- 1School of Breeding and Multiplication (Sanya Institute of Breeding and Multiplication), Hainan University, Sanya, China
- 2School of Tropical Agriculture and Forestry, Hainan University, Haikou, Hainan, China
- 3College of Biological Science and Engineering, North Minzu University, Yinchuan, China
- 4National Wolfberry Engineering Research Center, Wolfberry Science Research Institute, Ningxia Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Yinchuan, China
- 5Agricultural Biotechnology Centre, Ningxia Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Yinchuan, China
Flavonoids, a group of major bioactive ingredients, contribute to the nutritional and medicinal properties of wolfberry (Lycium barbarum). APETALA2/Ethylene response factors (AP2/ERFs) are widely distributed in plants and play crucial roles in regulating growth, development, and stress responses. However, the knowledge of AP2/ERF genes in wolfberry remains limited, and specific AP2/ERF family members involved in flavonoid biosynthesis have not been identified. Here, we systematically identified and characterized AP2/ERF proteins in wolfberry and identified key AP2/ERF family members involved in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis. LbAP2/ERF genes were identified via BLASTP and HMM analysis, using Arabidopsis AP2/ERF as queries and the L. barbarum genome. Gene duplication was analyzed with DupGen_finder, fruit RNA-seq was tested to determine expression profiles across five developmental stages, and LbAP2/ERF089 function was verified using transient overexpression and dual-luciferase assays. A total of 148 genes belonging to the L. barbarum AP2/ERF (LbAP2/ERF) family were identified, with dispersed duplication likely being the primary driver of their amplification. The LbAP2/ERF genes exhibit distinct expression profiles during different stages of fruit development, indicating their potential importance in wolfberry fruit development. Based on the metabolite and gene network analysis, a series of LbAP2/ERF genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis were identified, including LbAP2/ERF089, LbAP2/ERF011, LbAP2/ERF068, and LbAP2/ERF099. Functional analysis further revealed that LbAP2/ERF089 positively regulates flavonoid synthesis by activating the expression of biosynthetic genes LbLAR and LbDFR. Overall, our results provide new insights into the transcriptional regulation of flavonoid and anthocyanin biosynthesis and offer valuable genetic resources for enhancing the nutritional and medicinal value of wolfberry.
1 Introduction
Wolfberry, belonging to the genus Lycium within the Solanaceae family, plays a pivotal role as a valuable medicinal and edible resource in China. It is mainly distributed in the northwestern regions of China and certain areas in the Mediterranean Basin. The cultivation and trade of wolfberry fruits have generated substantial economic benefits for these regions (Amagase and Farnsworth, 2011; Jin et al., 2013). Research has demonstrated that wolfberry fruits are abundant in flavonoids such as rutin, quercetin, kaempferol, and myricetin (Miean and Mohamed, 2001; Bondia-Pons et al., 2014). These compounds possess a wide range of beneficial biological activities, including antioxidant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antiviral, anti-tumor, and neuroprotective effects (Amagase et al., 2009a, 2009; Jiang, 2014). Thus, the significant accumulation of flavonoids is often considered a defining characteristic of high-quality wolfberry fruits (Wang et al., 2018).
Flavonoids, including anthocyanins, are biosynthesized through the phenylpropanoid pathway (Sainz et al., 1997; Winkel-Shirley, 2001; Zhong et al., 2020). Phenylpropanoid metabolism initiates with the deamination of phenylalanine catalyzed by phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), generating trans-cinnamic acid. This intermediate is subsequently converted by cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) and 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase (4CL) to form p-coumaroyl-CoA. p-Coumaroyl-CoA condenses with three malonyl-CoA molecules catalyzed by chalcone synthase (CHS) and chalcone isomerase (CHI), followed by subsequent reduction and hydroxylation reactions to generate various flavonoids (Liu et al., 2019a; Shan et al., 2020). Most enzymes in flavonoid biosynthesis are encoded by a single gene in Arabidopsis, while in poplar, grape, and apple, these enzymes are encoded by multiple genes, though their functions remain mostly conserved (Sparvoli et al., 1994; Kim et al., 2003; Tsai et al., 2006). Similarly, the identified structural genes PAL, flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase (F3′H), leucoanthocyanidin reductase (LAR), and anthocyanidin reductase (ANR) in wolfberry that encode enzymes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis demonstrate functional conservation within the pathway (Zeng et al., 2014). As well as structural genes, various transcription factors such as MYB, bHLH, WD40, WRKY, and AP2/ERF are involved in the regulation of plant flavonoid biosynthesis (Zhao et al., 2021a; Gao et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). The transcription factors MYB11, MYB12, and MYB111, which belong to subgroup 7 of the R2R3-MYB family, have been reported to regulate flavonol biosynthesis (Stracke et al., 2007, 2009). VvWRKY26 regulates the hydroxylation steps of flavonoids in Vitis vinifera (Amato et al., 2017). The MdAP2–34 stimulates flavonoid accumulation via the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway by directly binding to and activating the MdF3′H promoter activity in Malus domestica (Han et al., 2022). In Lycium, LrMYB1, LrAN2, LrMYB113, and LrAN11 were shown to be potential regulators of flavonoid biosynthesis (Ye et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2020). Recently, LrMYB94 and LrWRKY32 were shown to collaboratively regulate the accumulation of quercetin-3-O-rutinoside and quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside in L. ruthencum by upregulating the expression of LrFLS, LrCHS, LrF3H, and LrCYP75B1 (Du et al., 2024).
The AP2/ERF transcription factor family is plant-specific and constitutes one of the largest transcription factor families in plants, with typically over 100 members in each species (Gao et al., 2020). Based on the number and type of conserved domains present, the AP2/ERF transcription factors can be divided into five subfamilies, including AP2 (APETALA2), RAV (Related to ABI3/VP1), DREB (Dehydration responsive element binding), ERF (Ethylene-responsive factor), and Soloist (Mizoi et al., 2012). The DREB and ERF subfamilies can be further subcategorized into six groups: clade B1-B6 and clade A1-A6 (Riechmann and Meyerowitz, 1998). These genes regulate various aspects of plant secondary metabolism, development, fruit ripening, and defense responses (Gao et al., 2020). For example, CitERF32, CitRAV1, and CitERF33 form a DREB-RAV transcription complex that enhances the accumulation of flavones and flavonols in citrus by interacting with the CitCHIL1 protein (Zhao et al., 2021a). The expression of LrAP2/ERF16 is associated with the accumulation of anthocyanins in Lycoris flower petals (Wang et al., 2023). In Solanum lycopersicum, the overexpression of SlERF.G3 activates the expression of SlFLS and early genes in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway, leading to increased flavonol accumulation in the fruit (Li et al., 2020b). Recent studies have shown that LbERF5.1 modulates carotenoid accumulation by interacting with LbCCD4.1 in Lycium (Zhao et al., 2023). However, the systematic identification and study of AP2/ERF genes in wolfberries are still lacking, and their involvement in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis in wolfberry fruit remains unclear.
In this study, we systematically identified and characterized 148 AP2/ERF proteins in wolfberry through phylogeny, gene structure, conserved domains, and gene duplication events. A series of potential genes involved in the flavonoid biosynthetic pathway were identified based on metabolite and gene network analyses. Further functional analysis revealed the role of a key AP2/ERF gene, LbAP2/ERF089, in regulating flavonoid and anthocyanin biosynthesis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant materials and treatment
The Ningqi No. 1 (NQ) and Ningxia Huangguo (NX) were grown at the National Wolfberry Germplasm Resource Nursery of the Ningxia Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences (38°38′N, 106°9′E, altitude 1100 meters). All the trees were 8 years old, planted with a row spacing of 2 meters and an individual spacing of 1 meter. During the peak fruiting period from June to July 2021, we sampled the fruits from three asexual plants of each variety at five developmental stages (S1-S5). After collecting the samples, all materials were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80 °C for RNA and metabolite extraction. Hydroponic seedlings of NQ were used for transient overexpression experiments.
2.2 Identification of AP2/ERF genes in wolfberry
The sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana AP2/ERF (AtAP2/ERF) proteins, retrieved from the Arabidopsis Information Resource (https://www.arabidopsis.org/), were used as queries for BLASTP searches to identify AP2/ERF family proteins, with the search restricted to entries having E-values < 1×10^-10. The genome sequence of L. barbarum was downloaded from the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) with accession number PRJNA640228 (Cao et al., 2021). The genome sequences of S. lycopersicum, P. inflata, Nicotiana tabacum, Capsicum annuum, Solanum melongena, and Solanum tuberosum were downloaded from the Solanaceae Genomics Network (https://solgenomics.net/). The genome sequences of Chromochloris zofingiensis, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Marchantia polymorpha, Physcomitrium patens, Ginkgo biloba, Zea mays, Sorghum bicolor, Hordeum vulgare, Oryza sativa, A. thaliana, Gossypium hirsutum, Phaseolus vulgaris, Cucumis melo, Carya illinoensis, Prunus persica, M. domestica, V. vinifera, Actinidia chinensis, and Coffea arabica were downloaded from the NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Concurrently, the AP2 domain (PF00847) from Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/) was utilized to construct a Hidden Markov Model (HMM), which was applied to screen protein datasets using HMMER3.0 (Wheeler and Eddy, 2013) under the same statistical threshold. Conserved AP2 domain validation was conducted across multiple databases, including SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/), CDD (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/cdd.shtml), and Pfam database (http://pfam.xfam.org/) to confirm their presence in candidate sequences. Protein sequences lacking the AP2 domain and redundant sequences were manually removed. Based on the deduced amino acid sequences of all AP2/ERF proteins, the ProtParam tool (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/) was used to predict their isoelectric point (pI) and molecular weight (MW). Subsequently, the online platforms ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/) and WoLF PSORT (https://wolfpsort.hgc.jp/) were used to predict the physicochemical properties and subcellular localization of the gene family, respectively.
2.3 Gene structure and conserved motif analysis
Conserved motif analysis of LbAP2/ERFs was performed using the MEME suite (https://meme-suite.org/meme/tools/meme), with parameters set as a maximum of 10 motifs and a minimum motif width of 6. A maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree was constructed using IQ-TREE (Minh et al., 2020), with the optimal substitution model VT+R6 selected via ModelFinder. Subsequently, TBtools (Chen et al., 2020) was employed to co-visualize gene structures, phylogenetic relationships, and conserved motif distributions, enabling integrated comparative analysis.
2.4 Gene duplication and evolutionary analysis
The full protein sequences of AP2/ERF from Arabidopsis and wolfberry were used for the phylogenetic tree construction. Multiple sequence alignment was performed using the ClustalW algorithm implemented in MEGA-X (Kumar et al., 2018), followed by ML tree inference with 1000 bootstrap replicates. OrthoFinder (Emms and Kelly, 2019) was employed to construct evolutionary relationships across 26 species, including C. zofingiensis, C. reinhardtii, M. polymorpha, P. patens, G. biloba, Z. mays, S. bicolor, H. vulgare, O. sativa, A. thaliana, G. hirsutum, P. vulgaris, C. melo, C. illinoensis, P. persica, M. domestica, V. vinifera, A. chinensis, C. arabica, P. inflata, N. tabacum, L. barbarum, C. annuum, S. melongena, S. tuberosum, and S. lycopersicum. Resulting trees were visualized using the ggplot2 package (Ito and Murphy, 2013) for visualization in the R statistical environment.
Inter-species and intra-species collinearity analysis was conducted with MCScanX (Wang et al., 2012), while Solanaceae-specific AP2/ERF phylogenetic trees were reconstructed using IQ-TREE2 (Minh et al., 2020) and visualized via iTOL (https://itol.embl.de/). Synonymous (Ks) and nonsynonymous (Ka) substitution rates for syntenic gene pairs were calculated using KaKs_calculator2.0 (Wang et al., 2010). Paralogous gene pairs derived from whole-genome duplication (WGD), tandem duplication (TD), proximal duplication (PD), transposed duplication (TRD), and dispersed duplication (DSD) were identified using the DupGen_finder pipeline (Qiao et al., 2019), with stringent filtering based on duplication event criteria.
2.5 LbAP2/ERF genes expression analysis
RNA-Seq data were obtained from previously published studies (Zhao et al., 2023), which included transcriptome profiles of both NQ and NX fruits at five developmental stages (S1-S5). The adapter sequences, low-quality reads (quality score < 15), and poly (A/T) tails were removed from raw reads using fastp (Chen et al., 2018) with default parameters except for setting the minimum length of reads to be retained as 30. The Hisat2 (Kim et al., 2015) software aligned clean reads to the reference genome using the default splice-junction database provided by the software and other default parameters. FeatureCounts software (Liao et al., 2014) estimated transcript abundances considering gene lengths and using the default counting mode. The Transcripts Per Million (TPM) measured the expression levels of the AP2/ERF genes. The expression patterns of each AP2/ERF gene in NQ and NX fruits across developmental stages were visualized as a heatmap using R software (https://www.r-project.org/).
2.6 Correlation and expression network analysis and WGCNA
Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) (Langfelder and Horvath, 2008) was applied to construct the co-expression network, using RNA-seq data from both NQ and NX fruits at five developmental stages (S1-S5) (Zhao et al., 2023). The co-expression association of all genes was extracted from RNA-Seq data in a non-targeted way, and the highly interconnected modules of co-expression genes were detected. Using the Hmisc package in R (Yadav and Roychoudhury, 2018), we calculated the correlation between the expression levels of AP2/ERF, structural genes involved in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis, and the content of flavonoid metabolites. We computed the Pearson correlation coefficients and significance p-values for these relationships. Utilize the pheatmap package in R (https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pheatmap/index.html) to generate a heatmap. Visualizing the interaction networks using Cytoscape v3.10.0 (Shannon et al., 2003).
2.7 Flavonoid metabolites analysis
Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass (UPLC-MS/MS)-Based Quantitative metabolomics and targeted metabolomics methods (Novogene, China) were used to construct metabolomics libraries from samples of NQ and NX. The detailed procedure for the detection and analysis of metabolites was described before (Zhao et al., 2024).
2.8 Overexpression LbAP2/ERF089 in wolfberry leaves
Total RNA was isolated from NQ leaves using a Takara RNA extraction kit, and single-stranded cDNA of LbAP2/ERF089 was synthesized with the Reverse Aid First-strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Based on wolfberry genome and transcriptome data, primers (Supplementary Table S1) were designed to amplify the CDS of LbAP2/ERF089 by Primer3 (Untergasser et al., 2012). PCR conditions were: pre-denaturation at 98°C for 3 min, followed by 30 cycles of 98°C denaturation for 10 s, 58°C annealing for 30 s, 68°C extension for 1 min, and a final extension at 68°C for 5 min. Purified amplicons were cloned into the expression vector pCambia1300-35S-GFP for Sanger sequencing. Transient overexpression in the wolfberry leaves was conducted following the protocols as described (Zhao et al., 2023). One-month-old hydroponically grown NQ seedlings were employed for transient overexpression assays. NQ seeds were surface-sterilized by soaking in pure water for ten minutes to remove impurities, followed by rinsing with 75% ethanol for 40 seconds, treating with 5% sodium hypochlorite for fifteen minutes, and finally washing with sterile water three times. The treated seeds were inoculated onto 1/2MS medium and cultured at 25°C under a 14h light/10h dark cycle with a light intensity of 4000 lx until the formation of two cotyledons. The seedlings were then transplanted into hydroponic tanks containing MS solution; the tanks were initially covered with plastic wrap (which was removed when the leaves touched it), and the seedlings were cultured until they reached one month of age. The pCambia1300-35S-LbAP2/ERF089-GFP vector and the empty vector were respectively transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101; the transformed Agrobacteria were subsequently suspended in an infection buffer consisting of 5 g/L D-glucose, 50 mM MES (pH 5.6), 2 mM Na3PO4·122O, and 0.1 mM acetosyringone. The bacterial suspension was adjusted to an OD600 of 1.0 and incubated at 20-25°C for 1–2 hours. A 1 mL syringe without a needle was used to inject the bacterial suspension into the abaxial surface of the 3rd-5th true leaves until a moist area appeared (Supplementary Figure S1). After infiltration, the plants were first cultured at 25°C in the dark for 12 hours, and then cultured at 25°C under a 14h light/10h dark cycle with a light intensity of 4000 lx for 72 hours. This generated LbAP2/ERF089-overexpressing plants, with pCambia1300-35S-GFP serving as the control. Samples were harvested for qRT-PCR and metabolome analyses, with at least 15 leaves selected for each biological replicate and a total of 3 replicates performed. Subsequently, the expression of LbAP2/ERF089 in overexpression plants was determined by quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The qRT-PCR primers used in this study were designed using Primer3 (Untergasser et al., 2012) (Supplementary Table S1). Using BIO-RAD CFX Connect™ Real-Time PCR System with L. barbarum Elongation factor 1 alpha (LbEF1a) as internal reference, qRT-PCR was performed according to our previous report (Zhao et al., 2021b), employing the 2-ΔΔCT method to calculate gene expression levels (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001). Additionally, metabolites in NQ leaves overexpressing LbAP2/ERF089 were quantified using UPLC-MS/MS-based metabolomics.
2.9 Transient transcription dual-luciferase assay
The 1000-bp upstream sequences of LbLAR and LbDFR were regarded as potential promoters. Genomic DNA from NQ leaves was extracted via the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide method. Primers (Supplementary Table S1) for amplifying these promoter sequences were designed using Primer3 (Untergasser et al., 2012), with PCR cloning conditions similar to those for LbAP2/ERF089. Promoters of LbLAR and LbDFR were amplified and cloned into the modified pH2GW7 vector (PJG094) containing the firefly luciferase (fLUC) gene and the Renilla luciferase gene (rLUC) as reporters, while the LbAP2/ERF089 cDNA was cloned into the PJF754 (pEAQ-HT-DEST2) vector as an effector. The plasmids were transferred into Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105 by electroporation and co-infiltrated into Nicotiana benthamiana leaves. The luciferase activities were measured using the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The relative reporter gene expression levels were expressed as the ratio of firefly LUC to Renilla luciferase (LUC/REN). Three independent transformations for each sample were performed.
2.10 Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were conducted using GraphPad Prism 8 software. Student’s t-test was used for pairwise comparisons (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
3 Results
3.1 Identification and phylogenetic analysis of LbAP2/ERF genes in wolfberry
A total of 148 high-confidence members of the AP2/ERF gene family were identified in the genome of L. barbarum through comprehensive analysis utilizing BLASTP and HMM. The LbAP2/ERF genes are distributed across all 12 chromosomes of wolfberry and are named according to their chromosomal positions, ranging from LbAP2/ERF001 to LbAP2/ERF148. These members display a wide range of amino acid lengths, varying from 126 to 1435 residues (Supplementary Tables S2, S3). To explore the phylogeny of LbAP2/ERF genes, a ML phylogenetic tree was constructed, including 148 LbAP2/ERF and 146 AtAP2/ERF proteins (Figure 1). Analysis showed LbAP2/ERFs, excluding RAV and Soloist, are distributed across AP2, ERF (B1-B6), and DREB (A1-A6) subfamilies, with ERF and DREB clearly categorized.
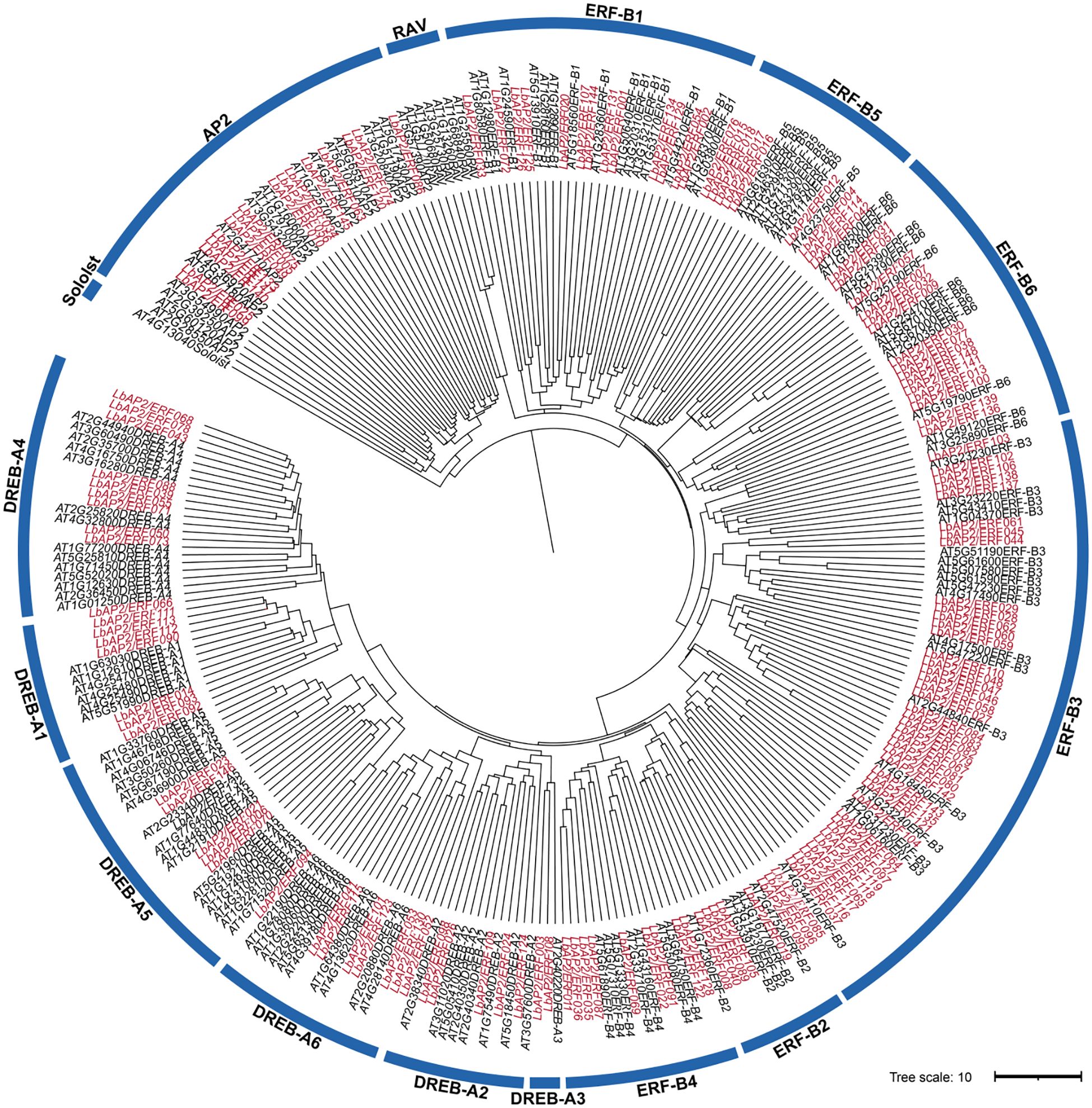
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis among AP2/ERF proteins of L. barbarum (NQ) and A. thaliana. The genes in L. barbarum are marked in red, while those in A. thaliana are marked in black.
3.2 Duplication and evolutionary analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family
To assess the evolutionary status of the AP2/ERF gene family in major plant lineages, a total of 4,650 AP2/ERF proteins identified in 26 plant species were used to construct a species tree. OrthoFinder showed that AP2/ERF genes were present in all selected species (Figures 2A, B). Two species of phycophyta, C. zofingiensis and C. reinhardtii, contain only eight and seven AP2/ERF proteins respectively. In contrast, seed plants have a much higher number of AP2/ERF proteins, with their counts far exceeding those in algal species. Among seed plants, monocotyledonous species such as O. sativa (124 proteins) and Z. mays (213 proteins, the highest number) displayed substantial variation. Dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants were distinctly clustered into different branches on the species tree. Notably, the number of AP2/ERF genes was not strongly correlated with species genome size, suggesting potentially distinct evolutionary processes for AP2/ERF genes across different species.
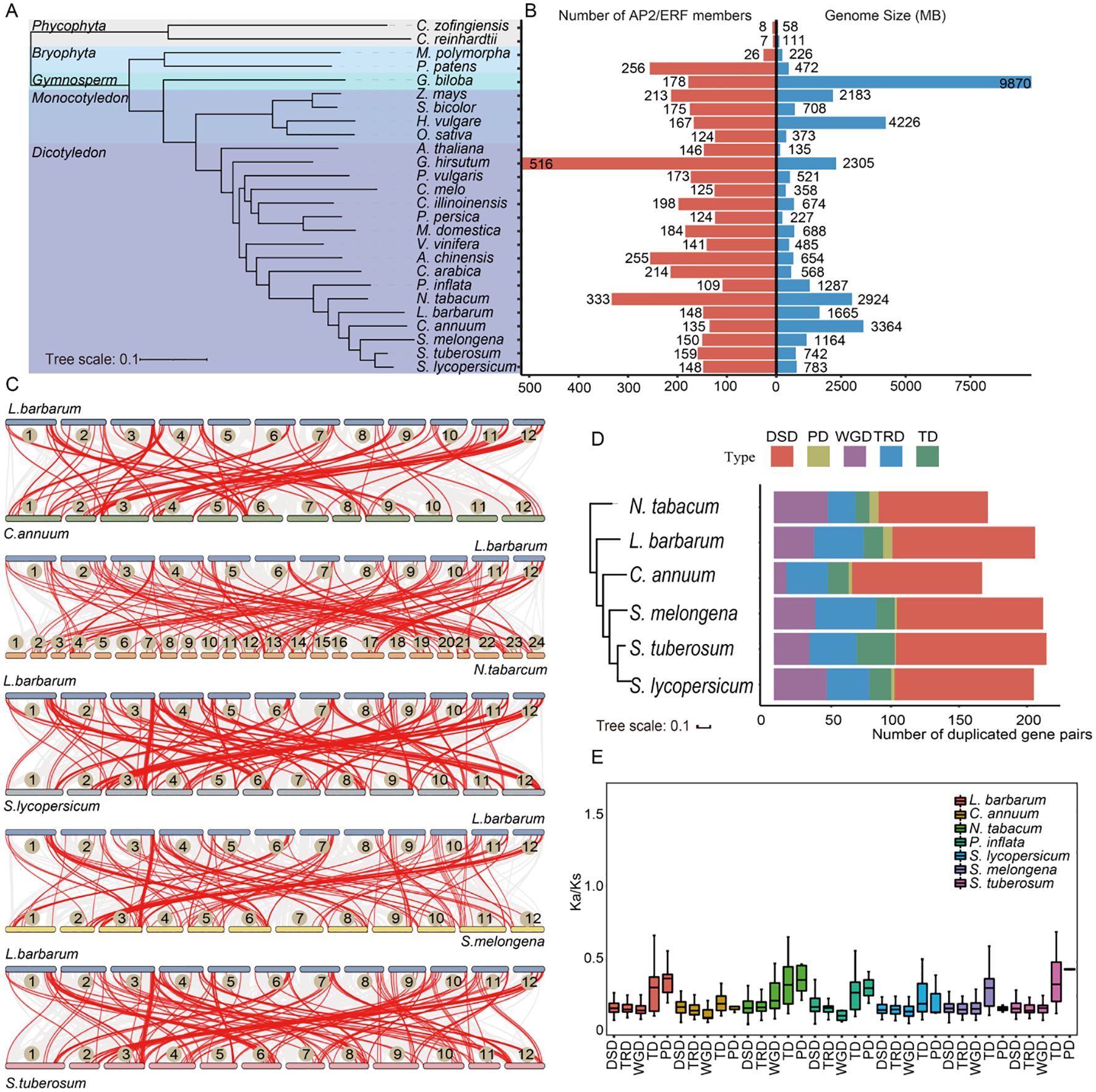
Figure 2. Evolutionary and gene duplication events analysis in multiple plants. (A) The species tree of the AP2/ERF family was constructed based on OrthoFinder. All selected plants were divided into five subgroups, distinguished by different colored branches. (B) The statistics of genome size and number of AP2/ERF family members for each species. (C) Synteny analyses of LbAP2/ERF genes between L. barbarum (NQ) and five other Solanaceae species. The gray lines in the background indicate the collinear block with wolfberry and other five plant species genomes, while red lines highlight syntenic AP2/ERF gene pairs. (D) The number of different modes of duplicated gene pairs in each species. The x-axis represents the number of duplicated gene pairs. The y-axis represents the species tree of Solanaceae species. (E) Ka/Ks ratios of Solanaceae species.
To further determine the evolutionary trajectory of the AP2/ERF gene family in Solanaceae species, an analysis of the evolution and duplication events of these genes was performed. In the L. barbarum genome, we identified 59 non-redundant AP2/ERF genes as paralogous genes, forming 35 paralogous gene pairs distributed across its 12 chromosomes, with no clustering observed in specific chromosomal regions (Supplementary Figure S2). L. barbarum and five other Solanaceae species genomes were compared to investigate the gene collinear relationship in Solanaceae species (Figure 2C, Supplementary Table S4). The results reveal that the genome of L. barbarum shares collinear relationships with that of C. annuum, N. tabacum, S. lycopersicum, S. melongena, and S. tuberosum, accounting for 119, 154, 180, 130, and 170 AP2/ERF collinear gene pairs, respectively. Each chromosome of the six Solanaceae species, except for the 11th chromosome of C. annuum, contains several genes that share collinear relationships with the LbAP2/ERFs in the L. barbarum, indicating that Solanaceae species exhibit a high degree of evolutionary conservation of putative AP2/ERFs.
Five gene duplication events were studied, revealing that among the 1,259 duplicated pairs in six Solanaceae species, DSD was the most prevalent mode, accounting for the maximum number of gene pairs, suggesting that the expansion of the AP2/ERF gene family was mainly associated with DSD. In contrast, only 25 PDs were identified in the AP2/ERF gene family (Figure 2D, Supplementary Table S5). For most AP2/ERF genes, the Ka/Ks was below 0.5, indicating strong purifying selection exerted on these genes (Figure 2E). In contrast, the gene pairs derived from PD and TD in L. barbarum had relatively higher Ka/Ks ratios compared with other types of duplicated gene pairs, suggesting that these specific gene pairs evolved at a higher rate than others.
3.3 Gene structure and conserved motif analysis of LbAP2/ERFs members
The conserved motifs of 148 LbAP2/ERF proteins were investigated using MEME software. Motif pattern analysis (Figures 3A, B) shows that each group features at least three distinct types of motifs. Notably, the AP2 subfamily, the DREB-A1 clade of the DREB subfamily, and the ERF-B3 clade of the ERF subfamily exhibit richly conserved motifs, exemplified by the intricate presence of five different types of motifs within LbAP2/ERF049. Additionally, a common trend of motif similarities can be observed across various groups. Gene structure analysis (Figure 3C) reveals that the LbAP2/ERF gene family consists of genes with varying numbers of exons, ranging from one to twenty-five. Subfamily AP2 displays diversity in exon composition, with genes in this subfamily have at least six exons. In contrast, DREB-A1 and DREB-A5 clades predominantly feature a streamlined exon structure, with most genes having a single exon, except for LbAP2/ERF111 and LbAP2/ERF070, which have two exons. Notably, ERF-B4 shows significant variability in exon number, ranging from just one exon in LbAP2/ERF069 to twenty-five exons in LbAP2/ERF011, making it the gene with the highest exon count in the entire gene pool. These results indicate that, with the exception of a few unique gene family members, genes within the same evolutionary branch exhibit similar conserved domains and intron distribution, suggesting a relative conservation of AP2/ERFs in L. barbarum.

Figure 3. Phylogenetic relationship, conserved domains and gene structure of LbAP2/ERFs in L. barbarum (NQ). (A) Phylogenetic tree of LbAP2/ERF proteins. (B) Motif composition of LbAP2/ERF proteins, with different colors representing ten different motifs. (C) Exon-intron structures of LbAP2/ERF genes. Blue boxes indicate exon regions, and black lines indicate introns.
3.4 Expression patterns analysis of LbAP2/ERF genes
Transcriptomic profiles of two wolfberry varieties, NQ and NX, were analyzed across five fruit developmental stages (S1–S5). Using a cutoff of |log2 (fold change) | ≥ 1 and adjusted p-value < 0.05, we identified 23,348 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the two cultivars. Among these, 44 LbAP2/ERF genes showed low expression across all five stages in both varieties, suggesting that these genes might not be the key regulators of fruit development. The expression patterns of the differentially expressed LbAP2/ERF genes were clustered into four main groups, labeled I to IV (Figure 4A). Genes from different subfamilies of LbAP2/ERF were distributed across these groups. Most of the LbAP2/ERF genes exhibited similar expression patterns in both varieties, suggesting that these genes may play similar biological roles in fruit development across different cultivars. However, the LbAP2/ERF genes in Group II showed significantly higher expression levels in NX, suggesting that these genes may be involved in the formation of cultivar-specific substances. Group II and I genes were predominantly expressed in the later stages (S4 to S5), while Group I and III genes exhibited higher expression in the early stages (S1 to S2).
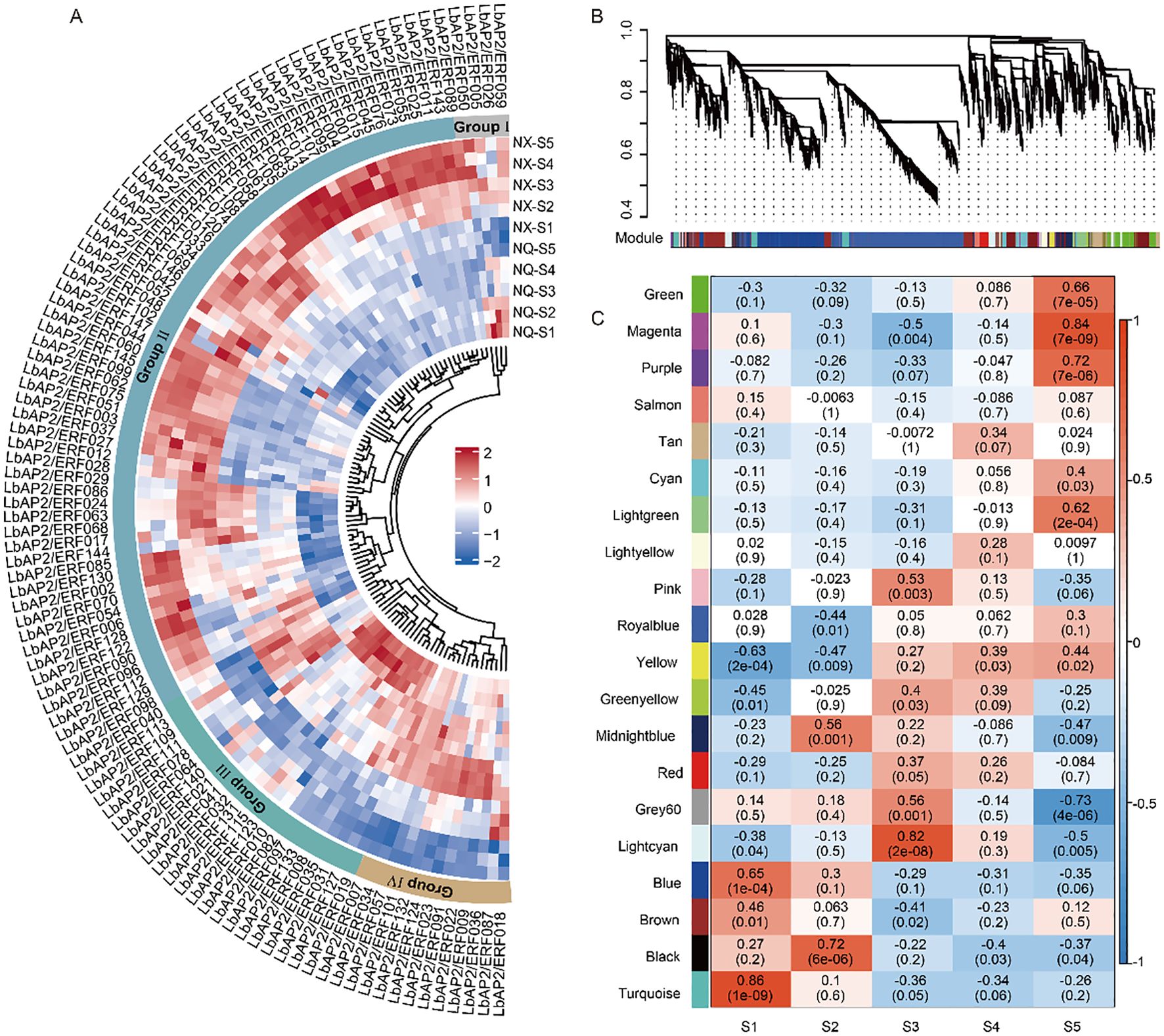
Figure 4. Expression analysis of LbAP2/ERF genes during wolfberry fruit development. (A) Heatmap of differentially expressed LbAP2/ERF genes in NQ and NX fruits at five developmental stages (S1-S5). Expression levels range from low (blue) to high (red). The central circular colors represent the clustering of LbAP2/ERF DEGs into Groups I (gray), II (light blue), III (light green), and I (light yellow). Scaled-TPM values were used to construct the heatmap based on hierarchical clustering analysis. (B, C) WGCNA of DEGs from NQ and NX fruits. (B) Hierarchical clustering tree showing 20 modules. Each leaf of the tree represents a DEG, and each major branch represents a module. (C) Correlation between modules and the fruit development process, with corresponding p-values in parentheses. The left color panel shows the modules, while the right color scale indicates the correlation between modules and the fruit development stage.
Weighted Gene Co-expression Network Analysis (WGCNA) based on 23,348 DEGs, which were assigned to 20 merged modules (Figures 4B, C; Supplementary Table S6). Eight modules, including green, magenta, purple, light green, light cyan, blue, black, and turquoise, showed significant correlations with fruit developmental stages (p < 0.001, correlation > 0.6). The blue, turquoise, black, and purple modules, with 37, 19, 3, and 1 AP2/ERF genes respectively, are rich in flavonoid-biosynthetic structural genes such as PAL, C4H, and F3’H. This suggests that these AP2/ERF genes in these modules may play a critical role in flavonoid synthesis during fruit development. In summary, LbAP2/ERF genes exhibit stage-specific expression patterns throughout fruit development and play crucial roles in regulating flavonoid synthesis and other aspects of fruit development.
3.5 Identification of AP/ERF genes involved in regulating flavonoid biosynthesis
Metabolomic analysis identified 180 differentially accumulated flavonoid metabolites (DAMs) in two wolfberry varieties, NQ and NX, at five developmental stages of fruit (fold change ≥ 2 or ≤ 0.5, VIP ≥ 1) (Supplementary Table S7). Within the WGCNA, a total of 34 LbAP2/ERF genes from the blue, black, purple, and turquoise modules exhibited significant correlations with various flavonoid metabolites. Notably, genes such as LbAP2/ERF089, LbAP2/ERF011, LbAP2/ERF068, and LbAP2/ERF099 showed strong associations, suggesting that these genes may play a crucial role in flavonoid synthesis during wolfberry fruit development (Supplementary Figure S3).
3.6 Functional analysis of LbAP2/ERF089 in flavonoid biosynthesis
Among the 34 AP2/ERF genes, we selected LbAP2/ERF089, which showed significant associations with multiple flavonoid synthesis genes and metabolites, to investigate its potential role in flavonoid biosynthesis (Figure 5A, Supplementary Table S6). An overexpression vector of LbAP2/ERF089 was constructed and transiently expressed in the leaves of L. barbarum. The accumulation of flavonoid metabolites, including quercitrin, aromadendrin-7-O-glucoside, 3’,5,5’,7-tetrahydroxyflavone, and twenty other flavonoid metabolites, was significantly higher in the plants overexpressing LbAP2/ERF089 compared to those with the empty vector (Figures 5B–E, Supplementary Table S8), indicating that overexpression of LbAP2/ERF089 promotes flavonoid accumulation.
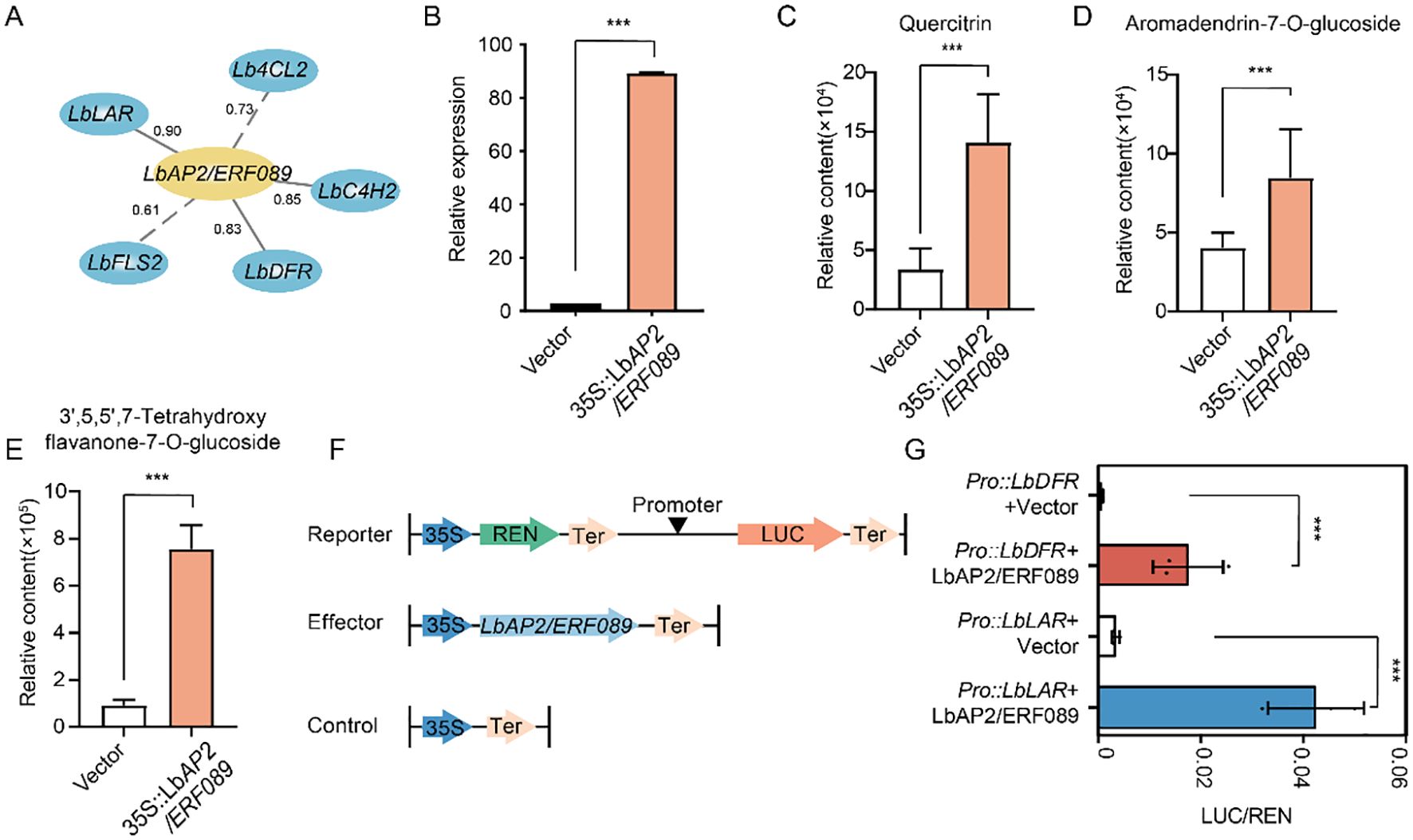
Figure 5. Functional analysis of LbAP2/ERF089 in flavonoid synthesis. (A) Correlation between LbAP2/ERF089 and structural genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis in NQ and NX fruits. The gray solid line indicates correlations above 0.8, while dashes represent correlations below 0.8. (B) Transcript levels of LbAP2/ERF089 in NQ leaves with transient overexpression. The relative expression levels of LbAP2/ERF089 were quantified by qRT-PCR. (C–E) Flavonoid accumulation profiles in NQ leaves after LbAP2/ERF089 transient expression. (C) Quercitrin, (D) Aromadendrin-7-O-glucoside, and (E) 3’,5,5’,7-Tetrahydroxyflavone content in the leaves of L. barbarum with transient expression of LbAP2/ERF089. (F) Schematic diagram of the effector and reporter plasmids used in the transient assay in leaf epidermal cells of N. benthamiana. REN, Renilla luciferase; LUC, firefly luciferase. (G) LbAP2/ERF089 activates the transcription of LbLAR and LbDFR (cloned from NQ). N. benthamiana leaves were infiltrated with different combinations of effectors and reporters. The LUC activity was normalized to the REN activity as an internal control. Student’s t-test was used for comparisons (***, p < 0.001).
To further confirm the results, we cotransfected the effector LbAP2/ERF089 (35S::LbAP2/ERF089) with the reporter containing the LbLAR, or LbDFR promoter driving luciferase (ProLbLAR::LUC, or ProLbDFR::LUC) in leaf epidermal cells of N. benthamiana, and the relative luciferase (LUC) activity was measured (Figure 5F). The results showed that co-expression with LbAP2/ERF089 (35S::LbAP2/ERF089) significantly increased the luciferase activity of ProLbLAR::LUC and ProLbDFR::LUC (Figure 5G), indicating that LbAP2/ERF089 functions as a transcriptional activator of LbLAR and LbDFR expression, thereby enhancing flavonoid and anthocyanin synthesis.
4 Discussion
The AP2/ERF genes comprise a large family of TFs that have been identified in various plants such as Zingiber officinale (Xing et al., 2021), Rosa chinensis (Li et al., 2020a), and Fagopyrum tataricum (Liu et al., 2019b). This study identified 148 potential AP2/ERF genes in L. barbarum based on published genome data. The number of AP2/ERF transcription factors and their subfamily members varies among plant species, with ERF and DREB classes representing more than 50% of the AP2/ERF transcription factors (Wu et al., 2015; Liu et al., 2023). In contrast, the number of Soloist-like AP2/ERF transcription factors is minimal, with most plant species possessing only one or none, as observed in Arabidopsis (Sakuma et al., 2002; Nakano et al., 2006). Similarly, the Soloist subfamily is absent in the AP2/ERF family of L. barbarum, and it is noteworthy that the RAV subfamily is also missing, indicating that this group has evolved or been lost in L. barbarum during evolution.
Gene duplication is a major source of new genes in evolution (Rezaee et al., 2020; Faraji et al., 2021). In the genome of L. barbarum, WGD events are the primary cause of gene family expansion (Cao et al., 2021). In most plants, WGD or SD plays a dominant role in the expansion of the AP2/ERF gene family, as evidenced by studies in pear (Li et al., 2018) and pumpkin (Li et al., 2022). We found that DSD may be the primary driver of LbAP2/ERF gene family’s amplification. This indicates that the AP2/ERF gene family in L. barbarum may exhibit a distinct evolutionary pattern.
The AP2/ERF family is a large class of transcription factors involved in various plant life processes (Ohme-Takagi and Shinshi, 1995), participating in both primary and secondary metabolism, such as artemisinin, flavonoid, and carotene metabolism (Zhao et al., 2019; Han et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023). The tissue-specific expression of AP2/ERF genes may influence the synthesis of secondary metabolites by regulating transcription processes (Shoji and Yuan, 2021). Consistent with previous studies, there are significant differences in the types and levels of flavonoid metabolites between NX and NQ (Du et al., 2024). We found that the expression of AP2/ERF genes belonging to Groups II reflects the specificity of varieties, indicating that these genes may be involved in regulating the synthesis of flavonoids in different varieties. Through integrated transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses, we identified 34 LbAP2/ERF genes associated with flavonoid metabolism. However, most of these genes are expressed at low levels during fruit development. Previous research has been confirmed that AP2/ERF genes are often rapidly and continuously induced under stress conditions, while their responses to other processes are relatively slower (Zhao et al., 2022). In addition, AP2/ERF genes play important roles in regulating the synthesis of flavonoid compounds (An et al., 2018; Yao et al., 2017; Ni et al., 2019, 2021; Mo et al., 2022). In this study, LbAP2/ERF089 was found to regulate flavonoid metabolism in wolfberries by interacting with LbLAR and LbDFR, consistent with previous research linking DFR and LAR to anthocyanin synthesis (Shan et al., 2020). Notably, overexpression of LbAP2/ERF089 also promoted accumulation of phenols and amino acids, with regulatory mechanisms needing further exploration.
In summary, we identified a total of 148 high-confidence AP2/ERF transcription factors in L. barbarum, including several key candidates implicated in flavonoid biosynthesis, such as LbAP2/ERF089, LbAP2/ERF068, and LbAP2/ERF099. Notably, LbAP2/ERF089 was functionally validated as a positive regulator of flavonoid accumulation in wolfberry. These findings establish a putative AP2/ERF-mediated regulatory network governing flavonoid metabolism in L. barbarum, providing a valuable genetic resource for future molecular breeding efforts aimed at enhancing flavonoid content.
5 Conclusion
In this study, we identified 148 LbAP2/ERF genes, with dispersed duplication serves as the primary driver of their amplification. Expression profiling of these genes during fruit development revealed distinct temporal expression patterns, indicating their diverse roles in wolfberry fruit biology. Additionally, several LbAP2/ERF genes involved in flavonoid biosynthesis were identified. Further research showed that LbAP2/ERF089 functions as a positive regulator of flavonoid biosynthesis. Taken together, our findings identify AP2/ERF transcription factors involved in regulating wolfberry flavonoid and anthocyanin biosynthesis and provide new insights into their roles in transcriptional regulatory mechanisms.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
RL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology. SX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QL: Data curation, Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing. CJ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. HL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YX: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YC: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Writing – review & editing. JZ: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was sponsored by the Key Research & Development Program of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (grant number 2022BBF01001 and 2021BEF02002), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 32060359, U23A20221), the Innovative Research Group Project of Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (grant number 2021AAC01001) and the Innovation Team for Genetic Improvement of Economic Forests (grant number 2022QCXTD04).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1632482/full#supplementary-material
References
Amagase, H. and Farnsworth, N. R. (2011). A review of botanical characteristics, phytochemistry, clinical relevance in efficacy and safety of Lycium barbarum fruit (Goji). Food Res. Int. 44, 1702–1717. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.03.027
Amagase, H., Sun, B. X., and Borek, C. (2009a). Lycium barbarum (goji) juice improves in vivo antioxidant biomarkers in serum of healthy adults. Nutr. Res. 29, 19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2008.11.005
Amagase, H., Sun, B. X., and Nance, D. M. (2009b). Immunomodulatory effects of a standardized Lycium barbarum fruit juice in Chinese older healthy human subjects. J. Medicinal Food 12, 1159–1165. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2008.0300
Amato, A., Cavallini, E., Zenoni, S., Finezzo, L., Begheldo, M., Ruperti, B., et al. (2017). A grapevine TTG2-Like WRKY transcription factor is involved in regulating vacuolar transport and flavonoid biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01979
An, J. P., Wang, X. F., Li, Y. Y., Song, L. Q., Zhao, L. L., You, C. X., et al. (2018). EIN3-LIKE1, MYB1, and ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR3 act in a regulatory loop that synergistically modulates ethylene biosynthesis and anthocyanin accumulation. Plant Physiol. 178, 808–823. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00068
Bondia-Pons, I., Savolainen, O., Törrönen, R., Martinez, J. A., Poutanen, K., and Hanhineva, K. (2014). Metabolic profiling of Goji berry extracts for discrimination of geographical origin by non-targeted liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 63, 132–138. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.067
Cao, Y. L., Li, Y. L., Fan, Y. F., Li, Z., Yoshida, K., Wang, J. Y., et al. (2021). Wolfberry genomes and the evolution of Lycium (Solanaceae). Commun. Biol. 4, 671. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02152-8
Chen, C. J., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H. R., Frank, M. H., He, Y. H., et al. (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 13, 1194–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen, S. F., Zhou, Y. Q., Chen, Y. R., and Gu, J. (2018). Fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, 884–890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560
Du, Y. W., Ma, H. Y., Liu, Y. Y., Gong, R., Lan, Y., Zhao, J. H., et al. (2024). Major quality regulation network of flavonoid synthesis governing the bioactivity of black wolfberry. New Phytol. 242, 558–575. doi: 10.1111/nph.19602
Emms, D. M. and Kelly, S. (2019). OrthoFinder: phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. 20, 238. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1832-y
Faraji, S., Heidari, P., Amouei, H., Filiz, E., and Poczai, P. (2021). Investigation and computational analysis of the Sulfotransferase (SOT) gene family in Potato (Solanum tuberosum): insights into sulfur adjustment for proper development and stimuli responses. Plants-Basel 10 (12), 2597. doi: 10.3390/plants10122597
Gao, Q. Q., Song, W. L., Li, X., Xiang, C. F., Chen, G., Xiang, G. S., et al. (2022). Genome-wide identification of bHLH transcription factors: discovery of a candidate regulator related to flavonoid biosynthesis in Erigeron breviscapus. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.977649
Gao, J., Zhang, Y. X., Li, Z. G., and Liu, M. C. (2020). Role of ethylene response factors (ERFs) in fruit ripening. Food Qual. Saf. 4, 15–19. doi: 10.1093/fqsafe/fyz042
Han, D., Huang, B. C., Li, Y. C., Dang, Q. Y., Fan, L. M., Nie, J. Y., et al. (2022). The MdAP2–34 modulates flavonoid accumulation in apple (Malus domestica Borkh.) by regulating MdF3’H. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 192, 111994. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.111994
Ito, K. and Murphy, D. (2013). Application of ggplot2 to pharmacometric graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst. Pharmacol. 2, e79. doi: 10.1038/psp.2013.56
Jiang, L. F. (2014). Preparation and antioxidant activity of Lycium barbarum oligosaccharides. Carbohydr. Polymers 99, 646–648. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.084
Jin, M. L., Huang, Q. S., Zhao, K., and Shang, P. (2013). Biological activities and potential health benefit effects of polysaccharides isolated from Lycium barbarum L. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 54, 16–23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2012.11.023
Kim, D., Landmead, B., and Salzberg, S. L. (2015). HISAT: a fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 12, 357–U121. doi: 10.1038/Nmeth.3317
Kim, S.-H., Lee, J.-R., Hong, S.-T., Yoo, Y.-K., An, G., and Kim, S.-R. (2003). Molecular cloning and analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes preferentially expressed in apple skin. Plant Sci. 165, 403–413. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9452(03)00201-2
Kumar, S., Stecher, G., Li, M., Knyaz, C., and Tamura, K. (2018). MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 35, 1547–1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096
Langfelder, P. and Horvath, S. (2008). WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinf. 9, 559. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Li, Y., Chen, Y., Zhou, L., You, S. J., Deng, H., Chen, Y., et al. (2020b). MicroTom metabolic network: rewiring tomato metabolic regulatory network throughout the growth cycle. Mol. Plant 13, 1203–1218. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.005
Li, D., Liu, X., Shu, L., Zhang, H., Zhang, S., Song, Y., et al. (2020a). Global analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in rose (Rosa chinensis) genome unveils the role of RcERF099 in Botrytis resistance. BMC Plant Biol. 20, 533. doi: 10.1186/s12870-020-02740-6
Li, X. L., Tao, S., Wei, S. W., Ming, M. L., Huang, X. S., Zhang, S. L., et al. (2018). The mining and evolutionary investigation of AP2/ERF genes in pear (Pyrus). BMC Plant Biol. 18, 46. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1265-x
Li, Q. F., Zhang, L., Chen, P. W., Wu, C. H., Zhang, H. X., Yuan, J. P., et al. (2022). Genome-wide identification of APETALA2/ETHYLENE RESPONSIVE FACTOR transcription factors in Cucurbita moschata and their involvement in ethylene response. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.847754
Liao, Y., Smyth, G. K., and Shi, W. (2014). FeatureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30, 923–930. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656
Liu, H. L., Su, B. B., Zhang, H., Gong, J. X., Zhang, B. X., Liu, Y. L., et al. (2019a). Identification and functional analysis of a flavonol synthase gene from grape hyacinth. Molecules 24 (8), 1579. doi: 10.3390/molecules24081579
Liu, M. Y., Sun, W. J., Ma, Z. T., Zheng, T. R., Huang, L., Wu, Q., et al. (2019b). Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum Tataricum). BMC Plant Biol. 19, 84. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-1681-6
Liu, X. J., Zhou, G. Y., Chen, S. S., Jia, Z. Z., Zhang, S. Q., Ren, M. J., et al. (2023). Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Tritipyrum and the response of TtERF_B2–50 in salt-tolerance. BMC Genomics 24 (1), 541. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09585-x
Livak, K. J. and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-delta delta C(T)) method. Methods 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Miean, K. H. and Mohamed, S. (2001). Flavonoid (myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin, and apigenin) content of edible tropical plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 49, 3106–3112. doi: 10.1021/jf000892m
Minh, B. Q., Schmidt, H. A., Chernomor, O., Schrempf, D., Woodhams, M. D., von Haeseler, A., et al. (2020). IQ-TREE 2: new models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 37, 2461–2461. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa131
Mizoi, J., Shinozaki, K., and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2012). AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta-Gene Regul. Mech. 1819, 86–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.08.004
Mo, R., Han, G., Zhu, Z., Essemine, J., Dong, Z., Li, Y., et al. (2022). The ethylene response factor ERF5 regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in ‘Zijin’ mulberry fruits by interacting with MYBA and F3H genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 7615. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147615
Nakano, T., Suzuki, K., Fujimura, T., and Shinshi, H. (2006). Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice[W]. Plant Physiol. 140, 411–432. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.073783
Ni, J., Bai, S., Zhao, Y., Qian, M., Tao, R., Yin, L., et al. (2019). Ethylene response factors Pp4ERF24 and Pp12ERF96 regulate blue light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in ‘Red Zaosu’ pear fruits by interacting with MYB114. Plant Mol. Biol. 99, 67–78. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0802-1
Ni, J., Premathilake, A. T., Gao, Y., Yu, W., Tao, R., Teng, Y., et al. (2021). Ethylene-activated PpERF105 induces the expression of the repressor-type R2R3-MYB gene PpMYB140 to inhibit anthocyanin biosynthesis in red pear fruit. he Plant J. 105, 167–181. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15049
Ohme-Takagi, M. and Shinshi, H. (1995). Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 7, 173–182. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.2.173
Qiao, X., Li, Q., Yin, H., Qi, K., Li, L., Wang, R., et al. (2019). Gene duplication and evolution in recurring polyploidization-diploidization cycles in plants. Genome Biol. 20, 38. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1650-2
Rezaee, S., Ahmadizadeh, M., and Heidari, P. (2020). Genome-wide characterization, expression profiling, and post-transcriptional study of GASA gene family. Gene Rep. 20, 100795. doi: 10.1016/i.genrep.2020.100795
Riechmann, J. L. and Meyerowitz, E. M. (1998). The AP2/EREBP family of plant transcription factors. Biol. Chem. 379, 633–646. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1998.379.6.633
Sainz, M. B., Grotewold, E., and Chandler, V. L. (1997). Evidence for direct activation of an anthocyanin promoter by the maize C1 protein and comparison of DNA binding by related Myb domain proteins. Plant Cell 9, 611–625. doi: 10.1105/tpc.9.4.611
Sakuma, Y., Liu, Q., Dubouzet, J. G., Abe, H., Shinozaki, K., and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2002). DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration-and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 290, 998–1009. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6299
Shan, X., Li, Y., Yang, S., Yang, Z., Qiu, M., Gao, R., et al. (2020). The spatio-temporal biosynthesis of floral flavonols is controlled by differential phylogenetic MYB regulators in Freesia hybrida. New Phytol. 228, 1864–1879. doi: 10.1111/nph.16818
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13, 2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303
Shoji, T. and Yuan, L. (2021). ERF gene clusters: working together to regulate metabolism. Trends Plant Sci. 26, 23–32. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2020.07.015
Sparvoli, F., Martin, C., Scienza, A., Gavazzi, G., and Tonelli, C. (1994). Cloning and molecular analysis of structural genes involved in flavonoid and stilbene biosynthesis in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Mol. Biol. 24, 743–755. doi: 10.1007/bf00029856
Stracke, R., De Vos, R. C., Bartelniewoehner, L., Ishihara, H., Sagasser, M., Martens, S., et al. (2009). Metabolomic and genetic analyses of flavonol synthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana support the in vivo involvement of leucoanthocyanidin dioxygenase. Planta 229, 427–445. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0841-y
Stracke, R., Ishihara, H., Huep, G., Barsch, A., Mehrtens, F., Niehaus, K., et al. (2007). Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J. 50, 660–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03078.X
Tsai, C. J., Harding, S. A., Tschaplinski, T. J., Lindroth, R. L., and Yuan, Y. (2006). Genome-wide analysis of the structural genes regulating defense phenylpropanoid metabolism in Populus. New Phytol. 172, 47–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2006.01798.x
Untergasser, A., Cutcutache, I., Koressaar, T., Ye, J., Faircloth, B. C., Remm, M., et al. (2012). Primer3–new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, e115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks596
Wang, C., Dong, Y., Zhu, L., Wang, L., Yan, L., Wang, M., et al. (2020). Comparative transcriptome analysis of two contrasting wolfberry genotypes during fruit development and ripening and characterization of the LrMYB1 transcription factor that regulates flavonoid biosynthesis. BMC Genomics 21, 295. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6663-4
Wang, L., Guo, D., Zhao, G., Wang, J., Zhang, S., Wang, C., et al. (2022). Group IIc WRKY transcription factors regulate cotton resistance to Fusarium oxysporum by promoting GhMKK2-mediated flavonoid biosynthesis. New Phytol. 236, 249–265. doi: 10.1111/nph.18329
Wang, Z., Song, G., Zhang, F., Shu, X., and Wang, N. (2023). Functional characterization of AP2/ERF transcription factors during flower development and anthocyanin biosynthesis related candidate genes in Lycoris. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 14464. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914464
Wang, Y., Tang, H., Debarry, J. D., Tan, X., Li, J., Wang, X., et al. (2012). MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Wang, L. M., Zhang, J., Dong, X. Y., Fu, Z. Z., Jiang, H., and Zhang, H. C. (2018). Identification and functional analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis genes in Phalaenopsis hybrids. Biol. Plantarum 62, 45–54. doi: 10.1007/s10535-017-0763-2
Wang, D., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Z., Zhu, J., and Yu, J. (2010). KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. 8, 77–80. doi: 10.1016/s1672-0229(10)60008-3
Wheeler, T. J. and Eddy, S. R. (2013). Nhmmer: DNA homology search with profile HMMs. Bioinformatics 29, 2487–2489. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt403
Winkel-Shirley, B. (2001). Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 126, 485–493. doi: 10.1104/pp.126.2.485
Wu, H., Lv, H., Li, L., Liu, J., Mu, S., Li, X., et al. (2015). Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factors family and the expression patterns of DREB genes in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis). PloS One 10, e0126657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126657
Xing, H., Jiang, Y., Zou, Y., Long, X., Wu, X., Ren, Y., et al. (2021). Genome-wide investigation of the AP2/ERF gene family in ginger: evolution and expression profiling during development and abiotic stresses. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 561. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03329-3
Yadav, M. L. and Roychoudhury, B. (2018). Handling missing values:a study of popular imputation packages in R. Knowledge-Based Syst. 160, 104–118. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.06.012
Yao, G., Ming, M., Allan, A. C., Gu, C., Li, L., Wu, X., et al. (2017). Map-based cloning of the pear gene MYB114 identifies an interaction with other transcription factors to coordinately regulate fruit anthocyanin biosynthesis. Plant J. 92, 437–451. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13666
Ye, G., Zheng, Z., Zhou, Y., Pu, X., Su, W., Guo, H., et al. (2021). The MYB transcription factor LrAN2, from Lycium ruthenicum, led to enhanced accumulation of anthocyanins and modified profile of the total glycoalkaloids in potato. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC) 147, 519–528. doi: 10.1007/s11240-021-02144-w
Zeng, S., Wu, M., Zou, C., Liu, X., Shen, X., Hayward, A., et al. (2014). Comparative analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis during fruit development in two Lycium species. Physiologia Plantarum 150, 505–516. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12131
Zhang, J., Zhao, H., Chen, L., Lin, J., Wang, Z., Pan, J., et al. (2023). Multifaceted roles of WRKY transcription factors in abiotic stress and flavonoid biosynthesis. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1303667
Zhao, M., Haxim, Y., Liang, Y., Qiao, S., Gao, B., Zhang, D., et al. (2022). Genome-wide investigation of AP2/ERF gene family in the desert legume Eremosparton songoricum: identification, classification, evolution, and expression profiling under drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.885694
Zhao, M., Li, J., Zhu, L., Chang, P., Li, L., and Zhang, L. (2019). Identification and characterization of MYB-bHLH-WD40 regulatory complex members controlling anthocyanidin biosynthesis in blueberry fruits development. Genes (Basel) 10 (7), 496. doi: 10.3390/genes10070496
Zhao, C., Liu, X., Gong, Q., Cao, J., Shen, W., Yin, X., et al. (2021a). Three AP2/ERF family members modulate flavonoid synthesis by regulating type IV chalcone isomerase in citrus. Plant Biotechnol. J. 19, 671–688. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13494
Zhao, J., Sun, C., Shi, F., Ma, S., Zheng, J., Du, X., et al. (2021b). Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis among 1-, 2- and 3-year old Atractylodes chinensis. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 354. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03131-1
Zhao, J., Xu, Y., Li, H., An, W., Yin, Y., Wang, B., et al. (2024). Metabolite-based genome-wide association studies enable the dissection of the genetic bases of flavonoids, betaine and spermidine in wolfberry (Lycium). Plant Biotechnol. J. 22, 1435–1452. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14278
Zhao, J., Xu, Y., Li, H., Zhu, X., Yin, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). ERF5.1 modulates carotenoid accumulation by interacting with CCD4.1 in Lycium. Horticulture Res. 10, uhad230. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhad230
Keywords: AP2/ERF family, wolfberry, flavonoids, LbAP2/ERF089, transcription factor
Citation: Li R, Xia S, Long Q, Jin C, Li H, Xu Y, Chen Y, Gan X, Zhang Y and Zhao J (2025) Functional analysis of AP2/ERF family members in flavonoid biosynthesis of wolfberry. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1632482. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1632482
Received: 21 May 2025; Accepted: 12 August 2025;
Published: 02 September 2025.
Edited by:
Elsayed Nishawy, Desert Research Center, EgyptReviewed by:
Mohammed Ali Abd Elhammed Abd Allah, Desert Research Center, EgyptSung Un Huh, Kunsan National University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Li, Xia, Long, Jin, Li, Xu, Chen, Gan, Zhang and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuanyuan Zhang, eXVhbnl1YW4uemhhbmdAaGFpbmFudS5lZHUuY24=; Jianhua Zhao, emhhb2ppYW5odWEwOTQzQDE2My5jb20=
 Ronghui Li
Ronghui Li Shijia Xia1,2
Shijia Xia1,2 Qiyuan Long
Qiyuan Long Cheng Jin
Cheng Jin Yuhui Xu
Yuhui Xu Yuchao Chen
Yuchao Chen Jianhua Zhao
Jianhua Zhao