- 1Department of Nematology, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India
- 2Centre for Plant Protection Studies, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India
- 3Department of Agricultural Entomology, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India
- 4World Vegetable Center South and Central Asia, Hyderabad, Telangana, India
- 5World Vegetable Center, Shanhua, Tainan City, Taiwan
Introduction: Root-knot disease in tomato, caused by Meloidogyne incognita, presents a major challenge to global tomato production. This study explored a sustainable management approach by evaluating host-plant resistance through grafting combined with bio-inputs in farmers’ fields with high natural infestations of M. incognita.
Methods: The commercial F1 hybrid Shivam® tomato was grafted onto bacterial wilt-resistant eggplant rootstocks, EG 203 and TS 03. Two field experiments were conducted with six treatment groups to compare the performance of 'EG 203-tomato' and 'TS 03-tomato' grafts against the non-grafted hybrid tomato, both with and without bio-input applications. The bio-input protocol included soil application of neem cake (250 kg/ha) and soil and seedling drenching at nursery and transplant stages using biocontrol agents (Bacillus subtilis, Trichoderma asperellum, and Purpureocillium lilacinum, each at 5 g/L).
Results: Results indicated that the 'EG 203-tomato' graft demonstrated strong resistance to M. incognita, while the 'TS 03-tomato' graft remained susceptible, akin to the non-grafted Shivam® hybrid. The EG 203-tomato graft treated with the bio-inputs achieved the highest suppression of M. incognita, with reductions of 76.8–77.7% juvenile populations in the soil, 62.0–66.1% in female populations within roots, 73.6–77.3% in egg masses per female, and 38.1–40.0% in eggs per egg mass. This treatment also resulted in the lowest root gall index, measured at 2.0–2.1.
Discussion: In both trial locations, 'EG 203-tomato' graft plants enriched with bio-inputs outperformed the non-grafted tomato in growth and yield metrics, achieving greater plant height (54.6–54.7 cm), leaf count (81.3–84.3 per plant), branch count (3.1–3.7) and fruit yield (10.8–11.5 kg/plant). These findings support the recommendation of EG 203-tomato grafts with bio-input management as an effective large-scale strategy for tomato growers combating M. incognita infestations.
1 Introduction
Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Miller), from the Solanaceae family, is the world’s most cultivated vegetable crop. Its fruits are highly valued both fresh and processed, as they provide essential vitamins and minerals, including vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol), vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium, magnesium, and folate. Additionally, tomatoes contain phytochemicals like lycopene and β-carotene, which have been linked to potential health benefits, including reduced risks of prostate cancer and cardiovascular diseases (Gatahi, 2020). Tomatoes cultivation spans approximately 168 countries, with a global production reaching 186.82 million tonnes across 5 million hectares (FAOSTAT, 2024). China leads production, followed by India, Turkey, the United States, Egypt, and Italy. India alone contributes approximately 20.33 million tonnes annually, covering 0.841 million ha (Ghalawat et al., 2024). Major tomato-growing regions in India include Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Bihar, Odisha, West Bengal, Telangana, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Maharashtra (Tiwari et al., 2022).
Despite its economic value, tomato productivity is hindered by various pests and diseases. Among the major constraints, the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid & White, 1919) is considered one of the most destructive pathogens affecting tomato cultivation, owing to its global prevalence, highly specialized parasitic behavior, and persistent yield suppression. After hatching from soil-borne eggs, second-stage juveniles (J2) of M. incognita invade feeder roots and puncture plant cells using their stylet. Upon reaching the vascular tissues, they establish a sedentary lifestyle and induce the formation of multinucleated giant cells in the root endodermis to facilitate continuous nutrient uptake. They reproduce parthenogenetically, forming egg masses containing 200–400 eggs on the root surface within 25–30 days of infection.This parasitic activity disrupts the uptake of water and nutrients, leading to nutrient imbalances that cause stunted growth and significant yield losses.Globally, M. incognita can reduce yields by 10-85% in tomato, with Indian losses ranging between 40-91% (Nagachandrabose and Baidoo, 2018). Additionally, M. incognita predisposes plants to pathogens like Fusarium oxysporum and Ralstonia solanacearum, forming a destructive nematode-disease complex (Parrado and Quintanilla, 2024).
Managing M.incognita remains a significant challenge due to its soil- and root-dwelling nature, sophisticated parasitic mechanisms, prolific reproduction, and broad host range. Although chemical nematicides such as DD mixture, DBCP, and carbofuran have historically been employed, growing concerns over environmental safety, human health risks, and stricter regulations have prompted a shift toward eco-friendly alternatives. As a result, sustainable, non-chemical strategies such as the use of nematode-free planting material, resistant cultivars, organic amendments, biological control agents, and heat-based treatments are gaining importance in tomato nematode management (Rawal, 2020). However, individual eco-friendly approaches typically result in only 10–40% suppression of nematode populations, which is often inadequate under high-infestation conditions (Seenivasan, 2017). Therefore, an integrated approach combining multiple cost-effective, practical, and high-efficacy methods is essential for sustainable management of M. incognita in nematode-endemic tomato-growing regions.
Host plant resistance provides an economical and environmentally safe approach to manage phytonematodes in crops. Tomato resistance to M. incognita has focused on the Mi-1 gene from Solanum peruvianum, which confers resistance to M. incognita (Wubie and Temesgen, 2019). However, Mi-1 resistance is temperature-sensitive and loses efficacy above 28°C, with some M. incognita populations overcoming this resistance, highlighting the need for alternative breeding approaches. The use of resistant rootstocks grafted onto commercial tomato scions has emerged as a promising, sustainable alternative to conventional and transgenic breeding (Shanmugam et al., 2024). Frey et al. (2020) demonstrated successful grafting of tomato using ‘Garden Gem’ as the scion and ‘Multifort’ as the rootstock, resulting in resistance to M. incognita under high temperatures and resistance to Fusarium wilt, enhancing growth and fruit yield. Grafting tomato scions onto the resistant rootstock Solanum sisymbriifolium (wild brinjal) has also effectively controlled M. incognita, significantly increasing fruit yields compared to non-grafted tomato plants (Baidya et al., 2017).
Neem (Azadirachta indica L.) is widely recognized for its pesticide properties, and neem cake, a byproduct of neem seed oil extraction, has demonstrated notable nematicidal effects. Soil amendment with neem cake significantly reduces M. incognita populations and promotes tomato growth (Meena et al., 2021). Among the eco-friendly strategies, biological control holds strong potential for sustainable nematode management. Notable biocontrol agents include Bacillus subtilis (Ehrenberg 1835) Cohn 1872, a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium (Sohrabi et al., 2020); Trichoderma asperellum Samuels, Lieckfeldt & Nirenberg 1999, an antagonistic fungus (Sohrabi et al., 2020); and Purpureocillium lilacinum Thom., a nematode egg-parasitic fungus (El-Ashry et al., 2021). While these agents have demonstrated effectiveness under laboratory and greenhouse conditions, their performance often declines under field conditions due to competition with native soil microflora. Therefore, to enhance their persistence and efficacy in field applications, the incorporation of organic amendments is recommended.
This study aimed to evaluate the response of tomato grafted onto Solanum melongena (bacterial wilt-resistant eggplant) rootstocks to M. incognita populations in field conditions. Additionally, the effectiveness of grafting in combination with promising bio-inputs, including neem cake, B. subtilis, T. asperellum, and P. lilacinum, was assessed as an integrated management strategy for M. incognita in heavily infested tomato fields.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Experimental site
Two field experiments were conducted from October 2022 to March 2023 in Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India. The first experiment was carried out in a farmer’s field at Vandikaranur village (11.006123° N, 76.830208° E) at an elevation of 435 m above mean sea level. The site featured red loamy soil with a pH of 7.13, organic matter content of 0.85%, electrical conductivity of 0.45 dS/m, and nutrient levels of 259 kg/ha nitrogen (N), 46 kg/ha phosphorus (P), and 569 kg/ha potassium (K). The experimental area spanned 1860 m2.
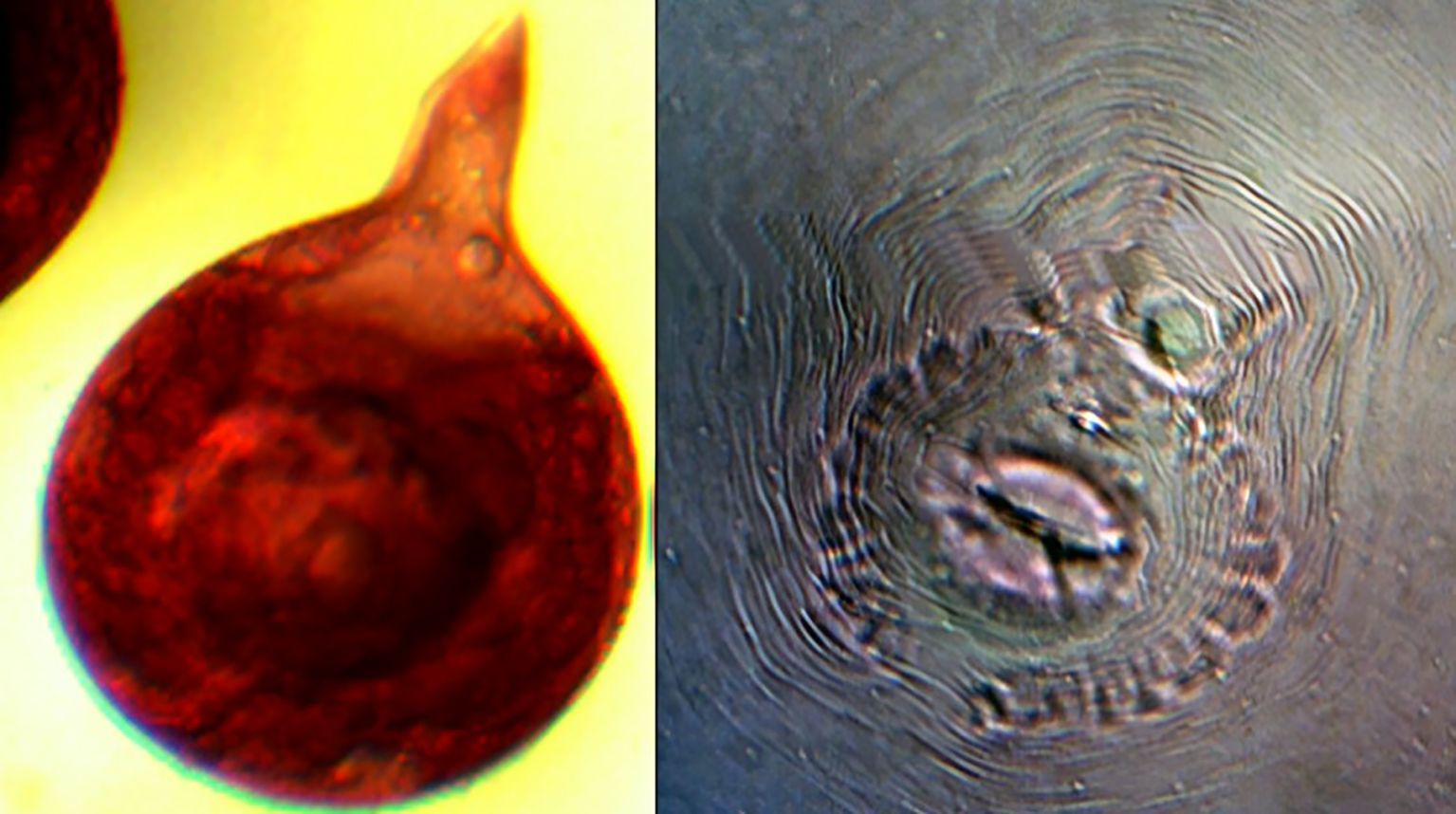
The second experiment was conducted concurrently in a farmer’s field at Karadimadai village (10.929349° N, 76.854019° E), located 431 m above mean sea level. The red loamy soil had a pH of 7.04, an organic matter content of 0.79%, an electrical conductivity of 0.41 dS/m, and nutrient levels of 242 kg/ha N, 41 kg/ha P, and 527 kg/ha K. The experimental area covered 1274 m2. Both sites had a history of continuous tomato cultivation and were naturally infested with Meloidogyne incognita. To confirm species identity, pear-shaped adult females were dissected from tomato roots, and their perineal patterns were examined under a compound microscope (40×) after mounting in anhydrous glycerin. All tested specimens displayed diagnostic features of M. incognita, including a high dorsal arch, coarse zigzag striae, and a characteristic tail whorl (Hartman and Sasser, 1985) (Figure 1).
2.2 Plant materials
Seeds of bacterial wilt-resistant eggplant (Solanum melongena) genotypes, specifically EG 203 and TS 03, were sourced from the World Vegetable Center, South and Central Asia, at the ICRISAT Campus in Hyderabad, Telangana. These genotypes served as rootstocks for grafting with the commercial tomato F1 hybrid Shivam® (HyVeg, Coimbatore, India). The Shivam® F1 hybrid features a determinate to semi-determinate tall growth habit, flat-round fruits with a green shoulder, and a weight of approximately 90–100 g. The fruits are firm, acidic in taste, and reach maturity 62–67 days after transplanting. The hybrid exhibits moderate resistance to the tomato leaf curl virus (ToLCV).
2.3 Bio-inputs
The neem cake utilized in this study was procured from the Kovai Oil Expeller Unit in Coimbatore, India. It contained Azadirachtin (850 ppm) along with macronutrients, including Nitrogen (1.5–3.0%), Phosphorus (0.5–1.55%), and Potassium (0.5–1.0%). Talc-based commercial formulations of Bacillus subtilis Bbv57 (2.5 x 108 cfu/g) and Trichoderma asperellum Tv1 (2.8 x 106 cfu/g) were sourced from the Department of Plant Pathology, Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India. Similarly, the talc-based formulation of Purpureocillium lilacinum TNAUPL1 (2.8 x 106 cfu/g) was obtained from the Department of Nematology at Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore, India.
2.4 Treatment components
Both field experiments included six treatment groups: (1) eggplant EG 203-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs, (2) eggplant TS 03-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs, (3) tomato Shivam® with bio-inputs, (4) eggplant EG 203=tomato Shivam® graft without bio-inputs, (5) eggplant TS 03–tomato Shivam® graft without bio-inputs, and (6) tomato Shivam® alone (non-treated control). In treatments involving bio-inputs, the protocol consisted of drenching the nursery growing medium with B. subtilis, T. asperellum, and P. lilacinum at 5 g/L, applied seven days after grafting. Subsequently, at the time of transplanting, seedlings received the same bio-input treatment, followed by a 30-minute shade-drying period prior to planting.
2.5 Seedling preparation and grafting process in nursery
In both experiments, tomato seedlings and eggplant rootstock were raised at a farmer-owned commercial nursery in Thondamuthur village (10.9899° N, 76.8409° E), Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu. Eggplant rootstock seeds were sown in 98-cell seedling trays sourced from Ms. Kaveri Agri Products, Krishnagiri, India, in July 2022, using decomposed coir pith supplied by M/s. RAR Coir Industries, Salem, Tamil Nadu, is the rooting medium. After sowing, the trays were stacked and covered with polythene sheets to maximize germination. Polythene was removed after three days, and the trays were arranged inside a shade-net house maintained at 30 ± 2°C, relative humidity of 60 ± 5%, with a 12.5:11.5 h light-to-dark cycle. Trays were irrigated thrice daily using a 500–750 mL sprinkling can.
Tomato Shivam® seeds were sown seven days later, following uniform nursery practices for both crops. For bio-input treatments, seedlings were drenched with a mixture of B. subtilis, T. asperellum, and P. lilacinum (5 g/L each) using an atomizer to saturate the seedling beds. This drenching was conducted at 16 days after sowing (DAS) for eggplant and 14 DAS for tomato. Non-bio-input treatments received plain water. No pest or disease incidence occurred during nursery growth.
Healthy 30-day-old eggplant seedlings (rootstock) and 21-day-old tomato seedlings (scion) with a 1.5–1.8 mm stem diameter were selected for grafting. Both scion and rootstock stems were cut at a 30° angle just above the cotyledon level to create slanted, matching surfaces with uniform stem thickness. The cut surfaces were then aligned and secured together using grafting clips(Ms. Varsha Enterprises, Bengaluru, India), following the method of Black et al. (2003). Grafted seedlings were kept in shade-net healing chambers for 8–10 days at 90% relative humidity to facilitate graft union and then transferred to a standard shade-net house for three days to harden. Once hardened, they were ready for field transplantation.
2.6 Field setup and planting
Both experimental fields were ploughed twice to achieve a fine tilth. The trials were conducted using a completely randomized block design (CRBD) with four replications, and each plot measured 10 m x 5 m, with a 3 m buffer zone. In bio-input plots, neem cake was incorporated into the topsoil at a rate of 250 kg/ha before planting. Farmyard manure (12.5 t/ha) and single superphosphate (1172 kg/ha) were applied uniformly across all plots before planting. Nitrogen (200 kg/ha) and potassium (250 kg/ha) were used in 5–6 split topdressings in 5-6 divided doses.
Grafted eggplant-tomato and tomato seedlings were carefully transported to the fields. A solution of 20 L water containing B. subtilis, T. asperellum, and P. lilacinum at 5 g/L each was prepared for seedling drenching treatments. Bio-input-treated seedlings were soaked in this solution and dried in the shade for 45 minutes.
Raised beds measuring 90 cm in width, with a 30 cm spacing between beds, were prepared in the plots. Drip irrigation lines were installed along each bed, and seedlings were planted at 120 × 60 cm spacing, with 70 plants per plot in both experiments. The agronomic practices were adhered to the Tamil Nadu Agricultural University Crop Production Guide 2022 (Anonymous, 2022).
Low to moderate infestations of pests and diseases were observed, including leafhopper (Amrasca biguttula), thrips (Thrips tabaci), whitefly (Bemisia tabaci), Phthorimaea absoluta, Liriomyza trifolii, Spodoptera litura, Helicoverpa armigera, bacterial leaf spot, early blight, Fusarium wilt, tomato leaf curl virus, and tomato mosaic virus. Pesticides were applied as needed following the crop production guide recommendations.
2.7 Soil sampling and nematode density assessment
The population density of M. incognita was assessed in each plot before planting and at harvest. Composite soil samples weighing 2.5-3.0 kg were collected per plot using a core sampler with a 1.0 cm diameter and 15 cm length. Twenty-five to thirty core samples were taken from each plot to form a composite sample. The composite samples were thoroughly mixed, and a 200 cm³ subsample was extracted by Cobb’s sieving technique, followed by the modified Baermann funnel method (Southey, 1986). Nematode populations were quantified by examining the suspension under a stereo zoom microscope (Kozo Zoom 645) at 40x magnification (Nagachandrabose et al., 2024).
2.8 Nematode infection assessment in roots
Five plants per plot were randomly selected following a zig-zag pattern and carefully uprooted at harvest. Roots were gently washed to remove adhering soil particles, and the root gall index was evaluated using a 1-5 scale (Taylor and Sasser, 1978): 1 = no galls/plant; 2 = 1–10 galls/plant; 3 = 11–30 galls/plant; 4 = 31–100 galls/plant; 5 = more than 100 galls/plant.
Secondary roots from each selected plant were collected, cut into 1 cm segments, and mixed thoroughly. A 1-g subsample was used to assess M. incognita female populations, egg mass count per gram of root, eggs per egg mass, egg mass parasitization, and biocontrol agent colonization.
To assess female M. incognita counts, 1-g root subsamples were stained with acid fuchsin-lactophenol and destained with plain lactophenol. The stained females were counted under a stereo-zoom microscope (40x magnification). For egg mass counts, 1-g subsamples were placed in a 90 mm Petri dish with water and examined directly under the microscope. To determine eggs per egg mass, 10 egg masses per treatment were dissected, placed in distilled water, crushed with a needle, and counted under the microscope at 40x magnification.
2.9 Re-isolation of introduced bioagents
To evaluate root colonization of B. subtilis, 1-g root subsamples from each treatment plot were surface-sterilized with 1% NaOCl and rinsed twice with distilled water. The sterilized roots were ground using a sterile pestle and mortar with 1 mL of distilled water, and the resulting slurry was transferred to test tubes containing 9 mL of distilled water. Serial dilutions were prepared up to 107, and the B. subtilis was isolated by plating the dilutions onto nutrient agar media. The plates were incubated at 28 ± 3°C for three days, after which colonies were examined. B. subtilis colonies were identified based on their distinct morphology, round or irregular shapes, thick, opaque, and cream-coloured, and were quantified as CFU/g root (Nagachandrabose et al., 2022) (Figure 2a).
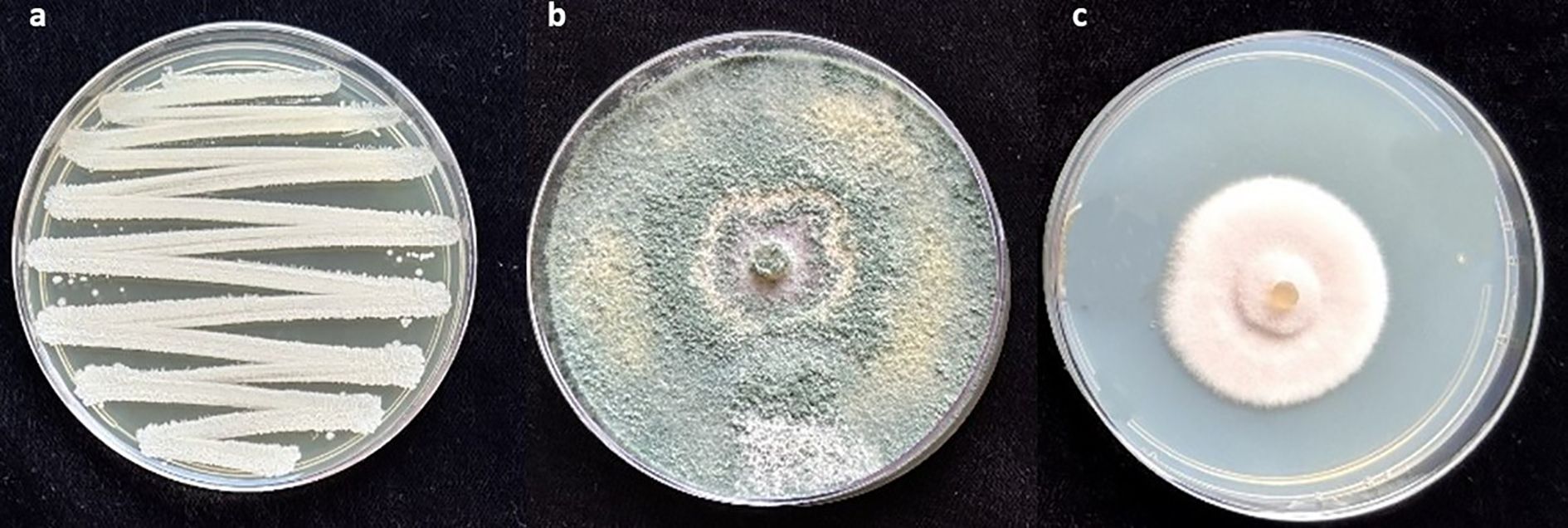
Figure 2. (a) Bacillus subtilis colonies showing round or irregular shapes, thick, opaque, and cream-coloured; (b) Trichoderma asperellum colonies with green, woolly, or cottony appearance; (c) Colonies of P. lilacinum with lilac-to-purple pigmentation and velvety texture.
Subsamples of P. lilacinum and T. asperellum were cultured on potato dextrose agar (PDA) and yeast molasses agar (YMA), respectively. Root sections were incubated at 28 ± 3°C for 15 days. Colonies of P. lilacinum were identified by their lilac-to-purple pigmentation and velvety texture (Figure 2c), while T. asperellum colonies were recognized by their green, woolly, or cottony appearance (Figure 2b). The bio-agents were quantified in terms of colony-forming units (CFUs) (Nagachandrabose et al., 2022).
The percentage of egg mass parasitization by the fungal biocontrol agents P. lilacinum and T. asperellum was also assessed (Nagachandrabose et al., 2022). For this, 10 egg masses were manually collected from each treatment root subsample using forceps, surface-sterilized with 1% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), rinsed twice with distilled water, and placed on PDA and YMA media in 90-mm Petri plates. The plates were incubated at 28 ± 3°C for 15 days, after which the fungi colonizing the eggs were identified based on their distinctive morphological characteristics. The percentage parasitization was calculated using the formula:
2.10 Growth metrics and yield assessment
Plant growth parameters, such as the number of branches per plant, the number of leaves per plant, plant height (cm), and fruit yield (kg/plant), were measured from five randomly selected and tagged plants. Measurements were taken at 15-day intervals throughout the crop cycle, and mean values were calculated. Fruit yield per replicate plot was recorded at each harvest, and the cumulative yield was calculated to determine the total fruit yield in tons per hectare (ha).
2.11 Statistical analysis
The normality of the data was assessed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. Nematode population data were log-transformed to ensure homogeneity before analysis. A one-way ANOVA was performed, and treatment means were compared using Tukey’s range test. The data analysis was done using SPSS 16.0 for Windows software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). The results are presented using untransformed data.
3 Results
3.1 Efficacy of eggplant-tomato grafting and bio-inputs on M. incognita
At the start of the experiment, the initial population of M. incognita second-stage juveniles (J2) did not show any significant variation among the treatment plots at either location (Tables 1, 2). Nevertheless, a comparatively higher pre-treatment infestation was recorded at Location I, averaging 435.1 ± 15.2 J2 per 200 cm³ of soil, whereas Location II recorded a slightly lower mean of 381.5 ± 16.4 J2 per 200 cm³. As the trials progressed, significant differences in the J2 populations at harvest were observed across the six treatment groups in both locations (Location I: F = 7.6; df = 5, 15; P< 0.001; Location II: F = 6.7; df = 5, 15; P< 0.001). By the end of the season, final J2 population densities varied between 146.9 and 604.7 J2 per 200 cm³ in Location I, and between 135.5 and 586.3 J2 per 200 cm³ in Location II, indicating differential treatment effects on nematode suppression.
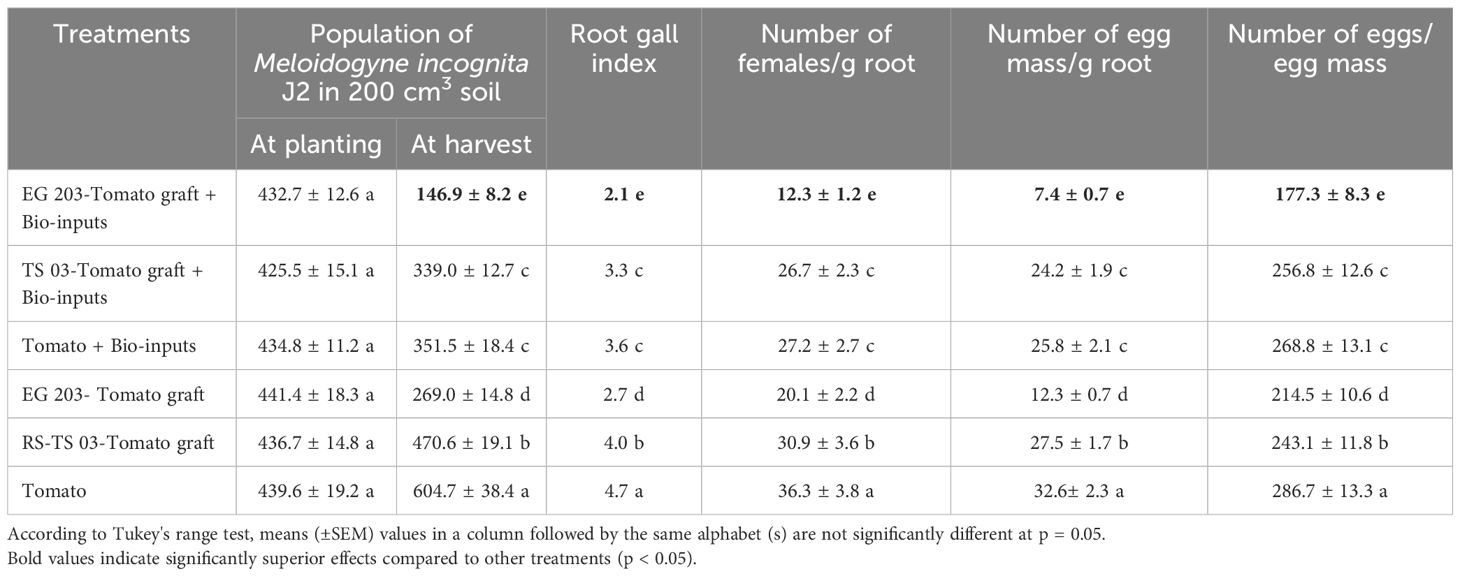
Table 1. Impact of eggplant-tomato grafting, alone and with bio-inputs, on Meloidogyne incognita infestation in tomato – Location I (Vandikaranur).
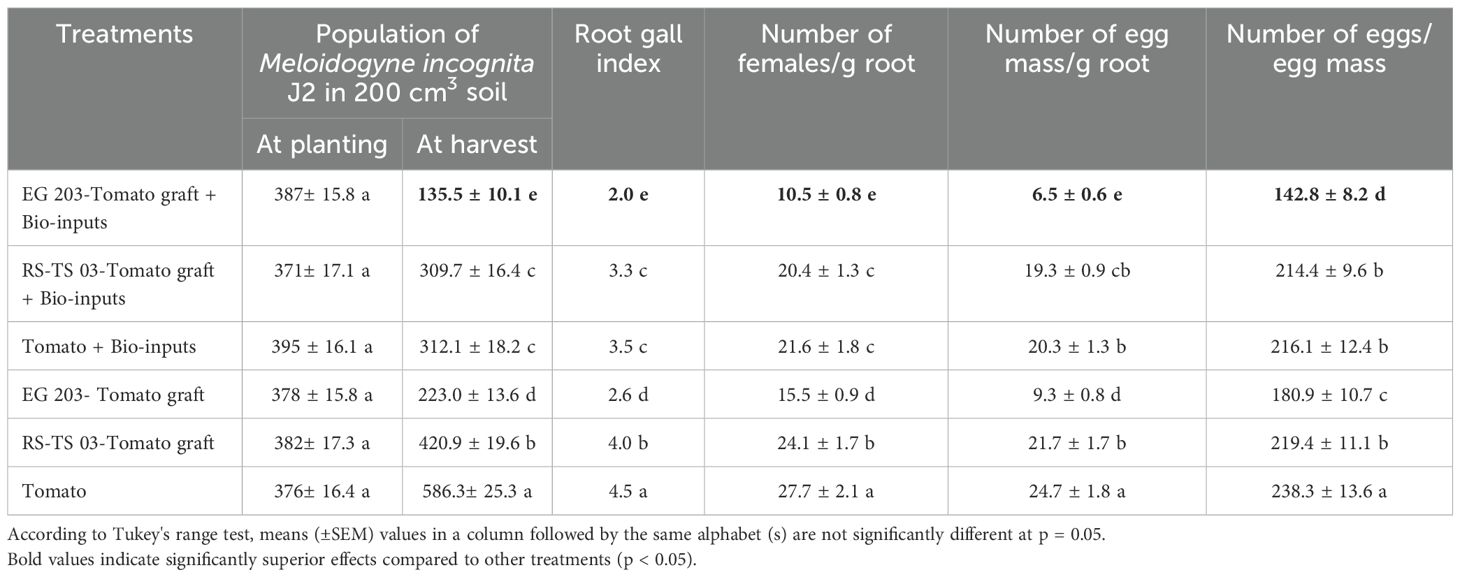
Table 2. Impact of eggplant-tomato grafting, alone and with bio-inputs, on Meloidogyne incognita infestation in tomato – Location II (Karadimadai).
In both experimental locations, the M. incognita populations in soil were significantly reduced in the EG 203-tomato grafts treated with bio-inputs, which proved to be the most effective treatment. Specifically, this combination led to a reduction of 77.7% in Location I and 76.8% in Location II when compared to the untreated tomato Shivam® control. Following this, the EG 203-tomato grafts without bio-inputs ranked second in effectiveness, achieving 55.5% and 61.9% reductions at Locations I and II, respectively. Meanwhile, intermediate suppression levels were observed in the TS 03-tomato graft with bio-inputs (43.9–47.1%) and tomato Shivam® with bio-inputs (41.8–46.7%). By contrast, the TS 03-tomato grafts and tomato Shivam® without bio-input treatments exhibited the highest M. incognita population densities, confirming their relatively poor nematode suppression performance.
The lowest root gall index (2.0–2.1) was consistently recorded in EG 203-tomato graft plants treated with bio-inputs across both locations (Figure 3). This treatment demonstrated superior nematode suppression. It was closely followed by EG 203-tomato grafts without bio-inputs, which recorded slightly higher root gall indices of 2.6 and 2.7. In contrast, moderate galling was observed in TS 03-tomato grafts and tomato Shivam® plants treated with bio-inputs, with indices ranging between 3.3 and 3.6. Notably, the highest levels of gall formation were found in untreated TS 03-tomato graft and tomato Shivam® plants, with root gall indices ranging from 4.0 to 4.7 (Tables 1, 2). These findings clearly illustrate the effectiveness of both grafting and bio-input application in minimizing root gall severity.
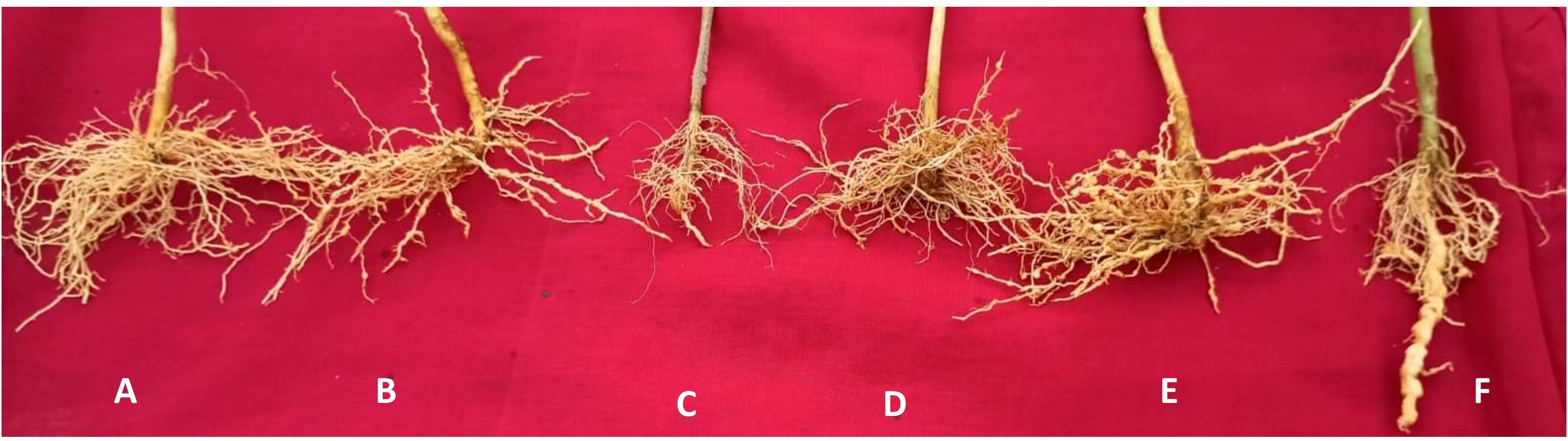
Figure 3. (A) Roots of EG 203-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs with fewer galls, (B) TS 03-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs with moderate galls, (C) tomato Shivam® with bio-inputs with moderate galls, (D) EG 203-tomato Shivam® graft without bio-inputs with moderate galls, (E) TS 03 -tomato Shivam® graft without bio-inputs with higher galls, and (F) tomato Shivam® alone (non-treated control) with heavy galls. Figure 4. Left: More gravid females of M. incognita in roots of tomato Shivam® alone (non-treated control), Right: Fewer gravid females of M. incognita in roots of EG 203-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs.
The adult female population of M. incognita was significantly lower (P< 0.05) in EG 203-tomato grafts treated with bio-inputs, with only 12.3 females per g of root recorded in Location I and 10.5 in Location II (Figure 4). In sharp contrast, untreated tomato Shivam® plants harbored the highest female populations, registering 36.3 females/g root in Location I and 27.7 in Location II. Meanwhile, EG 203-tomato grafts without bio-inputs exhibited moderately reduced infection rates, with 15.5 to 20.1 females/g root. Similarly, TS 03-tomato grafts and tomato Shivam® treated with bio-inputs showed intermediate female populations, ranging from 20.4 to 26.7 and 21.6 to 27.2 females/g root, respectively (Tables 1 and 2). These results reinforce the effectiveness of the EG 203-tomato graft and bio-input combination in significantly limiting nematode reproduction in root tissues.
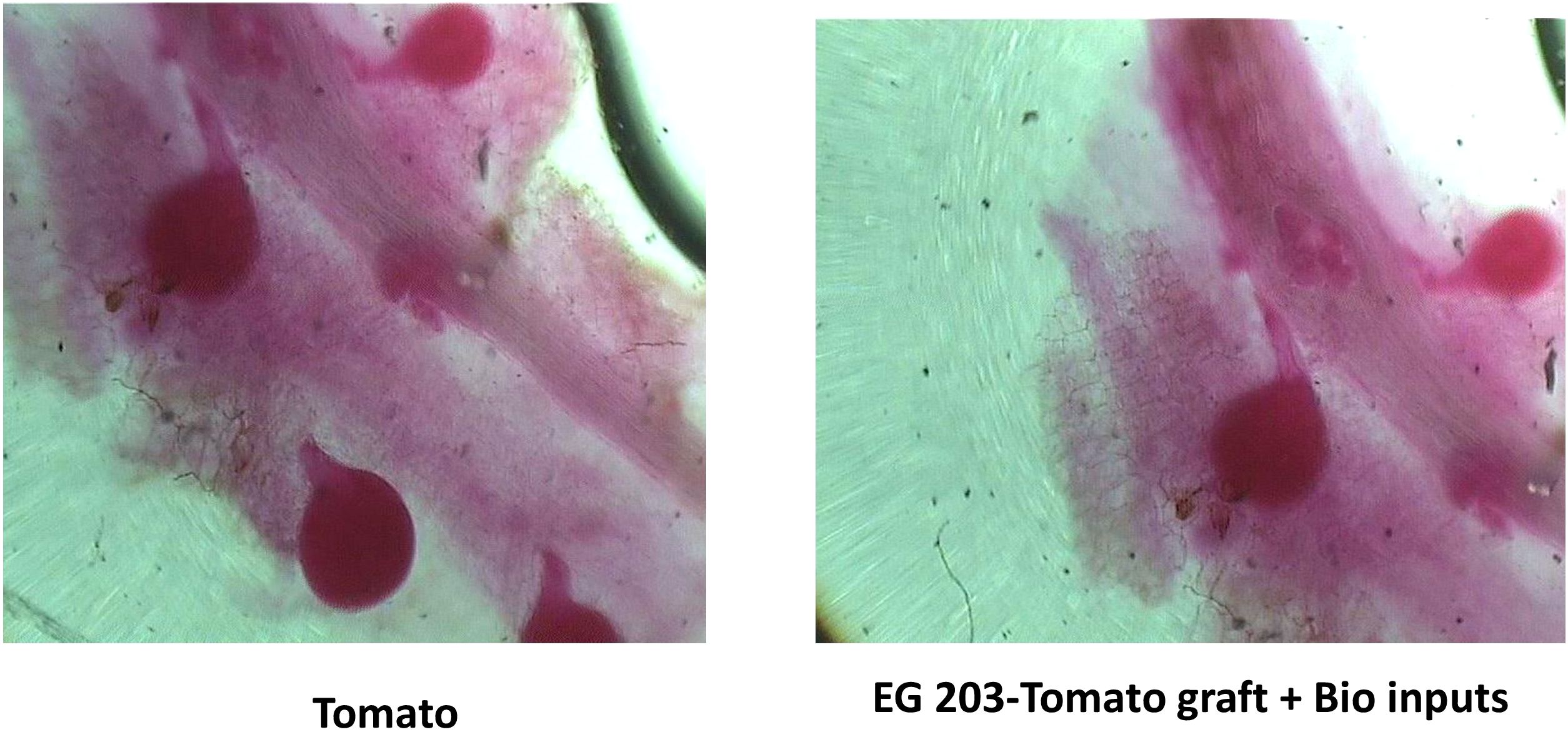
Figure 4. Left: More gravid females of M. incognita in roots of tomato Shivam® alone (non-treated control), Right: Less number of gravid females of M. incognita in roots of EG 203-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs.
The number of egg masses per g of root varied significantly across treatments in both locations (Location I: F = 8.1; df = 5, 15; P< 0.001; Location II: F = 7.3; df = 5, 15; P< 0.001), with counts ranging from 7.4 to 32.6 in Location I and 6.5 to 24.7 in Location II. Among the treatments, untreated tomato Shivam® and TS 03-tomato grafts recorded the highest egg mass production, indicating greater nematode reproduction in the absence of bio-inputs. Furthermore, the egg count per egg mass also showed statistically significant variation across treatments (Location I: F = 5.6; df = 5, 15; P< 0.001; Location II: F = 6.3; df = 5, 15; P< 0.001). Notably, EG 203-tomato grafts treated with bio-inputs exhibited the lowest egg counts per mass, reflecting a 38.1–40.0% reduction compared to untreated tomato Shivam® plants (Tables 1, 2). These findings demonstrate the combined efficacy of resistant rootstock and microbial inputs in suppressing nematode fecundity.
3.2 Efficacy of eggplant-tomato grafting and bio-inputs on crop biometry
Growth and yield parameters, including the number of branches per plant, number of leaves per plant, plant height, fruit yield per plant, and total fruit yield, were significantly enhanced in EG 203-tomato grafts treated with bio-inputs compared to other treatments (Tables 3, 4; Figure 5). Moreover, statistical analysis revealed significant differences in all measured biometric parameters between EG 203-tomato and TS 03-tomato grafts. Specifically, the number of branches (F = 84.85; df = 5,15; P< 0.001), number of leaves (F = 532.01; df = 5,15; P< 0.001), plant height (F = 564.45; df = 5,15; P< 0.001), and number of fruits (F = 1038.34; df = 5,15; P< 0.001) showed highly significant variation among the treatments. These results indicate that combining the resistant EG 203 rootstock with beneficial microbial consortia positively influenced vegetative growth and fruit production under nematode-infested conditions.
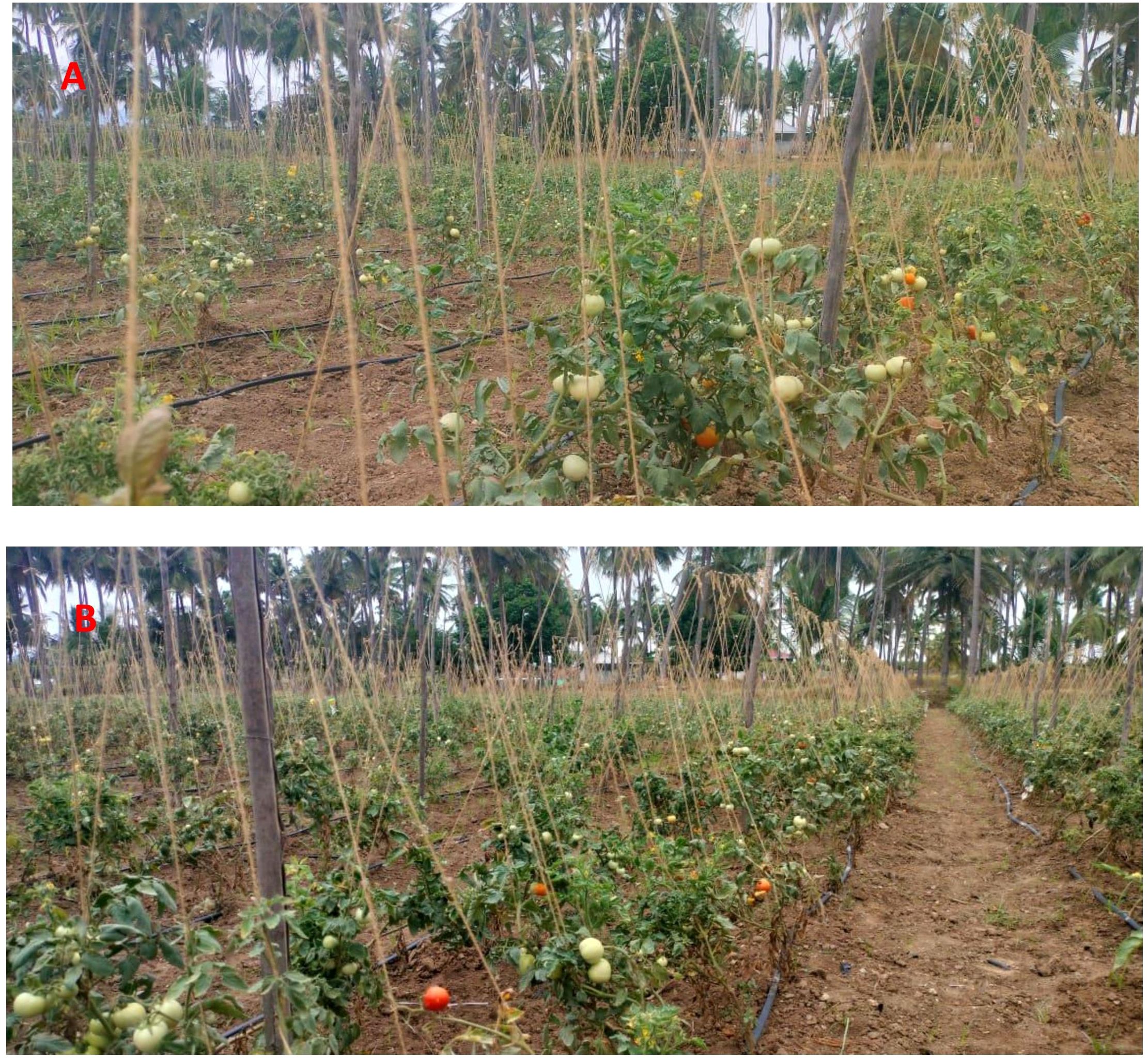

Figure 5. (A) Field view of EG 203-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs plots showing plants with good biometric characteristics. (B) Field view of tomato Shivam® alone (non-treated control) with patchy appearance and less biometric characteristics.
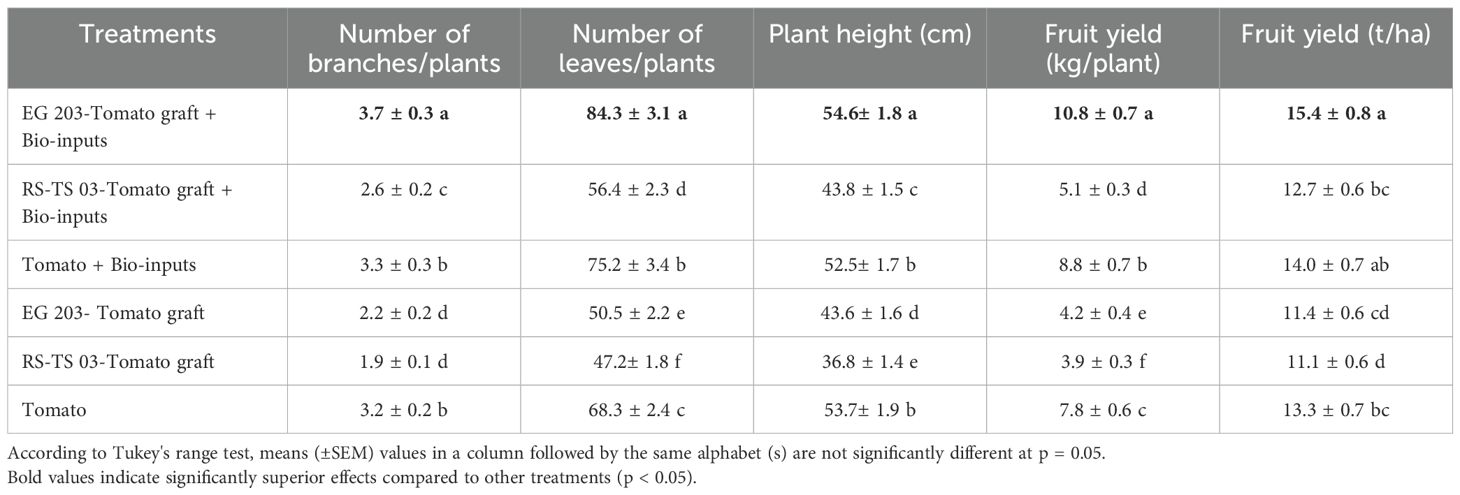
Table 3. Effect of eggplant-tomato grafting, with and without bio-inputs, on growth and yield metrics of tomato – Location I (Vandikaranur).
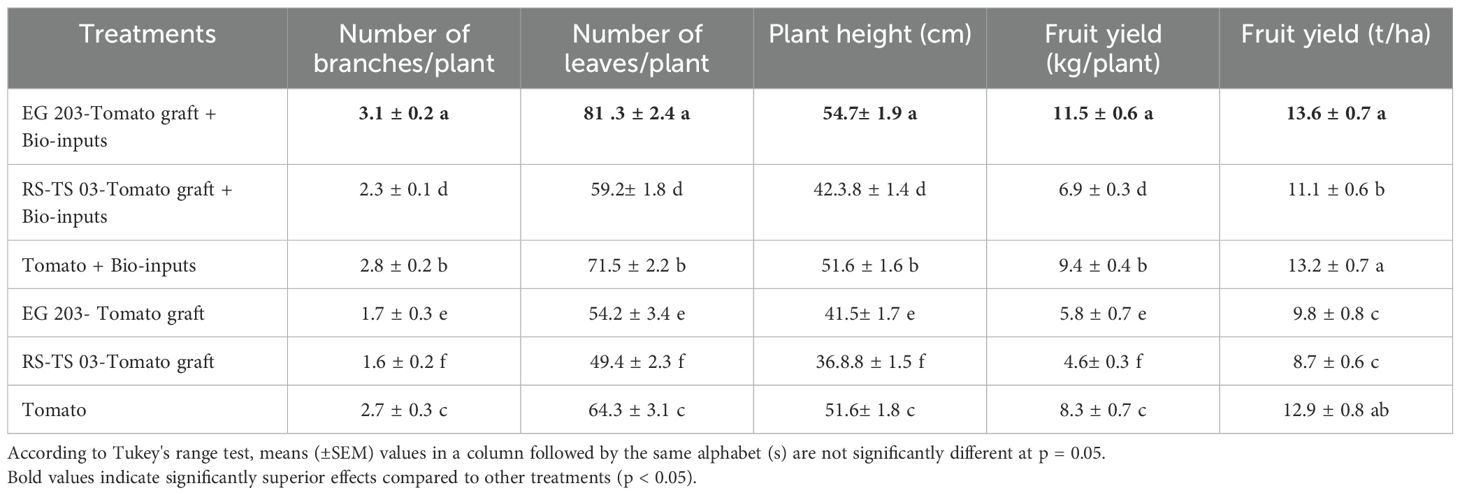
Table 4. Effect of eggplant-tomato grafting, with and without bio-inputs, on growth and yield metrics of tomato – Location II (Karadimadai).
Although EG 203-tomato grafts showed a slight delay in establishment during the first week after planting, they recovered by the second week and exhibited growth comparable to conventional tomato plants. Moreover, the grafted plants remained productive in the field for an additional month beyond the traditional tomatoes, enabling extended harvests and increased yield potential.
At both locations, EG 203-tomato grafts treated with bio-inputs exhibited superior growth and yield performance. These plants reached greater heights (54.6–54.7 cm), developed more branches (3.1–3.7), and produced a higher number of leaves (81.3–84.3), resulting in a fruit yield of 10.8–11.5 kg per plant. In contrast, TS 03-tomato grafts without bio-inputs showed significantly reduced growth, with shorter plant heights (36.8 cm), fewer branches (1.6–1.9), and leaves (47.2–49.4), culminating in a markedly lower fruit yield of 3.9–4.6 kg per plant. Notably, the application of bio-inputs consistently improved growth and yield parameters, regardless of the graft type, highlighting their role in enhancing tomato productivity.
3.3 Survival and parasitization potential of introduced bio-agents
The introduced bio-agents were successfully re-isolated from tomato roots, confirming their establishment and parasitic activity on M. incognita egg masses located on root surfaces (Figure 6). However, colonization potential varied significantly among treatments. Notably, colonization was markedly lower in TS 03-tomato grafts compared to both EG 203-tomato grafts and the non-grafted tomato Shivam®. In the EG 203-tomato grafts and tomato Shivam®, colonization levels of B. subtilis and T. asperellum were approximately twice as high (Figures 7, 8), while P. lilacinum exhibited a three-fold increase in colonization relative to the TS 03-tomato grafts (Figure 9). Similarly, the parasitization of egg masses by P. lilacinum was three times lower in TS 03 grafts (Figure 9). These observations collectively underscore the superior survival, colonization, and biocontrol efficacy of the bio-agents in EG 203-tomato grafts and tomato Shivam®, highlighting the importance of compatible graft combinations in enhancing biological control outcomes.
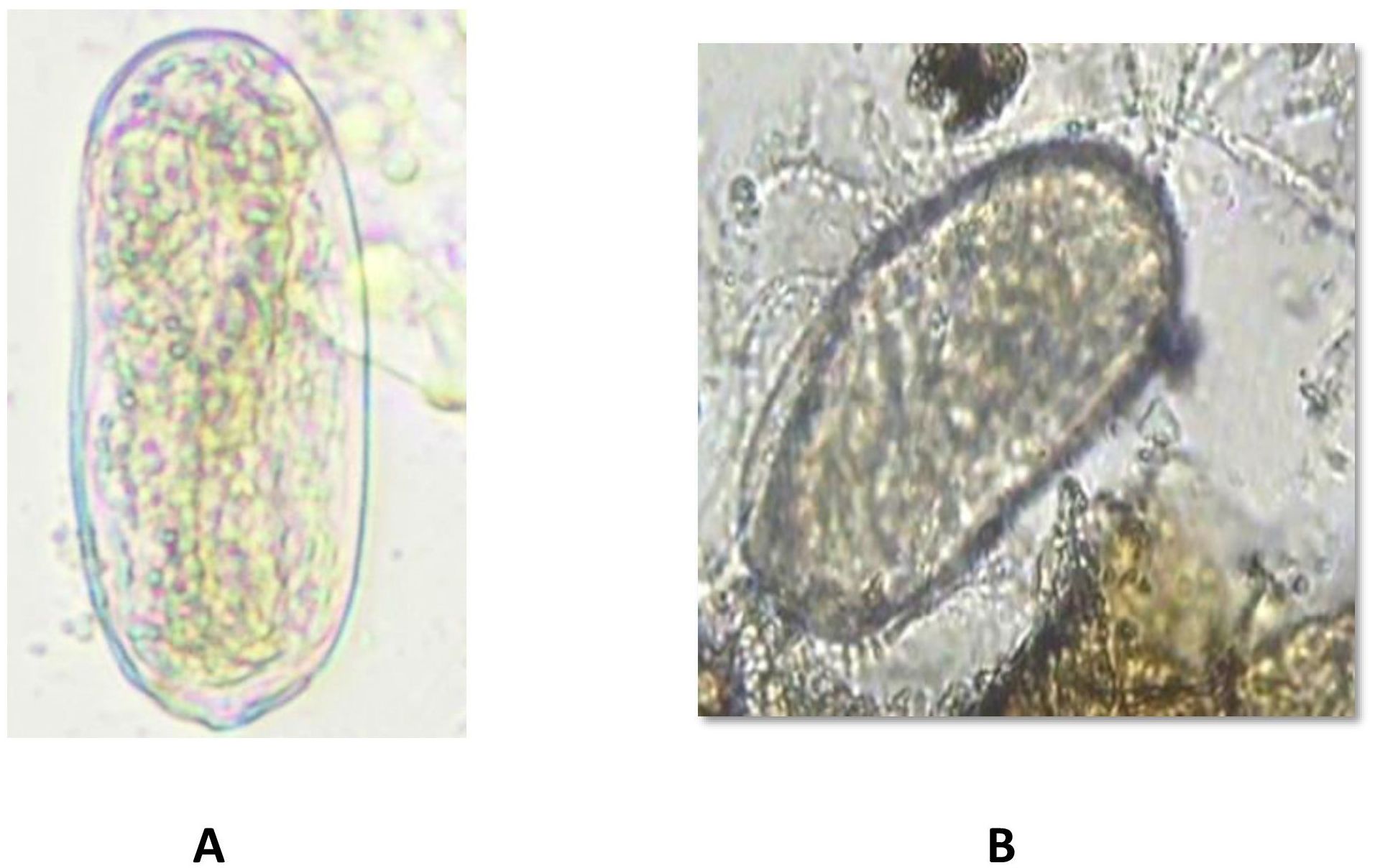
Figure 6. (A) Meloidogyne incognita egg in tomato Shivam® alone (non-treated control) remaining healthy. (B) Meloidogyne incognita egg in EG 203-tomato Shivam® graft with bio-inputs plots with Purpureocilium lilacinum parasitization.
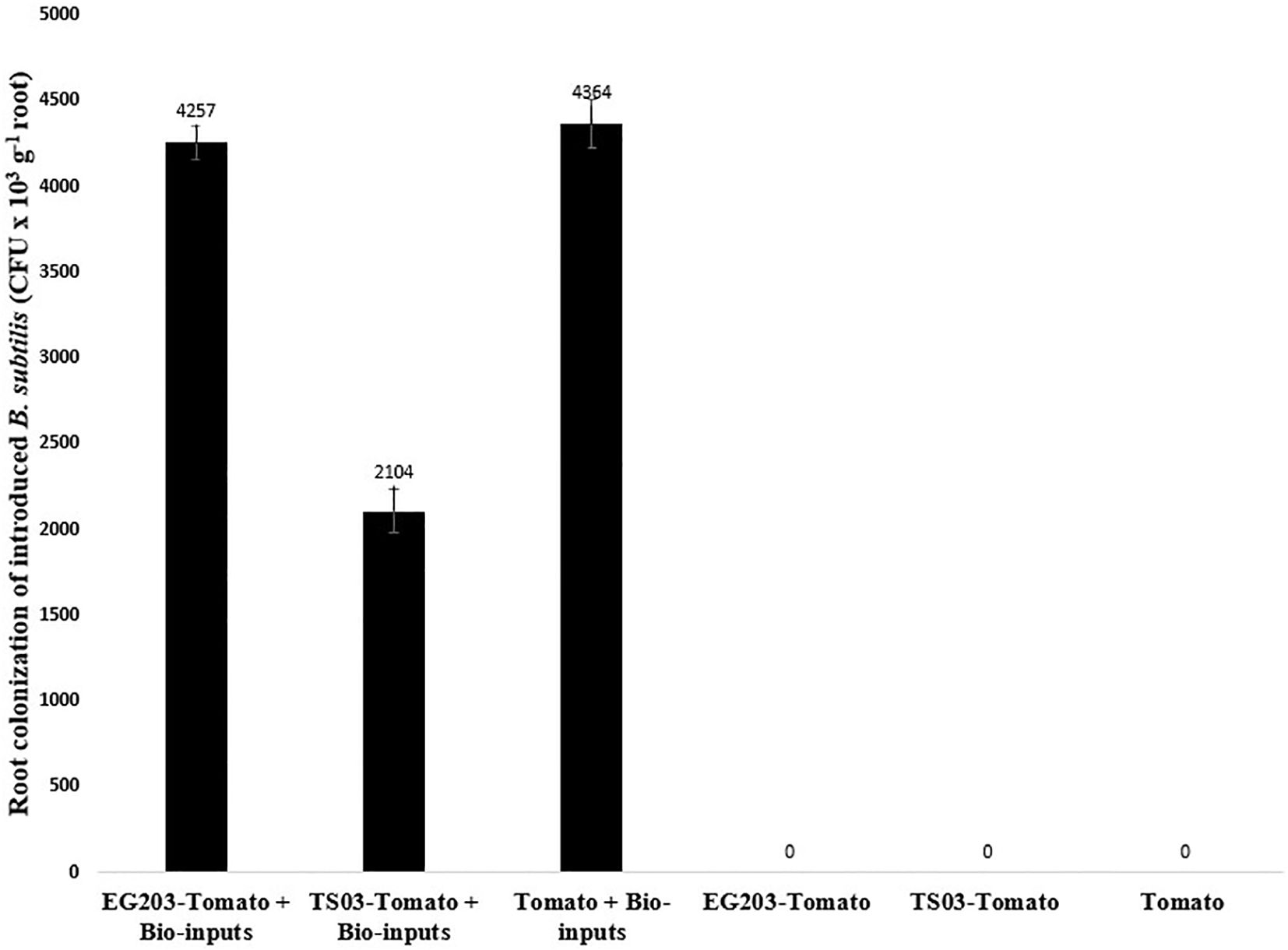
Figure 7. The colonization of grafted and non-grafted tomato roots by the introduced Bacillus subtilis.
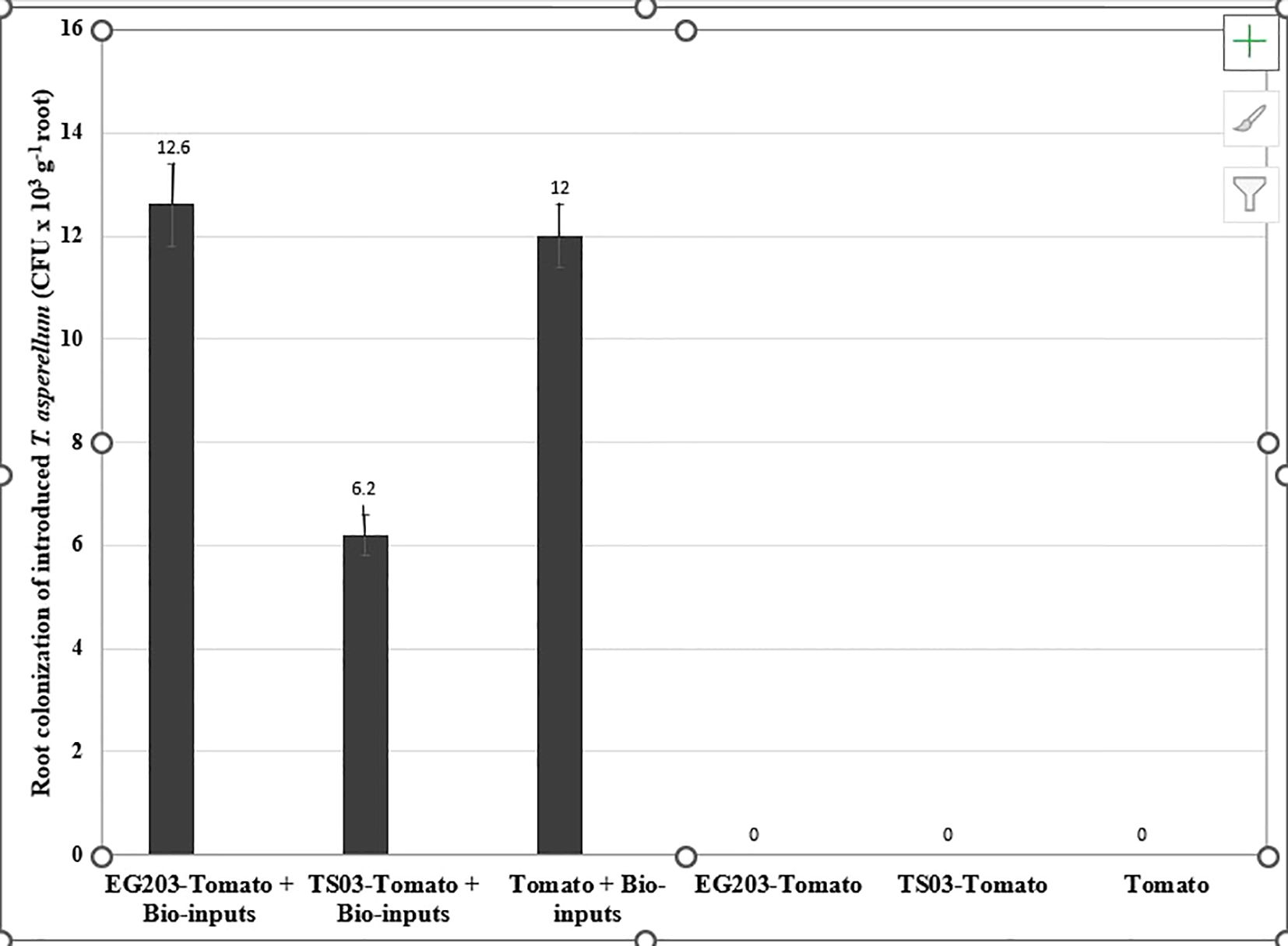
Figure 8. The colonization of grafted and non-grafted tomato roots by the introduced Trichoderma asperellum.
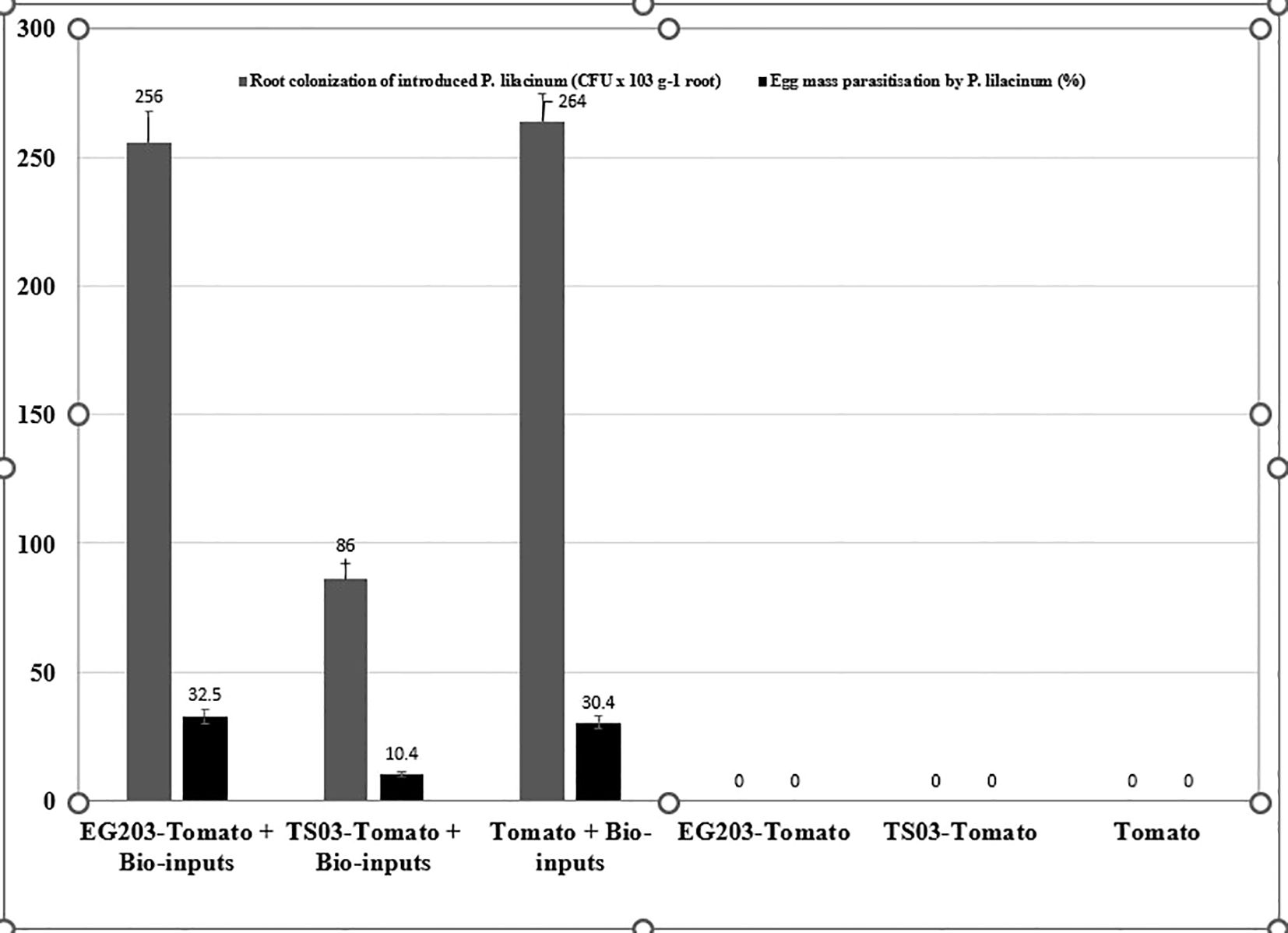
Figure 9. The colonization of grafted and non-grafted tomato roots was caused by the introduction of Purpureocillium lilacinum and its parasitization percentage on M. incognita egg mass.
4 Discussion
Grafting tomato scions with desirable horticultural traits onto rootstocks resistant to Meloidogyne incognita offers a viable management strategy for resource-limited tomato farmers. Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of root-knot nematode-resistant tomato varieties, such as ‘Celebrity,’ ‘Big Beef,’ and ‘Jetsetter’ as rootstocks for nematode-susceptible commercial cultivars like ‘Tropimech’ and ‘Power’ (Owusu et al., 2016). Similarly, grafting bacterial wilt-resistant varieties has effectively managed Ralstonia solanacearum and M. incognita using the same rootstocks (Kunwar et al., 2015). Recent advancements have expanded resistance strategies to include solanaceous plants for grafting, leveraging their strong resistance to M. incognita and facilitating the transfer of Mi gene resistance from Solanum torvum to cultivated tomato (Fullana et al., 2024).
The resistance conferred by such rootstocks is primarily attributed to the presence of Mi genes, which trigger a hypersensitive response (HR) in infected root tissues, leading to localized cell death and halting nematode development. These genes inhibit nematode penetration, feeding site formation, and reproduction. In addition, resistant rootstocks often possess enhanced lignification, thicker epidermal layers, and elevated levels of defensive enzymes and secondary metabolites, such as peroxidase, phenolics, and reactive oxygen species, which further fortify the root tissues against pathogen invasion. Collectively, these factors prevent nematode establishment and damage, making the rootstock an effective barrier against M. incognita.
Our study presents the first report of M. incognita resistance in an eggplant-tomato graft, specifically ‘EG 203-tomato,’ created by grafting a R. solanacearum-resistant eggplant rootstock (EG 203) with the commercial tomato cultivar Shivam®. Field evaluations of two eggplant rootstocks, EG 203 and TS 03, both resistant to bacterial wilt, demonstrated their potential to confer resistance to M. incognita. EG 203-tomato grafts exhibited the lowest root gall index (2.6–2.7) across the experimental locations, Vandikaranur and Karadimadai villages, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India. Conversely, TS 03-tomato grafts showed a higher gall index (4.0). These findings suggest that EG 203-tomato grafts resistant response, while TS 03-tomato grafts show susceptibility based on tomato resistance rating (Taylor and Sasser, 1978).
The resistance of EG 203-tomato grafts was evident in their ability to suppress M. incognita populations, even without bio-inputs. Reductions of 55.5–61.9% in soil M. incognita J2 populations, 45% in female nematode counts in roots, 62% in egg masses, and 24–25% in eggs per mass were observed. These results indicate that EG 203-tomato grafts may deploy both pre-infectional and post-infectional resistance mechanisms, disrupting nematode penetration, reproduction, and life cycle progression. Pre-infectional mechanisms may involve structural barriers such as thicker root epidermis and increased lignification, which hinder nematode entry. Post-infectional defenses may include localized hypersensitive responses (HR), oxidative bursts, and the upregulation of defense-related enzymes such as peroxidases, chitinases, and phenylalanine ammonia-lyase, which inhibit nematode feeding and development. These responses contribute to the suppression of giant cell formation and limit nematode reproduction within the root tissue. Additionally, resistance may be mediated by the expression of Mi-gene homologs, which are known to confer effective resistance against Meloidogyne spp. in certain solanaceous rootstocks (Abad et al., 2003; Williamson and Kumar, 2006). Further studies under controlled conditions are needed to confirm these resistance mechanisms.
The application of bio-inputs, including neem oil cake in soil and seedling drenches in the nursery and microbial agents (B. subtilis, T. asperellum, and P. lilacinum) in the field, further enhanced the suppression of the nematode M. incognita. Neem cake has been previously shown to reduce nematode population through its nematicidal component, azadirachtin, which inhibits M. incognita J2 mobility, root penetration, and reproduction while also activating systemic resistance, by inducing defense enzymes such as peroxidase, polyphenol oxidase, phenylalanine ammonia lyase, and superoxide dismutase, in bio-input-treated plants (Chandrawat et al., 2020; Gautam et al., 2021; d’Errico et al., 2023; Ambrogioni et al., 2003).
Among the microbial bioagents, viz., B. subtilis, T. asperellum, and P. lilacinum, B. subtilis exhibited higher colonization efficiency in tomato roots, confirming its active role in reducing M. incognita populations when applied through the soil, seed treatment, root dip, and seedling drench. In this study, B. subtilis was successfully re-isolated from tomato roots following its application in the nursery and at planting, confirming its active role in reducing M. incognita populations under field conditions. Previous studies have demonstrated the nematode suppressive activity of B. subtilis through the production of acetic acids, proteases, hydrogen cyanide, and indole acetic acid, as well as its ability to induce systemic resistance (Siddiqui, 2002; Singh and Siddiqui, 2010; Eltayeb, 2017; Basyony and Abo-Zaid, 2018).
Similarly, T. asperellum was re-isolated from tomato roots, although it did not parasitize M. incognita eggs in this study, suggesting that the strain (Tv 1) lacked egg-parasitic activity. Instead, its efficacy likely stemmed from its ability to induce systemic resistance by activating defense enzymes such as peroxidase, chitinase, and phenylalanine ammonia lyase (Naserinasab et al., 2011; Singh et al., 2017).
P. lilacinum was also effectively re-isolated and demonstrated significant parasitism of M. incognita eggs, aligning with previous reports of its nematode-suppressive potential (Das and Waquar, 2021). Its ability to produce toxic metabolites, including eucinostatins and paecilotoxins, and disrupt giant cell formation likely contributed to the observed reduction in nematode populations (Nagachandrabose et al., 2022).
Beyond nematode suppression, bio-input treatments consistently enhanced growth and yield metrics in EG 203-tomato grafts. Grafted tomatoes typically face yield trade-offs when using pathogen-resistant rootstocks (Owusu et al., 2016). However, our findings challenge this paradigm, as integrating bio-inputs with EG 203-rootstock improved resistance to biotic stresses and enhanced plant growth and productivity. This yield improvement is likely attributed to a combination of factors: the suppressive effects of the EG 203 rootstock, bio-input induced nematode suppression, and the growth-promoting properties of neem cake (Rizvi et al., 2015), B. subtilis (de O. Nunes et al., 2023), and P. lilacinum (Baron et al., 2020).
Overall, this study highlights the potential of EG 203-tomato grafts as an efficient and sustainable solution for managing M. incognita in tomato cultivation. Integrating grafting with bio-input treatments offers a dual benefit of resistance to nematode infections and enhanced crop productivity, positioning this approach as a promising strategy for sustainable tomato production in resource-limited farming systems.
5 Conclusion
This study demonstrates that grafting tomato onto the bacterial wilt-resistant rootstock EG 203 significantly enhances resistance to M. incognita under field conditions. When combined with selected biological agents B. subtilis, T. asperellum, and P. lilacinum—applied during nursery and field stages, this integrated strategy effectively suppresses nematode populations, reduces root damage, and improves plant growth and fruit yield. The EG 203 rootstock not only delays senescence but also sustains productivity, offering both agronomic and economic benefits to farmers. Scientifically, this work contributes to the growing evidence supporting rootstock-mediated resistance and highlights the synergistic role of biological control in nematode management. These findings present a promising, eco-friendly alternative to chemical nematicides and support the adoption of sustainable practices in tomato cultivation. Further research to dissect the underlying resistance mechanisms will enhance our understanding and scalability of this grafting–bio-input integration approach.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The manuscript presents research on animals that do not require ethical approval for their study.
Author contributions
SN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal Analysis, Supervision, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MS: Project administration, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SS: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Resources. TE: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Resources. RSh: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Software, Validation, Investigation, Data curation. KD: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Software, Validation, Data curation, Formal Analysis. RM: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. RSr: Funding acquisition, Resources, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was conducted as part of the CGIAR Research Initiative on Plant Health and is supported by contributors to the CGIAR Trust Fund (https://www.cgiar.org/funders). The authors also acknowledge the long-term strategic donors to the World Vegetable Center, including Taiwan, the United States, Australia, the United Kingdom, Germany, Thailand, South Korea, the Philippines, and Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abad, P., Favery, B., Rosso, M. N., and Castagnone-Sereno, P. (2003). Root-knot nematode parasitism and host response: molecular basis of a sophisticated interaction. Mol. Plant Pathol. 4, 217–224. doi: 10.1046/j.1364-3703.2003.00170.x
Ambrogioni, L., Caroppo, S., and Capella, A. (2003). “Valutazione in vitro nei confronti di uova, larve di secondo stadio libere e larve di secondo stadio incluse negli ovisacchi di Meloidogyne incognita (Kofoid et White) Chitwood,” in Oikos una Soluzione Naturale Contro i Nematodi Fitoparassiti. Eds. d’Errico, F. P., Lamberti, F., Capella, A., and Guarnone, A. (Sipcam, Milan, Italy), 21–27.
Anonymous (2022). Crop production Techniques of Horticultural Crops (Tamil Nadu, India: Tamil Nadu Agricultural University). Available online at: https://agritech.tnau.ac.in/horticulture/hortivegetablestomatoindex.html.
Baidya, S., Timila, R. D., Manandhar, H. K., and Manandhar, C. (2017). Management of root knot nematode on tomato through grafting root stock of Solanum sisymbriifolium. J. Nepal Agric. Res. Counc. 3, 27–31.
Baron, N. C., de Souza Pollo, A., and Rigobelo, E. C. (2020). Purpureocillium lilacinum and Metarhizium marquandii as plant growth-promoting fungi. PeerJ 8, e9005. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9005
Basyony, A. G. and Abo-Zaid, G. A. (2018). Biocontrol of the root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita, using an eco-friendly formulation from Bacillus subtilis, lab. and greenhouse studies. Egyptian. J. Biol. Pest Control. 28, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s41938-018-0094-4
Black, L. L., Wu, D. L., and Wang, J. F. (2003). “Grafting tomatoes for production in the hot-wet season,” in Asian Vegetable Research & Development Center, vol. 3. (AVRDC Publication, Shanhua, Taiwan), 551.
Chandrawat, B. S., Siddiqui, A. U., Bhati, S. S., and Saharan, V. (2020). Response of defence related enzymes in tomato treated with oilcakes against root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 9, 11001111. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2020.911.127
d’Errico, G., Sasanelli, N., Guastamacchia, F., Stillittano, V., and D’Addabbo, T. (2023). Efficacy of azadirachtin in the integrated management of the root knot nematode meloidogyne incognita on short-and long-cycle crops. Plants 12, 1362. doi: 10.3390/plants12061362
Das, N. and Waquar, T. (2021). Bio-efficacy of Purpureocillium lilacinum on management of root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita in tomato. Indian J. Nematol. 51, 129–136. doi: 10.5958/0974-4444.2021.00020.2
de O. Nunes, P. S., De Medeiros, F. H., De Oliveira, T. S., de Almeida Zago, J. R., and Bettiol, W. (2023). Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus licheniformis promote tomato growth. Braz. J. Microbiol. 54, 397–406. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00874-3
El-Ashry, R. M., Ali, M. A., Elsobki, A. E., and Aioub, A. A. (2021). Integrated management of Meloidogyne incognita on tomato using combinations of abamectin, Purpureocillium lilacinum, rhizobacteria, and botanicals compared with nematicide. Egyptian. J. Biol. Pest Control. 31, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s41938-021-00438-x
Eltayeb, F. M. E. (2017). The effects of Bacillus subtilis bacteria on Meloidogyne javanica (Nematode) infection and tomato plant growth. Eur. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Life Sci. 5, 45–51.
FAOSTAT (2024). Available online at: https://www.fao.org/about/who-we-are/departments/statistics-division (Accessed 27 October 2024).
Fullana, A. M., Expósito, A., Pujolà, M., Achaerandio, I., Cunquero, M., Loza-Alvarez, P., et al. (2024). Effect of grafting tomato onto Solanum torvum on the population dynamics of Meloidogyne incognita and M. javanica and crop yield losses. Plant Pathol. 73 (9), 1–13.
Frey, C. J., Zhao, X., Brecht, J. K., Huff, D. M., and Black, Z. E. (2020). High tunnel and grafting effects on organic tomato plant disease severity and root-knot nematode infestation in a subtropical climate with sandy soils. HortScience 55 (1), 46–54.
Gatahi, D. M. (2020). Challenges and opportunities in tomato production chain and sustainable standards. Int. J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 7, 235–262. doi: 10.22059/IJHST.2020.300818.361
Gautam, S. B., Chand, R., Maurya, M. K., Yadav, V. K., Vishwakarma, S. P., and Prasad, R. (2021). Effect of neem, Azadirachta indica products and vermi-compost on root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita population build-up in tomato crop roots. Pharma. Innovation J. 10, 1041–1044.
Ghalawat, S., Goyal, M., Mehla, S., Malik, J. S., and Yadav, E. (2024). Growth trend in area, production, and productivity of tomato in India and haryana. Indian J. Extension. Educ. 60, 72–76. doi: 10.48165/IJEE.2024.60314
Hartman, K. M. and Sasser, J. N. (1985). “Identification of Meloidogyne species on the basis of differential host test and perineal pattern morphology,” in An advanced treatise on Meloidogyne; Vol.II Methodology. Eds. Barker, K. R., Carter, C. C., and Sasser, J. N. (Coop. Publ. Dep. Plant Pathol., N.C. State University and U.S. Ageney Int. Dev., Raleigh N.C), 69–77.
Kunwar, S., Paret, M. L., Olson, S. M., Ritchie, L., Rich, J. R., Freeman, J., et al. (2015). Grafting using rootstocks with resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum against Meloidogyne incognita in tomato production. Plant Dis. 99, 119–124. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-09-13-0936-RE
Meena, P., Chandrawat, B. S., Ahir, R. R., Gugarwal, B., Meena, S., Nitharwal, N., et al. (2021). Management of tomato wilt complex caused by Meloidogyne incognita and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici through organic amendments. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 9, 1691–1693.
Nagachandrabose, S. and Baidoo, R. (2018). A guide to introductory nematology (New York, USA: Nova Science Publishers, Incorporated).
Nagachandrabose, S., Jayaraman, J., and Somasundaram, P. (2022). Application of liquid bio-inoculants through a drip irrigation system to manage slow decline disease caused by Tylenchulus semipenetrans in acid lime trees. Phytoparasitica 50, 243–253. doi: 10.1007/s12600-021-00950-8
Nagachandrabose, S., Rajendran, P., Ganeshan, S., Arunachalam, A., Somasundaram, P., Iyamperumal, M., et al. (2024). Resistance to Meloidogyne enterolobii in guava: Screening of cultivated and wild types, resistance principles, and graft compatibility. Sci. Hortic. 338, 113825. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2024.113825
Naserinasab, F., Sahebani, N., and Etebarian, H. R. (2011). Biological control of Meloidogyne javanica by Trichoderma asperellum BI and salicylic acid on tomato. Afr. J. Food Sci. 5, 276–280.
Owusu, S. B., Kwoseh, C. K., Starr, J. L., and Davies, F. T. (2016). Grafting for management of root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne incognita, in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Nematropica 46, 14–21.
Parrado, L. M. and Quintanilla, M. (2024). Plant-parasitic nematode disease complexes as overlooked challenges to crop production. Front. Plant Sci. 15, 1439951. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1439951
Rawal, S. (2020). A review on root-knot nematode infestation and its management practices through different approaches in tomato. Trop. Agroecosyst. 1, 92–96. doi: 10.26480/taec.02.2020.92.96
Rizvi, R., Singh, G., Safiuddin, Ali Ansari, R., Ali Tiyagi, S., and Mahmood, I. (2015). Sustainable management of root-knot disease of tomato by neem cake and Glomus fasciculatum. Cogent. Food Agric. 1, 1008859. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2015.1008859
Seenivasan, N. (2017). Management of Radopholus similis and Helicotylenchus multicinctus in ratoon banana grown under high density planting systems. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 17, 41–62. doi: 10.1080/15538362.2016.1250696
Shanmugam, S. P., Murugan, M., Shanthi, M., Elaiyabharathi, T., Angappan, K., Karthikeyan, G., et al. (2024). Evaluation of integrated pest and disease management combinations against major insect pests and diseases of tomato in Tamil Nadu, India. Horticulturae 10, 766. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae10070766
Siddiqui, I. A. (2002). Suppression of Meloidogyne javanica by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis in tomato. Nematol. Mediterranea. 30, 125–130.
Singh, P. and Siddiqui, Z. A. (2010). Biocontrol of root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita by the isolates of Bacillus on tomato. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 43, 552–561. doi: 10.1080/03235400801939904
Singh, U. B., Singh, S., Malviya, D., Chaurasia, R., Imran, M. O. H. D., and Rai, J. (2017). Harnessing biocontrol potential of Trichoderma asperellum for control of Meloidogyne incognita in tomato. Indian Phytopathol. 70, 331–335. doi: 10.24838/ip.2017.v70.i3.74239
Sohrabi, F., Sheikholeslami, M., Heydari, R., Rezaee, S., and Sharifi, R. (2020). Investigating the effect of Glomus mosseae, Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma asperellum on plant growth and controlling Meloidogyne javanica in tomato. Indian Phytopathol. 73, 293–300. doi: 10.1007/s42360-020-00227-w
Southey, J. F. (1986). Laboratory methods for work with plant and soil nematodes. Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food. Technical Bulletin, 2.
Taylor, A. L. and Sasser, J. N. (1978). Biology, identification and control of root-knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) (Raleigh, NC, USA: A cooperative publication of North Carolina State University, Dept. of Plant Pathology, and USAID).
Tiwari, J. K., Behera, T. K., Rai, N., Yerasu, S. R., Singh, M. K., and Singh, P. M. (2022). Tomato breeding for processing in India: Current status and prospects. Vegetable. Sci. 49, 123–132. doi: 10.61180/vegsci.2022.v49.i2.01
Williamson, V. M. and Kumar, A. (2006). Nematode resistance in plants: the battle underground. Trends Genet. 22, 396–403. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2006.05.003
Keywords: tomato grafts, root-knot nematode, host plant resistance, biorational inputs, integrated nematode management
Citation: Nagachandrabose S, Shanthi M, Shanmugam SP, Elaiyabharathi T, Sharmila R, Devrajan K, Manickam R and Srinivasan R (2025) Integrating grafting and bio-inputs for sustainable management of root knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita, in tomato cultivation. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1623444. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1623444
Received: 06 May 2025; Accepted: 24 July 2025;
Published: 29 August 2025.
Edited by:
Yueqiang Zhang, Southwest University, ChinaReviewed by:
Eustachio Tarasco, University of Bari Aldo Moro, ItalyEzequiel Muñoz Márquez, Centro de Investigación en Alimentación y Desarrollo AC, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Nagachandrabose, Shanthi, Shanmugam, Elaiyabharathi, Sharmila, Devrajan, Manickam and Srinivasan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ramasamy Srinivasan, c3JpbmkucmFtYXNhbXlAd29ybGR2ZWcub3Jn; Mookiah Shanthi, bXNoYW50aGllbnRvQHRuYXUuYWMuaW4=
†ORCID: Mookiah Shanthi, orcid.org/0000-0001-5737-4781
 Seenivasan Nagachandrabose
Seenivasan Nagachandrabose Mookiah Shanthi
Mookiah Shanthi Sankaran Pagalahalli Shanmugam3
Sankaran Pagalahalli Shanmugam3 Ramasamy Srinivasan
Ramasamy Srinivasan