- 1School of Pharmacy, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China
- 2School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 3Xinchang Pharmaceutical Factory, Zhejiang Medicine Co., Ltd., Shaoxing, Zhejiang, China
- 4Department of Pharmacy, School of Medicine, Hangzhou City University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
- 5Key Laboratory of Elemene Class Anti-Cancer Chinese Medicines; Engineering Laboratory of Development and Application of Traditional Chinese Medicines; Collaborative Innovation Center of Traditional Chinese Medicines of Zhejiang Province, Hangzhou Normal University, Hangzhou, China
- 6State Key Laboratory for Quality Ensurance and Sustainable Use of Dao-di Herbs, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
Introduction: Zerumbone is a pharmacologically active sesquiterpenoid with limited availability. This study aims to elucidate its biosynthetic pathway in Curcuma wenyujin by identifying and characterizing the key enzymes responsible for its production.
Methods: Candidate genes were selected via transcriptome analysis and phylogenetics. CwTPS8 and CwSDR1 were cloned and functionally characterized using in vitro enzyme assays and heterologous expression in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular docking and site-directed mutagenesis were applied to investigate the catalytic mechanism of CwTPS8.
Results: CwTPS8 was identified as a multifunctional sesquiterpene synthase that catalyzes the formation of α-humulene (a key zerumbone precursor) and β-caryophyllene as main products, along with several minor sesquiterpenes. Mutagenesis studies identified critical residues (e.g., Thr437, Cys436) that significantly shift product specificity toward α-humulene. CwSDR1 was characterized as a short-chain dehydrogenase that efficiently oxidizes 8-hydroxy-α-humulene to zerumbone. A de novo biosynthetic pathway was reconstructed in yeast, resulting in zerumbone production at 0.50 μg/L.
Discussion: This study expands the genetic toolkit for zerumbone biosynthesis and provides insights into enzyme engineering and metabolic engineering strategies to enhance production. Limitations in precursor supply and catalytic efficiency highlight areas for future optimization.
1 Introduction
Zerumbone, an important humulene-type sesquiterpenoids, exhibits antitumor effects through multiple mechanisms: inhibiting tumor cell growth and proliferation (Urla et al., 2023), inducing tumor cell apoptosis (Li et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023), suppressing tumor cell migration and invasion (Memari et al., 2022), inhibiting tumor angiogenesis (Tsuboi et al., 2014), modulating immune function (Li et al., 2020; Alsaffar et al., 2023), and reversing tumor multidrug resistance (Choi et al., 2011) (Figure 1). However, the sustainable supply of zerumbone is constrained by limited plant-derived raw materials and the challenges of chemical synthesis due to its complex stereochemistry (Kumar et al., 2025). In recent years, advances in biotechnology have positioned biosynthetic approaches as an alternative for the sustainable production of many natural products. Notably, the complete biosynthetic pathway of zerumbone has been elucidated, which includes an α-humulene synthase gene, a cytochrome P450 (CYP450) gene, and a short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) gene (Figure 1) (Yu et al., 2008; Okamoto et al., 2011; Yu et al., 2011). Despite the successful characterization of the zerumbone biosynthetic pathway, the limited number of characterized genes and their suboptimal catalytic efficiencies present a significant bottleneck, severely restricting heterologous production titers in microbial cell factories.
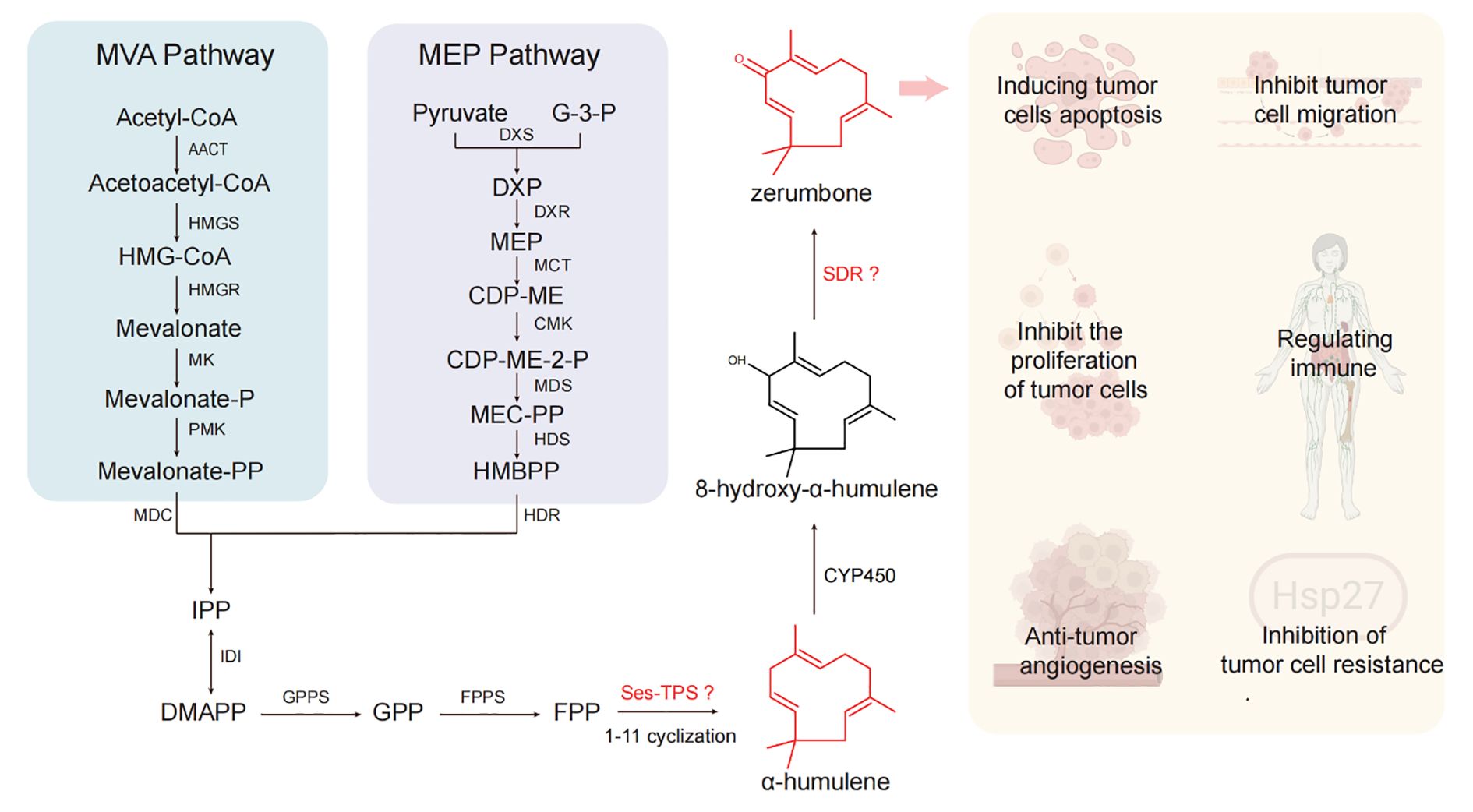
Figure 1. The biosynthetic pathway of zerumbone and its pharmacological effects. Illustrations used in pharmacological effects of zerumbone created with biorender.
Sesquiterpenoids exhibit broad applications in pharmaceutical, food, and cosmetic industries (Mai et al., 2021). Previous studies have isolated various sesquiterpenoid types from C. wenyujin, including cadinane-type and germacrane-type compounds (Chu et al., 2019; Lin et al., 2019; Li et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2025). Their carbon skeletons are formed through farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) cyclization catalyzed by sesquiterpene synthases, where FPP is synthesized via condensation of isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) in either the mevalonate (MVA) or methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) pathways (Vattekkatte et al., 2018; Durairaj et al., 2019; Ma et al., 2025). As the key enzymatic step in sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis, sesquiterpene synthase family members contain conserved metal-binding motifs: the “DDxxD” motif and “(N/D)Dxx(S/T)xxxE” motif (Christianson, 2006). These enzymes are classified into acyclic and 1-6, 1-7, 1-10, 1–11 cyclization patterns based on their FPP cyclization modes (Segura et al., 2003; Nie et al., 2024). Notably, humulene synthase—which catalyzes FPP conversion into the zerumbone precursor—belongs to the 1–11 cyclization- type sesquiterpene synthases.
The short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) superfamily, one of the three ancient oxidoreductase superfamilies, is characterized by a length of 250–350 amino acids and conserved structural features, including a Rossmann fold that binds to the NADH or NADPH, as well as a coenzyme-binding motif (TGxxxGxG) and a catalytic motif (YxxxK) (Labesse et al., 1994; Kramm et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2019; Marmont et al., 2020). A systematic classification based on conserved domains and catalytic functions divides SDRs into seven evolutionary subtypes: classical, extended, intermediate, complex, divergent, atypical, and unknown. These subtypes regulate plant secondary metabolism through NAD(P)H-dependent mechanisms (de Kraker et al., 2001; Kavanagh et al., 2008). The redox reactions mediated by the Rossmann fold are particularly crucial in terpenoid and alkaloid metabolism, as exemplified by peppermint SDRs that catalyze the stereoselective oxidation of (-)-trans-isopiperitenol (Davis et al., 2005; Fellows et al., 2018), and the SDR in opium poppy catalyzes the dehydrogenation of narcotine hemiacetal to noscapine (Chen and Facchini, 2014). SDRs also play a role in modulating lipid metabolism and stress-response pathways: In Elaeis guineensis, SDR suppresses saturated fatty acid biosynthesis and enhances their catabolism (Zhang et al., 2023a), Oryza sativa SDRs activate phytoalexin biosynthesis under stress (Kitaoka et al., 2016), and cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase modulates polyphenol biosynthesis, thereby enhancing drought tolerance (Wang et al., 2017). This functional versatility establishes SDRs as essential tools for redox regulation and stress-resistance engineering (Stavrinides et al., 2018).
To enrich the genetic resources of the zerumbone biosynthetic pathway and establish efficient microbial cell factories, this study employed transcriptomic data mining and functional characterization to successfully identify two key enzymes: CwTPS8, which exhibits humulene/caryophyllene synthase activity, and short-chain dehydrogenase CwSDR1, which specifically catalyzes the oxidation of 8-hydroxy-α-humulene to zerumbone. Furthermore, the catalytic mechanism of enzyme CwTPS8 was elucidated, and a Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell factory was constructed for the heterologous biosynthesis of zerumbone. These findings provide essential theoretical groundwork for the subsequent development of high-yield yeast chassis for zerumbone bioproduction.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Treatment of Curcuma wenyujin
The C. wenyujin used in this study was harvested from the Rui’an area of Wenzhou, Zhejiang Province, and was confirmed to be a genuine herb by Prof. Guo Zengxi of the Zhejiang Provincial Food and Drug Inspection Institute. Explants were taken from the junction of the root and stem, approximately 2 cm in length, and were inoculated onto modified MS solid medium containing 3 mg/L of 6-benzylaminopurine after surface disinfection. The explants were then cultured in an artificial climatic chamber at 22°C with a 12-hour light/12-hour dark photoperiod to induce clumped shoot formation. After a 30-day period, the clumped shoots were separated into individual plants and transferred to MS medium for continued culture until they reached the three-leaf stage. At the experimental treatment stage, uniform seedlings from a single group were selected and placed in MS liquid medium containing 250 μM methyl jasmonate (MeJA) for 1 hour and 6 hours, respectively. MS liquid medium without MeJA served as the blank control group. All treatments were conducted in a constant temperature light incubator set at 22°C with a photoperiod of 12 hours light and 12 hours dark. Three biological replicates were established for each treatment group. At the conclusion of the treatments, plant leaf samples were rapidly collected and transferred to an ultra-low-temperature freezer at -80°C for storage, following a quick-freezing treatment in liquid nitrogen. This process ensured the provision of standardized biological samples for subsequent RNA extraction experiments.
2.2 Bioinformatics analysis
Based on transcriptome data analysis, a total of 3 terpene synthase genes and 3 dehydrogenase genes were identified from C. wenyujin. These genes were compared with several currently reported terpene synthase and short-chain dehydrogenases using neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic analysis conducted with MEGA 7. In the MEGA 7 software, using a method with 1,000 bootstrap replicates, one candidate α-humulene synthase (CwTPS8) and one short-chain dehydrogenases (CwSDR1) were identified.
2.3 RNA isolation and gene cloning
RNA was extracted from the methyl jasmonate-treated warm tulip samples (flowers, leaves, and stems) using the Total RNA Fast Extraction Kit FastPure Plant (RC401, Vazyme, Nanjing, China). One microgram of RNA was reverse-transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA) using the Reverse Transcription Kit (RR092A, TaKaRa Japan), and the resulting cDNA was stored at -20°C. Primers were designed based on transcriptome data using Primer Premier 5.0 software (Supplementary Table S1). The complete open reading frames (ORFs) of CwTPS8 (genebank: PV682578) and CwSDR1 (genebank: PV682579) were obtained through amplification with 2× Phanta Max Master DNA polymerase (Nanjing Vazyme), using the cDNAs as templates. The amplified target fragments were then ligated into the B-Zero-Blunt vector and transformed into competent E. coli cells. After incubation, single colonies were selected for PCR with primers, and the clones with the correct bands were sequenced by Tsingke Biotech (Beijing, China). The successfully cloned strains were stored at -80°C.
2.4 Conserved structural domains and physicochemical property analysis
Amino acid multiple sequence comparisons of CwTPS8, OsTPS3, ZpTPS1, ZpTPS6 and ZSS1, as well as CwSDR1, AtSDR1, LiBDH and SoBDH2 were conducted using DNAMAN software. The analysis revealed that CwTPS8 contains the conserved motifs characteristic of terpene synthases, including “RxR”, “DDxxD” and “(N/D)Dxx(S/T)xxxE”; CwSDR1 possess the coenzyme-binding domain “TGxxxGxG” and the catalytic triad “SYK”. These domains were further analyzed for their physicochemical properties using tools available at (https://web.expasy.org/protparam/).
2.5 Plasmid construction
The target fragments were amplified using PCR with 2× Phanta Max Master DNA polymerase. The vectors pESC-Trp, pESC-Ura, pESC-Leu and pMAL-His (plasmid pMAL-c2x with His(8)-tag) were linearized with restriction endonucleases at the BamHI or EcoRI sites. The purified target fragments and linearized vectors were combined with Assembly Mix according to the instructions of the pEASY®-Uni Seamless Cloning and Assembly Kit (TransGen Biotech) and incubated at 50°C for 30 minutes. The resulting constructs were then transformed into the Trans T1 competent cells and plated on Luria-Bertani (LB) agar plates containing 100 μg/mL ampicillin. Successfully sequenced monoclonal colonies were subsequently selected for storage at -80°C. The primers for the seamless clones are shown in Supplementary Table S1.
2.6 Protein purification and in vitro enzymatic reaction of CwTPS8
Recombinant plasmid pMAL-His::CwTPS8 and the control plasmid pMAL-His were transformed into E. coli strain BL21 (DE3) and plated on LB solid medium containing 100 mg/mL ampicillin. Positive clones were selected and inoculated into LB medium containing ampicillin for 20 hours of shaking culture at 37°C and 200 rpm. The following day, the clones were inoculated 1:100 into 100 mL of LB medium containing the corresponding antibiotic and incubated at 37°C and 250 rpm until the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reached 0.6-0.8. IPTG was then added to a final concentration of 0.4 mM, and the cultures were induced by incubation at 25°C and 180 rpm for 18–20 hours. At the end of the induction, the cells were harvested using a cryo-centrifuge at 4°C, 7000 g for 10 minutes, and the medium was poured off to collect the organisms. Add 2 mL of enzyme buffer (40 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 20 mM imidazole; 250 mM NaCl) to resuspend the cells, then place them on ice. Break the cells using an ultrasonic crusher (30% power, ultrasound for 3 seconds at 10-second intervals for 5 minutes). Centrifuge at 4°C, 9000 × g for 45 minutes, collect the supernatant proteins, and combine them with an appropriate amount of Ni2+ at 4°C for 2–3 hours to facilitate binding. The column was pre-equilibrated with a buffer solution (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 250 mM NaCl). The supernatant proteins were then loaded onto the nickel-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) column using a pre-cooled buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 30 mM imidazole; 250 mM NaCl) to wash away the heterogeneous proteins. Subsequently, a buffer containing (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 100 mM imidazole; 250 mM NaCl) was used to elute the target proteins. Finally, the target proteins were concentrated using ultrafiltration tubes at 4°C and 4000 rpm. They were washed three times with ultrapure water for 30 minutes each time and then exchanged twice with cryoenzyme buffer (50 mM HEPES, 10 mM MgCl2, 5 mM DTT, 5% (v/v) glycerol, pH 7.5) before partitioning. The electrophoretic analysis of the purified protein is presented in Supplementary Figure S1. The purified proteins were flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately after purification and maintained at −80°C for storage. Protein concentration was quantified using the BCA Protein Assay Kit, employing bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a calibration standard. Enzymatic reactions were conducted by incubating the purified proteins with FPP substrate at 30°C with 120 rpm shaking for 3 hours, with the reaction mixture overlaid with an equal volume of n-hexane. Following the reaction, the hexane phase was carefully separated, concentrated to 200 µL under a gentle nitrogen stream, and preserved at 4°C.
To determine the catalytic activity of the recombinant protein CwTPS8, it was diluted to a concentration of 20 µg/mL using cryoenzyme buffer (50 mM HEPES, 10 mM MgCl2, 5 mM DTT, 5% (v/v) glycerol, pH 7.5). Various concentrations of FPP (10 µM, 25 µM, 50 µM, 100 µM, 125 µM, and 150 µM) were prepared with an equal volume of n-hexane and incubated for 10 minutes at 30°C. EDTA was then added to the reaction mixture to halt the reaction, followed by thorough mixing using vortexing. The mixture was centrifuged at 10,000 g for 1 minute, and the n-hexane layer was collected. After extracting with n-hexane three times, the extracts were concentrated to 70 µL under a stream of nitrogen for GC-MS detection. The Km and Vmax values were calculated using GraphPad Prism. All data were derived from three independent experiments.
2.7 Functional characterization of CwTPS8 and CwSDR1 in S. cerevisiae
The recombinant plasmid pESC-Trp::CwTPS8 as well as the control plasmid pESC-Trp were transformed into yeast cell (using TransGen Biotech’s Frozen Yeast Transformation II™ Kit). The cells were then cultured on solid SD-Trp medium for 3 days at 30°C. Positive clones were selected and incubated in SD-Trp medium for 20 hours. After this period, the OD600 was diluted to 0.2, and after an additional 12 hours, it was further diluted to 0.05 to initiate fermentation using 100 mL of SD-Trp medium containing glucose at 30°C and 200 rpm to start fermentation. After two days, the medium was replaced with 100 mL of defective medium containing galactose for an additional three days to induce gene expression. At the end of fermentation, the fermentation products were extracted through ultrasonic crushing using an equal volume of n-hexane, repeated three times, and concentrated using a rotary evaporator at 42°C and 70 rpm. The products were then dissolved in 1 mL of n-hexane, filtered through a 0.22 μm organic membrane, and stored at 4°C.
2.8 The construction of a yeast strain for the de novo synthesis of zerumbone
In a previous study, we developed an engineered yeast strain, designated FY94, capable of producing high levels of FPP (Hu et al., 2024). In this strain, the key genes involved in the FPP biosynthetic pathway—tHMG1, IDI, and ERG20, were overexpressed, while the coding gene for Erg9, which catalyzes the conversion of FPP to squalene, was downregulated. Additionally, three genes, ROX1, YJL064w and YPL062w, that reduce the metabolic flux of MVA pathway were knocked out. Here, the recombinant plasmid pESC-Trp::ZSS1 was transformed into strain FY94, resulting in the new strain FY94-1. Next, the plasmid pESC-Leu::CYP71BA1-AtCPR was introduced into FY94–1 to produce 8-hydroxy-α-humulene, leading to the creation of strain FY94-2. Finally, the plasmid pESC-Ura::CwSDR1 was transformed into FY94–2 to produce zerumbone, resulting in the final strain, FY94-3. The strains used in this study are listed in Supplementary Table S2.
2.9 Molecular docking and targeted mutation experiments
The protein sequence of CwTPS8 was submitted to SWISS-MODEL (http://swissmodel.expasy.org), using the structure of alpha-humulene synthase (B1B1U3.1.A) as a template to generate the protein structure model of CwTPS8. After obtaining the 3D structure of the substrate FPP using ChewBio3D, molecular docking of CwTPS8 and FPP was conducted in AutoDock Vina and subsequently visualized and analyzed structurally using PyMOL.
Using pESC-Trp::CwTPS8 as a template, the key amino acids of CwTPS8 were targeted for mutagenesis with the QuickChange Site-Directed Mutagenesis Kit (TransGene Biotech, Beijing, China) (see Supplementary Table S1 for mutation primers). The mutated vector was transformed into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae FY95 sensory strain (FY95 is an engineered yeast that produces more FPP than FY94) for qualitative and quantitative analysis and the genotype of FY95 was showed in Supplementary Table S2. The transformation and the first two activation steps are described in section 2.7. The key difference from the method outlined in section 2.7 is the addition of 10% n-dodecane to cover the fermentation after the transition to galactose medium. Bidirectional extraction was performed, and the n-dodecane layer was collected at the end of fermentation. This n-dodecane layer was then diluted 50-fold with n-hexane for product characterization and quantitative analysis using GC-MS. The samples were stored at 4°C.
2.10 GC-MS analysis
The qualitative and quantitative analyses of the samples were conducted using an Agilent 8890-7000GC/TQ gas chromatography-tandem triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Agilent, CA, USA) system under the following analytical conditions: A DB-5ms capillary column (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm) was utilized with an injection volume of 1 μL. The temperature program commenced at 80°C, followed by a gradient increase of 10°C·min-1 to 240°C (held for 2 minutes), and then ramped at 20°C min-1 to 260°C (held for an additional 2 minutes). Instrument parameters included an electron energy of 70 eV, an injector temperature maintained at 275°C, and an ion source temperature set at 280°C. Full scan mode was employed across a mass-to-charge (m/z) range of 30–350 for comprehensive spectral acquisition. β-Caryophyllene (purity ≥95%) and cryptomeridiol (purity ≥95%) standards were obtained from Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Zerumbone (purity ≥95%) was acquired from Sigma-Aldrich. The synthetic gene fragment encoding α-humulene synthase (GenBank Accession No. AB247331.1), used as a positive control, was supplied by Genecefe Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Jiangsu, China). β-Caryophyllene was used to generate a calibration curve for quantifying both α-humulene and β-caryophyllene, as their structural similarity and physicochemical properties are expected to yield comparable instrumental response factors. The standard curve of β-caryophyllene is provided in Supplementary Figure S2.
3 Results
3.1 The screening and cloning of candidate humulene synthase gene
In previous study, we performed transcriptome sequencing on C. wenyujin (Wei et al., 2022). Based on the gene annotation, three candidate sesquiterpene synthase genes were screened. To predict the functions of these genes, phylogenetic analysis was conducted (Figure 2A). The result showed that one of the candidate genes, named CwTPS8, was clustered into a clade with sesquiterpene synthase genes that catalyze the 1,11-cyclization of the substrate FPP, and exhibited close phylogenetic proximity to a functionally characterized humulene synthase gene, ZSS1. Whereas, CwTPS9 and CwTPS10 might produce acyclic sesquiterpene and products with 1,10-cyclization, respectively. The multiple alignments of CwTPS8 and humulene synthase genes from other plants showed that CwTPS8 has the metal-binding “DDxxD” motif and the substrate-stabilizing “(N/D) Dxx(S/T) xxxE” motif which were conserved in the sequences of class I terpene synthases (Figure 2B). Besides, a conserved basic residue cluster facilitating carbocation cascade termination in cyclic sesquiterpene biosynthesis, “RxR”, was also found in CwTPS8 (Figure 2B). Integrating phylogenetic and conserved domain analyses, we propose TPS8 encodes a 1,11-cyclizition sesquiterpene synthase with specific humulene-producing activity.
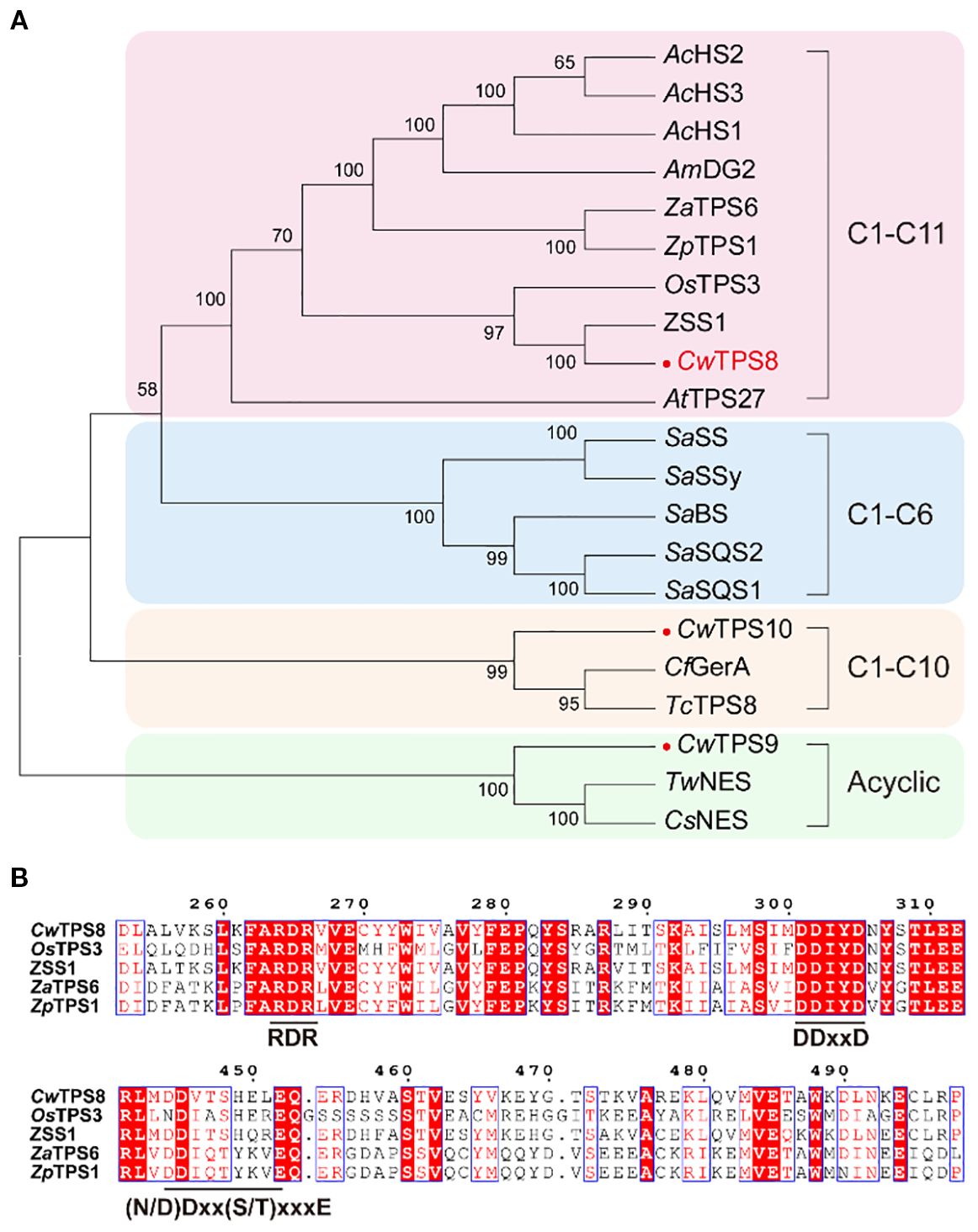
Figure 2. The phylogenetic analysis and conserved motif analysis of CwTPSs. (A) The phylogenetic tree of CwTPSs. The genes used in this analysis are listed in Supplementary Table S3; (B) The conserved motif analysis of CwTPS8 which has a conserved basic residue cluster “RxR” motif, the metal-binding “DDxxD” motif and the substrate-stabilizing “(N/D) Dxx(S/T) xxxE” motif.
3.2 CwTPS8 is a β-caryophyllene/α-humulene synthase
To determine whether CwTPS8 functions as the key sesquiterpene synthase in the zerumbone biosynthetic pathway, we characterized its activity through both in vitro enzymatic reactions and in vivo yeast fermentation assays.
Firstly, CwTPS8 was cloned into the prokaryotic expression plasmid pMAL-His and subsequently transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3). The recombinant proteins were induced using IPTG. After extraction and purification, the recombinant proteins were incubated with the substrate FPP. GC-MS analysis revealed that CwTPS8 could convert FPP into multiple sesquiterpene products, with β-caryophyllene (1) and α-humulene (2) being the two primary products (Figure 3A). Kinetic profiles of CwTPS8 for FPP are as follows: 28.17 µM (Km of α-humulene), 27.99 µM (Km of β-caryophyllene), 1.038 µM/min (Vmax of α-humulene), 13.29 µM/min (Vmax of β-caryophyllene), 0.002 s-1/µM (Kcat/Km of α-humulene), and 0.0254 s-1/µM (Kcat/Km of β-caryophyllene) (Supplementary Figure S3). In addition, CwTPS8 was cloned into the eukaryotic expression vector pESC-Trp and transformed into the engineered yeast strain FY94, which we previously developed for the high-yield production of FPP (Hu et al., 2024). After fermentation and product extraction, the resulting compounds were analyzed by GC-MS. The results showed that CwTPS8 is a multifunctional sesquiterpene synthase capable of producing five different sesquiterpene compounds (Figure 3B). Among these, β-caryophyllene (1) and α-humulene (2) are the primary products, and cryptomeridiol (5) is a minor product. Additionally, based on the retention index and mass spectrometry data, the other two products were identified as caryophyllenyl alcohol (3) and neointermedeol (4) (Supplementary Figure S4).
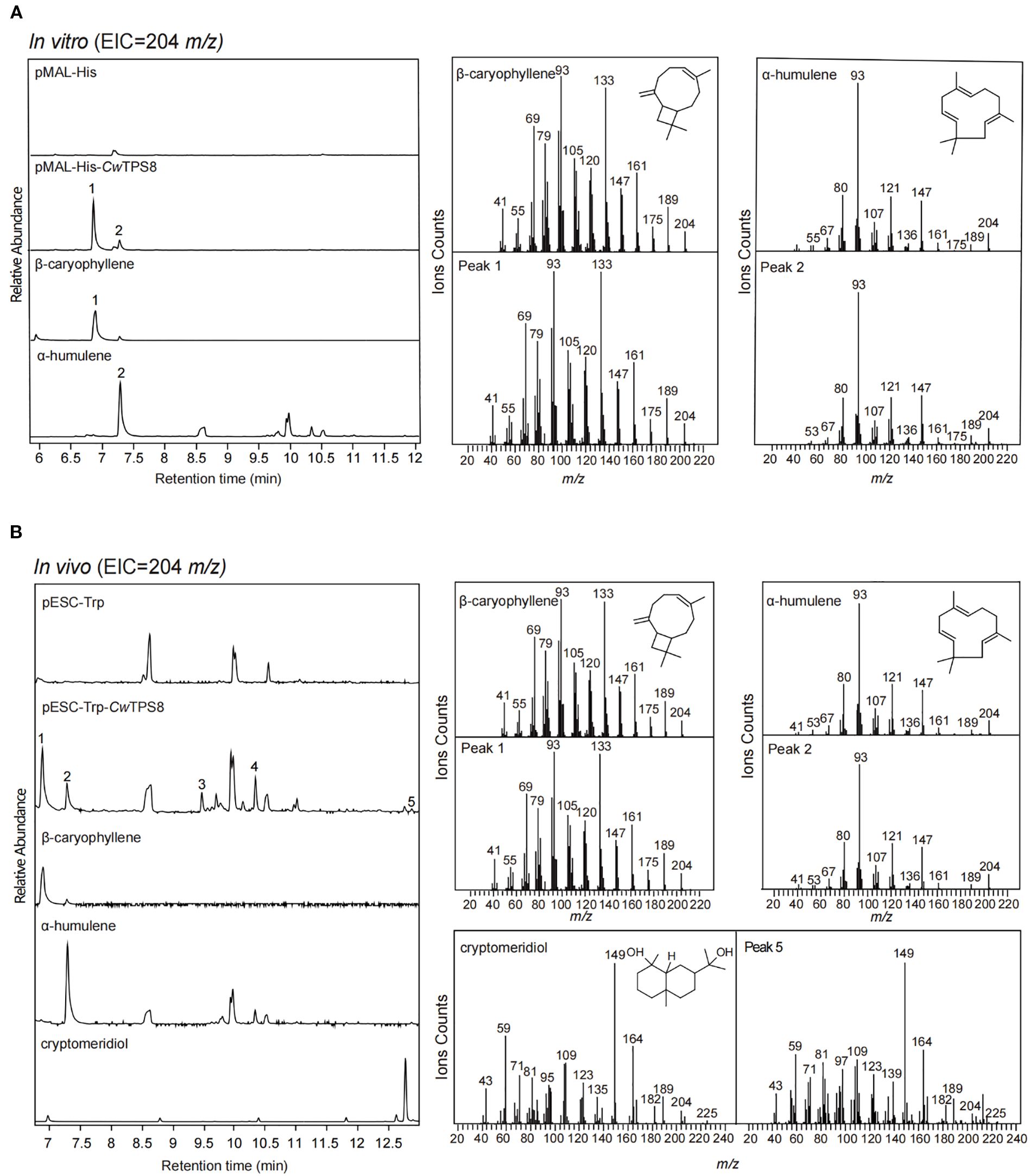
Figure 3. GC-MS analysis of the products of CwTPS8. (A) GC-MS analysis of the products of the in vitro enzymatic reaction of CwTPS8. Standards of β-caryophyllene, α-Humulene is a product of enzyme with characteristic function. (B) GC-MS analysis of the products of yeast strains expressing CwTPS8. Standards of cryptomeridiol (95% purity).
Collectively, our functional characterization demonstrates that CwTPS8 is a multifunctional sesquiterpene synthase capable of catalyzing diverse cyclization reactions from the substrate FPP. Primarily, it catalyzes the 1,11-cyclization of FPP to generate β-caryophyllene (1), α-humulene (2) and caryophyllenyl alcohol (3). Additionally, the enzyme exhibits secondary 1,10-cyclization activity, producing neointermedeol (4) and cryptomeridiol (5).
3.3 Residues that affect the generation of products
Under the catalytic action of CwTPS8, the pyrophosphate group of the substrate farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) undergoes cleavage to generate a farnesyl carbocation, which subsequently undergoes 1,11-cyclization to form the (E, E)-humulyl cation. This intermediate is then converted to α-humulene through a deprotonation step, while the biosynthesis of β-caryophyllene requires carbocation rearrangement of the (E, E)-humulyl cation followed by deprotonation (Yang et al., 2022). Single amino acid substitutions at or near the active site may critically influence catalytic efficiency and product specificity during this cascade. To find out the key residues affect the generation of products, site-directed mutagenesis experiments targeting key residues in the active site of CwTPS8 were conducted based on molecular docking analysis. (Figure 4A).
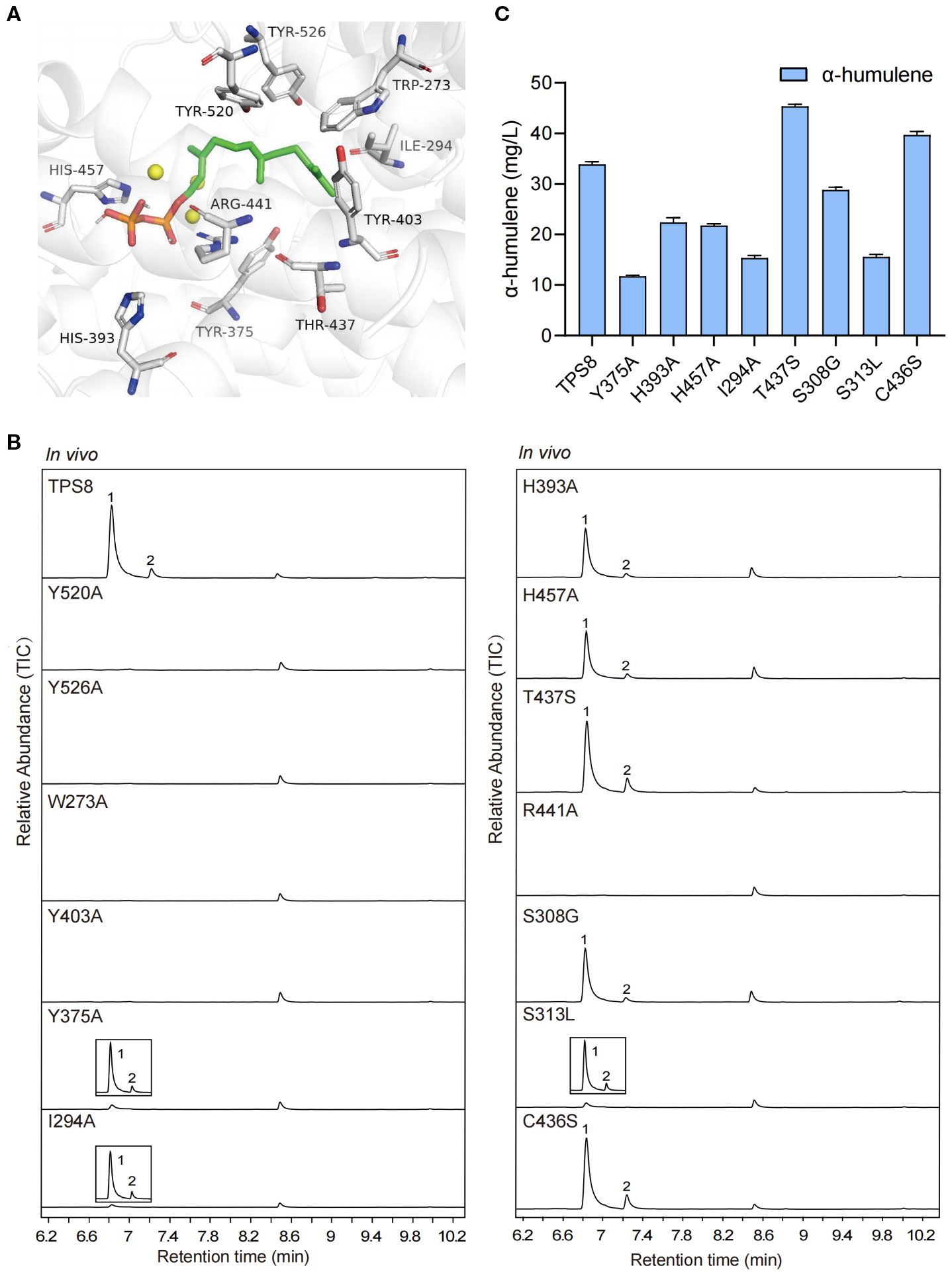
Figure 4. The molecular docking and site-directed mutagenesis research of CwTPS8. (A) The molecular docking of CwTPS8 and the substrate FPP. The labeled amino acids are key residues of the active pocket; (B) GC-MS analysis of products of the mutants. (C) The quantitative analysis of α-humulene in the mutants. Data are mean ± SD, n = 4.
The cyclization of the farnesyl carbocation is primarily influenced by the architecture of the active site, which consists of both aromatic and aliphatic residues. Aromatic residues stabilize reaction intermediates through cation-π interactions and direct cation migration toward specific cyclization pathways (Christianson, 2017). The aliphatic residues near the active site have been implicated in the cyclization and isomerization steps of certain sesquiterpene synthases (Gonzalez et al., 2014; Ker et al., 2020). First, we investigated the roles of the aromatic amino acids surrounding the active site, including Trp273, Tyr375, Tyr403, Tyr520, and Tyr526. These aromatic amino acids were substituted with alanine. The results revealed that the Y375A mutant significantly reduced the yields of the primary products, β-caryophyllene and α-humulene, while the W273A, Y403A, Y520A, and Y526A mutants completely abolished CwTPS8 activity (Figure 4B; Supplementary Figure S5). This finding demonstrates the critical role of aromatic side chains in stabilizing carbocation intermediates through π-π stacking. Next, we examined the function of the aliphatic residue Ile294 in the active site. After being replaced with alanine, the I294A mutant exhibited a dramatic reduction in product formation, with only hence β-caryophyllene and α-humulene were detected (Figure 4B). This result suggests that the hydrophobic side chains of aliphatic residues near the carbon chain of FPP, such as Ile294, are significant for stabilizing substrate intermediates through hydrophobic interactions.
In addition, previous studies have reported that the basic residues near the pyrophosphate group of FPP can facilitate the removal of the pyrophosphate group, promote the formation of carbocation intermediates, and ultimately lead to the generation of the products (Starks et al., 1997; Lopez-Gallego et al., 2010). In this study, we investigated the roles of Arg441, His393, and His457, which are located near the pyrophosphate group of FPP. All of these residues were substituted with the neutral amino acid alanine. The results showed that the H393A and H457A mutations exhibited a significant reduction in CwTPS8 activity, while the R441A mutation directly inactivated CwTPS8 (Figure 4B). These findings indicate that the positively charged residues surrounding the pyrophosphate group of FPP, such as Arg441, His393, and His457, play a crucial role in the activity of the sesquiterpene synthases.
Furthermore, we performed sequence alignments of CwTPS8 with other α-humulene synthases and β-caryophyllene synthases. First, we identified a significant difference at residue 437 when comparing it to humulene synthases. In typical humulene synthases, this residue is a conserved serine, whereas in CwTPS8, it is a threonine (Thr437) (Supplementary Figure S6A). In light of this finding, we substituted Thr437 with serine. Notably, the resulting mutant, T437S, exhibited an increased production of α-humulene (37%) and a decreased production of another primary product, β-caryophyllene (Figures 4B, C; Supplementary Figure S5). This result may be attributed to the substitution of serine, which reduces steric hindrance by eliminating a methyl group. This alteration enhances hydrogen bonding between the serine hydroxyl group and the adjacent arginine residue. The strengthened hydrogen-bond network increases the local electropositivity of the guanidinium group of arginine, thereby modulating the spatial orientation of the humulyl cation. This electrostatic steering promotes deprotonation, facilitating the formation of α-humulene over C2-C10 cyclization, which is essential for the production of β-caryophyllene. Consequently, this effectively directs the carbocation intermediate toward the α-humulene pathway. Additionally, by comparing with β-caryophyllene synthases, we identified three relatively conserved amino acids and constructed the mutants S308G, S313L, and C436S (Supplementary Figure S6B). The results indicated that the S308G and S313L mutations resulted in varying reductions in CwTPS8 activity, while the C436S mutation led to an 18% increase in the production of α-humulene, with the yield of β-caryophyllene remaining essentially unchanged (Figures 4B, C; Supplementary Figure S5). The effect of the C436S mutation may be similar to that of the T437S mutation, potentially influencing the quenching of the humulyl cation by enhancing hydrogen bonding with the adjacent arginine residue, thereby leading to an increase in α-humulene production.
3.4 Cloning and bioinformatics analysis of candidate short-chain dehydrogenase gene
After obtaining the key sesquiterpene synthase CwTPS8 involving in zerumbone biosynthetic pathway, we tried to screen the CYP450 enzyme that capable of converting humulene into 8-hydroxy-α-humulene in C. wenyujin. However, unfortunately, we failed to find this CYP450. Instead, we continued to investigate the short-chain dehydrogenase (SDR) that catalyzes the downstream synthesis of zerumbone.
To identify the SDR responsible for zerumbone biosynthesis in C. wenyujin, we collected a subset of dehydrogenase genes from various plants, including Lavandula angustifolia, Arabidopsis thaliana and Zingiber zerumbet, which are involved in the generation of terpenoid dehydrogenation products (Supplementary Table S3). Additionally, three candidate short-chain dehydrogenase genes were selected based on the functional annotation of the transcriptomic data. Subsequently, we conducted a phylogenetic analysis of these candidate genes alongside the previously mentioned plant-derived terpenoid SDRs. The results indicated that one of the candidate genes, CwSDR1, clustered into a clade with the reference SDRs (Supplementary Figure S7), suggesting conserved catalytic roles in terpenoid metabolism. Sequence analysis revealed that CwSDR1 is classified as an extended SDR, containing the characteristic Rossmann fold, the conserved cofactor-binding motif “TGxxxGxG” and the catalytic triad “SYK” motif (Figure 5A) (Zhang et al., 2023b).
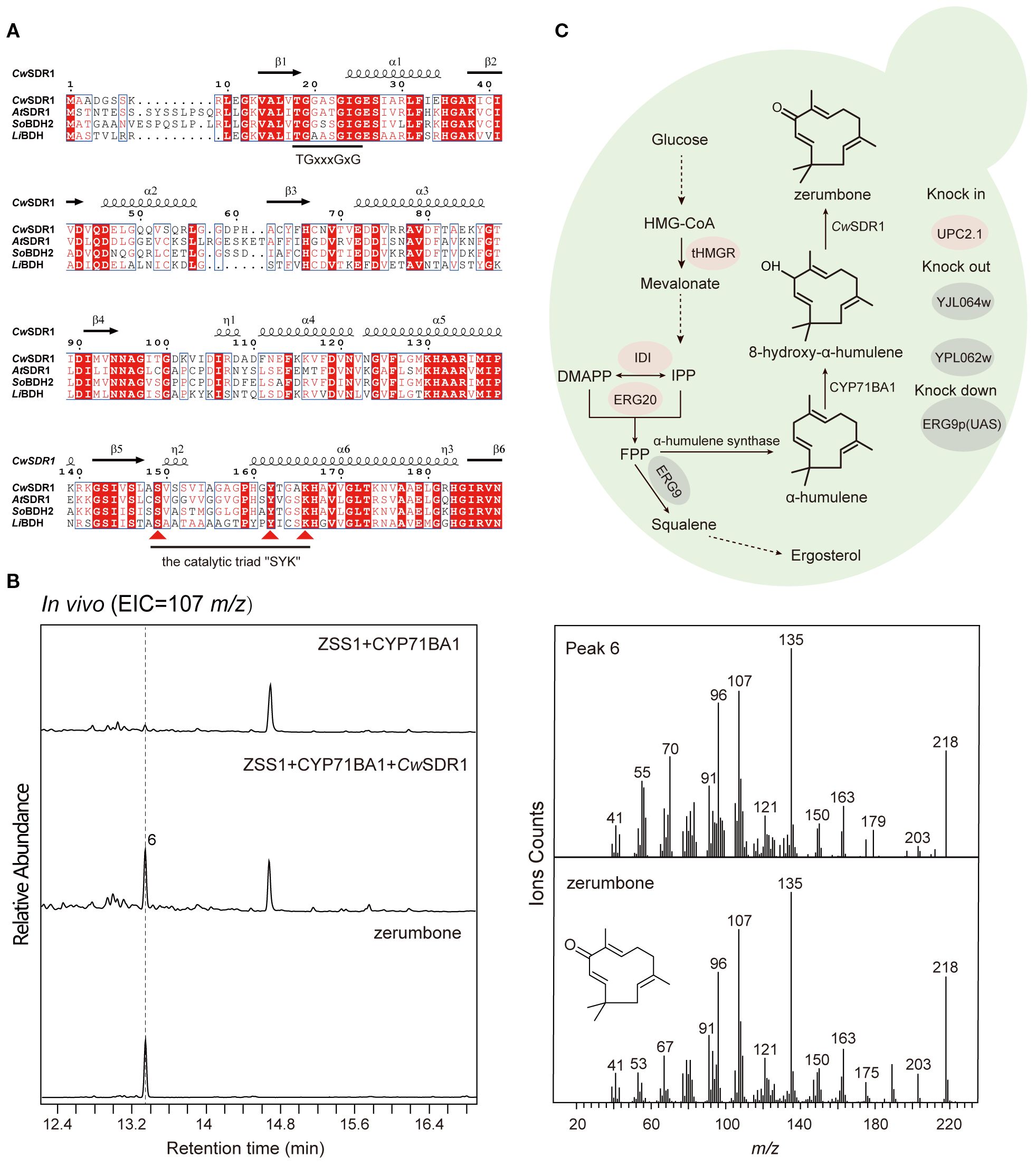
Figure 5. Sequence analysis and functional characterization of CwSDR1 and the construction of a yeast strain for the de novo synthesis of zerumbone. (A) Sequence analysis of CwSDR1, containing the Rossmann fold, the conserved cofactor-binding motif “TGxxxGxG” and the catalytic triad “SYK” motif; (B) GC-MS analysis of the products of yeast strains expressing CwSDR1; (C) Construction of the endogenous zerumbone biosynthetic pathway in yeast, with red highlighting overexpressed genes and gray indicating knockout/downregulated genes.
3.5 CwSDR1 catalyzes the conversion of 8-hydroxy-α-humulene into zerumbone
The gene CwSDR1 was cloned into the eukaryotic expression vector pESC-Ura and co-transformed with CYP71BA1, which produces 8-hydroxy-α-humulene, into the engineered yeast strain with high-yield α-humulene, FY94-1 (Supplementary Table S2). GC-MS analysis revealed that 8-hydroxy-α-humulene was undetectable in the fermentation products of the control strain harboring CYP71BA1. Instead, a trace amount of zerumbone was observed, likely due to the spontaneous conversion of the unstable allylic secondary alcohol group in 8-hydroxy-α-humulene under the mildly acidic intracellular environment of yeast. In contrast, a pronounced peak corresponding to zerumbone was detected in the engineered strain expressing CwSDR1 (Figure 5B). Quantitative analysis revealed a 357% increase in zerumbone production compared to the control strain. This result suggested that CwSDR1 is a short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) that catalyzes the dehydrogenation of 8-hydroxy-α-humulene to zerumbone (6). Additionally, the strain FY94–3 that capable of de novo biosynthesis of the anticancer compound zerumbone was constructed (Figure 5C). However, the yield of zerumbone reached only 0.50 μg/L (1.88 μg/g DCW), with a specific productivity of 0.03 μg/g DCW/h. This low yield may be attributed to the limited catalytic efficiency of the natural CYP450 oxidase, CYP71BA1.
4 Discussion
This study successfully cloned and functionally characterized two pivotal terpenoid biosynthetic genes from C. wenyujin: the multifunctional sesquiterpene synthase CwTPS8 and short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) CwSDR1. In vitro, CwTPS8 catalyzes the conversion of FPP into β-caryophyllene (1) and α-humulene (2), which is a precursor of zerumbone. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, CwTPS8 not only produced these primary products but also generated cryptomeridiol (5) and two accessory sesquiterpenoids: caryophyllenyl alcohol (3) and neointermedeol (4). Enzyme CwSDR1 was demonstrated to dehydrogenate 8-hydroxy-α-humulene into zerumbone (6). Mechanistic investigation of enzyme CwTPS8 through molecular docking and site-directed mutagenesis identified critical amino acid residues that govern catalytic activity. The change of its spatial conformation will directly inactivate the enzyme or greatly reduce the product yield.
While β-caryophyllene and α-humulene are the primary products of CwTPS8, the suboptimal yield of α-humulene restricts its utility in constructing high-titer zerumbone-producing microbial chassis. To address this bottleneck, future efforts will focus on enzyme engineering of CwTPS8 through molecular dynamics (MD)-guided rational design and evolutionary divergence analysis, combined with site-directed mutagenesis to refine catalytic specificity. Concurrently, synthetic biology strategies—including the integration of strong constitutive promoters and amplification of plasmid copy number—will be implemented to enhance the efficiency of α-humulene production.
The suboptimal yield of zerumbone catalyzed by the enzyme CwSDR1 may result from several bottlenecks: (1) insufficient activity of the P450 hydroxylase, which limits the supply of precursors; (2) inadequate NADPH regeneration capacity, constraining redox cofactor availability; and (3) the intrinsic catalytic inefficiency of CwSDR1. To address these limitations, future research could employ QM/MM simulations to elucidate the mechanistic details of hydroxylation and oxidative dehydrogenation reactions. These insights would inform substrate channel engineering and the identification of rate-limiting residues for targeted mutagenesis. Concurrent strategies include (1) optimizing cofactor utilization through enhanced NADPH recycling via overexpression of NAD+/NADH kinases and NADP+ pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes; (2) enzyme engineering via high-throughput screening of evolved CYP450 libraries to identify hyperactive variants for the hydroxylation step; and (3) metabolic rewiring through dynamic regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway to rebalance NADPH flux.
This study comprehensively elucidates two pivotal stages in the biosynthetic pathway of zerumbone: the formation of the sesquiterpene scaffold and terminal functionalization. Furthermore, CwTPS8 demonstrated catalytic promiscuity in both in vitro and in vivo systems, thereby expanding the enzyme repertoire for the diversification of sesquiterpenoids. These findings establish a theoretical framework for engineering high-yield terpenoid-producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell factories and optimizing the efficiency of zerumbone bioproduction.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
MX: Software, Writing – original draft, Validation, Data curation, Visualization, Methodology, Investigation. YX: Software, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Validation. GF: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Investigation. TL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. JM: Writing – original draft, Software, Investigation. DL: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Software. QW: Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. LT: Investigation, Funding acquisition, Data curation, Writing – original draft. XY: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Data curation, Project administration. TH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Key project at central government level: The ability establishment of sustainable use for valuable Chinese medicine resources (No. 2060302), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 2025M773896), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LY24H280006), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LQ23H280002), the Interdisciplinary Research Project of Hangzhou Normal University (2025JCXK02), and the Program of “Xinmiao” (Potential) Talents in Zhejiang Province (2025R441B068).
Conflict of interest
Authors QW and TH were employed by the company Zhejiang Medicine Co., Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1635141/full#supplementary-material
References
Alsaffar, R. M., Ali, A., Rashid, S. M., Ahmad, S. B., Alkholifi, F. K., Kawoosa, M. S., et al. (2023). Zerumbone protects rats from collagen-induced arthritis by inhibiting oxidative outbursts and inflammatory cytokine levels. ACS Omega 8, 2982–2991. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c05749
Chen, H., Yue, Y., Yu, R., and Fan, Y. (2019). A Hedychium coronarium short chain alcohol dehydrogenase is a player in allo-ocimene biosynthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 101, 297–313. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00904-z
Chen, X. and Facchini, P. J. (2014). Short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase catalyzing the final step of noscapine biosynthesis is localized to laticifers in opium poppy. Plant J. 77, 173–184. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12379
Choi, S. H., Lee, Y. J., Seo, W. D., Lee, H. J., Nam, J. W., Lee, Y. J., et al. (2011). Altered cross-linking of HSP27 by zerumbone as a novel strategy for overcoming HSP27-mediated radioresistance. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 79, 1196–1205. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2010.10.025
Christianson, D. W. (2006). Structural biology and chemistry of the terpenoid cyclases. Chem. Rev. 106, 3412–3442. doi: 10.1021/cr050286w
Christianson, D. W. (2017). Structural and chemical biology of terpenoid cyclases. Chem. Rev. 117, 11570–11648. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00287
Chu, C., Wang, S., Jiang, L., Liu, C., Zhang, H., and Yan, J. (2019). Microwave-assisted ionic liquid-based micelle extraction combined with trace-fluorinated carbon nanotubes in dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction to determine three sesquiterpenes in roots of Curcuma wenyujin. Phytochem. Anal. 30, 700–709. doi: 10.1002/pca.2848
Davis, E. M., Ringer, K. L., McConkey, M. E., and Croteau, R. (2005). Monoterpene metabolism. Cloning, expression, and characterization of menthone reductases from peppermint. Plant Physiol. 137, 873–881. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.053306
de Kraker, J. W., Franssen, M. C., Dalm, M. C., de Groot, A., and Bouwmeester, H. J. (2001). Biosynthesis of germacrene A carboxylic acid in chicory roots. Demonstration of a cytochrome P450 (+)-germacrene a hydroxylase and NADP+-dependent sesquiterpenoid dehydrogenase(s) involved in sesquiterpene lactone biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 125, 1930–1940. doi: 10.1104/pp.125.4.1930
Durairaj, J., Di Girolamo, A., Bouwmeester, H. J., de Ridder, D., Beekwilder, J., and van Dijk, A. D. J. (2019). An analysis of characterized plant sesquiterpene synthases. Phytochemistry 158, 157–165. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.10.020
Fellows, R., Russo, C. M., Silva, C. S., Lee, S. G., Jez, J. M., Chisholm, J. D., et al. (2018). A multisubstrate reductase from Plantago major: structure-function in the short chain reductase superfamily. Sci. Rep. 8 (1), 14796. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32967-1
Gonzalez, V., Touchet, S., Grundy, D. J., Faraldos, J. A., and Allemann, R. K. (2014). Evolutionary and mechanistic insights from the reconstruction of α-humulene synthases from a modern (+)-germacrene A synthase. J. Am. Chem. Soc 136, 14505–14512. doi: 10.1021/ja5066366
Hu, Y., Zhang, Q., Bai, X., Men, L., Ma, J., Li, D., et al. (2024). Screening and modification of (+)-germacrene A synthase for the production of the anti-tumor drug (-)-β-elemene in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 279, 135455. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135455
Kavanagh, K. L., Jörnvall, H., Persson, B., and Oppermann, U. (2008). Medium- and short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase gene and protein families: the SDR superfamily: functional and structural diversity within a family of metabolic and regulatory enzymes. Cell Mol. Life. Sci. 65, 3895–3906. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8588-y
Ker, D. S., Chan, K. G., Othman, R., Hassan, M., and Ng, C. L. (2020). Site-directed mutagenesis of β sesquiphellandrene synthase enhances enzyme promiscuity. Phytochemistry 173, 112286. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112286
Kitaoka, N., Wu, Y., Zi, J., and Peters, R. J. (2016). Investigating inducible short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases/reductases clarifies rice oryzalexin biosynthesis. Plant J. 88, 271–279. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13249
Kramm, A., Kisiela, M., Schulz, R., and Maser, E. (2012). Short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases in cyanobacteria. FEBS J. 279, 1030–1043. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08494.x
Kumar, M. N., Dandela, R., and Gopinath, P. (2025). A Review on zerumbone and its semisynthetic Analogs: Synthesis and Implications in Medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Chem. 154, 108074. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2024.108074
Labesse, G., Vidal-Cros, A., Chomilier, J., Gaudry, M., and Mornon, J. P. (1994). Structural comparisons lead to the definition of a new superfamily of NAD(P)(H)-accepting oxidoreductases: the single-domain reductases/epimerases/dehydrogenases (the ‘RED’ family). Biochem. J. 304, 95–99. doi: 10.1042/bj3040095
Li, Y., Liu, J., Wu, Y., Li, Y., and Guo, F. (2022). Guaiane-type sesquiterpenes from Curcuma wenyujin. Phytochemistry 198, 113164. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2022.113164
Li, J., Wang, L., Sun, Y., Wang, Z., Qian, Y., Duraisamy, V., et al. (2023). Zerumbone-induced reactive oxygen species-mediated oxidative stress re-sensitizes breast cancer cells to paclitaxel. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 70, 28–37. doi: 10.1002/bab.2326
Li, L., Wu, X. H., Zhao, X. J., Xu, L., Pan, C. L., and Zhang, Z. Y. (2020). Zerumbone ameliorates behavioral impairments and neuropathology in transgenic APP/PS1 mice by suppressing MAPK signaling. J. Neuroinflamm. 17, 61. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01744-1
Lin, W., Tu, H., Zhu, Y., Guan, Y., Liu, H., Ling, W., et al. (2019). Curcumolide, a unique sesquiterpenoid from Curcuma wenyujin displays anti-angiogenic activity and attenuates ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization. Phytomedicine 64, 152923. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152923
Liu, Y., Wu, S., Lan, K., Wang, Q., Ye, T., Jin, H., et al. (2023). An investigation of the JAZ family and the CwMYC2-like protein to reveal their regulation roles in the MeJA-induced biosynthesis of β-elemene in Curcuma wenyujin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 15004. doi: 10.3390/ijms241915004
Lopez-Gallego, F., Agger, S. A., Abate-Pella, D., Distefano, M. D., and Schmidt-Dannert, C. (2010). Sesquiterpene synthases Cop4 and Cop6 from Coprinus cinereus: catalytic promiscuity and cyclization of farnesyl pyrophosphate geometric isomers. Chembiochem 11, 1093–1106. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200900671
Ma, J., Li, D., Xu, M., Xia, Y., Fang, G., Wei, Q., et al. (2025). Multifunctional sesquiterpene synthase from Curcuma wenyujin reveals the biosynthetic mechanism of sesquiterpenes with diverse skeletons. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 318, 145152. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145152
Mai, J., Li, W., Ledesma-Amaro, R., and Ji, X. J. (2021). Engineering plant sesquiterpene synthesis into yeasts: A Review. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 69, 9498–9510. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03864
Marmont, L. S., Whitfield, G. B., Pfoh, R., Williams, R. J., Randall, T. E., Ostaszewski, A., et al. (2020). PelX is a UDP-N-acetylglucosamine C4-epimerase involved in Pel polysaccharide-dependent biofilm formation. J. Biol. Chem. 295, 11949–11962. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.014555
Memari, F., Mirzavi, F., Jalili-Nik, M., Afshari, A. R., Ghorbani, A., and Soukhtanloo, M. (2022). Tumor-inhibitory effects of zerumbone against HT-29 human colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Toxicol. 41, 402–411. doi: 10.1177/10915818221104417
Nie, S., Wang, S., Chen, R., Ge, M., Yan, X., and Qiao, J. (2024). Catalytic mechanism and heterologous biosynthesis application of sesquiterpene synthases. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 72, 6871–6888. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c00030
Okamoto, S., Yu, F., Harada, H., Okajima, T., Hattan, J.-I., Misawa, N., et al. (2011). A short-chain dehydrogenase involved in terpene metabolism from Zingiber zerumbet. FEBS J. 278, 2892–2900. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08211.x
Segura, M. J. R., Jackson, B. E., and Matsuda, S. P. T. (2003). Mutagenesis approaches to deduce structure-function relationships in terpene synthases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 20, 304–317. doi: 10.1039/b008338k
Starks, C. M., Back, K., Chappell, J., and Noel, J. P. (1997). Structural basis for cyclic terpene biosynthesis by tobacco 5-epi-aristolochene synthase. Science 277, 1815–1820. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5333.1815
Stavrinides, A. K., Tatsis, E. C., Dang, T. T., Caputi, L., Stevenson, C. E. M., Lawson, D. M., et al. (2018). Discovery of a short-chain dehydrogenase from Catharanthus roseus that produces a new monoterpene indole alkaloid. Chembiochem 19, 940–948. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201700621
Tsuboi, K., Matsuo, Y., Shamoto, T., Shibata, T., Koide, S., Morimoto, M., et al. (2014). Zerumbone inhibits tumor angiogenesis via NF-κB in gastric cancer. Oncol. Rep. 31, 57–64. doi: 10.3892/or.2013.2842
Urla, C., Stagno, M. J., Fuchs, J., Warmann, S. W., and Schmid, E. (2023). Anticancer bioactivity of zerumbone on pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 149, 3313–3323. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04237-1
Vattekkatte, A., Garms, S., Brandt, W., and Boland, W. (2018). Enhanced structural diversity in terpenoid biosynthesis: enzymes, substrates and cofactors. Org. Biomol. Chem. 16, 348–362. doi: 10.1039/c7ob02040f
Wang, Y., Fan, K., Wang, J., Ding, Z. T., Wang, H., Bi, C. H., et al. (2017). Proteomic analysis of Camellia sinensis (L.) reveals a synergistic network in the response to drought stress and recovery. J. Plant Physiol. 219, 91–99. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2017.10.001
Wang, J. G., Li, D. L., Fan, R., and Yan, M. J. (2023). Zerumbone combined with gefitinib alleviates lung cancer cell growth through the AKT/STAT3/SLC7A11 axis. Neoplasma 70, 58–70. doi: 10.4149/neo_2022_220418N423
Wei, Q., Lan, K., Liu, Y., Chen, R., Hu, T., Zhao, S., et al. (2022). Transcriptome analysis reveals regulation mechanism of methyl jasmonate-induced terpenes biosynthesis in Curcuma wenyujin. PloS One 17, e0270309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0270309
Wu, S., Lan, K., Wang, Q., Su, Y., Li, D., Ma, J., et al. (2025). Comprehensive characterization of the bHLH transcription factor family in Curcuma wenyujin and functional elucidation of CwbHLH27 in jasmonate-regulated sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 220, 109527. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109527
Yang, S., Wang, N., Kimani, S., Li, Y., Bao, T., Ning, G., et al. (2022). Characterization of terpene synthase variation in flowers of wild aquilegia species from Northeastern Asia. Hortic. Res. 9, uhab020. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhab020
Yu, F., Okamoto, S., Harada, H., Yamasaki, K., Misawa, N., and Utsumi, R. (2011). Zingiber zerumbet CYP71BA1 catalyzes the conversion of α-humulene to 8-hydroxy-α-humulene in zerumbone biosynthesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 1033–1040. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0506-4
Yu, F., Okamto, S., Nakasone, K., Adachi, K., Matsuda, S., Harada, H., et al. (2008). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of α-humulene synthase, a possible key enzyme of zerumbone biosynthesis in shampoo ginger (Zingiber zerumbet Smith). Planta 227, 1291–1299. doi: 10.1007/s00425-008-0700-x
Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Liu, J., Wang, S., et al. (2023b). Bioinformatic analysis of short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase proteins in plant peroxisomes. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1180647
Zhang, S. Y., Zhang, W. S., Martin, J. J. J., Qadri, R., Fu, X. P., Feng, M. L., et al. (2023a). Differential analysis of transcriptomic and metabolomic of free fatty acid rancidity process in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) fruits of different husk types. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1132024
Keywords: zerumbone, α-humulene, sesquiterpene synthase, short-chain dehydrogenase, Curcuma wenyujin
Citation: Xu M, Xia Y, Fang G, Li T, Ma J, Li D, Wei Q, Tu L, Yin X and Hu T (2025) Characterization of a sesquiterpene synthase and a short-chain dehydrogenase in zerumbone biosynthesis and the applications in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1635141. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1635141
Received: 26 May 2025; Accepted: 15 September 2025;
Published: 03 October 2025.
Edited by:
Qian Shen, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, ChinaReviewed by:
Shengli Wang, Tianjin University, ChinaRicardo Alfonso González-Hernández, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Xia, Fang, Li, Ma, Li, Wei, Tu, Yin and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaopu Yin, eWlueHBAaHpudS5lZHUuY24=; Tianyuan Hu, aHV0aWFueXVhbkBoem51LmVkdS5jbg==
 Mengdie Xu
Mengdie Xu Yimeng Xia1
Yimeng Xia1 Qiuhui Wei
Qiuhui Wei Xiaopu Yin
Xiaopu Yin Tianyuan Hu
Tianyuan Hu