- 1College of Wuliangye Technology and Food Engineering, Yibin Vocational and Technical College, Yibin, Sichuan, China
- 2Food Nutrition and Health Key Laboratory of Sichuan Universities, Sichuan Tourism University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3School of Educational Sciences, Chengdu Normal University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4Yibin Branch of Sichuan Tobacco Corporation, Yibin, Sichuan, China
- 5Nanguang Primary School in Xuzhou District of Yibin City, Yibin, Sichuan, China
Postbiotics have similar bioactivity to probiotics and are safer and more stable. The results indicate that postbiotics exert their effects through direct (antibacterial, antioxidant, immune regulatory) and indirect (regulating microbial homeostasis and metabolic pathways) mechanisms. In the field of animals, postbiotics can enhance the disease resistance of aquatic animals, improve the intestinal health and meat quality of broiler chickens, and promote nutrient absorption in ruminant animals. In the field of humans, postbiotics exhibit potential for anti-allergy, prevention of respiratory or digestive tract infections, adjuvant therapy for anti-cancer, and improvement of liver cirrhosis. Meanwhile, postbiotics have been applied in the research and development of medical preparations and functional foods, but the mechanism of action still needs to be further explored. Compared to probiotics, postbiotics do not require live bacteria to produce health benefits and have advantages such as high safety, easy storage, and convenient production. In the future, postbiotics have broad prospects in the fields of functional foods with unique flavors and nutritional health benefits, and disease prevention and control.
1 Introduction
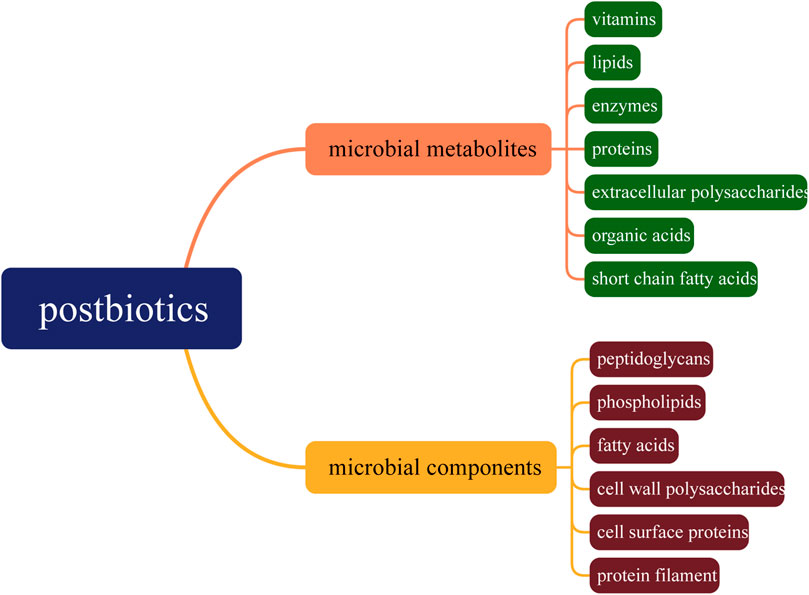
The application of probiotics by humans can be traced back to ancient times. However, it was not until 1907 that people discovered the impact of these microorganisms on health. In 1953, the term “probiotics” was first used to refer to active substances essential for the healthy development of life (Gasbarrini et al., 2016). In 2001, a panel of experts from the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and the World Health Organization officially defined probiotics as live bacteria that, when ingested in appropriate amounts, can exert beneficial effects on the health of the consumer (Bognanni et al., 2024). In recent years, the field of probiotics has received increasing attention (Gibson et al., 2017). According to the current definition, probiotics must be live microorganisms, and it does not apply to dead bacterial cells or cellular components. However, studies have found that inactivated bacteria still retain their biological activity towards the host (Almada et al., 2016; Shafipour et al., 2020), thus giving rise to the concept of postbiotics, which refers to the components of probiotics that remain beneficial to the host even after losing their activity (Malagon-Rojas et al., 2020). Currently, postbiotics are collectively referred to as inactivated microorganisms and their related components that are beneficial to host health, including microbial catabolic products, non-living microbial bodies, and components derived from cell lysis (Nataraj et al., 2020). As shown in Figure 1, postbiotics include microbial metabolites such as vitamins, lipids, enzymes, proteins, extracellular polysaccharides, organic acids, short chain fatty acids, as well as microbial components such as peptidoglycans, phospholipids, fatty acids, cell wall polysaccharides, cell surface proteins, and protein filament (Roy et al., 2024).
Probiotics generally refer to live, non-pathogenic microorganisms. However, clinical studies have shown that not only do live cells of probiotics exert health effects, but different non-viable parts of probiotic cells may also have certain beneficial effects (Sarkar, 2018). Depending on the process conditions for producing and storing probiotic products, the final product is a mixture containing both live and non-viable probiotic cells. By measuring the ratio of live cells (probiotics) to dead cells (postbiotics) in probiotic foods through in vitro experiments and assessing the properties of both fractions, it was found that the number of non-viable cells is much larger than that of live cells, and they have the same effects as live cells. This discovery indicates that a significant part of the health benefits of probiotic products is due to the presence of compounds such as postbiotics, which are naturally produced under special conditions (Fleming et al., 2019). Another technical issue with probiotic products is how to maintain the biological activity of probiotic cells. Compared to probiotics, postbiotics have the following advantages. The most significant advantage of postbiotics is their high stability. Compared to live probiotics that require storage under specific temperature and humidity conditions, postbiotics do not require live bacteria to produce health benefits, making them more stable and easier to store and transport (Zhong et al., 2024). Additionally, since postbiotics contain no live bacteria, they avoid secondary contamination and can be incorporated into products where adding live probiotics might cause discomfort, giving them broader application prospects in the food and beverage industry. The safety of postbiotics is another key advantage. They do not contain live bacteria that may cause infection or anaphylactic responses, making them more suitable for immunocompromised individuals or homo sapiens groups allergic to certain bacterial strains (Ma et al., 2023; Scott et al., 2022). This avoids potential issues such as the generation of antibiotic resistance genes and virulence factors in the body when using probiotics (Brial et al., 2018). The bioactivity of postbiotics also stands out as an advantage. The metabolites and cell wall components in postbiotics offer health benefits to the host, aiding in improving gut health, regulating the immune system, inhibiting pathogen growth, and reducing inflammatory responses. Therefore, it is necessary to obtain some safe and inexpensive alternatives to live probiotic cells. Evidently, postbiotics have research value as such alternatives.
2 Bioactivity of postbiotics
The biological mechanisms of most postbiotics are not fully understood. Scientific evidence indicates that postbiotics exert various biological effects through direct or indirect pathways, such as antibacterial, antioxidant, and immunomodulatory activities (Aguilar-Toala et al., 2018). Research suggests that the direct mechanism involves the interaction of postbiotics with different molecules or receptors, resulting in inhibitory effects (such as antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and antibacterial activities); the indirect mechanism involves the homeostasis of the microbiota, host metabolism, and signaling pathways, thereby affecting specific physiological responses (Singh et al., 2018).
2.1 Bioactivity of postbiotics in animals
Many researches on postbiotics in animals have shown that they possess certain health-promoting effects. It has been demonstrated that cell-free supernatant obtained from milk fermentation by controlling the pH of agar medium has the ability to protect mice from Salmonella infection (Dunand et al., 2019). At present, there is an urgent need to find environmentally friendly methods to replace antibiotics. Research indicated that the gut microbiota not only provided nutritional benefits, but also contributed to the development and differentiation of immune responses; probiotics can produce antibacterial compounds, compete for living space and nutrients, and inhibit virulence genes. However, the long-term addition of large amounts of live bacteria in aquaculture systems is often questioned, as these bacteria may also carry high levels of antibiotic resistance genes, making postbiotics a valuable alternative to live probiotics (Perez-Sanchez et al., 2018). Meanwhile, postbiotics have certain applications in the prevention and treatment of infectious diseases in aquaculture. Some of their soluble factors (such as short-chain fatty acids, organic acids, peptides, teichoic acid, peptidoglycan, extracellular polysaccharides, cell surface proteins, and vitamins) have effects on enhancing immune response, disease resistance, and antibacterial activity in certain aquatic animals (Yao et al., 2020), thereby reducing the risk of pathogenic infections in aquaculture animals. Adding four types of inactivated probiotics to rainbow trout feed can prevent furunculosis (Irianto and Austin, 2003). Furthermore, studies have shown that a new postbiotics extracted from lactic acid bacteria can modify the gut microbiota of rainbow trout and confer disease resistance (Mora-Sanchez et al., 2020). The beneficial bacterial cellular components and metabolites (postbiotics) of hybrid sturgeons have a positive effect on the growth of beneficial gut microbiota in hybrid sturgeons, but they do not affect the survival rate of sturgeons. They can promote the growth of beneficial gut microbiota in hybrid sturgeons, altering the composition and diversity of their gut microbiota (Wu et al., 2020).
Feeding broiler chickens with feed supplemented with postbiotics results in chicken meat with a 5% lower fat content compared to commercially available chicken meat, and a significant 11.13% increase in saturated fatty acid content. Broiler chickens fed with postbiotic supplemented feed not only have no residues of antibiotic substances, pesticides, and herbicides, but also exhibit better flavor (Kucheruk et al., 2019). Postbiotics have an immune-regulating effect on the jejunum tissue of broiler chickens; they modulated the activation of the innate immune response, and combined with pathogenic factors of gas-producing capsular protein, inhibited the activation of the standard gas-producing capsular protein immune response. Due to certain limitations on the addition of antibiotics with anti-inflammatory effects to feed, postbiotics were of great significance as alternatives to antibiotics for maintaining intestinal health in broiler chickens (Johnson et al., 2019). Researchers had shown that adding certain postbiotics to feed improved the growth performance of broiler chickens, reduced the number of Escherichia coli, increased acetic acid concentration, and accompanied related changes in cytokine expression in the ileum. Proportionally adding postbiotics could serve as an alternative to antibiotics in broiler chicken feed to improve growth and intestinal health (Kareem et al., 2016). Other research results indicated that under heat stress conditions, feeding postbiotics can enhance the antioxidant activity and meat quality of broiler chickens, and reduce acute-phase proteins, plasma cholesterol, and lipid peroxidation (Humam et al., 2020).
Postbiotics also exhibit certain biological activities in mammals. Wan Ibrahim et al. (Izuddin et al., 2020; Izuddin et al., 2019a) reported that supplementation of postbiotic L. plantarum RG14 in weaned lambs can promote rumen papilla growth, immune status, and gastrointestinal health. Lactobacillus plantarum RG14 also demonstrates high antioxidant capacity. Post-weaning supplementation with L. plantarum RG14 can increase antioxidant enzymes in serum and rumen fluid, and reduce lipid peroxidation in serum. After supplementation with L. plantarum RG14 in newly weaned lambs, rumen fermentation was improved, microbial parameters, blood metabolites, as well as post-weaning growth and nutrient intake genes were upregulated, indicating that it can enhance the growth performance, nutrient intake, and nutrient digestibility of weaned lambs (Izuddin et al., 2019b). Deoxynivalenol and aflatoxin in pig feed are harmful to newly weaned piglets, affecting their growth and nutrient digestibility. Supplementation with yeast cell wall mixture (postbiotics) can partially overcome the harmful effects of various mycotoxins in the diet on the growth and health of weaned piglets (Holanda et al., 2020). Based on research in various animals, postbiotics may be a suitable alternative to the use of probiotics, avoiding the potential risks associated with the use of live microorganisms. Postbiotics have broad application prospects in the field of animal feed.
2.2 Bioactivity of postbiotics in humans
In recent years, due to the difficulty in determining the bioactivity of probiotics, some new research directions have gradually emerged. For instance, postbiotics—metabolites produced by probiotics that exhibit similar health benefits—hold considerable research promise (Taverniti and Guglielmetti, 2011). The following briefly describes the bioactivity of postbiotics in humans.
2.2.1 Prevention and treatment of allergies
Due to the different composition of gut microbiota in allergic patients, regulating gut microbiota is an effective method to control allergic reactions, and this research strategy has certain application prospects (Pascal et al., 2018). Some researchers have found that probiotics have a certain role in the prevention and treatment of food allergies (Santos et al., 2020). For example, some live microorganisms, when given in sufficient amounts, seem to bring health benefits to the host, such as balancing the microbiota, restoring intestinal permeability, improving barrier function, and regulating immune responses, but may produce some minor side effects (Sotoudegan et al., 2019). However, postbiotics do not pose such risks, postbiotics enhance the endogenous probiotics of each host, rather than adding unfamiliar strains of probiotics to the gut microbial ecosystem, which can restore missing allergen-protective microorganisms, improve immune tolerance, treat allergies, and have no adverse side effects. The positive effects of postbiotics largely depend on the selection of maternal microbial strains, different preparation methods, the presence of multiple bioactive molecules, dosage, and the appropriate choice of drug delivery system. Therefore, postbiotics can serve as a new strategy to improve immune tolerance and treat food allergies without adverse side effects, especially in infants and children. Despite some research progress in postbiotics in allergy treatment, further research is still needed to fully understand how postbiotics can be used as an adjunctive therapy to prevent or treat a wide range of chronic diseases.
2.2.2 Prevention of respiratory and gastrointestinal infections
Children under the age of 5 are particularly susceptible to respiratory and gastrointestinal infections (Frank et al., 2019). Since early 1980, probiotics have been used to mitigate infections from common infectious diseases in children and infants (Amaral et al., 2017). However, it is worth noting that due to rare cases of infections associated with probiotics, such as necrotizing enterocolitis and pneumonia, the scientific community does not endorse the use of probiotic interventions in young children (Kothari et al., 2018). Given these challenges, supplementation with postbiotics has been proposed as an alternative strategy to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases in children. There have been reports on the use of heat-killed L. acidophilus for the treatment of acute diarrhea and heat-killed Lactobacillus acidophilus CBA L74 for the prevention of gastrointestinal and respiratory infections (Malagon-Rojas et al., 2020). Postbiotics offer the same beneficial therapeutic effects as similar probiotics, while avoiding the risks associated with live microorganisms, especially in high-risk groups such as children under the age of 5.
2.2.3 Adjuvant therapy for anti-cancer
It has been reported that the postbiotics produced by L. plantarum exhibit selective cytotoxic effects on various cancer cells under different combinations of dosage and time (Chuah et al., 2019), without causing toxicity or hemolysis to normal cells. Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry observations indicated that these postbiotics inhibited the proliferation and induced apoptosis of human breast cancer cells, reducing the survival rate of human breast cancer cells. The postbiotics produced by L. plantarum were selective towards various tumorigenic cells, suggesting that they possess certain anti-cancer properties. Therefore, they have great potential as functional supplements and adjuvant therapies for anti-cancer treatment, which can be further explored.
2.2.4 Therapy for cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is the terminal stage of chronic hepatitis development, dysbiosis of gut microbiota, loss of intestinal barrier function, and bacterial translocation are important causes of complications in cirrhosis. Although probiotics are well tolerated in patients with cirrhosis and can protect intestinal barrier function at multiple levels, studies have shown that in critically ill patients or those with extremely low immunity, probiotics may lead to opportunistic infections and even increase mortality. Therefore, their efficacy in treating intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in cirrhosis is unclear. In recent years, postbiotics have been proven to great potential therapeutic value in patients with cirrhosis. Postbiotics have various effects such as maintaining gut microbiota, protecting intestinal barrier function, and immune regulation, which are expected to improve the current situation of intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in cirrhosis, delay disease progression, and reduce the occurrence of subsequent complications. Postbiotics have a certain preventive and therapeutic effect on intestinal barrier damage in cirrhosis, and there is currently some research on the treatment of diseases related to intestinal microbiota dysbiosis with postbiotics; some researchers have found that postbiotics produced by E. coli 1917 can significantly inhibit the abnormal proliferation of pathogenic Enterobacteriaceae under intestinal inflammation conditions, alleviate intestinal microbiota dysbiosis, and ultimately treat enteritis (Sassone-Corsi et al., 2016). Postbiotics produced by Clostridium butyricum had good therapeutic effects on mice with non-alcoholic hepatitis induced by high-fat diet, improving intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in non-alcoholic hepatitis mice and enhancing intestinal barrier function, thus achieving good therapeutic effects on non-alcoholic hepatitis (Zhou et al., 2017). It can be seen that postbiotics have broad application prospects in regulating intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in cirrhosis, thereby improving disease progression and complications related to intestinal microbiota dysbiosis. However, most of the research is based on animals, and in order to evaluate the beneficial effects of postbiotics on humans, it is hoped that large-scale researches can be conducted on humans in the future.
In addition to focusing on the biological activity and other advantages of postbiotics, the safety of their application must also be considered. The negative effects of postbiotics were evaluated in a randomized controlled trial of infants using inactivated L. acidophilus, which showed an indirect correlation with infant gastrointestinal tympanites, severe dehydration, and vomiting responses (Florez et al., 2020). Although postbiotics exhibit promising biological activity, most of these effects are limited to in vitro or animal studies and do not account for host pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Therefore, the health benefits of postbiotics must be clinically validated (Salminen et al., 2021). In the preparation of postbiotics, exogenous microbial metabolites or lysates can be directly added, or microorganisms can be inactivated through methods such as pyrolysis, ultrasonication, high-pressure treatment, or enzymatic treatment, allowing for the study of whole inactivated microorganisms. Thus, the selection of inactivation methods must be aligned with existing production processes and cost considerations. In addition, sensory and nutritional factors need to be further considered. The extensive autolysis of microorganisms may release flavor-active metabolites such as peptides, nucleotides, and amino acids, which can enhance the taste and flavor of the product. However, inactivation treatment methods may also lead to the loss of antioxidants, polyphenols and vitamins, necessitating precise regulation during the process to ensure the product’s nutritional value (Marson et al., 2020).
3 Application of postbiotics
In recent years, postbiotics has been introduced into the fields of medicine, veterinary medicine, and food, playing a unique role in preventing and treating certain diseases, improving animal health, and developing functional foods (Rad et al., 2020; Rinaldi et al., 2020; Riwes and Reddy, 2020).
3.1 Applied to the prevention and treatment of diseases
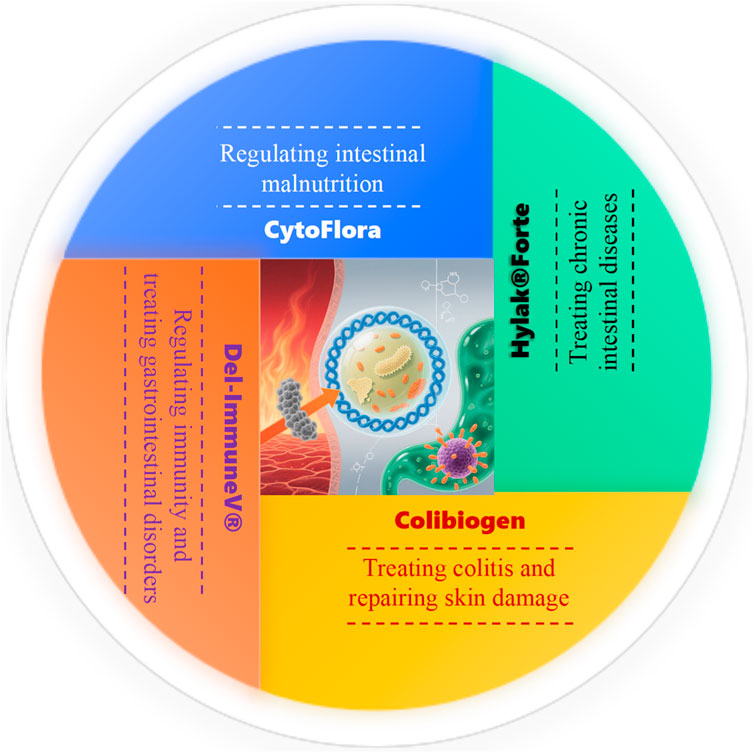
At present, free cell preparations obtained from different beneficial bacteria have been introduced into the prevention or treatment of diseases, with potential drug application value (Klein et al., 2013). Researchers are attempting to apply it to the matrix of pharmaceuticals and food, which may be a new strategy for preventing and assisting in the treatment of certain diseases. As shown in Figure 2, Colibiogen is a protein free commercial filtrate extracted from E. coli, containing amino acids, peptides, polysaccharides, and fatty acids. It can effectively resist antibiotic resistant and Salmonella, improve colitis in mice, and significantly reduce skin damage in patients with polymorphic solar rash (Aguilar-Toala et al., 2018). There is a product of postbiotics under the trademark CytoFlora, which is a mixture of cell wall isolates of Lactobacillus casei, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, L. salivarius, L. bulgaricus, L. acidophilus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, and Streptococcus thermophilus. It is used to regulate intestinal malnutrition, promote immune balance, and improve symptoms in children with autism (Ray et al., 2010; Roda et al., 2007). Hylak®Forte is a sterile liquid containing metabolites from E. coli DSM 4087, S. faecalis DSM 4086, L. acidophilus DSM 414, and Lactobacillus helveticus DS 4183, while, the main health benefits of Hylak®Forte include (Marov et al., 2014; Patil et al., 2019): promoting the growth of beneficial gut microbiota; adjusting the pH value of the intestinal environment and promoting the normal function of the digestive tract; energy supply of intestinal epithelial cells; regulating the balance of vitamin K. Another type of postbiotics is Del ImmuneV®, which is a registered and approved formulation by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which contains rodentiyl peptides, amino acids, and DNA fragments of Lactobacillus rhamnosus. It is usually recommended to use it together with probiotics for treatment, and research results had shown that Del-ImmuneV® could effectively reduce the degree of gastrointestinal disorders in patients with autism spectrum disorders.
3.2 Applied to functional foods
Compared with probiotics, postbiotics are more stable and safe in industry, therefore, the application of postbiotics in the research and development of functional foods has certain technological advantages (Barros et al., 2020). Currently, there are various food products with bioactive ingredients, such as dairy and non-dairy products with added probiotics, to meet the nutritional needs of consumers with different dietary styles (milk protein allergy sufferers, lactose intolerance sufferers, vegetarians). Researchers have shown that the secondary metabolites such as chlortetracycline and bacteriocins extracted from Bacillus sp. CS93 have stable and antibacterial properties, which make them widely used in food (Phister et al., 2004). On the one hand, some milk products and other products (such as Kombucha and pickled Chinese cabbage) may produce postbiotics during fermentation. On the other hand, postbiotics can also be purposefully added to various foods (Wasilewski et al., 2015). Researches have shown that the postbiotics from the supernatant of L. plantarum YML 07 can serve as a potential biological preservative, which can increase the shelf life of soybeans to 2 months (Rather et al., 2013). Nisin is an antibiotic produced by specific Streptococcus lactis and the only bacteriocin approved for use as a food preservative (Fusieger et al., 2020). At present, foods containing nisin include canned soups, baked goods, mayonnaise, and dairy products. Furthermore, extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) containing rare sugars have found new applications in the food industry due to their physicochemical properties (thickening, stability, or water binding ability) and palatability in food. However, except for dextran, due to the low EPS production of lactic acid bacteria, they have not yet been commercially developed as food additives (Ispirli et al., 2020). Another biological function of postbiotics is its detoxification of toxic metabolites, which has attracted widespread attention from scientists in recent years (Tomasik and Tomasik, 2020; Wang et al., 2019).
3.3 Applied to food packaging
Due to the harmful environmental impacts of synthetic packaging, the food manufacturing industry has developed organic packaging materials such as edible coating materials, which exhibit excellent gas barrier properties, extend food shelf life, and potentially contain antioxidant and antimicrobial compounds. MOHAMMADI R et al. utilized postbiotics to enhance the antibacterial properties of bacterial nanocellulose, developing antimicrobial films based on bacterial nanocellulose packaging materials (Mohammadi et al., 2022). The postbiotics demonstrated concentration-dependent antimicrobial activity against all studied bacterial strains. Research has shown that edible coatings developed using fermentation products of Saccharomyces boulardii ATCC MYA-796 and polysaccharides exhibit preservative effects on lamb meat, effectively reducing microbial growth, extending meat shelf life, and maintaining favorable sensory characteristics of lamb (Sivananthan and Petersen, 2018). ABBASI A et al. found that yeast composite films incorporating bacterial cellulose produced by yeast fermentation, along with carboxymethyl cellulose and glycerol, displayed high water solubility (42.86%), extended the shelf life of food packaging materials (Abbasi et al., 2023).
According to data from Future Market Insights, the global postbiotic supplements market is projected to reach $28.3 million by 2032, with the compound annual growth rate expected to increase from 7.6% during 2016–2021 to 11.5% during 2022–2032. Additionally, patent database searches revealed that from 2001 to 2020, there were a total of 2,215 global patents related to prebiotics and postbiotics. Compared to 2001–2010, the number of patents grew by 1.45% during 2011–2020 (Asif et al., 2023; Zang et al., 2024). Therefore, more research and clinical trials are needed in the future to enhance the control over the safety issues of postbiotics. It is necessary to establish industry, national, or international standards for postbiotics and improve the evaluation systems for their safety and functionality. In terms of technology and product development, it is also essential to explore more plant-based raw materials and microbial strains suitable for fermentation, optimize fermentation processes, and increase the yield of functional components in postbiotics. This will enable their broader application in products and facilitate the development of novel postbiotics with unique flavors and nutritional health benefits.
4 Conclusion
Compared with probiotics, postbiotics not only has the same beneficial effects, but also has some other advantages, such as known molecular structure, use after purification, specific mechanism of action, easier industrial scale production, easier production and storage, etc. Therefore, postbiotics has great application prospects in medical treatment and food. However, we lack the understanding of the specific mechanism of postbiotics in vitro and in vivo, and further research is needed to understand their beneficial effects on humans and animals.
Author contributions
XC: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization. CY: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Visualization. JH: Writing – review and editing, Investigation. WL: Writing – original draft, Methodology. CL: Conceptualization, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by Food Nutrition and Health Key Laboratory of Sichuan Universities (No. FN25Y14), Solid-State Fermentation Resource Utilization Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (No. 2024GTYY07), Innovation Training Program Project for University Students in Sichuan Province (No. S202512966070) and Scientific Research Project of Yibin Vocational and Technical College (No. 24JBGS-05).
Conflict of interest
Author WL was employed by Yibin Branch of Sichuan Tobacco Corporation.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbasi, A., Sabahi, S., Bazzaz, S., Tajani, A. G., Lahouty, M., Aslani, R., et al. (2023). An edible coating utilizing Malva sylvestris seed polysaccharide mucilage and postbiotic from Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. boulardii for the preservation of lamb meat. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 246, 125660. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125660
Aguilar-Toala, J. E., Garcia-Varela, R., Garcia, H. S., Mata-Haro, V., Gonzalez-Cordova, A. F., Vallejo-Cordoba, B., et al. (2018). Postbiotics: an evolving term within the functional foods field. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 75, 105–114. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2018.03.009
Almada, C. N., Almada, C. N., Martinez, R. C. R., and Sant'Ana, A. S. (2016). Paraprobiotics: evidences on their ability to modify biological responses, inactivation methods and perspectives on their application in foods. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 58, 96–114. doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2016.09.011
Amaral, M. A., Guedes, G., Epifanio, M., Wagner, M. B., Jones, M. H., and Mattiello, R. (2017). Network meta-analysis of probiotics to prevent respiratory infections in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 52, 833–843. doi:10.1002/ppul.23643
Asif, A., Afzaal, M., Shahid, H., Saeed, F., Ahmed, A., Shah, Y. A., et al. (2023). Probing the functional and therapeutic properties of postbiotics in relation to their industrial application. Food Sci. Nutr. 11, 4472–4484. doi:10.1002/fsn3.3465
Barros, C. P., Guimaraes, J. T., Esmerino, E. A., Duarte, M. C. K. H., Silva, M. C., Silva, R., et al. (2020). Paraprobiotics and postbiotics: concepts and potential applications in dairy products. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 32, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.cofs.2019.12.003
Bognanni, A., Fiocchi, A., Arasi, S., Chu, D. K., Ansotegui, I., Assa'Ad, A. H., et al. (2024). World allergy organization (WAO) diagnosis and rationale for action against Cow's milk allergy (DRACMA) guideline update - XII - Recommendations on milk formula supplements with and without probiotics for infants and toddlers with CMA. World Allergy Organ J. 17, 100888. doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2024.100888
Brial, F., Le Lay, A., Dumas, M. E., and Gauguier, D. (2018). Implication of gut microbiota metabolites in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 75, 3977–3990. doi:10.1007/s00018-018-2901-1
Chuah, L. O., Foo, H. L., Loh, T. C., Mohammed, A. N., Yeap, S. K., Abdul, M. N., et al. (2019). Postbiotic metabolites produced by Lactobacillus plantarum strains exert selective cytotoxicity effects on cancer cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 19, 114. doi:10.1186/s12906-019-2528-2
Dunand, E., Burns, P., Binetti, A., Bergamini, C., Peralta, G. H., Forzani, L., et al. (2019). Postbiotics produced at laboratory and industrial level as potential functional food ingredients with the capacity to protect mice against salmonella infection. J. Appl. Microbiol. 127, 219–229. doi:10.1111/jam.14276
Fleming, P. F., Berrington, J. E., and Jacobs, S. E. (2019). Addressing safety concerns of probiotic use in preterm babies. Early Hum. Dev. 135, 72–74. doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2019.05.016
Florez, I. D., Nino-Serna, L. F., and Beltran-Arroyave, C. P. (2020). Acute infectious diarrhea and gastroenteritis in children. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 22, 4. doi:10.1007/s11908-020-0713-6
Frank, N. M., Lynch, K. F., Uusitalo, U., Yang, J., Lonnrot, M., Virtanen, S. M., et al. (2019). The relationship between breastfeeding and reported respiratory and gastrointestinal infection rates in young children. BMC Pediatr. 19, 339. doi:10.1186/s12887-019-1693-2
Fusieger, A., Perin, L. M., Teixeira, C. G., de Carvalho, A. F., and Nero, L. A. (2020). The ability of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis bv. Diacetylactis strains in producing nisin. Ant. Van Leeuwenhoek 113, 651–662. doi:10.1007/s10482-019-01373-6
Gasbarrini, G., Bonvicini, F., and Gramenzi, A. (2016). Probiotics history. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 50, S116–119. doi:10.1097/MCG.0000000000000697
Gibson, G. R., Hutkins, R., Sanders, M. E., Prescott, S. L., Reimer, R. A., Salminen, S. J., et al. (2017). Expert consensus document: the international scientific association for probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 14, 491–502. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2017.75
Holanda, D. M., Yiannikouris, A., and Kim, S. W. (2020). Investigation of the efficacy of a postbiotic yeast cell wall-based blend on newly-weaned pigs under a dietary challenge of multiple mycotoxins with emphasis on deoxynivalenol. Toxins 12, 504. doi:10.3390/toxins12080504
Humam, A. M., Loh, T. C., Foo, H. L., Izuddin, W. I., Awad, E. A., Idrus, Z., et al. (2020). Dietary supplementation of postbiotics mitigates adverse impacts of heat stress on antioxidant enzyme activity, total antioxidant, lipid peroxidation, physiological stress indicators, lipid profile and meat quality in broilers. Animals 10, 982. doi:10.3390/ani10060982
Irianto, A., and Austin, B. (2003). Use of dead probiotic cells to control furunculosis in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (walbaum). J. Fish. Dis. 26, 59–62. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2761.2003.00414.x
Ispirli, H., özmen, D., Yılmaz, M. T., Sağdıç, O., and Dertli, E. (2020). Impact of glucan type exopolysaccharide (EPS) production on technological characteristics of sourdough bread. Food control. 107, 106812. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.106812
Izuddin, W. I., Loh, T. C., Foo, H. L., Samsudin, A. A., and Humam, A. M. (2019a). Postbiotic L. Plantarum RG14 improves ruminal epithelium growth, immune status and upregulates the intestinal barrier function in post-weaning lambs. Sci. Rep.-UK 9, 9938. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-46076-0
Izuddin, W. I., Loh, T. C., Samsudin, A. A., Foo, H. L., Humam, A. M., and Shazali, N. (2019b). Effects of postbiotic supplementation on growth performance, ruminal fermentation and microbial profile, blood metabolite and GHR, IGF-1 and MCT-1 gene expression in post-weaning lambs. BMC Vet. Res. 15, 315. doi:10.1186/s12917-019-2064-9
Izuddin, W. I., Humam, A. M., Loh, T. C., Foo, H. L., and Samsudin, A. A. (2020). Dietary postbiotic Lactobacillus plantarum improves serum and ruminal antioxidant activity and upregulates hepatic antioxidant enzymes and ruminal barrier function in post-weaning lambs. Antioxidants 9, 250. doi:10.3390/antiox9030250
Johnson, C. N., Kogut, M. H., Genovese, K., He, H., Kazemi, S., and Arsenault, R. J. (2019). Administration of a postbiotic causes immunomodulatory responses in broiler gut and reduces disease pathogenesis following challenge. Microorganisms 7, 268. doi:10.3390/microorganisms7080268
Kareem, K. Y., Loh, T. C., Foo, H. L., Akit, H., and Samsudin, A. A. (2016). Effects of dietary postbiotic and inulin on growth performance, IGF1 and GHR mRNA expression, faecal microbiota and volatile fatty acids in broilers. BMC Vet. Res. 12, 163. doi:10.1186/s12917-016-0790-9
Klein, G., Schanstra, J. P., Hoffmann, J., Mischak, H., Siwy, J., and Zimmermann, K. (2013). Proteomics as a quality control tool of pharmaceutical probiotic bacterial lysate products. PLoS One 8, e66682. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066682
Kothari, D., Patel, S., and Kim, S. (2018). Probiotic supplements might not be universally-effective and safe: a review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 111, 537–547. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.104
Kucheruk, M., Midyk, S., Zasekin, D., Ushkalov, V., and Kepple, O. (2019). Fatty acid containment in organic chicken-broilers meat and traditional growing. Food Sci. Tech.-Brazil 13, 51–57. doi:10.15673/fst.v13i4.1570
Ma, L., Tu, H., and Chen, T. (2023). Postbiotics in human health: a narrative review. Nutrients 15, 291. doi:10.3390/nu15020291
Malagon-Rojas, J. N., Mantziari, A., Salminen, S., and Szajewska, H. (2020). Postbiotics for preventing and treating common infectious diseases in children: a systematic review. Nutrients 12, 389. doi:10.3390/nu12020389
Marov, T., Omarova, L., Omarova, V., and Sarsenova, S. (2014). The chronic gastritis, the dysbacterio sis and the use of hylak forte at the treatment. Wiadomosci Lek. 67, 365–367.
Marson, G. V., de Castro, R., Belleville, M. P., and Hubinger, M. D. (2020). Spent brewer's yeast as a source of high added value molecules: a systematic review on its characteristics, processing and potential applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36, 95. doi:10.1007/s11274-020-02866-7
Mohammadi, R., Moradi, M., Tajik, H., and Molaei, R. (2022). Potential application of postbiotics metabolites from bioprotective culture to fabricate bacterial nanocellulose based antimicrobial packaging material. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 220, 528–536. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.08.108
Mora-Sanchez, B., Balcazar, J. L., and Perez-Sanchez, T. (2020). Effect of a novel postbiotic containing lactic acid bacteria on the intestinal microbiota and disease resistance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Biotechnol. Lett. 42, 1957–1962. doi:10.1007/s10529-020-02919-9
Nataraj, B. H., Ali, S. A., Behare, P. V., and Yadav, H. (2020). Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new Horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods. Microb. Cell Fact. 19, 168. doi:10.1186/s12934-020-01426-w
Pascal, M., Perez-Gordo, M., Caballero, T., Escribese, M. M., Lopez, L. M., Luengo, O., et al. (2018). Microbiome and allergic diseases. Front. Immunol. 9, 1584. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01584
Patil, S., Sawant, S., Hauff, K., and Hampp, G. (2019). Validated postbiotic screening confirms presence of physiologically-active metabolites, such as short-chain fatty acids, amino acids and vitamins in hylak® forte. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 11, 1124–1131. doi:10.1007/s12602-018-9497-5
Perez-Sanchez, T., Mora-Sanchez, B., and Balcazar, J. L. (2018). Biological approaches for disease control in aquaculture: advantages, limitations and challenges. Trends Microbiol. 26, 896–903. doi:10.1016/j.tim.2018.05.002
Phister, T. G., O'Sullivan, D. J., and Mckay, L. L. (2004). Identification of bacilysin, chlorotetaine, and iturin a produced by bacillus sp. strain CS93 isolated from pozol, a Mexican fermented maize dough. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 631–634. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.1.631-634.2004
Rad, A. H., Abbasi, A., Kafil, H. S., and Ganbarov, K. (2020). Potential pharmaceutical and food applications of postbiotics: a review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 21, 1576–1587. doi:10.2174/1389201021666200516154833
Rather, L. A., Seo, B. J., Kumar, V. J. R., Choi, U. H., Choi, K. H., Lim, J. H., et al. (2013). Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous antifungal compound from Lactobacillus plantarum YML 007 and its application as a food preservative. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1, 69–76. doi:10.1111/lam.12077
Ray, S., Sherlock, A., Wilken, T., and Woods, T. (2010). Cell wall lysed probiotic tincture decreases immune response to pathogenic enteric bacteria and improves symptoms in autistic and immune compromised. Explore 1, 1–5.
Rinaldi, F., Trink, A., and Pinto, D. (2020). Efficacy of postbiotics in a PRP-like cosmetic product for the treatment of alopecia area celsi: a randomized double-blinded parallel-group study. Dermatology Ther. 10, 483–493. doi:10.1007/s13555-020-00369-9
Riwes, M., and Reddy, P. (2020). Short chain fatty acids: postbiotics/metabolites and graft versus host disease colitis. Semin. Hematol. 57, 1–6. doi:10.1053/j.seminhematol.2020.06.001
Roda, A., Simoni, P., Magliulo, M., Nanni, P., Baraldini, M., Roda, G., et al. (2007). A new oral formulation for the release of sodium butyrate in the ileo-cecal region and Colon. World J. Gastroenterol. 13, 1079–1084. doi:10.3748/wjg.v13.i7.1079
Roy, L., Banerjee, A., Pan, N., Ghosh, R., Mondal, S., Das, M., et al. (2024). A spectroscopy-based proof-of-concept (POC) for developing loading of pathogen analyzer (LOPA) for dairy products. Heliyon 10, e38735. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38735
Salminen, S., Collado, M. C., Endo, A., Hill, C., Lebeer, S., Quigley, E., et al. (2021). The international scientific association of probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 649–667. doi:10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
Santos, S. C. D., Konstantyner, T., and Cocco, R. R. (2020). Effects of probiotics in the treatment of food hypersensitivity in children: a systematic review. Allergol. Immunopathol. Madr. 48, 95–104. doi:10.1016/j.aller.2019.04.009
Sarkar, S. (2018). Whether viable and dead probiotic are equally efficacious? Nutr. food Sci. 48, 285–300. doi:10.1108/NFS-07-2017-0151
Sassone-Corsi, M., Nuccio, S. P., Liu, H., Hernandez, D., Vu, C. T., Takahashi, A. A., et al. (2016). Microcins mediate competition among enterobacteriaceae in the inflamed gut. Nature 540, 280–283. doi:10.1038/nature20557
Scott, E., De Paepe, K., and Van de Wiele, T. (2022). Postbiotics and their health modulatory biomolecules. Biomolecules 12, 1640. doi:10.3390/biom12111640
Shafipour, Y. A., Moradi, M., Tajik, H., and Molaei, R. (2020). Design and preparation of antimicrobial meat wrapping nanopaper with bacterial cellulose and postbiotics of lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 321, 1–10. doi:10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108561
Singh, A., Vishwakarma, V., and Singhal, B. (2018). Metabiotics: the functional metabolic signatures of probiotics: current state-of-art and future research Priorities—Metabiotics: probiotics effector molecules. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 9, 147–189. doi:10.4236/abb.2018.94012
Sivananthan, K., and Petersen, A. M. (2018). Review of saccharomyces Boulardii as a treatment option in IBD. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 40, 465–475. doi:10.1080/08923973.2018.1469143
Sotoudegan, F., Daniali, M., Hassani, S., Nikfar, S., and Abdollahi, M. (2019). Reappraisal of probiotics' safety in human. Food Chem. Toxicol. 129, 22–29. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2019.04.032
Taverniti, V., and Guglielmetti, S. (2011). The immunomodulatory properties of probiotic microorganisms beyond their viability (ghost probiotics: proposal of paraprobiotic concept). Genes Nutr. 6, 261–274. doi:10.1007/s12263-011-0218-x
Tomasik, P. A., and Tomasik, P. (2020). Probiotics, non-dairy prebiotics and postbiotics in nutrition. Appl. Sci. 10, 1470. doi:10.3390/app10041470
Wang, N., Wu, W., Pan, J., and Long, M. (2019). Detoxification strategies for zearalenone using microorganisms: a review. Microorganisms 7, 208. doi:10.3390/microorganisms7070208
Wasilewski, A., Zielinska, M., Storr, M., and Fichna, J. (2015). Beneficial effects of probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and psychobiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 21, 1674–1682. doi:10.1097/MIB.0000000000000364
Wu, X., Teame, T., Hao, Q., Ding, Q., Liu, H., Ran, C., et al. (2020). Use of a paraprobiotic and postbiotic feed supplement (HWF™) improves the growth performance, composition and function of gut microbiota in hybrid sturgeon (Acipenser baerii x Acipenser schrenckii). Fish. Shellfish Immunol. 104, 36–45. doi:10.1016/j.fsi.2020.05.054
Yao, A. C., Sano, M., Dan, S., Leelakriangsak, M., and M, L. T. (2020). Postbiotics applications as infectious disease control agent in aquaculture. Biocontrol Sci. 25, 1–7. doi:10.4265/bio.25.1
Zang, T., Han, L., Lu, Z., Tan, L., Liang, D., Shen, X., et al. (2024). The history and prediction of prebiotics and postbiotics: a patent analysis. Nutrients 16, 380. doi:10.3390/nu16030380
Zhong, Y., Wang, T., Luo, R., Liu, J., Jin, R., and Peng, X. (2024). Recent advances and potentiality of postbiotics in the food industry: composition, inactivation methods, current applications in metabolic syndrome, and future trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 64, 5768–5792. doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2158174
Keywords: postbiotics, probiotics, bioactivity, disease prevention, functional food
Citation: Chen X, Yuan C, He J, Li W and Liao C (2025) Current research status and trends in the bioactivity of postbiotics. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 5:1692683. doi: 10.3389/frfst.2025.1692683
Received: 26 August 2025; Accepted: 04 September 2025;
Published: 12 September 2025.
Edited by:
Fei Chen, Huangshan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Li Pingping, Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Chen, Yuan, He, Li and Liao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiang He, aGoxMDU0OTk0MDk0QDEyNi5jb20=; Cheng Liao, MjUyNTk1Mjg4QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Xueling Chen
Xueling Chen Can Yuan2
Can Yuan2 Jiang He
Jiang He Wanwu Li
Wanwu Li Cheng Liao
Cheng Liao