- 1Physiotherapy Department and Motion Analysis Lab, Hôpital de la Tour, Meyrin, Switzerland
- 2University Savoie Mont-Blanc, Interuniversity Laboratory of Human Movement Sciences, Universite Jean Monnet Saint-Etienne, Saint-Étienne, France
- 3Kin’Aixpert, Viviers du Lac, France
- 4Simplexity Performance Solutions, La Motte Servolex, France
- 5School of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, Physiotherapy, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, QLD, Australia
Background: Ankle dorsiflexion range of motion plays a pivotal biomechanical role within the lower limb with implications both in rehabilitation, injury risk reduction and athletic performance. However, clinicians often lack practical guidance on diagnosing and differentiating the various joints or structures that have been shown to have a role in ankle dorsiflexion range of motion restriction.
Clinical question: To move beyond the “one size fits all approach” paradigm in musculoskeletal rehabilitation, we propose addressing the 2 following questions: (1) How can clinician utilize the weight-bearing lunge test findings to develop a clinical-decision making system for ankle dorsiflexion range of motion assessment? and (2) How can this system guide individualized interventions to restore ankle dorsiflexion range of motion specific to each athlete's needs?.
Solutions: We outline a 3-step framework for improving ankle dorsiflexion range of motion restriction: (1) having a quantitative and qualitative assessment using the weight-bearing lunge test to identify joint or structure involvement, (2) having confirmatory diagnostic testing to pinpoint mobility restrictions of the joint or structures involved, and (3) proposing targeted interventions based on individual findings, ensuring a personalized rehabilitation approach rather than a generalized global protocol.
Clinical application: This rehabilitation practice commentary addresses a notable gap in the existing literature on clinical choices regarding ankle dorsiflexion restriction treatment. By integrating this individual clinical decision-making system, clinicians can enhance rehabilitation and performance optimization beyond standard treatment methods.
Highlights
Findings
Ankle dorsiflexion range of motion plays a pivotal biomechanical role within the lower limb with implications for both rehabilitation and athletic performance. However, clinicians often lack practical guidance on diagnosing and differentiating the various joints or structures that can limit dorsiflexion range of motion.
Implications
Ankle dorsiflexion restriction can be effectively managed by using an individualized clinical decision-making approach consisting of a 3-step framework with the weight-bearing lunge test as its foundation. It involves quantitative and qualitative assessment to identify joint or structure involvement, confirmatory diagnostic testing to pinpoint mobility restrictions, and targeted interventions based on individual findings, ensuring a personalized rehabilitation approach.
Caution
There are no interventional data demonstrating that this clinical decision-making system with multiple treatment possibilities results in superior ankle dorsiflexion ROM gains than a generalized global protocol.
1 Introduction
Ankle dorsiflexion range of motion (ROM) is fundamental for numerous activities of daily living, such as walking, descending stairs (1, 2), and sporting movements (e.g., sprinting, cutting, and squatting) (3–5). During the stance phase of ambulatory tasks, the foot-ankle complex operates around 3 primary axes of rotations, known as the “heel rocker”, “ankle rocker” and “forefoot rocker” (2, 6). The “ankle rocker” describes the transition from foot flat to maximum tibial dorsiflexion until the heel begins to lift (6), representing a critical shift from force absorption to propulsion. The axis of rotation occurs at the talocrural joint, playing a pivotal biomechanical role (2).
Previous biomechanical studies have demonstrated that restricted ankle dorsiflexion ROM after foot-ankle traumatic injuries is related to a disruption in normal talar arthrokinematics, leading to sensorimotor and functional impairments (7, 8). Such impairments can compromise foot-ankle landing mechanics by preventing the foot from reaching its closed-pack position during full loading (9). Additionally, ankle dorsiflexion ROM deficit limits the ability to fully flex the knee during weight-bearing, increasing knee-valgus displacement and peak ground reaction forces (GRF) during landing, squatting and step down (3, 10–13). This suggests that restricted dorsiflexion may affect force absorption capacity, potentially increasing ankle and knee musculoskeletal loading due to sagittal and/or frontal-plane compensations. Consequently, ankle dorsiflexion deficit is a risk factor for various lower-limb injuries including lateral ankle sprain and chronic ankle instability (14–16), Achilles tendinopathy (17, 18), metatarsal bone stress fracture (19), plantar heel pain (20), and patellar tendinopathy (21, 22).
Beyond rehabilitation, ankle dorsiflexion ROM could also impact athletic performance as the tibia functions as an organic protractor guiding force applications against the ground (4). For example, athletes with greater dorsiflexion angles (i.e., triple flexion) demonstrate superior deceleration capacity during high-intensity cutting maneuvers, enabling them to dynamically lower their center of mass position when braking (23). Additionally, the “ankle rocker” ROM and stability can modulate braking GRF magnitude during deceleration (23, 24) while influencing the ratio of forces during acceleration (4, 25). Given its importance for both injury management and biomechanical efficiency for performance optimization, restoring ankle dorsiflexion ROM in athletes is essential.
Despite its clinical relevance and recognition as the gold-standard for dorsiflexion ROM assessment (16, 26), many clinicians do not utilize the weight-bearing lunge test (WBLT) in their practice (27, 28). The absence of quantitative measurement and qualitative information the WBLT can offer often results in a generalized “one fits all approach” treatment, incorporating generic and global interventions, such as stretching exercises, manual therapy and massage for every athlete (28, 29). A previous randomized controlled trial employing a pragmatic clinical methodology—rather than a one-size-fits-all research protocol—adapted manual therapy techniques to individual treatment responses and demonstrated a large effect size in improving dorsiflexion ROM (30). This supports the need for researchers and clinicians to adopt a systematic and individualized approach to address the specific anatomical structure(s) [e.g., non-contractile (31–34), contractile (35–37) or neural (38–40) tissues] that are restricting ankle dorsiflexion ROM in athletes (see Supplementary Figure S1).
2 Clinical questions
To move beyond the “one size fits all approach” paradigm in musculoskeletal rehabilitation, we propose addressing the following two questions: (1) How can clinician utilize the WBLT as a clinical-decision making system for ankle dorsiflexion ROM assessment? and (2) How can this system guide individualized interventions to restore ankle dorsiflexion ROM specific to each athlete's needs?
Ankle dorsiflexion restriction does not stem from a single cause but rather from multiple contributors that necessitate distinct therapeutic approaches (see Supplementary Figure S1). However, clinicians often lack practical guidance on diagnosing and differentiating these restrictions based on their patients' clinical presentations. Therefore, we aim to provide such guidance in our rehabilitation practice commentary based on existing research and our own experience evaluating and improving ankle dorsiflexion ROM in various musculoskeletal and sports injuries. Our clinical decision-making system presents a structured 3-step framework, utilizing the WBLT as the cornerstone of clinical reasoning. This framework includes: (1) quantitative and qualitative evaluation using the WBLT to identify potential joint and structure involvement in the dorsiflexion ROM restriction; (2) confirmatory diagnostic testing to pinpoint specific mobility restrictions within contractile, non-contractile and neural tissues; and (3) selection of targeted interventions based on individual assessment findings, for a tailored rehabilitation approach. This framework should be used in the acute or chronic phase of rehabilitation of any athlete that suffers from a dorsiflexion ROM deficit following a foot-ankle injury.
3 Clinical decision making-system
3.1 Step 1: conducting a quantitative and qualitative assessment of ankle dorsiflexion ROM
The initial assessment of ankle dorsiflexion ROM should include the WBLT (41). Although widely accepted in clinical practice, various versions and variations of the WBLT have emerged (26). We propose four standardized rules to enhance reliability and validity: (1) ensure weight-bearing on the tested leg during a tandem stance position (26); (2) standardize the position of the back foot with the heel raised off the floor to minimizes the influence of triceps surae or joint restrictions in the non-tested (back) leg (42); (3) avoid any lower limb movements compensations such as medial hip rotation and knee valgus that may influence ankle dorsiflexion ROM by aligning the patellar (when lunging forward) with an extension of this line up the wall (43); (4) palpate the posterior heel/flat pad during dorsiflexion to carefully monitoring heel lift off the ground and stop the test when the first movement is felt/observed. Following these principles ensures a reliable quantification of ankle dorsiflexion ROM, either through the toe-to-wall distance (44) or tibial inclination degrees (45). Using previous published MDC, clinically relevant impairments are defined as asymmetries exceeding 1.5 cm toe-to-wall distance or 4.7° tibial inclination angle (26, 44, 45). Our clinical experience suggests normative values for ankle dorsiflexion ROM of >9–10 cm and >40–42°.
Beyond the quantitative value (distance or angle measure), clinicians should assess patient-reported symptoms (qualitative aspects) during the WBLT, such as areas/zones of pain/discomfort or a blocking sensation, as these influence clinical decision-making (Figure 1). Based on literature and clinical experience, common pain or blocking sensation zones during the WBLT include:
• Anterior zone: talocrural joint [e.g., posterior talar glide (31, 32)] or transversal tarsal joint motion restriction (34).
• Anterolateral zone: inferior tibiofibular joint motion restriction (33).
• Medial retromalleolar zone: flexor hallucis longus (FHL) tendon tightness (37) or subtalar joint motion restriction (34).
• Lateral retromalleolar zone: potential fibularis tendon tightness (35) or inferior tibiofibular joint motion restriction (33).
• Posterior zone: triceps surae tendon tightness (36) or tibial nerve mechanosensitivity (38–40).
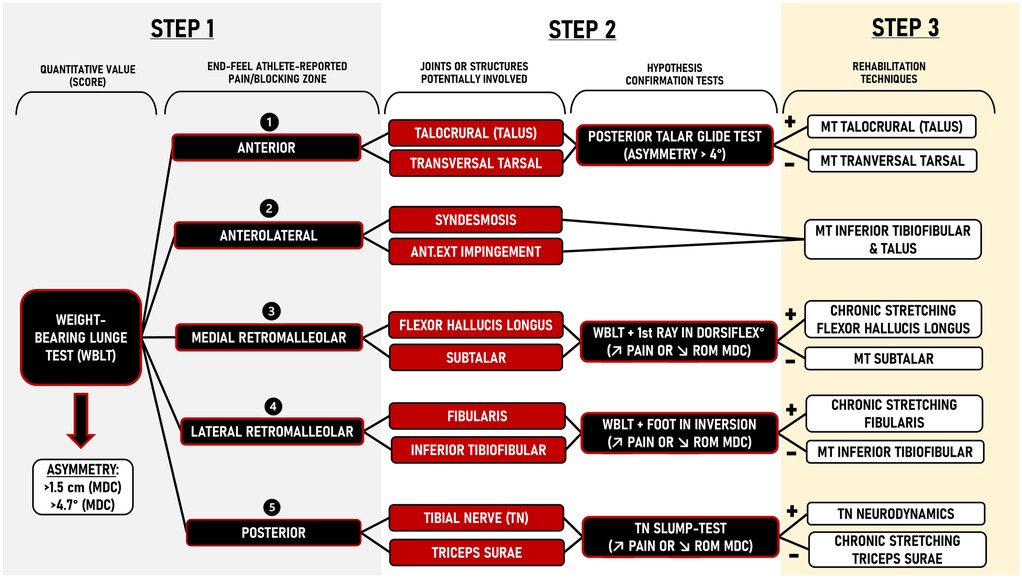
Figure 1. Ankle dorsiflexion range of motion clinical decision-making system using a 3-step framework. MDC, minimal detectable change; ANT.EXT, antero-external; ROM, range of motion; SLR, straight leg raise; MT, manual therapy; TN, tibial nerve; DORSIFLEX°, dorsiflexion.
It is important to mention that, while less common, bony osteophytes can also lead to anterior or anterolateral pain/blocking during the WBLT. This cause of pain and/or restriction can be identified by a hard end-feel during passive dorsiflexion ROM that can be confirmed on radiographs and may require surgical intervention (46).
3.2 Step 2: confirming the joints/structures involved in ankle dorsiflexion ROM restriction
The hypotheses regarding joint or structural involvement should be systematically tested using specific confirmation tests (Figure 1 & see Supplementary Figure S2). It is important to acknowledge that athletes may experience multiple zones of pain or blocking sensation (e.g., anterior and medial retromalleolar) or can change zones during the treatment, but the clinical reasoning process remains consistent.
3.2.1 Anterior pain/blocking
Anterior restriction is the most common limitation, suggesting involvement of the talocrural (31, 32), or transversal tarsal joints (34). Given that a posterior talar glide at the talocrural joint is an accessory motion essential for dorsiflexion, and a radiographic study demonstrated that 90% of dorsiflexion ROM occurs at the talocrural joint (34), its restriction warrants clinical investigation (31, 32). The posterior talar glide test (PTGT) is a highly reliable diagnostic tool (ICC = 0.94) for assessing posterior gliding of the talus (31, 32). This test is performed with the athlete seated on a table and an electronic inclinometer (e.g., smartphone) fixed on the tibia. The foot is in maximal dorsiflexion while the examiner stabilizes the talus and passively flexes the knee until a firm end-feel is encountered (31). The angle of passive knee flexion provides an indirect estimate of posterior talar glide (see Supplementary Figure S2). Asymmetries up to 4.7° indicate clinically relevant impairments and suggest the need for specific manual therapy treatment (see step 3) (Figure 1). A posterior talar glide restriction can also be confirmed by performing an antero-posterior talar mobilization assessment. If the PTGT or antero-posterior talar mobilization assessment is similar between sides, alternative restrictions to dorsiflexion ROM must be considered. Specifically, anterior blocking may also stem from limited motion in the transversal tarsal (navicular and cuboid) joints. A useful clinical tip involves applying a downward glide to the navicular and cuboid during the WBLT to determine whether this maneuver alleviates the anterior blocking sensation (see step 3).
3.2.2 Anterolateral pain/blocking
Anterolateral restriction suggests a potential syndesmosis or anterolateral impingement and requires integration of the patient's injury history, symptomatology, and imaging findings to distinguish between these two etiologies. In this case, it is relevant to focus on the restriction of amplitude of the inferior tibiofibular joint to improve ankle dorsiflexion ROM (Figure 1). A cadaver study has shown that a posterosuperior glide to the fibula at the inferior tibiofibular joint improves dorsiflexion ROM (33). A restriction at the inferior tibiofibular joint can assessed by performing a manual mobilization assessment (anterior or posterior glides) of this joint (see step 3). Applying a posterior glide to the fibula during an ankle dorsiflexion and evaluating its effect on ROM and/or symptoms (specifically looking for increased ROM or decreased symptoms) can also indicate if this treatment should be used (Table 1).
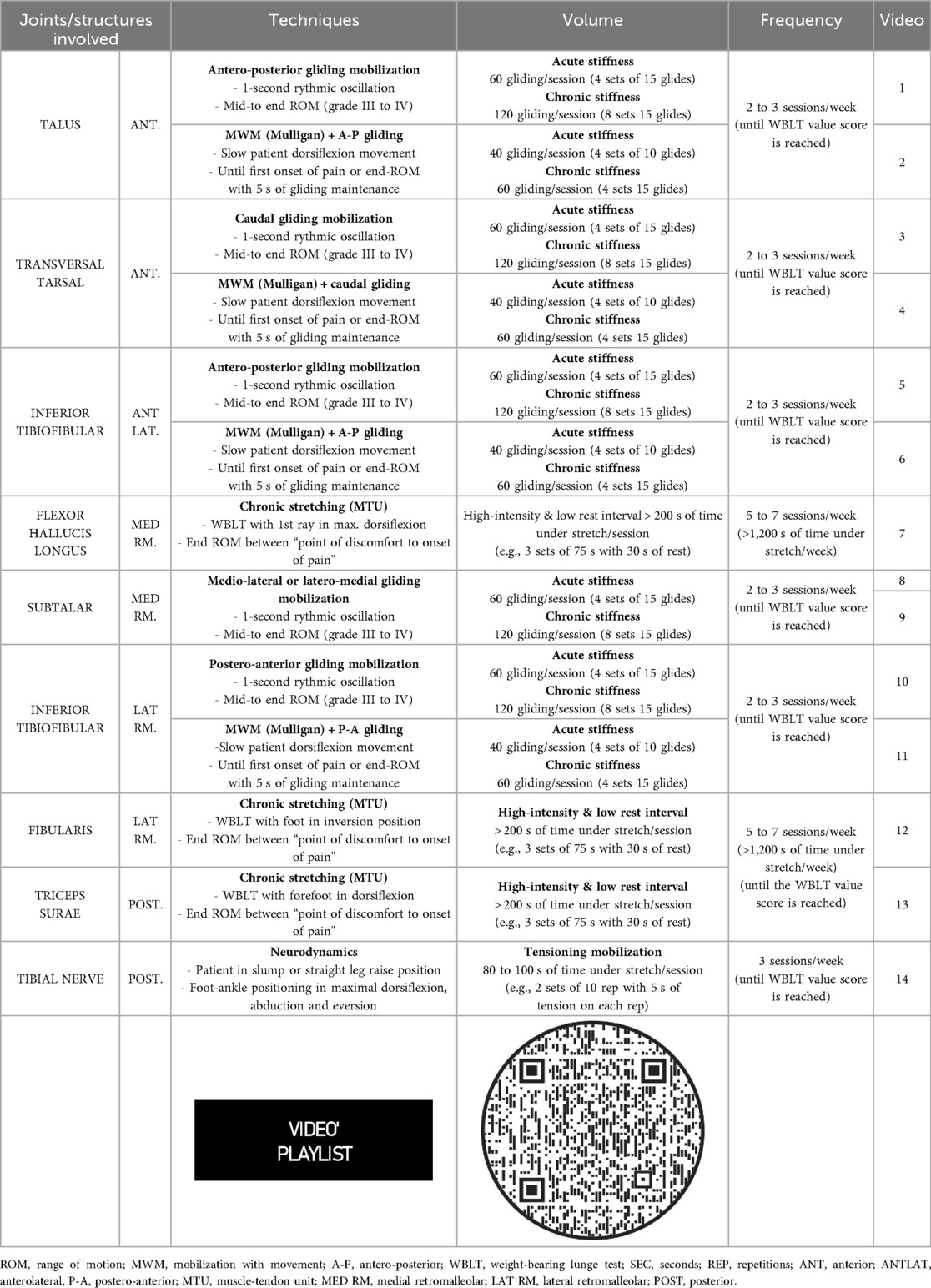
Table 1. Detailed rehabilitation techniques for improving ankle dorsiflexion range of motion restriction.
3.2.3 Medial retromalleolar pain/blocking
Medial retromalleolar restriction suggests potential involvement of the FHL tendon (37) or the subtalar joint (Figure 1) (34). The FHL originates along the posterior fibula, coursing distally to the muscle-tendon unit (MTU) junction above the fibro-osseous tunnel at the posterior medial ankle (47). Due to the low-lying position of the MTU junction, dorsiflexion of the ankle and the hallux causes distal migration of the tendon and may limit ROM (37). To confirm FHL tendon involvement, we recommend using a modified version of the WBLT by pre-positioning the hallux in maximal dorsiflexion (see Supplementary Figure S2). A ROM reduction (up to 1.5 cm or 4.7°) compared to the initial WBLT indicates FHL tendon tightness, requiring a specific chronic stretching protocol (see step 3) (Figure 1). If this test of FHL involvement is negative, and if medio-lateral or latero-medial subtalar mobilization glides are found to be restricted, improve dorsiflexion range and/or alleviate symptoms (Table 1), a specific focus should be placed on the subtalar joint as this joint also contributes to ankle sagittal plane motion (48).
3.2.4 Lateral retromalleolar pain/blocking
Lateral retromalleolar restriction suggests potential involvement of the fibularis tendon (35) or the inferior tibiofibular joint (see Supplementary Figure S2) (2, 33). The fibularis brevis and longus tendons are both contained within the retro-malleolar groove and may limit ankle dorsiflexion ROM (35, 47). To confirm fibularis tendon involvement, we recommend using a modified version of the WBLT by placing the foot-ankle complex in an inverted position on an inclined plate (∼25°) (see Supplementary Figure S2). A ROM reduction (up to 1.5 cm or 4.7°) compared to the initial WBLT indicates fibularis tendon tightness, requiring a specific chronic stretching protocol (see step 3) (Figure 1). If this confirmation test is negative, a specific focus should be placed on the inferior tibiofibular joint for its impact on ankle dorsiflexion ROM with the same clinical strategies as previously described under anterolateral pain/blocking above (33).
3.2.5 Posterior pain/blocking
Posterior restriction suggests potential triceps surae tightness (36) or tibial nerve mechanosensitivity (38–40). To confirm tibial nerve involvement, we recommend using a modified Straight Leg Raise (SLR) or modified slump-test in which ankle dorsiflexion, rearfoot eversion and forefoot abduction are performed (see Supplementary Figure S2) (49). Asymmetries up to 7.0° (>MDC) (50) or increased posterior leg pain suggest tibial nerve mechanosensitivity, requiring neurodynamic treatment (see step 3) (Figure 1). If the modified Straight Leg Raise or slump-test are negative, focus should be placed on triceps surae tightness, requiring a specific chronic stretching protocol (see step 3) (36).
3.3 Step 3: designing an individualized rehabilitation treatment
The final step of this clinical decision-making system involves selecting the appropriate interventions based on individual assessment findings from the confirmatory testing. This ensures that rehabilitation is tailored to the athlete needs (Figure 1 and Supplementary Figure S2).
3.3.1 Talocrural joint mobilizations (posterior glide)
Meta-analyses highlight the efficacy of manual therapy, particularly joint mobilization, in improving ankle dorsiflexion ROM and functional outcomes in individuals with chronic ankle instability (51–54). Among the various manual techniques, antero-posterior talar mobilization (Maitland) and mobilization with movement (MWM – Mulligan) are the most extensively studied and effective techniques (51, 55). Antero-posterior talar mobilizations are performed with the patient in a supine position while applying a posterior glide to the talus using the thumbs or webspace (Table 1). We recommend multiple sets of joint mobilizations using 1-second rhythmic oscillations to end range (Maitland grades III or IV) for approximately 60–120 s (Table 1), with reassessment of ankle dorsiflexion ROM at the end of each set. The frequency and volume of manual therapy play a crucial role in treatment outcomes. Higher doses (e.g., 48 min of manual therapy across 6 sessions vs. 9 min across 3 sessions over two weeks) have been shown to produce significantly greater ROM gains (1, 56–58).
MWM can be performed in non-weight-bearing or weight-bearing positions, with a weight-bearing MWM often considered a progression of an antero-posterior talar mobilizations or non-weight-bearing MWM. A non-weight-bearing MWM is performed in the same position and with the same technique as the antero-posterior talar mobilization. A weight-bearing MWM is performed with the patient standing on a treatment table or in tandem stance with the treatment (front) foot up on a step. A belt (looped around the patient's leg and the therapist), or one of the therapists' hands, is used to apply a postero-anterior force to the distal tibia, while the therapist simultaneously applies an antero-posterior force to talus. The patient performs slow dorsiflexion ROM until the first onset of pain or they reach the end of their ROM, holds this position for a few seconds and then slowly returns to the starting position. The glide is maintained throughout the entire movement (Table 1). Recommended volume per session varies from 40 gliding movements (4 sets of 10 glide) to 60 gliding movements (4 sets of 15 glide) (Table 1), with dorsiflexion ROM reassessed between each set (55). Antero-posterior talar mobilization and/or MWM should be performed 2–3 sessions per week until the desired WBLT score is achieved (providing reassessments identify improvements in dorsiflexion ROM). The manual therapy treatment can be supplemented with a home exercise program (e.g., mimicking the WBLT stopping at end-range or at onset of pain/blocking) to maintain the ROM gains achieved.
3.3.2 Transversal tarsal and subtalar joint mobilizations
Only one study has investigated the effectiveness of transversal tarsal mobilizations on ankle dorsiflexion ROM (59). Transversal tarsal joint mobilizations are performed with the patient in a supine position, stabilizing the rearfoot while applying a caudal/plantar-directed mobilization to the navicular and cuboid (Table 1). This technique can also be done as a weight-bearing MWM as a caudal glide applied to the transverse tarsal joint during dorsiflexion. Subtalar joint mobilizations are conducted in a side-lying position with the patient slightly rolled forward so their foot is slightly angled towards the floor. The talus is stabilized in the tibial mortise in maximal dorsiflexion (or stabilized by the therapist) and the calcaneus is mobilized laterally and medially using the thenar eminence (Table 1). We recommend applying similar manual intensity, volume, frequency, and dosage as used for talar mobilizations.
3.3.3 Inferior tibiofibular joint mobilizations
Research indicates that distal tibiofibular joint mobilizations over multiple sessions improve ankle dorsiflexion ROM (30), whereas a single session yields limited benefits (60, 61). Antero-posterior mobilization is performed in a supine position, stabilizing the distal tibia while applying a posterior glide to the distal fibula with the thenar eminence (Table 1) (60). This technique is recommended for patients with anterolateral pain or blocking sensation during the WBLT (Figure 1). If lateral retromalleolar pain occurs, a postero-anterior mobilization can be performed with the patient in a prone position. The therapist stabilizes the distal tibia and applies an anterior glide to the fibula (Table 1). These techniques can also be performed as MWM in weight-bearing or non-weight-bearing positions (Table 1) (30). We recommend applying a similar manual therapy prescription (intensity, volume, frequency, and dosage) as described previously.
Evidence suggests that a pragmatic, patient-responsive approach could yield superior outcomes compared to standardized uniform protocols. Adapting mobilization techniques to an individual's clinical presentation, as advocated in our model, has demonstrated clinically relevant benefits for ankle dorsiflexion ROM (30). Notably, improvements in dorsiflexion ROM after a single session (+1.7 cm vs. + 1.1–1.2 cm) and across three sessions of individualized manual therapy, were greater than that reported in studies that applied identical manual techniques (high velocity and low amplitude manipulation or MWM) to all participants (30, 62, 63).
3.3.4 Flexor hallucis, fibularis and triceps surae tendon chronic stretching
The effectiveness of stretching in modifying MTU properties and neural adaptations is influenced by three key factors: stretch intensity, total time under stretch, and duration (e.g., weeks) of stretching (64). Meta-analyses support static stretching as an effective strategy to increase ankle dorsiflexion ROM, particularly when restricted by triceps surae tightness (29, 65). We recommend a chronic stretching protocol (duration greater than 2 weeks) (66) for the triceps surae, FHL or fibularis muscle-tendons, adhering to the following principles: (1) stretch intensity should range from “point of discomfort” to “onset of pain”; (2) total time under stretch should reach at least 1,200 seconds per week, using high-intensity, low-rest intervals during stretching sessions (e.g., 3 sets of 75-second stretches with 30-second rest periods, six times per week); (3) the protocol should last a minimum of five weeks until the target WBLT score is achieved. The stretching position should be a weight-bearing lunge with the forefoot in dorsiflexion for the triceps surae, the hallux in maximal dorsiflexion for the FHL, and the foot in inversion for the fibularis (Table 1). If supra-maximal eccentric contractions have shown effects on improving flexibility of the posterior chain (67), it is also possible to consider this modality provided that you have the necessary equipment (heavy-load machines) to be able to target triceps surae, FHL or fibularis muscle-tendons.
3.3.5 Tibial nerve neurodynamics
Only one study has demonstrated that a static stretching protocol targeting the sciatic and tibial nerves—without stretching the triceps surae—effectively increases passive ankle dorsiflexion ROM (40). In cases where posterior pain or blocking is unrelated to triceps surae tightness, we recommend neurodynamic techniques focusing on tibial nerve mobilization, using tensioning exercises in a slump or straight leg raise position (68, 69). Given the variability in reported protocols (68, 70), we suggest a total time under stretch of the nerve of approximately 80–100 s per session by completing 2 sets of 10 repetitions (with 5 s of stretch in each repetition) three times per week (Table 1) (71).
4 Conclusion
This commentary addresses a notable gap regarding the lack of guidance in treating ankle dorsiflexion ROM restriction in athletes. Ankle dorsiflexion ROM is vital for rehabilitation and performance, with limited ROM leading to altered biomechanics and injury risk. The WBLT, the gold standard for assessing dorsiflexion ROM, is underutilized. We propose a new clinical decision-making framework involving three steps: quantitatively and qualitatively assessing dorsiflexion ROM, identifying the restriction source (joints, muscle-tendons, or neural tissue), and applying targeted interventions such as joint mobilizations, chronic stretching, and neurodynamic techniques. This individualized and analytical approach could then be followed by functional therapeutic exercises (e.g., single-leg squat, lateral step-down) that aimed to developed lower limb motor control and stability in ankle dorsiflexion position.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
RT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MM: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank all of our patients' and athletes' dorsiflexion restrictions that have allowed us to create this over the years of experience.
Conflict of interest
Author MM was employed by Simplexity Performance Solutions.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fspor.2025.1677383/full#supplementary-material
Supplementary Figure S1 | Anatomical joints and structures within the foot-ankle complex that have been shown to have a role in ankle dorsiflexion range of motion restriction (31–40).
Supplementary Figure S2 | Hypothesis confirmation tests of specific anatomical structures that have a role in ankle dorsiflexion range of motion restriction. Abbreviation: MDC, minimal detectable change; ROM, range of motion; WBLT, weight-bearing lunge test; TN, tibial nerve; SLR, straight leg raise; LAT, lateral; MED, medial.
References
1. Hoch MC, Andreatta RD, Mullineaux DR, English RA, Medina McKeon JM, Mattacola CG, et al. Two-week joint mobilization intervention improves self-reported function, range of motion, and dynamic balance in those with chronic ankle instability. J Orthop Res. (2012) 30:1798–804. doi: 10.1002/jor.22150
2. Medina McKeon JM, Hoch MC. The ankle-joint complex: a kinesiologic approach to lateral ankle sprains. J Athl Train. (2019) 54:589–602. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-472-17
3. Crowe MA, Bampouras TM, Walker-Small K, Howe LP. Restricted unilateral ankle dorsiflexion movement increases interlimb vertical force asymmetries in bilateral bodyweight squatting. J Strength Cond Res. (2020) 34:332–6. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003345
4. Alt T, Oeppert TJ, Zedler M, Goldmann J-P, Braunstein B, Willwacher S. A novel guideline for the analysis of linear acceleration mechanics—outlining a conceptual framework of “shin roll” motion. Sports Biomech. (2022) 24:1–18. doi: 10.1080/14763141.2022.2094827
5. Wu C-X, Liu H-B, Zhao Z-N, Wang Y-B, Luan Z-L. Effects of movement direction and limb dominance on ankle muscular force in sidestep cutting. Med Eng Phys. (2022) 110:103914. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2022.103914
6. Brockett CL, Chapman GJ. Biomechanics of the ankle. Orthop Trauma. (2016) 30:232–8. doi: 10.1016/j.mporth.2016.04.015
7. Hertel J. Functional anatomy, pathomechanics, and pathophysiology of lateral ankle instability. J Athl Train. (2002) 37:364–75. PMID: 1293755712937557
8. Hertel J, Corbett RO. An updated model of chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. (2019) 54:572–88. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-344-18
9. Hopkins JT, Son SJ, Kim H, Page G, Seeley MK. Characterization of multiple movement strategies in participants with chronic ankle instability. J Athl Train. (2019) 54:698–707. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-480-17
10. Sigward SM, Ota S, Powers CM. Predictors of frontal plane knee excursion during a drop land in young female soccer players. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2008) 38:661–7. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2008.2695
11. Fong C, Blackburn J, Norcross M, McGrath M, Padua D. Ankle-dorsiflexion range of motion and landing biomechanics. J Athl Train. (2011) 46(1):5–10. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-46.1.5
12. Cronström A, Creaby MW, Nae J, Ageberg E. Modifiable factors associated with knee abduction during weight-bearing activities: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. (2016) 46:1647–62. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0519-8
13. Emamvirdi M, Hosseinzadeh M, Letafatkar A, Thomas AC, Dos’Santos T, Smania N, et al. Comparing kinematic asymmetry and lateral step-down test scores in healthy, chronic ankle instability, and patellofemoral pain syndrome female basketball players: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:12412. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39625-1
14. Drewes LK, McKeon PO, Kerrigan DC, Hertel J. Dorsiflexion deficit during jogging with chronic ankle instability. J Sci Med Sport. (2009) 12:685–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2008.07.003
15. Youdas JW, McLean TJ, Krause DA, Hollman JH. Changes in active ankle dorsiflexion range of motion after acute inversion ankle sprain. J Sport Rehabil. (2009) 18:358–74. doi: 10.1123/jsr.18.3.358
16. Delahunt E, Bleakley CM, Bossard DS, Caulfield BM, Docherty CL, Doherty C, et al. Clinical assessment of acute lateral ankle sprain injuries (ROAST): 2019 consensus statement and recommendations of the international ankle consortium. Br J Sports Med. (2018) 52:1304–10. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2017-098885
17. Rabin A, Kozol Z, Finestone AS. Limited ankle dorsiflexion increases the risk for mid-portion achilles tendinopathy in infantry recruits: a prospective cohort study. J Foot Ankle Res. (2014) 7:48. doi: 10.1186/s13047-014-0048-3
18. Martin RL, Chimenti R, Cuddeford T, Houck J, Matheson JW, McDonough CM, et al. Achilles pain, stiffness, and muscle power deficits: midportion achilles tendinopathy revision 2018: clinical practice guidelines linked to the international classification of functioning, disability and health from the orthopaedic section of the American Physical Therapy Association. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2018) 48:A1–A38. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2018.0302
19. Troy KL, Davis IS, Tenforde AS. A narrative review of metatarsal bone stress injury in athletic populations: etiology, biomechanics, and management. PM R. (2021) 13:1281–90. doi: 10.1002/pmrj.12518
20. Koc TA, Bise CG, Neville C, Carreira D, Martin RL, McDonough CM. Heel pain—plantar fasciitis: revision 2023. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2023) 53:CPG1–CPG39. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2023.0303
21. Malliaras P, Cook JL, Kent P. Reduced ankle dorsiflexion range may increase the risk of patellar tendon injury among volleyball players. J Sci Med Sport. (2006) 9:304–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2006.03.015
22. Backman LJ, Danielson P. Low range of ankle dorsiflexion predisposes for patellar tendinopathy in junior elite basketball players: a 1-year prospective study. Am J Sports Med. (2011) 39:2626–33. doi: 10.1177/0363546511420552
23. Dos’Santos T, McBurnie A, Thomas C, Comfort P, Jones PA. Biomechanical determinants of the modified and traditional 505 change of direction speed test. J Strength Cond Res. (2020) 34:1285–96. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003439
24. Harper DJ, McBurnie AJ, Santos TD, Eriksrud O, Evans M, Cohen DD, et al. Biomechanical and neuromuscular performance requirements of horizontal deceleration: a review with implications for random intermittent multi-directional sports. Sports Med. (2022) 52:2321–54. doi: 10.1007/s40279-022-01693-0
25. King D, Burnie L, Nagahara R, Bezodis NE. Relationships between kinematic characteristics and ratio of forces during initial sprint acceleration. J Sports Sci. (2022) 40:2524–32. doi: 10.1080/02640414.2023.2172797
26. Powden CJ, Hoch JM, Hoch MC. Reliability and minimal detectable change of the weight-bearing lunge test: a systematic review. Man Ther. (2015) 20:524–32. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2015.01.004
27. McCann RS, Welch Bacon CE, Suttmiller AMB, Gribble PA, Cavallario JM. Assessments used by athletic trainers to decide return-to-activity readiness in patients with an ankle sprain. J Athl Train. (2024) 59:182–200. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-0037.22
28. Tourillon R, Delahunt E, Fourchet F, Picot B, M’Baye M. Ankle scientific knowledge is not translated into physiotherapy practice: a thematic analysis of French-speaking physiotherapists clinical behaviors. J Athl Train. (2025) 60(2):134–42. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-0575.23
29. Terada M, Pietrosimone BG, Gribble PA. Therapeutic interventions for increasing ankle dorsiflexion after ankle sprain: a systematic review. J Athl Train. (2013) 48:696–709. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-48.4.11
30. Nguyen AP, Pitance L, Mahaudens P, Detrembleur C, David Y, Hall T, et al. Effects of mulligan mobilization with movement in subacute lateral ankle sprains: a pragmatic randomized trial. J Man Manip Ther. (2021) 29:341–52. doi: 10.1080/10669817.2021.1889165
31. Denegar CR, Hertel J, Fonseca J. The effect of lateral ankle sprain on dorsiflexion range of motion, posterior talar glide, and joint laxity. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2002) 32:166–73. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2002.32.4.166
32. Vicenzino B, Branjerdporn M, Teys P, Jordan K. Initial changes in posterior talar glide and dorsiflexion of the ankle after mobilization with movement in individuals with recurrent ankle sprain. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2006) 36:464–71. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2006.2265
33. Fujii M, Suzuki D, Uchiyama E, Muraki T, Teramoto A, Aoki M, et al. Does distal tibiofibular joint mobilization decrease limitation of ankle dorsiflexion? Man Ther. (2010) 15:117–21. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2009.08.008
34. Smith MD, Lee D, Russell T, Matthews M, MacDonald D, Vicenzino B. How much does the talocrural joint contribute to ankle dorsiflexion range of motion during the weight-bearing lunge test? A cross-sectional radiographic validity study. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2019) 49:934–41. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2019.8697
35. Davda K, Malhotra K, O’Donnell P, Singh D, Cullen N. Peroneal tendon disorders. EFORT Open Rev. (2017) 2:281–92. doi: 10.1302/2058-5241.2.160047
36. Medeiros DM, Martini TF. Chronic effect of different types of stretching on ankle dorsiflexion range of motion: systematic review and meta-analysis. Foot (Edinb). (2018) 34:28–35. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2017.09.006
37. Michelson J, O’Keefe J, Bougioukas L. Increased flexor hallucis longus tension decreases ankle dorsiflexion. Foot Ankle Surg. (2021) 27:550–4. doi: 10.1016/j.fas.2020.07.007
38. Mitchell B, Bressel E, McNair PJ, Bressel ME. Effect of pelvic, hip, and knee position on ankle joint range of motion. Phys Ther Sport. (2008) 9:202–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2008.08.002
39. Andrade RJ, Lacourpaille L, Freitas SR, McNair PJ, Nordez A. Effects of hip and head position on ankle range of motion, ankle passive torque, and passive gastrocnemius tension. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2016) 26:41–7. doi: 10.1111/sms.12406
40. Andrade RJ, Freitas SR, Hug F, Le Sant G, Lacourpaille L, Gross R, et al. The potential role of sciatic nerve stiffness in the limitation of maximal ankle range of motion. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:14532. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32873-6
41. Bennell K, Talbot R, Wajswelner H, Techovanich W, Kelly D, Hall A. Intra-rater and inter-rater reliability of a weight-bearing lunge measure of ankle dorsiflexion. Austr J Physiother. (1998) 44:175–80. doi: 10.1016/S0004-9514(14)60377-9
42. Cady K, De Ste Croix M, Deighan M. Back foot influence on dorsiflexion using three different positions of the weight bearing lunge test. Phys Ther Sport. (2021) 47:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2020.10.005
43. Dill KE, Begalle RL, Frank BS, Zinder SM, Padua DA. Altered knee and ankle kinematics during squatting in those with limited weight-bearing–lunge ankle-dorsiflexion range of motion. J Athl Train. (2014) 49:723–32. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-49.3.29
44. Hoch MC, McKeon PO. Normative range of weight-bearing lunge test performance asymmetry in healthy adults. Man Ther. (2011) 16:516–9. doi: 10.1016/j.math.2011.02.012
45. Konor MM, Morton S, Eckerson JM, Grindstaff TL. Reliability of three measures of ankle dorsiflexion range of motion. Int J Sports Phys Ther. (2012) 7:279–87. PMID: 2266664222666642
46. Nery C, Baumfeld D. Anterior and posterior ankle impingement syndromes: arthroscopic and endoscopic anatomy and approaches to treatment. Foot Ankle Clin. (2021) 26:155–72. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2020.07.002
48. Behling A-V, Welte L, Rainbow MJ, Kelly L. Human in vivo talocrural contributions to ankle joint complex kinematics during walking, running, and hopping. Heliyon. (2025) 11:e41301. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e41301
49. Coppieters MW, Alshami AM, Babri AS, Souvlis T, Kippers V, Hodges PW. Strain and excursion of the sciatic, tibial, and plantar nerves during a modified straight leg raising test. J Orthop Res. (2006) 24:1883–9. doi: 10.1002/jor.20210
50. Boyd BS, Villa PS. Normal inter-limb differences during the straight leg raise neurodynamic test: a cross sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2012) 13:245. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-13-245
51. Weerasekara I, Osmotherly P, Snodgrass S, Marquez J, de Zoete R, Rivett DA. Clinical benefits of joint mobilization on ankle sprains: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. (2018) 99:1395–1412.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2017.07.019
52. Shi X, Han J, Witchalls J, Waddington G, Adams R. Does treatment duration of manual therapy influence functional outcomes for individuals with chronic ankle instability: a systematic review with meta-analysis? Musculoskelet Sci Pract. (2019) 40:87–95. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2019.01.015
53. Vallandingham RA, Gaven SL, Powden CJ. Changes in dorsiflexion and dynamic postural control after mobilizations in individuals with chronic ankle instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Athl Train. (2019) 54:403–17. doi: 10.4085/1062-6050-380-17
54. Kim H, Moon S. Effect of joint mobilization in individuals with chronic ankle instability: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Funct Morphol Kinesiol. (2022) 7:66. doi: 10.3390/jfmk7030066
55. Weerasekara I, Deam H, Bamborough N, Brown S, Donnelly J, Thorp N, et al. Effect of mobilisation with movement (MWM) on clinical outcomes in lateral ankle sprains: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Foot. (2020) 43:101657. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2019.101657
56. Green T, Refshauge K, Crosbie J, Adams R. A randomized controlled trial of a passive accessory joint mobilization on acute ankle inversion sprains. Phys Ther. (2001) 81:984–94. doi: 10.1093/ptj/81.4.984
57. Hoch MC, McKeon PO. Joint mobilization improves spatiotemporal postural control and range of motion in those with chronic ankle instability. J Orthop Res. (2011) 29:326–32. doi: 10.1002/jor.21256
58. McKeon PO, Wikstrom EA. Sensory-Targeted ankle rehabilitation strategies for chronic ankle instability. Med Sci Sports Exerc. (2016) 48:776–84. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000000859
59. Fraser JJ, Saliba SA, Hart JM, Park JS, Hertel J. Effects of midfoot joint mobilization on ankle-foot morphology and function following acute ankle sprain. A crossover clinical trial. Musculoskeletal Sci Pract. (2020) 46:102130. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2020.102130
60. Beazell JR, Grindstaff TL, Sauer LD, Magrum EM, Ingersoll CD, Hertel J. Effects of a proximal or distal tibiofibular joint manipulation on ankle range of motion and functional outcomes in individuals with chronic ankle instability. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2012) 42:125–34. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2012.3729
61. Nguyen AP, Mahaudens P, Detrembleur C, Hall T, Hidalgo B. Inferior tibiofibular joint mobilization with movement and taping does not improve chronic ankle dorsiflexion stiffness: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. J Manual Manipulat Ther. (2021) 29:73–82. doi: 10.1080/10669817.2020.1805690
62. Collins N, Teys P, Vicenzino B. The initial effects of a mulligan’s mobilization with movement technique on dorsiflexion and pain in subacute ankle sprains. Man Ther. (2004) 9:77–82. doi: 10.1016/S1356-689X(03)00101-2
63. Hidalgo B, Hall T, Berwart M, Biernaux E, Detrembleur C. The immediate effects of two manual therapy techniques on ankle musculoarticular stiffness and dorsiflexion range of motion in people with chronic ankle rigidity: a randomized clinical trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. (2018) 31:515–24. doi: 10.3233/BMR-170963
64. Weppler CH, Magnusson SP. Increasing muscle extensibility: a matter of increasing length or modifying sensation? Phys Ther. (2010) 90:438–49. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20090012
65. Young R, Nix S, Wholohan A, Bradhurst R, Reed L. Interventions for increasing ankle joint dorsiflexion: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Foot Ankle Res. (2013) 6:46. doi: 10.1186/1757-1146-6-46
66. Freitas SR, Mendes B, Le Sant G, Andrade RJ, Nordez A, Milanovic Z. Can chronic stretching change the muscle-tendon mechanical properties? A review. Scand J Med Sci Sports. (2018) 28:794–806. doi: 10.1111/sms.12957
67. Vetter S, Schleichardt A, Köhler H-P, Witt M. The effects of eccentric strength training on flexibility and strength in healthy samples and laboratory settings: a systematic review. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:873370. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.873370
68. Basson A, Olivier B, Ellis R, Coppieters M, Stewart A, Mudzi W. The effectiveness of neural mobilization for neuromusculoskeletal conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. (2017) 47:593–615. doi: 10.2519/jospt.2017.7117
69. Ellis R, Carta G, Andrade RJ, Coppieters MW. Neurodynamics: is tension contentious? J Man Manip Ther. (2021) 30:3–12. doi: 10.1080/10669817.2021.2001736
70. Neto T, Freitas SR, Marques M, Gomes L, Andrade R, Oliveira R. Effects of lower body quadrant neural mobilization in healthy and low back pain populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Musculoskeletal Sci Pract. (2017) 27:14–22. doi: 10.1016/j.msksp.2016.11.014
Keywords: ankle, range of motion, clinical reasoning, manual therapy, muscle stretching exercises
Citation: Tourillon R, M'Baye M and Smith M (2025) Restoring ankle dorsiflexion range of motion in athletes: an individualized clinical decision-making system. Front. Sports Act. Living 7:1677383. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2025.1677383
Received: 31 July 2025; Accepted: 29 September 2025;
Published: 22 October 2025.
Edited by:
Emiliano Cè, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Min Su, Soochow University, TaiwanCopyright: © 2025 Tourillon, M'Baye and Smith. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Romain Tourillon, cm9tYWluLnRvdXJpbGxvbkBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Romain Tourillon
Romain Tourillon Massamba M'Baye
Massamba M'Baye Michelle Smith
Michelle Smith