- 1Weifang Development Co., Ltd., Shandong Hi-speed Group, Weifang, Shandong, China
- 2School of Transportation Engineering, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, Shandong, China
In this study, the effects of surface treatment on concrete members with a silane-cement-based penetrant crystal composite coating were investigated. The protective effect of this composite coating was assessed via indoor durability tests and its influence on the service life of concrete structures was predicted. The results indicate that the silane-cement-based penetrant crystal composite coating can significantly reduce freeze-thaw damage to concrete, effectively delaying its onset while enhancing the resistance to chloride infiltration. While freeze-thaw cycles progressively weaken concrete’s survival capacity, the composite coating notably improves chloride ion erosion resistance—especially during early cyclic stages—by inducing microstructural densification and forming a surface protective layer. This may be attributed to the changes in the concrete microstructure during the initial stages and the protective layer formed by the coating on the surface. The coating permeability allows it to penetrate deep into the concrete, creating an effective barrier that minimises external chloride salt intrusion. This synergistic effect surpasses single-component coatings by integrating silane’s hydrophobicity with penetrant crystals’ self-healing properties, demonstrating superior resistance to coupled freeze-thaw and chloride attacks. In summary, the silane-cement-based penetrant crystal composite coating extends the service life of concrete structures and provides robust protection under harsh conditions, laying the groundwork for their practical use in engineering applications.
1 Introduction
Concrete is a structural and functional material widely used in modern engineering construction in a wide variety of structures, including houses, roads, bridge harbours, .dams, reservoirs, and underground engineering. In the 21st century, concrete constitutes more than 90% of the total amount of global engineering construction material (Jiang, 2022). In northern China, owing to the long winter time duration, low temperatures, and large diurnal temperature range, concrete undergoes repeated freeze-thaw cycles, resulting in increasingly significant concrete deterioration (Zhang et al., 2021), which affects its service life.
To ensure the safe performance and service life of buildings, it is particularly important to improve concrete durability. According to the protective measure action mechanisms for the durability degradation of concrete components, they are mainly divided into two types: external protection and internal enhancement, both at home and abroad. In terms of external protection, in addition to traditional concrete surface treatment technologies, there are new protective coating materials and technologies. In terms of internal enhancement, incorporating fibres and cementitious penetration crystals as common additives can significantly enhance the toughness and crack resistance of concrete. Among these, silane-impregnated and crystalline cementitious penetration materials have been widely used and studied (Lu, 2022).
Hydrolysis occurs in the presence of liquid water or water vapour inside a silane-impregnated concrete structure to produce silanols, which are further dehydrated and condensed to form siloxane chains owing to the alkaline environment within the concrete structure. The hydroxyl groups of the concrete matrix and siloxane chains are tightly connected through hydrogen bonding, and the hydroxyl groups of the siloxane chains are further dehydrated and condensed to form more stable Si-O bonds. The Si-O bond can be firmly attached to the concrete material surface and form a tough protective film, effectively improving the concrete durability. Simultaneously, the alkyl group in the siloxane chain prevents liquid water intrusion owing to its hydrophobicity, which further reduces the possibility of freeze-thaw damage and chloride erosion of concrete (Woo et al., 2007). Gao et al. (2011) found that the mass and strength loss rates of concrete after silane impregnation decreased, indicating that the freeze-thaw resistance of concrete was greatly improved. Tanaka and Miyagawa (2012) studied the results of both non-silane-impregnated and silane-impregnated concrete and found that the latter was more stable and durable. The drying shrinkage and chloride diffusion coefficient of silane-impregnated recycled low-shrinkage concrete were significantly reduced. Liu et al. (2023) conducted indoor chloride ion erosion resistance tests and simulated long-term seawater erosion tests on concrete with enhanced silane-impregnated coating durability. They found that the chloride ion erosion resistance of concrete showed a rapid and then slow increase with an increase in curing age, and the chloride ion diffusion coefficient of concrete exhibited a better negative correlation with curing age.
Recently, cementitious osmotic crystalline waterproofing materials have rapidly developed. The active chemicals in the waterproofing materials play a key role in the waterproofing properties of the material. To offer permanent waterproofing, cementitious osmotic crystalline waterproofing agents have a wide range of applications (Li et al., 2021). Guo et al. (2020) studied the effect of cementitious osmotic crystalline waterproofing materials on concrete durability in a salt-spray erosion environment and showed that cementitious osmotic crystalline waterproofing materials can effectively improve the impermeability of concrete. Yan et al. (2020) conducted freeze resistance experiments on concrete specimens with single cementitious penetration crystalline, inorganic waterproofing, and cementitious penetration crystalline composite coatings. Their results showed that the relative dynamic elasticity modulus of the specimens had a similar decreasing trend, and the relative dynamic elasticity modulus of the composite-coated concrete specimens was higher than that of the blank control and composite-coated concrete specimens after 300 freeze–thaw cycles.
In domestic and international studies, the maximum chloride ion concentration inside concrete that does not damage the passivation film of steel reinforcements is defined as the critical chloride ion concentration (Angst et al., 2009). This study mainly focused on the diffusion characteristics of chloride ions inside a concrete structure, analysed the transport process and mechanism of chloride ions, and constructed a corresponding chloride ion transport model to more accurately assess and predict the durability of concrete structures. Therefore, the establishment of a mathematical model to analyse the factors affecting the chloride ion penetration rate inside concrete structures after freeze-thaw damage, the study of the time required for the chloride ion concentration to increase to the critical concentration after freeze-thaw damage, and predicting the service life of concrete structures under the composite effect of freeze-thaw of chloride and salt have become key research topics (Deng, 2022).
Researchers have studied the effect of single silane and cementitious osmotic crystalline coatings on the durability of concrete components, simulated and analysed the penetration process and transport mechanism of chloride ions in concrete components through a variety of finite-element software and mathematical models, and predicted the service life of concrete structures. However, research on the durability enhancement effect of composite coatings on concrete components and service life prediction under chloride-salt freeze-thaw environments is limited. In this study, three kinds of durability tests, namely, rapid freeze-thaw cycle, rapid chloride ion penetration, and chloride-salt freeze-thaw composite tests, were designed to investigate the effect of silane-cementitious permeable crystalline composite coatings on the durability of concrete structures.
2 Durability performance tests
2.1 Test materials
2.1.1 Concrete materials
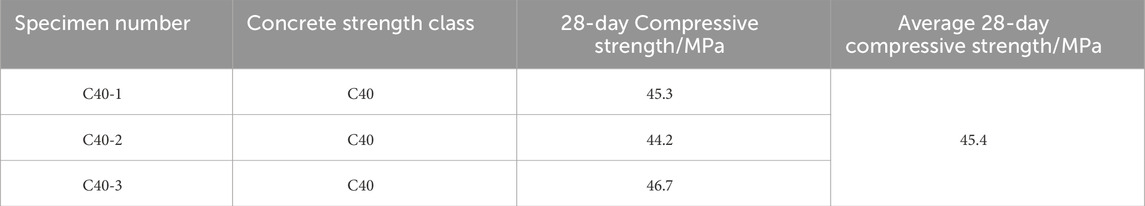
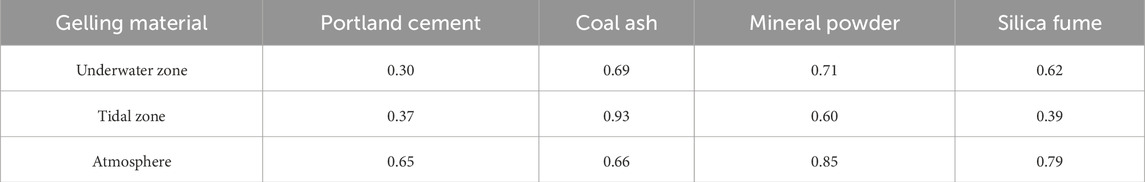
All test specimens were selected as C40 concrete strength class, and the concrete mix ratios are listed in Table 1.
Standard cubic specimens with dimensions of 150 × 150 × 150 mm were prepared using the same concrete batch. After a 28-day curing period, concrete cube compressive strength tests were performed according to the relevant provisions in the Standard for Test Methods of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Concrete (Standardization Administration of China (2019)). The results for the compressive strength of the concrete cube specimens after 28 days are presented in Table 2.
2.1.2 Silane impregnation
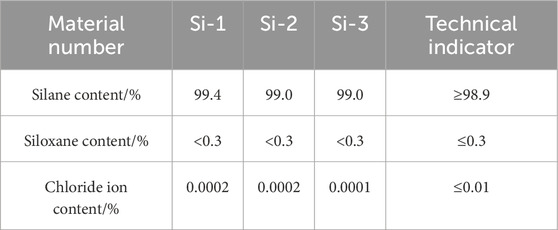
Owing to its hydrophobicity, silane can effectively isolate water, water vapour, and other chloride-carrying media after impregnation on the concrete surface, thereby improving the chloride ion penetration resistance of the concrete structure (Wang et al., 2021). The silane used in the test was STP1701-E15, which is a hydrophilic, solvent-free silane; its material properties are listed in Table 3.
2.1.3 Cementitious penetration crystallisation
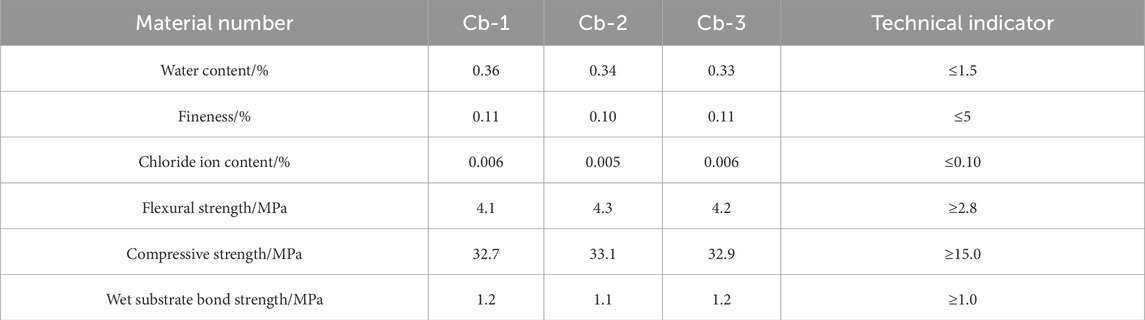
Cement-based osmotic crystalline waterproof materials use silicate cement, quartz sand, and other inorganic materials as substrates, active compound infiltration, and a variety of additives dry mixed into a greenish-grey powder waterproof material. The cementitious osmosis crystalline waterproof material is a green, non-toxic, odourless, and pollution-free product. Additionally, it is a rigid waterproof material, containing a wide variety of active substances. Finally, the active substances in the material through the water act as a carrier to the internal concrete infiltration, forming insoluble crystals in the concrete and blocking the pore channels, making the concrete dense and waterproof. The performance of the cement-based osmotic crystalline materials are listed in Table 4.
2.2 Test piece design and fabrication
2.2.1 Test piece design
Based on the standard requirements of the Test Methods for Long-Term Performance and Durability of Ordinary Concrete (Standardization Administration of China, 2009), combined with the specific objectives of the test, two groups of specimens were designed for conducting the rapid freeze-thaw cyclic (“Ft”) and rapid chloride penetration (“Cl”) tests. For the rapid freeze-thaw cyclic test, 100 × 100 × 400 mm concrete specimens were used; for the rapid chloride penetration test, concrete cylinders with a diameter of 100 mm ± 1 mm and a height of 50 mm ± 2 mm were used.
These specimen groups include concrete specimens without silane impregnation (“Bs”) and concrete specimens with silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite coating (“Si+Cb”), with “1” indicating that the specimen is the No. 1 specimen, with each group consisting of three specimens. For example, “Ft-Bs-1” is the No. 1 specimen of the blank control group without anti-corrosion coating for the rapid freeze-thaw cycle test; “Ft-Si+Cb-1” is the No. 1 specimen of the silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coating group for the rapid freeze-thaw cycle test; “Cl-Bs-1” is specimen No. 1 of the blank control group without anti-corrosion coating for the rapid chloride ion penetration test; and “Cl-Si+Cb-1” is specimen No. 1 of the silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coating group for the rapid chloride ion penetration test.
2.2.2 Test piece production
We prepared and cured standard specimens in a standard curing room according to test specifications and operational requirements. Before the rapid freeze-thaw test, the concrete specimens were transferred from the standard curing room to a curing pool for 4 days after the curing age reached 24 days. When the curing age reached 28 days, we removed the specimens from the curing pool and dried their surfaces. The concrete specimens without silane impregnation treatment were removed from the water directly and subjected to the rapid freeze-thaw cycle test. For the silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coating specimens, the first cementitious osmotic crystalline coating was a control dosage of 800 g/m2; after completing the coating, the specimens were sprinkled with water for maintenance for 3 days. The specific method and dosage are as follows: the completed concrete specimens are taken out of maintenance, with cold air blowing onto the saturated surface for drying; then, the silane impregnation material is brushed two times, the silane material amount was controlled at 300 g/m2; after the first silane impregnation material dries, the second brush coating is applied. After completing the above steps, the test blocks were dried naturally and subjected to the rapid freeze-thaw cycle test. The rapid freeze-thaw cycle test specimens are shown in Figure 1.
For the specimens subjected to the rapid chloride penetration test, when a conditioning age of 21 days was reached, the specimens were removed from the curing bath and processed with a cutting machine to standard sizes. These standard-sized specimens were then placed back in the curing bath and immersed until the required curing age for the test was reached. After curing for 28 days, the standard specimens were removed, and the surface was dried. For concrete specimens without silane impregnation, the rapid chloride penetration test were performed directly. For concrete specimens with silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coatings, the treatment and material dosage were based on the rapid freeze-thaw cycle test standards. After the specimens were completely dry, the rapid chloride penetration test was performed. The rapid chloride penetration test specimens are shown in Figure 2.
2.2.3 Rapid freeze-thaw cycle test
In accordance with Test Methods for Long-Term Properties and Durability of Ordinary Concrete (Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China (2009)), the fast freezing method was selected for the freeze-thaw cycle test, and the central freezing temperature during the freeze-thaw cycle was set at −15°C, the peak thawing temperature was 8°C ± 2°C, and the duration of one cycle was 2.5–4 h. The relative dynamic modulus of elasticity and mass loss rate of the concrete specimens were used to assess their frost resistance. The rapid freeze-thaw test equipment and dynamic elastic modulus tester are shown in Figures 3a,b, respectively.
2.3 Chloride rapid penetration test
The chloride ion diffusion coefficient can truly express the erosion ability of chloride ions inside a concrete structure by directly reflecting the chloride ion penetration rate inside the concrete structure. It is widely adopted as the key parameter for evaluating the durability of concrete components. The non-stationary chloride ion migration tester is shown in Figure 4a, the intelligent vacuum-water-saturation machine for concrete is shown in Figure 4b, and the microcomputer-controlled electro-hydraulic servo universal testing machine is shown in Figure 4c.
2.4 Chloride salt freeze-thaw composite test
The chlorine salt freeze-thaw composite test was conducted on cylindrical concrete specimens with a diameter of 100 mm ± 1 mm and height of 50 mm ± 2 mm. According to the maximum number of freeze-thaw cycles for each group of specimens, 50 freeze-thaw cycles were used in this study to design a group of chlorine salt freeze-thaw composite test specimens. Among them, “Ft+Cl” denotes the chlorine salt freeze-thaw composite test specimen; “Bs” denotes the silane-free impregnated concrete specimen; “Si+Cb” denotes the silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline coating concrete specimen; “Si+Cb” denotes the silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline coating concrete specimen; and “Bs” denotes the silane-free impregnated concrete specimen. In the composite coating concrete specimen name, “50” means 50 freeze-thaw cycles. For example, “Ft+Cl-Bs-50-1” represents the silane-impregnated concrete specimen without silane impregnation specimen for group 1 of the chlorine-salt freeze-thaw composite test; “Ft+Cl-Si+Cb” represents the silane-impregnated concrete specimen for group 1 of the chlorine-salt freeze-thaw composite test; “Ft+Cl-Si+Cb-50-1” represents specimen No. 1 of the silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite coating concrete specimen group of the chloride salt freeze-thaw composite test.
After the specimens reached the corresponding number of freeze-thaw cycles via the fast-freezing method, they were subjected to a rapid chloride penetration test to analyse the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient of the concrete specimens after freezing and thawing. The treated concrete specimens were placed in a specimen box and subjected to rapid freeze-thaw cycle testing. The test conditions were the same as those in the previous rapid freeze-thaw cycle test. After each specimen group reached the corresponding number of freeze-thaw cycles, the specimens were removed, vacuumed, and subjected to the rapid chloride penetration test. After test completion, the unsteady-state chloride migration coefficient of the concrete specimens was calculated from the test data.
3 Durability test results
3.1 Rapid freeze-thaw test
3.1.1 Quality loss rate analysis
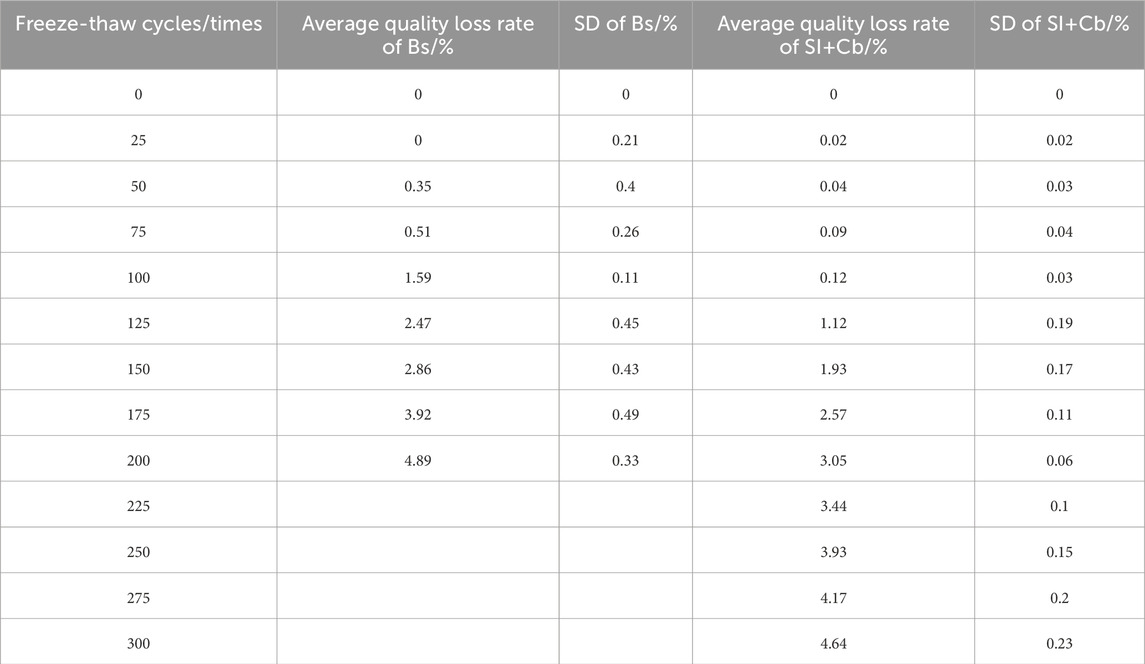
The changes in the mass loss rate during rapid freeze-thaw cycling of the silane-free impregnated concrete specimens and silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete specimens are shown in Table 5.
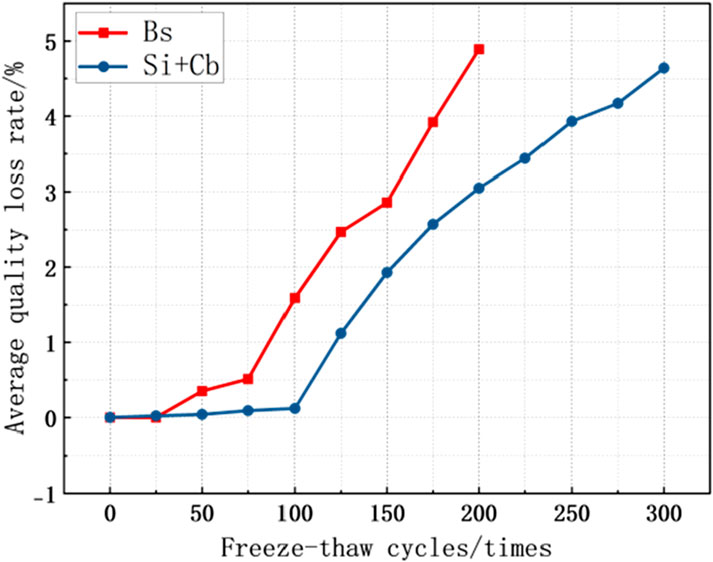
The mass loss rate trends of the concrete specimens without silane impregnation and with silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coating are shown in Figure 5.
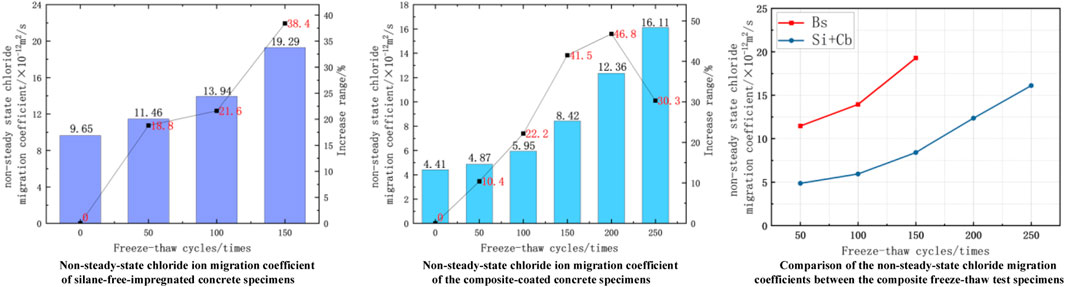
As can be seen in Figure 5, due to the dual protection of silane impregnation and cementitious penetration crystallisation, the quality of the composite-coated concrete specimens did not decrease significantly until 100 freeze-thaw cycles, the quality loss rate remains within 0.15%, and the specimens do not exhibit a phenomenon in which their quality after freezing and thawing is greater than the initial quality due to the cementitious penetration crystallisation curing in a water environment. After 100 freeze-thaw cycles, the mass loss reduction of the composite-coated concrete specimens was 92.5% compared with that of the non-silane-impregnated concrete specimens. From 125 to 225 freeze-thaw cycles, the mass loss rate of the specimens at this stage was significantly reduced owing to the significant shedding of cementitious penetration crystals caused by the destruction of water molecules. At 225 freeze-thaw cycles, the mass loss reduction of the composite-coated concrete specimens was 29.7% compared with that of the non-silane-impregnated concrete specimens. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 250, the specimen surface was completely exposed, and part of the mortar on the specimen surface started to flake off owing to the action of water molecules. The quality loss rate of the specimen was further reduced, and the quality loss rate of the composite-coated concrete specimen decreased by 19.6% compared with that of the non-silane-impregnated concrete specimen. As the number of freeze-thaw cycles continued to increase, the composite-coated concrete specimen cement mortar and fine aggregate also began to exhibit a large spalling. At this time, the quality loss rate began to increase; however, at 300 freeze-thaw cycles (i.e., at the end of the test), the quality loss rate of the specimen reached 4.64%, which is not yet more than the end of the test standard. It can be seen that the composite coating can significantly reduce the quality loss of concrete structures during freeze-thaw cycles compared with non-silane impregnation, and the effect is better in the early stages than in the later stages.
The conditions of the Concrete specimens without a silane-cementitious osmoticcrystalline composite coating and the concrete specimens with a silane-cementitious osmoticcrystalline composite coating after freeze-thaw cycles are shown in Figure 6.
3.1.2 Relative dynamic modulus analysis
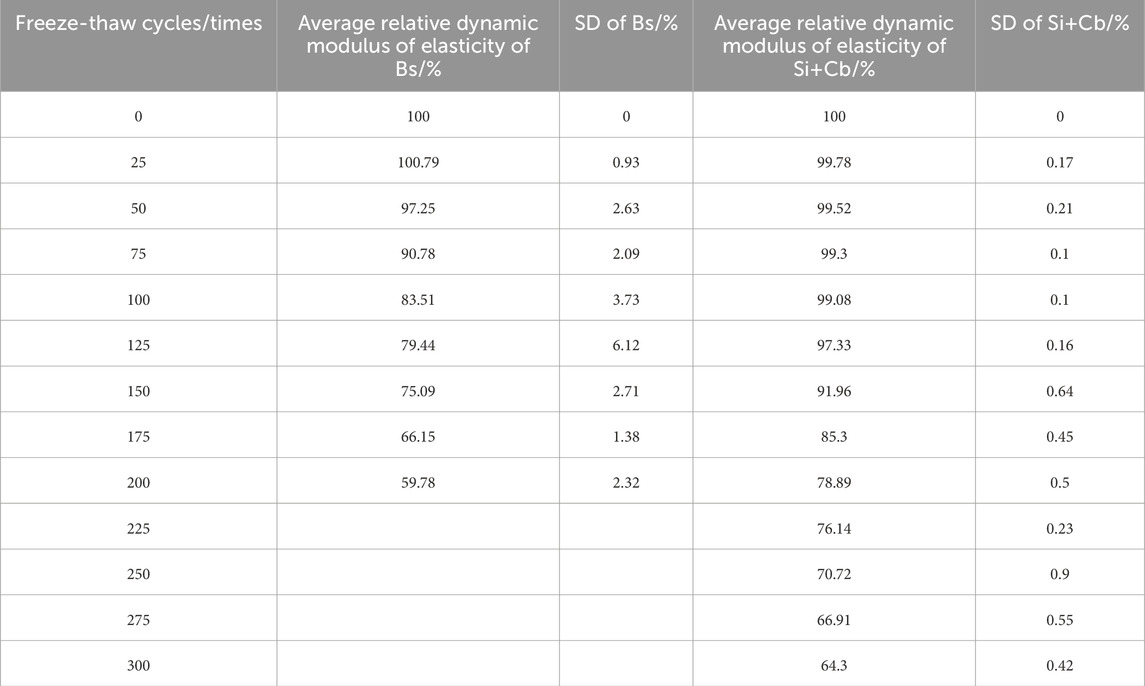
The relative dynamic modulus of elasticity of the concrete specimens without silane impregnation and with the silane-cementitious permeable crystalline composite coating are listed in Table 6.
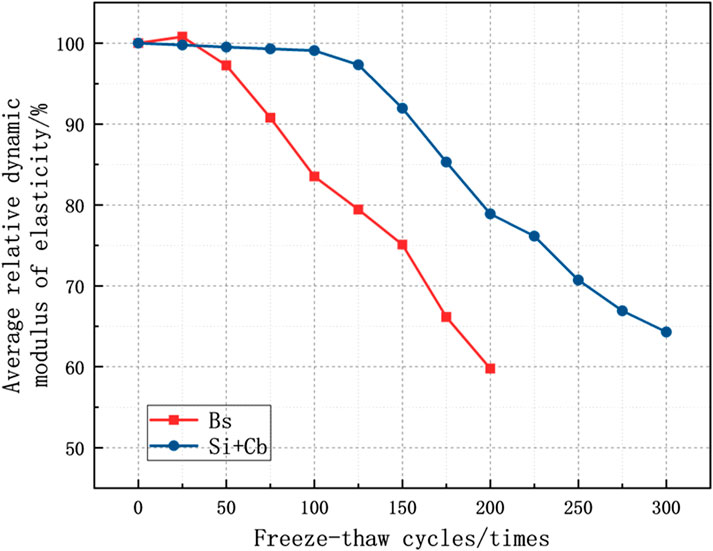
The relative kinetic elasticity model changes of the silane-free impregnated and silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete specimens are shown in Figure 7.
The determination of the dynamic elastic modulus of concrete specimens is shown in Figure 8.
The relative dynamic elastic modulus of the silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite coating concrete specimens did not decrease between 0 and 100 freeze-thaw cycles and remained above 99%; when the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 100, the relative dynamic elastic modulus increased by 18.6% compared with that of the concrete specimens without silane impregnation. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles ranged from 125 to 225, the cementitious protective layer was detached owing to the action of water molecules, and the protective ability of the internal concrete specimen was significantly weakened. The decreasing trend of the relative dynamic elasticity modulus increased significantly at this time, and the relative dynamic elasticity modulus decreased to 76.14% when the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 225. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 250, the cementitious protective layer was peeled off, the protective film formed by silane impregnation in the concrete pores slowed down the freeze-thaw damage caused by water molecules, the decreasing trend of the relative dynamic elastic modulus started to weaken, and the relative dynamic elastic modulus decreased to 70.72%. Before the test reached its end at 300 freeze-thaw cycles, silane impregnation continued to play a role, and the relative kinetic elastic modulus decline remained relatively slow. At the end of 300 freeze-thaw cycles, the relative dynamic modulus of the composite-coated concrete specimens decreased to 64.30%, which still did not reach the end of the test. This shows that the composite coating can significantly improve the freeze-thaw damage resistance of concrete structures compared with that of non-silane impregnation concrete.
Overall, the silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coating can, to a certain extent, reduce the quality loss of concrete components due to freeze-thaw damage, while being able to delay the concrete specimen freeze-thaw damage produced by the time node. Additionally, the effect during the early stages is better than that during the late stages.
3.1.2.1 Chloride rapid penetration test
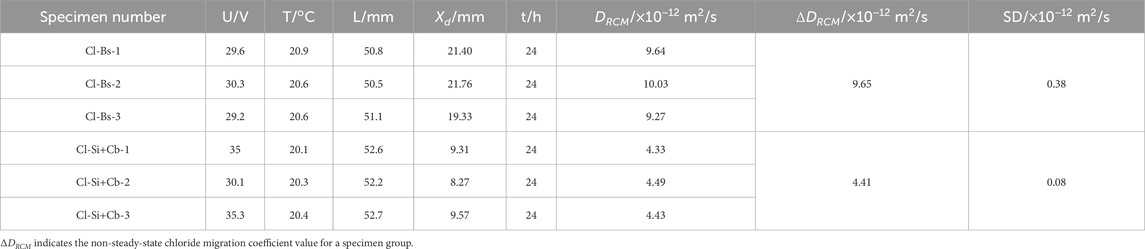
The rapid chloride penetration test results for the concrete specimens without silane impregnation and with the silane-cementitious permeable crystalline composite coating are listed in Table 7.
As can be seen in Figure 9, the non-steady-state chloride ion diffusion coefficient of the non-silane-impregnated concrete specimen is 9.65 × 10−12 m2/s, as shown in Figure 10. The non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of the silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite-coated concrete specimen is lower compared with that of the non-silane-impregnated concrete specimen due to the dual protection of the cementitious protective layer and silane-impregnated protective film, which reduces the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient by 54.3%. Additionally, it can be seen that the composite coating can improve the chloride ion erosion resistance of the concrete structure. This indicates that the composite coating can improve the ability of the concrete structure to resist chloride ion attack.
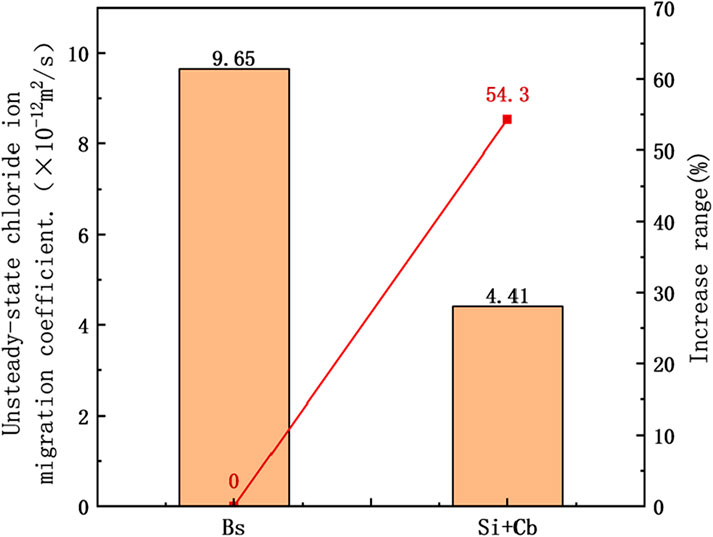
Figure 9. Non-steady state chloride migration coefficient of rapid chloride penetration test specimen.
The chloride ion penetration depth determination process and the corresponding results are shown in Figure 10.
3.1.2.2 Chloride salt freeze-thaw composite test
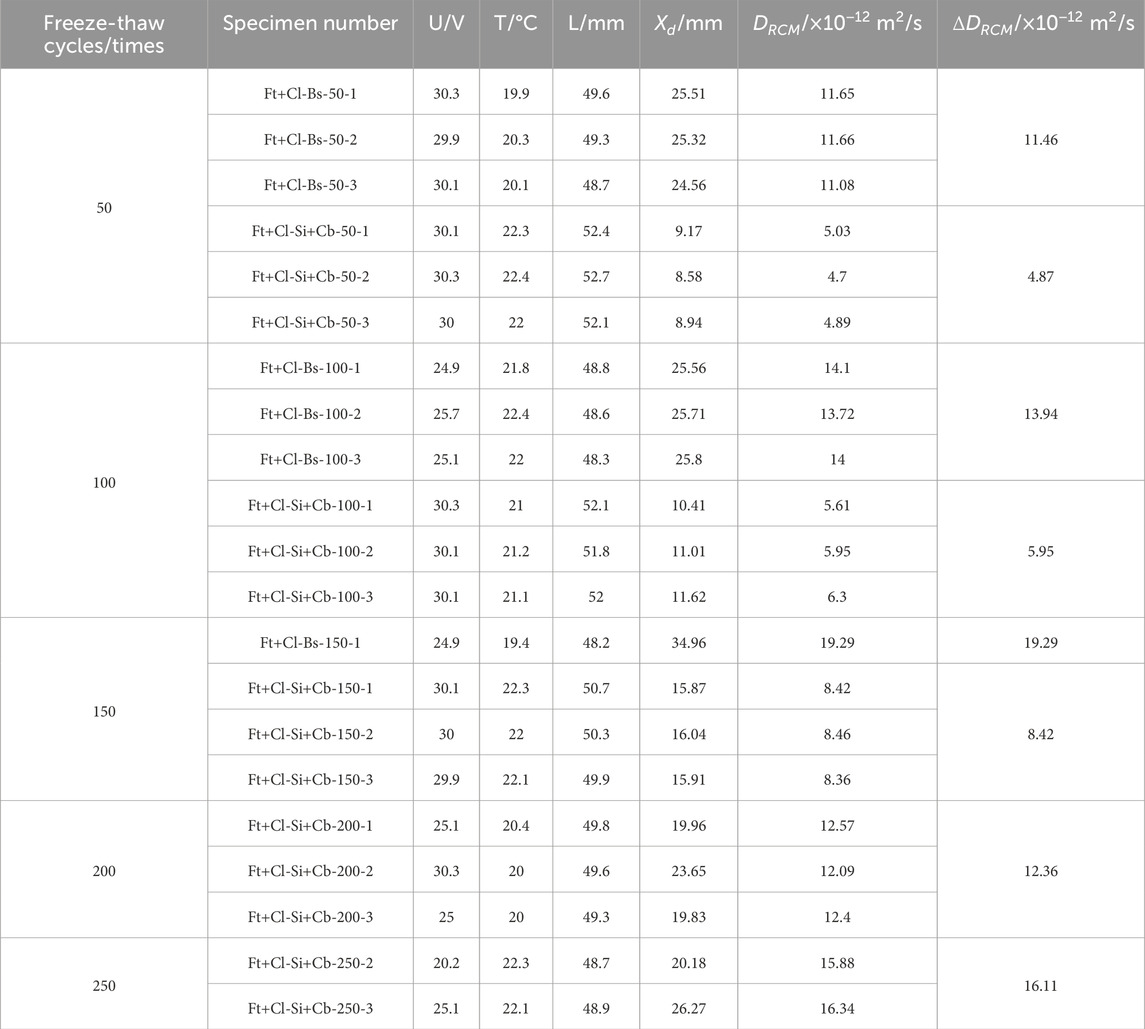
The chloride salt freeze-thaw composite test results for the concrete specimens without silane impregnation and with silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coating are presented in Table 8 and Figure 11, and a comparison of the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficients between the silane-free-impregnated and silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete specimens is shown in Figure 11.
At 50 freeze-thaw cycles, the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of silane-free impregnated concrete specimens increased to 11.46 × 10−12 m2/s, a 18.8% an increase. This indicates that a certain degree of freeze-thaw damage occurred in the specimens. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 100, the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient increased to 13.94 × 10−12 m2/s, a 21.6% increase relative to that at 50 cycles. This is because the cement mortar and fine aggregate on the specimen surface were severely spalled, and the specimen’s compactness decreased, which aggravated of the freeze-thaw damage. The chloride ion erosion resistance of the specimen began to decrease, and the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient increased. As the number of freeze-thaw cycles increased to 150, two of the silane-free-impregnated concrete specimens fractured, whereas the other specimen did not; however, it suffered extremely serious freeze-thaw damage, resulting in a serious decline in its chloride ion erosion resistance. At this time, the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of the specimen increased to 19.29 × 10−12 m2/s, a 38.4% increase relative to that at 100 cycles.
When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 50, the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete specimen increases from 4.41 × 10−12 to 4.87 × 10−12 m2/s, which is due to the freeze-thaw damage of the cementitious protective layer on the specimen surface, and chloride ions infiltrate to the interior of the cementitious layer under the action of the voltage, resulting in an increase in the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of the specimen. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reaches 100, freeze-thaw damage of the cementitious protective layer further occurs, and the invading chloride ions gradually increase and begin to contact the concrete specimen surface; consequently, the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient of the specimen increases to 5.95 × 10−12 m2/s, a 22.2% increase compared with that at the 50 cycles. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reaches 150, the cementitious protective layer is substantially detached due to freeze-thaw damage, and chloride ions start to penetrate into the pore space of the concrete specimen, at which time the chloride ion migration coefficient enhancement increases, and the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of the specimen increases to 8.42 × 10−12 m2/s, a 41.5% increase. As the number of freeze-thaw cycles continues to increase, the silane protective film inside the concrete pores is damaged due to repeated freeze-thaw cycles, at which time the chloride ions continue to erode into the specimen’s interior under the action of the voltage, and the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient reaches 12.36 × 10−12 m2/s, a 46.8% increase. With increasing chloride ion concentration inside the specimen, deep silane begins to play a role in chloride ion erosion resistance, and the chloride ion migration coefficient enhancement trend weakens, with a 30.3% enhancement.
After 50 freeze–thaw cycles for the non-silane-impregnated and silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite-coated concrete specimens, the non-silane-impregnated specimens began to suffer from freeze-thaw damage, and the chloride ion attack resistance of the specimens began to decrease; the composite-coated concrete specimens were subjected to freeze-thaw damage in a portion of the cementitious protection layer area, and the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of these specimens increased to 57.5% compared with that of the non-silane-impregnated specimens. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles increased to 100, the freeze-thaw damage of the concrete specimens without silane impregnation was further aggravated, the surface mortar fell off, and its chloride ion erosion resistance was greatly reduced. For the silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite-coated concrete specimens, the cementitious protective layer further suffered from freeze-thaw damage, most of the protective layer area was detached, and chlorine ion penetration increased. At this time, the composite-coated concrete specimens were more susceptible to freeze-thaw damage than those without silane impregnation. The non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of the composite-coated concrete specimens decreased to 57.3% compared with that of the non-silane-impregnated concrete specimens. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 150, the freeze-thaw damage of the concrete specimen without silane impregnation continued to develop, and the cracks on the specimen surface decreased the concrete compactness inside the specimen, which further accelerated the chloride ion penetration. The silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete specimen with the cementitious protective layer basically completes the exfoliation of the chloride ions, which begin to penetrate into the pore space inside the concrete, and the non-steady-state chloride ions of the composite-coated specimen increases at this time. At this time, the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient of the composite-coated specimen decreased to 56.3% compared with that of the non-silane-impregnated concrete specimen. When the number of freeze-thaw cycles reached 200, the silane protective film of the composite-coated concrete specimen was also damaged under repeated freeze-thaw erosion; therefore, the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient of the composite-coated concrete specimen significantly increased at this time compared with that of the pre-freeze-thaw period.
In summary, freeze-thaw damage significantly reduces the chloride ion erosion resistance of concrete structures, and silane-cementitious penetration crystals can improve the chloride ion penetration resistance of concrete structures to a certain extent in a chloride salt freeze-thaw environment and decrease the chloride ion erosion speed and depth. The resistance of the silane–cementitious penetration crystal composite coating in the pre-freeze–thaw concrete structure to chloride ion erosion was better than that of the late freeze-thaw structure.
4 Service life prediction of concrete elements in freeze-thaw environments with chlorinated salts
4.1 Duracrete concrete structure life prediction model
Based on multiple influencing factors proposed by Duracrete, a concrete structure life prediction model can be formulated as shown in Equation 1:
with
where
4.2 Duracrete concrete structure life prediction model modification
According to the results shown in Figure 11, the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficients of both specimen groups are directly proportional to the number of freeze-thaw cycles, and the rate of increase gradually accelerates. This trend is similar to the change rule of the mass loss rate and relative dynamic elastic modulus obtained in the rapid freeze-thaw test, showing the mathematical characteristics of the exponential function. Therefore, the exponential function mathematical model in Equation 3 was adopted to show the mathematical relationship between the number of freeze-thaw cycles and the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient of the specimen:
where
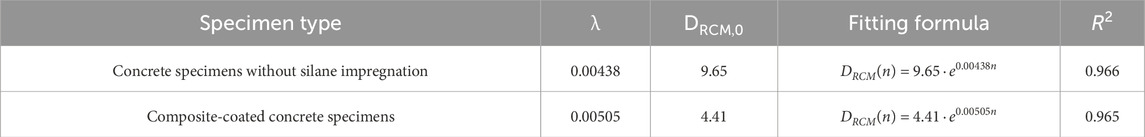
The data were fitted using the exponential function model described above and the fitting coefficients λ for the two concrete specimen groups were obtained, as presented in Table 12.
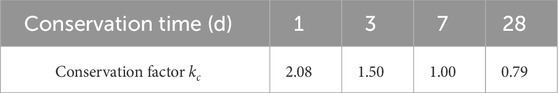
The Duracrete life prediction model for concrete structures reflects the intrinsic chloride diffusion coefficient patterns over time. To effectively correlate this model with the number of concrete freeze-thaw cycles and the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient, an accurate relationship between the number of rapid freeze-thaw test cycles and time needs to be established to provide a more comprehensive and accurate theoretical support for concrete structural durability assessment. Two parameters need to be considered: (i) the ratio between the number of indoor rapid freeze-thaw test cycles and the actual number of natural freeze-thaw cycles and (ii) the number of natural freeze-thaw cycles per year in the region.
In the indoor rapid freeze-thaw test, the degree of freeze-thaw damage experienced by concrete was significantly exacerbated by the accelerated test conditions, as the temperature increasing and decreasing rate far exceeded the freeze-thaw cycling rate under natural conditions. Additionally, the degree of damage caused to concrete by a single indoor rapid freeze-thaw test cycle far exceeds the effects of a single freeze-thaw cycle in real engineering applications. This difference must be considered when assessing the durability and predicting the service life of concrete structures.
Lin (2004) conducted a detailed investigation of the endurance service life of buildings in Tianjin, Dalian, and Shandong provinces in China using an indoor freeze-thaw cycle test. The results show that one indoor rapid freeze-thaw test cycle in Shandong is equivalent to 11.9–17.2 freeze-thaw cycles in the natural environment, in which the scaling factor in Yantai City, Shandong Province, is 11.9. Taking Yantai City as an example, the scaling factor S between the number of indoor rapid freeze-thaw test cycles and the number of natural freeze-thaw cycles is set to 11.9 in the correction model.
China’s specification for determining the number of annual freeze-thaw cycles of the actual engineering location includes the average daily temperature in a year below −3°C, the number of predetermined water level rise and fall, the actual engineering local temperature in a year from 3°C to −3°C and then back to 3°C, and meteorological data records. Zhong et al. (2016) reported the annual average number of natural freeze-thaw cycles in various parts of China; for example, this number in Shandong Province is approximately 100. Accordingly, in the revised model, the annual number of natural freeze-thaw cycles was set to 100 in Shandong Province.
The relationship between S and the number of natural freeze-thaw cycles per year in the area where the actual project is located Ny is shown in Equation 4:
Thus, the relationship between the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient and the concrete structure’s age considering freeze-thaw damage is shown in Equation 5:
Combined with Equation 2, the relationship for the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient, accounting for both freeze-thaw damage and curing age corrections of the concrete structure, is derived and expressed as Equation 6:
4.3 Service life prediction for concrete elements
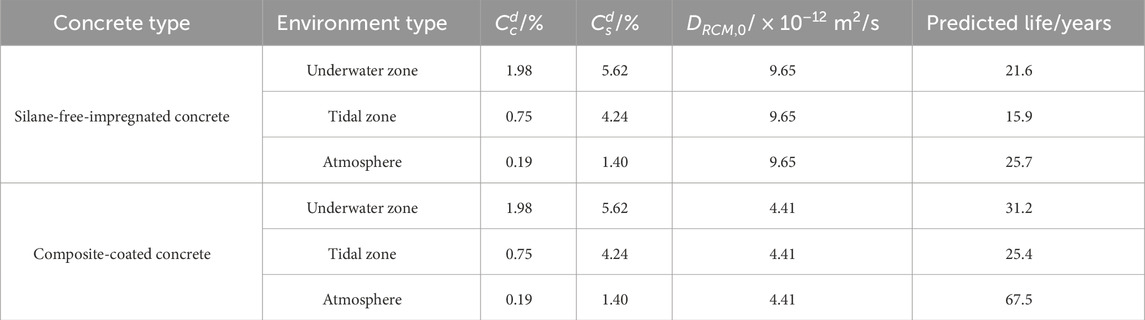
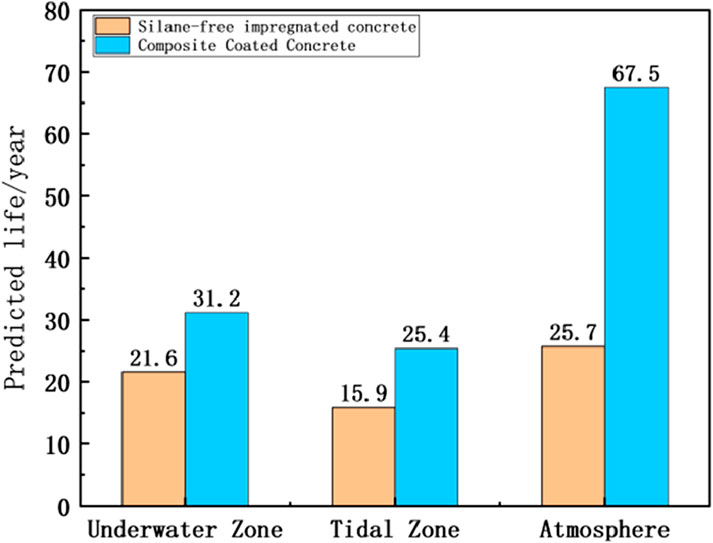
The service life of silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete structures in actual engineering environments in Yantai City was simulated using the mathematical equation obtained from the modified fitting. The predicted service life calculation results for concrete structures in each region considering freeze-thaw damage are presented in Table 13 and Figure 12.
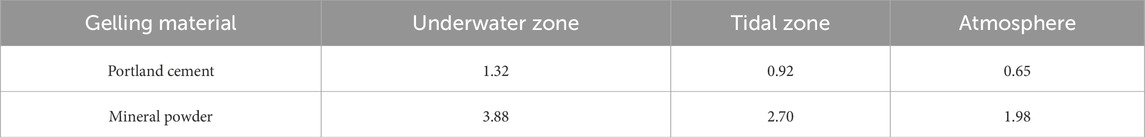
As shown in Figure 12, the lifespan improvement varies across different environmental regions. Specifically, the service life of silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete improved by 44.4%, 59.7%, and 162.6% in the underwater, tidal, and atmospheric regions, respectively. These results demonstrate that silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coatings significantly increase the service life of concrete structures in freeze-thaw damage environments.
5 Conclusion
In this study, the effects of silane-cementitious osmotic crystallisation composite coatings on the antifreeze performance of concrete structures, the resistance to chloride ion erosion and penetration, and the service life of concrete under chloride salt freeze-thaw environments were systematically investigated. For these purposes, rapid freeze-thaw cycling tests, rapid chloride ion penetration tests, and chlorine salt freeze-thaw composite tests were conducted. Based on the results, the main conclusions of this study can be summarized as follows:
(1) Silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coatings can significantly reduce the quality loss of concrete structures owing to freeze-thaw damage, delay the time node of freeze-thaw damage to concrete structures, and the effect during the early stages is better than that during the late stages.
(2) Owing to the dual protection of the cementitious protective layer and the silane-impregnated protective film, the non-steady-state chloride ion migration coefficient of the silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite-coated concrete specimens decreased by 54.3% compared with that of the concrete specimens without silane impregnation. The composite coating effectively improves the chloride ion attack resistance of concrete structures.
(3) Freeze-thaw damage significantly reduces the chloride ion erosion resistance of concrete structures, whereas silane-cementitious penetration crystallisation composite coatings can significantly improve the chloride ion penetration resistance of concrete structures under chloride salt freeze-thaw cyclic environments and decrease the chloride ion erosion speed and depth. The silane-cementitious penetration crystalline composite coating was more effective in improving the chloride ion erosion resistance of concrete structures in the pre-freeze–thaw period than in the post-freeze–thaw period.
(4) The mathematical relationship between the number of freeze-thaw cycles and the non-steady-state chloride migration coefficient was used to modify the Duracrete concrete structural life prediction model. Using the modified model, the service life of silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite-coated concrete structures considering freeze-thaw damage was calculated. The results show that the silane-cementitious osmotic crystalline composite coating significantly improves the service life of concrete structures under freeze-thaw damage and satisfied the durability performance requirements of concrete structures under freeze-thaw conditions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YB: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. LW: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review and editing. YW: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review and editing. WJ: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZL: Visualization, Writing – review and editing. GL: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. WT: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. QZ: Methodology, Validation, Writing – review and editing. FT: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Shandong Provincial Department of Transport (Grant No. 2024B90) and the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. ZR2021ME227).
Conflict of interest
Authors YB, LW, YW, ZL, WT, and QZ were employed by Weifang Development Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Angst, U., Elsener, B., Larsen, C. K., and Vennesland, Ø. (2009). Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete: a review. Cem. Concr. Res. 39, 1122–1138. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2009.08.006
Deng, J. (2022). Durability study on multi-measure composite action of concrete under chloride salt freeze-thaw environment. Guangzhou: Guangzhou University.
Gao, J. X., Deng, W. H., and Yang, Z. Y. (2011). Influence of silane treatment on the freeze-thaw resistance of concrete. Adv. Mater. Res. 1270 (250–253), 565–568. doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amr.250-253.565
Guo, W., Guo, X., Wang, Z., and Li, Z. (2020). Investigation on moisture damage prevention of a spherical hinge structure of a swivel bridge. Coatings 10 (10), 955. doi:10.3390/coatings10100955
Jiang, J. (2022). Ultrasonic identification of concrete based on multi-scale homogenisation damage. University of freeze-thaw method. (Zhejiang: Zhejiang University). doi:10.27461/d.cnki.gzjdx.2022.001210
Li, C., Niu, Z., Wu, H., and Cao, Y. (2021). Preparation and performance of new cementitious osmotic crystalline water repellent. Mater. Guide 35 (S1), 216–219.
Lin, B. (2004). “Research and practice of frost durability index of concrete for harbour construction in China,” In Proceedings of Durability Design and Construction of Concrete Structures, Nanjing: Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, 11.
Liu, H., Zhu, H., Fan, C., Fan, Z., and Yang, H. (2023). Research on durability enhancement technology of cast-in-place concrete structures in marine environment. Build. Struct. 53 (S2), 1329–1335. doi:10.19701/j.jzjg.23S2053
Lu, C. (2022). Experimental study on durability of concrete structural materials under salty environment in Northwest China and life prediction and assessment. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Science and Technology. doi:10.27206/d.cnki.ggsgu.2022.000121
Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China (2009). Standard for long-term performance and durability test method of ordinary concrete: gb/t 50082-2009. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press.
Standardization Administration of China (2009). Standard for test methods of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete (GB/T 50082-2009). Beijing: China Standards Press.
Standardization Administration of China (2019). Standard for test methods of physical and mechanical properties of concrete (GB/T 50081-2019). Beijing: China Standards Press.
Tanaka, H., and Miyagawa, T. (2012). Durability improvement by low shrinkage concrete impregnated with silane water-repellent material. Symposium 2012 Concr. Struct. Sustain. Community Proc. 2012, 285–288.
Wang, P., Li, C., and Ni, J. (2021). Durability enhancement analysis and life calculation of silane-protected concrete structures. Chin. J. Corros. Prot. 41 (05), 712–716. doi:10.11902/1005.4537.2020.200
Woo, R. S. C., Zhu, H. G., Chow, M. M. K., Leung, C. K. Y., and Kim, J. K. (2007). Barrier performance of silane–clay nanocomposite coatings on concrete structure. Compos. Sci. Technol. 68 (14), 2828–2836. doi:10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.10.028
Yan, W., Wu, Z., Niu, F., Wan, T., and Zheng, H. (2020). Study on the service life prediction of freeze-thaw damaged concrete with high permeability and inorganic crystal waterproof agent additions based on ultrasonic velocity. Constr. Build. Mater. 259, 120405. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120405
Zhang, Y., Xu, F., and Zheng, S. (2021). A review of research on freeze-thaw damaged concrete. Concrete 3, 10–14. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2021.03.003
Keywords: silane impregnation, cement-based osmotic crystallisation, composite coating, freeze-thaw damage, chloride ion penetration resistance
Citation: Bo Y, Weihua L, Wenlong Y, Junkai W, Lulu Z, Lin G, Tongfang W, Zhenxiang Q and Tao F (2025) Protective effect of a silane-cement-based permeable crystalline composite coating on concrete structures under freeze-thaw chloride environments. Front. Mater. 12:1627957. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2025.1627957
Received: 23 May 2025; Accepted: 17 June 2025;
Published: 09 July 2025.
Edited by:
Qing-feng Liu, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ping Duan, China University of Geosciences Wuhan, ChinaAmir Ali Shahmansouri, Washington State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Bo, Weihua, Wenlong, Junkai, Lulu, Lin, Tongfang, Zhenxiang and Tao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fu Tao, Z3JlZW52aWxsYWdlXzE3QDE2My5jb20=
 Yang Bo1
Yang Bo1 Fu Tao
Fu Tao