- 1School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Hangzhou, China
- 2Zhejiang Academy of Forestry, Hangzhou, China
- 3Independent Researcher, Miki, Kagawa, Japan
- 4Songyang Institute, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, Lishui, China
Introduction: Dendrobium is a multi-purpose medicinal orchid that grows on the edge of highaltitude cliffs. The content of water-soluble polysaccharides (WSPs), which primarily play a pharmacological role, is the main criterion for evaluating the quality of Dendrobium orchid. Therefore, it is necessary to study the regulatory manner involved in the accumulation of WSPs.
Methods: D. officinale were treated with methyl jasmonate (MeJA), and WSPs content was measured at different time points to assess the dynamic accumulation pattern. To clarify the role of one finger (Dof) family genes in the MeJA-mediated WSP metabolic pathway, a bioinformatics analysis identified Dof members in D. huoshanense, D. nobile and D. officinale. Based on expression patterns and co-expression analysis, a regulatory factor, DoDof4 was identified.
Results: In this study, the elicitation of D. officinale by methyl jasmonate (MeJA) increased WSP production, which was further amplified by extending the treatment period. Analysis of transcriptomic data revealed that members of the DNA-binding with Dof gene family members accounted for 4% of all differentially expressed genes coding for transcription factors, following MeJA induction. To clarify the role of Dof family genes in the MeJA-mediated WSP metabolic pathway, a bioinformatics analysis identified 29, 29 and 22 Dof members in D. huoshanense, D. nobile and D. officinale, respectively and these were divided into four groups. DoDof4 was encoded a 31.16 kDa protein composed of 292 amino acids, and was targeted on chromosome 3. Furthermore, DoDof4 was a typical transcription factor that localized in the nucleus, displayed transcriptional activity and increased the WSPs accumulation. DoDof4 was co-expressed with 15 genes involved in the WSP metabolic pathway, eight of which displayed a positive Pearson's correlation coefficient. Additionally, correlation analysis revealed the possible downstream targets (KM980199 and KP203853) of DoDof4.
Discussion: The results of the present study suggest that DoDof4 acts as an important regulator in the WSPs metabolic pathway, exhibiting potential values for the improvement of WSPs in Dendrobium species.
1 Introduction
The orchid, comprising over 29,000 species, is one of the largest and most diverse families of angiosperms (Pérez-Escobar et al., 2024). Among these, Dendrobium (almost 1,800 species) was the largest genera in the Orchidaceae. In natural conditions, Dendrobium usually grows epiphytically on cliffs at an altitude of 1000–3000 m above sea level, on warm and humid branches of trees or rocks. The stems of Dendrobium in both vegetative and reproductive stages are rich in active secondary metabolites, such as alkaloids, flavonoids, and others (Li et al., 2024). The pharmacologically most active components of Dendrobium are the water-soluble polysaccharides (WSPs) (Teixeira da Silva and Ng, 2017). WSPs displayed antioxidant, anti-degenerative, anticancer, and immune-regulating effects (Tang et al., 2017). Dendrobium WSPs can facilitate an increase in water uptake by plants growing in abiotic stress environments (drought or salt stress), thus improving their abiotic stress tolerance (He et al., 2017; Yu et al., 2017, 2019). Previous research (Yu et al., 2021b; Si et al., 2022) revealed that there are two biosynthetic pathways for the production of WSPs. Initially, sucrose is converted into glucose and fructose, followed by the production of fructose-6P. Phosphomannomutase (PMM) converts fructose-6P to mannose-1P, which is catalyzed by GDP-mannose-pyrophosphorylase (GMP) to generate GDP-mannose. Sucrose is then converted into UDP-glucose, and then into GDP-glucose by Uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGP). In addition, UDP-glucose can also generate UDP-galactose in response to UDP glucose 4-epimerase (UGE). Finally, GDP-mannose, GDP-glucose, and UDP-galactose can be transported from the cytoplasm to the Golgi apparatus with the help of GDP-mannose transporter (GMT), where the D. officinale WSPs are generated by CELLULOSE SYNTHASE-LIKE A (CSLA) (He et al., 2017). Although there are some inducible methods to increase WSP content in Dendrobium, such as moderate stress treatments or the addition of bioinducers (Li et al., 2023), the intrinsic molecular mechanisms underlying the metabolic pathway of WSPs are unknown. Therefore, there is practical value in studying how genes regulate the metabolic pathway of WSPs in Dendrobium.
Transcription factors (TFs), also known as trans-acting factors, are important regulatory proteins that can affect gene expression and participate in multiple critical biological processes such as signal transduction, stress response, and the synthesis of bioactive compounds (Strader et al., 2021). Based on their protein structure, TFs are generally composed of four structural domains: the N-terminal DNA-binding domain, the C-terminal transcriptional regulatory domain, the nuclear localization signaling domain (NLS), and the oligomerization site (Gupta et al., 2015). The DNA-binding domain can bind to specific bases of the target gene’s promoter, and in doing so, promote or inhibit the expression level of the target gene (Udvardi et al., 2007). Most TFs have only one DNA-binding domain, but some TFs, such as GT2 and APETALA2 of Arabidopsis thaliana, contain two DNA-binding domains (Guo et al., 2005). The DNA-binding domain of the same type of TF is a relatively conserved amino acid sequence, so TFs can be categorized into different TF gene families based on their specific and conserved DNA-binding domains. A wide range of TFs have been identified in plants, such as the B-box (BBX), basic leucine zipper (bZIP), WRKYGOK (WRKY), myeloblastosis (MYB), basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH), and others (Tian et al., 2020).
The DNA-binding with one finger (Dof) proteins, including 2,589 members of the ZF superfamily, according to the plant TF database, are widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom, ranging from green unicellular algae to vascular plants, so they are a class of plant-specific TFs (Gupta et al., 2015). Dof TFs were first identified in maize (Zea mays) (Yanagisawa and Izui, 1993), and have since been identified in a large number of plant species, such as A. thaliana (Xu et al., 2020), Spinacia oleracea (Yu et al., 2021a), Durio zibethinus (Khaksar et al., 2019), Maninot esculenta (Zou et al., 2019), Vitis vinifera (Wang et al., 2021) and others. Dof proteins, which contain 100–400 amino acids with a variable sequence of C-terminal transcriptional regulatory domains, as well as 50–52 highly conserved amino acids at the N-terminus that form a specific DNA-binding domain with a characteristic motif CX2CX21CX2C, have the ability to form a single zinc finger structural domain (Kang et al., 2016). The DNA-binding domains of Dof TFs can activate or repress the expression of target genes by specifically binding to bases containing [T/A]AAAG or its complementary sequence CTTT[T/A] (Cominelli et al., 2011). Moreover, when there are two binding sites, the binding capacity of the structural domains of Dof is two-fold higher than that of a single binding site (Zou and Sun, 2023). However, the Cucurbita moschata Dof protein recognizes and binds to AAGT of the downstream target gene promoter (Kisu et al., 1998) whereas the Tamarix chinensis Dof protein recognizes and binds to TGCG (Wang et al., 2024). The Dof structural domain can bind to specific bases alone to mediate DNA-protein binding. Sorghum bicolor Dof21 binds to the P-box (CCTTTTG) element of the promoter of GRANULE-BOUND STARCH SYNTHASE I (SbGBSSI), a key gene for starch synthesis, and activates its expression (Xiao et al., 2022). The Dof structural domain can also interact with other TFs to mediate protein-protein binding (Wu et al., 2018). Musa acuminata ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR 9 (MaERF9) activates the expression of fruit ripening-related genes, although MaDof23, a transcriptional repressor that interacts with MaERF9, blocks the binding sites in the promoters of fruit ripening-related genes, thereby reducing the activation effect brought about by MaERF9 in order to delay fruit ripening (Feng et al., 2016). Prunus avium (Pav) Dof6 binds directly to the promoters of genes related to cell wall modification to regulate their expression and accelerate fruit ripening, while PavDof2/15 directly regulate fruit softening, by delaying it (Zhai et al., 2022). The PavDof2/15-mediated abscisic acid (ABA) signal positively regulates the expression of 9-CIS-EPOXYCAROTENOID DIOXYGENASE 1 (PavNCED1), and also interacts with the auxin response element (AuxRE) AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR 8 (PavARF8), forming the ABA-PavARF8-PavDofs module to indirectly regulate fruit softening (Zhai et al., 2022). These studies indicate that the Dof binding domain is a protein structural domain with dual functions, reflecting the functional diversity of Dof TFs.
In order to understand the roles of Dof in Dendrobium, we identified Dof from D. huoshanense, D. nobile and D. officinale genomes, presenting the first systematic comparison of three Dendrobium species. Furthermore, we employed D. officinale as a model system to elucidate how MeJA regulate the synthesis of WSPs. Our study provides valuable information that would allow WSP content to be amplified in the future by artificially inducing Dof gene expression in transgenic plants.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant materials and MeJA treatment
Protocorm-like bodies (PLBs) were generated using a previously described in vitro regeneration protocol (Zeng et al., 2023), and cultivated in Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium (Murashige and Skoog, 1962) containing 0.5 mg·L-1 6-benzyladenine (6-BA; Aladdin, Shanghai, China), 0.2 mg·L-1 1-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA; Aladdin), 20% banana puree (prepared fresh), 2% (w/v) sucrose (Aladdin) and 0.7% agar to induce proliferation (Zeng et al., 2023). Cultures were placed under controlled environmental conditions (25°C; 12-h photoperiod; 50 µmol m-2 s-1 cold fluorescent white light). Following the acclimatization of in vitro-regenerated plants (Zeng et al., 2023), the leaves of 36-month-old plants with uniform growth were sprayed with 0.1 mM methyl jasmonate (MeJA) (98% purity, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), which was dissolved in trace ethanol (99.5% purity, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). Leaves were sprayed every 30 d for a total of 90 d to investigate the effect of MeJA on WSP content and transcript levels of D. officinale genes. The treated stems were collected at three time points (30, 60, and 90 d), with three replications per time point. Plants sprayed with distilled water supplemented with trace ethanol served as the control (CK). Each treatment group included three replications. Samples were stored immediately at -80°C. Frozen samples of plants that had been treated with 0.1 mM MeJA for 30 d were sent to Biomarker Technologies (Beijing, China) to determine the transcript levels of D. officinale genes.
2.2 RNA-seq and transcriptome analysis
RNA-seq libraries were carried out as reported (Si et al., 2022), and the cDNA products accord with quality assessment were sequenced through the BMKCloud platform (www.biocloud.net). High-quality clean reads were cherry-picked by removing adapters and low-quality sequences, compared with the chromosome-level D. officinale genome, and normalized to fragments per kilobase per million fragment-mapped reads (FPKM). Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using DESeq2 version 1.38.3 based on a false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05, and |log2FoldChange| > 1. Gene Ontology (GO), Eukaryotic Orthologous Groups (KOG), and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were performed using the BMKCloud server with the P-value less than 0.05.
2.3 Identification and physicochemical properties analysis of Dof genes
The Hidden Markov Model (HMM) of Dof proteins’ structural domain (PF02701) was downloaded from password-encrypted Interpro (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/). The whole genome sequences of D. nobile (accession no. 94219), D. huoshanense (accession no. 154293) and D. officinale (accession no. 142615) which were downloaded from IMP (https://www.bic.ac.cn/IMP) were analyzed by HMM Search of TBtools v2.118 (Chen et al., 2023), using an E-value > 0.05 as the filtering criterion to remove redundancy. After removing incomplete sequences in the conserved structural domains, using Conserved Domains Database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi), 22 DoDof proteins, 29 DhDof proteins and 29 DnDof proteins (Supplementary Tables S1-S3) were finally identified. In addition, the 80 Dof proteins were analyzed at the ExPASy online website (https://www.expasy.org/) to determine the size, molecular weight (MW), isoelectric point (pI), instability index, aliphatic index, and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) for each protein. Finally, the subcellular localization of the Dof proteins were predicted in WoLF PSORT (https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/).
2.4 Phylogenetic analysis and multiple sequence alignment of Dof proteins
To explore the evolutionary relationships between the 80 Dof proteins, they were compared with 36 A. thaliana Dof proteins and 30 Oryza sativa Dof proteins that were downloaded from PlantTFDB (Supplementary Table S4). They were subjected to multiple sequence alignment using ClustalX v2.1 (http://www.clustal.org/). A phylogenetic tree of these 80 proteins was constructed with MEGA v11.0 (https://megasoftware.net/) using the neighbor-joining method (Saitou and Nei, 1987) with a bootstrap value of 1000 and was visualized using Chiplot (https://www.chiplot.online/).
2.5 Chromosome localization and collinearity analysis of Dof proteins
Collinearity analysis of the Dof proteins was performed and visualized in TBtools using the One Step MCScanX Super Fast modulation. The genome files and annotation files of A. thaliana and O. sativa, as representative dicot and monocot model plant, respectively, were downloaded from CNCD-NGDC (https://download.cncb.ac.cn/gwh/Genome/Plants/). Collinearity analyses were performed in TBtools with the Dual Synteny Plot.
2.6 Validation of transcriptomic data and investigation of the expression profiles of DoDof genes in different organs by qRT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from different organs of D. officinale (roots, leaves, flowers, and stems), MeJA-treated leaves (0.1 mM, 30 d), and control leaves using the Quick RNA Isolation Kit (0416–50 GK, Huayueyang, Beijing, China). After ensuring the purity and concentration of RNA by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) and a NanoDrop2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), the Evo M-MLV RT Kit II (Accurate Biology, Hunan, China) was used to obtain first-strand cDNA. The quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) reaction, which contained 5 μL 2× iTaq™ universal SYBR® Green (Bio-Rad Laboratories), 1 μL cDNA, 0.4 μL of each primer (10 μM), and RNase-free water supplemented to 10 μL, was run in an Applied Biosystems 7500 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). ELONGATION FACTOR 1 ALPHA (EF-1α) was used as the reference gene (Yu et al., 2021b). Relative gene expression of the 22 DoDof genes was calculated by the 2-ΔΔCt method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001). The quantitative PCR primers, listed in Supplementary Table S5, were generated by Integrated DNA Technologies (https://sg.idtdna.com/).
2.7 Co-expression analysis between the enzyme-encoding genes and DoDof genes
Multiple enzyme-encoding genes involved in the WSP metabolic pathway were previously identified (Yu et al., 2021b; Si et al., 2022). The correlations between these enzyme-encoding genes and the DoDof genes was assessed as Pearson’s correlation coefficients with SPSS v. 27.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA), and a co-expression network was generated in Cytoscape v3.10.0 (https://cytoscape.org/).
2.8 Molecular cloning, subcellular localization and transcriptional activation assay of DoDof4
The coding sequence of DoDof4 (without the stop codon TGA) was cloned using the PrimeSTAR Max premix (Takara, Dalian, China). To determine the subcellular localization of DoDof4, DoDof4 was inserted into the SpeI and BamHI sites of a 35S promoter-driven pHB vector (Haq et al., 2021) containing yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) with In-Fusion Cloning Kit (Takara). After verification by sequencing (Zhejiang Sunya Co., Hangzhou, China), recombinant plasmid pHB-DoDof4-YFP and the negative control pHB-YFP were transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101 (Weidi Biotechnology Co., Shanghai, China) through a previously published freeze-thaw protocol (Yu et al., 2021b), and used to infect the one-month-old Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. After 48 h, subcellular localization of YFP in N. benthamiana leaves, and the staining leaves with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI; Sigma-Aldrich), were observed on a confocal microscope (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) under a 488 nm excitation filter. To evaluate the transcriptional activation or repression of DoDof4, coding sequence of DoDof4 without the termination codon TGA was cloned into pGBKT7 (Takara) to construct the pGBKT7-DoDof4 as previously reported (Yu et al., 2021b). Yeast AH109 (Weidi) transformed with pGBKT7-Empty and pGBKT7-DoDof4 were grown on a synthetic dropout (SD) without tryptophan (SD/-Trp) medium and SD without adenine, tryptophan, and histidine (SD/-Ade-Trp-His) medium respectively at 29°C. X-α-Gal (Coolaber, China) was additionally dropped to displayed color reaction. pGBKT7-Lam and pGBKT7-P53 were selected as negative and positive controls, respectively.
2.9 Transient transformation of DoDof4 in D. officinale PLBs
The DoDof4 coding sequence without the termination codon TGA was inserted into pCAMBIA1301 vector (CAMBIA, Canberra, Australia) to overexpress the DoDof4 gene. DoDof4 gene into pCAMBIA2300 (CAMBIA) using sgDoDof4-F and sgDoDof4-R primers, which were designed on the CRISPRdirect website (https://crispr.dbcls.jp/) to construct pCAMBIA2300-DoDof4-CRISPR/Cas9 (DoDof4CRISPR). The verified plasmids, pCAMBIA1301 (overexpression-empty), pCAMBIA2300-CRISPR/Cas9 (knockout-empty), pCAMBIA1301-DoDof4 (DoDof4OE), and DoDof4CRISPR were transferred into 25 mL of A. tumefaciens GV3101 following the method described in 2.8. A single colony was selected and sub-cultured in yeast mannitol medium containing 0.1 mg·mL-1 rifampicin and 0.1 mg·mL-1 kanamycin (Macklin, Shanghai, China) for 2 d until OD600 was 0.8, then centrifuged at 5000 rpm·min-1. MS, which was used as infiltration solution (1 mL) that contained 1 mol·L-1 acetosyringone (Sigma-Aldrich), 1.95 g·mL-1 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid (MES; Sigma-Aldrich), and 0.1% Tween-20 (Sigma-Aldrich), was injected to a depth of 0.5 cm into the center of each D. officinale PLB. PLBs were subsequently soaked in the infiltration solution for 4 d (25°C, 24h darkness) to generate pCAMBIA1301, DoDof4OE, pCAMBIA2300-CRISPR/Cas9 and DoDof4CRISPR lines, respectively. pCAMBIA1301 and DoDof4OE transgenic lines were selected on PLB proliferation medium containing 30 mg·L-1 hygromycin B (Yeasen). pCAMBIA2300-CRISPR/Cas9 and DoDof4CRISPR transgenic lines were selected on PLB proliferation medium containing 25 mg·L-1 kanamycin. After 30 d of transient transfection, PLBs were collected and stored immediately at -80°C. Using the technique outlined in 2.7., total RNA was extracted from transgenic PLBs. DoDof4 expression was examined by qRT-PCR (see 2.6.). The primers used for qRT-PCR are listed in Supplementary Table S6.
2.10 Extraction and determination of WSPs in D. officinale
WSPs in D. officinale samples (100 mg of leaves or PLBs) were ultrasonically extracted using an established method (Yu et al., 2018). WSP content was determined on an UV-3600 multi-directional spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) at 488 nm using the phenol-concentrated sulfuric acid method (Ogura et al., 2023) and was expressed as mg·g-1. To investigate the composition of WSPs, rapid hydrolysis and pre-column derivatization were executed using 0.5 mol·L-1 1-phenyl-3-methyl-5-pyrazolopyrimidone (PMP; Sigma-Aldrich), as described by Yu et al. (2019). Thereafter, 5 μL of filtered supernatant was injected into an Agilent 1260 (Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with an Ultimate XB-C18 column (Welch Materials, Shanghai, China) to detect monosaccharide content. Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich) and mannose (Sigma-Aldrich) were used as internal standards, and their content was expressed as mg·g-1.
2.11 Statistical analysis
All experiments in this paper were performed as three or more independent replicates. The mean ± standard deviation (SD) of the data were calculated and graphs were created in GraphPad Prism v. 8.0.2 (GraphPad, Boston, MA, USA). Statistical analyses were performed in SPSS Statistics v. 27.0. In all graphs, *** represents a very highly significant difference (P < 0.001), ** represents a highly significant difference (P < 0.01), and * represents a significant difference (P < 0.05). RNA-Seq analysis (including transcriptome sequencing, library preparation, transcriptome sequencing, and transcriptome analysis) was conducted at BMKCloud (https://www.biocloud.net/).
3 Results
3.1 MeJA stimulated the accumulation of WSPs in D. officinale
Various hormones, as well as biotic and abiotic stresses affect plant health and growth, and ultimately influence the regulation of a number of related genes. MeJA is a signaling molecule that stimulates stress responses and induces the synthesis of a wide range of metabolites. We took D. officinale as a model system to explore the effect of MeJA on Dendrobium species. WSP content increased in MeJA-treated plants, when compared to the control, even more so when treatment period was extended from 30 to 90 d. These findings confirmed that MeJA promotes the accumulation of WSPs in D. officinale (Figure 1).
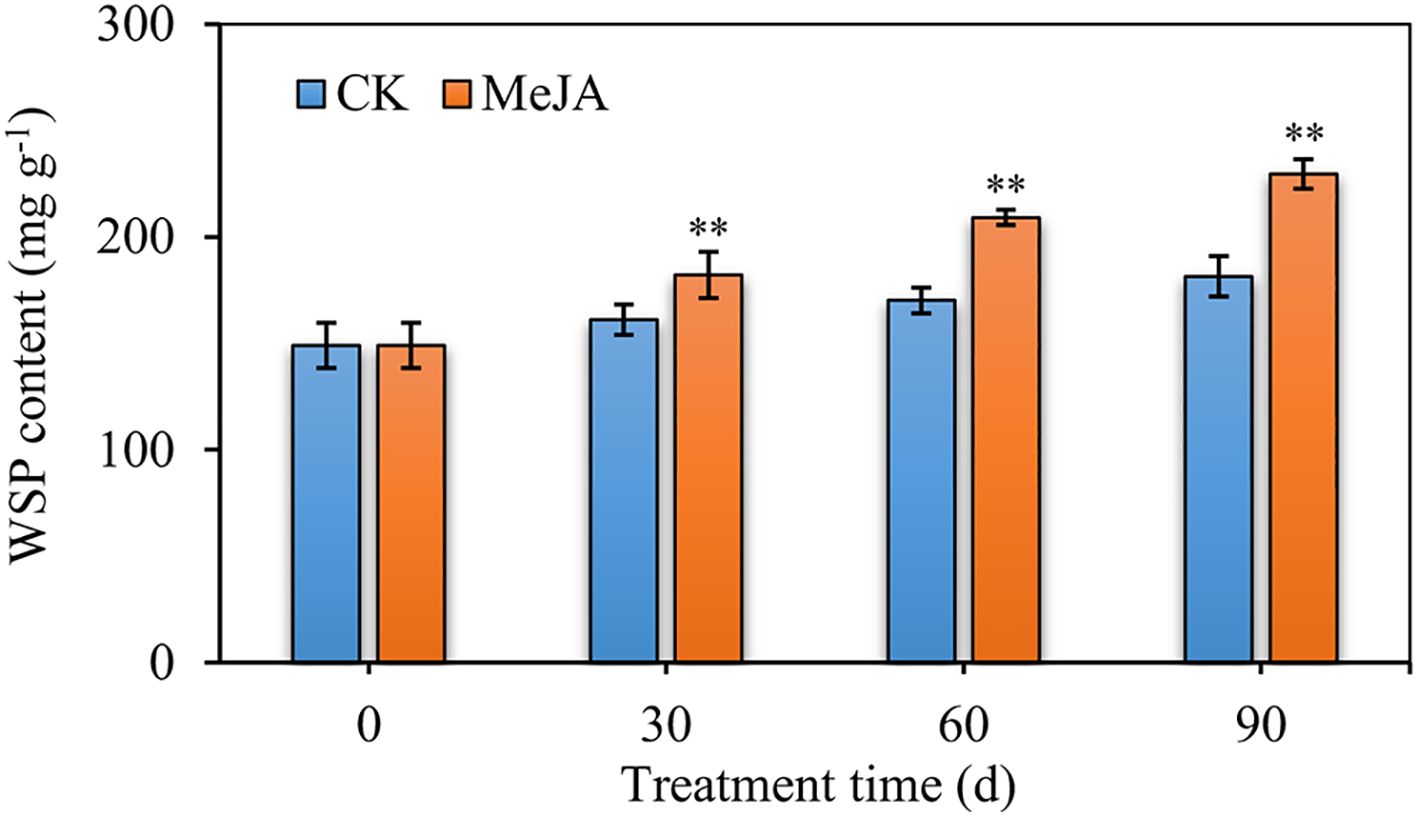
Figure 1. The water-soluble polysaccharide (WSPs) content of 36-month-old D. officinale plants after MeJA treatment for 30, 60, and 90 d. CK represents the control group and MeJA represents the experimental group induced by 0.1 mM MeJA. Mean values and standard deviations (SDs) indicated by error bars. Significant differences: **(P < 0.01).
3.2 Transcriptomic analysis of D. officinale after MeJA treat
To examine the transcriptomic changes in plants following MeJA treatment, PE150 sequencing was performed on six D. officinale samples (MeJA-treated and distilled water-treated with trace ethanol, each in three replicates) using the Illumina NovaSeq6000 sequencing platform. After sequencing quality control, a total of 37.35 Gb of clean data was obtained, including 5.79 Gb of clean data in each sample, and the Q30 base percentage was at least 92.28%. The number of clean reads in each sample ranged from 19,347,994 to 22,825,395. Compared to the high-quality D. officinale genome, the alignment efficiency of clean reads was between 87.66 and 89.77%. Based on the transcriptomic data, a total of 5945 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened, including 2981 up-regulated DEGs and 2954 down-regulated DEGs (Figure 2A), accounting for about half of all DEGs. The functions of these DEGs were analyzed by clusters of eukaryotic orthologous groups (KOG) annotation, revealing a total of 24 categories that were annotated based on the orthologous and evolutionary relationships between eukaryotes (Figure 2B). Based on KOG, only ‘general function prediction’ was most annotated functional classification, followed by ‘post translation modification, protein turnover, chaperones’, and ‘signal transduction mechanisms’, while ‘nuclear structure and cytoskeleton’ had fewest annotations. Intuitively, ‘energy production and conversion’, ‘carbohydrate transport and metabolism’, and ‘secondary metabolites biosynthesis, transport and catabolism’ were closely related to WSP biosynthesis. Volcano plots were used to show differential changes in the expression of DEGs, indicating large and significant differences in up-regulated DEGs (Figure 2C). KEGG enrichment analysis showed a total of 5945 DEGs that were annotated in KEGG pathways, and 20 pathways had highest P-values (Figure 2D). Among them, up-regulated DEGs were mainly clustered into the ‘plants hormone signal transduction pathway’, followed by ‘carbon metabolism’. For carbon metabolism, ‘glycolysis/gluconeogenesis’, ‘pentose phosphate pathway’, ‘fructose and mannose metabolism’, and ‘carbon fixation in photosynthetic organisms’ were associated with WSP biosynthesis. For the down-regulated DEGs, the only pathway was ‘photosynthesis-antenna protein’. In the biological pathways from GO enrichment analysis, the largest group was biological processes (BP), followed by molecular functions (MF) (Figure 2E). The number of up-regulated and down-regulated DEGs differed for each function. In general, the DEGs were concentrated in ‘cellular and metabolic processes’, ‘cellular anatomical entity’, and ‘catalytic activity and binding’. In addition, 16 TFs were predicted among the DEGs (Figure 3A), and seven TFs (bHLH, AP2/ERF, C2H2, bZIP, NAM/ATAF1/2/CUC2 (NAC), Golden2, ARR-B, Psr1 (GARP), B3) from over 20 DEGs accounted for 7/20 of all TFs. The number of predicted DEG members in MYB, WRKY, C3H, Dof, Trihelix, Nuclear Factor Y (NF-Y), and Fatty Acyl-CoA Reductase 1 (FAR1) TF families ranged from 10 to 20, and the number of members in TCP and Whirly TF families was less than 10 (Figure 3B). The WRKY, bZIP, AP2/ERF, MYB, and bHLH TF families were previously identified in D. officinale (He et al., 2017; Zeng et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022), whereas the families of TFs that the D. officinale Dofs belong to remain unclear. Furthermore, expression of the enzyme-encoding genes involved in WSP biosynthesis was positively correlated with Dof genes (Pearson’s R2 > 0.8) (Figure 3C). Therefore, the Dof genes were studied in more detail to appreciate how they regulate the accumulation of WSPs.
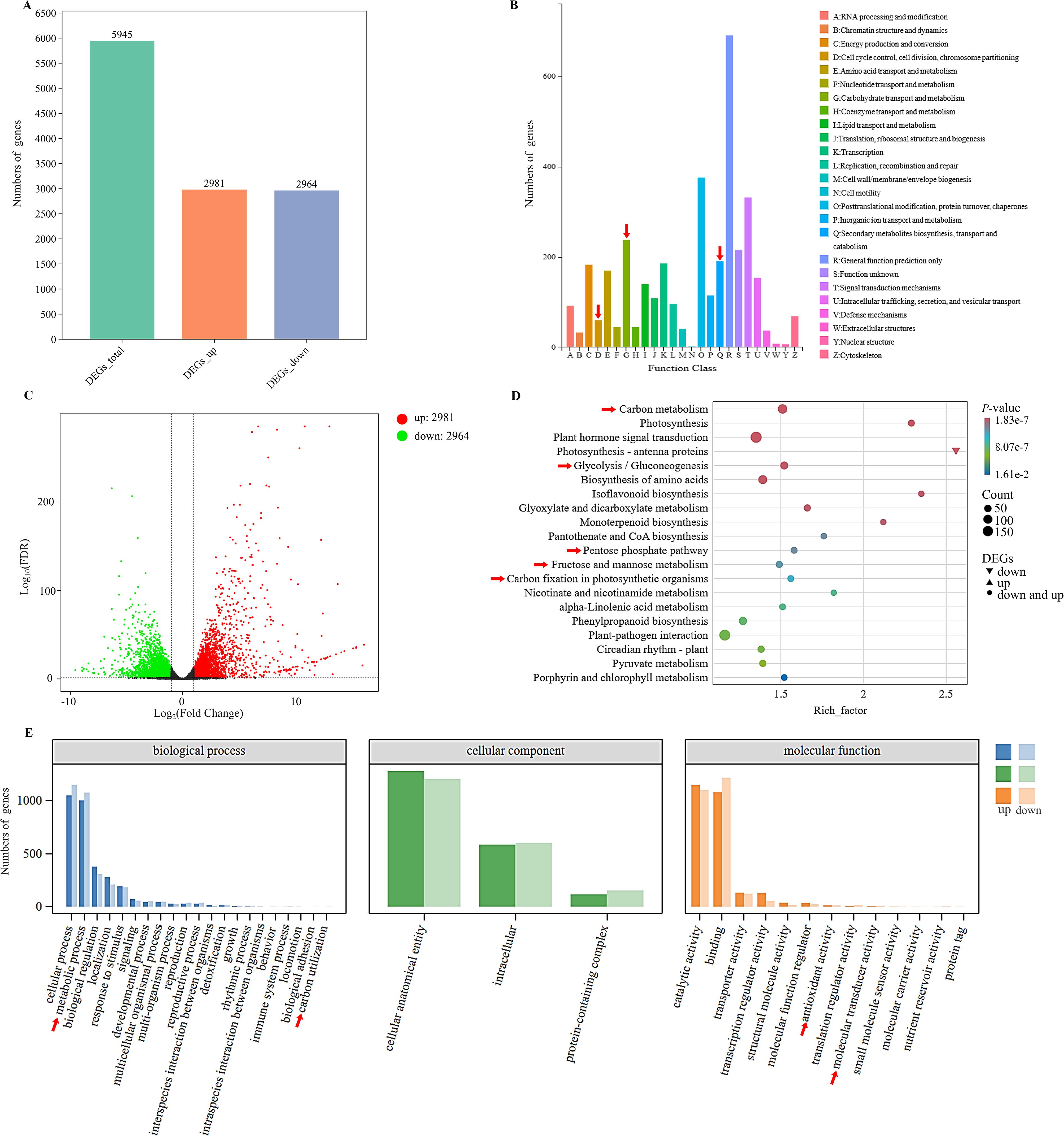
Figure 2. Differential transcriptomic analysis between the control and MeJA-treated samples. (A) Distribution of total differentially expressed genes (DEGs), up-regulated DEGs and down-regulated DEGs with relative expression levels. (B) KOG function annotation analysis. A to Z represent the 24 distinct KOG functional categories. (C) Volcano plot of DEGs. Red, green, and black represent up-regulated DEGs, down-regulated DEGs, and DEGs that did not display significant changes, respectively. (D) KEGG functional annotation of DEGs. The colors of circles or triangles represent different P-values and the size corresponds to the number of enriched genes. (E) GO functional annotation of DEGs. Red arrows highlight functional modules involved in the biosynthesis of water-soluble polysaccharides.
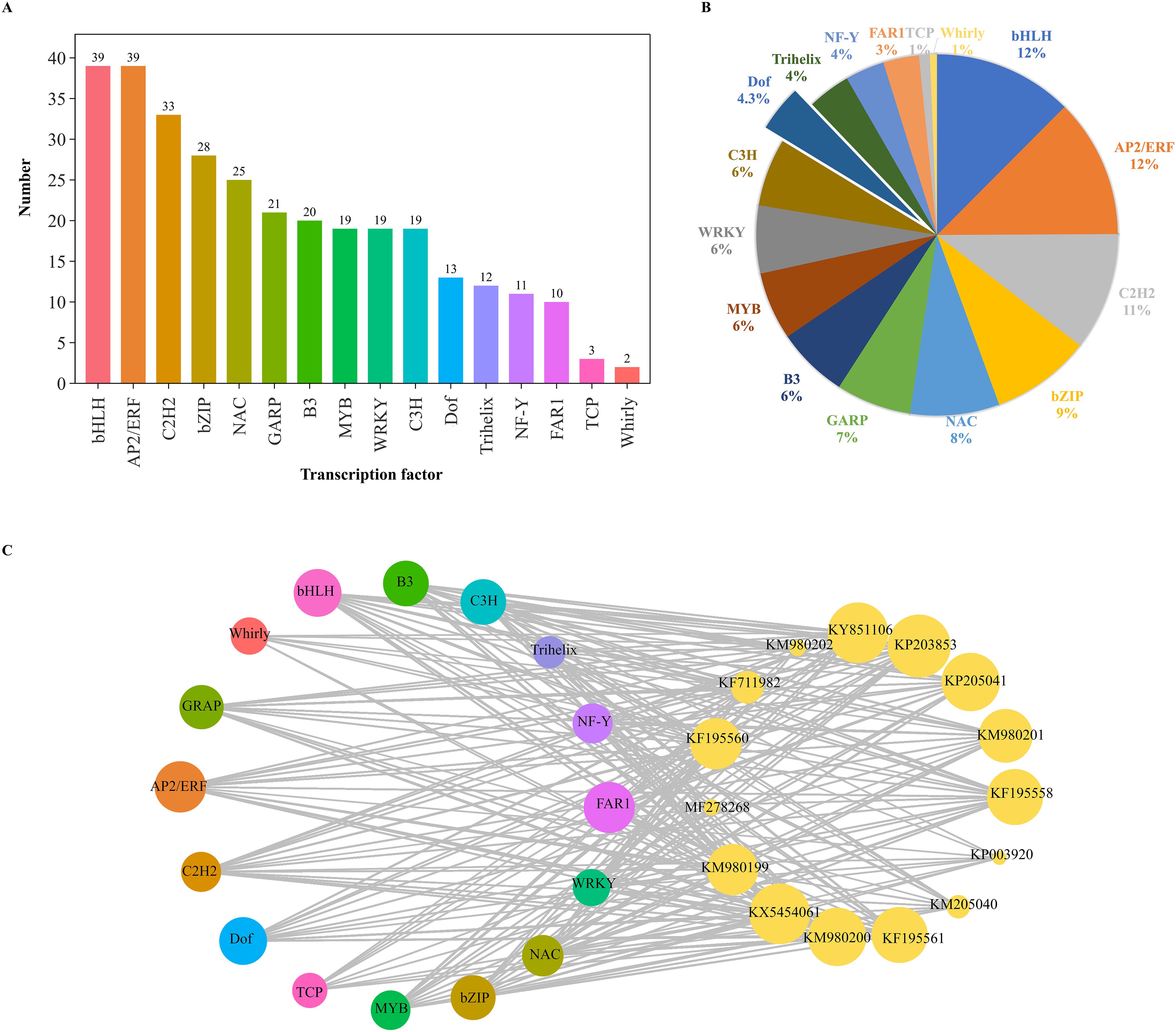
Figure 3. Analysis of differentially expressed transcription factors. (A) Number of DEGs encoding transcription factors. (B) Relative proportion of DEGs encoding transcription factors. (C) Correlation of the expression between polysaccharide biosynthetic genes and DoDof genes. DoGMT (KY851106, MF278268): GDP-mannose transporter, DoGMP (KF195560, KP203853): GDP-mannose-pyrophosphorylase, DoCSLA (KM980199, KM980200, KP003920, KM980201, KM980202, KF195561, KP205040, KP205041): CELLULOSE SYNTHASE-LIKE A, DoPMM (KF195558): Phosphomannomutase, DoUGP (KF711982): Uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, DoUGE (KX54540): UDP glucose 4-epimerase.
3.3 Identification and physicochemical properties analysis of Dof genes
After screening the D. nobile, D. huoshanense and D. officinale genome following the characteristic Dof structural domain (PF02701), and removing redundant and incomplete sequences, 80 Dof genes were identified. Among these Dof proteins, D. nobile and D. huoshanense have an identical number (n = 29) of Dof genes, and the number of DoDof genes were lowest (n= 22). Based on a distribution of individual Dof genes on the corresponding chromosomes, they were sequentially named DhDof1-DhDof29, DnDof1-DnDof29, and DoDof1-DoDof22.
To better understand the roles and mechanisms of these Dof proteins, we systematically predicted and analyzed their physicochemical properties (Supplementary Table S7). Our results revealed that three Dendrobium species exhibited similar levels in terms of average size (Supplementary Figure S1A), MW (Supplementary Figure S1B), pI (Supplementary Figure S1C), instability index (Supplementary Figure S1D), aliphatic index (Supplementary Figure S1E), and GRAVY (Supplementary Figure S1F) for their Dof proteins. The size in the Dof proteins ranged from 109 (DnDof7) to 626 (DhDof1), and their molecular weights ranged between 12.05 (DnDof7) and 71.12 kDa (DhDof1), and their pIs ranged from 5.17 (DnDof14) to 9.79 (DoDof3). The instability index of all Dof proteins exceeded 40, which indicates that they are highly stable. Combined with aliphatic index and GRAVY, all Dof proteins were classified as hydrophilic proteins.
3.4 Phylogenetic analysis and multiple sequence alignment Dof proteins
To explore the evolutionary relationships within the Dof gene family of Dendrobium, a phylogenetic tree of AtDof, OsDof, DhDof, DnDof and DoDof genes was shown in Figure 4. Dof genes were divided into four groups according to their phylogenetic relationships (Figure 4). Group A contained the largest number of Dof genes (n = 48), groups B/C/D contained 34, 32, and 32 Dof genes. Further analysis revealed that the Dof genes from Dendrobium species clustered closely together, rather than randomly distributed with those from A. thaliana and O. sativa. Multiple sequence alignment showed that all Dof genes consist of 50 highly conserved amino acids that form a CX2CX21CX2C sequence at the N-terminus, namely the Dof structural domain (Supplementary Figure S2). This suggests that Dof genes are relatively conserved during the evolution of Dendrobium species.
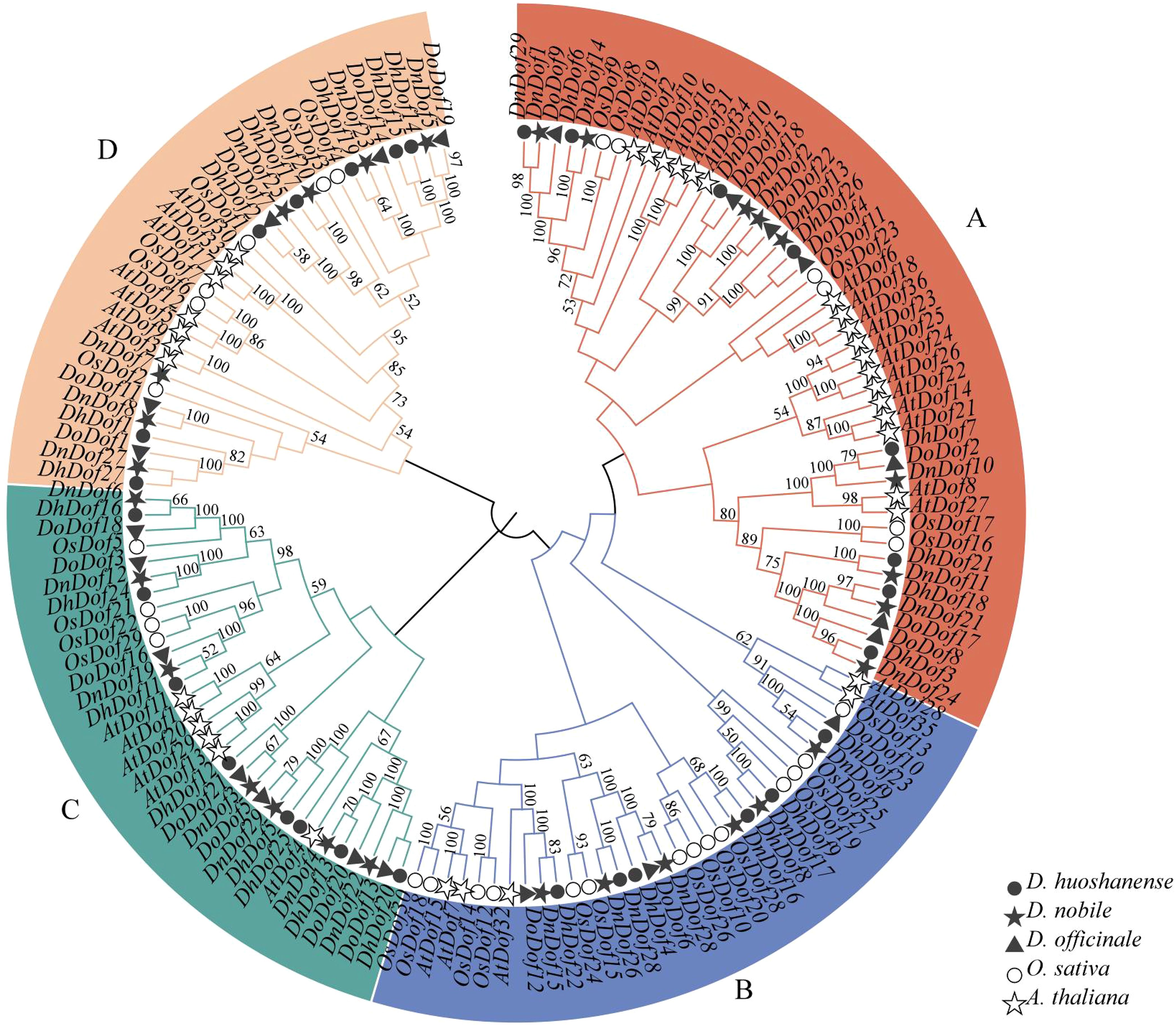
Figure 4. Phylogenetic relationship between the DhDof, DnDof, DoDof, OsDof, and AtDof genes. The phylogenetic tree was generated with MEGA software using the neighbor-joining method with 1000 bootstrap values. (A–D) are defined based on the Arabidopsis thaliana Dof family.
3.5 Chromosome localization and collinearity analysis of Dof genes
Supplementary Figure S3 showed the location of the Dof genes in D. huoshanense (Supplementary Figure S3A), D. nobile (Supplementary Figure S3B) and D. officinale (Supplementary Figure S3C) chromosomes. The 29 DhDof genes were unevenly mapped on the 15 chromosomes while no DhDof genes localized on Chr3/10/12/15. Chr8 possessed the highest number (n = 5) of DoDof genes (DoDof12-DoDof 16). The 29 DhDof genes exhibited random distribution across 15 chromosomes, mirroring the distribution pattern observed in D. huoshanense. Among all chromosomes, Chr3 exhibited the highest density (n = 5) of DhDof genes (DhDof2-DhDof6) while Chr2/7/13/16 lacked DhDof genes. The 22 DoDof genes were unevenly distributed across the 13 chromosomes. Chr19 had the highest number (n = 5) of DoDof genes (DoDof18-DoDof 22) while five chromosomes (Chr7/8/10/15/16) had no DoDof genes. An interspecies (i.e., between three Dendrobium species) analysis revealed that D. officinale and D. nobile displayed the highest level of collinearity (n = 32), and D. officinale and D. huoshanense had 21 pairs (Supplementary Figure S4A). This indicates that D. officinale and D. nobile have a closer relationship than D. officinale and D. huoshanense. In addition, there were 25 collinear genes when compared with A. thaliana, and even fewer (n = 8) between D. officinale and O. sativa (Supplementary Figure S4B).
3.6 Tissue-specific expression analysis of DoDof genes
The expression of genes in plants is closely related to their functions, so the expression of four tissues in D. officinale (flower, leaf, stem, and root) were analyzed (Supplementary Table S8). The expression pattern revealed that 22 DoDof genes exhibited a distinct organ-specific expression. These were divided further into 5 groups I-V (Figure 5A). In group I, 6 DoDof genes exhibited high expression in many tissues. For example, DoDof12 exhibited high expression in leaf and stem, DoDof14 had high expression in root and leaf, DoDof17 showed high expression in flower and root, and DoDof4/6/8 had high expression in flower, root, and stem. In group II, eight genes (DoDof3, DoDof5, DoDof13, DoDof15, DoDof16, DoDof18, DoDof20, and DoDof22), and in group III, DoDof2, DoDof7, and DoDof19 displayed high expression in root and stem, and relatively uniform expression in flower, root, and stem. DoDof10 and DoDof11, which formed part of group IV, displayed low expression in all tissues. In group V, the remaining DoDof genes were expressed mainly in flower and had similarly low expression in other tissues. Overall, most genes were highly expressed in flower, but many genes were also expressed in root and stem. Highly expressed DoDof genes were also identified in each tissue (Figure 5B). Compared with the expression patterns of the 22 DoDof genes, DoDof17 displayed the highest expression in flower and root, and DoDof14 displayed the highest expression in leaf. Expression in stem was dominated by DoDof2 and DoDof4, then by DoDof6, and finally DoDof8 and DoDof12. A Venn diagram (Figure 5C) revealed that no genes were highly expressed in all tissues, while three genes (DoDof4/6/8) were highly expressed in flower, stem, and root.
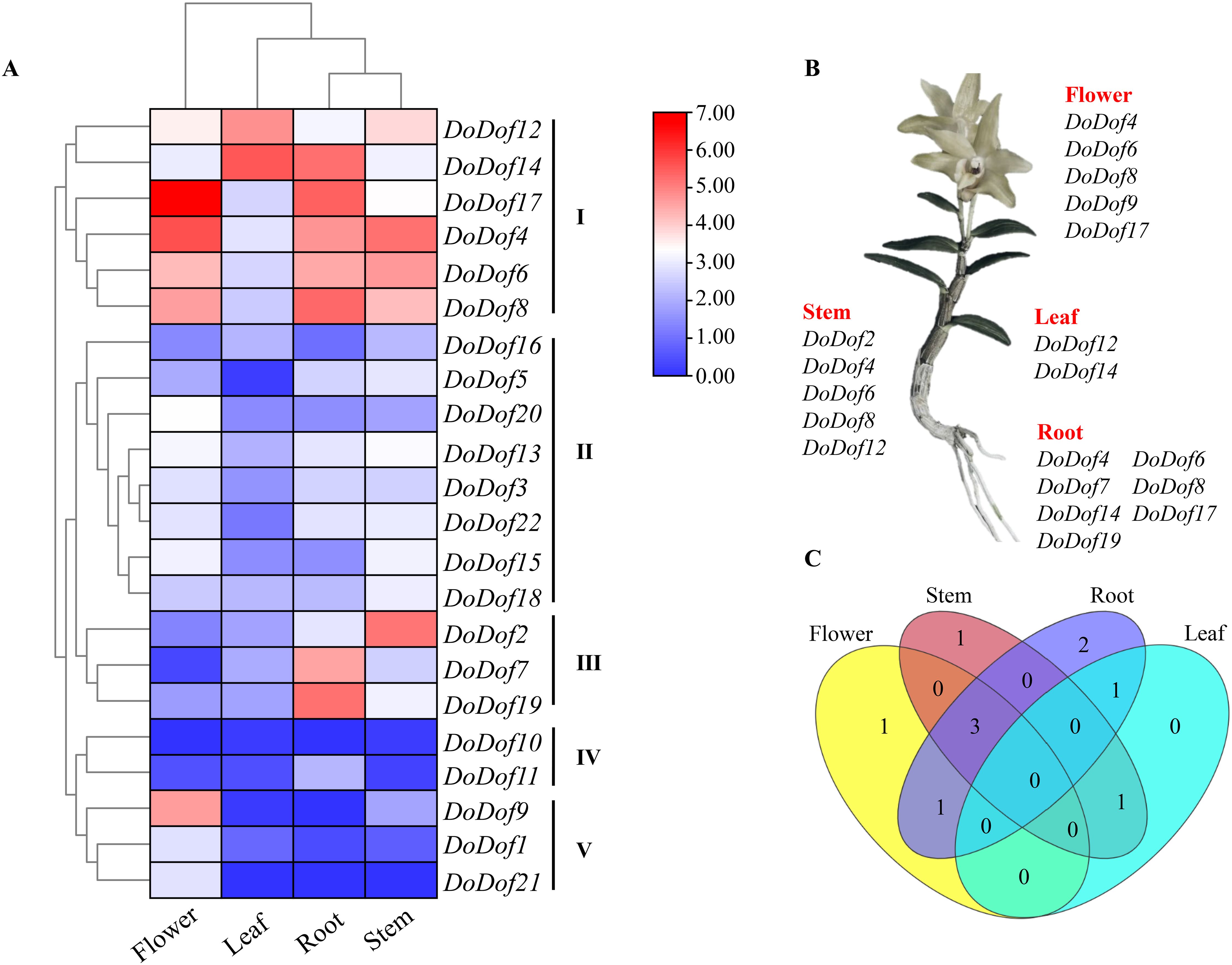
Figure 5. Expression pattern analysis of DoDof genes. (A) Tissue-specific expression in flower, leaf, root, and stem of D. officinale. Red and blue in the heatmap represent high and low relative expression, respectively. (B) Identification of highly expressed DoDof genes in each tissue. (C) Venn diagram of DoDof genes in different tissues.
3.7 Expression patterns of DoDof genes following treatment with MeJA
In order to assess the relationships between DoDof genes and MeJA, the relative expression levels of DoDof genes were examined by qRT-PCR after 30 d of MeJA treatment to validate the corresponding transcriptomic data. The change in patterns of DoDof genes was consistent with the trend of the transcriptome data, which indicates that the transcriptomic data was reliable (Figure 6). After MeJA induction, the expression of 14 DoDof genes (DoDof1/2/3/4/5/6/8/11/16/17/18/20/21/22) was up-regulated. The expression of DoDof9 did not change before and after induction, and the remaining seven genes showed different degrees of down-regulated expression after induction. DoDof4/6 were highly up-regulated, 2.44- and 3.79-fold, respectively, after MeJA treatment. Very few genes of same subfamilies showed same expression trend. For example, relative expression of DoDof1/11 was lower before and after induction, and relative expression of DoDof7/14/19 decreased after induction. These findings suggest that MeJA has a significant effect on expression of DoDof genes and may thus play a role in the regulation of plant WSP biosynthesis.
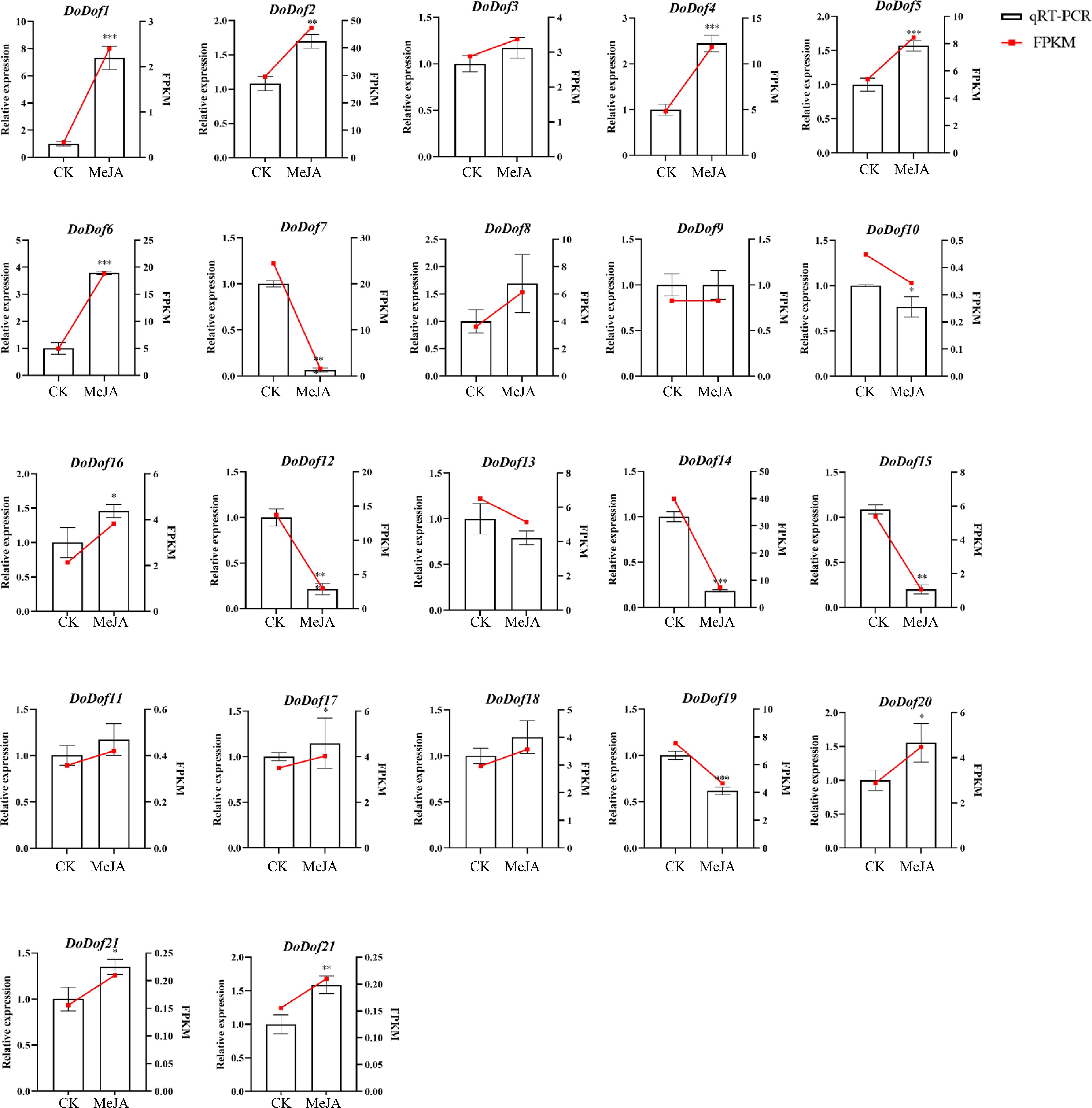
Figure 6. Expression levels of DoDof genes induced by MeJA, as determined by qRT-PCR. The X-axis shows the different treatments of PLBs: CK represents the control group and MeJA represents the experimental group induced by 0.1 mM MeJA. The Y-axis represents the relative expression level. Mean values and standard deviations (SDs) indicated by error bars. Significant differences: *(P < 0.05), **(P < 0.01), and ***(P < 0.001).
3.8 Correlation analysis between DoDof genes and enzyme-encoding genes involved in the biosynthesis of water-soluble polysaccharides
DoPMM (KF195558), DoGMP (KF195560, KP203853), DoGMT (KY851106, MF278268), DoUGP (KF711982), DoUGE (KX54540), and DoCSLA (KM980199, KM980200, KP003920, KM980201, KM980202, KF195561, KP205040, KP205041), which were highly expressed in flowers and stems (Figure 7A), were identified. According to the 2020 edition of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia (Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, 2020), the stems of D. officinale are usually used as medicine, while the flowers, roots, and leaves are non-medicinal parts. Analysis of the expression of DoDof genes in different tissues revealed that DoDof2/4/6/8/12 had highest expression in stem, so they were selected for correlation analysis with these 16 enzyme-encoding genes by SPSS Statistics version 27.0 (Figure 7B). DoDof4 had a notable co-expression relationship with 8 enzyme-encoding genes (KM980199, KM980202, KF195561, KF195558, KX545406, KF711982, KP203853, and MF27968). DoDof2 was correlated with 6 enzyme-encoding genes (KP203853, KX545406, KF711982, MF27968, KF195561, and KF195558), DoDof8 was highly and positively correlated with KF711982, no enzyme-encoding gene had a high positive correlation with DoDof6 or DoDof12.
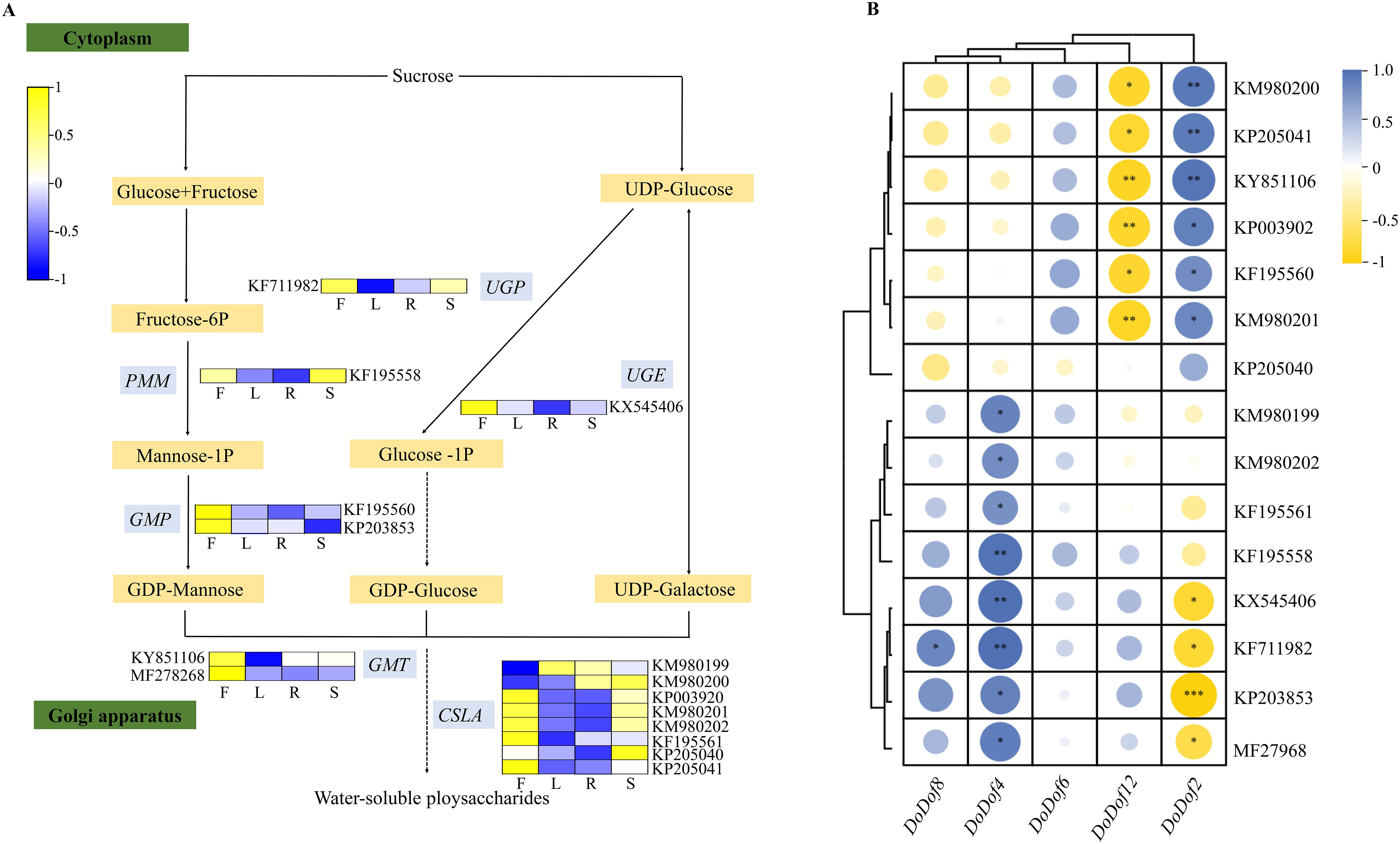
Figure 7. Expression of enzyme-encoding genes involved in the metabolic pathway of water-soluble polysaccharides (WSPs), and a correlation analysis with DoDof genes. (A) Tissue-specific expression of enzyme-encoding genes involved in the metabolic pathway of WSPs. F, L, R, and S in the heatmap denote flower, leaf, root, and stem tissues, respectively. DoPMM (KF195558): Phosphomannomutase, DoGMP (KF195560, KP203853): GDPmannose-pyrophosphorylase, DoGMT (KY851106, MF278268): GDP-mannose transporter, DoUGP (KF711982): Uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase, DoUGE (KX54540): UDP glucose 4-epimerase, DoCSLA (KM980199, KM980200, KP003920, KM980201, KM980202, KF195561, KP205040, KP205041): CELLULOSE SYNTHASE-LIKE. (B) Correlation analysis between enzyme-encoding genes and DoDof genes. Significant differences: *(P < 0.05), **(P < 0.01), and ***(P < 0.001).
3.9 Subcellular localization and transcriptional activation assay of DoDof4
DoDof4 showed 99.65% similarity with the original sequence. DoDof4 open reading frame (ORF) consisted of 876 bp encoding 292 amino acids (Figure 8A) and the predicted molecular weight was 27.84 kDa. The protein sequence contains one Dof domain at the N-terminus indicating that cloned DoDof4 belongs to the Dof family. Subcellular localization analyses revealed that pHB-DoDof4-YFP was localized in the nucleus (Figure 8C). Furthermore, pGBKT7-DoDof4 plasmid and positive control grew well on SD/-Ade-Trp-His medium, which degraded the X-α-Gal and changed the color of yeast colony from white to blue. pGBKT7-Empty and negative control did not grow on the SD/-Ade-Trp-His medium (Figure 8B), suggesting that DoDof4 was a transcriptional activator.
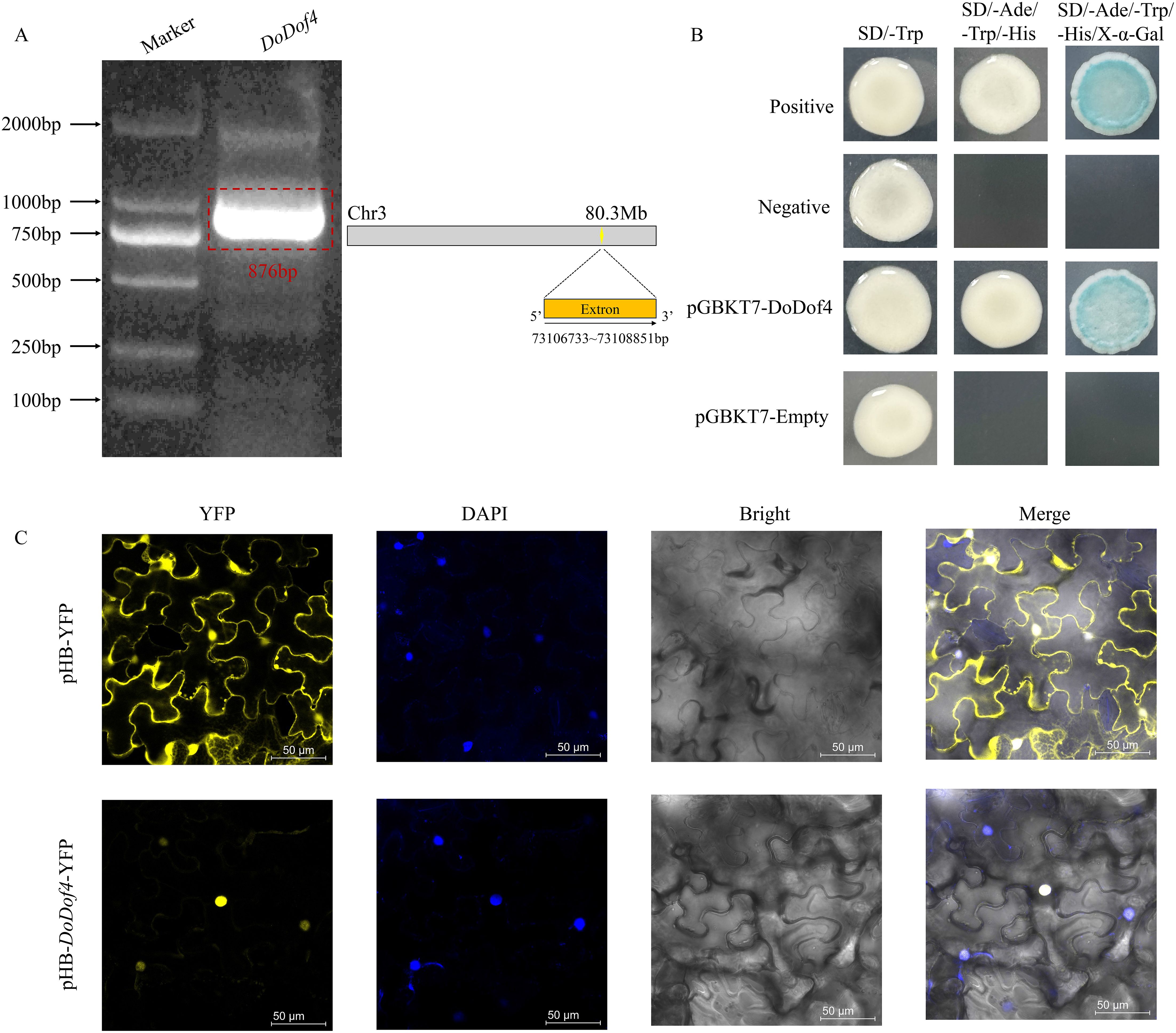
Figure 8. (A) Cloning of the gene. (B) Transcriptional activation of DoDof4 in yeast cells. SD/-Trp: Synthetic dropout medium-Tryptophan. SD/-Ade/-Trp/-His: Synthetic dropout medium-Adenine/-Tryptophan/-Histidine. SD/-Ade/-Trp/-His/X-α-Gal: Synthetic dropout medium-Adenine/-Tryptophan/-Histidine with X-α-Gal. (C) Subcellular localization. pHB-YFP, as the positive control, or pHB-DoDof4-YFP, were individually transiently infected into Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. YFP is a nucleus and membrane co-localized signal. Scale bars = 50 μm.
3.10 Transient transformation validated of DoDof4
Plasmids (pCAMBIA1301, pCAMBIA2300-CRISPR/Cas9, DoDof4OE, and DoDof4CRISPR) were then separately transformed into the D. officinale PLBs (Figure 9A). After 4 d of transient transformation, DoDof4OE transgenic lines were greener than other lines (Figure 9B). After 30d, RNA was extracted from the transgenic lines, and their cDNA was reverse transcribed. The qRT-PCR results showed that the relative expression of the DoDof4OE line was higher than that of the pCAMBIA1301 line (Figure 9C). Sequencing results revealed a 3 bp deletion in DoDof4CRISPR (Supplementary Figure S5). These results validated successful genetic transformation.
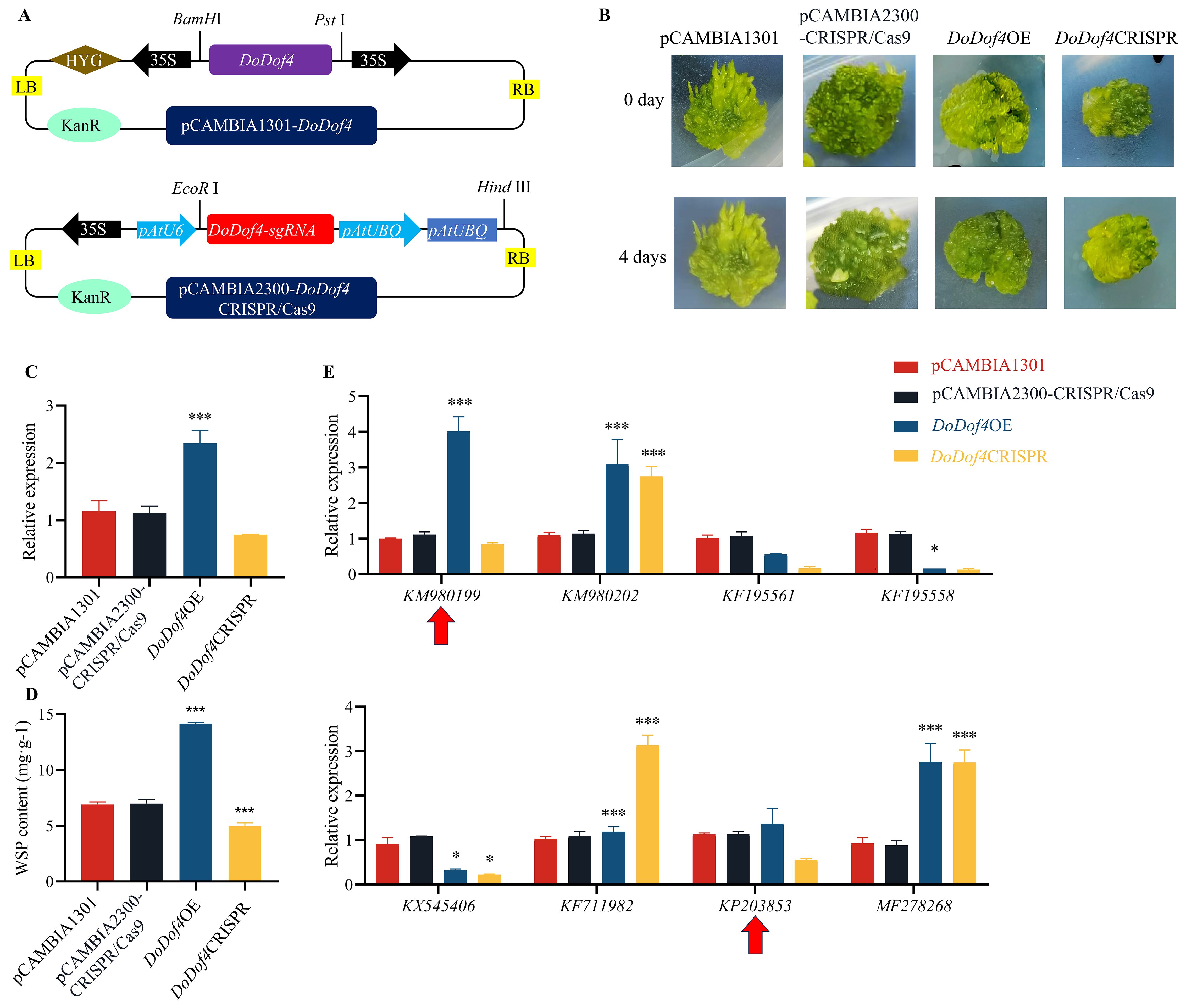
Figure 9. Functional analysis of the DoDof4 gene. (A) Diagram of DoDof4OE and DoDof4CRISPR vector construction. The coding sequence without the termination codon TGA of DoDof4 was constructed on pCAMBIA1301 vector. DoDof4-sgRNA were ligated to the pCAMBIA2300-CRISPR/Cas9 vector. (B) Changes to D. officinale PLBs after transformation. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of the DoDof4 gene. (D) Analysis of water-soluble polysaccharide content in transgenic PLBs. (E) qRT-PCR analysis of DoDof4 and enzyme-encoding genes. Red arrows (KM980199 and KP203853) indicate potential targets of DoDof4 to regulate WSP production in D. officinale. Bar indicates the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of three replicates (n = 10). Significant differences between groups: * (P < 0.05), and *** (P < 0.001).
3.11 DoDof4 enhances WSP content in D. officinale
WSP content in the DoDof4OE transgenic line was 1.5-fold higher than that in the pCAMBIA1301 transgenic lines (Figure 9D). HPLC detection revealed that the WSPs in D. officinale were predominantly composed of glucose and mannose. The contents of glucose and mannose in DoDof4OE showed a sharp increase relative to pCAMBIA1301. Furthermore, the mannose/glucose ratio in DoDof4OE was 1.87-fold higher than that in pCAMBIA1301 and the mannose/glucose ratio in DoDof4CRISPR was the lowest. These results imply that DoDof4 may significantly stimulate the biosynthesis of WSPs in D. officinale, possibly by regulating mannose transportation (Supplementary Figure S6). Therefore, the relative expression of KM980199, KM980202, KF195561, KF195558, KX545406, KF711982, KP203853, and MF278268 were characterized in pCAMBIA1301 and DoDof4OE transgenic PLBs to explore how DoDof4 regulates the biosynthesis of WSPs. The relative expression of KM980199 and KP203853 increased in the DoDof4OE line (Figure 9E), indicating that DoDof4 may regulate WSP biosynthesis by converting mannose-1P to GDP-mannose.
4 Discussion
Bioactive polysaccharides in plants have a wide range of nutritional and health functions, as well as medicinal value. Although most research has focused on extraction, purification, biological activity and structural characterization of WSPs, there are a few studies on their biosynthetic mechanism. The medicinal orchid has a rich content of WSPs, mainly in its stems. The concentration and induction period of MeJA treatment are important for the production of specialized metabolites. Previously, D. officinale seedlings treated with 0.1 mM MeJA markedly stimulated the accumulation of WSPs (Yuan et al., 2017), but the time-response relationship is unclear. To better understand the mechanism of Dendrobium responding to MeJA, we used D. officinale as model, treating them with 0.1 mM MeJA for 30 to 90 d. After stimulation with MeJA, the content of WSPs increased, even more over time. WRKY, bZIP, AP2/ERF, MYB, and bHLH are shown to be associated with resistance to various abiotic stresses (He et al., 2017; Zeng et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022). Dof members accounted for 4% of all DEGs and their homologous genes exhibited a link to secondary metabolism. For example, ZmDof36 can specially bind to genes involved in starch synthesis at downstream promoters such as Alkylglycerone Phosphate Synthase 1a (ZmAGPS1a), ZmISA3, and ZmGBSSI, to positively up-regulate starch biosynthesis (Wu et al., 2019). However, Actinidia deliciosa Dof3 transactivated the starch degradation gene AdBAM3 (β-amylase 3), affecting fruit flavor (Zhang et al., 2018). In addition, overexpression CrDof assisted the intracellular lipid content of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and may regulate the expression of crucial genes such as CrBCC1, CrFAT1, and CrSQD1 (Jia et al., 2019). Moreover, in Fragaria ananassa, FaDof2 positively controlled the expression of FaEGS2 and FaEOBII, which are involved in eugenol synthesis, thereby regulating the volatile phenylpropanoid pathway (Molina-Hidalgo et al., 2017). The promoter regions of enzyme-encoding genes involved in WSP biosynthesis contained many Dof binding sites (Supplementary Figure S7), such as [T/A]AAAG or their complementary sequences CTTT[T/A]. Furthermore, the enzyme-encoding genes involved in the metabolic pathway of WSPs were significantly (P > 0.8) associated with the Dof genes (Figure 3C). However, the regulatory mechanism by which Dof modulates the accumulation of WSPs remains unclear in Dendrobium species.
To investigate the distribution and functional of Dof genes to regulate WSPs in Dendrobium species, we identified 29 Dof members in D. huoshanense and D. nobile, along with 22 Dof members in D. officinale. These were less than the number of Dof genes in A. thaliana (n = 36) (Xu et al., 2020), Capsicum annuum (n = 33) (Wu et al., 2016), and Brassica rapa (n = 76) (Ma et al., 2015), but similar to the number in Cyperus esculentus (n = 29) (Fu et al., 2024). Although three Dendrobium species had conserved chromosome numbers (n = 19), the D. huoshanense, D. nobile D. officinale showed species-specific Dof genes localization patterns. DhDof and DnDof genes were unevenly distributed on 15 chromosomes, while DoDof genes only localized to just 13 chromosomes. These studies indicate similar results not only in the Dof gene family, but also in other gene families. During evolution, plants’ chromosomes undergo changes such as fusion and cleavage, resulting in processes such as gene recombination, transfer, and elimination, prompting uneven gene distribution. This phenomenon is prevalent among plants, driving them towards optimal evolution. The collinearity between D. officinale and A. thaliana (eight pairs) was less than that between D. officinale and O. sativa (25 pairs), which is consistent with the evolutionary pattern of dicotyledonous plants (Fu et al., 2024). Compared with D. hosannae, D. officinale and D. nobile displayed higher collinearity, indicating a closer evolutionary relationship between D. officinale and D. nobile.
Dof genes were categorized into 4 groups based on the phylogenetic analysis, which was consistent with previous reports (Moreno-Risueno et al., 2007). The expression profiles of 22 DoDof genes in flower, leaf, root, and stem were analyzed. Among them, five DoDof genes (DoDof2/4/6/8/12) were highly expressed in stem, suggesting their role in WSP biosynthesis. High expression of DoDof4/6/7/8/14/17/19 in root, and of DoDof12 and DoDof14 in leaf, may be related to resistance to abiotic stresses. After analysis of transcriptomic data, Dof genes in the MeJA treatment were screened. qRT-PCR analysis demonstrated that DoDof1/2/3/4/5/6/8/11/16/17/18/20/21/22 were strongly up-regulated, DoDof9 was unchanged, and the 7 genes (DoDof7/10/12/13/14/15/19) were down-regulated. Among the DoDof genes that were highly expressed in stem, DoDof4 displayed the highest expression. WSP was higher in DoDof4OE lines than in pCAMBIA1301 lines (Figure 9D). Additionally, DoDof4OE exhibited significantly increased mannose and glucose contents, along with a higher mannose/glucose ratio (Supplementary Figure S6). These results indicate that DoDof4 is a positive regulator of WSP accumulation, particularly in the transportation of mannose. Conversely, ZmDof36 decreased WSP content in the seed endosperm, and ultimately contributed to the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism. SRF1 (a Dof gene) in sweet potato modulated polysaccharide metabolism in storage roots, reducing the glucose and fructose contents (Tanaka et al., 2009). In O. sativa, OsDof11 promoted the expression of SUCROSE TRANSPORTER 1 (OsSUT1), SUGAR WILL EVENTUALLY BE EXPORTED TRANSPORTER 11 (OsSWEET11), and OsSWEET14, thereby regulating sugar transport (Wu et al., 2018). Based on the above-mentioned evidence, we propose that D. officinale may have evolved a specialized mechanism to biosynthesize and accumulate WSPs as a way to adapt to extreme environments. Furthermore, two polysaccharide biosynthetic genes (KM980199 and KP203853) were potential targets of nucleus-localized DoDof4 to regulate WSP production in D. officinale. DoDof4 might combine DoCSLA (KM980199) and DoGMP (KP203853) genes to positively regulate the metabolic pathway of D. officinale WSPs.
5 Conclusion
This study aimed to appreciate details about the genetic regulation of the WSPs metabolic pathway in Dendrobium species by MeJA. DhDof, DnDof and DoDof genes whose physicochemical properties, chromosome localization, collinearity was analyzed. DoDof genes were expressed in flower, stem, leaf, and root. WSP content in transgenic DoDof4 plants was significantly correlated with DoCSLA (KM980199) and DoGMP (KP203853), two genes related to the WSP biosynthetic pathway. DoDof4 might play a role in the WSPs metabolic pathway. This study lays a foundation for exploring additional functions of the Dof genes to better understand the molecular mechanism of the WSPs metabolic pathway from the perspective of transcriptional regulation, and fortify cultivation practices of Dendrobium species.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. This data can be found here: China National Center for Bioinformation (CNCB, https://www.cncb.ac.cn/) under BioProject accession number PRJCA043716.
Author contributions
ZX: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. GZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. FZ: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. XD: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. YS: Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. JT: Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by a Key Scientific and Technological Grant of Zhejiang for Breeding New Agricultural Varieties (2021C02074-1), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LY23H280003), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32000257, 32401543), Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department (Y202456134), and Zhejiang Xin-miao Talents Program (2025R410BC068). We appreciate the considerable help from the Public Platform of Pharmaceutical Research Center, Academy of Chinese Medical Science, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the considerable experimental support from the Public Platform of Pharmaceutical Research Center, Academy of Chinese Medical Science, Zhejiang Chinese Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1617856/full#supplementary-material
References
Chen, C., Wu, Y., Li, J., Wang, X., Zeng, Z., Xu, J., et al. (2023). TBtools-II: A "one for all, all for one" bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 16, 1733–1742. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.09.010
Cominelli, E., Galbiati, M., Albertini, A., Fornara, F., Conti, L., Coupland, G., et al. (2011). Dof binding sites additively contribute to guard cell-specificity of AtMYB60 promoter. BMC Plant Biol. 11, 162. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-162
Feng, B., Han, Y., Xiao, Y., Kuang, J., Fan, Z., Chen, J., et al. (2016). The banana fruit Dof transcription factor MaDof23 acts as a repressor and interacts with MaERF9 in regulating ripening-related genes. J. Exp. Bot. 67, 2263–2275. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw032
Fu, C., Liao, Z., Jiang, N., and Yang, Y. (2024). Genome-wide identification and molecular evolution of Dof transcription factors in Cyperus esculentus. BMC Genomics 25, 667. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10565-y
Guo, A., He, K., Liu, D., Bai, S., Gu, X., Wei, L., et al. (2005). DATF: a database of Arabidopsis transcription factors. Bioinformatics. 21, 2568–2569. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti334
Gupta, S., Malviya, N., Kushwaha, H., Nasim, J., Bisht, N. C., Singh, V. K., et al. (2015). Insights into structural and functional diversity of Dof (DNA binding with one finger) transcription factor. Planta. 241, 549–562. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2239-3
Haq, F., Xu, X., Ma, W., Shah, S., Liu, L., Zhu, B., et al. (2021). A Xanthomonas transcription activator-like effector is trapped in nonhost plants for immunity. Plant Commun. 3, 100249. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2021.100249
He, C., Yu, Z., Teixeira da Silva, J. A., Liu, X., Wang, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2017). DoGMP1 from Dendrobium officinale contributes to mannose content of water-soluble polysaccharides and plays a role in salt stress response. Sci. Rep. 7, 41010. doi: 10.1038/srep41010
Jia, B., Xie, X., Wu, M., Lin, Z., Yin, J., Lou, S., et al. (2019). Understanding the functions of endogenous DOF transcript factor in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 12, 67. doi: 10.1186/s13068-019-1403-1
Kang, W., Kim, S., Lee, H., Choi, D., and Yeom, S. I. (2016). Genome-wide analysis of Dof transcription factors reveals functional characteristics during development and response to biotic stresses in pepper. Sci. Rep. 6, 33332. doi: 10.1038/srep33332
Khaksar, G., Sangchay, W., Pinsorn, P., Sangpong, L., and Sirikantaramas, S. (2019). Genome-wide analysis of the Dof gene family in durian reveals fruit ripening-associated and cultivar-dependent Dof transcription factors. Sci. Rep. 9, 12109. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48601-7
Kisu, Y., Ono, T., Shimofurutani, N., Suzuki, M., and Esaka, M. (1998). Characterization and expression of a new class of zinc finger protein that binds to silencer region of ascorbate oxidase gene. Plant Cell Physiol. 39, 1054–1064. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a029302
Li, C., Cai, X., Shen, Q., Chen, X., Xu, M., Ye, T., et al. (2022). Genome-wide analysis of basic helix-loop-helix genes in Dendrobium catenatum and functional characterization of DcMYC2 in jasmonate-mediated immunity to Sclerotium delphinii. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.956210
Li, K., Liang, Y. M., Chen, Z., Zheng, P., Zhang, G., Yan, B., et al. (2024). Genome-wide identification of the alkaloid synthesis gene family CYP450, gives new insights into alkaloid resource utilization in medicinal Dendrobium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 259, 129229. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129229
Li, D., Ye, G., Li, J., Lai, Z., Ruan, S., Qi, Q., et al. (2023). High light triggers flavonoid and polysaccharide synthesis through DoHY5-dependent signaling in Dendrobium officinale. Plant J. 115, 1114–1133. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16284
Livak, K. J. and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ma, J., Li, M., Wang, F., Tang, J., and Xiong, A. (2015). Genome-wide analysis of Dof family transcription factors and their responses to abiotic stresses in Chinese cabbage. BMC Genomics 16, 33. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1242-9
Molina-Hidalgo, F., Medina-Puche, L., Cañete-Gómez, C., Franco-Zorrilla, J. M., López-Vidriero, I., Solano, R., et al. (2017). The fruit-specific transcription factor FaDOF2 regulates the production of eugenol in ripe fruit receptacles. J. Exp. Bot. 68, 4529–4543. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erx257
Moreno-Risueno, M. A., Díaz, I., Carrillo, L., Fuentes, R., and Carbonero, P. (2007). The HvDoF19 transcription factor mediates the abscisic acid-dependent repression of hydrolase genes in germinating barley aleurone. Plant J. 51, 352–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2007.03146.x
Murashige, T. and Skoog, F. (1962). A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plantarum. 15, 473–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Ogura, I., Sugiyama, M., Tai, R., Mano, H., and Matsuzawa, T. (2023). Optimization of microplate-based phenol-sulfuric acid method and application to the multi-sample measurements of cellulose nanofibers. Anal. Biochem. 681, 115329. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2023.115329
Pérez-Escobar, O. A., Bogarín, D., Przelomska, N. A. S., Ackerman, J. D., Balbuena, J. A., Bellot, S., et al. (2024). The origin and speciation of orchids. New Phytol. 242, 700–716. doi: 10.1111/nph.19580
Saitou, N. and Nei, M. (1987). The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454
Si, C., Zeng, D., Yu, Z., Teixeira da Silva, J. A., Duan, J., He, C., et al (2022). Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the main metabolites in Dendrobium officinale leaves during the harvesting period. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 190, 24–34. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.08.026
Strader, L., Weijers, D., and Wagner, D. (2021). Plant transcription factors - being in the right place with the right company. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 65, 102136. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2021.102136
Tanaka, M., Takahata, Y., Nakayama, H., Nakatani, M., and Tahara, M (2009). Altered carbohydrate metabolism in the storage roots of sweet potato plants overexpressing the SRF1 gene, which encodes a Dof zinc finger transcription factor. Planta. 230, 737–746. doi: 10.1007/s00425-009-0979-2
Tang, H., Zhao, T., Sheng, Y., Zheng, T., Fu, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2017). Dendrobium officinale Kimura et Migo: A review on its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and industrialization. Evid-based Compl. Alt. Med. 2017, 7436259. doi: 10.1155/2017/7436259
Teixeira da Silva, J. A. and Ng, T. B. (2017). The medicinal and pharmaceutical importance of Dendrobium species. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 101, 2227–2239. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8169-9
Tian, F., Yang, D., Meng, Y., Jin, J., and Gao, G. (2020). PlantRegMap: charting functional regulatory maps in plants. Nucleic. Acids Res. 48, 1104–1113. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1020
Udvardi, M. K., Kakar, K., Wandrey, M., Montanari, O., Murray, J., Andriankaja, A., et al. (2007). Legume transcription factors: global regulators of plant development and response to the environment. Plant Physiol. 144, 538–549. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.098061
Wang, P., Wang, D., Li, Y., Li, J., Liu, B., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). The transcription factor ThDof8 binds to a novel cis-element and mediates molecular responses to salt stress in Tamarix hispida. J. Exp. Bot. 75, 3171–3187. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae070
Wang, Z., Wang, Y., Tong, Q., Xu, G., Xu, M., Li, H., et al. (2021). Transcriptomic analysis of grapevine Dof transcription factor gene family in response to cold stress and functional analyses of the VaDof17 gene. Planta. 253, 55. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03574-8
Wu, J., Chen, L., Chen, M., Zhou, W., Dong, Q., Jiang, H., et al. (2019). The DOF-domain transcription factor ZmDOF36 positively regulates starch synthesis in transgenic maize. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00465
Wu, Z., Cheng, J., Cui, J., Xu, X., Liang, G., Luo, X., et al. (2016). Genome-wide identification and expression profile of Dof transcription factor gene family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00574
Wu, Y., Lee, K., Yoo, Y., Wei, J., Kwon, S. Y., Lee, S. W., et al. (2018). Rice transcription factor OsDOF11 modulates sugar transport by promoting expression of sucrose transporter and SWEET genes. Mol. Plant 11, 833–845. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2018.04.002
Xiao, Q., Liu, T., Ling, M., Ma, Q., Cao, W., Xing, F., et al. (2022). Genome-wide identification of Dof gene family and the mechanism dissection of SbDof21 regulating starch biosynthesis in sorghum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 12152. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012152
Xu, P., Chen, H., and Cai, W. (2020). Transcription factor CDF4 promotes leaf senescence and floral organ abscission by regulating abscisic acid and reactive oxygen species pathways in Arabidopsis. EMBO Rep. 21, e48967. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948967
Yanagisawa, S. and Izui, K. (1993). Molecular cloning of two DNA-binding proteins of maize that are structurally different but interact with the same sequence motif. J. Bio. Chem. 268, 16028–16036. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)82353
Yu, Z., He, C., Teixeira da Silva, J. A., Zhang, G., Dong, W., Luo, J., et al. (2017). Molecular cloning and functional analysis of DoUGE related to water-soluble polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale with enhanced abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. 131, 579–599. doi: 10.1007/s11240-017-1308-2
Yu, Z., He, C., Teixeira da Silva, J. A., Luo, J., Yang, Z., Duan, J., et al. (2018). The GDP-mannose transporter gene (DoGMT) from Dendrobium officinale is critical for mannan biosynthesis in plant growth and development. Plant Sci. 277, 43–54. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.07.021
Yu, H., Ma, Y., Lu, Y., Yue, J., and Ming, R. (2021a). Expression profiling of the Dof gene family under abiotic stresses in spinach. Sci. Rep. 11, 14429. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93383-6
Yu, Z., Yang, Z., Teixeira da Silva, J. A., Luo, J., and Duan, J. (2019). Influence of low temperature on physiology and bioactivity of postharvest Dendrobium officinale stems. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 148, 97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.10.014
Yu, Z., Zhang, G., Teixeira da Silva, J. A., Zhao, C., and Duan, J. (2021b). The methyl jasmonate-responsive transcription factor DobHLH4 promotes DoTPS10, which is involved in linalool biosynthesis in Dendrobium officinale during floral development. Plant Sci. 309, 110952. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110952
Yuan, Z., Zhang, J., and Liu, T. (2017). Enhancement of polysaccharides accumulation in Dendrobium officinale by exogenously applied methyl jasmonate. Biol. Plantarum. 61, 438–444. doi: 10.1007/s10535-016-0702-7
Zeng, D., Si, C., Zhang, M., Duan, J., and He, C. (2023). ERF5 enhances protocorm-like body regeneration via enhancement of STM expression in Dendrobium orchid. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 65, 2071–2085. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13534
Zeng, D., Teixeira da Silva, J. A., Zhang, M., Yu, Z., Si, C., Zhao, C., et al. (2021). Genome-wide identification and analysis of the APETALA2 (AP2) transcription factor in Dendrobium officinale. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 5221. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105221
Zhai, Z., Xiao, Y., Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Peng, X., Feng, C., et al. (2022). Abscisic acid-responsive transcription factors PavDof2/6/15 mediate fruit softening in sweet cherry. Plant Physiol. 190, 2501–2518. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac440
Zhang, A., Wang, Q., Tong, Y., Li, M., Grierson, D., Ferguson, I., et al. (2018). Transcriptome analysis identifies a zinc finger protein regulating starch degradation in kiwifruit. Plant Physiol. 178, 850–863. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00427
Zou, X. and Sun, H. (2023). Dof transcription factors: specific regulators of plant biological processes. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1044918
Keywords: Dendrobium orchid, DOF, expression analysis, water-soluble polysaccharides, MeJA
Citation: Xu Z, Zhang G, Zheng F, Deng X, Sun Y, Teixeira da Silva JA, Shen X and Yu Z (2025) Comprehensive analysis of Dof transcription factors in Dendrobium species and functional characterization of DoDof4 in the accumulation of water-soluble polysaccharides. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1617856. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1617856
Received: 25 April 2025; Accepted: 02 July 2025;
Published: 07 August 2025.
Edited by:
Jie Li, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Chen Li, Hubei University of Medicine, ChinaHai-Li Liu, Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Zhang, Zheng, Deng, Sun, Teixeira da Silva, Shen and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoxia Shen, c2hlbnhpYW94aWFAemNtdS5lZHUuY24=; Zhenming Yu, eXV6aGVubWluZ0B6Y211LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhangting Xu
Zhangting Xu Guihua Zhang2†
Guihua Zhang2† Jaime A. Teixeira da Silva
Jaime A. Teixeira da Silva Zhenming Yu
Zhenming Yu