- 1Department of Physical Education and Military Training, Zhejiang Ocean University, Zhoushan, China
- 2Department of Sports Science, College of Natural Science, Jeonbuk National University, Jeonju, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Physical Education, Kunsan National University, Gunsan, Republic of Korea
- 4Faculty of Physical Education, Tomsk State University, Tomsk, Russia
Elite football players are particularly vulnerable to sports injuries due to the demands of high-intensity training and competition, which negatively affect their athletic careers and the economic interests of their clubs. Currently, the structural classification of injury scenarios and types in football remains unclear, hindering players' understanding of injuries and the implementation of effective preventive measures. This study aims to refine the structural classification of football-related injuries and update the corresponding scenarios, prevention strategies, and treatment approaches for general sports injuries, degenerative injuries, and accidental injuries. Researchers screened relevant literature from PubMed, SportDiscus, and Google Scholar databases from May 2000 to May 2025. For general sports injuries, skeletal muscle injuries (muscle fiber injuries, tendon injuries) can be prevented through eccentric strength training, while joint injuries (ligament injuries, muscle imbalances) require a focus on neuromuscular control training. Degenerative injuries necessitate systematic treatment, and surgical intervention should be adopted, when necessary, followed by a personalized rehabilitation program. Accidental injuries (concussions and fractures) can be mitigated using protective gear, rule modifications, and enhanced safety measures education. This article emphasizes the importance of a structured classification system for injury prevention and differentiated treatment strategies for elite football players. This will provide a theoretical basis for establishing clear understanding among individual athletes and reducing the occupational risk of injury in football.
1 Introduction
According to official Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) data, football is one of the most popular sports in the world, with the 2022 World Cup alone attracting a global audience of 5 billion viewers across various media platforms (1). Currently, the total number of professional athletes registered with FIFA is 128,876 (2). This study primarily focuses on elite-level football players. In the field of sports science, the definition of elite athletes has long been a subject of debate due to the diversity of sports and the complexity of evaluation criteria. Swanna et al. (2015), proposed a five-dimensional classification scoring system (competitive standards, competitive success, experience, the competitiveness of the athlete's home country, and the global competitiveness of the sport) to define the scope of elite athletes (3). William et al. (2017), advocate prioritizing quantitative performance data (such as personal bests) and only referencing competitive experience and success in high-level leagues when such data is unavailable (e.g., in team sports), rather than international representation (4). Zentgraf et al. (2024), analyzed and compared elite and semi-elite athletes based on neurophysiological indicators, characterizing elite athletes as “high-performance outliers” within their specific sports, emphasizing their specialization and international level (5).
Based on the aforementioned studies, we define elite athletes as individuals who have reached national or international competitive levels in their specific sport, consistently participate in high-level competitions, and possess a long-term background of organized, specialized training. They are generally engaged in professional leagues, national teams, or the Olympic framework, exhibiting exceptional competitive prowess and a robust will to succeed, and are considered “high-performance outliers” in their domain. This elite group, owing to extended exposure to intense competition and training loads, encounters markedly elevated injury risks compared to average athletes (6), rendering the occurrence and prevention of their sports injuries a matter of considerable concern.
To avoid conceptual overlap with the “contact/non-contact” mechanism-based classification, this study adopts a structural framework of “General Sports Injuries—Degenerative Injuries—Accidental Injuries,” in order to better serve practical decision-making in injury prevention and rehabilitation. Among these, “General Sports Injuries” primarily refer to those that can be reduced in incidence or severity through planned physical and technical training, and are predominantly non-contact in mechanism (e.g., muscle, tendon, and ligament injuries) (7). “Degenerative Injuries” are also mostly derived from non-contact mechanisms (such as tendinopathy, degenerative meniscus injury, etc.) (8). It is worth noting that in elite athletes, acute traumatic meniscus tears are also frequently observed. Although such injuries are usually categorized as contact injuries, they deserve particular attention because they involve not only preventive measures but also post-treatment rehabilitation (9). Regarding contact injuries, due to their high degree of randomness and difficulty in preventing them through training, this paper categorizes them under “Accidental Injuries”.
General sports injuries in football include muscle/tendon injury, joint (non-bone)/ligament injury, contusion, fracture, and laceration (10). Among these, nearly one-third are muscle injuries, and the majority (92%) affect the lower extremity (11). According to previous studies, players' performance in high-intensity exercise and technical skills usually significantly declines when they suffer moderate to severe muscular injuries (12). Therefore, current research primarily focuses on muscle and ligament injuries in the lower limbs and their prevention. Muscle injuries vary in their mechanisms, and prevention strategies also differ. Thus, this study divides muscle injuries into tendon injuries and muscle fiber injuries based on their anatomical characteristics. Hamstring strains, for example, primarily occur during high-speed movements or excessive stretching (13), with eccentric strengthening protocols demonstrating preventive efficacy (14). Additionally, tendon injuries often occur during high-impact activities such as sprinting and jumping (14), with some studies indicating that balance training may reduce the risk of tendon injuries (15). Furthermore, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tears have been extensively studied due to their severity and prolonged rehabilitation. These injuries can occur during deceleration and acceleration movements, primarily due to excessive loading of the ACL (16). Neuromuscular training has been widely employed in the prevention of ACL injuries, with previous research indicating its positive effects on improving lower limb muscle control and reducing injury risk (17). In summary, current evidence suggests that certain muscle injuries (muscle fiber and tendon) and ligament injuries in football can be effectively prevented through scientifically designed exercise interventions.
Football-related injuries include more complicated pathological disorders, including tendinopathies and articular cartilage lesions in addition to common sports injuries (8). Long recovery times and complicated aetiologias are common characteristics of these degenerative injuries, which frequently require medication or surgery. For instance, meniscal lesions are among the most common degenerative injuries in football players (18), with their pathogenesis typically ascribed to the combination of compressive force and transverse-plane tibiofemoral rotation as the knee transitions from flexion to extension during rapid cutting or pivoting (19). Depending on the type and severity of the meniscal injury, treatment options may include meniscectomy, meniscus repair, or meniscal reconstruction (19). To safely return to play, postoperative patients need systematic rehabilitation programs that gradually improve lower limb stability and joint function.
In addition to the aforementioned preventable injuries occurring during training and competition, football also involves accidental injuries, such as muscle cramps, concussions, and fractures (10). The occurrence of muscle cramps may be related to disturbances in hydration and electrolyte balance or abnormal spinal reflex activity caused by sustained muscle fatigue; however, the precise mechanisms remain unclear (20). According to earlier research, taking supplements containing trace elements (calcium, potassium, sodium) and drinking enough water may help reduce muscle cramping (21). Increased safety awareness during games and better instruction on safety procedures may help minimize accidental injuries (such as fractures and concussions).
In elite football, the occurrence of injury events can result in substantial medical costs, negatively impact team performance, and even prematurely end an athlete's professional career (22). Consequently, reducing football-related injuries is essential to protecting players' health and clubs’ financial stability (22). By categorizing the most frequent injuries in professional football into three main categories: general sports injuries, degenerative injuries, and accidental injuries, this study aims to enhance the structural classification of football injuries. The study further updates the knowledge of injury processes and related prevention and treatment techniques for each category based on the most recent research findings. The objective is to provide a more coherent framework for understanding the fundamental reasoning and top preventive priorities related to football injuries. The goal of this work is to provide football practitioners with a better-organized perspective on injury typology while laying the theoretical groundwork for improving elite football performance and optimizing health management systems.
2 Literature search
This study adopted a narrative review approach rather than a systematic review. The primary aim was to provide a structured synthesis of injury types and prevention strategies among elite football players. A structured literature search was conducted across the following electronic databases: Google Scholar, PubMed, and SPORTDiscus (via EBSCOhost), covering the period from May 2000 to May 2025.
To ensure both breadth and sensitivity, the search strategy combined Boolean operators (AND, OR) and truncation symbols (*) for keyword combinations. Both Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) and free-text terms were used. Keywords included but were not limited to: “elite athletes” OR “professional footballers” OR “soccer” AND (“injury” OR “injuries” OR “injury epidemiology” OR “muscle” OR “tendon” OR “joint” OR “ligament” OR “muscle imbalance” OR “meniscus” OR “tendinopathy” OR “fracture” OR “concussion” OR “injury prevention” OR “injury intervention” OR “treatment” OR “rehabilitation training”). All keywords are used for searching in the title, abstract, and keyword fields.
The literature screening adhered rigorously to the established inclusion and exclusion criteria (refer to Table 1). Each publication underwent a review procedure comprising title, abstract, and full-text evaluations, and was included solely if it particularly featured elite football players and had usable statistics or pertinent intervention details. The reference lists of included research were meticulously examined to discover any other eligible studies that may have been overlooked in database searches.
3 Occurrence and prevention strategies of general sports injuries in football
Compared to training sessions, football games had a significantly higher frequency of injuries (23). Taking the 2022 World Cup as an example, the injury rate during the competition period was 20.6 per 1,000 h, while during training it was only 2.1 per 1,000 h (24). Moreover, elite football players are exposed to the combined demands of high-intensity training and frequent competition throughout the year, and this high exposure rate is associated with an increased risk of injury (25). The most common injuries in football involve the ankle and knee joints, as well as the muscles and ligaments of the thigh and lower leg (23). Mechanisms of injury and injury prevention measures vary because of the anatomical regions where injuries occur. Research indicates that exercise-induced muscle injuries are associated with repetitive high-intensity eccentric contractions, with prevention primarily focused on strength enhancement (26). However, joint (non-bone) injuries during athletic activity are often related to excessive joint displacement under high-load conditions (27), with prevention strategies typically involving flexibility and balance training (28). To provide a more comprehensive and accurate analysis of injury-related factors across different anatomical regions, including internal mechanisms and external situational triggers, and to guide the selection of more appropriate preventive approaches, the present study investigates preventable football injuries from two perspectives: skeletal muscle and joint-related injuries. Figure 1 presents a summary of the categories and sites of injuries sports injuries in football, predominantly concerning structural harm to skeletal muscles, joints, and tendons.
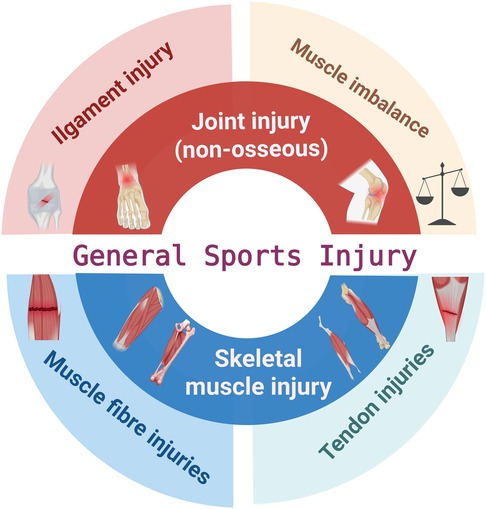
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of general sports injuries in football. The adductor icon in the panel is adapted from Corcoran et al. (148). Created using BioRender (ID: HA28P4FWQG).
3.1 Injuries and prevention of general sports injuries involving skeletal muscles in football
The most frequently injured anatomical region in football is the lower limbs (23). According to statistics from the 2022 FIFA World Cup, muscle and tendon injuries were the most prevalent injury type, with hamstring strains being the most frequently diagnosed condition (24).
Skeletal muscle serves as the primary effector organ of the locomotor system, accounting for approximately 40% of total body weight and making significant contributions to various bodily functions (29). Its core function is converting chemical energy into mechanical energy to generate force and power, maintain body posture, and produce movements that affect activity (29). Skeletal muscle is naturally plastic, meaning that it can change both structurally and functionally in response to contractile activity (endurance exercise, electrical stimulation, denervation), loading conditions (resistance training, microgravity), substrate supply (nutritional interventions), or environmental factors (hypoxia) (30). These adaptive responses not only enhance muscle strength and flexibility but also optimize neuromuscular control and tissue repair capacity, ultimately contributing to a reduced risk of injury during athletic activity (30). Muscle fiber injuries and tendon injuries are the two categories into which skeletal muscle injuries in football are classified in this study based on the structural characteristics of muscle tissue. The underlying mechanisms of each type are examined independently, and related preventive measures are compiled and suggested.
3.1.1 Muscle fiber injuries
Muscle fibers constitute the basic structural units of skeletal muscle, with multiple fibers forming muscle bundles that collectively compose skeletal muscle tissue (29). A muscle cell is represented by each muscle fiber, which is the fundamental cellular unit of a sarcomere (a muscle ganglion, the contractile apparatus necessary to generate force) (31).
Strains, partial tears, and muscle ruptures are among the most prevalent muscle fiber injuries in football (8). Most of these injuries occur during high-intensity activities such as sprinting, jumping, or striking (32). When the mechanical strain applied to the muscle exceeds its physiological capacity, internal stress within the muscle can increase by several orders of magnitude, leading to varying degrees of muscle fiber disruption, which is frequently accompanied by inflammation or damage to the surrounding connective tissues (33). Excessive eccentric loading is recognized as the most common cause of acute muscle fiber injuries (34). Table 2 delineates muscle fiber injuries frequently observed in elite soccer players throughout athletic endeavors, alongside the elevated prevalence of these injuries in particular sporting contexts and preventive strategies corroborated by extant literature. The hamstrings, adductors, quadriceps, and calf muscle groups are the most often injured muscle fibers (35), often linked to high-velocity running, abrupt directional changes, jumping, and explosive actions (36–39). Preventive therapies largely encompass eccentric training and injury prevention programs(e.g., FIFA1+) (40–43).
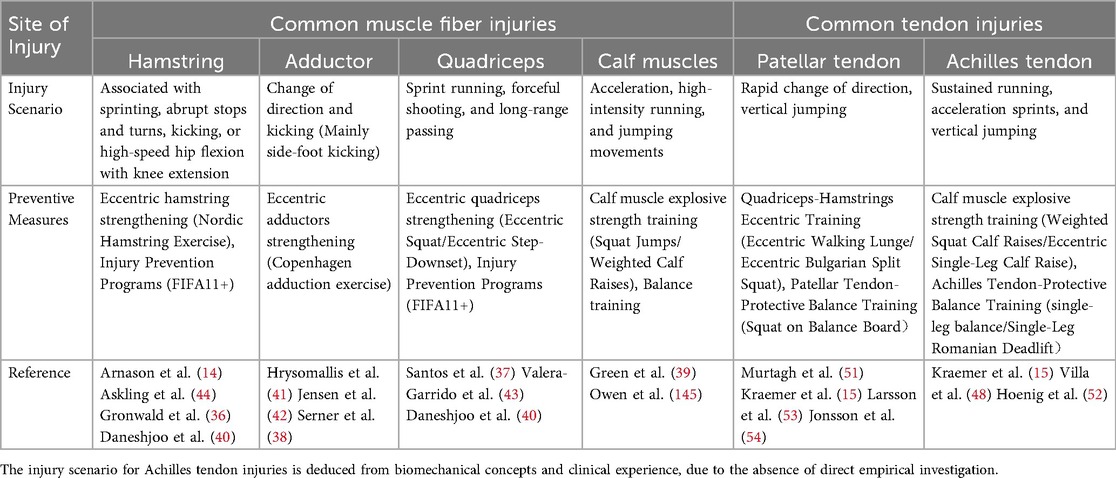
Table 2. Skeletal muscle injuries as general sports injuries in football: scenarios & training-based prevention strategies.
Previous studies have demonstrated that implementing eccentric strengthening exercises during the preseason can optimize physical capacity and increase muscle strength, thereby reducing the incidence of muscle injuries during competition. Askling et al. (2003), for instance, reported that the incidence of hamstring-related injuries in athletes was substantially reduced by preseason eccentric strengthening of the hamstrings (44). In a similar vein, Ishøi et al. (2016) discovered that the Copenhagen Adduction exercise in preseason training programs increased hip adductor strength and reduced the likelihood of adductor injuries during matches (45).
3.1.2 Tendon injuries
Tendons, mostly consisting of highly organized collagen fibers, are essential to the human musculoskeletal system, facilitating force transmission and governing the dynamic interplay between muscles and bones, while also offering mechanical protection (46).
In football, common tendon injuries include tendon rupture and tendon avulsion (8), most frequently affecting the patellar tendon (47) and the Achilles tendon (48). These injuries are typically associated with single-leg support and jumping actions (47, 48). Tendon ruptures (avulsions) during football activities typically arise from acute overload, wherein the applied force surpasses the tendon's ultimate tensile strength, leading to fiber failure and rupture (14). Reviewing the mechanisms of tendon overuse injury induction in animal models, it is mainly due to excessive mechanical loading (49, 50). Table 2 summarizes the prevalent tendon injuries sustained by elite football players during competition, identifies the high-risk sports situations linked to these injuries, and outlines the exercise training preventive methods endorsed by available literature. The patellar tendon and Achilles tendon are especially susceptible to damage, frequently occurring in high-impact, repetitive load situations such as running, jumping, and directional shifts (51, 52). Associated preventive strategies encompass eccentric resistance training and balance training, designed to augment tendon load-bearing capacity and enhance coordination of lower limb muscles (15, 53, 54).
Prior studies have shown that eccentric strength training, whether conducted independently or alongside balance training, can significantly reduce the incidence of tendon injuries. Kraemer et al. (2009) discovered that integrating proprioceptive balance training into football programs markedly reduced the occurrence of tendon injuries in athletes (15). Likewise, Langberg et al. (2007) demonstrated that high-load eccentric exercise could alleviate degenerative alterations in tendons (55).
3.2 Injuries and prevention of general sports injuries involving joint (non-bone) in football
Joints, comprising the articular capsule and articular cartilage, serve as the points of articulation between bones and are essential components of the human musculoskeletal system (56). Joints enable flexible movement between bones while ensuring stability and support during motion (57). In football, the lower limbs are particularly engaged due to the need for frequent sprinting (with and without the ball), directional changes, jumping, and kicking (shooting and passing). Consequently, joint injuries in football primarily affect the knee and ankle, often arising from mechanical stress or impacts in these areas (28).
The knee joint is a complex hinge structure made up of the femur, tibia, and patella, allowing for flexion-extension in the sagittal plane and varus-valgus rotation in the frontal plane (58). Common football-related knee injuries include ligamentous injuries and cartilage damage (59).
The ankle joint consists of the articulating surfaces of the distal tibia and fibula with the talar trochlea, facilitating coordinated rearfoot motion (60). Rearfoot motion typically occurs across three primary planes: sagittal (plantarflexion–dorsiflexion), frontal (inversion–eversion), and transverse (internal–external rotation) (61). Due to the frequent ball-contact actions in football and the relatively weak structure of the lateral ankle ligaments (e.g., the anterior talofibular ligament), inversion forces can frequently lead to sprains (62). In the 2022 FIFA World Cup, ankle sprains accounted for 17% of all documented injuries (63).
Joint stability is primarily provided by ligaments, while the surrounding musculature plays a secondary, yet supportive, role. Together, they ensure reliable joint function (58). This study will examine prevalent joint injury mechanisms, occurrence scenarios, and effective preventative techniques in football, emphasizing two essential stabilizers of joint integrity: the periarticular muscles and ligaments.
3.2.1 Impaired joint mobility caused by ligamentous injuries
Ligaments are pieces of dense connective tissue that are dominated by collagen fibers that give them a high tensile strength (64). Their principal role is to inhibit excessive or aberrant joint motions, thus preserving joint stability (64). In football, the most common joint(non-bone) injuries are ligament injuries associated with sprains (10). During the 2022 FIFA World Cup, ligament injuries accounted for 13% of all reported injuries, predominantly occurring in the knee and ankle joints (10).
The knee joint relies on the ACL to prevent anterior displacement of the tibia relative to the femur, while the posterior cruciate ligament restricts posterior displacement (59). Consequently, ACL tears constitute one of the most serious knee injuries in football (65). Medial collateral ligament (MCL) injuries are also frequent, while lateral collateral ligament and posterior cruciate ligament injuries are relatively rare (63).
Ankle injuries in football frequently occur due to player-to-player contact, particularly from a direct impact to the medial side of the lower leg or ankle (66). Lateral ankle sprains are the most common form of ankle injury, with the anterior talofibular ligament typically being the first structure to be compromised (67).
Most ligament injuries in football occur when muscles fail to adequately absorb ground reaction forces. Sustained high-impact forces over a short period may increase joint loading and result in ligament rupture (61). Rarer ligament injuries generally result from substantial external impacts during intense match situations. Table 3 delineates ligament injuries frequently observed in elite football players within the context of general sports injuries, including high-risk sports scenarios and preventive exercise training approaches substantiated by available literature. Ligament injuries (ACL and MCL), commonly arise from abrupt halts, swift directional shifts, or landing maneuvers, especially during offensive and defensive engagements and sliding tackles (66, 68, 69). Associated preventive strategies encompass muscle balance training and neuromuscular training, designed to augment ligament load-bearing capacity and enhance joint stability (70–74).
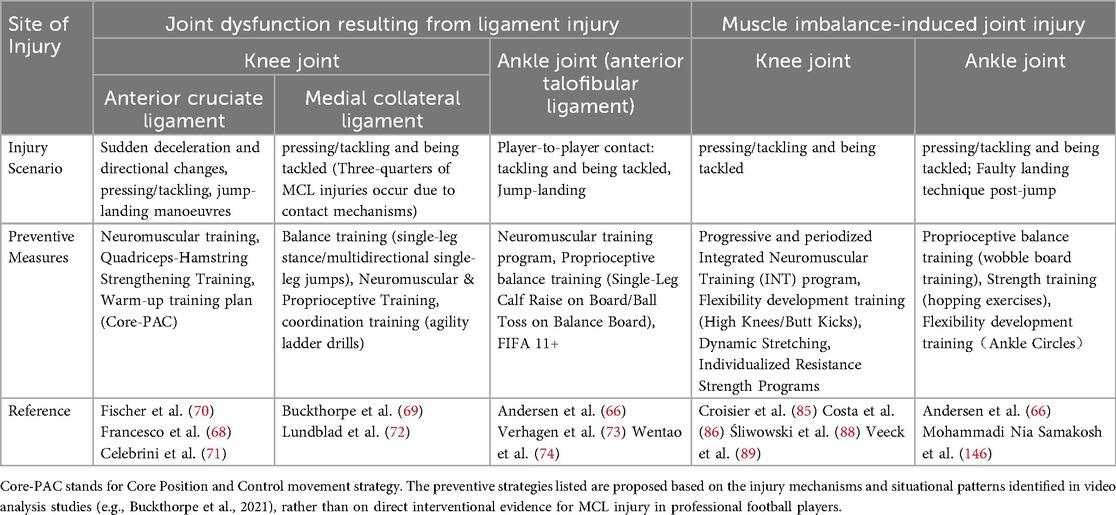
Table 3. Joint (non-bone) injuries as general sports injuries in football: scenarios & training-based prevention.
Previous studies have demonstrated that strength and balance training can significantly reduce the incidence of ligament injuries. Myklebust et al. (2003) demonstrated that possible to prevent anterior cruciate ligament injuries with specific neuromuscular training (75). Fischer et al. (2006) demonstrated that proprioceptive balancing board interventions effectively prevented repeated ankle sprains (70). In addition, Waldén, M. et al. (2012) demonstrated that implementing neuromuscular warm-up protocols significantly decreased the incidence of ACL injuries among adolescent female football players (76).
3.2.2 Joint injuries caused by muscle imbalances
Joint sprains are prevalent injuries in football and have garnered significant attention due to their elevated recurrence rates (77). Previous studies indicate that muscle strength and balance play key roles in preventing targeted muscular injuries (78), while muscle imbalance can increase the incidence of joint injuries in athletes (79). Therefore, it can be suggested that muscle imbalance affects joint stability and thereby increases the incidence of joint (non-bone) injuries. Imbalance in muscle strength typically denotes an abnormal bilateral asymmetry between homologous muscle groups and a disruption in the agonist-antagonist ratio (78).
The quadriceps cover the entire front of the thigh, extending from the hip to the knee joint (80), and function as the primary muscles for knee extension (58). The hamstrings, situated on the posterior aspect of the thigh, extend from the ischial tuberosity to the lower leg and function as the principal muscles for knee flexion. Additionally, the sartorius, gluteus maximus, gracilis, and gastrocnemius also assist in knee flexion and extension (81). Previous studies have shown that the hamstring-to-quadriceps (H/Q) strength ratio is a significant risk factor for hamstring strains in football (58) and is also strongly correlated with non-contact ACL injuries, particularly among female players (82).
The ankle dorsiflexor group (primarily tibialis anterior) is located on the front of the lower leg and is responsible for dorsiflexion of the ankle, while the plantar flexor group, mainly situated on the back of the lower leg, facilitates plantar flexion (83). The tibialis anterior and posterior muscles facilitate ankle inversion, whereas the peroneus longus and brevis muscles are responsible for eversion movements (83). Similarly, in ankle injury studies, Fousekis K et al. (2012) identified that eccentric isokinetic strength asymmetry between dorsiflexion and plantar flexion is an independent risk factor for non-contact ankle sprains in football players (84).
Regarding injury prevention, Prior studies prove that muscle imbalance-related injuries can be mitigated through compensatory strategies or training modifications (85), and that Dynamic Stretching can enhance joint stability and reduce the occurrence of joint injuries during play (86).
Interestingly, aside from muscle imbalances, Witvrouw E et al. (2003) concluded that increased tightness raises the risk of subsequent injury in certain muscle groups (hamstrings, quadriceps), even though flexibility independently influences other muscle injuries (adductors, calves) (87). Table 3 delineates the muscle imbalances that precipitate joint injuries in elite soccer players, contextualized within general sports injuries, and recommends preventive training measures grounded in existing evidence. Effective prevention and control strategies must prioritize comprehensive training programs that encompass lower limb muscle group strength coordination, balance, and neuromuscular control to improve joint stability and motor control capabilities (85, 86, 88, 89).
In summary, numerous studies have investigated and validated preventive strategies for general sports injuries, including muscle fiber injuries, tendon injuries, joint and ligament injuries, and injuries caused by muscle imbalances. However, the levels of evidence and strengths of recommendation for these interventions vary considerably. To provide sports medicine clinicians, coaches, and athletic trainers with a clearer understanding of the scientific basis and practical value of different preventive measures, this study summarizes and classifies the levels of evidence and grades of recommendation for these strategies according to the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine (OCEBM) system (Table 4).
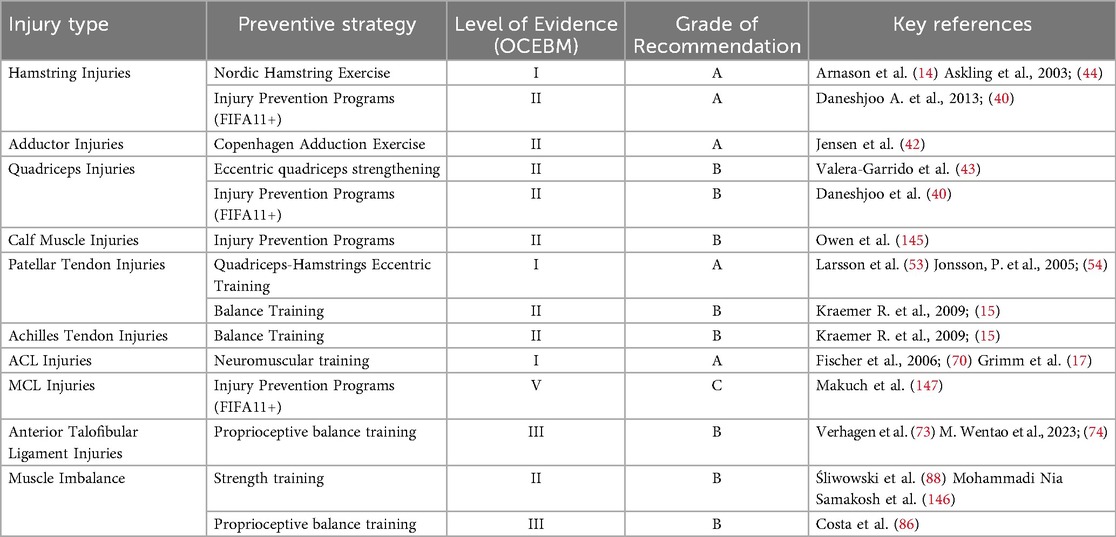
Table 4. Levels of evidence and grades of recommendation for prevention strategies of general sports injuries in elite football.
4 Treatment and rehabilitation of degenerative injuries in football
Elite athletes often begin specializing in a sport at an early age, pursuing intensive training in a single sport for more than eight months per year (90). However, early specialization exposes many athletes to an increased risk of overuse injuries (91). These chronic degenerative changes resulting from prolonged high-load training are characteristic of overuse injuries, which differ fundamentally in pathophysiology from acute injuries and are often difficult to prevent through conventional training interventions (92). Research on football injuries has revealed that, alongside those that can be prevented by training, a range of joint-related degenerative injuries exists, including meniscus lesions, osteochondral lesions of the talus (OLT), tendinopathy, and bursitis (8).
It should be noted that the same anatomical structure may sustain either degenerative or traumatic injuries. For example, meniscal injuries in elite athletes can be either degenerative, resulting from cumulative loading, or traumatic, caused by acute contact (9). The ESSKA consensus emphasizes the importance of distinguishing these two mechanisms due to their different etiologies and treatment strategies (93). While degenerative lesions are generally managed conservatively, acute traumatic tears—though classified as contact injuries—often require surgical intervention and structured rehabilitation, and are therefore frequently considered alongside degenerative injuries in clinical practice (94).
In addition to meniscal injuries, Figure 2 further illustrates the common degenerative injuries observed in football players, which are primarily concentrated in the lower limb joints and encompass different categories of injury. Degenerative injuries often require prolonged drug treatment or surgical intervention, and even after treatment, rehabilitation training is still necessary to return to the field. Severe degenerative injuries can even affect lifelong health and career longevity. This study will summarize and analyze the treatment methods and phased rehabilitation procedures for prevalent degenerative injuries in football, offering theoretical references for athletes' health management.
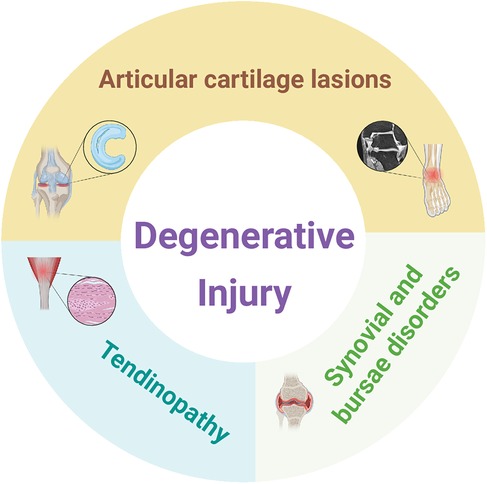
Figure 2. Classification diagram of degenerative injury in football. The magnetic resonance tomography of the ankle joint icon in the panel is adapted from Biehl et al. (149). Created using BioRender (ID: BX28L8JGDC).
4.1 Meniscus injuries and OLT in football
Meniscal injuries are the most common pathological knee injuries (95). Between 1996 and 2006, approximately 850,000 meniscal operations were performed each year in the United States, accounting for 10% to 20% of all orthopaedic procedures, with an incidence rate of 61 cases per 100,000 individuals (95). Chomiak J. et al. (2000) examined severe injuries in elite football players in the Czech Republic and determined that meniscal injuries constituted 8% of serious injuries, rendering it one of the most common degenerative injuries (18).
The mechanism of meniscal injury typically involves varus or valgus forces acting directly on a flexed knee when the foot is in contact with the ground, often accompanied by internal rotation of the femur (19, 96). Specifically, a valgus force applied to a flexed knee can result in medial meniscus tears (96). Treatment strategies should be customized to the severity and location of the meniscal tears.
For degenerative meniscal tears, most guidelines recommend at least 3–6 months of non-operative management (anti-inflammatory and analgesic medications, quadriceps strengthening, and unloader bracing) (97, 98). Acute traumatic meniscal tears often require operative treatment (meniscectomy, meniscal repair, meniscal reconstruction, meniscal scaffolds) depending on the injury characteristics (98). For athletes to re-establish their pre-injury performance levels and resume playing, it is essential to undergo high-quality rehabilitation following surgery.
According to current recommendations, post-operative rehabilitation after meniscal surgery is divided into three key phases. During the protective rehabilitation phase (0–2 weeks), the focus is on quadriceps activation, crutch weaning, and achieving a range of motion between 0° and 30°. In the functional rehabilitation phase (3–6 weeks), the objective is to enhance lower extremity strength, improve balance and proprioception, and range of motion up to 90°. The exercise rehabilitation phase (7–12 weeks), emphasizes the gradual increase in training burden to regain athletic ability. Additionally, football-specific training should be integrated to standardize movements that are specific to the sport (97, 99–102). Figure 3 depicts a comprehensive rehabilitation training regimen for meniscus tears post-surgery, with distinct rehabilitation techniques chosen based on the specific objectives of each phase.
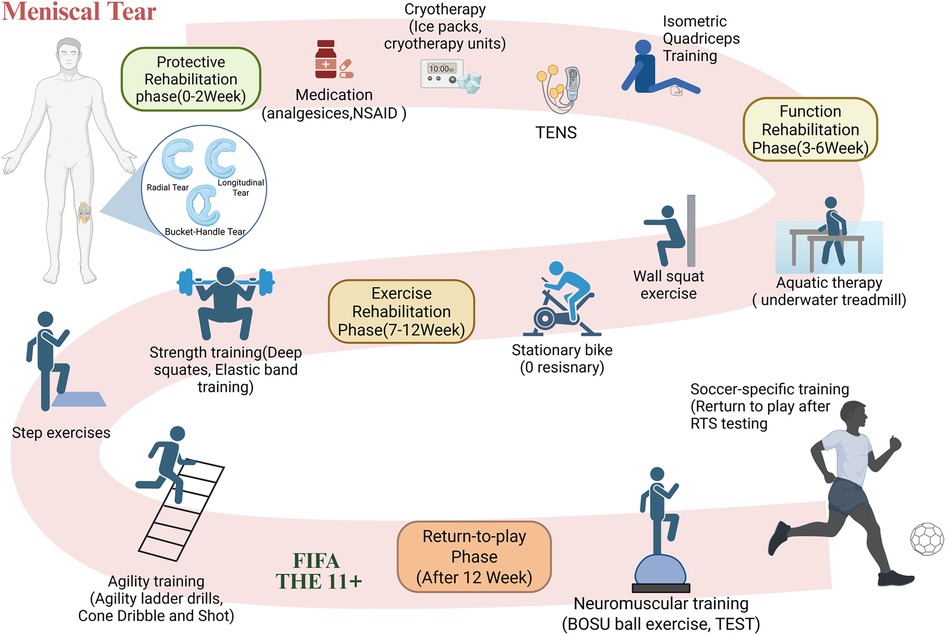
Figure 3. Flowchart of the phased rehabilitation protocol after meniscal tear surgery. This figure outlines the phase-based rehabilitation protocol following meniscal tear surgery, including protective, functional, exercise, and return-to-play phases, incorporating. TENS, aquatic therapy, strength and agility training, and football-specific interventions. NSAID: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications. TENS: Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation. Isometric Quadriceps training: performed with a towel placed under the knee; the thigh is contracted and pressed downward. TEST: Task-explicit sensorimotor training. RTS testing: return-to-sport testing. FIFA 11+: FIFA 11 + warm-up training program. Created using BioRender (ID: HH28D5WDPS).
In addition to meniscus injuries, common cartilage lesions in football players also include OLT (62). Although the anatomical locations differ, both meniscal tears and OLT share similar etiologies, involving either chronic mechanical overload or acute trauma (103). OLT accounts for 50% to 70% of all acute ankle sprains and fractures and may present mechanical symptoms such as ankle clicking or joint locking (104). For asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic OLT cases, nonoperative treatment is typically recommended, including rest, ice application, temporary offloading, and bracing for joint malalignment (104). For traumatic osteochondral lesions (e.g., OLT) patients, operative treatment is required (marrow stimulation, osteochondral autograft, and osteochondral allograft) (103).
Post-operative OLT rehabilitation is also staged, similar to meniscal injury rehabilitation. However, the protective phase is extended to six weeks due to the ankle's increased load-bearing demands. Additionally, proprioceptive training is heavier. In the protective rehabilitation phase (0–6 weeks), the objective is to enhance lower extremity strength, emphasize balance training, and restore full range of motion. During the functional rehabilitation phase (7–12 weeks), underwater treadmill training can be employed to restore range of motion and enhance lower limb strength. In the exercise rehabilitation phase (months 3–6), training should be gradually intensified, focusing on proprioceptive training and regaining athleticism. Football-specific exercises should be developed gradually, and football-specific movements must be standardized. Finally, during the return-to-play phase (after 6 months), gradually increase the intensity of football-specific training and complete the return-to-sport testing to return to play (105–107). Figure 4 illustrates an example of a rehabilitation training plan following OLT injury surgery, with specific rehabilitation methods selected for different rehabilitation goals.
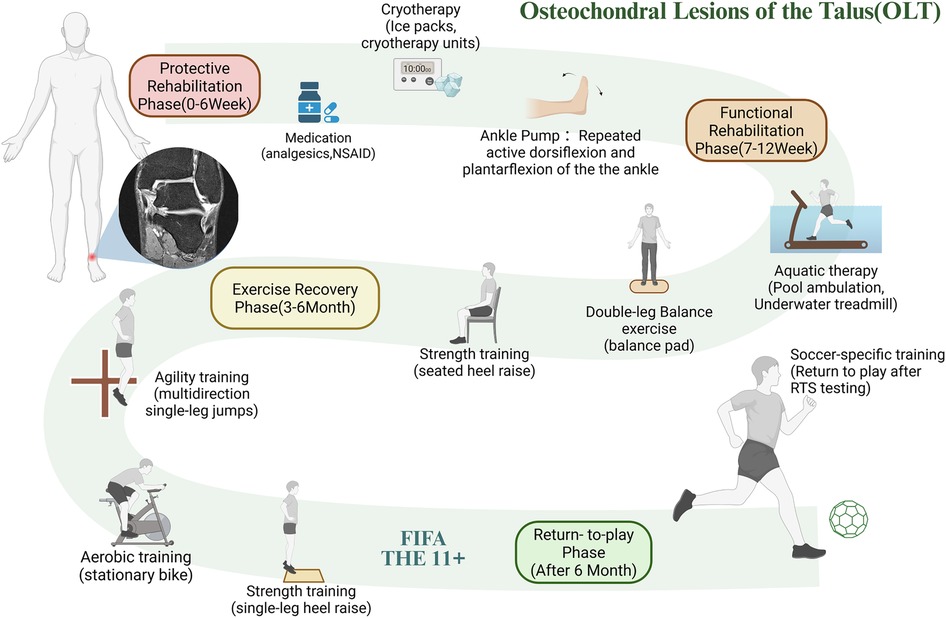
Figure 4. Flowchart of the phased rehabilitation protocol after OLT surgery. This figure presents the staged rehabilitation for talar OLT, including protective, functional, exercise recovery, and return-to-play phases, involving ankle pump, balance, aquatic training, and sport-specific assessment. RTS testing return-to-sport testing. The magnetic resonance tomography of the ankle joint icon in the panel is adapted from Biehl et al. (149). Created using BioRender (ID: NS28D5W7JL).
It is important to emphasize that the intensity of rehabilitation training should be progressively increased in accordance with the individual's recovery conditions. Conversely, it may result in an elevated risk of re-injury, reduced recuperation effects, and an extended recovery period (9).
4.2 Tendinopathy in football
Tendons are subjected to significant mechanical tension and loads during sports exercise (108). The prevalence of tendinopathy has consistently increased as elite athletes continue to raise the intensity, frequency, and duration of their training to achieve higher performance (108). In football, the lower limb tendons endure prolonged periods of elevated load due to sudden stops, changes in direction, and kicking movements (23). Consequently, Achilles tendinopathy and patellar tendinopathy are common issues among professional players. Aiyegbusi A I et al. (2021) discovered that the prevalence of Achilles tendinopathy in Nigerian football players was as high as 15.9% (109). According to Hägglund M. et al. (2011), patellar tendinopathy accounted for 1.5% of all injuries among elite European football players between 2001 and 2009, with a notably high recurrence rate (110).
Tendinopathy is a clinical syndrome that usually, but not always, implies an overuse tendon injury and is characterized by pain, diffuse or localized swelling, and impaired function (110). The pathomechanism that is most widely accepted posits that protracted mechanical stress during athletic activity results in the degradation of extracellular matrix and the disruption of collagen fibers (111). When the rate of degeneration exceeds that of repair, it results in pathological tendon thickening or hardening (111, 112). Tendinopathies are frequently accompanied by inflammatory pathologies in the adjacent connective tissues (tendonitis, peritendinitis, and tenosynovitis) (113).
The initial course of action for tendinopathy is conservative treatment, with operative options being evaluated if nonoperative measures are unsuccessful (113). Treatment methods include:
(1) Eccentric training. In terms of therapeutic efficacy, Stanish W D et al. (1986), 200 patients performed daily eccentric loading exercises, with 44% reporting complete pain relief and 43% reporting significant improvement (114). Mechanistically, eccentric training enhances the abundance of cytoskeletal proteins within tendon cells, thereby improving biomechanical properties during healing (115). It also appears to reduce glycolytic metabolism in fibrotic tendons, potentially linked to improved peripheral vascularization (116).
(2) Nonoperative Treatment: oral non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs), extracorporeal shockwave treatment/low-intensity pulsed ultrasound, and corticosteroid injections, etc (112–114, 117).
(3) Operative Treatment: endoscopic procedures, and minimally invasive tendon stripping/tenotomies, etc (117).
4.3 Synovial and bursae disorders in football
Bursitis is a common cause of musculoskeletal pain, with prevalent types including prepatellar, olecranon, trochanteric, and retrocalcaneal (118). Such injuries often occur in high-intensity sports. It has been estimated that synovial/bursae injuries (Synovitis/capsulitis) accounted for 4% of all injuries at the 2022 FIFA World Cup in Qatar (24). These injuries were more common in players who had been training in shooting for an extended period, which is linked to iliopsoas bursa friction (119). The onset of bursitis is directly related to repeated friction from adjacent muscles or tendons; when mechanical loading exceeds the tissue's tolerance threshold, it triggers an inflammatory response (118). The risk of bursitis more than triples in athletic populations who engage in persistent high-load activities (120).
Treatment should follow a “conservative-first, stepwise-escalation” approach. Nonoperative treatment, including cryotherapy, activity modification, and NSAIDs, is usually the first line of intervention (118). Surgical options, such as bursectomy, may be considered if symptoms persist, as in cases of refractory trochanteric bursitis (118). Individualized rehabilitation programs should be incorporated as part of post-treatment care to reduce the likelihood of recurrence.
5 Contextualization and prevention and control of accidental injuries in football
Due to the high physical demands and intense body contact inherent in football matches (121), most players often engage in risky and aggressive behaviors (heading duels and tackling) despite being aware of the potential dangers (122). These accidental injuries are typically classified as contact injuries, caused directly by physical collisions or external forces. Nevertheless, the professional football culture of “playing through injury” may hinder players' ability to accurately assess the risks associated with injuries (123), thereby increasing the probability of accidental injuries, including fractures and head and neck trauma. Data from the 2022 FIFA World Cup revealed that the incidence of accidental injuries (bone fractures, skin lacerations, and head/neck injuries) was 0.7 per 1000 h, which corresponds to approximately 12% of all injury cases (24). Moreover, studies have found that, compared to amateur football players, most contact injuries occur among professional football players (50%–70%) (124). Within this category, aside from head and neck injuries and fractures, soft tissue contact injuries (such as contusions, strains, and sprains) are recognized as a major category of concern (124, 125). Although the incidence of accidental injuries is relatively low, they often result in prolonged absences from training or competition (24). To reduce the incidence of accidental injuries, the following measures are recommended:
(1) Strengthen safety education for athletes to raise awareness of high-risk movements and enhance personal safety and injury prevention knowledge.
(2) Optimize match regulations (126), and ensure that referees penalize dangerous play strictly and promptly (127).
(3) Emphasize the importance of protective equipment (shin guards, goalkeeper gloves, and protective headgear).
(4) Evidence suggests that the prevention of soft tissue contact injuries should go beyond general measures for accidental injuries and include structured training programs focusing on dynamic stability and controlled body contact, which enhance neuromuscular control and joint stability in collision scenarios and thereby reduce the incidence of contact-related muscle and ligament injuries (128, 129).
This research analyses the causes of unintentional injuries, particularly those arising from contact mechanisms, to offer preventive recommendations for the safety of athletes.
5.1 Accidental head and neck injuries in football
In elite football, heading is a crucial skill predominantly used for tackling and shooting (130). Heading is the second most effective shooting technique, accounting for 18.4% of all goals (131). Previous research has demonstrated that players execute between 1 and 9 headers per match (132). Between 1998 and 2004, concussions, neck strains, and facial contusions were the most common types of head and neck injuries in FIFA tournaments, with an incidence rate of 12.5 per 1,000 h of play (133). Head and neck injuries predominantly result from contact mechanisms, most commonly head-to-head collisions (38%) and elbow-to-head impacts (16%) (134).
It is particularly noteworthy that in a study of head and neck injuries in Qatar's professional football league over eight seasons, concussions accounted for approximately 30% to 45% of all head and neck injuries (135). Sport-related concussion, caused by external forces to the head or body, is a transient brain dysfunction typically classified as a mild traumatic brain injury (136). The accumulation of multiple mild injuries may lead to long-term neurological disorders, including chronic traumatic encephalopathy, cognitive dysfunction, and depression (136). Consequently, they are a priority for prevention and control.
The following preventive measures are also implemented to reduce the potential danger to brain health from headers in football. (1) Neck training can be implemented to enhance head stability, thereby decreasing the likelihood of injury Gillies L. et al. (2022) demonstrated that a progressive neck strengthening program for athletes reduced head and neck injuries, including concussions (137). (2) The burden on the cranium may be alleviated through the development and utilization of protective gear, such as protective headgear.
5.2 Accidental fractures in football
Elite football players experienced a fracture incidence of 0.27 per 1000 h (95% CI 0.25 to 0.30) from 2001 to 2013 (138). The average professional football team may experience 1 to 2 fractures per season (138). The wrist was the most common site of fractures in the upper extremities, with a prevalence of 60%. Conversely, lower extremity fractures were more likely to necessitate hospitalization, despite accounting for only 32% of cases (139). In the occurrence of upper extremity fractures in football, goalkeepers have a 7-fold higher incidence compared to non-goalkeeper players, with an average extension of more than 1 week of out-of-play time (140). For common fractures like distal radius fractures, patients have a recovery rate of 79%; however, the average time to return to play is 9 weeks (141). The tibia and fibula are the primary bones involved in lower limb fractures in football, with 61% of affected players experiencing fractures to both bones. It's important to note that transverse or short oblique fractures account for 95% of tibial fractures, which are most frequently the result of direct impact during tackling/tackled (142). Although 80% of players with tibial fractures eventually accomplish full recovery, the rehabilitation period can last up to 38 weeks, and only 73% of them return to their pre-injury level of performance (141).
Fracture prevention strategies in football focus on two main approaches. (1) Emphasizing the importance of protective gear: shin guards are essential for preventing tibial shaft fractures, and goalkeeper gloves help protect against hand fractures (143). Experimental evidence by Tatar Y. et al. (2014) showed that shin guards can absorb up to 95% of impact force and reduce impact strain by up to 51% (143). (2) Prioritizing natural grass over artificial turf for matches. According to Calloway S. P. et al. 2004), players are at a higher risk of foot injuries on artificial turf compared to natural grass surfaces (144).
6 Limitations of the current research
Although this review provides a structured perspective on common injury types and intervention strategies in football, several limitations remain.
(1) Due to the large number of keywords and alternative terms involved in this study, and the fact that most references were retrieved through Google Scholar—which lacks a built-in electronic search engine—it was not feasible to provide a detailed literature screening process or a full PRISMA flow diagram.
(2) Due to substantial heterogeneity among the included studies in terms of study populations, intervention methods, and outcome measures, a meta-analysis could not be conducted. As a result, this review is limited to descriptive synthesis, making it difficult to provide clear quantitative conclusions.
(3) The scope of this review is relatively broad, covering multiple types of structural injuries; however, it does not provide detailed stratification by injury type, phase, or severity. As a result, some recommendations are inevitably generalized and should be interpreted with caution in practical applications.
(4) The proposed categorization of injuries into three types—general sports injuries, degenerative injuries, and accidental injuries—entails some degree of overlap. For instance, chronic tendinopathy may exhibit both pathological and training-related characteristics. Further interdisciplinary consensus is needed to refine and standardize these classifications.
(5) The lack of distinction between contact and non-contact mechanisms may limit the applicability of targeted prevention strategies, as exemplified by ACL injuries.
(6) This study did not stratify injuries by temporal stage (acute, sub-acute, or chronic) or by severity, although these factors play a critical role in shaping treatment strategies and guiding the course of rehabilitation.
(7) This study did not comprehensively differentiate the traumatic and degenerative etiologies and mechanisms of all structural injuries, but instead discussed representative cases such as meniscal lesions. This approach may reduce the precision and practical utility of the conclusions for injury prevention and clinical management.
(8) The evidence base for the prevention and treatment recommendations in this study is limited, with most evidence derived from small-sample observational studies or expert opinion, and lacking support from high-quality randomized controlled trials. Therefore, the robustness and generalizability of the conclusions remain somewhat limited.
7 Conclusions
The high incidence of sports injuries among elite football players underscores the urgent need to establish comprehensive prevention and treatment strategies. However, inconsistencies in the current injury classification frameworks have hindered effective clinical and performance-based decision-making. This review proposes a revised classification, dividing injuries into three main categories: general sports injuries, degenerative injuries, and accidental injuries. Each type involves distinct mechanisms and challenges, necessitating targeted intervention approaches.
General sports injuries—such as hamstring strains, ACL tears, and ankle sprains—can be effectively prevented through eccentric strengthening, neuromuscular control training, and balance exercises. Degenerative injuries, including meniscal lesions, OLT of the talus, and tendinopathies, often require pharmacological or surgical treatment, followed by individualized, phase-based rehabilitation programs. Although accidental injuries such as concussions and fractures are inherently unpredictable, their risk can be mitigated using protective equipment, safety education, and rule modifications.
By introducing this adjusted classification system, practitioners, coaches, and sports medicine professionals can better identify injury risks early, design individualized injury prevention programs, and implement targeted rehabilitation strategies aligned with football-specific biomechanical demands. Future research should focus on evidence-based, position-specific, and sex-specific injury prevention strategies to enhance player safety, prolong peak performance, and support sustainable career development in elite football.
Author contributions
YZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Writing – original draft. JWeig: Visualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. WL: Project administration, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation. JWeip: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Fédération Internationale de Football Association. Inside FIFA. (2025) Available online at: https://inside.fifa.com (Accessed May 16, 2025).
2. Fédération Internationale de Football Association. FIFA World Cup Qatar 2022 Global Engagement & Audience Detailed Report. (2024). Available online at: https://digitalhub.fifa.com/m/336c30db79dafa93/original/FIFA-World-Cup-Qatar-2022-Global-Engagement-Audience-Executive-Summary.pdf (Accessed November 29, 2024).
3. Swann C, Moran A, Piggott D. Defining elite athletes: issues in the study of expert performance in sport psychology. Psychol Sport Exerc. (2015) 16:3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.psychsport.2014.07.004
4. Williams DA, Day S, Stebbings G. What does “elite” mean in sport and why does it matter? Sport Exerc Scientist. (2017) 51(6):1.
5. Zentgraf K, Musculus L, Reichert L, Will L, Roffler A, Hacker S, et al. Advocating individual-based profiles of elite athletes to capture the multifactorial nature of elite sports performance. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:26351. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76977-8
6. Gurau TV, Gurau G, Voinescu DC, Anghel L, Onose G, Iordan DA, et al. Epidemiology of injuries in men’s professional and amateur football (part I). J Clin Med. (2023) 12:5569. doi: 10.3390/jcm12175569
7. Lemes IR, Pinto RZ, Lage VN, Roch BAB, Verhagen E, Bolling C, et al. Do exercise-based prevention programmes reduce non-contact musculoskeletal injuries in football (soccer)? A systematic review and meta-analysis with 13 355 athletes and more than 1 million exposure hours. Br J Sports Med. (2021) 55:1170–8. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2020-103683
8. Fuller CW, Ekstrand J, Junge A, Andersen TE, Bahr R, Dvorak J, et al. Consensus statement on injury definitions. Scandinavian Med Sci Sports. (2006) 16:83–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2006.00528.x
9. Kuhn AW, Brophy RH. Meniscus injuries in soccer. Sports Med Arthrosc Rev. (2024) 32:156. doi: 10.1097/JSA.0000000000000389
10. López-Valenciano A, Ruiz-Pérez I, Garcia-Gómez A, Vera-Garcia FJ, Croix MDS, Myer GD, et al. Epidemiology of injuries in professional football: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. (2020) 54:711–8. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2018-099577
11. Ekstrand J, Hägglund M, Waldén M. Epidemiology of muscle injuries in professional football (soccer). Am J Sports Med. (2011) 39:1226–32. doi: 10.1177/0363546510395879
12. Portillo J, Abián P, Calvo B, Paredes V, Abián-Vicén J. Effects of muscular injuries on the technical and physical performance of professional soccer players. Phys Sportsmed. (2020) 48:437–41. doi: 10.1080/00913847.2020.1744485
13. Jokela A, Valle X, Kosola J, Rodas G, Til L, Burova M, et al. Mechanisms of hamstring injury in professional soccer players: video analysis and magnetic resonance imaging findings. Clin J Sport Med. (2023) 33:217. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0000000000001109
14. Arnason A, Andersen TE, Holme I, Engebretsen L, Bahr R. Prevention of hamstring strains in elite soccer: an intervention study. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2008) 18:40–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2006.00634.x
15. Kraemer R, Knobloch K. A soccer-specific balance training program for hamstring muscle and patellar and achilles tendon injuries: an intervention study in premier league female soccer. Am J Sports Med. (2009) 37:1384–93. doi: 10.1177/0363546509333012
16. Shimokochi Y, Shultz SJ. Mechanisms of noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injury. J Athl Train. (2008) 43:396–408. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-43.4.396
17. Grimm NL, JacobsJr JC, Kim J, Denney BS, Shea KG. Anterior cruciate ligament and knee injury prevention programs for soccer players: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med. (2015) 43:2049–56. doi: 10.1177/0363546514556737
18. Chomiak J, Junge A, Peterson L, Dvorak J. Severe injuries in football players. Am J Sports Med. (2000) 28:58–68. doi: 10.1177/28.suppl_5.s-58
19. Brindle T, Nyland J, Johnson DL. The meniscus: review of basic principles with application to surgery and rehabilitation. J Athl Train. (2001) 36:160–9.16558666
20. Maughan RJ, Shirreffs SM. Muscle cramping during exercise: causes, solutions, and questions remaining. Sports Med. (2019) 49:115–24. doi: 10.1007/s40279-019-01162-1
21. Edouard P. Exercise associated muscle cramps: discussion on causes, prevention and treatment. Sci Sports. (2014) 29:299–305. doi: 10.1016/j.scispo.2014.06.004
22. Hägglund M, Waldén M, Magnusson H, Kristenson K, Bengtsson H, Ekstrand J. Injuries affect team performance negatively in professional football: an 11-year follow-up of the UEFA champions league injury study. Br J Sports Med. (2013) 47:738–42. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2013-092215
23. Drummond FA, Soares DdS, Silva Hd, Entrudo D, Younes SD, Neves VdS, et al. Incidence of injuries in soccer players – mappingfoot: a prospective cohort study. Rev Bras Med Esporte. (2021) 27:189–94. doi: 10.1590/1517-8692202127022020_0067
24. Serner A, Chamari K, Hassanmirzaei B, Moreira F, Bahr R, Massey A, et al. Time-loss injuries and illnesses at the FIFA world cup Qatar 2022. Sci Med Football. (2025) 9(3):275–82. doi: 10.1080/24733938.2024.2357568
25. Arliani GG, Belangero PS, Runco JL, Cohen M. The Brazilian football association (CBF) model for epidemiological studies on professional soccer player injuries. Clinics. (2011) 66:1707–12. doi: 10.1590/S1807-59322011001000007
26. Brentano MA, Martins Kruel LF. A review on strength exercise-induced muscle damage: applications, adaptation mechanisms and limitations. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. (2011) 51(1):1–10.21297557
27. Woo SL-Y, Abramowitch SD, Kilger R, Liang R. Biomechanics of knee ligaments: injury, healing, and repair. J Biomech. (2006) 39:1–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.10.025
28. Kuijt M-TK, Inklaar H, Gouttebarge V, Frings-Dresen MHW. Knee and ankle osteoarthritis in former elite soccer players: a systematic review of the recent literature. J Sci Med Sport. (2012) 15:480–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2012.02.008
29. Frontera WR, Ochala J. Skeletal muscle: a brief review of structure and function. Calcif Tissue Int. (2015) 96:183–95. doi: 10.1007/s00223-014-9915-y
30. Flück M, Hoppeler H. Molecular basis of skeletal muscle plasticity-from gene to form and function. In: Amara SG, Bamberg E, Blaustein MP, Grunicke H, Jahn R, Lederer WJ, Miyajima A, Murer H, Offermanns S, Pfanner N, editors. Reviews of Physiology Biochemistry and Pharmacology. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer (2003). p. 159–216. doi: 10.1007/s10254-002-0004-7
31. Mukund K, Subramaniam S. Skeletal muscle: a review of molecular structure and function, in health and disease. WIRES Syst Biol Med. (2020) 12:e1462. doi: 10.1002/wsbm.1462
32. Corazza A, Orlandi D, Baldari A, Gatto P, Stellatelli M, Mazzola C, et al. Thigh muscles injuries in professional soccer players: a one year longitudinal study. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. (2014) 3:331–6. doi: 10.32098/mltj.04.2013.15
33. Tidball JG. Mechanisms of muscle injury, repair, and regeneration. Compr Physiol. (2011) 1:2029–62. doi: 10.1002/j.2040-4603.2011.tb00387.x
34. Goode AP, Reiman MP, Harris L, DeLisa L, Kauffman A, Beltramo D, et al. Eccentric training for prevention of hamstring injuries may depend on intervention compliance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. (2015) 49:349–56. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2014-093466
35. Magistrali M, Stefanini L, Abate M, Biancalana G, Stegagno A, Cugia P, et al. Epidemiology of non-contact muscle injuries in the Italian male elite under-19 football (soccer) championship. Sports Med - Open. (2024) 10:75. doi: 10.1186/s40798-024-00738-0
36. Gronwald T, Klein C, Hoenig T, Pietzonka M, Bloch H, Edouard P, et al. Hamstring injury patterns in professional male football (soccer): a systematic video analysis of 52 cases. Br J Sports Med. (2022) 56:165–71. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2021-104769
37. Geiss Santos RC, Van Hellemnondt F, Yamashiro E, Holtzhausen L, Serner A, Farooq A, et al. Association between injury mechanisms and magnetic resonance imaging findings in rectus femoris injuries in 105 professional football players. Clin J Sport Med. (2022) 32:e430. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0000000000000935
38. Serner A, Mosler AB, Tol JL, Bahr R, Weir A. Mechanisms of acute adductor longus injuries in male football players: a systematic visual video analysis. Br J Sports Med. (2019) 53:158–64. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2018-099246
39. Green B, Lin M, Schache AG, McClelland JA, Semciw AI, Rotstein A, et al. Calf muscle strain injuries in elite Australian football players: a descriptive epidemiological evaluation. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2020) 30:174–84. doi: 10.1111/sms.13552
40. Daneshjoo A, Rahnama N, Mokhtar AH, Yusof A. Effectiveness of injury prevention programs on developing quadriceps and hamstrings strength of young male professional soccer players. J Hum Kinet. (2013) 39:115–25. doi: 10.2478/hukin-2013-0074
41. Hrysomallis C. Hip adductors’ strength, flexibility, and injury risk. J Strength Cond Res. (2009) 23:1514. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181a3c6c4
42. Jensen J, Hölmich P, Bandholm T, Zebis MK, Andersen LL, Thorborg K. Eccentric strengthening effect of hip-adductor training with elastic bands in soccer players: a randomised controlled trial. Br J Sports Med. (2014) 48:332–8. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091095
43. Valera-Garrido F, Jiménez-Rubio S, Minaya-Muñoz F, Estévez-Rodríguez JL, Navandar A. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous needle electrolysis and rehab and reconditioning program for rectus femoris muscle injuries: a cohort study with professional soccer players and a 20-week follow-up. Appl Sci. (2020) 10:7912. doi: 10.3390/app10217912
44. Askling C, Karlsson J, Thorstensson A. Hamstring injury occurrence in elite soccer players after preseason strength training with eccentric overload. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2003) 13:244–50. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0838.2003.00312.x
45. Ishøi L, Sørensen CN, Kaae NM, Jørgensen LB, Hölmich P, Serner A. Large eccentric strength increase using the Copenhagen adduction exercise in football: a randomized controlled trial. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2016) 26:1334–42. doi: 10.1111/sms.12585
46. O’Brien M. Anatomy of tendons. In: Maffulli N, Renström P, Leadbetter WB, editors. Tendon Injuries: Basic Science and Clinical Medicine. London: Springer (2005). p. 3–13. doi: 10.1007/1-84628-050-8_1
47. Hägglund M, Zwerver J, Ekstrand J. Epidemiology of patellar tendinopathy in elite male soccer players. Am J Sports Med. (2011) 39:1906–11. doi: 10.1177/0363546511408877
48. Villa FD, Buckthorpe M, Tosarelli F, Zago M, Zaffagnini S, Grassi A. Video analysis of achilles tendon rupture in male professional football (soccer) players: injury mechanisms, patterns and biomechanics. BMJ Open Sport Exercise Med. (2022) 8:e001419. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2022-001419
49. Neviaser A, Andarawis-Puri N, Flatow E. Basic mechanisms of tendon fatigue damage. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. (2012) 21:158–63. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2011.11.014
50. Wang JH-C. Mechanobiology of tendon. J Biomech. (2006) 39:1563–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiomech.2005.05.011
51. Murtagh CF, Stubbs M, Vanrenterghem J, Boyle O, Morgans A, Drust R, et al. Patellar tendon properties distinguish elite from non-elite soccer players and are related to peak horizontal but not vertical power. Eur J Appl Physiol. (2018) 118:1737–49. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-3905-0
52. Hoenig T, Gronwald T, Hollander K, Klein C, Frosch K-H, Ueblacker P, et al. Video analysis of achilles tendon ruptures in professional male football (soccer) reveals underlying injury patterns and provides strategies for injury prevention. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. (2023) 31:1795. doi: 10.1007/s00167-023-07384-1
53. Larsson MEH, Käll I, Nilsson-Helander K. Treatment of patellar tendinopathy—a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. (2012) 20:1795. doi: 10.1007/s00167-011-1825-1
54. Jonsson P, Alfredson H. Superior results with eccentric compared to concentric quadriceps training in patients with jumper’s knee: a prospective randomised study. Br J Sports Med. (2005) 39:847–50. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2005.018630
55. Langberg H, Ellingsgaard H, Madsen T, Jansson J, Magnusson SP, Aagaard P, et al. Eccentric rehabilitation exercise increases peritendinous type I collagen synthesis in humans with achilles tendinosis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2007) 17:61–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2006.00522.x
56. Hinchcliff KW, Kaneps AJ, Geor RJ. Equine exercise physiology: the science of exercise in the athletic horse. Elsevier Health Sciences. (2008) 2:132–42. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-7020-2857-1.X5001-X
57. Wooley PH, Grimm MJ, Radin EL. The structure and function of joints. In: A Textbook of Rheumatology. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2005). p. 149–73.
58. Abulhasan JF, Grey MJ. Anatomy and physiology of knee stability. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. (2017) 2:34. doi: 10.3390/jfmk2040034
59. Makuch R, Kucharski A, Pilarski K, Chrościcka A, Gała K, Czajka A, et al. Knee joint injuries in football players: types of injuries, etiology, diagnostics and prevention. Quality Sport. (2024) 15:51945–51945. doi: 10.12775/QS.2024.15.51945
60. Huson A. Joints and movements of the foot: terminology and concepts. Acta Morphol Neerl Scand. (1987) 25:117–30.3453583
61. Hewett TE, Ford KR, Hoogenboom BJ, Myer GD. Understanding and preventing acl injuries: current biomechanical and epidemiologic considerations - update 2010. N Am J Sports Phys Ther. (2010) 5:234.21655382
62. Walls RJ, Ross KA, Fraser EJ, Hodgkins CW, Smyth NA, Egan CJ, et al. Football injuries of the ankle: a review of injury mechanisms, diagnosis and management. World J Orthop. (2016) 7:8–19. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i1.8
63. Aiello F, Avery L, Gardner T, Rutherford H, McCall A, Impellizzeri FM, et al. Broadening our understanding of injury mechanisms to include at-risk situations: an overview of potential injuries at the FIFA men’s world cup Qatar 2022TM. Sci Med Football. (2024) 0:1–10. doi: 10.1080/24733938.2024.2372304
64. Benjamin M, Ralphs JR. Tendons and ligaments - an overview. Histol Histopathol. (1997) 12:1135–44. doi: 10.14670/HH-12.1135
65. Nawas H, Fleming H, Purcell S. ACL Injuries in soccer players: prevention and return to play considerations. Mo Med. (2023) 120:446–50.38144932
66. Andersen TE, Floerenes TW, Arnason A, Bahr R. Video analysis of the mechanisms for ankle injuries in football. Am J Sports Med. (2004) 32:69–79. doi: 10.1177/0363546503262023
67. Hertel J. Functional anatomy, pathomechanics, and pathophysiology of lateral ankle instability. J Athl Train. (2002) 37:364–75.12937557
68. Della Villa F, Buckthorpe M, Grassi A, Nabiuzzi A, Tosarelli F, Zaffagnini S, et al. Systematic video analysis of ACL injuries in professional male football (soccer): injury mechanisms, situational patterns and biomechanics study on 134 consecutive cases. Br J Sports Med. (2020) 54:1423–32. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2019-101247
69. Buckthorpe M, Pisoni D, Tosarelli F, Danelon F, Grassi A, Della Villa F. Three main mechanisms characterize medial collateral ligament injuries in professional male soccer—blow to the knee, contact to the leg or foot, and sliding: video analysis of 37 consecutive injuries. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2021) 51:611–8. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2021.10529
70. Fischer DV. Neuromuscular training to prevent anterior cruciate ligament injury in the female athlete. Strength Cond J. (2006) 28:44. doi: 10.1519/00126548-200610000-00008
71. Celebrini RG, Eng JJ, Miller WC, Ekegren CL, Johnston JD, Depew TA, et al. Effect of a novel movement strategy in decreasing ACL risk factors in female adolescent soccer players: a randomized controlled trial. Clin J Sport Med. (2014) 24:134. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0000000000000014
72. Lundblad M, Hägglund M, Thomeé C, Hamrin Senorski E, Ekstrand J, Karlsson J, et al. Medial collateral ligament injuries of the knee in male professional football players: a prospective three-season study of 130 cases from the UEFA elite club injury study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. (2019) 27:3692–8. doi: 10.1007/s00167-019-05491-6
73. Verhagen E, van der Beek A, Twisk J, Bouter L, Bahr R, van Mechelen W. The effect of a proprioceptive balance board training program for the prevention of ankle sprains: a prospective controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. (2004) 32:1385–93. doi: 10.1177/0363546503262177
74. Wentao M. Problems and strategies for the prevention of ankle injuries in soccer. Rev Bras Med Esporte. (2023) 29:e2023_0011. doi: 10.1590/1517-8692202329012023_0011
75. Myklebust G, Engebretsen L, Brækken IH, Skjølberg A, Olsen O-E, Bahr R. Prevention of anterior cruciate ligament injuries in female team handball players: a prospective intervention study over three seasons. Clin J Sport Med. (2003) 13:71. doi: 10.1097/00042752-200303000-00002
76. Waldén M, Atroshi I, Magnusson H, Wagner P, Hägglund M. Prevention of acute knee injuries in adolescent female football players: cluster randomised controlled trial. Br Med J. (2012) 344:e3042. doi: 10.1136/bmj.e3042
77. Jain N, Murray D, Kemp S, Calder J. Frequency and trends in foot and ankle injuries within an English premier league football club using a new impact factor of injury to identify a focus for injury prevention. Foot Ankle Surg. (2014) 20:237–40. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2014.05.004
78. Croisier JL. Muscular imbalance and acute lower extremity muscle injuries in sport. Int SportMed J. (2004) 5:169–76.
79. Devan MR, Pescatello LS, Faghri P, Anderson J. A prospective study of overuse knee injuries among female athletes with muscle imbalances and structural abnormalities. J Athl Train. (2004) 39:263–7.15496997
80. Pasta G, Nanni G, Molini L, Bianchi S. Sonography of the quadriceps muscle: examination technique, normal anatomy, and traumatic lesions. J Ultrasound. (2010) 13:76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jus.2010.07.004
81. Buitrago ER, Quintero ID, Ballesteros LE. Popliteus muscle. An anatomical study. Int Arch Med. (2018) 11:1–6.
82. Myer GD, Ford KR, Barber Foss KD, Liu C, Nick TG, Hewett TE. The relationship of hamstrings and quadriceps strength to anterior cruciate ligament injury in female athletes. Clin J Sport Med. (2009) 19:3. doi: 10.1097/JSM.0b013e318190bddb
83. Brockett CL, Chapman GJ. Biomechanics of the ankle. Orthop Trauma. (2016) 30:232–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mporth.2016.04.015
84. Fousekis K, Tsepis E, Vagenas G. Intrinsic risk factors of noncontact ankle sprains in soccer: a prospective study on 100 professional players. Am J Sports Med. (2012) 40:1842–50. doi: 10.1177/0363546512449602
85. Croisier J-L, Ganteaume S, Binet J, Genty M, Ferret J-M. Strength imbalances and prevention of hamstring injury in professional soccer players: a prospective study. Am J Sports Med. (2008) 36:1469–75. doi: 10.1177/0363546508316764
86. Costa PB, Herda TJ, Herda AA, Cramer JT. Effects of dynamic stretching on strength, muscle imbalance, and muscle activation. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (2013) 46:586–93. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000138
87. Witvrouw E, Danneels L, Asselman P, D’Have T, Cambier D. Muscle flexibility as a risk factor for developing muscle injuries in male professional soccer players: a prospective study. Am J Sports Med. (2003) 31:41–6. doi: 10.1177/03635465030310011801
88. Śliwowski R, Jadczak Ł, Hejna R, Wieczorek A. The effects of individualized resistance strength programs on knee muscular imbalances in junior elite soccer players. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0144021. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144021
89. Veeck F, Ruas CV, Pinto MD, Grazioli R, Cardoso GP, Albuquerque T, et al. Low pre-season hamstring-to-quadriceps strength ratio identified in players who further sustained in-season hamstring strain injuries: a retrospective study from a Brazilian serie a team. Sports. (2023) 11:89. doi: 10.3390/sports11040089
90. McLellan M, Allahabadi S, Pandya NK. Youth sports specialization and its effect on professional, elite, and Olympic athlete performance, career longevity, and injury rates: a systematic review. Orthop J Sports Med. (2022) 10:23259671221129594. doi: 10.1177/23259671221129594
91. Jayanthi NA, Post EG, Laury TC, Fabricant PD. Health consequences of youth sport specialization. J Athl Train. (2019) 54:1040–9. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-380-18
92. Cosca DD, Navazio F. Common problems in endurance athletes. Am Fam Physician. (2007) 76:237–44.17695568
93. Kopf S, Beaufils P, Hirschmann MT, Rotigliano N, Ollivier M, Pereira H, et al. Management of traumatic meniscus tears: the 2019 ESSKA meniscus consensus. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. (2020) 28:1177–94. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-05847-3
94. D’Amico E, Boettcher B, Johnson S, Johnson A, Kruse RC. Current concepts in management of medial meniscus injury in the athlete. Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep. (2025) 13:28. doi: 10.1007/s40141-025-00501-w
95. Kim S, Bosque J, Meehan JP, Jamali A, Marder R. Increase in outpatient knee arthroscopy in the United States: a comparison of national surveys of ambulatory surgery, 1996 and 2006. Jbjs. (2011) 93:994. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.I.01618
96. Sari MAIP. Physiotherapy management in Meniscus injury. Kinesiol Physiother Comprehen. (2022) 1:19–21. doi: 10.62004/kpc.v1i1.4
97. Yim J-H, Seon J-K, Song E-K, Choi J-I, Kim M-C, Lee K-B, et al. A comparative study of meniscectomy and nonoperative treatment for degenerative horizontal tears of the medial meniscus. Am J Sports Med. (2013) 41:1565–70. doi: 10.1177/0363546513488518
98. Doral MN, Bilge O, Huri G, Turhan E, Verdonk R. Modern treatment of meniscal tears. Efort Open Rev. (2018) 3:260–8. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.3.170067
99. Lind M, Nielsen T, Faunø P, Lund B, Christiansen SE. Free rehabilitation is safe after isolated meniscus repair: a prospective randomized trial comparing free with restricted rehabilitation regimens. Am J Sports Med. (2013) 41:2753–8. doi: 10.1177/0363546513505079
100. Hanna T, Smith NP, Sebastianelli WJ. Treatment, return to play, and performance following meniscus surgery. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. (2022) 15:157–69. doi: 10.1007/s12178-022-09754-7
101. Gastaldo M, Gokeler A, Della Villa F. High quality rehabilitation to optimize return to sport following lateral meniscus surgery in football players. Ann Jt. (2022) 7:36. doi: 10.21037/aoj-21-32
102. Cavanaugh JT, Killian SE. Rehabilitation following meniscal repair. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. (2012) 5:46–58. doi: 10.1007/s12178-011-9110-y
103. McGahan PJ, Pinney SJ. Current concept review: osteochondral lesions of the talus. Foot Ankle Int. (2010) 31:90–101. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2010.0090
104. O’Loughlin PF, Heyworth BE, Kennedy JG. Current concepts in the diagnosis and treatment of osteochondral lesions of the ankle. Am J Sports Med. (2010) 38:392–404. doi: 10.1177/0363546509336336
105. D’Hooghe P, Murawski CD, Boakye LAT, Osei-Hwedieh DO, Drakos MC, Hertel J, et al. Rehabilitation and return to sports: proceedings of the international consensus meeting on cartilage repair of the ankle. Foot Ankle Int. (2018) 39:61S–7S. doi: 10.1177/1071100718781862
106. Schwartz AM, Niu S, Mirza FA, Thomas AR, Labib SA. Surgical treatment of talus OCL: mid- to long-term clinical outcome with detailed analyses of return to sport. J Foot Ankle Surg. (2021) 60:1188–92. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2021.05.002
107. Patel S, Marrone W. The evolution of rehabilitation and return to sport following cartilage surgery. Int J Sports Phys Ther. (2023) 18:551–7. doi: 10.26603/001c.77508
108. Wong J. Types and epidemiology of tendinopathy. Clin Sports Med. (2003) 22:675–92. doi: 10.1016/S0278-5919(03)00004-8
109. Aiyegbusi AI, Owoeye IO, Balogun OJ, Fapojuwo OO, Akinloye OA. Prevalence of achilles tendinopathy and associated selected intrinsic risk factors among Nigerian footballers. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. (2021) 11:118–27. doi: 10.32098/mltj.01.2021.13
110. Khan KM, Maffulli N. Tendinopathy: an achilles’ heel for athletes and clinicians. Clin J Sport Med. (1998) 8:151. doi: 10.1097/00042752-199807000-00001
111. Dean BJF, Dakin SG, Millar NL, Carr AJ. Review: emerging concepts in the pathogenesis of tendinopathy. Surgeon. (2017) 15:349–54. doi: 10.1016/j.surge.2017.05.005
112. Cardoso TB, Pizzari T, Kinsella R, Hope D, Cook JL. Current trends in tendinopathy management. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. (2019) 33:122–40. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2019.02.001
113. Ackermann PW, Renström P. Tendinopathy in Sport. Sports Health. (2012) 4:193–201. doi: 10.1177/1941738112440957
114. Stanish WD, Rubinovich RM, Curwin S. Eccentric exercise in chronic tendinitis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (1986) 208:122–40. doi: 10.1097/00003086-198607000-00014
115. Kaux J-F, Drion P, Libertiaux V, Colige A, Hoffmann A, Nusgens B, et al. Eccentric training improves tendon biomechanical properties: a rat model. J Orthop Res. (2013) 31:119–24. doi: 10.1002/jor.22202
116. Kaux J-F, Libertiaux V, Leprince P, Fillet M, Denoel V, Wyss C, et al. Eccentric training for tendon healing after acute lesion: a rat model. Am J Sports Med. (2017) 45:1440–6. doi: 10.1177/0363546517689872
117. Irby A, Gutierrez J, Chamberlin C, Thomas SJ, Rosen AB. Clinical management of tendinopathy: a systematic review of systematic reviews evaluating the effectiveness of tendinopathy treatments. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2020) 30:1810–26. doi: 10.1111/sms.13734
118. Aaron DL, Patel A, Kayiaros S, Calfee R. Four common types of bursitis: diagnosis and management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. (2011) 19:359. doi: 10.5435/00124635-201106000-00006
119. Le Gall F, Carling C, Reilly T. Injuries in young elite female soccer players: an 8-season prospective study. Am J Sports Med. (2008) 36:276–84. doi: 10.1177/0363546507307866
120. Alvarez-Nemegyei J. Risk factors for pes anserinus tendinitis/bursitis. J Clin Rheumatol. (2007) 13:63–5. doi: 10.1097/01.rhu.0000262082.84624.37
121. Barnes C, Archer DT, Hogg B, Bush M, Bradley PS. The evolution of physical and technical performance parameters in the English premier league. Int J Sports Med. (2014) 35:1095–100. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1375695
122. Zech A, Wellmann K. Perceptions of football players regarding injury risk factors and prevention strategies. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0176829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176829
123. Roderick M, Waddington I, Parker G. PLAYING HURT: managing injuries in English professional football. Int Rev Sociol Sport. (2000) 35:165–80. doi: 10.1177/101269000035002003
124. Gurau TV, Gurau G, Musat CL, Voinescu DC, Anghel L, Onose G, et al. Epidemiology of injuries in professional and amateur football men (part II). J Clin Med. (2023) 12:6293. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196293
125. Lathlean TJH, Gastin PB, Newstead SV, Finch CF. The incidence, prevalence, severity, mechanism and body region of injury in elite junior Australian football players: a prospective cohort study over one season. J Sci Med Sport. (2018) 21:1013–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2018.03.002
126. Beaudouin F, Aus der Fünten K, Tröß T, Reinsberger C, Meyer T. Head injuries in professional male football (soccer) over 13 years: 29% lower incidence rates after a rule change (red card). Br J Sports Med. (2019) 53:948–52. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2016-097217
127. Fuller CW, Junge A, Dvorak J. An assessment of football referees’ decisions in incidents leading to player injuries. Am J Sports Med. (2004) 32:17–22. doi: 10.1177/0363546503261249
128. Fritz Tchomche H, Bingquan L, Shoukat S. Impact of core stability training on football-specific performance and injury prevention: a review: impact of core stability training on footballers. Ther J Ther Rehabil Sci. (2024) 5:11–7. doi: 10.54393/tt.v5i04.243
129. Huxel Bliven KC, BE A. Core stability training for injury prevention. Sports Health. (2013) 5:514–22. doi: 10.1177/1941738113481200
130. Sarajärvi J, Volossovitch A, Almeida CH. Analysis of headers in high-performance football: evidence from the English premier league. Int J Perform Anal Sport. (2020) 20:189–205. doi: 10.1080/24748668.2020.1736409
131. Ali MFM, Katis A, Patsika G, Kellis E. Goal scoring characteristics in soccer: are they technique and time dependent? Asia Pac J Adv Bus Soc Stud. (2015) 1:186–94.
132. McCunn R, Beaudouin F, Stewart K, Meyer T, MacLean J. Heading in football: incidence, biomechanical characteristics and the association with acute cognitive function—a three-part systematic review. Sports Med. (2021) 51:2147–63. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01492-z
133. Fuller CW, Junge A, Dvorak J. A six year prospective study of the incidence and causes of head and neck injuries in international football. Br J Sports Med. (2005) 39:i3–9. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2005.018937
134. Beaudouin F, der Fünten KA, Tröß T, Reinsberger C, Meyer T. Time trends of head injuries over multiple seasons in professional male football (soccer). Sports Med Int Open. (2019) 3:E6–E11. doi: 10.1055/a-0808-2551
135. Chebbi S, Bjerregaard A, Tabben M, Chamari K, Holtzhausen L. Injury surveillance of head and neck injuries with a special focus on sport-related concussions: eight seasons observational study in professional football in Qatar. J Sci Med Sport. (2024) 27:844–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2024.08.202
136. McCrory P, Meeuwisse W, Dvorak J, Aubry M, Bailes J, Broglio S, et al. Consensus statement on concussion in sport—the 5th international conference on concussion in sport held in Berlin, October 2016. Br J Sports Med. (2017) 51:838–47. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-097699
137. Gillies L, McKay M, Kertanegara S, Huertas N, Nutt S, Peek K. The implementation of a neck strengthening exercise program in elite rugby union: a team case study over one season. Phys Ther Sport. (2022) 55:248–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2022.05.003
138. Larsson D, Ekstrand J, Karlsson MK. Fracture epidemiology in male elite football players from 2001 to 2013: “how long will this fracture keep me out?”. Br J Sports Med. (2016) 50:759–63. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2015-095838
139. Kuczinski A, Newman JM, Piuzzi NS, Sodhi N, Doran JP, Khlopas A, et al. Trends and epidemiologic factors contributing to soccer-related fractures that presented to emergency departments in the United States. Sports Health. (2019) 11:27–31. doi: 10.1177/1941738118798629
140. Andersson JK, Bengtsson H, Waldén M, Karlsson J, Ekstrand J. Hand, wrist, and forearm injuries in male professional soccer players: a prospective cohort study of 558 team-seasons from 2001 to 2002 to 2018–2019. Orthop J Sports Med. (2021) 9:2325967120977091. doi: 10.1177/2325967120977091
141. Robertson GAJ, Wood AM, Bakker-Dyos J, Aitken SA, Keenan ACM, Court-Brown CM. The epidemiology, morbidity, and outcome of soccer-related fractures in a standard population. Am J Sports Med. (2012) 40:1851–7. doi: 10.1177/0363546512448318
142. Cattermole HR, Hardy JR, Gregg PJ. The footballer’s fracture. Br J Sports Med. (1996) 30:171–5. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.30.2.171
143. Tatar Y, Ramazanoglu N, Camliguney AF, Saygi EK, Cotuk HB. The effectiveness of shin guards used by football players. J Sports Sci Med. (2014) 13:120–7.24570615
144. Calloway SP, Hardin DM, Crawford MD, Hardin JM, Lemak LJ, Giza E, et al. Injury surveillance in major league soccer: a 4-year comparison of injury on natural grass versus artificial turf field. Am J Sports Med. (2019) 47:2279–86. doi: 10.1177/0363546519860522
145. Owen AL, Wong DP, Dellal A, Paul DJ, Orhant E, Collie S. Effect of an injury prevention program on muscle injuries in elite professional soccer. J Strength Cond Res. (2013) 27:3275. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e318290cb3a
146. Mohammadi Nia Samakosh H, Brito JP, Shojaedin SS, Hadadnezhad M, Oliveira R. What does provide better effects on balance, strength, and lower extremity muscle function in professional male soccer players with chronic ankle instability? Hopping or a balance plus strength intervention? A randomized control study. Health Care (Don Mills). (2022) 10:1822. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10101822
147. Makuch R, Kucharski A, Pilarski K, Chrościcka A, Gała K, Czajka A, et al. Knee joint injuries in football players: types of injuries, etiology, diagnostics and prevention. Qual Sport. (2024) 15:51945. doi: 10.12775/QS.2024.15.51945
148. Corcoran D, McNamara T, Feehan J, Tripodi N. Adductor magnus: extending the knowledge – a short review of structure and function. Int J Osteopath Med. (2023) 49:100671. doi: 10.1016/j.ijosm.2023.100671
Keywords: hamstring injury, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury, tendon injury, joint sprain, muscle imbalance, degenerative injuries, concussion, fracture
Citation: Zeng Y, Ji W, Shi Y, Liu W and Ji W (2025) Sports injuries in elite football players: classification, prevention, and treatment strategies update. Front. Sports Act. Living 7:1643789. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1643789
Received: 9 June 2025; Accepted: 26 August 2025;
Published: 8 September 2025.
Edited by:
Jia Han, Shanghai University of Medicine and Health Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Fernando Jorge Santos, Instituto Politecnico de Setubal (IPS), PortugalRatakorn Aimkosa, Mae Fah Luang University, Thailand
Copyright: © 2025 Zeng, Ji, Shi, Liu and Ji. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenduo Liu, bHdkMTIwNEBqYm51LmFjLmty; Weiping Ji, MjAyNDAwMTZAempvdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yinping Zeng
Yinping Zeng Weiguo Ji3,†
Weiguo Ji3,† Wenduo Liu
Wenduo Liu