- National Key Laboratory of Wheat and Maize Crop, Collaborative Innovation Center of Henan Grain Crops, Agronomy College, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou, China
The transcriptomes of bread wheat Yunong 201 and its ethyl methanesulfonate derivative Yunong 3114 were obtained by next-sequencing technology. Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) in the wheat strains were explored and compared. A total of 5907 and 6287 non-synonymous SNVs were acquired for Yunong 201 and 3114, respectively. A total of 4021 genes with SNVs were obtained. The genes that underwent non-synonymous SNVs were significantly involved in ATP binding, protein phosphorylation, and cellular protein metabolic process. The heat map analysis also indicated that most of these mutant genes were significantly differentially expressed at different developmental stages. The SNVs in these genes possibly contribute to the longer kernel length of Yunong 3114. Our data provide useful information on wheat transcriptome for future studies on wheat functional genomics. This study could also help in illustrating the gene functions of the non-synonymous SNVs of Yunong 201 and 3114.
Introduction
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is one of the three most important cereals (i.e., maize, rice, and wheat), with more than 600 million tons harvested annually (Shewry, 2009). In wheat breeding programs, yield can be divided into three components, namely, spike number per acre, grain number per spike, and thousand-grain weight. Grain weight is mainly determined by grain size in bread wheat. Therefore, kernel size, which is extensively studied in wheat breeding programs, is a key factor affecting wheat yield. Grain size is mainly controlled by heredity. Previously, many genes related to grain size of rice have been successfully cloned (Song et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2008, 2012; Weng et al., 2008; Li et al., 2011). Some quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling grain shape and size in bread wheat have been mapped through marker analysis in different wheat populations (Breseghello and Sorrells, 2006; Wu et al., 2015). Many of them were associated with the orthologs of rice grain traits QTLs (Lu et al., 2015; Wu et al., 2015; Zanke et al., 2015). For example, GRAIN SIZE 3 (GS3) is a major QTL for rice grain length and weight (Fan et al., 2006), TaGS-D1 was the syntenic gene in wheat (Zhang et al., 2014). These studies revealed that grain size of bread wheat is regulated via a complex molecular genetic mechanism. However, in bread wheat, the genetic study of grain size has been limited to date because of its large de novo genome. Next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology (Goff et al., 2002) provides a novel method to identify, map, and quantify transcriptomes (Kyndt et al., 2012); this method can also be used for rapid characterization of transcript sequences, gene expression (Wang et al., 2009), and genomic variation in polyploid plants with de novo genomes (Goff et al., 2002; Marioni et al., 2008). The first homolog-specific sequence assembly of wheat transcriptome is based on Roche 454 and Illumina GAIIx (Schreiber et al., 2012). Moreover, the genome of wheat and of its relative were analyzed by recent studies utilizing high-throughput sequencing, which provided references for further study (Brenchley et al., 2012; Ling et al., 2013; The International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium [IWGSC], 2014). Subsequently, large amount of advances have been acquired on wheat transcriptome (Duan et al., 2012; Pfeifer et al., 2014; Tanaka et al., 2014; Pingault et al., 2015).
The correlation between the genetic variants and the phenotypes is still a central question for crop improvements. Ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) induces a large spectrum of mutations, including truncations and missense mutations, thereby allowing to be a readily used chemical in traditional breeding programs because of its flexibility, non-transgenicity, and stable inheritability (McCallum et al., 2000; Henikoff et al., 2004). Furthermore, EMS can create random point mutations at high density in polyploid plants. Many studies has focused on creation of mutations via EMS in specific genes of plants, and all the mutations are G–A or C–T transitions in bread wheat (Feiz et al., 2009; Uauy et al., 2009; Slade et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2014). Through RNAseq, large number of genetic variants across the transcriptomes could be identified. The possible transcriptional mechanism of trait regulation due to genetic variants including single nucleotide polymorphism substitutions has been reported in many crops such as in rice (Mao et al., 2010), but still insufficient in wheat.
A Chinese wheat cultivar Yunong 201, which was released in 2006 (No. Yushenmai2006006), is a high-quality noodle wheat strain that is disease-resistant. Meanwhile, its EMS mutagenesis-derived Yunong 3114 shows longer kernel length and higher production. In the present study, to better understand the genetic basis of kernel size in bread wheat, Illumina (Solexa) sequencing technology was applied in bread wheat Yunong 201 and its EMS mutant line Yunong 3114 to generate their transcriptomes. Gene profiles of Yunong 201 and 3114 were obtained by de novo sequencing. Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) were analyzed. This study provided important information to further understand the transcriptome of hexaploid wheat and determine the wheat-specific genes related to grain size.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials
A Chinese winter wheat cultivar Yunong 201 showing outstanding dry, white noodle quality was treated by 1.0% EMS (0.1 mol/L Na2HPO4 ⋅12H2O, pH 7.0). An elite M2 line was screened from the EMS-mutagenized population encompassing 2000 lines because of its longer kernel length and higher grain weight; this line was self-crossed for three times into a M5 line Yunong 3114. Yunong 201 and its derived line Yunong 3114 were planted and grown at the Zhengzhou Scientific Research and Education Center of Henan Agricultural University during 2011–2012 cropping seasons under non-stressed conditions. Grains were collected at different developmental stages from both lines at 7, 14, 21, 28, and 35 days after flowering, and mature seeds (stored 1 year at 4°C after harvested); pooled samples were obtained by mixing eighteen grains from three spikes of each wheat strain at each developmental stage mentioned above; these samples were used for the generation of small RNA libraries of Yunong 201 and 3114.
RNA Sequencing
The total RNA of each sample was extracted with Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Full-length cDNAs were synthesized with a TruSeq RNA Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina), according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The cDNA libraries were sequenced on Illumina Hiseq 2000, according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A 10 Gb raw reads were obtained from each cDNA library, and a total of 120 Gb raw reads were generated from the different developmental staged seeds of Yunong 201 and 3114.
Pretreatment of Data and Development of Unigenes
Raw reads were first trimmed by using SeqClean1 86–64, Newbler 2.5.3 (Kumar and Blaxter, 2010), and Lucy 1.20p (Chou and Holmes, 2001) to remove low-quality reads, vector sequences, and reads whose length was less than 50 bp. The trimmed reads were subjected to polygenetic analysis with CD-HIT version 4.0 (Huang et al., 2010) at a sequence identity threshold of 99%. Possible contaminated sequences were removed by aligning to the NT library. The trimmed non-redundant reads were assembled to contigs by Newbler 2.5.3. One or more contigs were assembled to isotigs. A total of 12 groups of isotigs were developed from the small RNA libraries of Yunong 201 and 3114.
Discovery of SNV
All SNVs of Yunong 201 and 3114 were obtained based on the wheat reference sequence mapping (URGI)2 (He et al., 2014). We focused on the sites with non-synonymous mutation. EMS treatment can trigger high-density point mutation on wheat material. We selected the mutation sites occurring in all samples. To explore the different biological mechanisms between Yunong 201 and 3114, three SNV types were significant. The first SNV type was that the mutation sites were same between Yunong 201 and 3114, and the mutation was non-synonymous as compared with reference sequence, but the nucleotides after mutation were different between Yunong 201 and 3114, we considered this mutation significant. The second type was that the nucleotides of Yunong 201 were changed into other nucleotides, but the nucleotides of Yunong 3114 were still the same as the reference sequence. The third SNV indicated that mutation occurred specifically in Yunong 3114, but not in Yunong 201. Thus, we studied the same and different mutation sites between Yunong 201 and Yunong 3114.
Sequence Annotation
Isotigs and singlets sequences were subjected to polygenetic analysis by CD-HIT version 4.0 (Huang et al., 2010) with an identity of 95%. Chromosome mapping and comparison with known genome segments were also performed. Using the BLAST program (Camacho et al., 2009) (a searched threshold of 1e–10), we searched for unigenes in EST libraries of 10 species related to NCBI3 and DFCI4. Nucleotides and protein were separately annotated by comparing the unigenes with those in the NT library (E-value < 1e–5) and the NR library (BLASTX; E-value < 1e–5; similarity of protein >30%). Moreover, we also annotated the sequences based on the wheat sequence database of French National Institute for Agricultural Research5 (INRA). We mainly referenced the sequence of T. aestivum chromosome 3B (ta3b, genomic scaffold, cultivar Chinese Spring) in URGI.
Functional Annotation
We identified the annotated unigene sequences for the possible functions through the Gene Ontology Consortium6. Sequences were mapped to the reference authoritative pathways in Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG)7 to determine the active biological pathways in annotated unigene sequences.
Heat Map Analysis
Heat map is shown for preliminary SNV gene expression (logFoldChange) in the mutant strain at different developmental stages with respect to the wild type. Heat map was generated via Microsoft Excel, and logFold-Change values were used. The highest, medium, and lowest values are shown in color red, black, and green, respectively.
Results
Investigation of Agronomic Traits in Yunong 201 and 3114
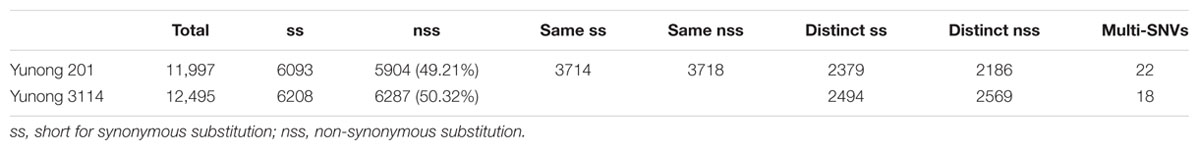
Wheat strain Yunong 3114 showed longer kernel length, higher grain weights, and higher yield compared with Yunong 201 (data not shown); the former did not also show obvious difference on kernel width (detailed data in Figure 1). Therefore, the higher grain weight of Yunong 3114 resulted from its relatively longer kernel length than that of Yunong 201. The grains with different developmental stages at 7, 14, 21, 28, and 35 days after flowering, and mature seeds (stored 1 year at 4°C after harvested) were collected from both lines; these grains were used to generate six pairs of small RNA libraries of Yunong 201 and 3114 for sequencing. Transcriptomes of both Yunong 201 and 3114 were obtained for the SNVs analysis.
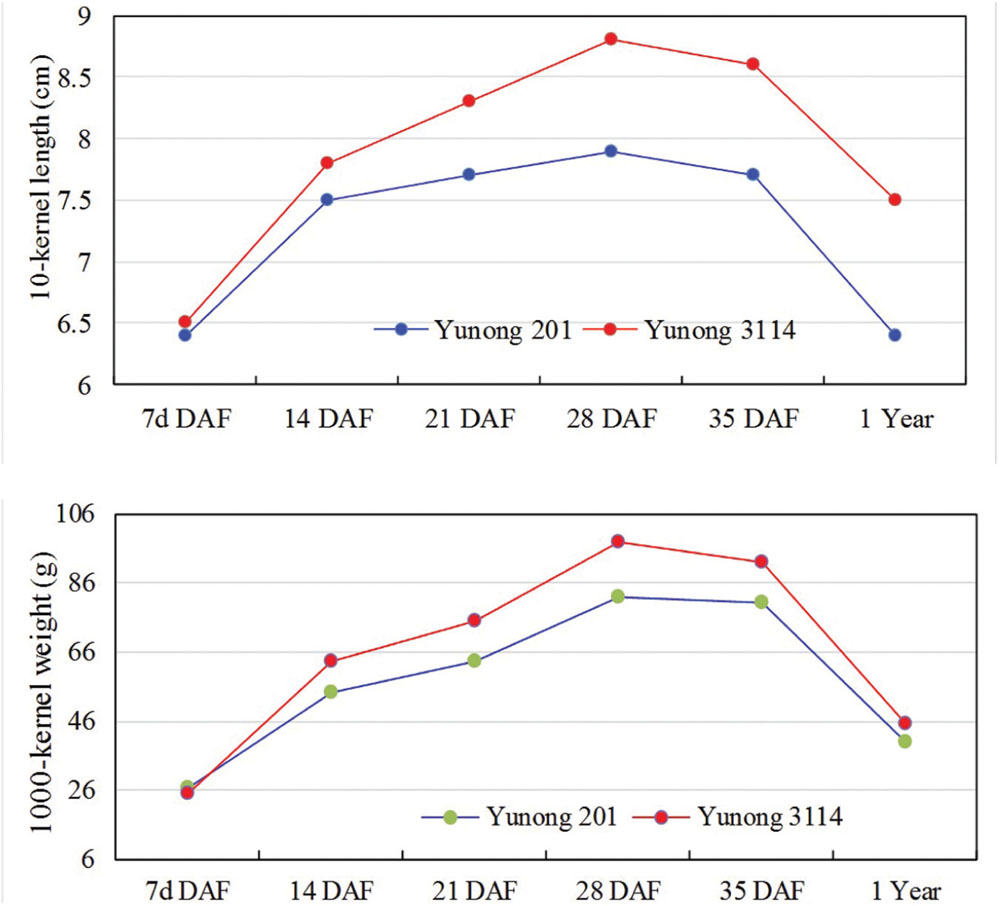
FIGURE 1. Kernel size parameters of Yunong 201 and 3114 during six seed developmental stages. DAF, days after flowering.
Discovery of SNVs in Yunong 201 and 3114
As the wheat reference sequence in URGI (Unité de Recherche Génomique Info)8 was mapped, SNVs in both Yunong 201 and 3114 were detected. A large number of genetic variations were identified across the transcriptomes of both strains, including non-synonymous, synonymous, stop–gain, stop–loss, and stop–stop SNVs (Figure 2). To maintain data credibility, the non-synonymous SNVs that could be simultaneously annotated in reference sequence were analyzed. Non-synonymous SNVs accounted for 49.21% (5904) and 50.32% (6287) in Yunong 201 and 3114 of overall variations occurring in CDS regions, respectively (Table 1). A total of 7432 same mutated positions in Yunong 201 and 3114 were also observed, including 3714 synonymous SNVs and 3718 non-synonymous SNVs. Yunong 3114 had 2569 distinct non-synonymous SNVs, and Yunong 201 had 2186 distinct non-synonymous SNVs as compared to reference sequence (Table 1). Furthermore, one SNV site may induce both synonymous and non-synonymous mutations that were acted as the multi-SNVs. A total of 22 and 18 multi-SNVs in Yunong 201 and 3114 were recorded, respectively.
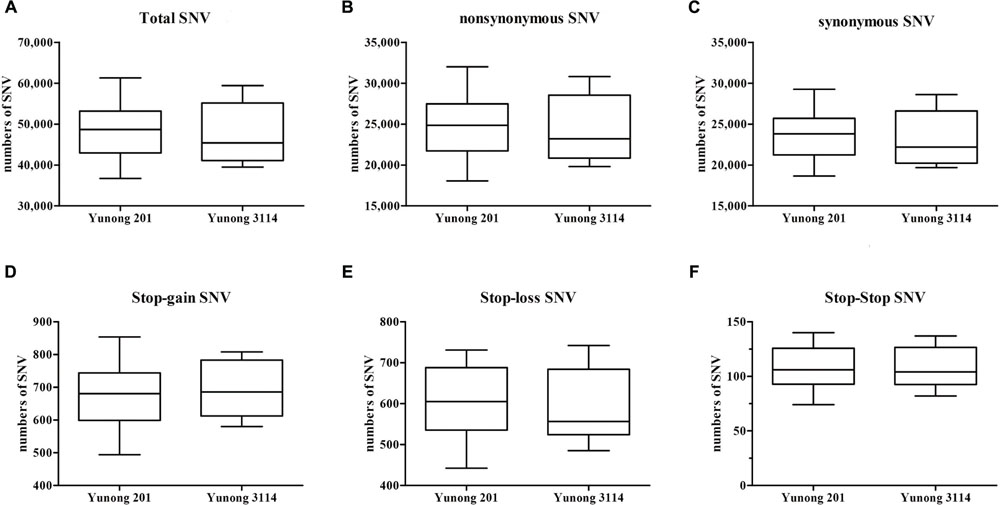
FIGURE 2. Single nucleotide variants (SNVs) between Yunong 201 and 3114. (A–C) The total SNV, non-synonymous, and synonymous SNVs in Yunong 201 and 3114. (D–F) Three specific kinds of SNVs, namely, stop–gain, stop–loss, and stop–stop.
Ethyl methanesulfonate preferentially induces G residues alkylation, thereby resulting in many G→A and C→T transitions [CG→TA; (Greene et al., 2003; Till et al., 2007; Tsai et al., 2011; Monson-Miller et al., 2012)]. Thus, in accordance with previous findings, C→T and G→A transitions were the most prevalent patterns of nucleotide substitutions (Figure 3A; Supplementary Figure S1), and the total GC content of Yunong 201 was higher than that of Yunong 3114. Based on the reference wheat sequence, the transitions were higher than transversions both in Yunong 201 and in 3114 (Figures 3B,C). Moreover, the mutations in the first and second codes were significantly more frequent than the third code, both in Yunong 201 and 3114. Our data indicated that the genetic variations were significantly different between the Yunong wheat strains and reference sequence; meanwhile, the difference was smaller between Yunong 201 and 3114, which is mainly because Yunong 3114 was derived from Yunong 201.
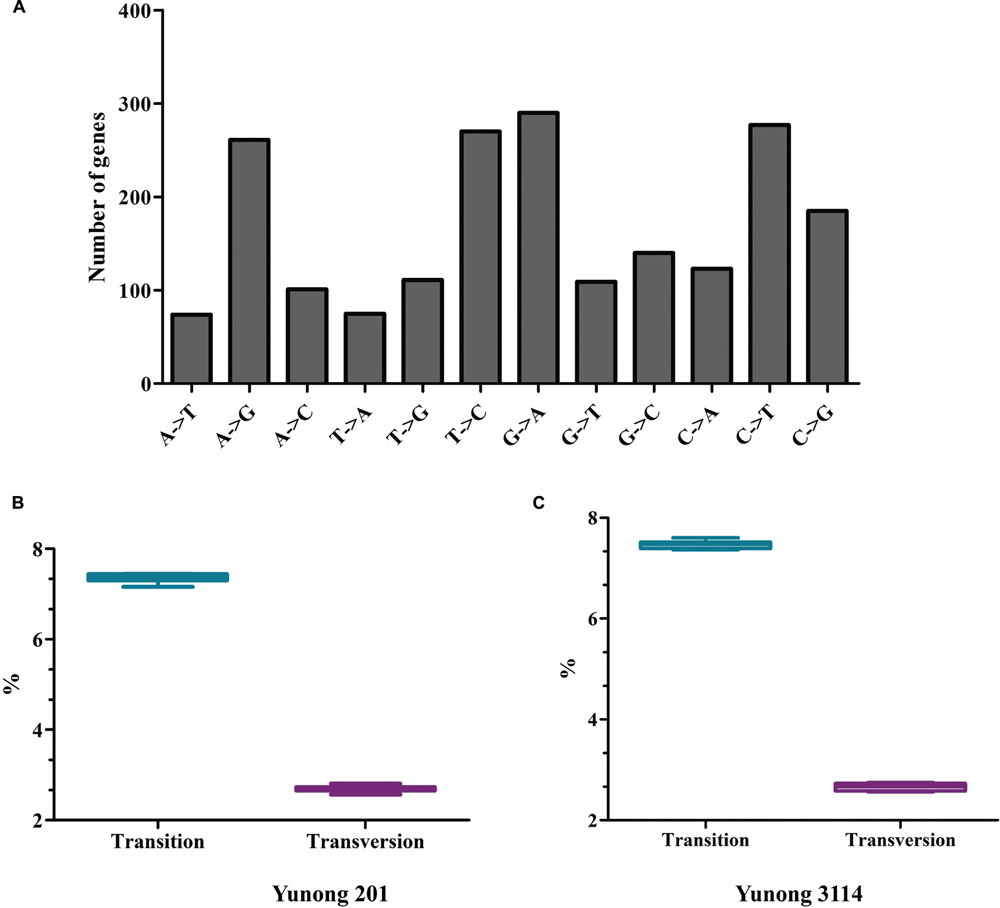
FIGURE 3. Patterns of nucleotide substitution for Yunong 201 and 3114 based on reference sequence. (A) Number of genes with different type of nucleotide substitution. (B,C) Percentage (%) of transition and transversion substitutions in Yunong 201 and Yuong 3114. Unpaired t-test was used, P-value < 0.0001.
SNVs and Gene Functional Analysis
Based on the reference sequence, a total of 4021 genes with SNVs were acquired, and most genes have one mutated position (Figure 4). A total of 1147 genes in Yunong 201 had one mutant position where 576 genes underwent a non-synonymous mutation (Figure 4). Meanwhile, a total of 1167 genes had one SNV positions in Yunong 3114, 564 of which had a non-synonymous mutation. We also detected 4755 non-synonymous SNVs and 1168 genes with non-synonymous mutations by comparing Yunong 3114 with Yuong 201 (Table 2). Moreover, genes carrying transistions were more than those undergone to transversions (Figure 5). SNVs were distributed in different scaffolds and contigs of the reference genome. EMS-induced mutagenesis produces high mutant rate in plant. Therefore, we also analyzed the mutagenesis frequencies (Figure 6). However, the mutation sites were distributed atypically across the transcriptome (Figure 6; Supplementary Figure S2). The mutant gene numbers in different mutation patterns were determined, as shown in Supplementary Figure S3.
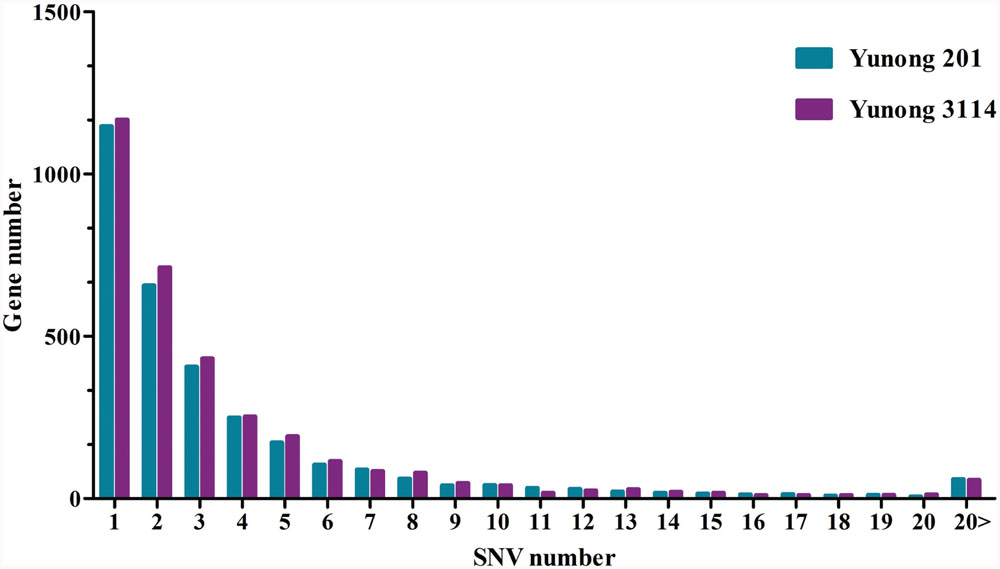
FIGURE 4. Relationship between SNV and genes in Yunong 201 and 3114 based on the reference sequence. The x axis represents the number of SNV mutations on a single gene sequence. The y axis showed number of genes with SNVs. The number of genes with one SNV ranks as the top.
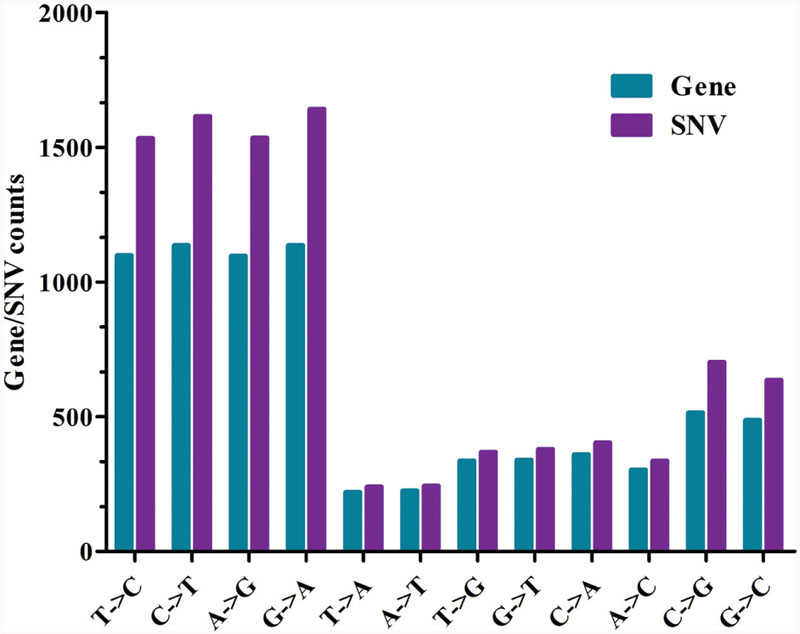
FIGURE 5. Mutation analysis in Yunong 3114 and 201. The x axis indicates the type of mutations; the y axis represents the number of mutant genes or number of SNVs.
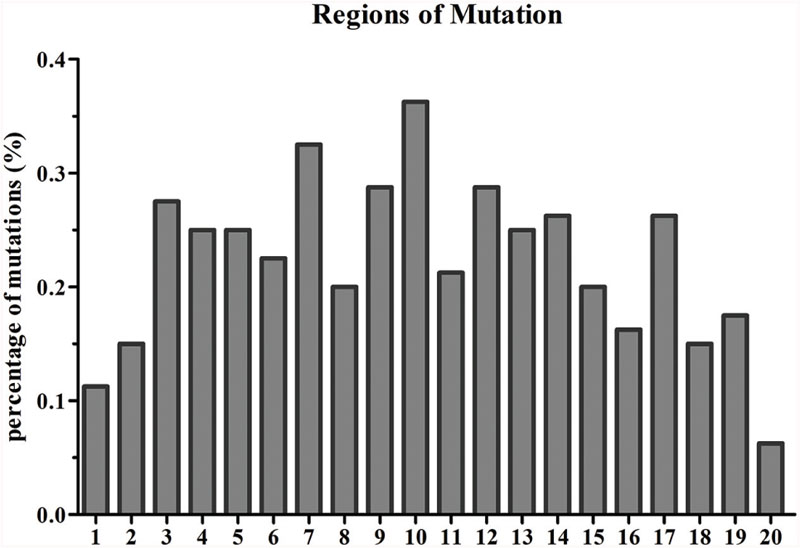
FIGURE 6. Single nucleotide variant regions in the gene. A gene was equally divided into 20 regions, the percentage of mutant in each region was statistically calculated. The y axis showed the percentage of mutant; the x axis represented the gene regions.
All the mutant genes with G to A or C to T transitions in the mutant strain compared with Yunong 201 were extracted; function annotation and enrichment analyses were performed. These genes were annotated in ATP binding, zinc ion binding, and nucleotide binding (Figure 7A); they were also mainly enriched in components, such as intracellular membrane-bound and intracellular organelles (Figure 7B); moreover, their functions were enriched in cellular protein metabolic process, modification-dependent macromolecule catabolic process, and cellular protein catabolic process (Figure 7C). The preliminary expression levels of these mutant genes were also analyzed by heat map analysis (Figure 8). For all the six developmental stages, most of these mutant genes were significantly differentially expressed, which indicated that the SNVs on these genes might be associated with the longer kernel length and higher kernel weight of Yunong 3114.
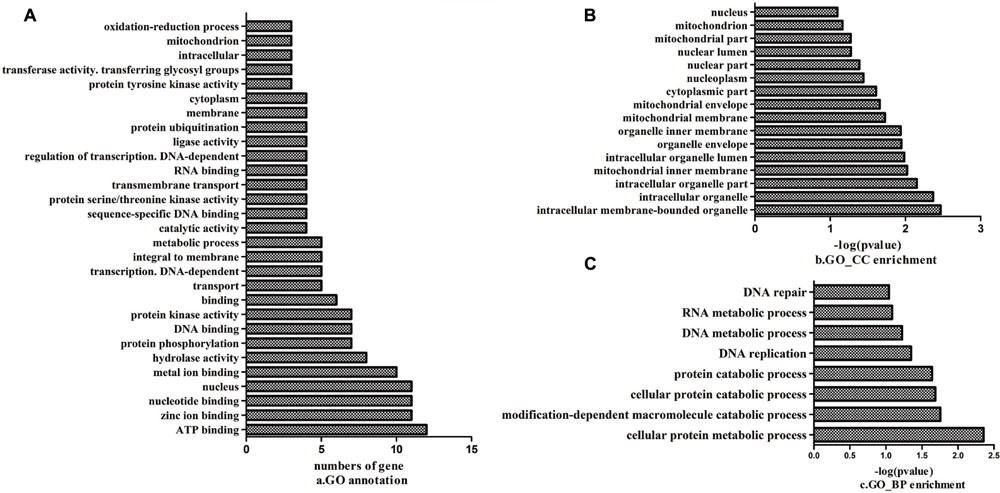
FIGURE 7. Function annotation and enrichment for the genes with G→A and/or C→T mutations. (A) The annotated biological processes; (B) The enrichment of cellular component; (C) The enrichment of biological process.

FIGURE 8. Preliminary Expression of genes with mutations of G->A and/or C->T between Yunong 201 and Yunong 3114 in different days. Horizontal axis represent the genes and vertical axis represent the time. The preliminary expression level for a gene in some days was described by the grids, which was calculated by the logFC (FC stands for ‘fold change’). The change of color from green to red represents the expression value from the low to high.
Discussion
Next-generation sequencing has been applied in many species, specifically in crop breeding, to explore genomic variations for investigating population evolutionary history, discovering marker-trait linkages, and genetic cause of phenotype variation. EMS-induced mutagenesis is one of the most effective, reliable, powerful, and frequently used technologies in plant. In the present study, Illumina (Solexa) NGS technology was applied to obtain the transcriptomes of bread wheat strain Yunong 201 and its EMS mutant line Yunong 3114. We comprehensively analyzed the SNVs and their impact on genes in Yunong 3114. Our data demonstrated that transcriptomes could also be used for SNV analysis, and a set of SNVs had significant impact on the expression levels of the mutant genes, potentially associated with the superior traits such as the longer kernel length and higher kernel weight of Yunong 3114. However, further validations are necessary.
Non-synonymous SNVs in Yunong 3114 and 201
Non-synonymous changes directly determine the amino acid change and further affect protein structure, stability, or location. Thus, the identification of non-synonymous sequence variations that can potentially affect gene or protein functionality is the focus of the current study. Stop–gain SNVs may lead to functional consequences due to protein truncation, transcript degradation, and dominant negative influences of protein species (Nagy and Maquat, 1998). The stop–loss non-synonymous SNVs of Yunong 3114 were also significantly less than that of Yunong 201. Current computational methods estimating loss-of-function in genes carrying variants are based on evolutionary conservation and functional redundancy on gene level (Rausell et al., 2014). For all non-synonymous SNVs, [A/G] and [T/C] are the most common base changes both in Yunong 201 and 3114, which agrees with the results of previous studies in legume species (Hand et al., 2008; Deulvot et al., 2010; Gaur et al., 2012; Leonforte et al., 2013). The nucleotide substitution in the first code in Yunong 3114 was significantly more frequent than in Yunong 201. Increased divergence in nucleotide composition shows a corresponding, predictable change in the amino acid compositions of the encoded proteins (Wang et al., 2004). Efficient transcription or mRNA processing is responsible for the high expression of GC-rich genes (Kudla et al., 2006). In early replicating regions, G and C nucleotides are more often misincorporated (Eyre-Walker and Hurst, 2001; Muyle et al., 2011). The distribution of GC content is a remarkable characteristic of genome organization that is often associated with many genomic features, such as meiotic recombination, gene density, and gene length (Mouchiroud et al., 1991; Duret et al., 1995; Duret and Arndt, 2008).
SNVs Impact on Gene Functionality
Most genes had one to three SNV positions both in Yunong 201 and 3114. The genes that underwent non-synonymous SNVs were significantly involved in ATP binding and metal and zinc ion binding; they specifically regulated protein kinase activity, protein phosphorylation, cellular protein metabolic process, and modification-dependent macromolecular catabolic process. Metal ions are crucial elements in enzymatic reaction events in all photosynthetic organisms, such as cyanobacteria, algae, and plants. Metal ions play important roles in maintaining substrate binding in the active site of metalloenzymes and controlling the redox activity of metalloenzymes in enzymatic reaction (Pospisil, 2014). Some oxidoreductases are also important in the metabolic responses. Protein phosphorylation and protein kinase activity play important roles in the regulation of carbon and nitrogen metabolite production in plants (Huber, 2007). Therefore, SNVs in Yunong 3114 may have impact on these metabolic processes, subsequently influencing the metabolism, energy or nutrient accumulation, and grain growth.
We also analyzed and compared the non-synonymous SNVs of the genes associated with these biological processes in both Yunong 201 and 3114. Some SNVs only occurred in Yunong 3114, and these SNVs potentially implicated the relatively superior trait. If the genomic architectures of the traits studied are highly complex, dozens or even hundreds of causative polymorphisms with minor effects may exist across the genome. For example, SNVs on genes of protein phosphatase 5 (PP5), glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase (GDPD), dephospho-CoA kinase, and alkylated DNA repair protein alkB homolog 1, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2, and ABA responsive element binding factor may have impact on wheat gene function, thus may result in changes on biological process associated with grain size. It has been reported that Arabidopsis protein phosphatase 5 (AtPP5) performs multi enzymatic activities such as biologically active photoreceptor and protein phosphatase activity (Ryu et al., 2005). The AtPP5 is capable to form a complex with AtHsp90 under heat shock conditions, enhancing thermotolerance in Arabidopsis (Park et al., 2012). Arabidopsis SNC4 encodes a receptor-like kinase with two predicted extracellular GDPD domains and also plays a role as resistance protein (Bi et al., 2010). Another Arabidopsis protein shaven3 also has two tandemly repeated GDPD-like domains which were suggested to be involved in primary cell wall organization (Hayashi et al., 2008). The ABA responsive element binding factor has been found in rice such as OsABF1 (Oryza sativa ABA responsive element binding factor 1) gene which is involved in abiotic stress responses and ABA signaling in rice (Amir Hossain et al., 2010), and OREB1 whose phosphorylation plays important roles in regulating signal integration in the complex stress signaling network of plant cells (Hong et al., 2011). SNVs distributed in these genes might trigger alterations on the secondary structure of proteins that possibly impacts the subsequent functions (such as DNA binding and transcriptional activity) of target genes involved in multiple agronomic traits in wheat. The clues obtained from this study could facilitate the further illustration of gene function with the non-synonymous SNVs between Yunong 201 and 3114.
Conclusion
The current study analyzed the SNVs on transcriptome levels of bread wheat Yunong 201 and its EMS mutagenesis strain Yunong 3114. Our data provided useful information on wheat transcriptome by presenting new resources that could be used in future studies on wheat functional genomics. In addition, detecting new genetic variation for wheat and further information on gene functions that eventually generate new phenotypic variation provide insight into wheat breeding program.
Author Contributions
FC designed the project. FC, ZZ, and XZ performed RNA-seq experiments. FC wrote the paper. FC, ZD, YY, and DC performed the computational analyses.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by the 973 projects (2014CB160303 and 2014CB138105), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-13-0776) of China, and Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province (14IRTSTHN010).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpls.2016.01193
FIGURE S1 | Patterns of nucleotide substitution in the SNVs of Yunong 201 and 3114 based on the reference genome. (A) Nucleotide substitutions of the SNVs for Yunong 201; (B) Nucleotide substitutions of the SNVs for Yunong 3114.
FIGURE S2 | Different SNVs of 18 functional genes between Yunong 201 and 3114. Boxes with letters show the mutant positions.
FIGURE S3 | Mutant gene numbers in different mutation patterns in both Yunong 201 and 3114.
Footnotes
- ^ http://sourceforge.net/projects/seqclean/
- ^ https://urgi.versailles.inra.fr/blast/blast.php
- ^ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
- ^ ftp://occams.dfci.harvard.edu/pub/bio/tgi/data
- ^ https://urgi.versailles.inra.fr/blast/blast.php
- ^ http://www.geneontology.org/
- ^ http://www.genome.jp/kegg/
- ^ https://urgi.versailles.inra.fr/
References
Amir Hossain, M., Lee, Y., Cho, J. I., Ahn, C. H., Lee, S. K., Jeon, J. S., et al. (2010). The bZIP transcription factor OsABF1 is an ABA responsive element binding factor that enhances abiotic stress signaling in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. 72, 557–566. doi: 10.1007/s11103-009-9592-9
Bi, D., Cheng, Y. T., Li, X., and Zhang, Y. (2010). Activation of plant immune responses by a gain-of-function mutation in an atypical receptor-like kinase. Plant Physiol. 153, 1771–1779. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.158501
Brenchley, R., Spannagl, M., Pfeifer, M., Barker, G. L., D’Amore, R., Allen, A. M., et al. (2012). Analysis of the bread wheat genome using whole-genome shotgun sequencing. Nature 491, 705–710. doi: 10.1038/nature11650
Breseghello, F., and Sorrells, M. E. (2006). Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172, 1165–1177. doi: 10.1534/genetics.105.044586
Camacho, C., Coulouris, G., Avagyan, V., Ma, N., Papadopoulos, J., Bealer, K., et al. (2009). BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10:421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Chou, H. H., and Holmes, M. H. (2001). DNA sequence quality trimming and vector removal. Bioinformatics 17, 1093–1104. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/17.12.1093
Deulvot, C., Charrel, H., Marty, A., Jacquin, F., Donnadieu, C., Lejeune-Henaut, I., et al. (2010). Highly-multiplexed SNP genotyping for genetic mapping and germplasm diversity studies in pea. BMC Genomics 11:468. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-468
Duan, J., Xia, C., Zhao, G., Jia, J., and Kong, X. (2012). Optimizing de novo common wheat transcriptome assembly using short-read RNA-Seq data. BMC Genomics 13:392. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-392
Duret, L., and Arndt, P. F. (2008). The impact of recombination on nucleotide substitutions in the human genome. PLoS Genet. 4:e1000071. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000071
Duret, L., Mouchiroud, D., and Gautier, C. (1995). Statistical analysis of vertebrate sequences reveals that long genes are scarce in GC-rich isochores. J. Mol. Evol. 40, 308–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00163235
Eyre-Walker, A., and Hurst, L. D. (2001). The evolution of isochores. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 549–555. doi: 10.1038/35080577
Fan, C., Xing, Y., Mao, H., Lu, T., Han, B., Xu, C., et al. (2006). GS3, a major QTL for grain length and weight and minor QTL for grain width and thickness in rice, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Theor. Appl. Genet. 112, 1164–1171. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0218-1
Feiz, L., Martin, J. M., and Giroux, M. J. (2009). Creation and functional analysis of new Puroindoline alleles in Triticum aestivum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 118, 247–257. doi: 10.1007/s00122-008-0893-1
Gaur, R., Azam, S., Jeena, G., Khan, A. W., Choudhary, S., Jain, M., et al. (2012). High-throughput SNP discovery and genotyping for constructing a saturated linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). DNA Res. 19, 357–373. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dss018
Goff, S. A., Ricke, D., Lan, T. H., Presting, G., Wang, R., Dunn, M., et al. (2002). A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296, 92–100. doi: 10.1126/science.1068275
Greene, E. A., Codomo, C. A., Taylor, N. E., Henikoff, J. G., Till, B. J., Reynolds, S. H., et al. (2003). Spectrum of chemically induced mutations from a large-scale reverse-genetic screen in Arabidopsis. Genetics 164, 731–740.
Hand, M. L., Ponting, R. C., Drayton, M. C., Lawless, K. A., Cogan, N. O., Charles Brummer, E., et al. (2008). Identification of homologous, homoeologous and paralogous sequence variants in an outbreeding allopolyploid species based on comparison with progenitor taxa. Mol. Genet. Genomics 280, 293–304. doi: 10.1007/s00438-008-0365-y
Hayashi, S., Ishii, T., Matsunaga, T., Tominaga, R., Kuromori, T., Wada, T., et al. (2008). The glycerophosphoryl diester phosphodiesterase-like proteins SHV3 and its homologs play important roles in cell wall organization. Plant Cell Physiol. 49, 1522–1535. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcn120
He, Q., He, Q., Liu, X., Wei, Y., Shen, S., Hu, X., et al. (2014). Genome-wide prediction of cancer driver genes based on SNP and cancer SNV data. Am. J. Cancer Res. 4, 394–410.
Henikoff, S., Till, B. J., and Comai, L. (2004). TILLING. Traditional mutagenesis meets functional genomics. Plant Physiol. 135, 630–636. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.041061
Hong, J. Y., Chae, M. J., Lee, I. S., Lee, Y. N., Nam, M. H., Kim, D. Y., et al. (2011). Phosphorylation-mediated regulation of a rice ABA responsive element binding factor. Phytochemistry 72, 27–36. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2010.10.005
Huang, Y., Niu, B., Gao, Y., Fu, L., and Li, W. (2010). CD-HIT Suite: a web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 26, 680–682. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq003
Huber, S. C. (2007). Exploring the role of protein phosphorylation in plants: from signalling to metabolism. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 35(Pt 1), 28–32. doi: 10.1042/BST0350028
Kudla, G., Lipinski, L., Caffin, F., Helwak, A., and Zylicz, M. (2006). High guanine and cytosine content increases mRNA levels in mammalian cells. PLoS Biol. 4:e180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.0040180
Kumar, S., and Blaxter, M. L. (2010). Comparing de novo assemblers for 454 transcriptome data. BMC Genomics 11:571. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-571
Kyndt, T., Denil, S., Haegeman, A., Trooskens, G., De Meyer, T., Van Criekinge, W., et al. (2012). Transcriptome analysis of rice mature root tissue and root tips in early development by massive parallel sequencing. J. Exp. Bot. 63, 2141–2157. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err435
Leonforte, A., Sudheesh, S., Cogan, N. O., Salisbury, P. A., Nicolas, M. E., Materne, M., et al. (2013). SNP marker discovery, linkage map construction and identification of QTLs for enhanced salinity tolerance in field pea (Pisum sativum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 13:161. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-161
Li, Y., Fan, C., Xing, Y., Jiang, Y., Luo, L., Sun, L., et al. (2011). Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat. Genet. 43, 1266–1269. doi: 10.1038/ng.977
Ling, H. Q., Zhao, S., Liu, D., Wang, J., Sun, H., Zhang, C., et al. (2013). Draft genome of the wheat A-genome progenitor Triticum urartu. Nature 496, 87–90. doi: 10.1038/nature11997
Lu, J., Chang, C., Zhang, H.-P., Wang, S.-X., Sun, G., Xiao, S.-H., et al. (2015). Identification of a novel allele of TaCKX6a02 associated with grain size, filling rate and weight of common wheat. PLoS ONE 10:e0144765. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144765
Mao, H., Sun, S., Yao, J., Wang, C., Yu, S., Xu, C., et al. (2010). Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 19579–19584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014419107
Marioni, J. C., Mason, C. E., Mane, S. M., Stephens, M., and Gilad, Y. (2008). RNA-seq: an assessment of technical reproducibility and comparison with gene expression arrays. Genome Res. 18, 1509–1517. doi: 10.1101/gr.079558.108
McCallum, C. M., Comai, L., Greene, E. A., and Henikoff, S. (2000). Targeting induced local lesions IN genomes (TILLING) for plant functional genomics. Plant Physiol. 123, 439–442. doi: 10.1104/pp.123.2.439
Monson-Miller, J., Sanchez-Mendez, D. C., Fass, J., Henry, I. M., Tai, T. H., and Comai, L. (2012). Reference genome-independent assessment of mutation density using restriction enzyme-phased sequencing. BMC Genomics 13:72. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-72
Mouchiroud, D., D’Onofrio, G., Aissani, B., Macaya, G., Gautier, C., and Bernardi, G. (1991). The distribution of genes in the human genome. Gene 100, 181–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90364-H
Muyle, A., Serres-Giardi, L., Ressayre, A., Escobar, J., and Glemin, S. (2011). GC-biased gene conversion and selection affect GC content in the Oryza genus (rice). Mol. Biol. Evol. 28, 2695–2706. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr104
Nagy, E., and Maquat, L. E. (1998). A rule for termination-codon position within intron-containing genes: when nonsense affects RNA abundance. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23, 198–199. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0004(98)01208-0
Park, J. H., Kim, W. Y., Chae, H. B., Kim, M. G., and Lee, S. Y. (2012). Serine/threonine protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) interacts with substrate under heat stress conditions and forms protein complex in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal. Behav. 7, 535–538. doi: 10.4161/psb.19699
Pfeifer, M., Kugler, K. G., Sandve, S. R., Zhan, B., Rudi, H., Hvidsten, T. R., et al. (2014). Genome interplay in the grain transcriptome of hexaploid bread wheat. Science 345, 1250091. doi: 10.1126/science.1250091
Pingault, L., Choulet, F., Alberti, A., Glover, N., Wincker, P., Feuillet, C., et al. (2015). Deep transcriptome sequencing provides new insights into the structural and functional organization of the wheat genome. Genome Biol. 16, 29. doi: 10.1186/s13059-015-0601-9
Pospisil, P. (2014). The role of metals in production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in photosystem II. Plant Cell Physiol. 55, 1224–1232. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu053
Rausell, A., Mohammadi, P., McLaren, P. J., Bartha, I., Xenarios, I., Fellay, J., et al. (2014). Analysis of stop-gain and frameshift variants in human innate immunity genes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 10:e1003757. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003757
Ryu, J. S., Kim, J. I., Kunkel, T., Kim, B. C., Cho, D. S., Hong, S. H., et al. (2005). Phytochrome-specific type 5 phosphatase controls light signal flux by enhancing phytochrome stability and affinity for a signal transducer. Cell 120, 395–406. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.12.019
Schreiber, A. W., Hayden, M. J., Forrest, K. L., Kong, S. L., Langridge, P., and Baumann, U. (2012). Transcriptome-scale homoeolog-specific transcript assemblies of bread wheat. BMC Genomics 13:492. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-492
Slade, A. J., McGuire, C., Loeffler, D., Mullenberg, J., Skinner, W., Fazio, G., et al. (2012). Development of high amylose wheat through TILLING. BMC Plant Biol. 12:69. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-69
Song, X. J., Huang, W., Shi, M., Zhu, M. Z., and Lin, H. X. (2007). A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat. Genet. 39, 623–630. doi: 10.1038/ng2014
Tanaka, T., Kobayashi, F., Joshi, G. P., Onuki, R., Sakai, H., Kanamori, H., et al. (2014). Next-generation survey sequencing and the molecular organization of wheat chromosome 6B. DNA Res. 21, 103–114. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dst041.
The International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium [IWGSC] (2014). A chromosome-based draft sequence of the hexaploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) genome. Science 345:1251788. doi: 10.1126/science.1251788
Till, B. J., Cooper, J., Tai, T. H., Colowit, P., Greene, E. A., Henikoff, S., et al. (2007). Discovery of chemically induced mutations in rice by TILLING. BMC Plant Biol. 7:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-7-19
Tsai, H., Howell, T., Nitcher, R., Missirian, V., Watson, B., Ngo, K. J., et al. (2011). Discovery of rare mutations in populations: TILLING by sequencing. Plant Physiol. 156, 1257–1268. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.169748
Uauy, C., Paraiso, F., Colasuonno, P., Tran, R. K., Tsai, H., Berardi, S., et al. (2009). A modified TILLING approach to detect induced mutations in tetraploid and hexaploid wheat. BMC Plant Biol. 9:115. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-9-115
Wang, E., Wang, J., Zhu, X., Hao, W., Wang, L., Li, Q., et al. (2008). Control of rice grain-filling and yield by a gene with a potential signature of domestication. Nat. Genet. 40, 1370–1374. doi: 10.1038/ng.220
Wang, H. C., Singer, G. A., and Hickey, D. A. (2004). Mutational bias affects protein evolution in flowering plants. Mol. Biol. Evol. 21, 90–96. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msh003
Wang, S., Wu, K., Yuan, Q., Liu, X., Liu, Z., Lin, X., et al. (2012). Control of grain size, shape and quality by OsSPL16 in rice. Nat. Genet. 44, 950–954. doi: 10.1038/ng.2327
Wang, Y., Cheng, X., Shan, Q., Zhang, Y., Liu, J., Gao, C., et al. (2014). Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew. Nat. Biotechnol. 32, 947–951. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2969
Wang, Z., Gerstein, M., and Snyder, M. (2009). RNA-Seq: a revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 57–63. doi: 10.1038/nrg2484
Weng, J., Gu, S., Wan, X., Gao, H., Guo, T., Su, N., et al. (2008). Isolation and initial characterization of GW5, a major QTL associated with rice grain width and weight. Cell Res. 18, 1199–1209. doi: 10.1038/cr.2008.307
Wu, Q. H., Chen, Y. X., Zhou, S. H., Fu, L., Chen, J. J., Xiao, Y., et al. (2015). High-density genetic linkage map construction and QTL mapping of grain shape and size in the wheat population Yanda1817 x Beinong6. PLoS ONE 10:e0118144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118144
Zanke, C. D., Ling, J., Plieske, J., Kollers, S., Ebmeyer, E., Korzun, V., et al. (2015). Analysis of main effect QTL for thousand grain weight in European winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by genome-wide association mapping. Front. Plant Sci. 6:644. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00644
Keywords: wheat, ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS), mutation, next-generation sequencing, transcriptome, single nucleotide variations (SNVs)
Citation: Chen F, Zhu Z, Zhou X, Yan Y, Dong Z and Cui D (2016) High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals Single Nucleotide Variants in Longer-Kernel Bread Wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 7:1193. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01193
Received: 24 February 2016; Accepted: 25 July 2016;
Published: 08 August 2016.
Edited by:
Chengdao Li, Murdoch University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Andrea Mazzucato, Tuscia University, ItalyZhongfu Ni, China Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2016 Chen, Zhu, Zhou, Yan, Dong and Cui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Feng Chen, Y2hmMDA4OEAxNjMuY29t
 Feng Chen
Feng Chen Zibo Zhu
Zibo Zhu