- Department of Agricultural Biology, National Institute of Agricultural Sciences, Rural Development Administration, Jeonju, Republic of Korea
Plant synthetic biology is rapidly emerging as an innovative approach to solving complex problems in human health and agriculture. Although conventional metabolic engineering primarily focuses on microbial systems for large-scale biomolecules production, these platforms often face limitations in expressing plant-derived enzymes and synthesizing structurally complex molecules. In contrast, recent advances in plant synthetic biology have integrated multidisciplinary tools, from molecular biology and biochemistry to synthetic circuit design and computational modeling, to engineer plant systems with enhanced traits. These include improved yield, nutritional quality, environmental resilience, and synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant functional biomolecules. This review focuses on the fundamental technologies that have enabled such advances, which include DNA synthesis, programmable gene circuits, and CRISPR/Cas-based genome editing. We discussed recent applications of reprogramming plant metabolic pathways and existing obstacles, such as transformation efficiency, regulatory bottlenecks, and pathway instability. This review provides key case studies and a forward-looking perspective on the evolution of plant synthetic biology as a robust foundation for sustainable biomanufacturing and production of functional biomolecules.
Introduction
In recent decades, synthetic biology has emerged as a transformative approach for engineering biological systems to address the global challenges in agriculture, medicine, and bioenergy (Rizzo et al., 2023). Initially, the field focused on using genetically tractable microbial platforms such as Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce valuable plant natural products (PNPs) (Martin et al., 2003). These microbial systems enable the efficient screening of enzyme combinations and pathway reconstruction. For example, terpenoid precursors have been successfully produced in E. coli by engineering the mevalonate pathway (Martin et al., 2003), which has enabled scalable biosynthesis of plant natural products through synthetic regulatory circuits and dynamic control elements. Despite their utility, microbial systems in synthetic biology face challenges such as the toxicity of target compounds, which can impair cell growth, stability, and yield (Han and Miao, 2024), as well as suboptimal metabolic flux and inherent limitations in biosynthetic capacity (Kim et al., 2025). Moreover, microbial systems, particularly prokaryotes, face significant limitations in synthetic biology due to their inability to perform complex eukaryotic post-translational modifications, which hinders the production of properly modified proteins (Brunk et al., 2018). Challenges also arise in producing plant-derived metabolites because of metabolic burden and the absence of necessary biosynthetic pathways (Wu et al., 2016).
Plant-based chassis is gaining recognition as a vital platform in synthetic biology because it naturally accommodates intricate metabolic networks, compartmentalized enzymatic processes, and unique plant biochemical environments that are challenging to replicate entirely in microbial systems (Han and Miao, 2024). This integration facilitates the production of structurally complex metabolites that are otherwise difficult to replicate (Lin et al., 2023; Gharat et al., 2025; Grzech et al., 2023; Zhu et al., 2021).
Plant synthetic biology, defined as the application of engineering principles to plant systems, has seen significant growth since the mid-2000s (Andrianantoandro et al., 2006). Plant synthetic biology necessitates the integration of advanced technologies such as synthetic circuit design, genome editing, and omics-driven pathway discovery, while also considering unique plant-specific features including vacuolar sequestration, tissue-specific gene expression, and plastidial compartmentalization. These features are critical for the biosynthesis of structurally complex metabolites (Han and Miao, 2024; Jores et al., 2021). Recent technological advancements, including cost-effective DNA synthesis and precise genome editing systems, have greatly improved the feasibility of reprogramming plant hosts to enhance or introduce novel biosynthetic capabilities, thereby enabling scalable production of pharmaceutically relevant compounds directly within plant chassis (Baltes and Voytas, 2015; Sadre, 2024; Yang et al., 2022).
Applications of plant synthetic biology range from improving yield, stress resistance, and nutritional content to enabling de novo biosynthesis of anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and neuroactive agents directly in plant or plant-compatible chassis systems (Zhang et al., 2025). Compared to traditional breeding or microbial metabolic engineering, these plant-based strategies provide biologically compatible platforms that overcome issues related to enzyme expression, toxicity, and structural complexity, thus offering promising alternatives for the sustainable bioproduction of therapeutics and nutraceuticals (Han and Miao, 2024). Instead of concentrating exclusively on modifications at the level of individual genes, contemporary strategies prioritize the reconfiguration of metabolic systems. This is achieved through Design-Build-Test-Learn (DBTL) frameworks, which facilitate predictive modeling and systematic enhancement of biosynthetic capabilities (Goshisht, 2024; Lin et al., 2023) (Figure 1).
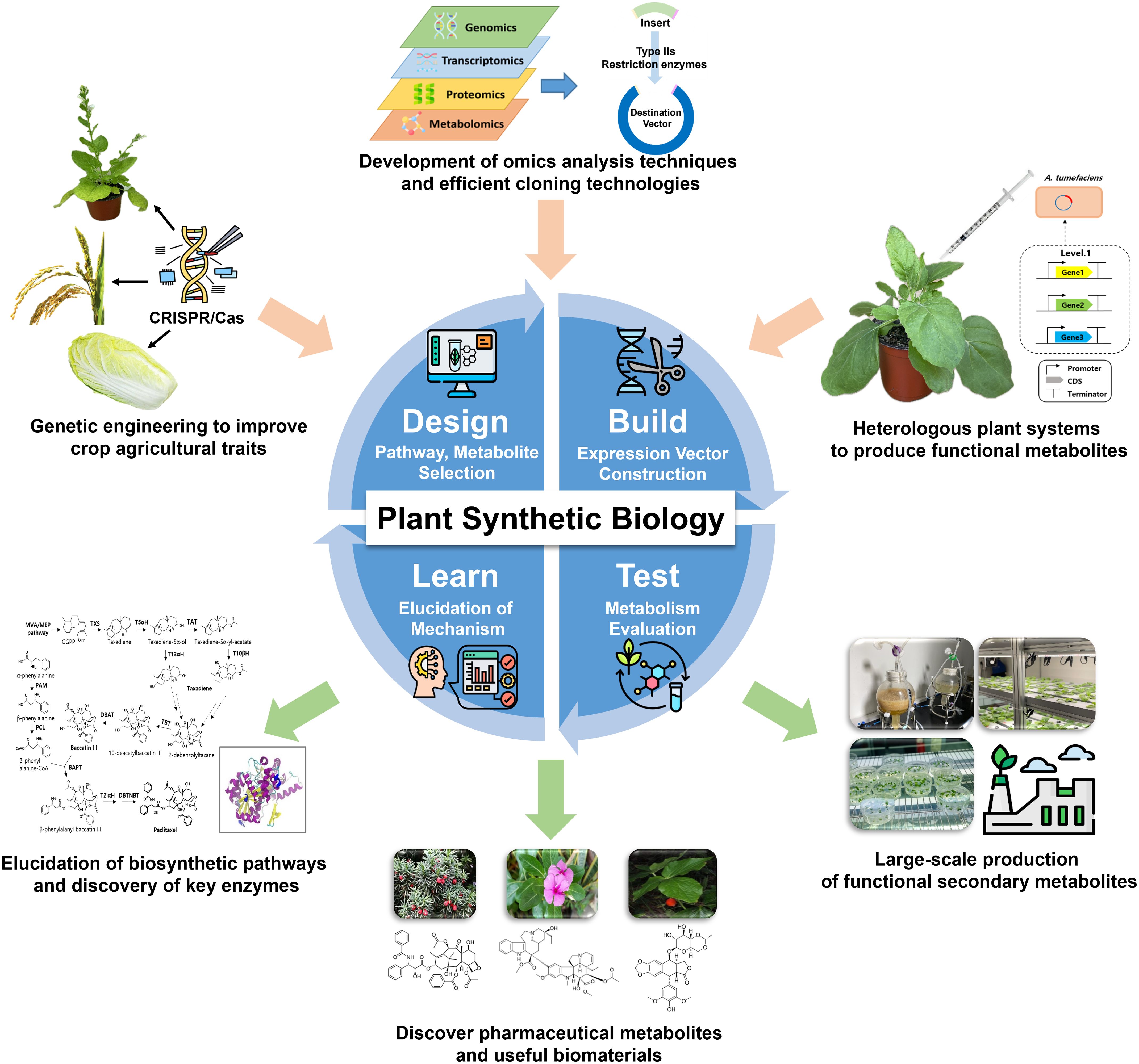
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the core technologies and their applications in the field of plant synthetic biology. Multi-omics data guides the design of biosynthetic pathways from crops and medicinal plant sources. In the Build phase, expression vectors are assembled and introduced into chassis like Nicotiana benthamiana via Agrobacterium. The Test phase evaluates metabolite yield and stability using LC-MS or GC-MS in tissue culture or greenhouse systems. The Learn phase applies computational tools to refine pathway design and overcome regulatory bottlenecks, aiming for scalable production of functional biomolecules such as flavonoids and alkaloids.
This review highlights key technological advancements in plant synthetic biology, primarily from 2020 to 2024, while incorporating insights from studies conducted in early 2025, with a focus on genome editing, combinatorial pathway engineering, and functional genomics. Emphasis is placed on recent case studies that demonstrate how plant systems are being developed into programmable bio-factories for efficient and scalable production of pharmaceutically relevant functional biomolecules. By bridging foundational concepts and application-focused strategies, this review aimed to clarify the distinct advantages of plant-based systems and inspire future innovations in therapeutic biosynthesis.
Integrating omics and genome editing for functional pathway engineering
The integration of omics technologies with genome editing tools has opened a new era in metabolic pathway engineering, enabling the precise and efficient production of valuable natural compounds in plants and microbes (Kumar et al., 2021). Combining the comprehensive, systems-level insights provided by omics with the targeted manipulation capabilities of CRISPR/Cas-based genome editing enables researchers to identify, modify and optimize complex biosynthetic pathways, enhancing existing metabolites or generating novel compounds (Hassan et al., 2021; Kumar et al., 2021; Singh et al., 2022).
Omics technologies including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, offer comprehensive data on gene expression, protein function, and metabolite profiles (Dai and Shen, 2022). These data-driven platforms enable the reconstruction of entire biosynthetic networks and the identification of key regulatory points. For example, metabolomics can reveal the accumulation patterns of secondary metabolites, while transcriptomics helps identify gene clusters responsible for their biosynthesis (Wang et al., 2025).
Once candidate genes or regulatory elements have been identified, genome editing tools such as CRISPR/Cas9, base editors or prime editors can be used to knock out, activate or fine-tune the target genes (Ma et al., 2023). This integrative approach allows biosynthetic pathways to be engineered in a rational way, tailored to specific production goals.
Glutamate decarboxylase (GAD), a key enzyme in GABA biosynthesis, exists in five genes in tomatoes. Among these, two (SlGAD2 and SlGAD3) are expressed during fruit development. To increase GABA content in tomatoes, CRISPR/Cas9 technology was used to edit these two genes (Nonaka et al., 2017). As a result, GABA accumulation increased by 7- to 15-fold, indicating that targeted genome editing can enhance the accumulation of functional compounds. Chavez et al. (2022) conducted a co-expression analysis of transcriptomic and metabolomic data to identify candidate genes involved in tropane alkaloid biosynthesis, followed by functional validation of these candidate genes in yeast. This integrated approach significantly accelerated pathway discovery by efficiently decoding complex plant pathways and overcoming the traditional bottleneck of labor-intensive genetic mutant screening. Although omics-integrated discovery is powerful, downstream in planta validation remains essential for pathway fidelity.
Plant transformation remains a critical prerequisite for the effective application of genome editing technologies. However, its implementation is often hindered by gene delivery and regeneration barriers, which vary considerably across species and genotypes (Altpeter et al., 2016). Future research is, therefore, expected to focus on overcoming these limitations through advances in tissue culture methodologies, the development of novel transformation strategies, and the establishment of genotype-independent delivery systems (Altpeter et al., 2016; Ma et al., 2023). Together, these integrative omics and genome-editing strategies not only identify candidate genes with high confidence but also establish the foundation for their functional assembly into synthetic pathways. The following section explores how these discoveries transition into pathway reconstruction for compound production.
Identification and reconstruction of the biosynthetic pathways for natural products derived from plants
Advancements in omics technologies have significantly accelerated our understanding of plant metabolic networks. Owing to their structural diversity and bioactivity, plant secondary metabolites (PSMs) are critical components in pharmaceutical, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries (Yeshi et al., 2022). Bioinformatics methods and systems biology approaches have proven effective in identifying correlations between metabolite production and gene expression related to PSM biosynthesis. These tools are particularly valuable for understanding the complex biological relationships in plants (Al Aboud, 2024). Integrated omics and bioinformatics pipelines are now routinely used to map these responses to gene function, enabling pathway mining even in non-model species (Shen et al., 2023; Singh et al., 2022).
Heterologous systems are essential for reconstructing and validating the biosynthetic pathways of natural products identified through omics research (Luo et al., 2015). These systems enable researchers to express biosynthetic gene clusters from various organisms in genetically tractable hosts, facilitating functional validation of gene activity and production of target metabolites that are often undetectable in the original source organism. Among plant-based hosts, Nicotiana benthamiana has become a popular platform for several reasons, including its large leaves, rapid biomass accumulation, simple and efficient Agrobacterium-mediated transformation, high transgene expression levels, and the availability of extensive literature and standardized protocols (Golubova et al., 2024; Jiang et al., 2024; Li et al., 2019).
Transient expression systems using N. benthamiana have enabled the rapid reconstruction of biosynthetic pathways for a wide range of valuable plant-derived compounds, including flavonoids such as diosmin (Lee et al., 2024a) and chrysoeriol (Lee et al., 2024b), costunolide and linalool (Park et al., 2022), triterpenoid saponins (Reed et al., 2023), and anticancer precursors such as paclitaxel intermediates (Zhang et al., 2023). For example, diosmin biosynthesis requires the coordinated expression of five to six flavonoid pathway enzymes, including dioxygenases and methyltransferases, producing diosmin at up to 37.7 µg/g fresh weight (FW) in N. benthamiana leaves under transient expression conditions (Lee et al., 2024a). Reed et al. (2023) exemplified this by reconstructing the biosynthesis of QS-7 saponin, a class of vaccine adjuvants, via the co-expression of 19 pathway genes, including multiple cytochrome P450s and glycosyltransferases, achieving 7.9 µg/g dry weight (DW) yields in planta. These cases demonstrate the potential of plant chassis to outperform microbial systems by providing a compatible cellular environment for complex post-translational modifications and metabolite compartmentalization, processes often limited in microbial hosts, thereby enabling the biosynthesis of structurally complex metabolites. To realize this potential at an industrial scale, priority should be given to improving infiltration efficiency, optimizing vector design, enhancing host traits, and integrating stable chassis lines to ensure continuous yields.
Despite its versatility as a heterologous and transient expression platform in synthetic biology, N. benthamiana faces several challenges. These include complex metabolic networks that cause side reactions, immune responses, transcript silencing, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and unwanted modifications, reducing yield and complicating purification processes (Alvisi et al., 2021; Beritza et al., 2024; Sukenik et al., 2018). However, these challenges can be overcome by reducing the metabolic background, using inducible or tissue-specific expression, suppressing immune responses and gene silencing, performing glycoengineering and precise genome editing, and integrating high-throughput screening with automated cultivation. Together, these approaches can enhance the platform’s potential for sustainable natural product biosynthesis.
In synthetic biology, a variety of alternative platforms beyond N. benthamiana such as microbial hosts, other plant species, moss, algae, and cell-free systems, are actively employed to complement existing methods. For example, the functional roles of key artemisinin biosynthesis genes such as AaADS and CYP71AV1 have been successfully reconstituted in heterologous host plants (Firsov et al., 2021). Additionally, Salvia miltiorrhiza, the use of an artificial transcription factor (SmMYB36-VP16) in a hairy root system significantly enhanced the yields of tanshinones and phenolic acids (Jia et al., 2024).
Large-scale production of advantageous metabolites through the strategic modification of metabolic pathways
Strategic modification of metabolic pathways by synthetic biology enables the scalable and sustainable production of valuable metabolites, which has significant applications in pharmaceuticals, biofuels, nutraceuticals, and specialty chemicals (Guo et al., 2017). PSMs such as complex alkaloids, terpenoids, and flavonoid glycosides, are known for their notable pharmaceutical properties. Recent developments in plant synthetic biology have made it possible to reconstruct biosynthetic pathways in heterologous plant hosts, offering new opportunities for the sustainable production of essential pharmaceuticals as recognized by the World Health Organization (WHO) (Sadre, 2024). Although chemical synthesis is feasible, it is resource-intensive and limited by the structural complexity of many PSMs. This has led to increased interest in synthetic biology as a viable alternative for metabolite production (Han and Miao, 2024).
Artemisinin production in Artemisia annua has been successfully increased using synthetic biology, which reprograms the plant’s native biosynthesis route (Hassani et al., 2023). Through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in A. annua, important enzymes and trichome-specific transcription factors were co-overexpressed, increasing artemisinin content in T0 lines by up to 3.2-fold and in T1 progeny by roughly 2.2-fold. These results suggested that transcription factor–guided metabolic engineering can enhance medicinal plant yields, offering a stable, cost-effective artemisinin supply. Further improvements may come from targeting pathway bottlenecks and trichome development.
Heterologous expression platforms, such as N. benthamiana, which allow for rapid and high-yield transient expression, have been widely adopted to produce specialized metabolites (Molina-Hidalgo et al., 2021). Coupled with Agrobacterium-mediated infiltration, these systems enabled the delivery of biosynthetic gene cassettes and combinatorial pathway testing. These strategies can be broadly categorized into transcriptional regulation and modular pathway reconstruction. In transcriptional regulation strategies, transient expression of VmMYBA1 and VmMYBA2 from bilberry in N. benthamiana leaves induced anthocyanin accumulation like delphinidin-3-rutinoside and activated expression of dihydroflavonol 4-reductase (DFR) and anthocyanidin synthase (ANS) genes for flavonoid biosynthesis (Karppinen et al., 2021).
On the other hand, modular reconstruction strategies, such as the synthesis of glucoraphanin (Barnum et al., 2022), monoterpenoid indole alkaloid (MIA) precursors (Dudley et al., 2022), and complex pathway stacking (Reed et al., 2023; Jia et al., 2024), have broadened the diversity and scale of metabolites that can be produced in plants.
In addition, cannabinoids and their glucosides are synthesized in N. benthamiana and yeast through the transient expression of multi-gene biosynthetic pathways (Gülck et al., 2020). These studies underscore the complementary strengths of plant and microbial platforms for pathway reconstruction and reveal important issues such as metabolite instability, off-target glycosylation, and scalability, which differ based on the compound class and host plant context (Gülck et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2024a).
Despite these encouraging experimental findings, translation to industry remains limited. The flexibility and scalability of plant-based systems have been demonstrated to produce complex bioactive molecules. Table 1 summarizes representative case studies from 2020 to 2024 in plant synthetic biology, including host species, engineering strategies, outcomes, and references. Strategic pathway engineering can achieve microgram-to-milligram yields per gram biomass with improved stability and yield. However, further optimization of metabolic flux and processes is necessary to achieve industrial-scale, cost-effective production.
Discussion
Plant synthetic biology has made significant progress; however, its widespread application remains limited by various technical, computational, and regulatory challenges. For instance, modular pathway reconstruction has been enabled by the DBTL framework. Nevertheless, the lack of real-time metabolic feedback control often results in suboptimal flux and yield (Goshisht, 2024). Also, the complex and context-dependent nature of plant metabolic networks means that identical interventions can yield different outcomes across species, tissues, and environments (Barnum et al., 2022; Han and Miao, 2024; Reed et al., 2023). Large-scale engineering typically causes flux imbalances, accumulation of toxic intermediates, and unexpected yield reductions, even when pathway gene optimization is applied (Han and Miao, 2024). The fact that many advances in plant synthetic biology remain at the proof-of-concept stage underscores the urgent need for reliable, field-ready systems capable of consistent and stable metabolite production in agricultural settings. Many proof-of-concept advances fail to scale effectively in agricultural or industrial contexts, underscoring the importance of incorporating scale-up considerations early in the design phase (Han and Miao, 2024).
As noted earlier, transformation and gene delivery barriers remain significant constraints in plant synthetic biology, particularly in species with recalcitrant regeneration systems (Altpeter et al., 2016). Overcoming these challenges is essential for translating genome editing successes into scalable, plant-based bioproduction platforms. Target selection remains challenging because many plant genomes are either un-sequenced or lack high-quality annotations (Cheng et al., 2025). Currently, transformation-free delivery systems and tissue culture-independent technologies, such as viral vectors and nanocarrier-based DNA delivery, are being developed to address these challenges (Zhou et al., 2023). As discussed above, N. benthamiana enables efficient transient expression but faces protein stability and consistency issues at an industrial scale. Selecting a production chassis requires considering metabolite stability, pathway length, and crosstalk, as these factors can also influence regulatory approval (Barnum et al., 2022; Han and Miao, 2024).
Regulation poses a significant challenge for synthetic plant biology. Regulations concerning genetically modified or genome-edited plants vary widely and are often in flux across many countries, which can hinder or delay the development and commercialization of new products. Moreover, the unique features of synthetic biology such as novel traits or entirely new metabolic pathways may not align with traditional risk assessment frameworks. Inconsistencies in national regulations can impact trade and global competitiveness, while regulatory gaps create uncertainty for developers. Although the foundational knowledge of plant synthetic biology has grown quickly, significant technical and regulatory hurdles still prevent its full translation to commercial and global applications (Atimango et al., 2024). Therefore, progress depends not only on technological or biological advances, but also on proactive policy alignment and stakeholder engagement (Bandyopadhyay et al., 2020). Bridging technical feasibility, computational predictability, and regulatory readiness is essential to ensure a smooth transition from the laboratory to the market.
Future opportunities
Given these interconnected challenges, plant synthetic biology is a vital tool for enhancing biomolecule production and advancing environmentally sustainable agricultural practices (Atimango et al., 2024; Bandyopadhyay et al., 2020). Integrating technical, computational, and policy solutions from the outset is essential, as persistent bottlenecks hinder large-scale deployment (Altpeter et al., 2016). Long-term progress in plant synthetic biology requires interdisciplinary collaboration. To address challenges in plant systems, engineers, computer scientists, and plant biologists must work together to develop innovative technologies, such as context-independent and chassis-agnostic genetic constructs (Altpeter et al., 2016). Design efforts are facilitated by standardized modular cloning techniques like Golden Gate and Loop assembly. Additionally, AI-driven models are beginning to emerge that can predict pathway bottlenecks prior to physical prototyping (Goshisht, 2024). Integrating predictive modeling and AI-driven simulations with early-stage regulatory planning can reduce trial and error during development and accelerate readiness for industrial applications.
Therefore, predictive computational modeling, international standards, stakeholder frameworks, and the development of reliable, commercially deployable bio-foundries should be prioritized in synthetic biology. This coordinated approach will enable plant synthetic biology to have a revolutionary and long-lasting impact on food, health, and the green economy in the future (Han and Miao, 2024). Through these collaborative efforts, plant systems can enhance agricultural productivity, promote environmental sustainability, and facilitate the development of biomaterials (Atimango et al., 2024; Bandyopadhyay et al., 2020). By addressing both scientific and socioeconomic challenges, plant synthetic biology offers sustainable solutions for biotechnology and agriculture. Progress in this field is expected to accelerate with continued research and collaboration.
Author contributions
SP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. VM: Writing – review & editing. KH: Writing – review & editing. JK: Writing – review & editing. SL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the RURAL DEVELOPMENT ADMINISTRATION (Korea) through Rural Program for Agricultural Science and Technology Development (Project No.RS-2023-00231699, No.RS-2024-00399037).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al Aboud, N. M. (2024). Unlocking the genetic potential: Strategies for enhancing secondary metabolite biosynthesis in plants. J. Saudi Soc Agric. Sci. 23, 542–554. doi: 10.1016/j.jssas.2024.06.004
Altpeter, F., Springer, N. M., Bartley, L. E., Blechl, A. E., Brutnell, T. P., Citovsky, V., et al. (2016). Advancing crop transformation in the era of genome editing. Plant Cell 28, 1510–1520. doi: 10.1105/tpc.16.00196
Alvisi, N., van Noort, K., Dwiani, S., Geschiere, N., Sukarta, O., Varossieau, K., et al. (2021). β-Hexosaminidases along the secretory pathway of Nicotiana benthamiana have distinct specificities toward engineered helminth N-glycans on recombinant glycoproteins. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.638454
Andrianantoandro, E., Basu, S., Karig, D. K., and Weiss, R. (2006). Synthetic biology: New engineering rules for an emerging discipline. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2, 2006.02028. doi: 10.1038/msb4100073
Atimango, A. O., Wesana, J., Kalule, S. W., Verbeke, W., and De Steur, H. (2024). Genome editing in food and agriculture: From regulations to consumer perspectives. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 87, 103127. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2024.103127
Baltes, N. J. and Voytas, D. F. (2015). Enabling plant synthetic biology through genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 33, 120–131. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2014.11.008
Bandyopadhyay, A., Kancharla, N., Javalkote, V. S., Dasgupta, S., and Brutnell, T. P. (2020). CRISPR-Cas12a (Cpf1): A versatile tool in the plant genome editing tool box for agricultural advancement. Front. Plant Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.584151
Barnum, C. R., Endelman, B. J., Ornelas, I. J., Pignolet, R. M., and Shih, P. M. (2022). Optimization of heterologous glucoraphanin production in planta. ACS Synth. Biol. 11, 1865–1873. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00030
Beritza, K., Watts, E. C., and van der Hoorn, R. A. L. (2024). Improving transient protein expression in agroinfiltrated Nicotiana benthamiana. New Phytol. 243, 846–850. doi: 10.1111/nph.19894
Brunk, E., Chang, R. L., Xia, J., Hefzi, H., Yurkovich, J. T., Kim, D., et al. (2018). Characterizing posttranslational modifications in prokaryotic metabolism using a multiscale workflow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, 11096–11101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811971115
Chavez, B. G., Srinivasan, P., Glockzin, K., Kim, N., Montero Estrada, O., Jirschitzka, J., et al. (2022). Elucidation of tropane alkaloid biosynthesis in Erythroxylum coca using a microbial pathway discovery platform. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119, e2215372119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2215372119
Cheng, L. T., Wang, Z. L., Zhu, Q. H., Ye, M., and Ye, C. Y. (2025). A long road ahead to reliable and complete medicinal plant genomes. Nat. Commun. 16, 2150. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57448-8
Dai, X. and Shen, L. (2022). Advances and trends in omics technology development. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 9. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.911861
Dudley, Q. M., Jo, S., Guerrero, D. A. S., Chhetry, M., Smedley, M. A., Harwood, W. A., et al. (2022). Reconstitution of monoterpene indole alkaloid biosynthesis in genome engineered Nicotiana benthamiana. Commun. Biol. 5, 949. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03904-w
Firsov, A., Pushin, A., Motyleva, S., Pigoleva, S., Shaloiko, L., Vainstein, A., et al. (2021). Heterologous biosynthesis of artemisinin in Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. Separations 8, 75. doi: 10.3390/separations8060075
Gharat, S. A., Tamhane, V. A., Giri, A. P., and Aharoni, A. (2025). Navigating the challenges of engineering composite specialized metabolite pathways in plants. Plant J. 121, e70100. doi: 10.1111/tpj.70100
Golubova, D., Tansley, C., Su, H., and Patron, N. J. (2024). Engineering Nicotiana benthamiana as a platform for natural product biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 81, 102611. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2024.102611
Goshisht, M. K. (2024). Machine learning and deep learning in synthetic biology: Key architectures, applications, and challenges. ACS Omega 9, 9921–9945. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05913
Grzech, D., Hong, B., Caputi, L., Sonawane, P. D., and O’Connor, S. E. (2023). Engineering the biosynthesis of late-stage vinblastine precursors precondylocarpine acetate, catharanthine, tabersonine in Nicotiana benthamiana. ACS Synth. Biol. 12, 27–34. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.2c00434
Gülck, T., Booth, J. K., Carvalho, Â., Khakimov, B., Crocoll, C., Motawia, M. S., et al. (2020). Synthetic biology of cannabinoids and cannabinoid glucosides in Nicotiana benthamiana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Nat. Prod. 83, 2877–2893. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.0c00241
Guo, W., Sheng, J., and Feng, X. (2017). Mini-review: In vitro metabolic engineering for biomanufacturing of high-value products. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 15, 161–167. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2017.01.006
Han, T. and Miao, G. (2024). Strategies, achievements, and potential challenges of plant and microbial chassis in the biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites. Molecules 29, 2106. doi: 10.3390/molecules29092106
Hassan, M. M., Zhang, Y., Yuan, G., De, K., Chen, J. G., Muchero, W., et al. (2021). Construct design for CRISPR/Cas-based genome editing in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 26, 1133–1152. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2021.06.015
Hassani, D., Taheri, A., Fu, X., Qin, W., Hang, L., Ma, Y., et al. (2023). Elevation of artemisinin content by co-transformation of artemisinin biosynthetic pathway genes and trichome-specific transcription factors in Artemisia annua. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1118082
Jia, E., Li, H., He, F., Xu, X., Wei, J., Shao, G., et al. (2024). Metabolic engineering of artificially modified transcription factor SmMYB36-VP16 for high-level production of tanshinones and phenolic acids. Metab. Eng. 86, 29–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2024.08.004
Jiang, X., Zhang, Z., Wu, X., Li, C., Sun, X., Wu, F., et al. (2024). Heterologous biosynthesis of betanin triggers metabolic reprogramming in tobacco. Metab. Eng. 86, 308–325. doi: 10.1016/j.ymben.2024.11.002
Jores, T., Tonnies, J., Wrightsman, T., Buckler, E. S., Cuperus, J. T., Fields, S., et al. (2021). Synthetic promoter designs enabled by a comprehensive analysis of plant core promoters. Nat. Plants 7, 842–855. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00932-y
Karppinen, K., Lafferty, D. J., Albert, N. W., Mikkola, N., McGhie, T., Allan, A. C., et al. (2021). MYBA and MYBPA transcription factors co-regulate anthocyanin biosynthesis in blue-coloured berries. New Phytol. 232, 1350–1367. doi: 10.1111/nph.17669
Kim, G. B., Kim, H. R., and Lee, S. Y. (2025). Comprehensive evaluation of the capacities of microbial cell factories. Nat. Commun. 16, 2869. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58227-1
Kumar, A., Anju, T., Kumar, S., Chhapekar, S. S., Sreedharan, S., Singh, S., et al. (2021). Integrating omics and gene editing tools for rapid improvement of traditional food plants for diversified and sustainable food security. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 8093. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158093
Lee, S. B., Lee, S. E., Lee, H., Kim, J. S., Choi, H., Lee, S., et al. (2024b). Engineering Nicotiana benthamiana for chrysoeriol production using synthetic biology approaches. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1458916
Lee, H., Park, S., Lee, S. B., Song, J., Kim, T. H., and Kim, B. G. (2024a). Tailored biosynthesis of diosmin through reconstitution of the flavonoid pathway in Nicotiana benthamiana. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1464877
Li, J., Mutanda, I., Wang, K., Yang, L., Wang, J., and Wang, Y. (2019). Chloroplastic metabolic engineering coupled with isoprenoid pool enhancement for committed taxanes biosynthesis in Nicotiana benthamiana. Nat. Commun. 10, 4850. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12879-y
Lin, J., Yin, X., Zeng, Y., Hong, X., Zhang, S., Cui, B., et al. (2023). Progress and prospect: biosynthesis of plant natural products based on plant chassis. Biotechnol. Adv. 69, 108266. doi: 10.1016/j.bioteChadv.2023.108266
Luo, Y., Li, B. Z., Liu, D., Zhang, L., Chen, Y., Jia, B., et al. (2015). Engineered biosynthesis of natural products in heterologous hosts. Chem. Soc Rev. 44, 5265–5290. doi: 10.1039/c5cs00025d
Ma, Z., Ma, L., and Zhou, J. (2023). Applications of CRISPR/Cas genome editing in economically important fruit crops: recent advances and future directions. Mol. Hortic. 3, 1. doi: 10.1186/s43897-023-00049-0
Martin, V. J. J., Pitera, D. J., Withers, S. T., Newman, J. D., and Keasling, J. D. (2003). Engineering a mevalonate pathway in Escherichia coli for production of terpenoids. Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 796–802. doi: 10.1038/nbt833
Molina-Hidalgo, F. J., Vazquez-Vilar, M., D’Andrea, L., Demurtas, O. C., Fraser, P., Giuliano, G., et al. (2021). Engineering metabolism in Nicotiana species: A promising future. Trends Biotechnol. 39, 901–913. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2020.11.012
Nonaka, S., Arai, C., Takayama, M., Matsukura, C., and Ezura, H. (2017). Efficient increase of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) content in tomato fruits by targeted mutagenesis. Sci. Rep. 7, 7057. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06400-y
Park, S., Mani, V., Kim, J. A., Lee, S. I., and Lee, K. (2022). Combinatorial transient gene expression strategies to enhance terpenoid production in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1034893
Reed, J., Orme, A., El-Demerdash, A., Owen, C., Martin, L. B. B., Misra, R. C., et al. (2023). Elucidation of the pathway for biosynthesis of saponin adjuvants from the soapbark tree. Science 379, 1252–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.adf3727
Rizzo, P., Chavez, B. G., Leite Dias, S., and D’Auria, J. C. (2023). Plant synthetic biology: from inspiration to augmentation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 79, 102857. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2022.102857
Sadre, R. (2024). Plant synthetic biology for human health: Advances in producing medicines in heterologous expression systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 87, 103142. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2024.103142
Shen, S., Zhan, C., Yang, C., Fernie, A. R., and Luo, J. (2023). Metabolomics-centered mining of plant metabolic diversity and function: Past decade and future perspectives. Mol. Plant 16, 43–63. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2022.09.007
Singh, K. S., van der Hooft, J. J. J., van Wees, S. C. M., and Medema, M. H. (2022). Integrative omics approaches for biosynthetic pathway discovery in plants. Nat. Prod. Rep. 39, 1876–1896. doi: 10.1039/d2np00032f
Sukenik, S. C., Karuppanan, K., Li, Q., Lebrilla, C. B., Nandi, S., and McDonald, K. A. (2018). Transient recombinant protein production in glycoengineered Nicotiana benthamiana cell suspension culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1205. doi: 10.3390/ijms19041205
Wang, Y., Gao, R., Gu, T., Li, X., Wang, M., Wang, A., et al. (2025). Metabolomics and transcriptomics reveal the role of the terpene biosynthetic pathway in the mechanism of insect resistance in Solanum habrochaites. J. Agric. Food Chem. 73, 6253–6269. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c10397
Wu, G., Yan, Q., Jones, J. A., Tang, Y. J., Fong, S. S., and Koffas, M. A. G. (2016). Metabolic burden: cornerstones in synthetic biology and metabolic engineering applications. Trends Biotechnol. 34, 652–664. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2016.02.010
Yang, Y., Chaffin, T. A., Ahkami, A. H., Blumwald, E., and Stewart, C. N., Jr. (2022). Plant synthetic biology innovations for biofuels and bioproducts. Trends Biotechnol. 40, 1454–1468. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2022.09.007
Yeshi, K., Crayn, D., Ritmejerytė, E., and Wangchuk, P. (2022). Plant secondary metabolites produced in response to abiotic stresses has potential application in pharmaceutical product development. Molecules 27, 313. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010313
Zhang, Y., Wiese, L., Fang, H., Alseekh, S., Perez de Souza, L., Scossa, F., et al. (2023). Synthetic biology identifies the minimal gene set required for paclitaxel biosynthesis in a plant chassis. Mol. Plant 16, 1951–1961. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.10.016
Zhang, D., Xu, F., Wang, F., Le, L., and Pu, L. (2025). Synthetic biology and artificial intelligence in crop improvement. Plant Commun. 6, 101220. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2024.101220
Zhou, H., Eun, H., and Lee, S. Y. (2023). Systems metabolic engineering for the production of pharmaceutical natural products. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 37, 100491. doi: 10.1016/j.coisb.2023.100491
Keywords: plant synthetic biology, functional biomolecules, CRISPR/Cas, metabolic engineering, large-scale production
Citation: Park S, Mani V, Ha K, Kim JA and Lee S (2025) Plant synthetic biology: from knowledge to biomolecules. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1562216. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1562216
Received: 17 January 2025; Accepted: 15 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Evangelos Tatsis, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Itay Gonda, Volcani Center, IsraelCopyright © 2025 Park, Mani, Ha, Kim and Lee. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Soyoung Park, cHN5MDIwM0Brb3JlYS5rcg==; Sichul Lee, c2Npcm9uMTAxNUBrb3JlYS5rcg==
 Soyoung Park
Soyoung Park Vimalraj Mani
Vimalraj Mani Kihun Ha
Kihun Ha Jin A. Kim
Jin A. Kim Sichul Lee
Sichul Lee