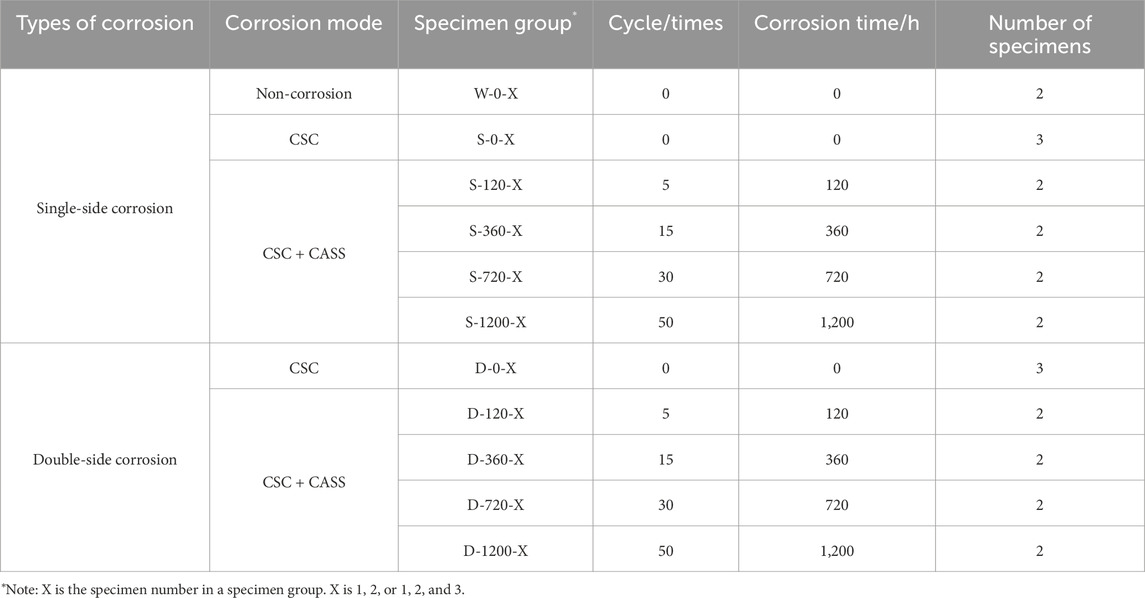
SPA-H weathering steel plate (3 mm thickness) was hot-rolled from China Yanshan Iron and Steel Group Co., Ltd. The steel has a minimum yield strength of 355 MPa, ultimate tensile strength of 490 MPa, and elongation of 22%. Copper-accelerated acetic acid-salt spray testing (CASS) was used to simulate atmospheric corrosion. A total of 24 specimens were tested, including non-corrosion, single-side CSC, double-side CSC, single-side coupled corrosion (CSC + CASS) specimens, and double-side coupled corrosion (CSC + CASS) specimens, as shown in Table 1. Specimens were wire-cut along the rolling direction, with corroded and uncorroded areas defined (Figure 1). The setups for single-side and double-side corrosion consider the real conditions that structural plates may encounter in practice.
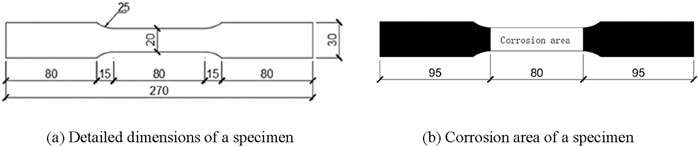
Figure 1. Dimensions of a specimen (Unit: mm). (a) Detailed dimensions of a specimen (b) Corrosion area of a specimen.
Commercial rusting and rust-fixing agents were used for CSC (Lu et al., 2024). Specimens were cleaned, sprayed with a rusting agent, water-sprayed for 3 days, and finally coated with a rust-fixing agent. The CSC lasted 96 h, changing the steel color from initial dark gray to final reddish-brown (Lu et al., 2024). CASS followed ISO 9227:2022 (ISO 9227, 2022) and used a salt solution (50 g/L NaCl) with added CuCl2·2H2O (0.26 g/L). Specimens were exposed to alternating dry/wet cycles at 50°C, with sampling intervals at 120, 360, 720, and 1,200 h.
According to Ref. 26, The corrosion initially transitions from reddish-brown to black-brown, creating an uneven surface with protrusions and hollows. A clearly defined boundary with a step-like morphology between the corroded and uncorroded regions is readily visible to the naked eye. White light interferometry (WLI) analysis further confirms that the bottom surface of double-side corroded specimens exhibits more pronounced pitting characteristics, with fewer but deeper corrosion pits and higher surface roughness than the top surface (Lu et al., 2024).
The experimental results (Lu et al., 2024) indicated that SPA-H weathering steel underwent significant degradation under coupled corrosion (CSC + CASS). Corrosion depth and pit density increased over time, with the bottom surface experiencing more severe damage, characterized by larger and deeper pits and extensive black-brown corrosion spots covering over 50% of the area after 1,200 h. This degradation leads to noticeable thickness reduction.
2.2 Corrosion model
The corrosion model is generally established in two forms of corrosion rate: mass loss rate (η) and average corrosion depth (d). The study presents two corrosion models, using mass loss rate (η) and average corrosion depth (d) as variables, respectively, and names them Corrosion Model 1 and Corrosion Model 2 to support the development of corresponding constitutive models. The model function is obtained by fitting experimental data using Origin software. The first term of these corrosion models represents the corrosion rate (mass loss rate or average corrosion depth) during the CSC stage, while the second term corresponds to the corrosion rate during the CASS stage. The binomial expression effectively captures the effects of different corrosion test methods (CSC or CSC + CASS) and corrosion time.
2.2.1 Corrosion model 1
Based on Ref. (Lu et al., 2024), Corrosion Model 1 is proposed using power functions to fit the experimental data. As shown in Equations 1, 2.
Single-side corrosion,
Double-side corrosion,
η is the mass loss rate (%), and t is the corrosion time (h).
2.2.2 Corrosion model 2
The Corrosion Model 2 is given as follows, referring to the form of Model 1, as shown in Equations 3, 4.
Single-side corrosion,
Double-side corrosion,
d is the average corrosion depth (mm), and t is the corrosion time (h).
2.3 Mechanical properties after corrosion
Figure 2 shows the stress-strain curves for uncorroded and corroded specimens. Each curve features elastic stages, a yielding plateau, stress hardening, and a downward phase. Comparing Figures 2a,b, it is observed that corrosion reduced yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and final elongation. Double-side corroded specimens exhibit significantly lower yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and elongation than single-side corroded specimens because double-side corrosion more severely weakens the specimen’s thickness (cross-sectional area).
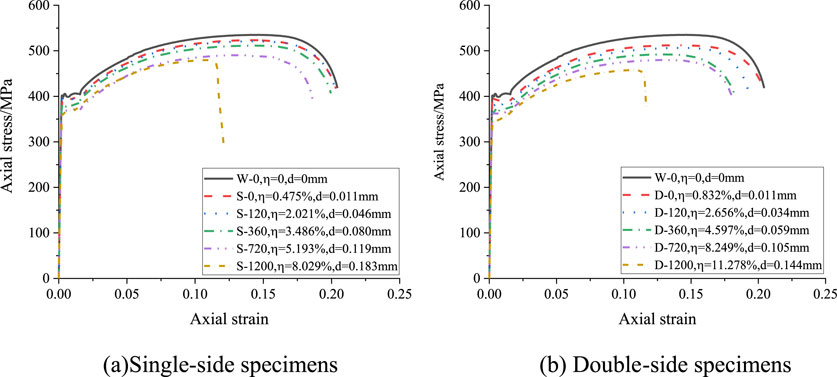
Figure 2. Axial stress Vs. Axial strain (Lu et al., 2024). (a) Single-side specimens (b) Double-side specimens.
3 Key parameters of a typical stress-strain curve
3.1 Typical stress-strain curve
The typical stress-strain curve of weathering steel represents the relationship between stress and strain during deformation, consisting of several key stages. Initially, the curve is linear in the elastic region, and the material returns to its original shape when the stress is removed. As the material reaches the yield platform, it begins to deform plastically, meaning it will not return to its original shape. In the plastic region, the material undergoes permanent deformation as stress increases. The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) is the maximum stress the material can withstand before necking begins. Finally, during the necking and fracture stages, the material’s cross-sectional area decreases after reaching the UTS, leading to fracture. Therefore, the true stress-strain curve of weathering steel shown in Figure 2 can be simplified into Figure 3, which enables the extraction of key mechanical properties, including yield strength (fy), ultimate tensile strength (fu), fracture strength (ff), as well as strains such as ultimate strain (εu), fracture strain (εf), and hardening point strain (εh), along with the elasticity modulus (E). These properties are essential for comparing mechanical performance and developing constitutive relationships. For the corroded steel, key mechanical properties (shown in Figure 3) must be those with degraded performance after corrosion (Lu et al., 2024).
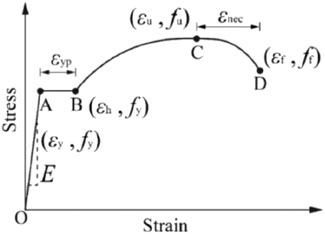
Figure 3. Mechanical properties obtained in stress-strain curve (Guo et al., 2024).
The key parameter data for the uncorroded specimens obtained from Figure 2 are shown in Table 2. The subscript “0” represents the data for uncorroded specimens. These key data fully comply with JIS G 3125 (JIS, 2010), which requires a minimal yield strength of 355 MPa and a minimal UTS of 490 MPa. Its mechanical performance indicators are also essentially consistent with the Chinese standards GB/T4171-2008 ().
3.2 The degradation expressions of key mechanical parameters based on corrosion model 1
3.2.1 Single-side corrosion
3.2.2 Double-side corrosion
3.3 The degradation expressions of key mechanical parameters based on corrosion model 2
3.3.1 Single-side corrosion
3.3.2 Double-side corrosion
Equations 5–36 are derived through data fitting and are commonly used in corrosion studies (Guo et al., 2024; Jia et al., 2018; Xu et al., 2016). These expressions demonstrate the degradation of weathering steel material performance parameters as the corrosion rate increases, with clear physical significance.
4 Constitutive model development and validation
4.1 Form of the constitutive model
The challenge in establishing the constitutive model is accurately describing the third and fourth segments (Figure 3), which correspond to the plastic hardening and necking stages. Guo et al. (Guo et al., 2024) compared the constitutive model proposed in Ref. (Nie et al., 2019). with the one based on Ref. (Esmaeily and Xiao, 2005). and concluded that the model proposed in Ref. (Nie et al., 2019). better reflects the constitutive behavior of weathering steel and low-alloy steel after corrosion. However, the constitutive models presented in Refs. (Guo et al., 2024). and (Nie et al., 2019) do not ensure the continuity of the piecewise strain function at the boundaries, particularly at the critical strain points (εy and εu) shown in Figure 3.
Drawing on the form of the model proposed by Ref. (Nie et al., 2019). and considering the boundary values of strain to ensure the smooth continuity of the curve, the modified constitutive relationship for weathering steel under coupled corrosion applicable to this study is shown in Equation (37). The meanings of the variables in Equation (37) are shown in Figure 3.
Parameters m1 and m2 represent the hardening and necking segments, respectively. A larger m1 results in a greater stress increase per unit strain, which enhances the residual strength after yielding. A larger m2 leads to a faster stress drop, reducing necking deformation capacity and accelerating fracture. The material stress and strain parameters in Equation 37 are shown in Figure 3, which can be calculated using Equations 5–36 with either the mass loss rate (η) or the average corrosion depth (d) as the variable. Therefore, parameters m1 and m2 can also be expressed in terms of the mass loss rate or the average corrosion depth based on different Corrosion Models 1 or 2.
4.2 Constitutive model 1— the constitutive model expressed with mass loss rate (η)
A constitutive model incorporating the mass loss rate (η) as a variable revealed that the parameters m1 and m2 apply to single-sided and double-sided corrosion specimens, as shown in Equation 38. Accordingly, a unified constitutive model based on η is proposed, where η is expressed as a percentage (%).
4.3 Constitutive model 2— the constitutive model expressed with average corrosion depth (d)
Using the same approach, the constitutive model expressed in average corrosion depth (d) is formulated as shown in Equation 39. The unit of average corrosion depth (d) is millimeters (mm).
4.4 Constitutive model validation using test data
To validate the accuracy of the proposed Constitutive Models 1 and 2, stress-strain curves for SPA-H weathering steel were generated and compared with experimental results, as shown in Figures 4, 5. The models exhibit good agreement with the test curves in the elastic stage and demonstrate even better consistency in the plastic hardening stage (as highlighted in the magnified view). Furthermore, the differences between single-sided and double-sided corrosion were assessed by analyzing the stress values at the 1/4, 1/2, and 3/4 points along the stress-strain curves under various corrosion rates, as illustrated in Figure 6.
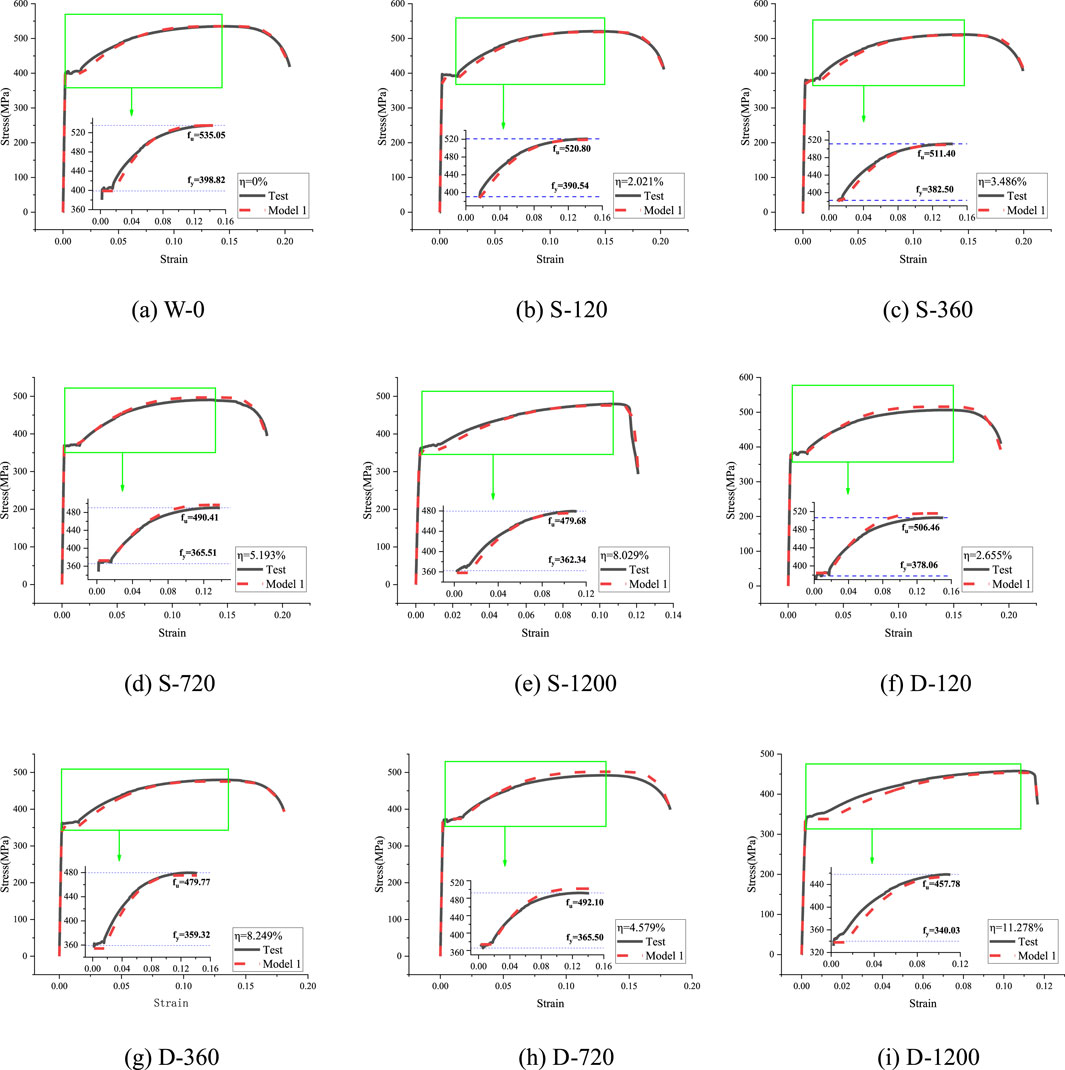
Figure 4. Comparison of stress-strain curves for Constitutive Model 1. (a) W-0. (b) S-120. (c) S-360. (d) S-720. (e) S-1200. (f) D-120. (g) D-360. (h) D-720. (i) D-1200.
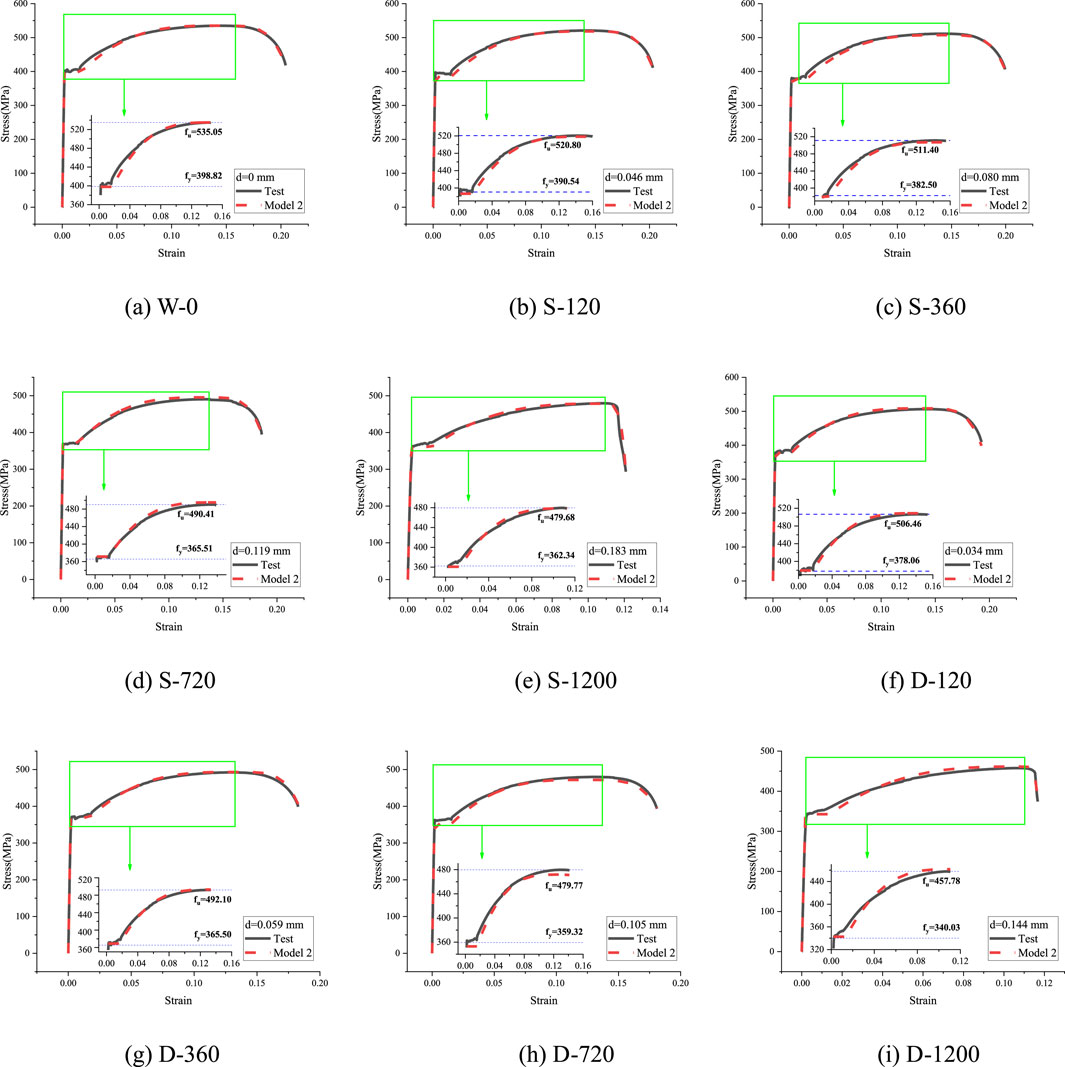
Figure 5. Comparison of stress-strain curves for Constitutive Model 2. (a) W-0. (b) S-120. (c) S-360. (d) S-720. (e) S-1200. (f) D-120. (g) D-360. (h) D-720. (i) D-1200.
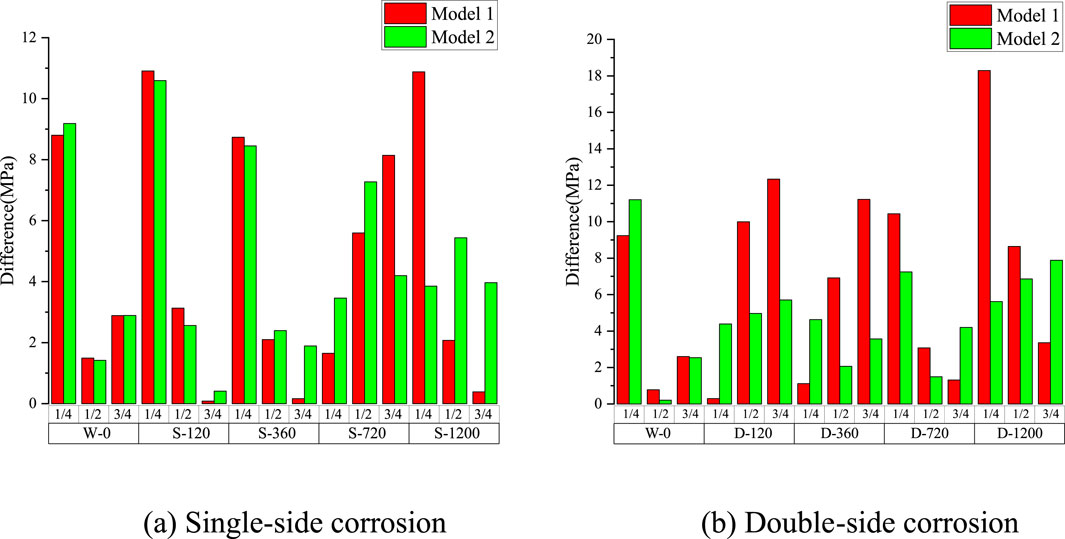
Figure 6. Difference analysis of Constitutive Model 1 and Constitutive Model 2. (a) Single-side corrosion (b) Double-side corrosion.
Figures 4–6 show that for single-sided corrosion specimens, the difference between Constitutive Model 1 and Constitutive Model 2 is very small, especially in the short-to-medium-term corrosion stage (corrosion time ≤720 h). However, for specimens with a corrosion time of 1,200 h, the absolute deviation (MPa) of Constitutive Model 1 is more than twice that of Constitutive Model 2. The difference between the two constitutive models is more noticeable for double-sided corrosion specimens. Specifically, for specimens with a corrosion time ≤720 h, the absolute difference (MPa) of Constitutive Model 1 is about twice that of Constitutive Model 2, and for specimens with a corrosion time of 1,200 h, the difference is approximately three times larger. Figure 6 shows that the absolute deviation between most specimens’ constitutive model and experimental values is mainly between the stress-strain curves’ 1/4 point and 1/2 point, just past the yield plateau in Figures 4, 5.
Nevertheless, when the absolute differences are expressed as a percentage of the total strength, the maximum error for single-sided corrosion specimens is only 2.76%, while for double-sided corrosion specimens, it is 4.51%. Both values fall within the acceptable error margin (5%) for engineering design. Furthermore, Figure 6 illustrates that, regardless of whether the specimen undergoes single-sided or double-sided corrosion, the absolute deviation of Constitutive Model 2 varies smoothly without significant fluctuations.
In summary, both constitutive models accurately reflect the material properties of SPA-H weathering steel after coupled corrosion, with Constitutive Model 2, based on average corrosion thickness, providing a better experimental fit.
4.5 Reliability analysis of constitutive models
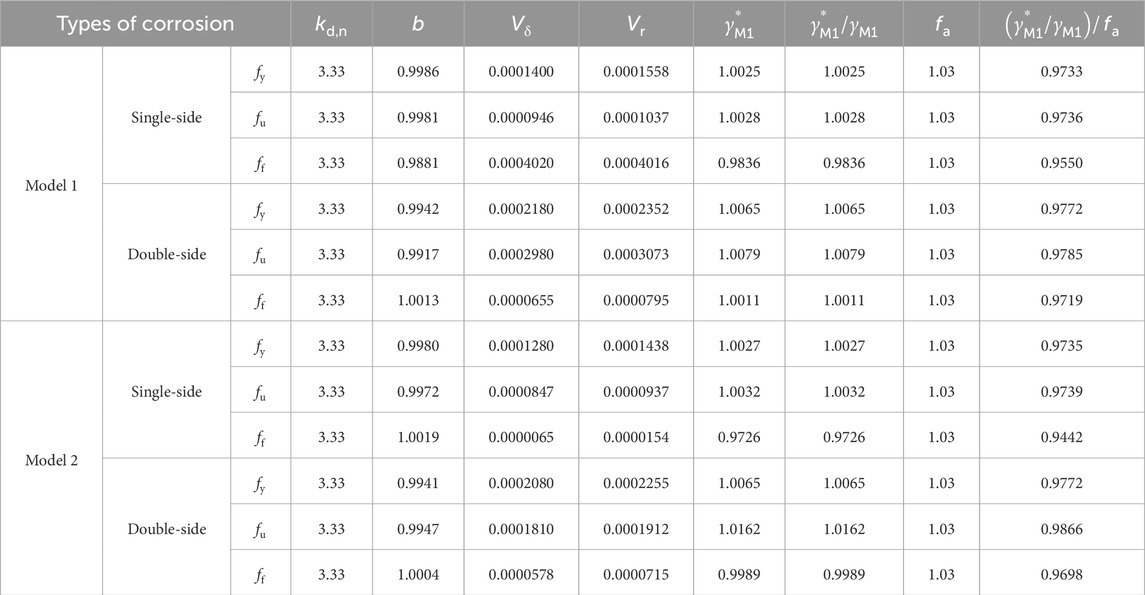
Using all test data and the calculation results of the fitted formula and following the standard procedure outlined in (EN, 1990, 2005), this study assessed the reliability of the Constitutive Models 1 and 2. The same methods and parameters specified by Behzadi Sofiani et al. (Behzadi-Sofiani et al., 2021) were applied. The reliability analysis results are summarized in Table 3, according to the requirement of
4.6 The constitutive model 1 validation using other experiments
Although Section 4.3 has demonstrated the reliability of the constitutive model proposed in this study, the reliability and applicability of the proposed constitutive models may require further experimental validation due to the limited number of experimental specimens. ISO 12944–2:2017 (ISO 12944, 2017) determines the classification of atmospheric corrosion environments without considering the specific medium in the corrosive environment. It only uses the mass loss and thickness loss of low-carbon steel during the first year of exposure to determine the corrosion grade of the environment. This approach led the authors to hypothesize that although the corrosion products of weathering steel may differ in different corrosive environments and the effects on its microstructure may vary, the degradation patterns of macroscopic mechanical strength based on the same corrosion rate variable may be similar, or even the same.
Although the corrosion study of weathering steel has been a hot topic, experimental data on the degradation of mechanical properties after corrosion remains very limited. In order to explore the feasibility of this hypothesis and to validate the reliability of the constitutive model proposed in this study, corrosion test data of Q355NH weathering steel (Guo et al., 2024), which has mechanical properties similar to those of SPA-H weathering steel in this study, were selected for comparison. Since Ref. (Guo et al., 2024). only used the mass loss rate to construct the constitutive model, the comparison was conducted using Constitutive Model 1. Additionally, since Ref. (Guo et al., 2024). only provided the yield strength (fy) and ultimate tensile strength (fu) of uncorroded weathering steel, only these two indicators were compared in Table 4.
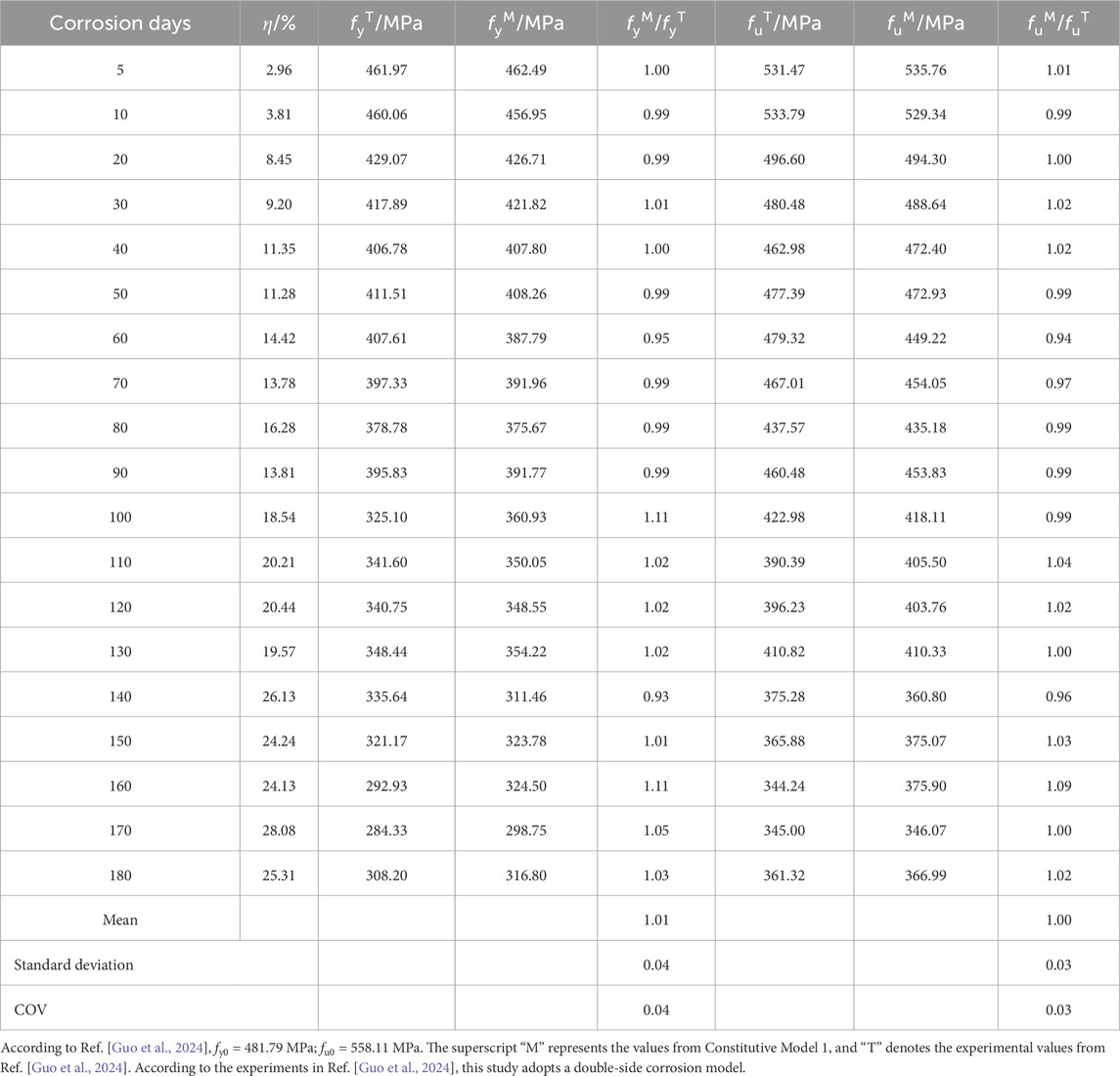
Table 4. Comparison of Model 1 with the experimental stress results from Ref (Guo et al., 2024).
The perfect comparison results in Table 4 provide preliminary confirmation of the author’s hypothesis and the reliability of Constitutive Model 1 in this study. Further validation of the author’s assumption can be conducted through more published experimental data in the future.
5 Finite element validation and application of constitutive model 2
This study aims to apply the developed material constitutive model in finite element (FE) analysis to simulate the mechanical behavior of corroded structural members numerically. Ideally, the stochastic corrosion method—accounting for the weakening effects of randomly distributed corrosion pits on the steel cross-section—should be used (Gu et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024). However, this method involves a complex computational process and requires high-precision corrosion surface scanning data, resulting in low efficiency for engineering design and limited applicability in commercial FE software.
The most straightforward and widely used numerical analysis method is the uniform corrosion approach, which assumes a uniform reduction in the thickness of structural members (Senevirathna et al., 2023; Shu et al., 2020). However, this method does not account for the mechanical degradation of corroded steel or the randomness in corrosion pit distribution. Moreover, modeling numerous corrosion pits at the structural component level is nearly impossible. The equivalent material property method (Zhang et al., 2024) was proposed to address these limitations, which converts geometric loss due to corrosion into equivalent degradation of material properties (Sun, 2015; Yang, 2015; Zuo, 2017). Modifying parameters such as Young’s modulus and yield strength enables predicting the mechanical performance of corroded structures during the preprocessing stage of finite element (FE) analysis. Due to its simplicity and ease of implementation, it has become a mainstream approach in corrosion-related structural research (Zhang et al., 2024). However, it still fails to account for sectional weakening caused by corrosion.
In reality, corrosion in steel structures leads to both cross-sectional loss and mechanical property degradation. The former reduces the effective cross-section, thereby diminishing load-bearing capacity, while the latter alters the material’s microstructure, reducing strength and ductility. These two effects jointly compromise structural safety. From this perspective, the present study integrates geometric reduction, modeled using the uniform corrosion method, with mechanical degradation, represented by the equivalent material property method, in finite element (FE) analysis to provide a more comprehensive assessment of corrosion effects on structural performance.
In engineering practice, average corrosion depth is easier to measure than mass loss, especially for in-service structures. For practical structural assessments, multiple local de-rusting points can be selected, and ultrasonic thickness gauges can be used to measure the residual thickness at various locations, allowing for calculating average corrosion depth. Therefore, this study adopts Constitutive Model 2—based on average corrosion thickness—as the material constitutive model while incorporating the corresponding geometric reduction. The commercial FE software ABAQUS is used to simulate the tensile behavior of corroded specimens, thereby validating both the proposed constitutive model and the integrated numerical method.
5.1 FE modeling
In FE analysis using ABAQUS, after establishing the solid geometric model of the specimen, the cut function is used to “thin” the thickness of the corroded area to simulate the reduction in the specimen’s cross-sectional geometry caused by corrosion.
According to the method in Ref. (Xin and Veljkovic, 2021), the nominal stress-strain data obtained from Constitutive Model 2 is first converted into the true stress-strain data required for the finite element model. Additionally, to simulate specimen fracture at the necking region, material damage must be configured: select “Ductile Damage” from the “Material Behaviors” dropdown menu and input the corresponding “Fracture Strain” value.
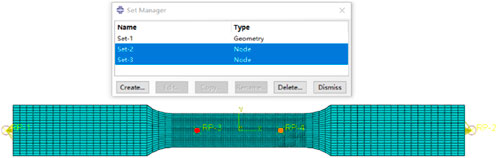
In the finite element analysis, to accurately replicate the monotonic tensile test of the specimen, the gripping sections at both ends are coupled to reference points RP-1 and RP-2, respectively (as shown in Figure 7). RP-1 is set as a fixed end with full constraints (U1 = U2 = U3 = UR1 = UR2 = UR3 = 0) to simulate the stationary grip in the physical test, while RP-2 is assigned as the loading end (U2 = U3 = UR1 = UR2 = UR3 = 0), where all constraints are maintained except for displacement along the length direction (X-axis). A displacement load of 20 mm is applied to RP-2 to replicate the movement of the loading grip in the experiment.
5.2 Mesh sensitivity analysis
In this study, the finite element analysis in ABAQUS adopts the solid element type C3D8R. Mesh size is a critical factor affecting the accuracy of numerical analysis and computational cost. A mesh sensitivity analysis was conducted to balance computational efficiency and simulation accuracy.
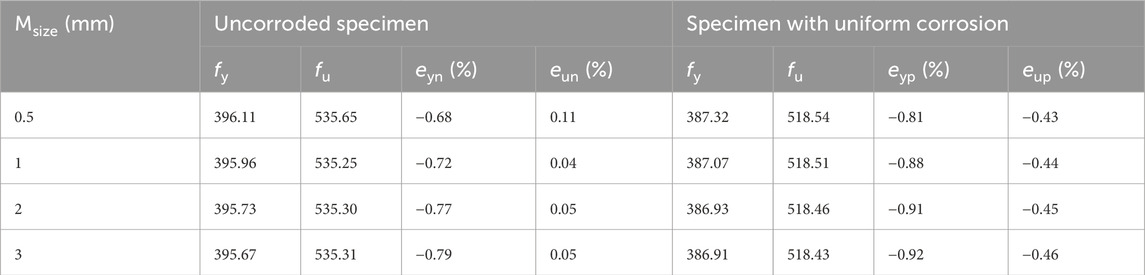
The global mesh size was initially set to 4 mm. For the tensile section (i.e., the corroded region), local mesh refinement was performed with 3 mm, 2 mm, 1 mm, and 0.5 mm mesh sizes to evaluate their influence on the simulation results. Specimen S-120 was selected as a representative case for the sensitivity study, and the analysis results are shown in Table 5. Msize represents the mesh size in the corroded section, where eyn and eun denote the errors between the numerical and experimental results for yield and ultimate strength, respectively. The variations in eyn and eun across different mesh sizes are relatively small, with maximum errors of −0.92% and −0.46%, respectively. Based on the results in Table 5, a mesh size of 1 mm in the corroded region provides a good balance between accuracy and efficiency.
Therefore, considering all factors, the final mesh strategy used in this study sets the global mesh size to 4 mm, while the tensile (corroded) section is locally refined to 1 mm, as shown in Figure 7.
The strain in the real test was calculated based on deformation measured using extensometers with a 50 mm gauge length. Reference points RP-3 and RP-4 were symmetrically arranged to simulate the real test, as shown in Figure 7. The distance is 50 mm between them to obtain displacement for calculating the deformation and strain.
5.3 FE analysis results and discussions
The stress-strain curve comparisons of selected representative specimens are shown in Figure 8, where the simulated curves generally match well with the experimental ones. A comparison of key material properties obtained from ABAQUS simulations and experimental results for all specimens is presented in Table 6. The simulation results of all specimens show that the errors in key material properties compared to experimental data are all within ±10%, indicating high accuracy and reliability of the proposed constitutive model and finite element analysis method. For stress-related parameters, the error ranges are −3.40%–1.06% for yield strength (fy), −3.76%–0.87% for ultimate tensile strength (fu), and −3.88%–9.45% for fracture strength (ff). For strain-related parameters, the error ranges are −4.11%–8.77% for yield strain (εy), −0.20%–7.26% for hardening point strain (εh), −3.10%–6.05% for ultimate strain (εu), and −1.18%–5.95% for fracture strain (εf). Taking the S-720 specimen shown in Figure 9 as an example, the simulation results indicate that failure occurs when the fracture strain is reached, with necking observed at the fracture point, consistent with the experimental failure mode. Overall, the simulation results show good agreement with the experimental data, demonstrating high accuracy and stability in both stress and strain and can accurately predict the mechanical behavior of the material from yield to failure. The comparison of stress-strain curves, strength data, strain data, and failure modes validates the effectiveness and engineering applicability of Constitutive Model 2 and its FE implementation.
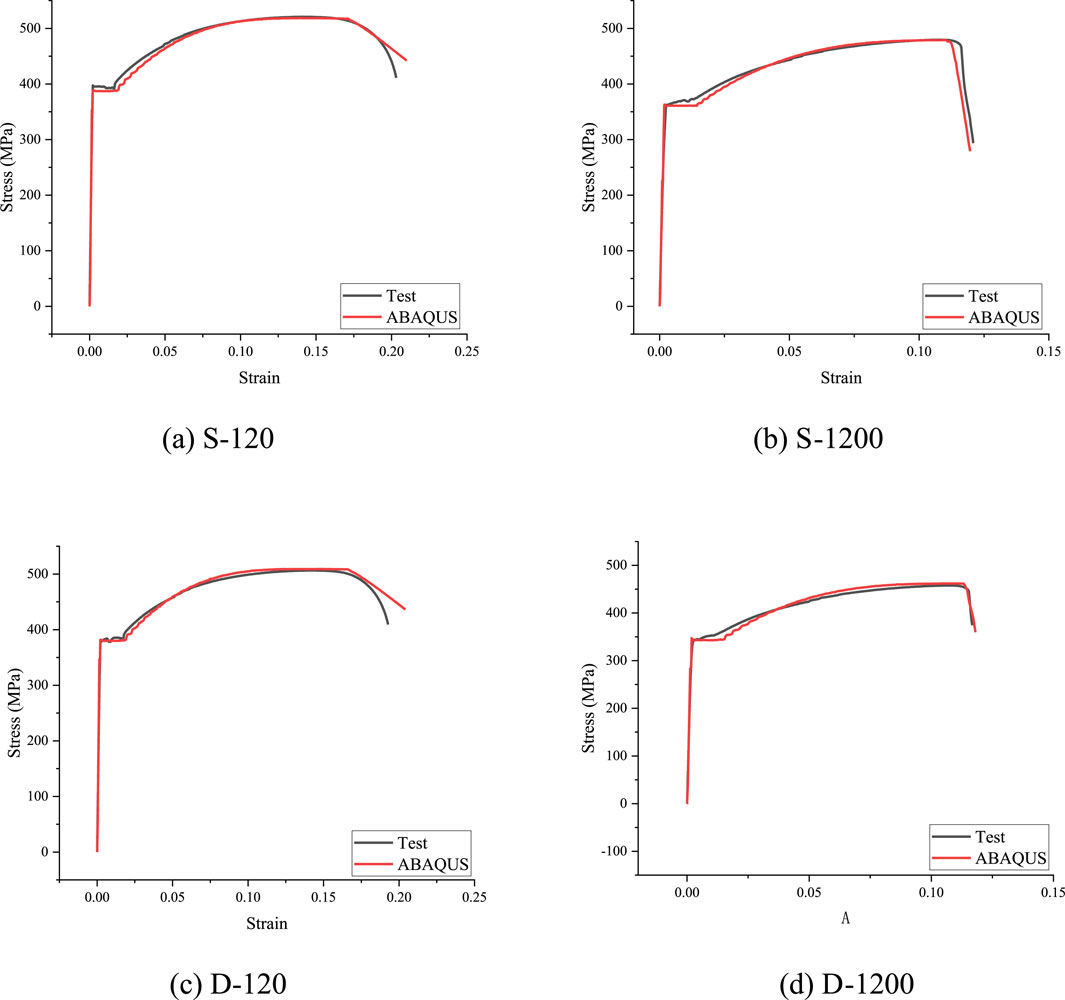
Figure 8. Comparison of stress-strain curves between ABAQUS and test. (a) S-120. (b) S-1200. (c) D-120. (d) D-1200.

Figure 9. Failure modes of ABAQUS and test of specimen S-720. (a) ABAQUS simulation failure mode. (b) Tensile test failure modes.
6 Limitations and future perspectives
6.1 Limitations of the current study
Although this study proposes constitutive models and finite element analysis methods and validates their effectiveness and accuracy in predicting material mechanical behavior, several limitations remain. First, the sample size of the test specimens in this study is insufficient, leading to inevitable fitting errors in the constitutive models. Second, while the finite element model, based on the combination of uniform corrosion and equivalent material property methods, effectively simulates the impact of corrosion on material mechanical performance, it does not fully account for the random distribution of corrosion pits and their effects on structural and mechanical properties. Lastly, the current models are primarily based on simple unidirectional material constitutive relations and numerical methods. Further research and improvement are required to address more complex material behaviors, such as seismic and dynamic loads.
6.2 Future perspectives
1. Future studies could explore more refined and complex corrosion models, particularly considering the random distribution of corrosion pits, different corrosive media, and the impact of multi-factor coupling. Additionally, combining more experimental data would further improve the accuracy of the corrosion models and enhance the agreement between simulation results and actual engineering situations.
2. With advancements in materials science, new constitutive models should consider the effects of multi-factor coupling on material properties. Future work could build upon existing models, incorporating additional mechanical characteristics and complexities to enhance model adaptability.
3. Future research could validate and optimize the constitutive models and finite element analysis methods with more corrosion test data from actual engineering applications. Combining advanced detection technologies, such as 3D scanning and ultrasonic testing, would provide more accurate material performance data, increasing the practical application value of the research.
4. With the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, their application could significantly predict corrosion performance and optimize finite element analysis models. Data-driven approaches can improve analysis efficiency and accuracy.
7 Conclusion
This study developed two constitutive models for SPA-H weathering steel under the coupled effects of process chemical solution corrosion and atmospheric corrosion based on coupling corrosion test data and mathematical regression methods. The main conclusions are as follows:
1. This study provides degradation expressions for the key mechanical parameters of SPA-H weathering steel, using mass loss rate and average corrosion depth as variables applicable to both single-side and double-side corrosion. These expressions demonstrate the degradation of material performance parameters of weathering steel as the corrosion rate increases, with clear physical significance.
2. Two constitutive models for coupled corrosion of SPA-H weathering steel were proposed based on mass loss rate and average corrosion depth, respectively. This study validated two models through external experimental data and finite element simulations, showing reliable results and computational accuracy that meet engineering requirements. Reliability analysis indicates that the proposed constitutive models are dependable and applicable when the design partial safety factor is 1.0 or higher. The constitutive model based on average corrosion depth is more suitable for finite element numerical analysis due to its simplicity in operation.
3. The finite element numerical method proposed in this study, which integrates uniform corrosion (thickness reduction) and equivalent material property methods (mechanical property degradation), has been validated through experiments and proven effective and reliable. It accurately simulates materials’ mechanical performance and failure behavior with promising engineering applications. This innovative method combines the simulation of corrosion degradation and mechanical performance changes, providing a more efficient prediction tool and offering new insights for the design optimization of weathering steel with high engineering application potential.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
WN: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Resources, Project administration. LL: Writing – original draft, Resources, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization. HP: Data curation, Writing – original draft, Validation. JZ: Writing – review and editing, Software, Data curation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the China Scholarship Council (CSC202206560008).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Author Anonymous (2025). Available online at: https://luxunique.co.uk/benefits-of-cortensteel/?srsltid=AfmBOorrBTGesA22lTFiVgewNm5paXiRPHKPktfgO8riEmlrIfUkKvVt
Behzadi-Sofiani, B., Gardner, L., Wadee, M. A., Dinis, P. B., and Camotim, D. (2021). Behaviour and design of fixed-ended steel equal-leg angle section columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 182, 106649. doi:10.1016/j.jcsr.2021.106649
Bender, R., Féron, D., Mills, D., Ritter, S., Bäßler, R., Bettge, D., et al. (2022). Corrosion challenges towards a sustainable society. Mater. Corros. 73 (11), 1730–1751. doi:10.1002/maco.202213140
Esmaeily, A., and Xiao, Y. (2005). Behavior of reinforced concrete columns under variable axial loads: analysis. ACI Struct. J. 102 (5), 736. doi:10.14359/14669
GB50017 (2017). Standard for design of steel structures. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press.
Gu, S., Li, G. P., Ren, S. B., Han, F., Gu, Y., Kong, C., et al. (2023). Study on hysteresis constitutive and fracture behaviors of corroded constructional steel under artificial atmospheric environment. Structures 56, 104860. doi:10.1016/j.istruc.2023.07.050
Guo, Q., Wu, Z., Xing, Y., Lu, Y., Zhang, F., and Li, W. (2024). Corrosion evolution and mechanical property deterioration of Q355NH weathering steel in long-term neutral salt spray environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 411, 134193. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134193
Guo, X., Zhu, J., Kang, J., Duan, M., and Wang, Y. (2020). Rust layer adhesion capability and corrosion behavior of weathering steel under tension during initial stages of simulated marine atmospheric corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 234, 117393. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117393
Guo, X. Y., Kang, J. F., Zhu, J. S., and Duan, M. H. (2019). Corrosion behavior and mechanical property degradation of weathering steel in marine atmosphere. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 31 (9), 04019181. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0002814
Han, C., Li, Z., Yang, X., and Wang, J. (2024). Corrosion behavior and mechanical performance of weathering steel in industrial and rural atmospheric environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 411, 134284. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.134284
Hopkin, D., Anastasov, S., Illingworth, D., McColl, B., Loughlin, E. O., and Taylor, A. (2018). A structural fire strategy for an exposed weathering steel-framed building. J. Institution Struct. Eng. 96 (1), 60–66. doi:10.56330/kwvl5159
Hou, B., Li, X., Ma, X., Du, C., Zhang, D., Zheng, M., et al. (2017). The cost of corrosion in China. npj Mater. Degrad. 1 (1), 4. doi:10.1038/s41529-017-0005-2
ISO 12944-2, Paints and varnishes — corrosion protection of steel structures by protective paint systems —Part 2: classification of environments (2017). The International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland.
ISO 9227 (2022). Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres — salt spray tests. Geneva, Switzerland: ISO.
Jia, C., Shao, Y., Guo, L., and Liu, Y. (2018). Incipient corrosion behavior and mechanical properties of low-alloy steel in simulated industrial atmosphere. Constr. Build. Mater. 187, 1242–1252. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.08.082
Jiang, Z. Q., Wang, H. W., Lan, T., Li, Y., Wang, Y. Z., and Liu, X. C. (2024). Research on the constitutive relation of different material zones of weathering steel Q355GNHB. J. Constr. Steel Res. 212, 108281. doi:10.1016/j.jcsr.2023.108281
Jis, G. (2010). (E), Superior atmospheric corrosion resisting rolled steels, 4-1-24. Akasaka, Minato-ku, Tokyo: Japanese Standards Association, 107–8440. JAPAN.
Kim, J. H., Serpantié, A., Barlat, F., Pierron, F., and Lee, M. G. (2013). Characterization of the post-necking strain hardening behavior using the virtual fields method. Int. J. Solids Struct. 50 (24), 3829–3842. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2013.07.018
Krivy, V., Urban, V., and Kreislova, K. (2016). Development and failures of corrosion layers on typical surfaces of weathering steel bridges. Eng. Fail. Anal. 69, 147–160. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.12.007
Křivý, V., Vašek, Z., Vacek, M., and Mynarzová, L. (2022). Corrosion damage to joints of lattice towers designed from weathering steels. Materials 15, 3397. doi:10.3390/ma15093397
Kweon, H. D., Heo, E. J., Lee, D. H., and Kim, J. W. (2018). A methodology for determining the true stress-strain curve of SA-508 low alloy steel from a tensile test with finite element analysis. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 32, 3137–3143. doi:10.1007/s12206-018-0616-8
Lu, L. F., Wang, J. P., Ma, Z. Y., Ding, S. L., Li, R., and Wang, W. (2024). A comprehensive investigation of the process and atmospheric coupling corrosion on corroded and mechanical properties of the SPA-H weathering steel. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 20, e03352. doi:10.1016/j.cscm.2024.e03352
Ma, X. M., Zheng, M., Xu, W. C., Lu, D. Z., Ma, F. B., and Hou, B. R. (2021). Study of corrosion cost and control strategy. Mar. Sci. 45 (2), 161–168. doi:10.11759/hykx20200428001
Mabry, W. (2016). Steely resolve: sculptors working in steel. Sculpt. Rev. 65 (3), 8–15. doi:10.1177/074752841606500302
Morcillo, M., Chico, B., Díaz, I., Cano, H., and de la Fuente, D. (2013). Atmospheric corrosion data of weathering steels. A review. Corros. Sci. 77, 6–24. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2013.08.021
Morcillo, M., Díaz, I., Cano, H., Chico, B., and de la Fuente, D. (2019). Atmospheric corrosion of weathering steels. Overview for engineers. Part II: testing, inspection, maintenance. Constr. Build. Mater. 222, 750–765. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.155
Nie, B., Xu, S., Yu, J., and Zhang, H. (2019). Experimental investigation of mechanical properties of corroded cold-formed steels. J. Constr. Steel Res. 162, 105706. doi:10.1016/j.jcsr.2019.105706
Raja, V. B., Palanikumar, K., Renish, R. R., Babu, A. G., Varma, J., and Gopal, P. (2021). Corrosion resistance of corten steel–A review. Mater. Today Proc. 46, 3572–3577. doi:10.1016/j.matpr.2021.01.334
Senevirathna, C. R., Bandara, C. S., and Siriwardane, S. C. (2023). Numerical and code-based investigation on the impact of corrosion on the ultimate compressive strength of steel angle members using thickness reduction method. CivilEng 4 (2), 506–521. doi:10.3390/civileng4020029
Shi, K. J. (2019). Application of new materials in contemporary landscape design. Adv. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1, 25–33. doi:10.37155/2717-526x-0101-5
Shu, Q., Wang, K., Yuan, G., Zhang, Y., Lu, L., and Liu, Z. (2020). Assessing capacity of corroded angle members in steel structures based on experiment and simulation. Constr. Build. Mater. 244, 118210. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118210
Sun, L. (2015). Research on seismic damage performance and vulnerability of in-service steel frame structures in offshore atmospheric environment [D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology.
Wang, Y., Chang, C., Xu, S., and Soares, C. G. (2024). Probabilistic constitutive model for corroded structural steel with stochastic pits under monotonic tension. Eng. Struct. 304, 117599. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2024.117599
Wang, Z., Liu, J., Wu, L., Han, R., and Sun, Y. (2013). Study of the corrosion behavior of weathering steels in atmospheric environments. Corros. Sci. 67, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.corsci.2012.09.020
Xin, H., and Veljkovic, M. (2021). Evaluation of high strength steels fracture based on uniaxial stress-strain curves. Eng. Fail. Anal. 120, 105025. doi:10.1016/j.engfailanal.2020.105025
Xin-liang, G., Gui-qin, Fu, Miao-yong, Z., and Zhi-yin, D. (2012). Corrosion behavior of low-alloy weathering steel in environment containing chloride ions. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 34 (11), 1282–1287. doi:10.13374/j.issn1001-053x.2012.11.005
Xu, S., Wang, H., Li, A., Wang, Y., and Su, L. (2016). Effects of corrosion on surface characterization and mechanical properties of butt-welded joints. J. Constr. steel Res. 126, 50–62. doi:10.1016/j.jcsr.2016.07.001
Yang, C. (2015). Research on seismic performance and seismic vulnerability of corroded steel frame structures in acidic atmospheric environments [D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology.
Zhang, Y., Liu, Y., and Yang, F. (2022). Ductile fracture modelling of steel plates under tensile and shear dominated states. J. Constr. Steel Res. 197, 107469. doi:10.1016/j.jcsr.2022.107469
Zhang, Y., Wang, H., and Wang, W. (2024). A method to calculate seismic behavior of a corroded beam-to-column joint considering distribution randomness of corrosion depth. J. Constr. Steel Res. 212, 108267. doi:10.1016/j.jcsr.2023.108267
Keywords: weathering steel, corrosion, mechanical properties, constitutive models, finite element analysis
Citation: Nie W, Lu L, Peng H and Zhang J (2025) Constitutive models for SPA-H weathering steel under coupled process and atmospheric corrosion. Front. Mater. 12:1612013. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1612013
Received: 15 April 2025; Accepted: 20 May 2025;
Published: 02 June 2025.
Edited by:
Xiangyu Zhong, Tohoku University, JapanReviewed by:
Henara Lillian Costa, Federal University of Rio Grande, BrazilJihui Wang, Tianjin University, China
Copyright © 2025 Nie, Lu, Peng and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Linfeng Lu, bHVsaW5mZW5nQGNoZC5lZHUuY24=
 Weizhong Nie1
Weizhong Nie1 Linfeng Lu
Linfeng Lu