- Key Laboratory of Biology and Genetic Improvement of Oil Crops, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Oil Crops Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Wuhan, China
Peanut is a worldwide important oil crop and serves as a major source of vegetable oil. Seed oil is stored as oil bodies (OB), which are subcellular structures in the cytoplasm. Oil bodies accumulate triacylglycerols (TAGs) inside and surrounded by a monolayer of phospholipids (PL) with oil-body-membrane proteins. Oleosins have been demonstrate to be the predominant oil-body-membrane proteins and played a crucial role in maintaining oil body stability. In this study, 12 oleosin genes were identified in peanut, distributed across 9 chromosomes and classified into three lineages (U, SH, and SL). Most AhOle genes exhibited high expression levels in developing seeds, a pattern that aligns with the expression profiles of U, SH, and SL oleosins. Several cis-elements were found in the promoters of AhOle genes, such as LTR, ABRE, and TCA-element. Expression analysis confirmed that these genes were responsive to treatments involving drought, cold stress and various plant hormones. The AhOle11 gene was cloned due to its highest expression level observed during seed development. Subcellular localization analysis demonstrated that AhOle11 gene was localized in oil bodies. Overexpression AhOle11 in Arabidopsis significantly increased in seed oil content and an increased oil body density, thereby supporting its critical role in oil accumulation. Nevertheless, the fatty acid profiles in transgenic seeds exhibited only minor alterations. This study contributes to a comprehensive understanding of the oleosin family in peanut and provides valuable insights for genetic improvement aimed at enhancing oil accumulation.
1 Introduction
Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is one of the important oilseed crop worldwide, which are rich in oil, protein, sugar, resveratrol and other nutrients (Bishi et al., 2015). The peanut kernel contains 45-58% oil, primarily composed of palmitic (C16:0), steric (C18:0), oleic (C18:1), linoleic (C18:2), arachidic (C20:0), eicosenoic (C20:1), behenic (C22:0) and lignoceric (C24:0) acids (Chapman and Ohlrogge, 2012; Shasidhar et al., 2017). Seed oil is stored as triacylglycerol (TAG) within oil bodies (OB), where they serve as a primary source of energy and nutrients during germination (Chapman and Ohlrogge, 2012). The unique structure of oil bodies allows for efficient storage and mobilization of TAGs, which are the most energy-dense form of lipids.
Oil bodies are composed of a central core of TAGs encased by a monolayer of phospholipids (PL), which is embedded with oil-body-membrane proteins such as oleosin, caleosin, and steroleosin (Hsieh and Huang, 2004; Manan et al., 2017; Shao et al., 2019). Oleosins are the most abundant and well-studied proteins in oil bodies. They are characterized by a long hydrophobic hairpin structure that spans the monolayer, with a hydrophilic N-terminal domain exposed to the cytoplasm (Tzen and Huang, 1992; Frandsen et al., 2001; Shao et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2022). Oleosins, with their unique structure and abundance, are primarily involved in stabilizing the oil body and preventing its fusion with other oil bodies (Huang, 1994; Deleu et al., 2010; Huang and Huang, 2015; Shimada and Hara-Nishimura, 2015). The oleosin genes have been identified across a diverse range of organisms, including algae, moss and higher plants (Huang, 1996). Based on their amino acid sequences and tissue-specific expression patterns, oleosin genes are divided into six lineages: primitive (P oleosin), universal (U oleosin), seed low-molecular-weight (SL oleosin), seed high-molecular-weight (SH oleosin), tapetum oleosins (T oleosin), and mesocarp (M oleosin) (Fang et al., 2014; Huang and Huang, 2015). The P lineage is the most ancestral and is found in green algae, mosses, and ferns (Huang and Huang, 2015, 2016). The U lineage is universally present in all land plants and is characterized by a conserved C-terminal AAPGA motif (Zou et al., 2024). The SL and SH lineages are seed-specific, with the SL clade evolving first from the U clade and later giving rise to the SH, M, and T lineages (Shimada et al., 2008). The M lineage is present in Lauraceae, while the T lineage has been exclusively detected in the tapetum of Brassicaceae (Chen et al., 2019).
Oleosins play several important roles in plant cells. One of their primary functions is to stabilize oil bodies, preventing their aggregation and fusion. The absence of oleosins leads to the compression and fusion of oil bodies, resulting in enlarged oil bodies within AtOLE1-knockout Arabidopsis seeds (Shimada et al., 2008). Additionally, oleosins are involved in lipid metabolism, influencing the oil content and fatty acid composition (Siloto et al., 2006; Hu et al., 2009; Liu et al., 2013; Hu et al., 2023). Down-regulating the expression levels of oleosins in Arabidopsis resulted in a significantly reduction in oil content (Shimada et al., 2008; Wu et al., 2010). Over-expression oleosin genes in Arabidopsis led to altered fatty acid composition and a slight increase in oil content (Chen et al., 2019; Ojha et al., 2021). Oleosins also contribute to the stress response by modulating oil body size and number in accordance with metabolic demands. The analysis of the expression profiles of Theaceae oleosin genes revealed that SL2 oleosin was up-regulated, whereas SL1 and SL3 oleosins were down-regulated under drought stress (Zhang et al., 2023). Furthermore, SH1 and SH4 oleosins were up-regulated in response to both cold and heat stress (Zhang et al., 2023). When the Atole1 mutant was exposed to freezing conditions, its germination rate decreased by approximately 50% (Shimada et al., 2008). However, the overexpression of SbOle1, SbOle2, and SbOle3 in Atole1 mutant significantly restored normal germination rates under freezing conditions (Ojha et al., 2021).
Oleosins are crucial for lipid storage, metabolism, and oil body dynamics; however, the characteristics and functions of oleosins in peanut remain largely unknown. In this study, oleosin genes from the ShiTouQi cultivar were identified, and their physical and chemical properties, gene structure, phylogenetic tree, and expression pattern were analyzed. One of them with the highest expression level in developing seeds was cloned and its function was characterized in Arabidopsis. This study aims to establish a foundation for an understanding of molecular biological functions of peanut oleosin genes and provides valuable insights for genetic improvement efforts focused on enhancing oil content in peanut.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Identification of peanut oleosin genes members and properties analysis
The genomic sequences of a cultivated peanut A. hypogaea cv. ShiTouQi were downloaded from Peanut Genome Resouce (http://peanutgr.fafu.edu.cn/index.php). The peanut oleosin genes were identified using two tools: BLASTP search and HMMER. The protein sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana oleosin genes, obtained from TAIR (https://www.arabidopsis.org/), were used as queries for BLASTP searches against the annotated peanut proteins and to identify peanut oleosin homologs. The conserved oleosin domain (PF01277) was then employed to identify the proteins through HMMER program (Finn et al., 2011). By integrating the sequences derived from both methods, peanut oleosin proteins were identified.
The gene structure information was retrieved from Peanut Genome Resouce (http://peanutgr.fafu.edu.cn/index.php). The chromosome location, gene structure and conserved domain were visualized using MG2C (https://qiaoyundeng.github.io/) and TBtools (Chao et al., 2021). The predicted molecular weights and theoretical isoelectric points (PI) were calculated using Expasy - ProtParam (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/). The conserved domains were identified using Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/).
2.2 Gene duplication and phylogenetic analysis of peanut oleosin genes
The oleosin protein sequences of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) were retrieved from BnTIR (https://yanglab.hzau.edu.cn/BnTIR). The oleosin protein sequences of Arachis duranensis and Arachis ipaensis were obtained from Peanut Base (https://www.peanutbase.org/). Multiple sequence alignments of the oleosin protein sequences were performed using ClustalW software (Higgins and Sharp, 1988). A phylogenetic tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method in the MEGA X, employing 1000 bootstrap replicates (Kumar et al., 2018). The evolutionary tree was visualized using the online tool iTOL (https://itol.embl.de/itol.cgi).
The collinearity within and between A. hypogaea, A. duranensis and A. ipaensis was established using MCScanX (http://chibba.pgml.uga.edu/duplication/) incorporated into TBtools. The collinear relationships of oleisin genes were drawn using Circos (Krzywinski et al., 2009).
2.3 Cis-elements in the promoter regions of peanut oleosin genes
The promoter sequences of peanut oleosin genes were extracted from the ShiTouQi genome using TBtools, encompassing a 2000bp DNA sequence upstream of the ATG start codon. The cis-elements in the promoter regions were predicted using New PLACE websites (https://www.dna.affrc.go.jp/PLACE/?action=newplace). The positions of cis-elements were visualized using TBtools.
2.4 Expression profile analysis of peanut oleosin genes
The multi-tissue transcriptome data used in this study were downloaded from Peanut Genome Resouce (http://peanutgr.fafu.edu.cn/index.php). Additionally, transcriptome data of leaves subjected to drought and cold stress, as well as those treated with plant hormone, were also obtained from this database. The heat maps were generated using TBtools.
2.5 RNA extraction and RT-PCR
To validate the expression profile, roots, leaves, stems, flowers, and developing seeds at 20, 30, 40, 50, and 60 days after pollination (DAP) of Zhonghua 12 were collected and five development stages as described previously (Huai et al., 2020). Total RNA was extracted using RNAprep Pure Plant Kit (DP 441, TIANGEN, China). First strand cDNA was syntheisized from 1 µg RNA using HiScript III 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (R 312-02, Vazyme). Quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) was performed according to the instructions of ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme, China). The primers for RT-qPCR were designed using NCBI (Supplementary Table S3). The relative expression levels of genes were calculated by the 2−△△CT method. The experiment was performed using three biological replicates.
2.6 Cloning of AhOle11
Total RNA was extracted from developing seeds of Zhonghua 12 at 40 days after pollination using TRIzol reagent (DP 424, TIANGEN, China), following the manufacturer’s protocol. Reverse transcription was performed using HiScript IV 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (R412-01, Vazyme, China) as described by the manufacturer. The AhOle11 (AH16G32210) gene was cloned using the primers: 5’-ATGTCTGATCAAACAAGGACA-3’ and 5’- TCAATACCCTTGTGTGCCCTC-3’.
2.7 Subcellular localization of AhOle11
The AhOle11 gene without a stop codon were amplified by PCR, and inserted between the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter and the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene. The resulting plasmids were designated as pHBT-AhOle11-GFP. The empty vector pHBT-GFP was analyzed as a control. The AtOle5 (AT3G27660) from Arabidopsis was fused with the red fluorescent protein (RFP) gene. The p35S:AtOle5-RFP construct was used as an oil body marker. The pHBT-GFP and pHBT-AhOle11-GFP were each transiently co-expressed with the oil body marker in Arabidopsis protoplasts by PEG transformation, respectively (Yoo et al., 2007). Fluorescence signals were detected using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Nikon C2-ER, Japan). GFP was excited at 488nm, while RFP was excited at 561 nm.
2.8 Expression of AhOle11 in Arabidopsis
The AhOle11 gene was amplified via PCR and inserted into the pBinGlyRed2 vector, which contains a DsRed2 driven by 35S promoter. As a result, the AhOle11 was positioned between the seed-specific soybean glycinin-1 promoter and its 3’UTR.The recombinant plasmid was introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101 and transformed into Arabidopsis by the floral dip method. DsRed-positive seeds were identified using a green LED flashlight with a red camera filter lens (Huai et al., 2023).
2.9 Analysis of seed oil content and fatty acid composition
The oil content and fatty acid composition of mature DsRed-positive Arabidopsis seeds were analyzed as previously described (Huai et al., 2018). In brief, 20 mg grounded seeds were placed into a glass tube. Subsequently, 1.5ml of 2.5% sulfuric acid-methanol solution, 0.35 ml of toluene and 0.3 ml of C15:0 (internal standard) solution in methanol (10 mg/ml) were added. Fatty acids were transmethylated at 90°C for 30–45 min. After cooling to room temperature, 1 ml H2O and 1 ml hexane were added into the tube. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm microporous membrane and transferred into an autosampler vial. The fatty acid contents were determined by gas chromatograph (GC) using an Agilent 7890B with flame ionization detection and the DB-23 column. The concentration of fatty acids methyl esters (FAMEs) was quantified based on the ratio of different FAMEs peak areas relative to the internal standardization (C15:0). The fatty acid composition is expressed as absolute concentrations (mg/g). Three biological replicates per line were analyzed in this experiment. Statistically significant differences were analyzed using Student’s t-test by the SPSS SPSS19.0; The phenotypes was performed on GraphPad Prism 8.0.
2.10 Visualization of oil body
Fixation of seeds and lipid staining were performed as previously described with modifications (Cai et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2019). Mature seeds were imbibed in distilled water for 20~30 min for seed coat removal. Then embryos were immediately immersed in formalin-acetic acid-alcohol (FAA) fixative (formalin: acetic acid: 50% ethanol = 1:1:18 v/v) for at least 24 h. The fixed tissues were trimmed using a scalpel and subsequently immersed in 15% sucrose solution at 4°C until they sank. They were then transferred to a 30% sucrose solution at 4°C and incubated until they sedimented. The fixed tissues were embedded with optimal cutting temperature compound (OCT) compound. Cryosections (8~10 µm) were prepared using a Cryostat Microtome (Thermo, CRYOSTAR NX50, USA). The cryosections were stained with BODIPY 493/503 for 20 min and subsequently washed with PBS (pH 7.4). Thereafter, the sections were re-stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) for 10 min in the dark, followed by additional washes with PBS (pH 7.4). Image observation for BODIPY and DAPI was performed using a confocal laser scanning microscope (Nikon C2-ER, Japan). DAPI was excited at 330-380nm, while BODIPY was excited at 488 nm.
3 Result
3.1 Identification of oleosin genes in peanut
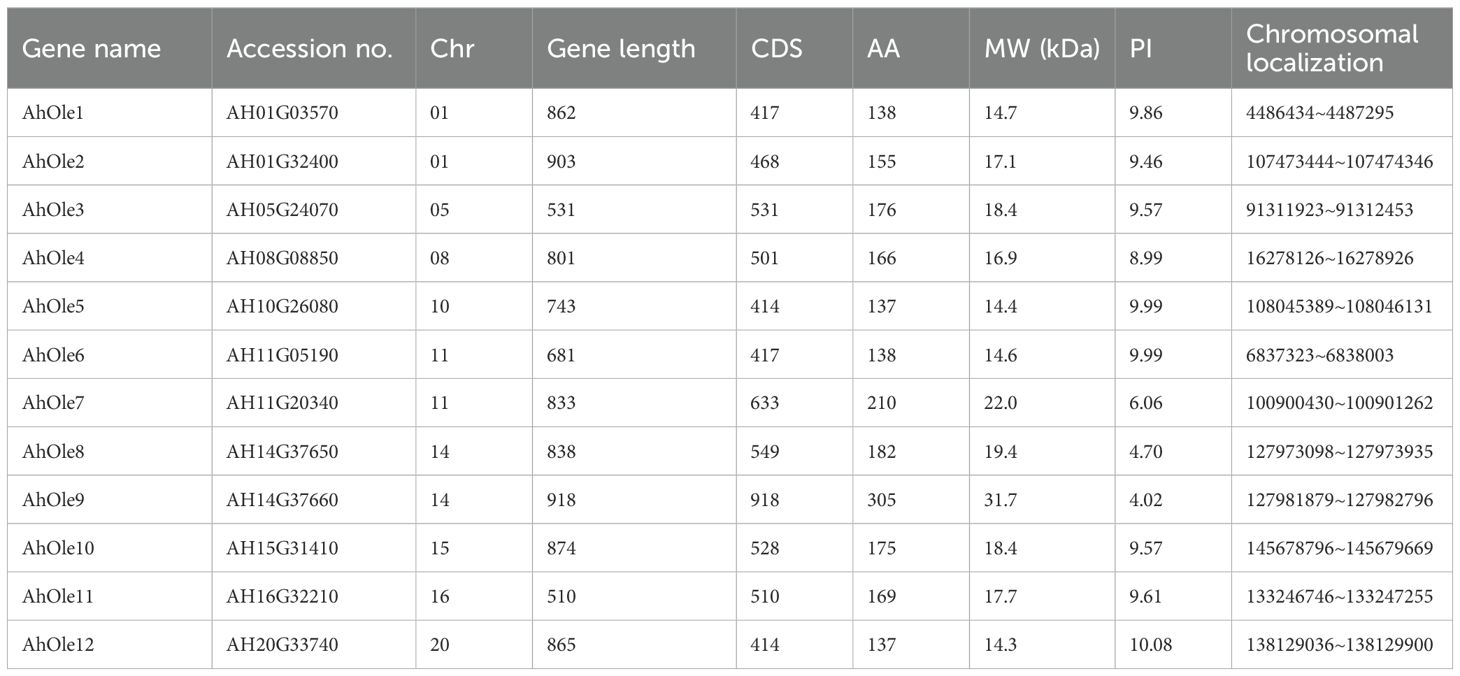
A total of 12 oleosin genes were identified in the peanut genome and were designated as AhOle1~AhOle12 based on their chromosomal locations (Table 1). The coding sequences (CDSs) of peanut oleosin genes ranged from 414 to 918 bp in length, encoding proteins consisting of 137 to 305 amino acids, with molecular weights from 14.3 to 31.7 kDa (Table 1). All AhOle genes were intronless throughout their entire open reading frames (Figure 1A). Furthermore, all AhOles contained solely the oleosin domain (Figure 1B).
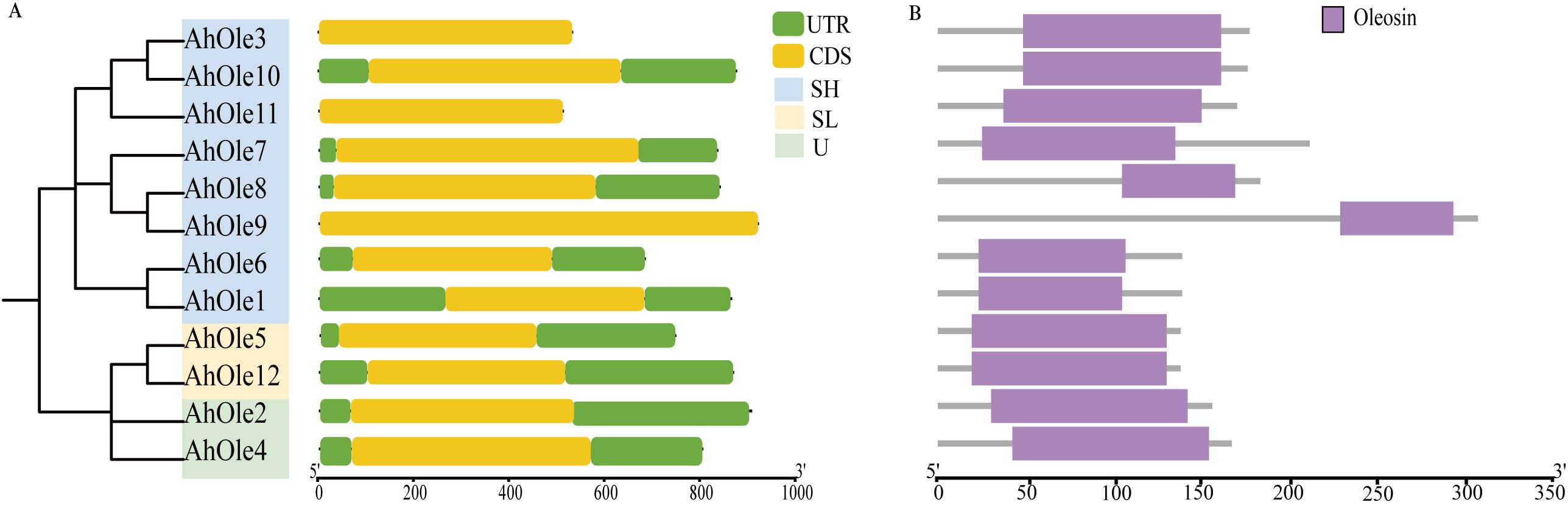
Figure 1. Gene structures and conserved domain of AhOle genes in Peanut. (A) Gene structure of AhOle genes. (B) The conserved domains of AhOles.
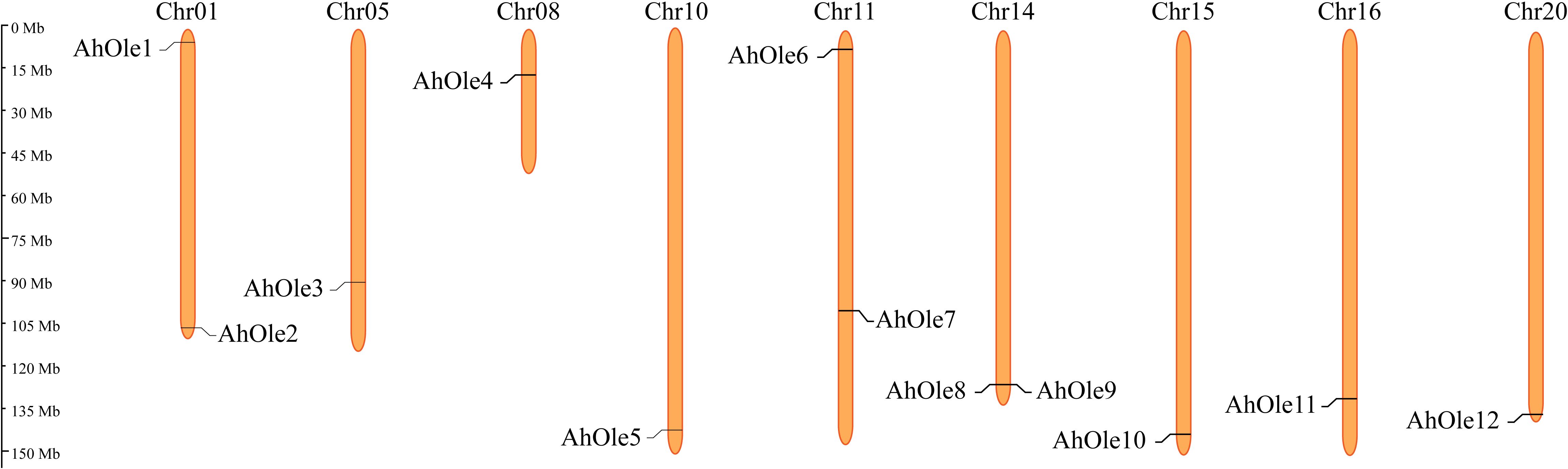
The AhOle genes were unevenly distributed across 9 chromosomes in peanut, an allotetraploid comprising A and B subgenomes. Five AhOle genes was detected on Chr01, Chr05, Chr08 and Chr10 in subgenome A, whereas seven AhOle genes was located on Chr11, Chr14 Chr15, Chr16 and Chr20 in subgenome B. Notably, Chr05, Chr08, Chr10, Chr15, Chr16 and Chr20 each contained only a single AhOle gene, whereas Chr01, Chr11 and Chr14 each harbored two such genes (Figure 2).
3.2 Phylogenetic and synteny analysis of AhOles
An un-rooted phylogenetic tree was constructed in MEGA X based on the protein sequences sourced from A. hypogaea (12 AhOles), A. duranensis (6 AdOles), A. ipanesis (7 AiOles), A. thaliana (17 AtOles) and B. napus (48 BnOles). The oleosin proteins were divided into four groups: U, SL, SH and T lineages. AhOle was classified into U, SL and SH lineages, but no AhOle was detected in T lineage (Figure 3A). AhOle2 and AhOle4 were grouped into the U lineage, while AhOle5 and AhOle12 were grouped into the SL lineage. Eight AhOles were grouped into the SH lineage, including AhOle1, AhOle3, AhOle6, AhOle7, AhOle8, AhOle9, AhOle10 and AhOle11 (Figure 3A). These results indicate that only three common oleosin proteins are present in peanut: U, SL and SH oleosins.
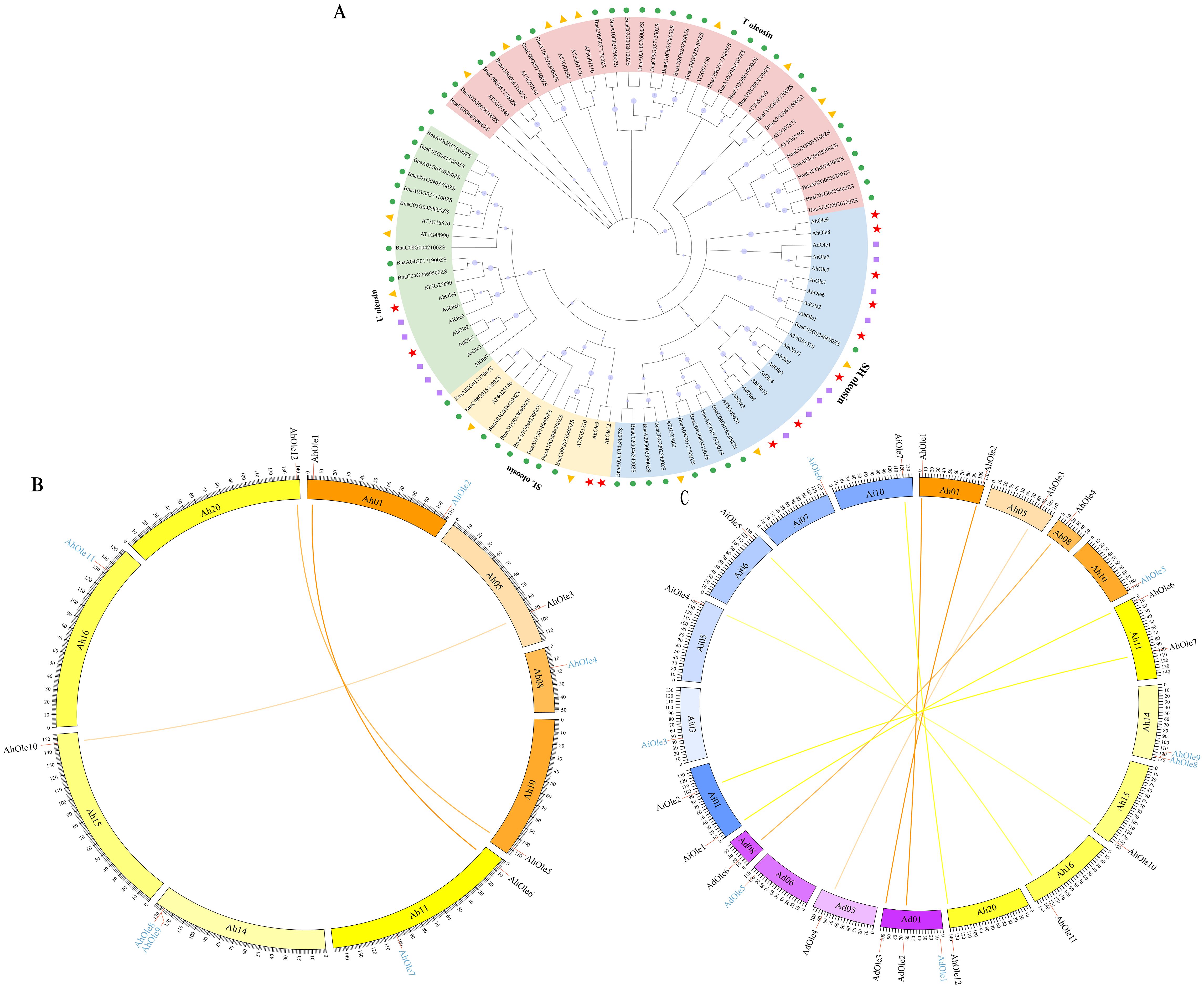
Figure 3. Phylogenetic and synteny analysis of oleosin genes in peanut. (A) Phylogenetic analysis of oleosins from A. hypogaea, A. duranensis, A. ipanesis, A. thaliana and B. napus. The oleosin family members were categorized into four groups: T, U, SL and SH lineages. Various shapes denoted different plant species. (B) Syntenic analysis of AhOle genes on the chromosomes in A. hypogaea. Ah01–Ah10, chromosomes from the A subgenome; Ah11–Ah20, chromosomes from the B subgenome. The colored lines indicate the syntenic gene pairs between A and B subgenomes. The blue character represents the non-syntenic AhOle genes. (C) Interspecies collinearity analysis in A. hypogaea, A. duranensis, and A. ipaensis. Ah01–Ah20, chromosomes from A. hypogaea; Ad01-Ad10, chromosomes from A. duranensis; Ai01-Ai10, chromosomes from A. ipaensis. The colored lines indicate the syntenic gene pairs between A. hypogaea and A. duranensis, as well as between A. hypogaea and A. ipaensis. The blue character represents the non-syntenic genes.
Through intragenomic comparison analysis, three collinear gene pairs in A. hypogaea were obtained (Figure 3B). AhOle genes on Chr01, Chr05 and Chr10 were syntenic to AhOle genes on corresponding Chr11, 15 and 20. The AhOle2 and AhOle4 in subgenome A were not paired, as well as four AhOle genes in subgeome B (AhOle7, AhOle8, AhOle9 and AhOle11) (Figure 3B).
To achieve a deeper understanding of the phylogenetic mechanisms occurring in the peanut oleosin family, the synteny maps of the oleosin genes in the A. hypogaea (AABB) genome and their homologous genes in two ancestral species A. duranensis (AA) and A. ipaensis (BB) were constructed. Through intergenomic comparison analysis, four gene pairs between A. hypogaea and A. duranensis and five gene pairs between A. hypogaea and A. ipaensis were identified (Figure 3C). The syntenic genes of AdOle1 and AdOle5 in A. duranensis were not found in A. hypogaea, as well as AiOle3 and AiOle6 in A. ipaensis. In addition, no syntenic genes of AhOle5, AhOle8 and AhOle9 were identified in A. duranensis and A. ipaensis (Figure 3C). AhOle8 and AhOle9 were found to be homologous gene pairs, potentially resulting from tandem duplication events (Figure 3A).
3.3 Expression profiles of oleosin genes in peanut
To elucidate the roles of AhOle genes during different growth and developmental stages in peanuts, the expression patterns of these genes were analyzed using transcriptome data from the reference A. hypogaea cv. ShiTouQi. A heat-map of AhOle genes was created to demonstrate their expression profile (Figure 4). AhOle8 and AhOle9 were not expressed in any of the tested tissues, whereas other AhOle genes exhibit high expression. Among them, the expression levels of AhOle4, AhOle5, AhOle11 and AhOle12 were found to be the highest during seed development. The expression level of AhOle3 and AhOle10 in developing seeds were observed moderately high, followed by AhOle1, AhOle6 and AhOle2. AhOle7 was exclusively expressed at the initial and final stages of seed development (Figure 4).
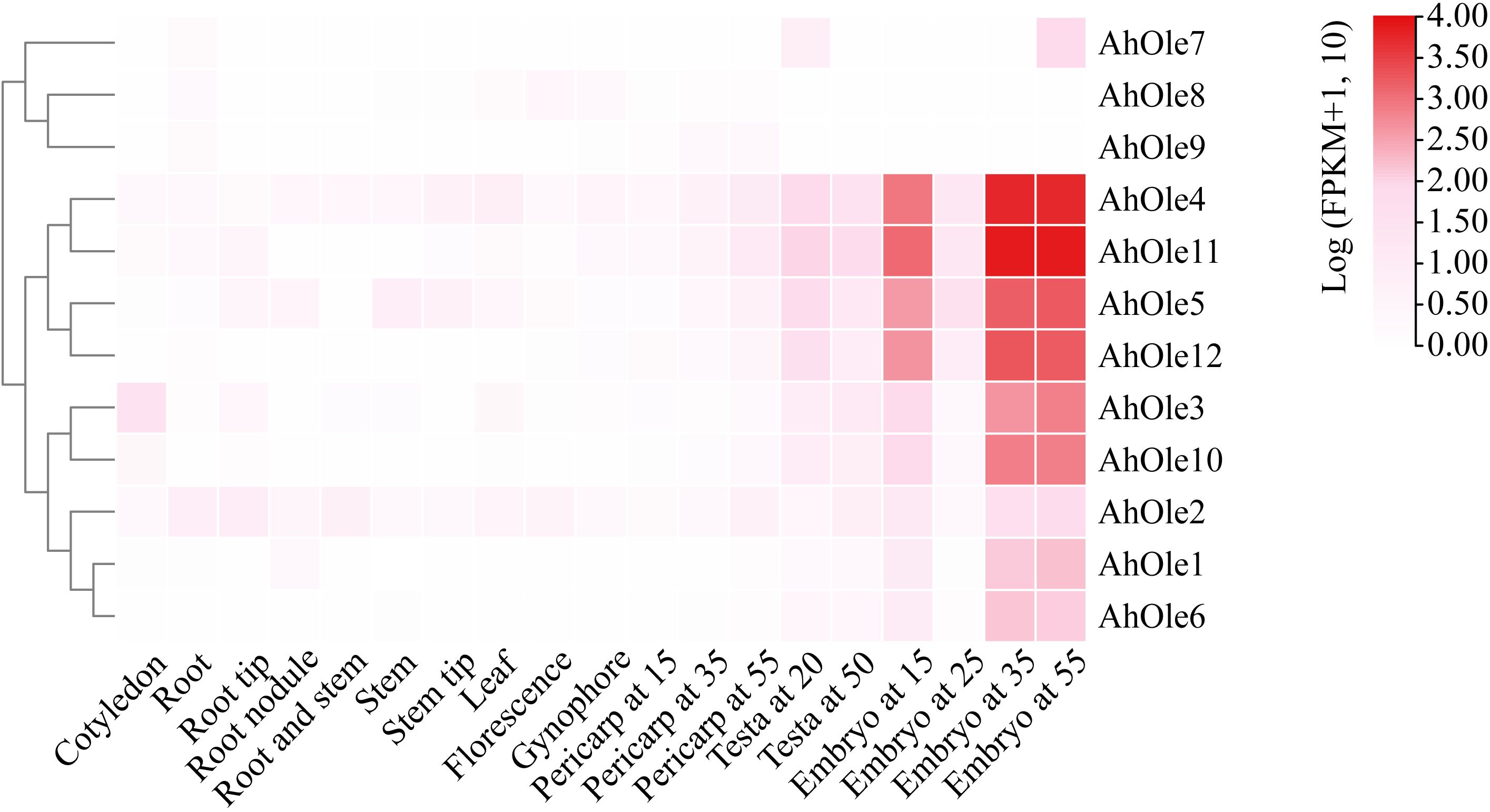
Figure 4. Expression profiles of AhOle genes across different tissues and developmental stages in peanut.
To validate the transcriptome data, the expression levels of SH (AhOle1/6, AhOle3/10, and AhOle11), SL (AhOle5/12), and U (AhOle2) Oleosin genes were further investigated in Zhonghua12 tissues. The results indicated that eight genes exhibited significantly different expression patterns (Supplementary Figure S1). AhOle1/6 are expressed in stems, leaves, and seeds. AhOle2 and AhOle11 are expressed in all the tissues, and transcription abundance is the highest in seeds. AhOle3/10 exhibited predominant expression in seeds and displayed a pattern of increasing expression level along with seed development (Supplementary Figure S1A). The expression of AhOle5/12 is significantly higher in the later stage of seeds and leaves than in other tissues (Supplementary Figure S1A). In addition, comparison analysis of AhOle1/6, AhOle2, AhOle3/10, AhOle5/12, and AhOle11 expression throughout peanut seed developmental stage showed higher transcription accumulation during 30 and 60 DAP, with AhOle11 demonstrating the highest expression abundance among those genes (Supplementary Figure S1B). This result indicates that qPCR analysis of AhOle gene expression patterns was consistent with transcriptome data.
3.4 Cis-elements of AhOles gene and respond to stress analysis
Oleosin genes have been reported to be regulated in response to various abiotic stresses. The cis-elements within promoters play a crucial role in modulating gene transcription. To investigate the potential cis-elements involved in response of peanut to abiotic stresses, the upstream 2000-bp regions of AhOle genes were analyzed. A diverse array of cis-element was identified, including those associated with development, phytohormone responses, and stress tolerance (Figure 5A). For instance, the LTR element (CCGAAA), which is linked to low temperature tolerance, was identified in promoters of AhOle2, AhOle7, AhOle8 and AhOle11. The MYB binding sites (TAACTG) implicated in drought inducibility was found in all AhOle gene promoters. The ABRE element (AAGAA-motif), which responds to abscisic acid (ABA), was present in the promoters of AhOle1, AhOle2, AhOle3, AhOle5, AhOle6, AhOle7, AhOle8, AhOle10, AhOle11 and AhOle12. The TGACG-motif and CGTCA-motif, both responsive to jasmonic acid (JA), were identified in the promoters of AhOle2, AhOle5, AhOle6, AhOle7, AhOle8, AhOle10, AhOle11 and AhOle12. The TCA-element, which respond to salicylic acid (SA), was detected in the promoters of AhOle1, AhOle2, AhOle3, AhOle6, AhOle8, AhOle11 and AhOle12. The GARE-motif, associated with gibberellin (GA) response, was present in the promoters of AhOle2, AhOle3, AhOle4, AhOle5, AhOle6, AhOle7, AhOle10, AhOle11 and AhOle12. The ERELEE4-motif, involved in ethylene response, was found in the promoters of AhOle4, AhOle5, AhOle6, AhOle8, AhOle10, AhOle11 and AhOle12 (Figure 5A).
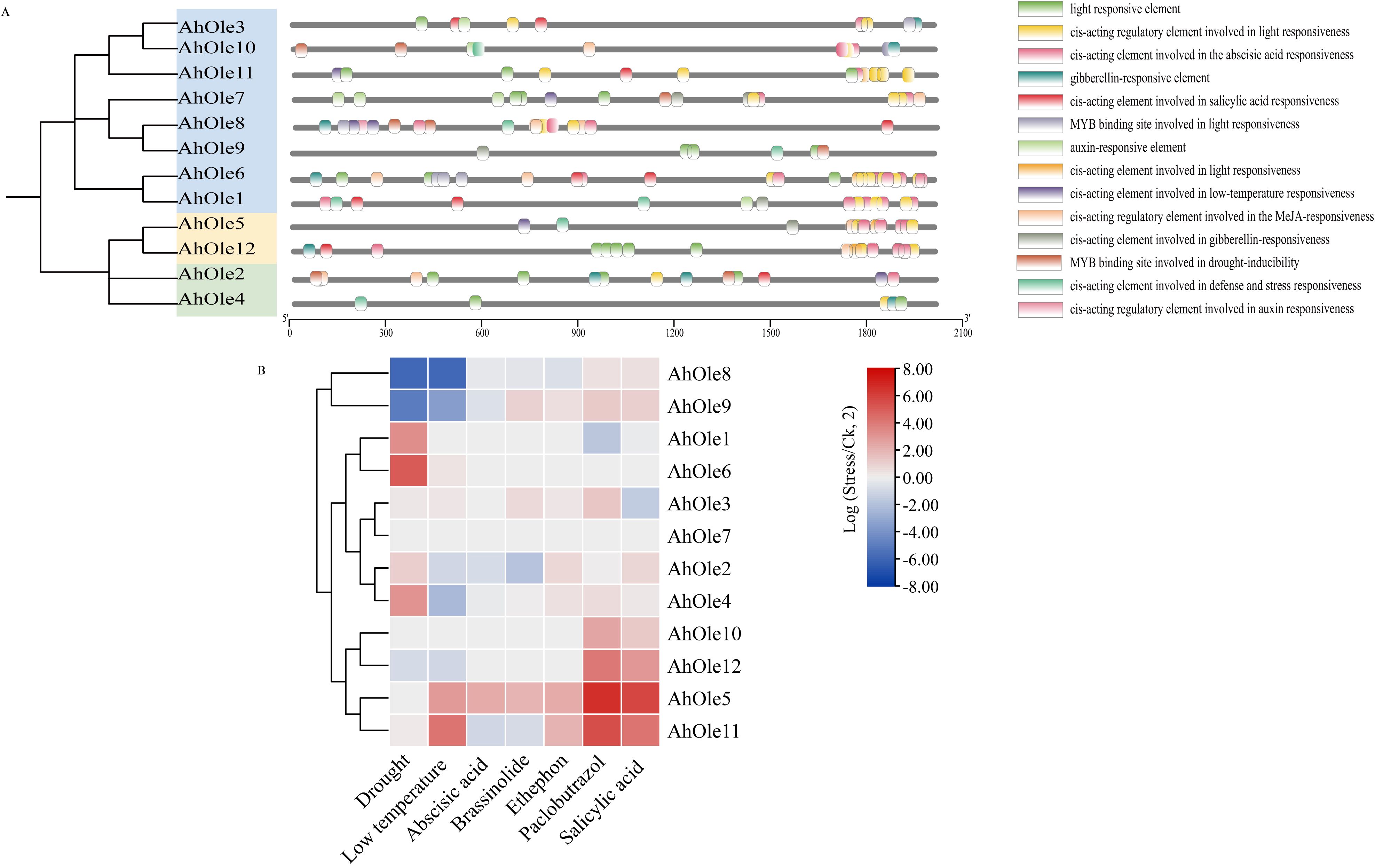
Figure 5. Predicted cis-elements in the promoter regions of AhOle genes along with their responses to abiotic stresses and plant hormones. (A) Predicted cis-elements in the promoter regions of AhOle genes. (B) The expression profiles of AhOle genes in peanut leaves treated with drought and cold stresses, as well as six plant hormones. The transcriptome data were download from Peanut Genome Resouce.
The transcriptome data of peanut leaves subjected to drought and cold stress, as well as those treated with plant hormone, were downloaded and analyzed (Figure 5B). The expression levels of AhOle1, AhOle4 and AhOle6 were significantly up-regulated under drought stress, while those of AhOle8 and AhOle9 were significantly down-regulated. Under cold stress, the expression level of AhOle11 was significantly up-regulated, whereas those of AhOle4, AhOle8 and AhOle9 were significantly down-regulated. Following treatment with paclobutrazol, the expression level of AhOle5, AhOle10 and AhOle11 were significantly up-regulated. Additionally, the expression level of AhOle5 and AhOle11 were significantly up-regulated after treated with salicylic acid (Figure 5B).
The expression of AhOle8 was down-regulated in response to both drought and cold stresses, along with three MYB elements and one LTR element in its promoter. The expression of AhOle11 was up-regulated upon exposure to salicylic acid, with a TCA-element detected in its promoter. Meanwhile, the expression levels of AhOle5, AhOle10, and AhOle11 were up-regulated following treatments with abscisic acid, salicylic acid, and ethephon, respectively, which is consistent with the predicted cis-elements. These findings suggested that AhOle genes play an important role in peanut development and responses to abiotic stress.
3.5 Subcellular localization of AhOle11
The AhOle11 gene was selected for further functional analysis, as it belongs to the SH lineage and exhibited the highest expression level during seed development (Figures 3, 4). To investigate the subcellular localization of AhOle11, it was fused with GFP and subsequently co-expressed with an oil body marker in Arabidopsis protoplasts. As anticipated, the green fluorescence from the empty vector was observed throughout the entire cell. In contrast, the green fluorescence of AhOle11 was completely co-localized with the red fluorescence of the oil body marker (Figure 6). These results indicated that AhOle11 was located within the oil body, where oleosin exerts its function.
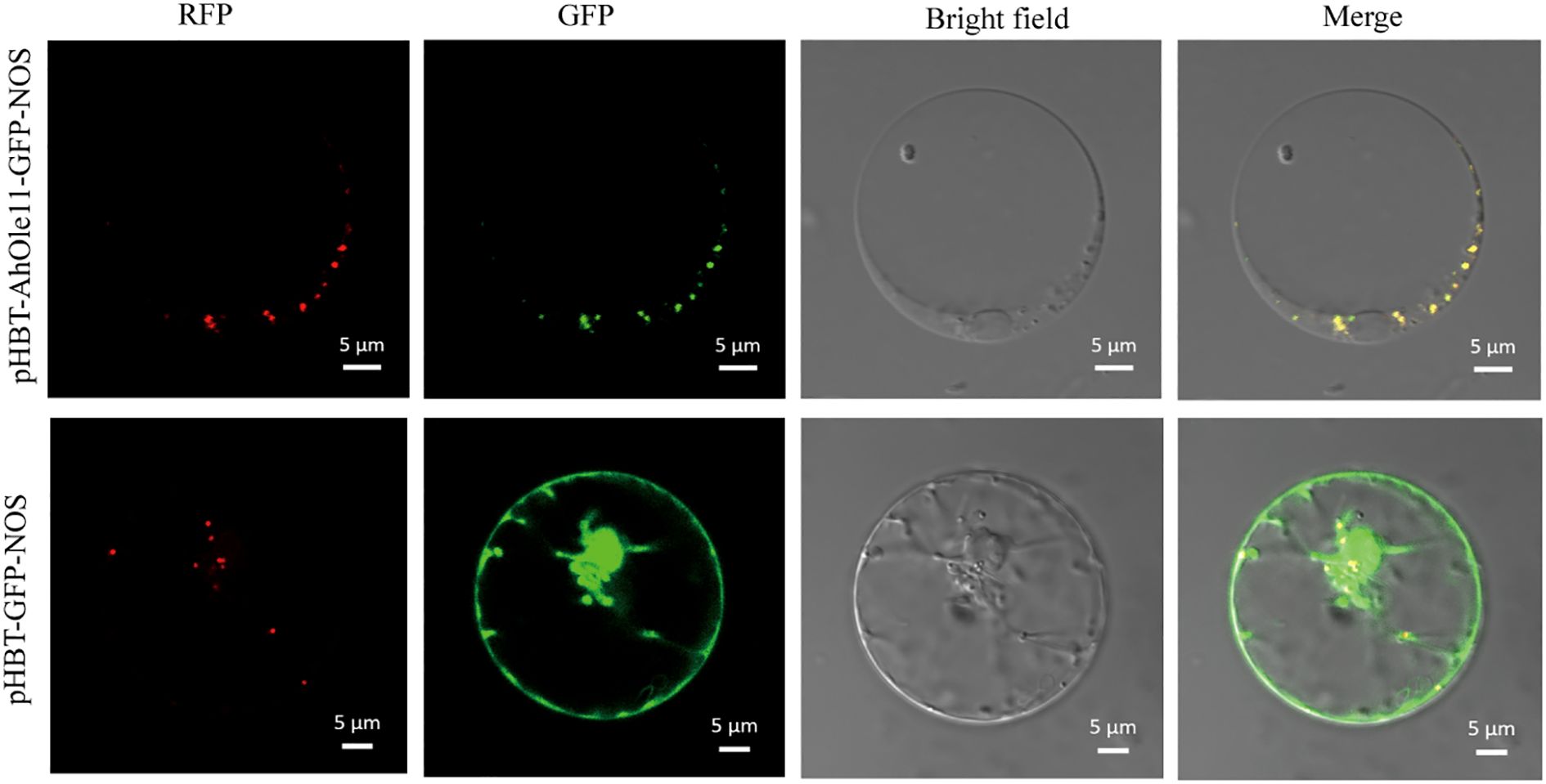
Figure 6. Subcellular localization of AhOle11 in Arabidopsis protoplast cell. pHBT-GFP-NOS was used as a control, RFP was an oil body marker, Bar= 5µm.
3.6 Overexpression of AhOle11 in Arabidopsis
To further confirm the function of AhOle11 in plants, the AhOle11 gene was overexpressed in the Arabidopsis. A total of ten AhOle11-overexpressing lines were obtained. The oil content and fatty acid composition of DsRed positive seeds from three homozygous T3 lines (OX-1, OX-7, and OX-8) were determined by gas chromatography. The oil contents in Arabidopsis WT seeds varied between 31.2% and 32.9%, whereas the oil content in AhOle11-overexpressing lines ranged from 33.7% to 40.8% (Figure 7A). The oil contents in seeds of AhOle11-overexpressing lines were significantly higher than that in WT seeds. Among the overexpressing lines, the OX-8 line exhibited the highest oil content (38.4%~40.8%), which represents a 22.4% increase compared to the control (Figure 7A). Then the oil bodies in seeds of WT and overexpressing lines were analyzed. Compared to WT, a significant higher oil body density was observed in the overexpressing lines, whereas no significant difference in oil body size was observed between them (Figure 7D). The result visibly illustrated that AhOle11-overexpressing lines contained higher level of oil accumulation in seed more than WT.
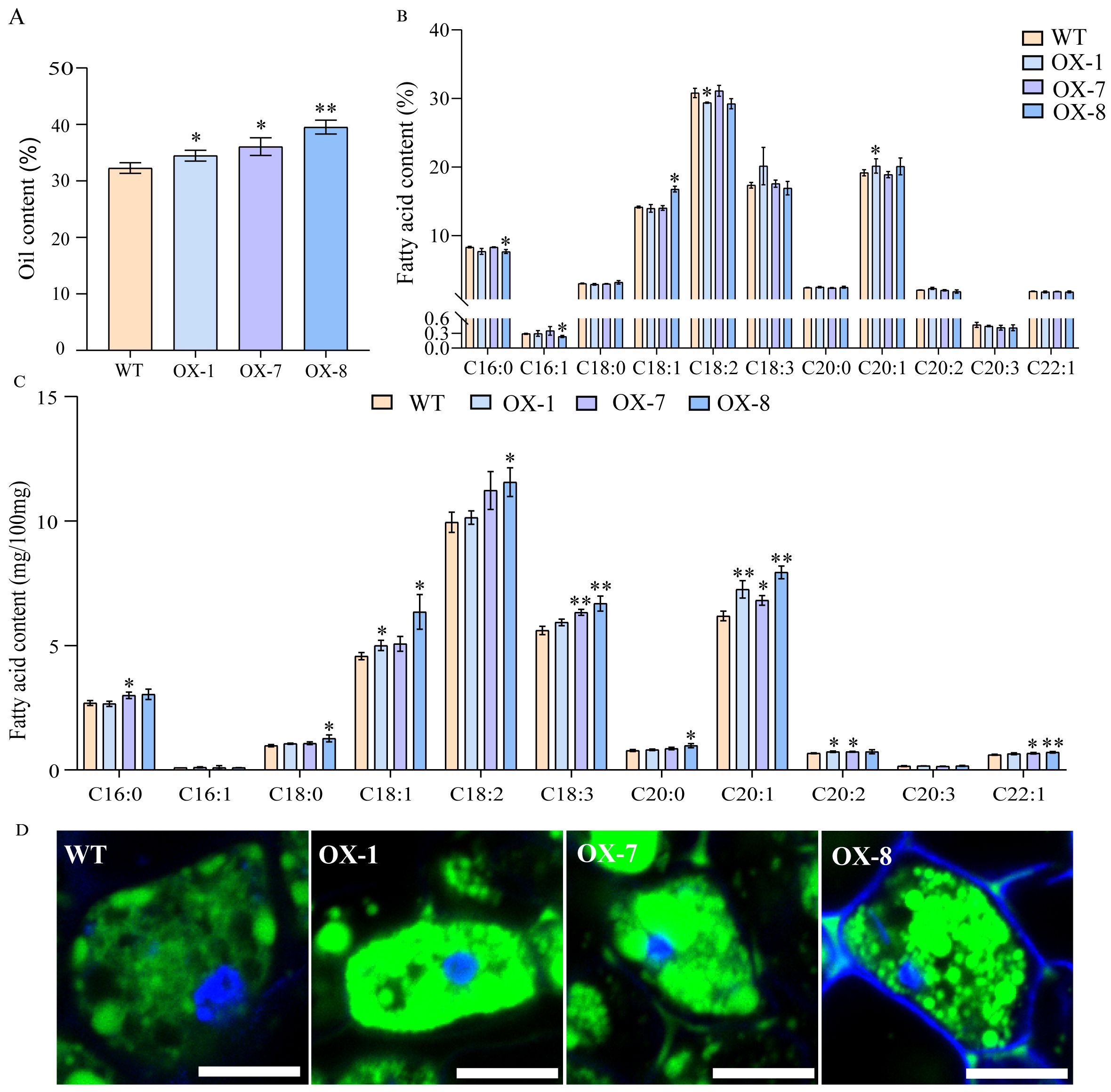
Figure 7. The oil contents and fatty acid compositions in Arabidopsis seeds harvested from wild-type and AhOle11-overexpressing lines. (A) Oil content in transgenic seeds and the wild type (WT). (B) Relative contents of fatty acids transgenic seeds and the WT. C16:0, palmitic acid; C16:1, palmitoleic acid; C18:0, stearic acid; C18:1, oleic acid; C18:2, linoleic acid; C18:3, linolenic acid; C20:0, arachidic acid; C20:1, eicosenoic acid; C20:2, eicosadienoic acid; C20:3, eicosatrienoic acid; C22:1, erucic acid. (C) Absolute contents of fatty acids transgenic seeds and the WT. (D) The oil body stained with bodipy. The green was oil body, Bar=10µm. The asterisks indicate significant differences between WT and Overexpression line according to Student’s t-test, * and ** mean significant correlation at the 0.05 and 0.01 probability levels, respectively.
In addition, the absolute quantification of fatty acid levels was examined in lines overexpressing AhOle11. Compared to WT, significant increases in fatty acid contents were observed in the following: C18:1, C20:1 and C20:2 in OX-1; C16:0, C18:3, C20:1, C20:2 and C22:1 in OX-7; as well as C18:0, C18:1, C18:2, C18:3, C20:0, C20:1 and C22:1 in OX-8 (Figure 7C). In terms of the relative fatty acid compositions, the contents of C20:1 in OX-1 and C18:1 in OX-8 were significantly elevated, while the contents of C18:2 in OX-1 and C16:0 as well as C16:1 in OX-8 were significantly reduced (Figure 7B). In summary, overexpression of AhOle11 led to a significant increase in total fatty acid production, while the overall fatty acid composition remained largely consistent.
4 Discussion
Oleosin proteins are proposed to function as stabilizers that maintaining the integrity of oil bodies, preventing their aggregation and fusion (Tzen and Huang, 1992). They play critical roles in energy provision during seed development and germination. In this study, a total of 12 AhOle genes were identified in peanut, an important oil crop with global significance (Table 1). The oleosin gene family has been identified in Arabidopsis, rapeseed, cotton and sorghum, comprising 17, 48, 25 and 3 members in their respective genomes (Kim et al., 2002; Chen et al., 2019; Ojha et al., 2021; Yuan et al., 2021). Six and seven oleosin genes were identified in A. duranensis (AA genome) and A. ipaensis (BB genome), respectively, which are the ancestral species of cultivated peanut (AABB genome) (Jiang et al., 2023). The number of oleosin genes in cultivated peanut was nearly equivalent to the combined total of oleosin genes in its two ancestral peanut species. Gene duplication and gene loss were also observed in the oleosin gene family. The syntenic genes for AdOle1 and AdOle5 in A. duranensis and AiOle3 and AiOle6 in A. ipaensis were not found in cultivated peanut (Figure 3C). AdOle genes always appear in pairs with AiOle genes, and nearly all of these homologous AdOle or AiOle genes maintained a syntenic relationship with AhOle genes (Figure 3C). A tandem duplication event was observed, as evidenced by the homologous gene pairs AhOle8 and AhOle9 being located on the same chromosome (Figure 3B).
The common structural features of oleosin proteins, characterized by the conserved oleosin domain (PF01277), which is proposed to consist of β-strand structure and to interact with lipids (Huang, 1996; Umate, 2012). All the identified AhOles contained this conserved oleosin domain (Figure 1B), supporting that the genes identified in this study are members of the oleosin gene family. The molecular weight of AhOles ranged from 14.3 to 22.0 kDa (Table 1), consistent with the previously reported range of 15 to 26 kDa in other plants (Hsieh and Huang, 2004). The PI value of AhOles ranged from 4.02 to 10.08 (Table 1), aligning with the values observed for oleosin members in cotton, Theaceae, and wild peanuts (Yuan et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2023). Gene structure analysis showed that AhOle genes contain a single exon without any intron, which is in agreement with previously reported findings (Huang and Huang, 2015). It has been hypothesized that the oil body proteins may have acquired introns during early embryonic evolution, but subsequently lost them over time (Liu et al., 2012).
The phylogeny of the oleosin gene family in land plants has revealed that oleosin genes could be classified into six lineages: M, P, T, U, SL and SH (Huang, 2017). P oleosins have been identified in liverworts, mosses, ferns and gymnosperms, while M oleosins have been discovered exclusively in Lauraceae and T oleosins solely in Brassicaceae. U oleosins are ubiquitously present in all land plants, including Selaginella moellendorffii. SL oleosins are found in seeds of both gymnosperms and angiosperms, while SH oleosins predominantly found in seeds of angiosperms (Kim et al., 2002; Fang et al., 2014; Huang and Huang, 2015). In this study, the AhOle genes were divided into three lineages: U, SL, and SH (Figure 3A). No T oleosin was identified in peanut, which is specifically expressed in pollens during chorionic formation and pollen development (Kim et al., 2002). AhOle2 and AhOle4 were grouped into the U lineage, while AhOle5 and AhOle12 were grouped into the SL lineage. Eight AhOles were grouped into the SH lineage, including AhOle1, AhOle3, AhOle6, AhOle7, AhOle8, AhOle9, AhOle10 and AhOle11 (Figure 3A). The expression pattern of U, SL and SH oleosins in Oryza sativa and Zea mays showed that SH and SL oleosins mainly expressed in developing seeds, whereas U oleosins expressed across different tissues with lower expression level (Huang and Huang, 2015). Notably, both AhOle2 and AhOle4, which belong to the U lineage, were expressed across all tissues, but AhOle4 exhibited higher expression level (Figure 4). Apart from AhOle8 and AhOle9, the remaining AhOle genes, which belong to SL and SH lineages, were predominantly expressed in developing seeds (Figure 4). The expression of AhOle8 and AhOle9, which also belong to the SH lineage, were not detected in any of the examined tissues (Figure 4). The SL and SH oleosins have been reported to regulate both the size of oil bodies and the oil content in seeds (Chen et al., 2019; Yuan et al., 2021). Therefore, the SH oleosin gene AhOle11, which demonstrated the highest expression level during seed development, was selected for function analysis.
Previous studies have demonstrated that oleosin genes are involved in plant stress response by modulating oil body size and number in accordance with metabolic demands. For instance, in comparison to WT, both the Arabidopsis Atole1 mutant and the Atole1/Atole2 double mutant exhibited a substantially reduced germination rate when subjected to freezing treatment at -30°C (Shimada et al., 2008). When SbOle1, SbOle2, and SbOle3 were expressed in Atole1 mutant, the seed germination rate was restored to the WT level (Ojha et al., 2021). It suggests that oleosins can enhance freezing tolerance in seeds and promote seed germination. Furthermore, it is widely acknowledged that plant hormones play a critical role in regulating plant adaptation to stress. Specifically, the expression levels of oleosins were observed to increase 6~10 folds after treated with ABA, MeJA, and JA treatment in rapeseed and soybean (Hays et al., 1999; Guo et al., 2021). Hence, the expression levels of AhOle genes in response to plant stress and phytohormones were investigated. In this study, an analysis of the AhOle promoter regions revealed a diverse array of cis-elements associated with stress response, phytohormone regulation and plant development. These elements include motifs responsive to ABA (ABRE, AAGAA-motif), JA (TGACG-motif, CGTCA-motif), SA (TCA-element), low temperature (LTR, CCGAAA) and drought (MYB, TAACTG) (Figure 5A). Meanwhile, transcriptome analysis of peanut leaves treated with drought, low temperature and plant hormones revealed that the expression of AhOle genes were regulated by these conditions. For example, AhOle5, AhOle10, and AhOle11 were significantly up-regulated in response to paclobutrazol (a GA inhibitor), SA and low-temperature treatments, while AhOle8 and AhOle9 were significantly down-regulated under low-temperature and drought conditions (Figure 5B). These findings suggest that AhOle genes play an important role in plant stress responses.
Oleosins have been reported to regulate the seed oil content in Arabidopsis, rapeseed and castor (Lu et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2019). The GmOle1 was identified as a regulatory factor for oil content through GWAS. Overexpression of GmOle1 resulted in a significant increase in the number of oil bodies, and led to a 10.6% increase in seed oil content (Zhang et al., 2019). Similarly, the overexpression of oleosin genes cloned form safflower, rapeseed and cotton in Arabidopsis also significantly elevated the seed oil content (Lu et al., 2018; Chen et al., 2019; Yuan et al., 2021). These reported oleosins were predominantly in the SH and SL lineages. In this study, the function of AhOle11 was analyzed, a member of SH lineage (Figure 3A). Subcellular localization analysis showed that AhOle11 was specifically located within the oil body, where oleosin proteins perform their functions (Figure 6). Overexpression AhOle11 in Arabidopsis resulted in a significant increase in seed oil content (Figure 7A), which aligns with the previously reported functions of SH oleosins from Arabidopsis, rapeseed and soybean (Chen et al., 2019; Yuan et al., 2021). Furthermore, oleosins have also been reported to modulate the fatty acid composition of seeds. In Arabidopsis oleosin knocking-out mutants, the C18:1 content decrease while the C20:1 content increased (Siloto et al., 2006). In Arabidopsis lines overexpressing BnOle, the C18:2 content increased while the C20:1 decreased (Chen et al., 2019). However, the changes in fatty acid composition observed in the three AhOle11-overexpressing lines in this study displayed distinct patterns. The contents of C20:1 in OX-1 and C18:1 in OX-8 were significantly elevated, while the contents of C18:2 in OX-1 and C16:0 as well as C16:1 in OX-8 were significantly reduced (Figure 7B). In addition, research has indicated that oleosins play a significant role in modulating the number and size of oil bodies. The size of oil bodies in rice ole16/ole18 double mutant becomes significantly larger and more irregular, which is consistent with the findings observed in Arabidopsis mutants ole2, ole3, ole4, as well as the double mutants ole1/ole2 and ole1/ole3 (Shimada et al., 2008; Wu et al., 2010). In the present study, overexpression AhOle11 led to a significant increase in oil body density, but without causing any substantial changes in oil body size dimensions (Figure 7D), a finding consistent with the effects observed for GmOle1 (Zhang et al., 2019). In conclusion, these results demonstrated that the overexpression of AhOle11 led to a significantly increase seed oil content and oil body density, indicating its potential to enhance oil accumulation in peanut seeds.
5 Conclusion
In this study, a total of 12 oleosin genes in peanut were identified in peanut genome. Base on phylogenetic analysis, these oleosin genes were divided into three lineages: U, SL, and SH. Apart from the AhOle8 and AhOle9 genes, the remaining AhOle genes were highly expressed during seed development. Most AhOle genes were found to be regulated by abiotic stresses and phytohormones, with corresponding cis-elements identified in their promoters. It suggested that AhOle genes play a critical role in peanut development and responses to abiotic stress. Furthermore, the SH oleosin gene AhOle11 was cloned and characterized, which demonstrated the highest expression level during in seed development. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that AhOle11 was specifically localized to oil bodies. Overexpression of the AhOle11 gene in Arabidopsis resulted in an increase in seed oil content and oil body density, with only minimal effects on fatty acid composition. Therefore, this study provides significant insights for future functional analyses of oleosin genes and present potential candidate genes to enhance oil content in peanut seeds.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
MH: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. JW: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. XX: Validation, Writing – review & editing. LH: Resources, Writing – review & editing. NL: Writing – review & editing, Validation. LY: Validation, Writing – review & editing. YC: Validation, Writing – review & editing. XW: Writing – review & editing, Validation. YK: Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Validation, Writing – review & editing. HJ: Writing – review & editing, Resources. BL: Writing – review & editing, Validation. YL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. DH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Key R&D Program of China (2023YFD1202800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (32472041), the Project of the Development for High-quality Seed Industry of Hubei Province (HBZY2023B003), Key Research and Development Program of Hubei Province (2021BBA077) and Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2024-2060299-089-031). The funders had no role in experiment design, data analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1623513/full#supplementary-material.
References
Bishi, S. K., Lokesh, K., Mahatma, M. K., Khatediya, N., Chauhan, S. M., and Misra, J. B. (2015). Quality traits of Indian peanut cultivars and their utility as nutritional and functional food. Food Chem. 167, 107–114. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.06.076
Cai, Y., Goodman, J. M., Pyc, M., Mullen, R. T., Dyer, J. M., and Chapman, K. D. (2015). Arabidopsis SEIPIN proteins modulate triacylglycerol accumulation and influence lipid droplet proliferation. Plant Cell. 27, 2616–2636. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00588
Chao, J. T., Li, Z. Y., Sun, Y. H., Aluko, O. O., Wu, X. R., Wang, Q., et al. (2021). MG2C: a user-friendly online tool for drawing genetic maps. Mol. Hortic. 1, 16. doi: 10.1186/s43897-021-00020-x
Chapman, K. D. and Ohlrogge, J. B. (2012). Compartmentation of triacylglycerol accumulation in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 2288–2294. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R111.290072
Chen, K., Yin, Y. T., Liu, S., Guo, Z. Y., Zhang, K., Liang, Y., et al. (2019). Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of oleosin genes in Brassica napus L. BMC Plant Biol. 19, 294. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1891-y
Deleu, M., Vaca-Medina, G., Fabre, J. F., Roïz, J., and Valentin, R. M. Z. (2010). Interfacial properties of oleosins and phospholipids from rapeseed for the stability of oil bodies in aqueous medium. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 80, 125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2010.05.036
Fang, Y., Zhu, R. L., and Mishler, B. D. (2014). Evolution of oleosin in land plants. PloS One 9, e103806. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103806
Finn, R. D., Clements, J., and Eddy, S. R. (2011). HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, W29–W37. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr367
Frandsen, G. I., Mundy, J., and Tzen, J. T. (2001). Oil bodies and their associated proteins, oleosin and caleosin. Physiol. Plant 112, 301–307. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-3054.2001.1120301.x
Guo, X. Y., Zhang, W. H., and Lin, F. (2021). Functional analysis of soybean oleosin gene GmOLE2. J. Nanjing Agric. Uni. 44, 477–486. doi: 10.7685/jnau.202008027
Hays, D. B., Wilen, R. W., Sheng, C. X. M., Maurice, M., and Pharis, R. P. (1999). Embryo-specific gene expression in microspore-derived embryos of brassica napus. an interaction between abscisic acid and jasmonic acid. Plant Physiol. 119, 1065–1072. doi: 10.1104/pp.119.3.1065
Higgins, D. G. and Sharp, P. M. (1988). CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene 73, 237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7
Hsieh, K. and Huang, A. H. C. (2004). Endoplasmic reticulum, oleosins, and oils in seeds and tapetum cells. Plant Physiol. 136, 3427–3434. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.051060
Hu, J. H., Chen, F., Zang, J. X., Li, Z., Wang, J., Wang, Z. R., et al. (2023). Native promoter-mediated transcriptional regulation of crucial oleosin protein OLE1 from Prunus sibirica for seed development and high oil accumulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 253, 126650. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126650
Hu, Z. Y., Wang, X. F., Zhan, G. M., Liu, G. H., Hua, W., and Wang, H. Z. (2009). Unusually large oilbodies are highly correlated with lower oil content in Brassica napus. Plant Cell Rep. 28, 541–549. doi: 10.1007/s00299-008-0654-2
Huai, D. X., Xue, X. M., Li, Y., Wang, P., Li, J. G., Yan, L. Y., et al. (2020). Genome-wide identification of peanut KCS genes reveals that ahKCS1 and ahKCS28 are involved in regulating VLCFA contents in seeds. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 406. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00406
Huai, D. X., Wu, J., Xue, X. M., Hu, M. L., Zhi, C. Y., Pandey, M. K., et al. (2023). Red fluorescence protein (DsRed2) promotes the screening efficiency in peanut genetic transformation. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1123644. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1123644
Huai, D. X., Zhang, Y. Y., Zhang, C. Y., Cahoon, E. B., and Zhou, Y. M. (2018). Substrate specificities of fatty acid elongae BnaA.FAE1 and BnaC.FAE1 from rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 40, 624–632. doi: 10.7505/j.issn.1007-9084.2018.05.003
Huang, A. H. C. (1994). Structure of plant seed oil bodies. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 4, 493–498. doi: 10.1016/S0959-440X(94)90210-0
Huang, A. H. C. (1996). Oleosins and oil bodies in seeds and other organs. Plant Physiol. 110, 1055–1061. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.4.1055
Huang, A. H. C. (2017). Plant lipid droplets and their associated proteins: potential for rapid advances. Plant Physiol. 176, 1894–1918. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.01677
Huang, M. and Huang, A. H. C. (2015). Bioinformatics reveal five lineages of oleosins and the mechanism of lineage evolution related to structure/function from green algae to seed plants. Plant Physiol. 169, 453–470. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.00634
Huang, M. D. and Huang, A. H. (2016). Subcellular lipid droplets in vanilla leaf epidermis and avocado mesocarp are coated with oleosins of distinct phylogenic lineages. Plant Physiol. 171, 1867–1878. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00322
Jiang, H. H., Wen, S. H., Lu, Y. T., Chen, G., and Wang, T. (2023). Genome-wide analysis and stress-responsive expression profiling of the oleosin gene family in diploid wild species arachis duranensis and arachis ipaensis. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 47, 94–104. doi: 10.19802/j.issn.1007-9084.2023050
Kim, H. U., Hsieh, K., Ratnayake, C., and Huang, A. H. C. (2002). A novel group of oleosins is present inside the pollen of Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 22677–22684. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109298200
Krzywinski, M., Schein, J., Birol, I., Connors, J., Gascoyne, R., Horsman, D., et al. (2009). Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 19, 1639–1645. doi: 10.1101/gr.092759.109
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., and Tamura, K. (2018). MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 35, 1547–1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096
Liu, W. X., Liu, H. L., and Qu, L. Q. (2013). Embryo-specific expression of soybean oleosin altered oil body morphogenesis and increased lipid content in transgenic rice seeds. Theor. Appl. Genet. 126, 2289–2297. doi: 10.1007/s00122-013-2135-4
Liu, Q., Sun, Y. P., Su, W., Yang, J., Liu, X. M., Wang, Y. F., et al. (2012). Species-specific size expansion and molecular evolution of the oleosins in angiosperms. Gene 509, 247–257. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.08.014
Lu, Y. B., Chi, M. H., Li, L. X., Li, H. Y., Noman, M., Yang, Y., et al. (2018). Genome wide identification, expression profiling, and functional validation of oleosin Gene family in Carthamus tinctorius L. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 1393. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01393
Manan, S., Chen, B., She, G., Wan, X., and Zhao, J. (2017). Transport and transcriptional regulation of oil production in plants. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 37, 641–655. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2016.1212185
Ojha, R., Kaur, S., Sinha, K., Chawla, K., Kaur, S., Jadhav, H., et al. (2021). Characterization of oleosin genes from forage sorghum in Arabidopsis and yeast reveals their role in storage lipid stability. Planta. 254, 97. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03744-8
Shao, Q., Liu, X. F., Su, T., Ma, C. L., and Wang, P. P. (2019). New insights into the role of seed oil body proteins in metabolism and plant development. Front. Plant Sci. 10, 1568. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.01568
Shasidhar, Y., Vishwakarma, M. K., Pandey, M. K., Janila, P., Variath, M. T., Manohar, S. S., et al. (2017). Molecular mapping of oil content and fatty acids using dense genetic maps in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 8, 794. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00794
Shimada, T. L. and Hara-Nishimura, I. (2015). Leaf oil bodies are subcellular factories producing antifungal oxylipins. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 25, 145–150. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2015.05.019
Shimada, T. L., Shimada, T., Takahashi, H., Fukao, Y., and Hara-Nishimura, I. (2008). A novel role for oleosins in freezing tolerance of oilseeds in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 55, 798–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03553.x
Siloto, R. M. P., Findlay, K., Lopez-Villalobos, A., Yeung, E. C., Nykiforuk, C. L., and Moloney, M. M. (2006). The accumulation of oleosins determines the size of seed oilbodies in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 18, 1961–1974. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.041269
Tzen, J. T. and Huang, A. H. C. (1992). Surface structure and properties of plant seed oil bodies. J. Cell Biol. 117, 327–335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.2.327
Umate, P. (2012). Comparative genomics of the lipid-body- membrane proteins oleosin, caleosin and steroleosin in magnoliophyte, lycophyte and bryophyte. Genom Proteom Bioinf. 10, 345–353. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2012.08.006
Wu, Y. Y., Chou, Y. R., Wang, C. S., Tseng, T. H., Chen, L. J., and Tzen, J. T. (2010). Different effects on triacylglycerol packaging to oil bodies in transgenic rice seeds by specifically eliminating one of their two oleosin isoforms. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 48, 81–89. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.12.004
Yoo, S. D., Cho, Y. H., and Sheen, J. (2007). Arabidopsis mesophyll protoplasts: a versatile cell system for transient gene expression analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2, 1565–1572. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.199
Yuan, Y. C., Cao, X. Z., Zhang, H. J., Liu, C. Y., Zhang, Y. X., Song, X. L., et al. (2021). Genome wide identification and analysis of oleosin gene family in four cotton species and its involvement in oil accumulation and germination. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 569. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03358-y
Zhang, W., Xiong, T., Ye, F., Chen, J. H., Chen, Y. R., Cao, J. J., et al. (2023). The lineage specific evolution of the oleosin family in Theaceae. Gene. 868, 147385. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147385
Zhang, D., Zhang, H. Y., Hu, Z. B., Chu, S. S., Yu, K. Y., Lv, L. L., et al. (2019). Artificial selection on GmOLEO1 contributes to the increase in seed oil during soybean domestication. PloS Genet. 15, e1008267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008267
Zhao, H. Q., Wang, X. F., and Gao, S. P. (2022). Progress on the functional role of oleosin gene family in plants. Hereditas. 44, 1128–1140. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.22-149
Keywords: peanut, oil-body-membrane protein, oleosin, fatty acid, oil content
Citation: Hu M, Wu J, Xue X, Huang L, Liu N, Yan L, Chen Y, Wang X, Kang Y, Wang Z, Jiang H, Liao B, Lei Y and Huai D (2025) Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of oleosin genes in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front. Plant Sci. 16:1623513. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1623513
Received: 07 May 2025; Accepted: 15 July 2025;
Published: 06 August 2025.
Edited by:
Chuyu Ye, Zhejiang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Sehrish Manan, Jiangsu University, ChinaRiddhi Rajyaguru, ICAR-Indian Institute of Groundnut Research, India
Copyright © 2025 Hu, Wu, Xue, Huang, Liu, Yan, Chen, Wang, Kang, Wang, Jiang, Liao, Lei and Huai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dongxin Huai, ZHhodWFpQGNhYXMuY24=; Yong Lei, bGVpeW9uZ0BjYWFzLmNu
 Meiling Hu
Meiling Hu Jie Wu
Jie Wu Li Huang
Li Huang Liying Yan
Liying Yan Yuning Chen
Yuning Chen Xin Wang
Xin Wang Huifang Jiang
Huifang Jiang Boshou Liao
Boshou Liao Yong Lei
Yong Lei Dongxin Huai
Dongxin Huai