- 1Division of Plant Pathology, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi, India
- 2State Key Laboratory of North China Crop Improvement and Regulation, Hebei Agricultural University, Baoding, China
- 3Indian Council of Agricultural Research, National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources, New Delhi, India
- 4Centre for Crop Health, University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba, QLD, Australia
- 5School of Agriculture and Environmental Science, University of Southern Queensland, Toowoomba, QLD, Australia
Spot blotch, caused by Bipolaris sorokiniana, is an important disease that leads to significant economic losses in wheat globally. Due to the complexity of B. sorokiniana infection, identification of wheat lines with strong resistance to spot blotch is challenging. Hence, the introduction of effective disease management strategies through the manipulation of genes involved in B. sorokiniana–wheat interaction remains essential. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a vital role in gene regulation and are increasingly used to predict molecular networks and genes associated with disease development or resistance. In this study, we employed small RNA sequencing to profile miRNAs in a resistant (IC566637) and a susceptible (Agra Local) wheat genotype following B. sorokiniana infection. A total of 726 miRNAs, predominantly 21 to 22 nucleotides in length, were identified. Among these, 140 are differentially expressed (DE) and associated with the modulation of 894 genes. The Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analysis revealed these target genes as secondary metabolites, ATB-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NB-LRR), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) genes, and hormones associated with plant–pathogen interaction and defense signal transduction. The regulatory network constructed from this data highlights key miRNA–target interactions likely contributing to disease resistance. Quantitative RT-PCR validation of nine selected miRNAs and their corresponding target genes further supports their potential role in modulating wheat defense responses. These findings provide a comprehensive resource for understanding miRNA-mediated regulation in the wheat–B. sorokiniana pathosystem and identified promising candidate genes for future resistance breeding and genome editing efforts.
1 Introduction
Spot blotch, caused by Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc.), is among the most dreadful diseases of wheat worldwide and a serious issue in Southeast Asia due to hot and humid weather conditions (Chaurasia et al., 2000; Chand et al., 2008; Vaish et al., 2011; Al-Sadi, 2016). In India, although the disease was first reported in 1914, its incidence became more frequent after the green revolution, as the introduction of dwarf varieties with narrow genetic diversity aggravated the disease both domestically as well as in its neighboring countries such as China, Bangladesh, and Nepal (Singh et al., 2016; Gupta et al., 2018). Other than wheat, B. sorokiniana is also responsible for root rot and leaf spot diseases in other cereals such as oat, barley, maize, and rice (Devi et al., 2018; Basak et al., 2024).
In wheat, yield losses due to spot blotch disease range from 15%–25% and can lead to total crop loss in severe epidemic conditions (Sahu et al., 2016). The present wheat varieties lack sufficient resistance to this disease due to the pathogen’s hemibiotrophic nature, high population diversity, and its ability to alter the expression of host defense genes (Aggarwal et al., 2009; Gurjar et al., 2018; Singh et al., 2018; Tembo et al., 2018; Aggarwal et al., 2019). Understanding the molecular basis of host–pathogen interactions is essential to develop durable resistance and informed breeding strategies.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that play key roles in regulating gene expression during plant development and stress responses, including biotic stresses caused by pathogens. These molecules also regulate immune signaling pathways during pathogen infection and disease development (Islam et al., 2018; Šečić et al., 2021). For instance, ath-miR393, induced by flg22, was the first identified miRNA associated with plant immunity, conferring resistance to Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato by targeting receptors in auxin signaling (Navarro et al., 2006). Other miRNAs, such as ath-miR398b, ath-miR160a, and ath-miR773, have been associated with the regulation of pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) and cell-wall-associated defense responses in Arabidopsis (Li et al., 2010). In rice, overexpression of miR164a, targeting NAC (NAM, ATAF1/2, and CUC2) transcription factor, was linked with susceptibility to Magnaporthe oryzae (Wang et al., 2018). Notably, this regulatory module is conserved for various crop diseases, including sheath blight, late blight, and root/stem rot diseases in rice, tomato, and soybean, respectively.
In wheat, miR156, miR166, miR167, miR398, and miR399 were associated with resistance to leaf rust, while miR7723 promotes susceptibility (Kumar et al., 2016). Furthermore, the defense-related genes such as Leucine-rich repeat (LRR) receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase (targeted by bdi-miR167), Resistance to Peronospora parasitica (RPP)8 (targeted by TamiR007), and Resistance to Pseudomonas maculicola (RPM)1-like (targeted by TamiR138) were among the major types targeted by miRNAs (Kumar et al., 2016). However, the role of miRNAs in wheat defense against B. sorokiniana remains unclear due to technological limitations and the absence of a complete wheat reference genome. For instance, Inal et al. (2014) utilized microarray technology to identify miRNAs (miR164, miR169, miR319, and miR398) involved in the wheat–B. sorokiniana interaction but failed to detect significant differences in their expression in resistant and susceptible cultivars. Later, Sharma et al. (2021) reported only the miRNAs (ptc-miR169, ptc-miR1450, and tae-miR156) identified from other pathosystems.
More recently, Vasistha et al. (2025) used differentially expressed (DE) genes in B. sorokiniana-infected wheat genotypes to predict miRNAs; however, the absence of direct small RNA (sRNA) profiling limited the resolution and accuracy of miRNA identification in the study. In light of these gaps, our study adopts a comprehensive approach using sRNA sequencing to analyze the differential expression of miRNAs in resistant and susceptible wheat genotypes following B. sorokiniana infection. Furthermore, with the gold standard chromosomal-level wheat genome assembly, a more comprehensive chromosome-wise in silico miRNA prediction allows the discovery of both the novel and conserved miRNAs. This enables the construction of a complete “atlas” of miRNAs involved in B. sorokiniana–wheat interaction, providing a more robust and precise understanding of the gene regulatory networks in this host–pathogen interaction (Jaiswal et al., 2019).
Our analysis revealed a set of DE miRNAs associated with the regulation of key defense-related genes, including those involved in hormone signaling, secondary metabolism, ABC transporters, NB-LRR resistance proteins, and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades. Further validation through stem loop qRT-PCR supported the involvement of selected miRNAs and their targets in modulating wheat’s response to infection. To our knowledge, this is the first study to provide a publicly available sRNA dataset specific to the wheat–B. sorokiniana interaction. These findings not only enhance our understanding of miRNA-mediated defense mechanisms in wheat but also identify promising candidate targets for future functional validation and genetic improvement efforts aimed at enhancing spot blotch resistance.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material and fungal inoculation
The spot-blotch-resistant wheat genotype IC566637 was obtained from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)—National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR), New Delhi, India, while Agra Local served as the susceptible control. Seeds were sown in 4-inch. pots containing pre-sterilized soil and maintained at 25 ± 2 °C in the greenhouse at the Division of Plant Pathology, ICAR—Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), New Delhi. A pure culture of B. sorokiniana isolate BS-22 (virulent on Agra Local, NCBI accession number ON892001, Indian Type Culture Collection identification number 9114), mass-cultured using potato dextrose agar medium and autoclaved sorghum grains (25–30 days), was used for the study. Seedlings at the three- to four-leaf stage were inoculated with the spore suspension (104 conidia/mL) using a precision hand atomizer. Sterile distilled water was used as untreated control. To maintain high humidity (>90%), the plants were kept in a humidity chamber box for 24–48 h. Treatments consisted of susceptible inoculated (SI) and susceptible untreated control (SC) as well as resistant inoculated (RI) and resistant untreated control (RC). Leaf samples from inoculated and control plants were collected at 0, 12, 24, 36, 48, and 60 h post-inoculation in liquid nitrogen and stored in a deep freezer at -80°C until further use. Each sample consisted of three biological replicates.
2.2 RNA extraction, small RNA library preparation, and sequencing
For small RNA sequencing (sRNA-seq), two biological replicates per treatment were used, with samples pooled across time points. Total RNA was extracted from leaf tissue using the Direct-ZOL mini kit (Zymo Research) following standard protocols. RNA concentration and purity were measured using a Nanodrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, 2000). The proportion of miRNA in the samples were determined using a Bioanalyzer (Agilent), while RNA quantification was performed with the Qubit RNA HS assay kit (Thermo Scientific). QIAseq® miRNA Library Kit (Qiagen) standard protocol was used to generate the sRNA-seq libraries. In brief, 63 ng of total RNA was used as initial input. The 3′ adapters were selectively ligated to the 3′OH group of miRNAs, followed by 5′ adapter ligation. The ligated fragments were subjected to reverse transcription with Unique Molecular Index (UMI) assignment by priming using reverse transcription primers. The resulting cDNA was then amplified and barcoded through PCR amplification (17 cycles). The Illumina-compatible sequencing libraries were quantified using the Qubit fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA). Finally, single-end sequencing was performed for 50 cycles on Illumina NovaSeq 6000 High Output sequencing platform using SE50 read length and sequencing chemistry.
2.3 Sequencing data analysis, identification of known and novel miRNAs
Raw reads of 16–40 bases in length were filtered and mapped to the Triticum aestivum reference genome (PRJNA669381) using Bowtie (https://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net/index.shtml) (Langmead et al., 2009). The reads were then specifically aligned to sRNA. The obtained reads were further aligned with noncoding RNA database to filter out rRNA, tRNA, and snoRNAs. The remaining unaligned and high-quality reads (Q30 ≥ 90%) were classified as known or novel miRNAs through a homology approach against Viridiplantae miRNAs from miRBase22 (miRBase) (Friedländer et al., 2012) using the NCBI-BLAST-2.2.304 with an e-value cutoff of e-4 and non-gapped alignment. Non-homologous sequences were analyzed using Mireap_0.22b, and those forming stem loop structures were considered as novel miRNAs. To eliminate the potential effect of B. sorokiniana miRNAs on wheat, all of the detected miRNAs were cross-referenced against B. sorokiniana genome.
2.4 Differential expression analysis of miRNA and its target prediction
Read counts for known and novel miRNAs were obtained to analyze their expression patterns. DE analysis was conducted using DESeq (version 2) (Anders and Huber, 2010), an R package with a threshold of log2 (fold change, FC) ≥1 and false discovery rate (FDR) ≤0.05. Read variations were normalized using DESeq2’s library normalization method, where size factors were calculated and each count was divided by its corresponding factor. The average normalized read counts of samples in each condition were utilized for differential gene expression calculation. For target prediction analysis, miRNAs with a copy number ≥5 were selected. These miRNA sequences were used as input along with wheat–B. sorokiniana transcriptome sequences (unpublished) to the miRanda tool (Griffiths-Jones et al., 2008), with the following default parameters: (1) using the strict alignment in the seed region (offset positions 2–8), preventing detection of target sites containing gaps or non-canonical base pairing in this region, (2) maximum expectation, and (3) target accessibility—allowed maximum energy to unpair the target site (UPE) 25. The DE miRNAs across eight sRNA-seq samples were clustered based on their log2FC values, with those displaying similar expression patterns grouped using R package Heatmap version 1.0. The associated target genes of DE miRNAs were analyzed for the GO and the KEGG enrichment to identify significantly enriched functional categories.
2.5 Annotation of miRNA-target genes, GO and KEGG pathway analysis
The identified target gene sequences were annotated with the BLAST2GO software (BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (nih.gov), GO (http://www.geneontology.org/), KEGG (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/), Pfam (http://pfam.xfam.org/), InterPro (InterPro (ebi.ac.uk)), and Panther (pantherdb.org). Furthermore, the identified target genes were analyzed for GO (http://www.geneontology.org/) and KEGG (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/) (Kanehisa and Goto, 2000) enrichment analysis with FDR cutoff of 0.05. The networks of DE miRNAs along with their associated DE target genes were prepared using Cytoscape (v.3.10.2) (Shannon et al., 2003).
2.6 Validation of miRNAs and their target genes by qRT-PCR
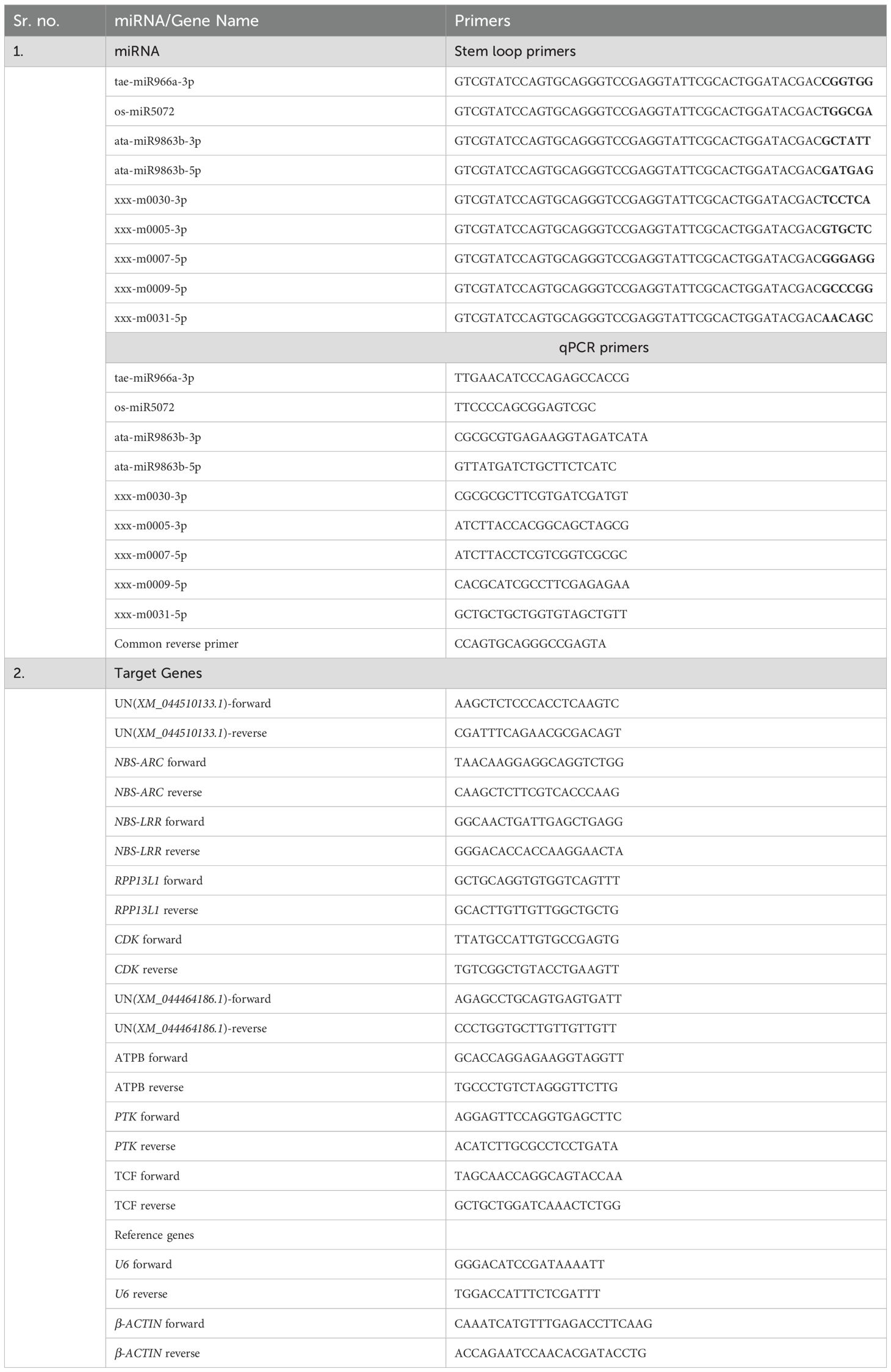
The same samples used for sRNA-seq were also employed to validate miRNA expression and their corresponding target genes. RNA isolated from infected leaves was converted into cDNA using the Verso cDNA synthesis kit (Thermo Scientific) with miRNA-specific stem loop primers (Kramer, 2015). As per the protocol described by Varkonyi-Gasic et al. (2007), forward and universal reverse primers were designed for the selected nine miRNAs. The U6 small nuclear RNA (U6 snRNA) was the internal control gene for normalization. The correlation of miRNA expression in qRT-PCR (log2FC) and sRNA-seq was analyzed using the scatter plot. Based on the sequences of nine predicted target genes associated with the nine selected miRNAs, their specific qPCR primers were designed on GeneScript (Real Time PCR Primer Design - Real Time PCR Probe Design - GenScript). β-actin was used as an internal control gene. The qRT-PCR analysis of miRNAs and their corresponding target genes was performed using the Bio-Rad CFX96 system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., India) in the genomics laboratory of the Discovery Centre, ICAR-IARI, New Delhi, India. The list of primers used is given in Table 1.
3 Results
3.1 High-throughput sequencing and identification of known and novel miRNAs
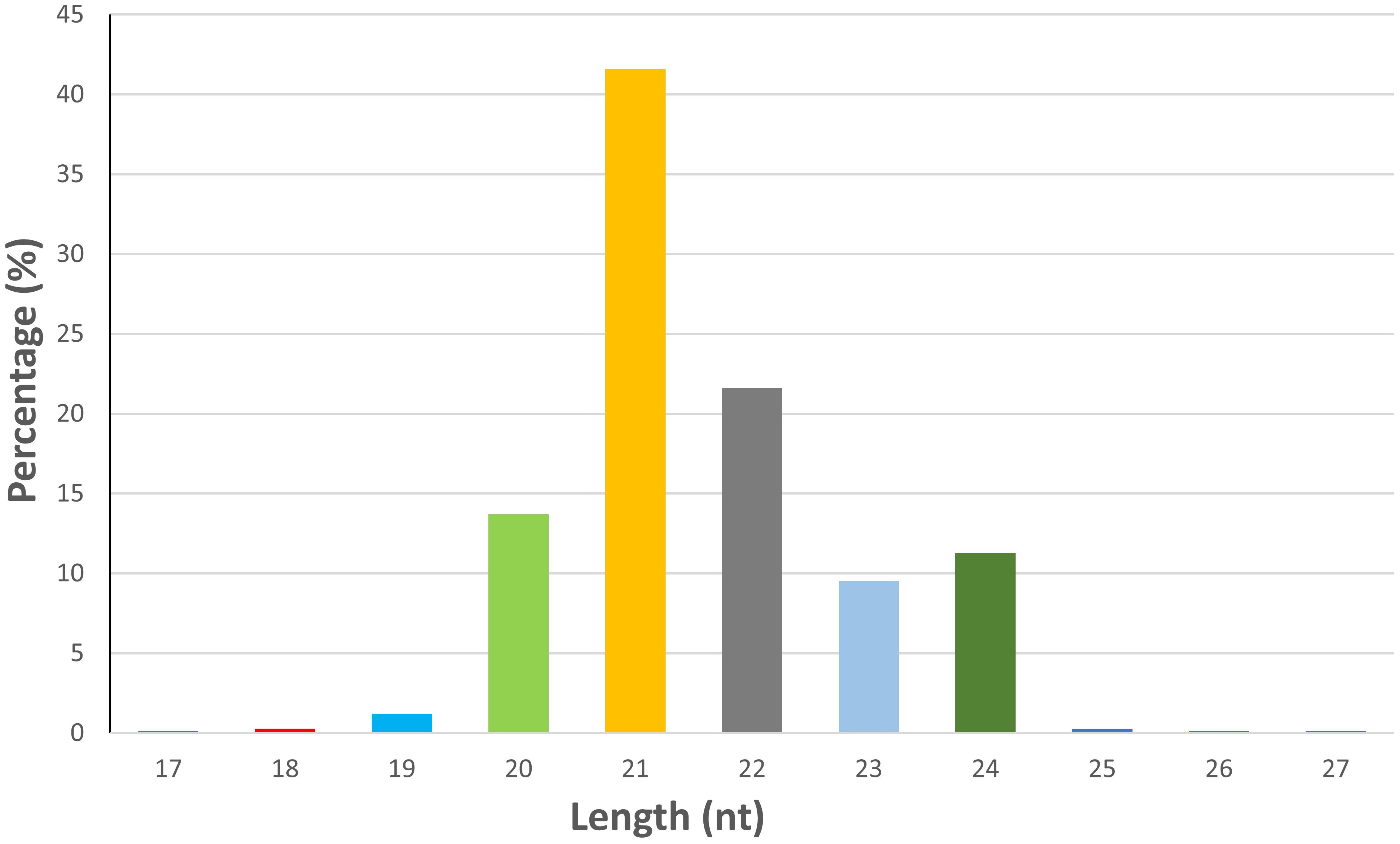
An average of 19.73 million reads were generated as raw reads from the eight wheat samples comprising untreated and B. sorokiniana-inoculated wheat leaves. This data has been uploaded in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database of NCBI with Bioproject number PRJNA944096. After stringent quality filtering and removal of low-quality reads, adapters, and sequences shorter than 16 nt, an average of 12.2 million high-quality reads (Q30 ≥ 90%) with a read length between 16 and 40 nt were retained for downstream analysis (Supplementary Table S1). A total of 736 miRNAs were identified across all samples, including 418 known and 318 novel miRNAs (Supplementary Table S2). The majority of the identified miRNAs were 21 nt (41.57%) in length, followed by 22 nt (21.60%), 20 nt (13.72%), and 24 nt (11.27%) (Figure 1). The symptomatic response of the resistant genotype IC566637 and suscpetible variety Agra local at 4 days post-inoculation is shown in Figure 2.
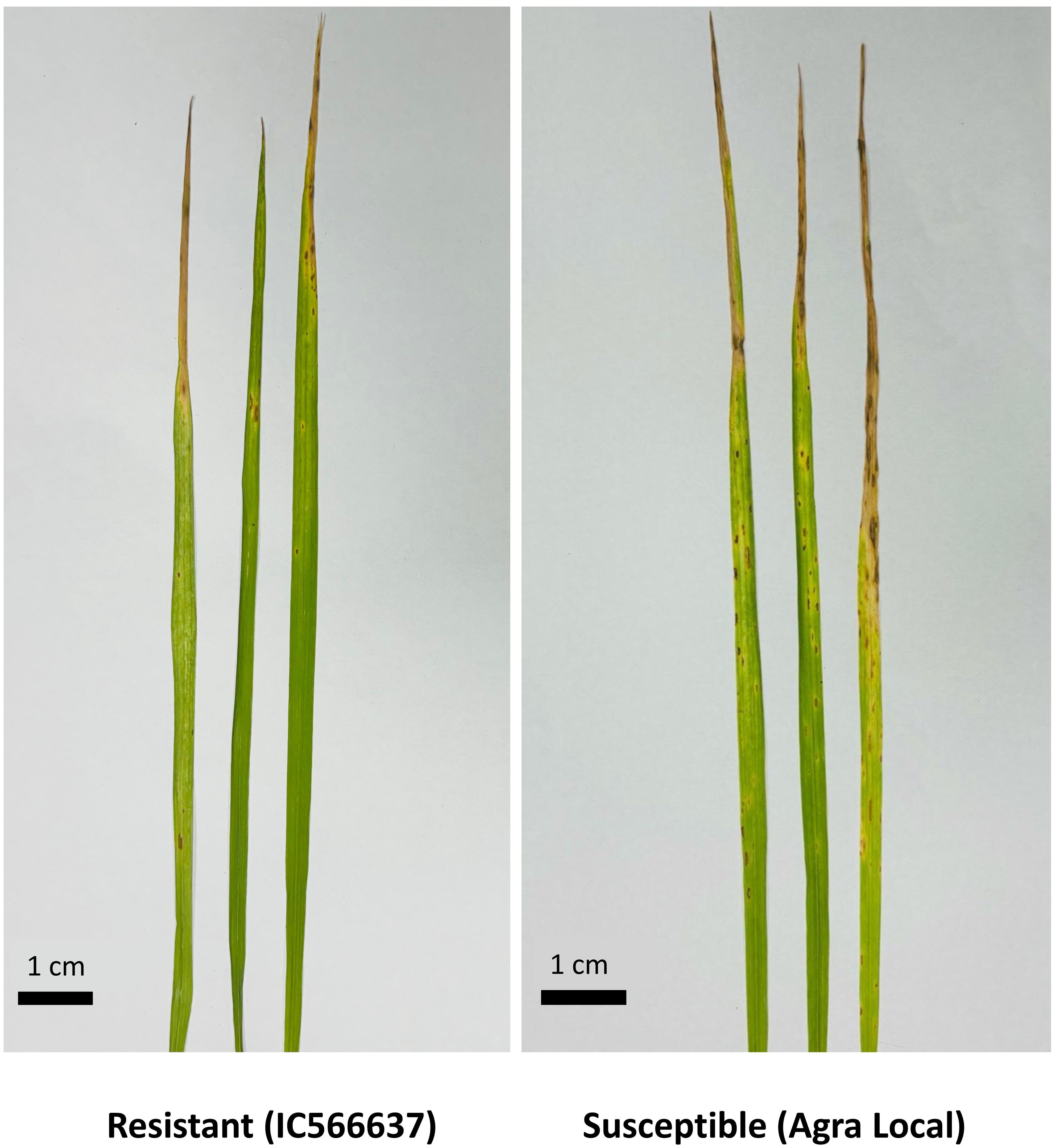

Figure 2. Visual symptoms on wheat leaves at 7 days post-inoculation with Bipolaris sorokiniana. Representative images show disease response in resistant (left) and susceptible (right) wheat lines.
3.2 MicroRNA expression profiles upon B. sorokiniana infection
Among the 736 identified miRNAs across the control and treated groups of the two wheat lines, 140 were DE miRNAs in response to infection. The number of DE miRNAs was slightly higher in SI than in RI (Supplementary Table S3). Specifically, 44 miRNAs were upregulated and 43 downregulated in SI, whereas 37 were upregulated and 47 downregulated in RI. A total of 31 DE miRNAs were common between RI and SI, indicating that some miRNA-mediated regulatory responses are common to both resistant and susceptible backgrounds. However, genotype-specific expression patterns were also evident: 30 and 23 miRNAs were uniquely up- and downregulated in RI, while 25 and 31 were unique to SI, respectively. A total of 12 miRNAs were found to be upregulated in both the RI and SI, with all exhibiting higher log2FC values in SI, suggesting stronger transcriptional activation of these miRNAs under susceptible background (Figures 3A, B). Interestingly, several miRNAs showed contrasting expression in RI and SI; tae-miR1122b-3p, tae-miR9662a-3p, bdi-miR5054, gma-miR395i, osa-miR5072, and ppt-miR894 were downregulated in RI and were found to be upregulated in SI (Figure 4A). Conversely, ata-miR5181-3p, osa-miR5503, cme-miR156j, osa-miR5076, and tae-miR7757-5p were found to be upregulated in RI and downregulated in SI (Figure 4B).
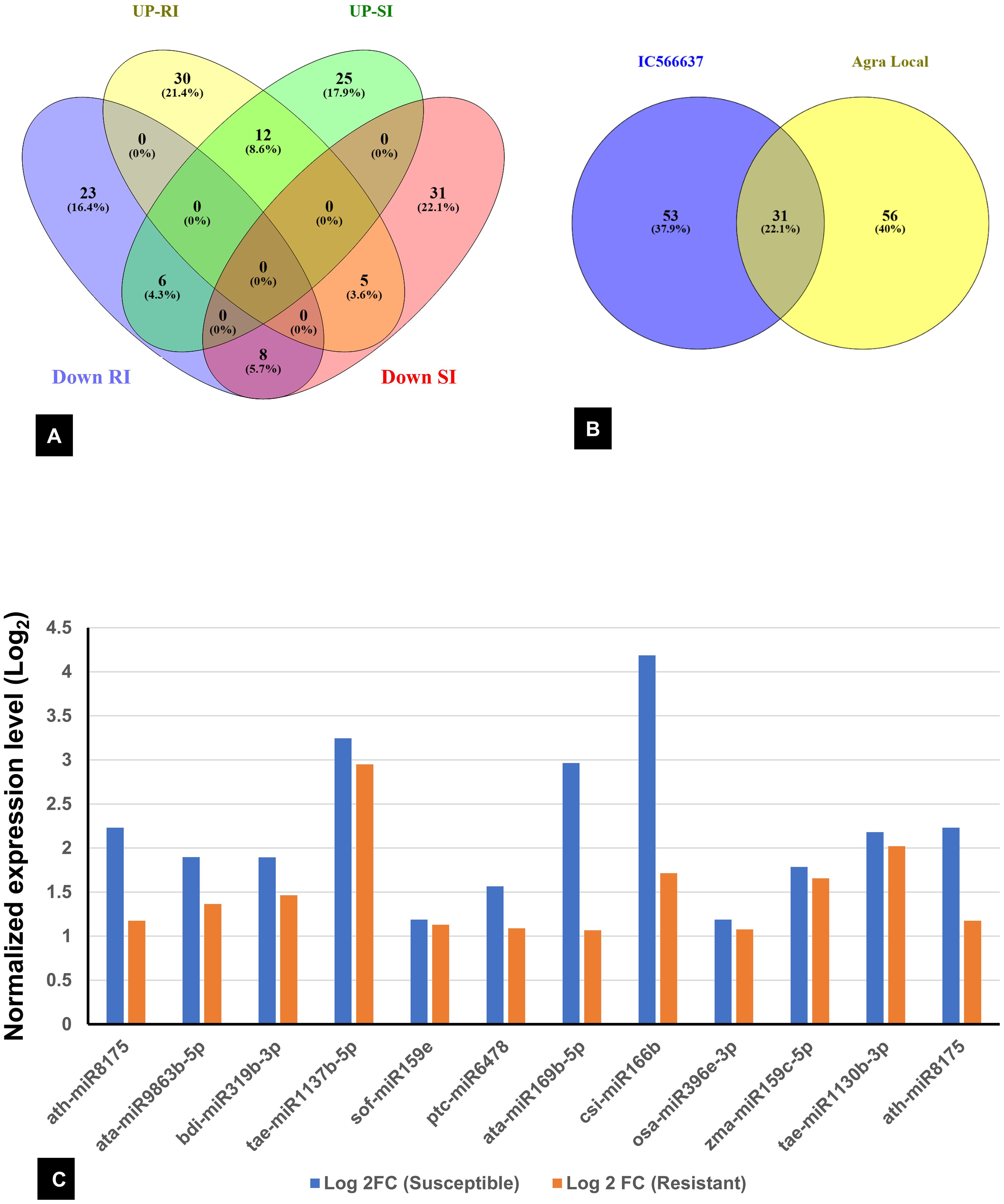
Figure 3. (A) Venn diagram showing common and exclusive differentially expressed (DE) miRNAs across all samples. (B) Total DE miRNA in resistant IC566637 and susceptible Agra Local; UP-RI and DR-RI: upregulated and downregulated in resistant IC566637 inoculated with B. sorokiniana, respectively; UP-SI and DOWN-SI: upregulated and downregulated in susceptible Agra Local inoculated with B. sorokiniana, respectively. (C) List of miRNAs up-regulated in both IC566637 and Agra Local.
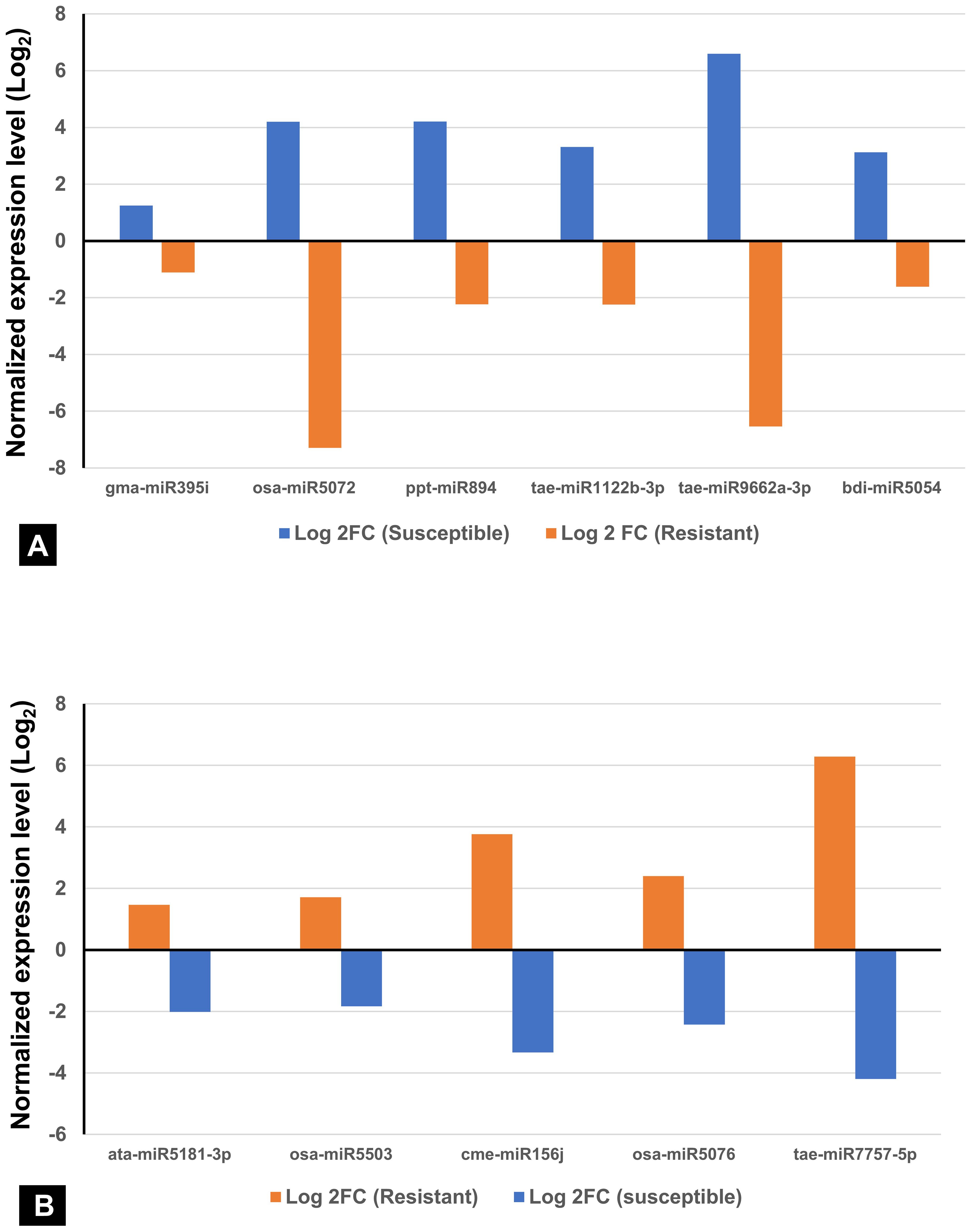
Figure 4. Contrasting expression patterns of miRNAs in spot-blotch-resistant wheat genotype (IC566637) and susceptible variety (Agra Local) after B. sorokiniana infection. (A) miRNA upregulated in susceptible and downregulated in resistant lines. (B) miRNA upregulated in resistant and downregulated in susceptible lines.
3.3 Prediction of miRNA targets
For the 140 DE miRNAs, a total of 894 putative target genes were predicted and functionally annotated based on GO, KEGG, Panther, InterPro, and Pfam (Supplementary Table S4). The identified target genes represented a broad range of functional categories. Majority of the identified target genes were associated with cellular signaling processes such as protein kinases, including serine/threonine protein kinases and calcium-transporting ATPases. Several targets were involved in plant-defense-associated functions, including xylanase inhibitors (TAXI-IV and XI-IB), beta-1,3-glucanase (Glb3), peroxidases (Prx111-A and Prx112-M), chitinases, and resistance-related proteins such as RPP13-like, Nucleotide-binding Apaf-1 R proteins CED-4 (NB-ARC), and LRR proteins. In addition, a number of target genes encoded transcription factors, including WRKY10 and zinc finger proteins (ZFPs), which are often linked with regulatory control of gene expression. Several transporter proteins were also identified among the targets, such as members of the sulfite exporter TauE/SafE family, putative zinc transporter (ZIP1), and ABC transporters. Furthermore, multiple transferase enzymes were predicted, including acyl transferases (acT1) and ubiquitin transferases (RING-type E3).
3.4 GO and KEGG pathway analysis of target genes
The GO enrichment analysis of predicted target genes was grouped into biological process, cellular components, and molecular functions (Figure 5). For the specific DE miRNAs in IC566637, the predicted target genes participated in 144, 114, and 12 GO terms for biological process, molecular function, and cellular component, respectively (Supplementary Table S5; Figure 5A). However, the predicted target genes for DE miRNAs specific in Agra Local participated in 92, 104, and five GO terms for biological process, molecular function, and cellular component, respectively (Supplementary Table S6; Figure 5B). The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis indicated that the predicted target genes were mainly involved in 15 significantly enriched pathways (Table 2). In the resistant genotype IC566637, the most enriched pathways included biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis, diterpenoid biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, and the MAPK signaling pathway. In the susceptible genotype Agra Local, the enriched pathways included linoleic acid metabolism, phenylpropanoid biosynthesis, glucosinolate biosynthesis, cysteine and methionine metabolism, valine, leucine, and isoleucine metabolism, plant–pathogen interaction, and ubiquinone and other terpenoid–quinone biosynthesis.
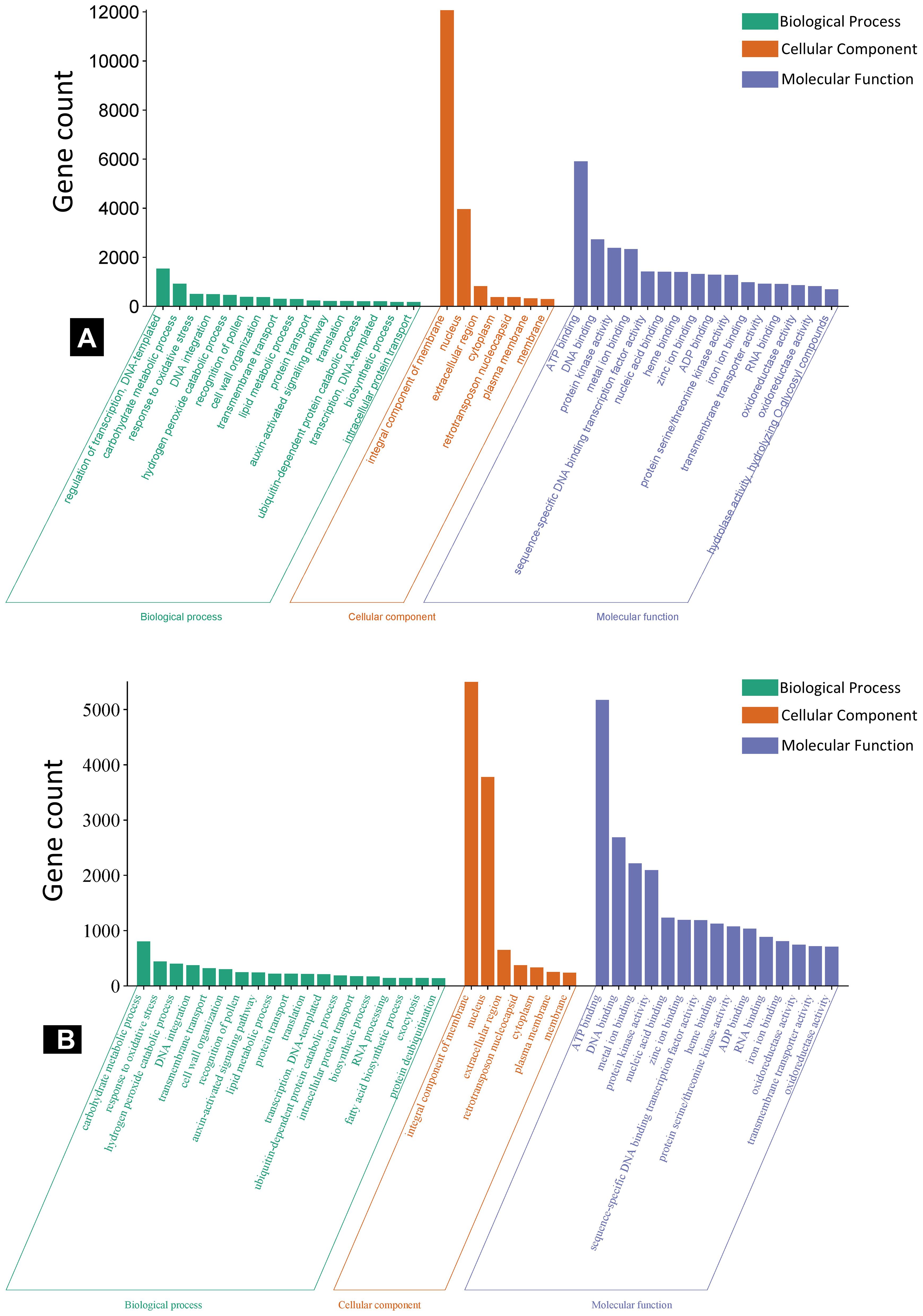
Figure 5. WEGO plots showing GO enrichment analysis of miRNA target genes in spot-blotch-resistant wheat genotype IC566637 (A) and susceptible variety Agra Local (B) infected with B. sorokiniana.
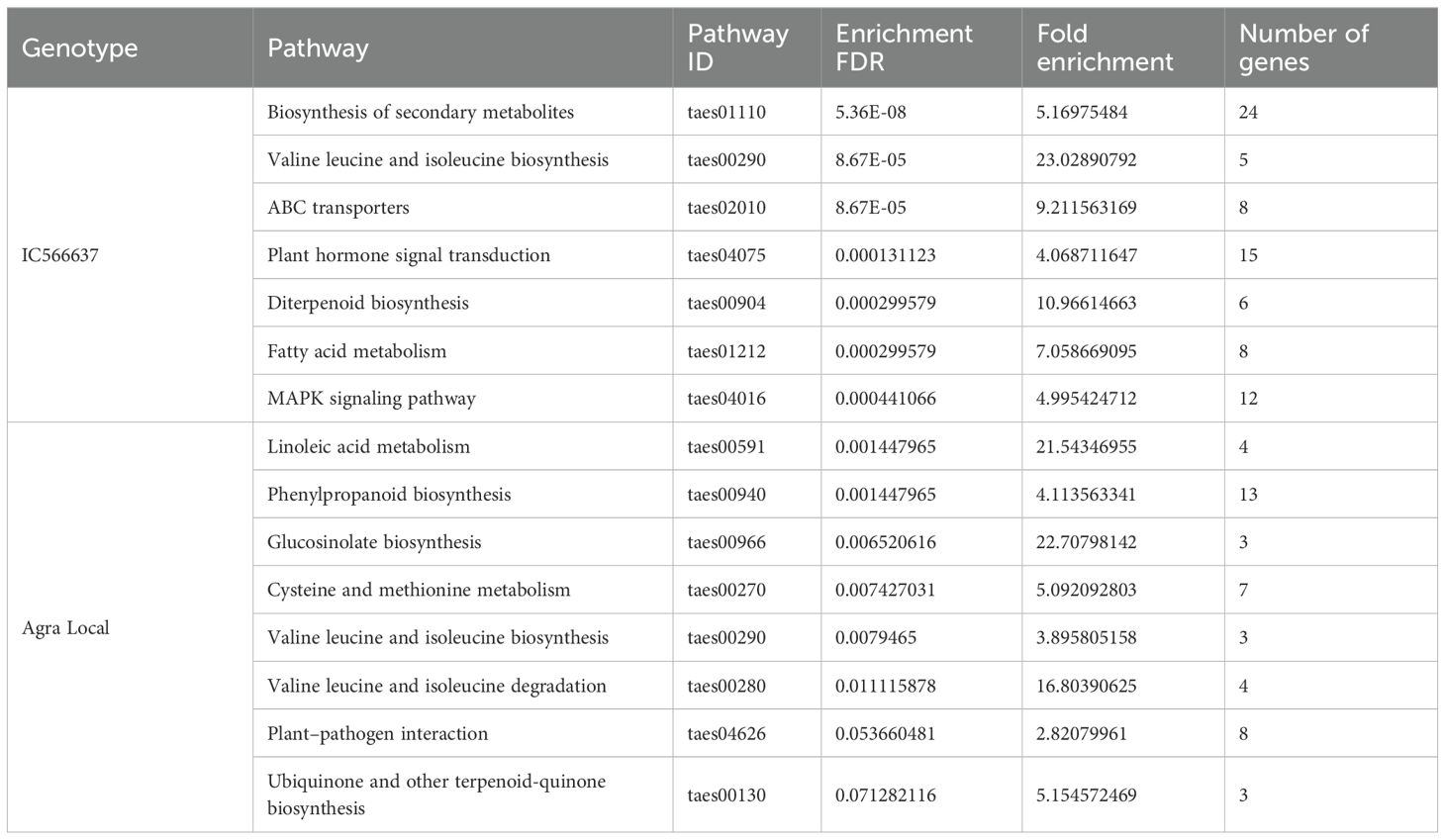
Table 2. KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of predicted target genes associated with DE miRNAs in spot-blotch-resistant wheat genotype IC566637 and susceptible variety Agra Local after B. sorokiniana infection.
3.5 Clustering analysis of DE miRNAs
Hierarchical clustering and heat map analysis revealed distinct expression patterns with upregulated (green) and downregulated (red) miRNAs in IC566637 and Agra Local, forming two separate clades that indicate expression heterogeneity (Figure 6). For IC566637, clade A contained upregulated and clade B with downregulated miRNAs in RI compared to RC samples (Figure 6A). However, in Agra Local, clade A shows downregulated and clade B with highly upregulated miRNAs in SI compared to SC samples (Figure 6B). The predicted DE target genes of miRNA for IC566637 in clade A were predominantly enriched in GO terms with transporter activity (calcium ion transmembrane transport, ABC transporters, ATPase coupled transporter activity, transmembrane transporters, and methyltransferase), cytokinin and hormone metabolic process, RNAi effector complex, RISC complex, and COPII vesicle coat and vesicle tethering complex (Figure 6C). However, the predicted DE target genes in IC566637 were mainly enriched with organic acid, carbohydrate, carboxylic acid metabolic process, extracellular region, lyase and acyltransferase activity, hydrolase activity acting on glycosyl bonds, and sulfur compound binding (Figure 6D). The predicted DE target genes of miRNA in clade A of Agra Local were mainly enriched in carbohydrate metabolic process, ion transport, small molecule metabolic process, organic substance transport, cell wall, external encapsulating structure, extracellular region, and transporter activity (Figure 6E). For miRNAs in Agra Local (clade B), the DE-predicted target genes were mainly enriched in hormone-mediated signaling pathway, cellular response to hormone stimulus, endogenous stimulus and organic substance, pre-ribosome small subunit precursor, eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 complex, nuclear membrane, CCAAT-binding factor complex, SLIK (SAGA-like) complex, clathrin-coated vesicle, 1-phosphatidylinositol binding, minor groove of adenine–thymine-rich DNA binding, DNA-binding transcription activator activity, and transcription corepressor activity (Figure 6F). The results suggest that miRNAs exhibiting varying expression levels could have unique functions in regulating their target genes engaged in different biological pathways during B. sorokiniana and wheat interaction.
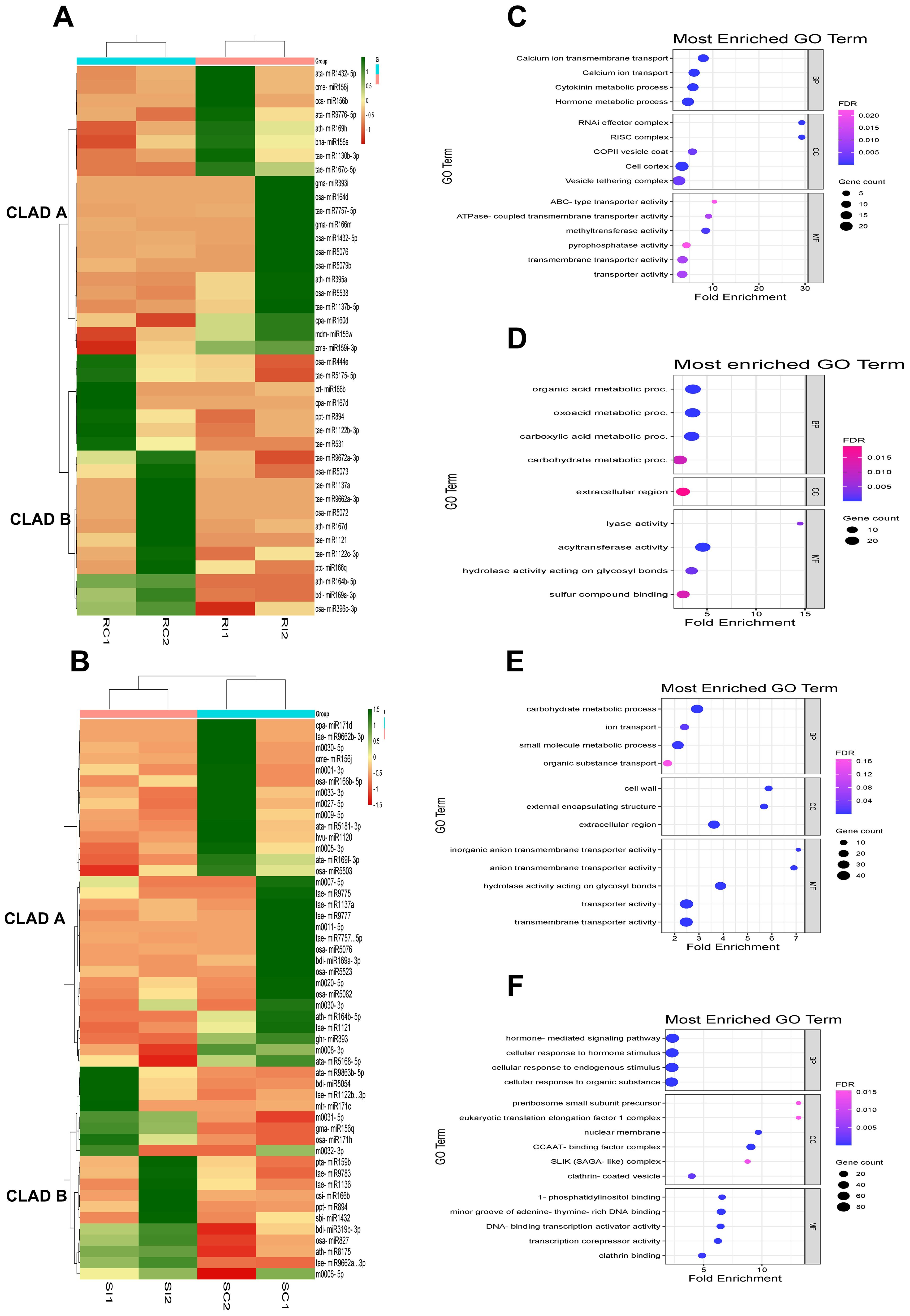
Figure 6. Clustering of expression profiles of DE miRNAs and GO enrichment analysis of their target genes in (A) resistant IC566637 and (B) susceptible Agra Local infected with B. sorokiniana. (C) GO enrichment analysis for target genes associated with DE miRNAs in IC566637 in clade A and (D) clade B. (E) GO enrichment analysis for target genes associated with DE miRNAs in Agra Local in clade A and (F) clade (B) The GO enrichment analysis of DE target genes was analyzed for DE miRNAs cladewise, with p-value cutoff of 0.05.
3.6 Validation of miRNAs and their target genes by qRT−PCR
In this study, we evaluated the expression of nine miRNAs selected based on lowest p-value and highly variable expression (either significantly upregulated or downregulated) and their corresponding target genes associated with defense response against B. sorokiniana in IC566637 and Agra Local. Among these, the expression of four known miRNAs (tae-miR9662a-3p, osa-miR5072, ata-miR9863b-3p, and ata-miR9863b-5p) and five novel miRNAs (xxx-m0030-3p, xxx-m0005-3p, xxx-m0007-5p, xxx-m0009-5p, and xxx-m0031-5p), respectively, was assessed at five different (12, 24, 36, 48, and 60 h) time points using qRT-PCR (Figure 7). The expression of these miRNAs varied considerably across different time points. Notably, three known miRNAs (tae-miR9662a-3p, osa-miR5072, and ata-miR9863b-3p) exhibited contrasting expression patterns: they were downregulated in IC566637 and upregulated in Agra Local. For instance, the expression of tae-miR9662a-3p reduced considerably in RI, which corresponded with the upregulation of its target gene (XM_044510133.1: gene involved in defense response to fungus) that reached 8.06-fold increase at 36 h. Conversely, in SI, the expression of tae-miR9662a-3p drastically increased to 59.74-fold at 48 h, while its target gene was downregulated. Similarly, osa-miR5072 and ata-miR9863b-3p were found to be downregulated in RI and upregulated in SI. The osa-miR5072 exhibited its highest expression in SI at 29.12 times that of the control, while ata-miR9863b-3p reached 3.59 times that of the control in SI. Correspondingly, the target genes for osa-miR5072 (NB-ARC protein) and ata-miR9863b-3p (NB-LRR protein) were downregulated in SI while being upregulated in RI, reaching up to 17.89-fold at 24 h and 2.83-fold at 36 h, respectively. The expression of ata-miR9863b-5p was significantly upregulated in both RI and SI, reaching up to 4.11-fold and 6.07-fold at 48 h, respectively. Notably, its target gene, putative disease resistance (RPP13-like protein 1), showed differential regulation. In RI, the gene was positively regulated by the miRNA with an upregulation of 13.19-fold compared to the control. Conversely, in SI, a negative regulation was observed, where the target gene was found to be downregulated. Among the predicted novel miRNAs evaluated for expression, four miRNAs—xxx-m0030-3p, xxx-m0005-3p, xxx-m0007-5p, and xxx-m0009-5p—were found to be downregulated in SI. Contrarily, the corresponding target genes for xxx-m0030-3p (cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase), xxx-m0005-3p (peroxidase), and xxx-m0007-5p (ATP-binding, involved in defense response) were up-regulated in SI, rising to 5.23-fold at 60 h, 3.3-fold at 60 h, and 1.56-fold at 24 h, respectively, showing a negative regulatory relationship. However, for the target gene for xxx-m0009-5p (protein kinase), a positive regulation was observed, where the target gene was also downregulated in SI. The other miRNA xxx-m0031-5p was significantly upregulated in SI, rising to 5.12-fold compared to the control at 48 h, with corresponding downregulation of its target gene (transcription cofactor). The expression profile of these DE miRNAs in qRT-PCR showed a strong correlation (R2 = 0.915) with sRNA-seq data (Figure 8). The stem loop structures of validated miRNAs were depicted (Figure 9).
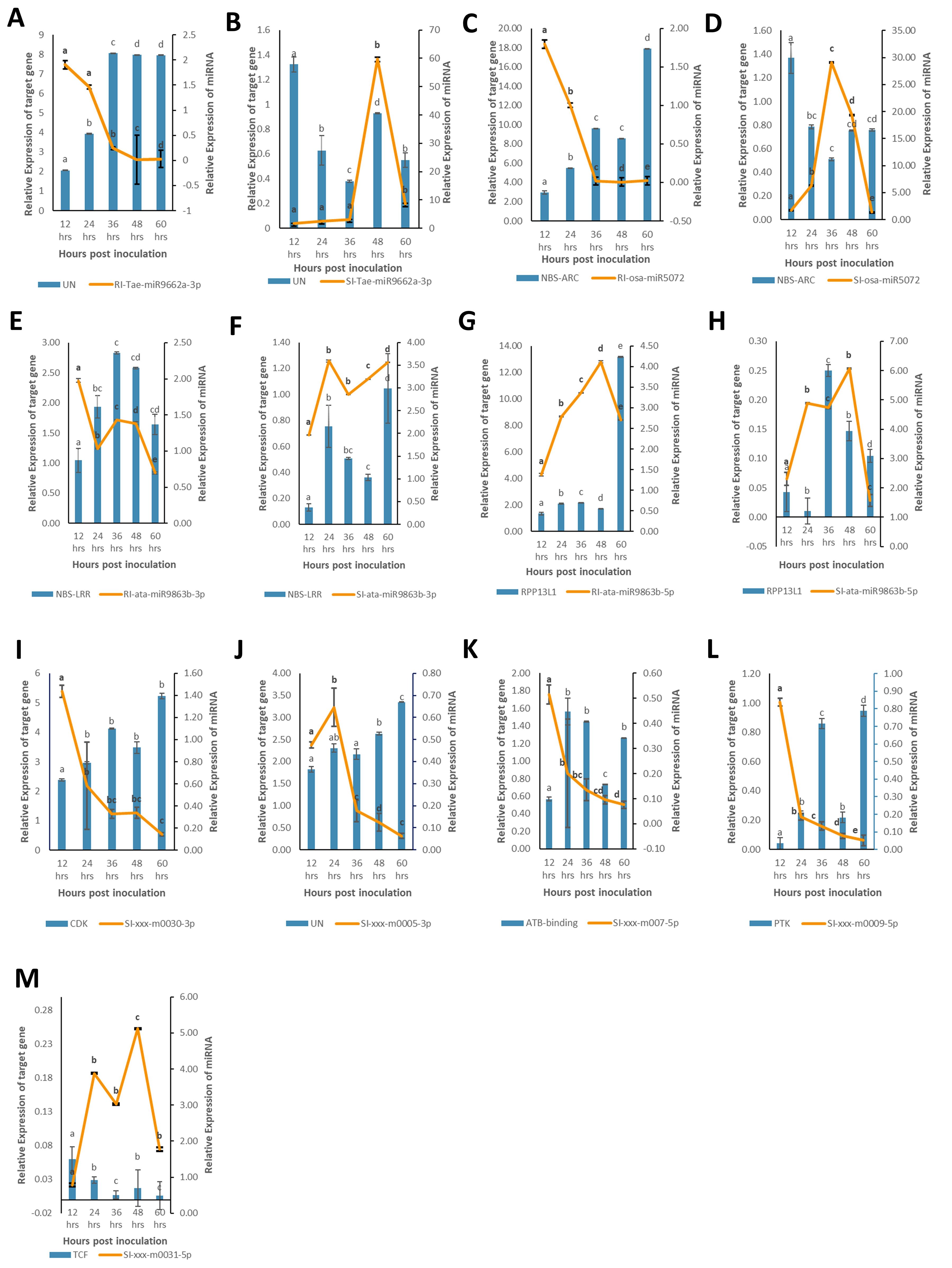
Figure 7. Expression profiles of nine selected miRNAs (line charts) and their associated nine target genes (bar charts) in resistant IC566637 and susceptible Agra Local infected with B. sorokiniana through qRT-PCR analysis. The relative abundance of miRNAs and its associated target gene is depicted on the right and left y-axis, respectively. Each bar indicates the mean values of three biological replicates ± standard error (n = 3). Based on post-hoc Tukey’s HSD test (p-value < 0.05), significant difference is represented by various lowercase letters. Subpanels (A–H) represent the expression profiles of conserved miRNAs and their target genes in resistant and susceptible lines, respectively. Subpanels (I–M) show the expression profiles of novel miRNAs in the susceptible line. UN, uncharacterized; NB-ARC, nucleotide-binding ARC domain encoding gene; NB-LRR, nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat domain encoding gene; RPP13L1, putative disease resistance RPP-13 like protein-1; CDK, cyclin-dependent serine–threonine protein kinase; PTK, protein kinase; TCF, transcription cofactor.
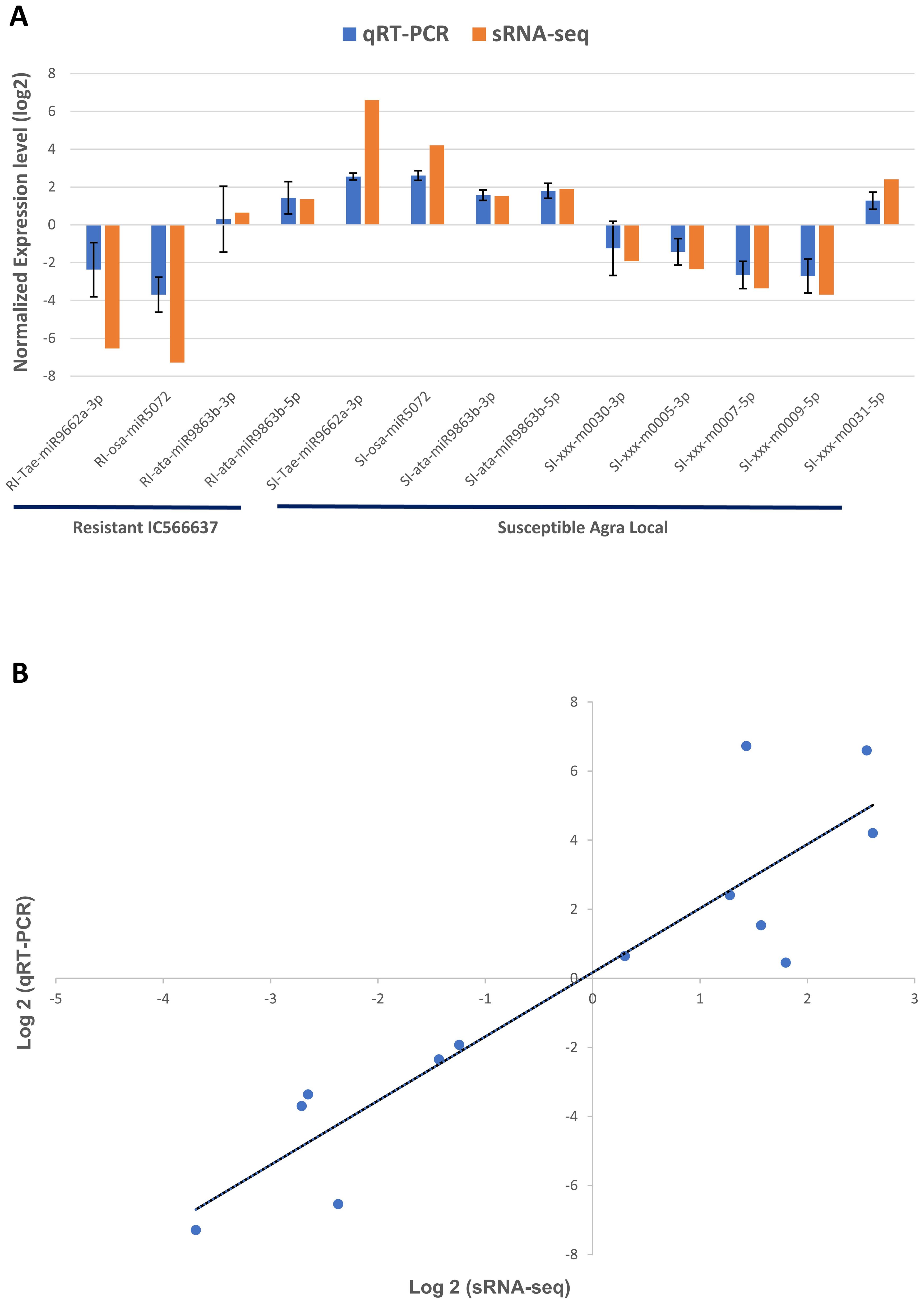
Figure 8. Log2FC values of DE miRNAs in (A) qRT-PCR and small-RNA seq and their (B) correlation analysis by scatter plot. The error bar indicates the mean ± standard error values of log2 fold change for the three biological replicates for the miRNAs validated through qRT-PCR.

Figure 9. Stem loop structures of known and novel differentially expressed miRNAs validated through stem loop-qRT-PCR. (A) tae-miR9662a-3p, (B) osa-miR5072, (C) ata-miR9863b-3p, (D) ata-miR9863b-5p, (E) novel xxx-m0030-3p (Chr7A: 234026622.234926533), (F) novel xxx-m0005-3p (Chr1A: 162410073.162409980), (G) novel xxx-m0007-5p (Chr3B: 829583.829643), (H) novel xxx-m0009-5p (Chr3A: 71549420.71549340), and (I) novel xxx-m0031-5p (Chr6B: 676244915.676244828). The mature sequence of the respective miRNA is represented in red. The stem loop structures are visualized using RNA fold server (RNAfold web server).
4 Discussion
Spot blotch is among the most devastating diseases of wheat, triggering significant economic losses, which are expected to be aggravated in climate change scenarios. The hemibiotrophic lifestyle and high population diversity of the pathogen, coupled with the lack of qualitative resistance in wheat, pose significant challenges in managing spot blotch disease. In plants, during pathogen infection, variation in miRNA level modulates gene expression, which regulates molecular pathways, including signals for biotic stress responses (Anders and Huber, 2010; Li et al., 2010; Friedländer et al., 2012). To investigate miRNA-mediated regulation in response to B. sorokiniana, sRNA-seq analysis was conducted on the resistant genotype IC566637 and susceptible variety Agra Local. In this study, 726 miRNAs with a length of 20–24 nt were identified from the sRNA-seq data (Figure 1), consistent with the earlier reports from Su et al. (2022) and Jin et al. (2024). The correlation between the qRT-PCR and sRNA-seq experiments was R2 = 0.915, indicating a strong correlation and, thus, consistency and reliability of the high-throughput sequencing for the discovery of novel and DE miRNAs. Therefore, the miRNA seq data from this study will enrich the wheat miRNA library.
Plant miRNAs play a crucial role in regulating metabolic pathways by targeting associated genes. In this study, among the DE miRNA target genes identified in IC566637, 24 were significantly enriched in secondary metabolite biosynthesis, 15 in plant hormone signal transduction, and 12 in the MAPK signaling pathway. However, for the target genes from Agra Local, 13 genes showed significant enrichment in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway, eight in plant–pathogen interaction pathway, glucosinolate and ubiquinone, and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis, indicating that these genes modulated by the DE miRNAs possibly play a vital role in wheat’s response to B. sorokiniana infection. Previous experimental studies in wheat have demonstrated that hormone-mediated signaling components, particularly those linked to salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and ethylene (ET) pathways, play key roles in the wheat–B. sorokiniana interaction (Eisa et al., 2013; Sahu et al., 2016). These reports highlighted that the differential activation of SA- and JA-mediated responses contributes to variation in resistance and susceptibility among wheat genotypes. Consistent with these findings, the enrichment of hormone-related pathways in our dataset suggests the engagement of phytohormone signaling as part of the defense response to spot blotch. Notably, our results further extend this understanding by revealing that several of these hormone-associated genes are potential targets of DE miRNAs, indicating a possible regulatory layer through which miRNAs fine-tune hormonal signaling and downstream defense mechanisms. Studies have also shown that these miRNA families regulate defense-related genes directly or indirectly by synthesizing small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) involved in gene silencing. The miRNAs can regulate their target genes, which can be attributed to the plant’s response to disease either directly or indirectly. In our study, the regulatory network analysis of DE miRNAs and their target genes (Figure 10) identified ata-miR9863b-3p, ata-miR9863b-5p, tae-miR5175-5p, tae-miR9662a-3p, cme-miR156j, and zma-miR159c-5p that directly regulate the plant immune receptor genes (NB-LRR) or genes that are directly involved in host–pathogen interactions. Similar results have been reported by Liu et al. (2014), where miR9863a and miR9863b were found to target and repress the expression of many NB-LRR genes in wheat and barley. Several other DE miRNAs and their corresponding target genes were found to be indirectly involved in plant immunity, mainly bdi-miR531, tae-miR531, ata-miR5181-3p, osa-miR1848, and novel miRNA xxx-m0064-5p, which were discovered to have complex and diversified target genes (Figure 10). Some of these target genes of DE miRNAs have pleiotropic effects regulating plant growth and development, which, in turn, influences disease response (Islam et al., 2018; Šečić et al., 2021).
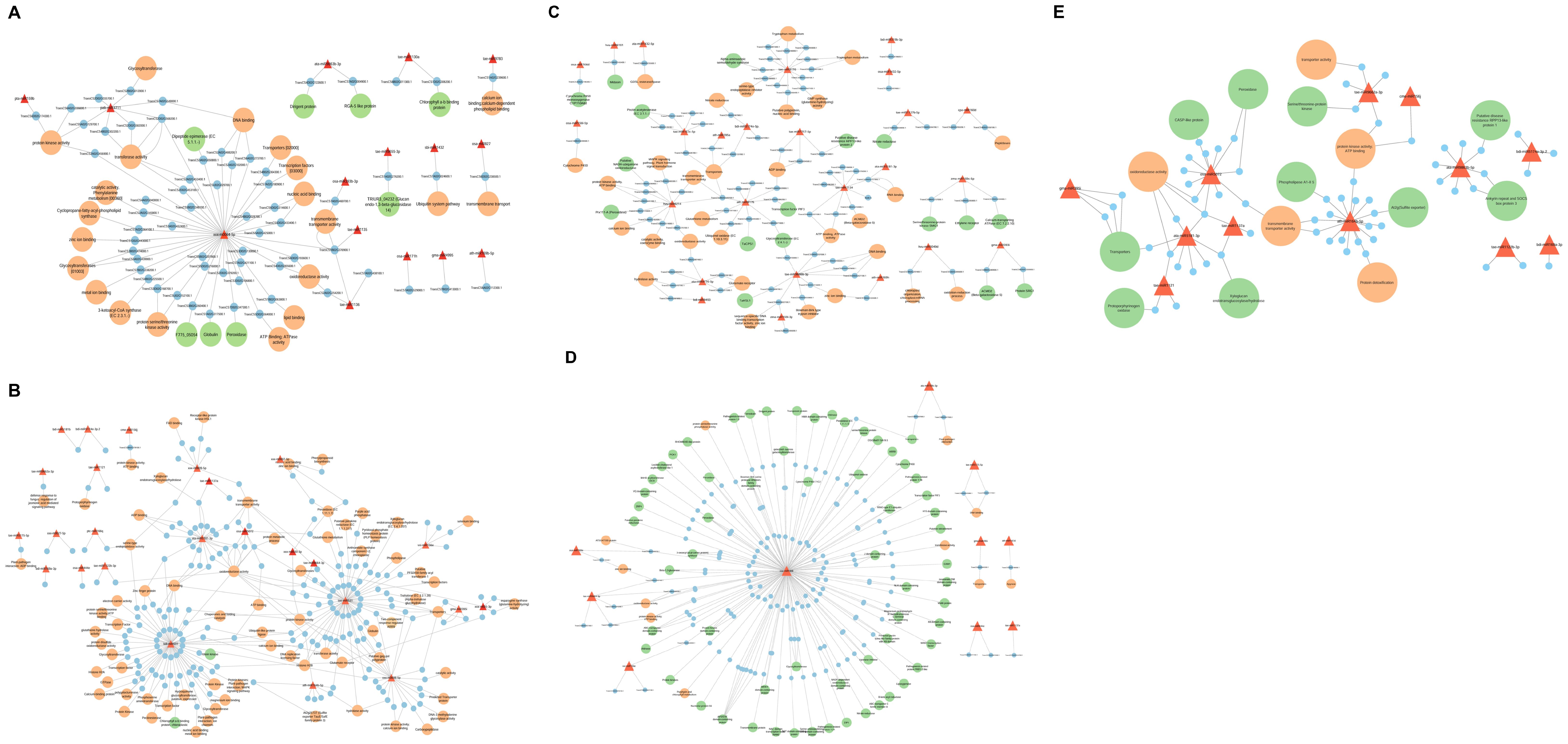
Figure 10. Regulatory networks of DE miRNAs and their corresponding target genes in resistant genotype IC566637 and susceptible variety Agra Local after B. sorokiniana infection. (A) DE miRNAs upregulated in Agra Local. (B) DE miRNAs downregulated in Agra Local. (C) DE miRNAs upregulated in IC566637. (D) DE miRNAs downregulated in IC566637. (E) Common DE miRNAs in IC566637 and Agra Local.
MicroRNAs regulate their target genes either positively (Su et al., 2019) or negatively (Schwab et al., 2005), as also observed in our study. For instance, the regulation modes of ata-miR9863b-5p on its target gene expression were different in the two wheat lines, with a positive and negative regulatory role in RI and SI, respectively. This irregular expression pattern of miRNA–target genes has also been observed in rice and sugarcane (Su et al., 2019, 2022) in response to rice black-streaked dwarf virus, sorghum mosaic virus, and sugarcane smut. Both the novel miRNA xxx-m0009-5p and its target gene encoding a protein kinase were downregulated in SI, suggesting a possible positive regulatory relationship between the miRNA and its target gene. The expression pattern of tae-miR9662a-3p, osa-miR5072, and ata-miR9863b-3p exhibited contrasting behavior in the two wheat lines, showing downregulation in resistant genotype and upregulation in the susceptible variety. Notably, their corresponding target genes NB-ARC (XM_044482261.1) and NB-LRR (XM_044591884.1), involved in defense response to fungus, also demonstrated contrasting expression, being upregulated in RI and downregulated in SI. Interestingly, all of these target genes showed significant upregulation in RI and conversely downregulation in SI, both at 36 h post-infection, indicating it as the critical stage of defense against B. sorokiniana in wheat. Furthermore, NB-LRR genes are among the most widely investigated disease resistance gene families in plants (Jones and Jones, 1997). Liu et al. (2014) documented that miR9863 leads to the silencing of NB-LRR genes in wheat and barley, significantly reducing gene transcripts at 36 h post-inoculation. A negative regulation in the expression of NB-LRR transcripts was associated with the expression of miR482, thus conferring resistance to cotton against Verticillium dahliae (Zhu et al., 2013). Similar responses are reported for tomato and poplar for infection against Cytospora chrysosperma and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides by targeting NB-LRR transcripts (Ouyang et al., 2014; Su et al., 2018). Furthermore, poplar miR472a and Arabidopsis miR472 also trigger the synthesis of secondary phasiRNAs for systemic NB-LRR silencing (Boccara et al., 2015). The expression of ata-miR9863b-5p was found to increase more fold in SI (up to 6.07-fold) than RI (up to 4.11-fold) at 48 h. Consequently, its target gene (RPP13L1) was upregulated in RI and downregulated in SI. Moreover, it should be noted that the expression of RPP13L1 increased to a higher fold in earlier time points after infection. Thus, this differential regulation of expression could be attributed to miRNA expression abundance in SI wherein the higher level of miRNA expression increased the likelihood of target silencing. Conversely, in RI, rapid target transcript abundance diluted miRNA efficacy. The key determinant of resistance or susceptibility lies in rapid signal recognition and the efficacy of host’s defense response following pathogen invasion (Su et al., 2022). Arvey et al. (2010) have proved that the abundance of target mRNA dilutes the activity of miRNA and siRNA. The RPP13-like genes are a part of the NB-LRR superfamily and are significantly upregulated in wheat when challenged with Puccinia striiformis f. sp. tritici and Blumeria graminis f. sp. tritici, causing stripe rust and powdery mildew diseases, respectively (Zhang et al., 2021).
In plant species, protein kinases are key signaling molecules that regulate protein activity through reversible phosphorylation and also play crucial roles in host–pathogen interactions (Cohen, 2000; Zhu et al., 2017; Goyal et al., 2018; Jiang et al., 2021). They are involved in both compatible (susceptibility) and incompatible (resistance) interactions. In this study, the expression of xxx-m0030-3p was downregulated in SI, accompanied by the upregulation of its target gene XM_044508546.1, which encodes a cyclin-dependent serine/threonine protein kinase (CDK). The results indicate the involvement of CDK in wheat’s susceptibility to B. sorokiniana infection. In Arabidopsis, CDK proteins such as CDK9-like proteins, CDKC1, and CDKC2 play crucial roles in infection and increase susceptibility to the cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) (Cui et al., 2007). A MAPK in wheat (TaMAPK4), a positive regulator of defense in wheat–P. striiformis f. sp. tritici infection, is targeted by tae-miR164 (Wang et al., 2018).
5 Conclusion
In the present research, a comprehensive miRNA database was developed to analyze wheat’s response to B. sorokiniana infection. A total of 418 known and 318 novel miRNAs were identified, among which 140 DE miRNAs were predicted to be involved in wheat’s response to B. sorokiniana, targeting 894 genes. Following infection, the number of DE miRNAs was slightly higher in the susceptible variety Agra Local (87) than the resistant genotype IC566637 (84). KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the predicted targets of these DE miRNAs were predominantly associated with defense pathways, including biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, ABC transporters, plant hormone signal transduction, MAPK signaling, and plant–pathogen interaction. Regulatory network analysis highlighted key miRNAs, particularly from miR9863, miR156, and miR159 families, specifically targeting NB-LRRs or kinase genes. Furthermore, the expression profiles of four known miRNAs (tae-miR9662a-3p, osa-miR5072, ata-miR9863b-3p, and ata-miR9863b-5p) and five novel miRNAs (xxx-m0030-3p, xxx-m0005-3p, xxx-m0007-5p, xxx-m0009-5p, and xxx-m0031-5p), along with their corresponding target genes, were evaluated with qRT-PCR. The study identified the expression of putative disease resistance RPP13-like protein and other uncharacterized NB-LRR/protein kinase genes known widely in plant–pathogen interactions. Overall, this work represents an initial broad-scale survey of wheat miRNA responses to B. sorokiniana. While pooling of time points allowed the generation of an exploratory dataset, the parallel qRT-PCR analysis of individual time point samples provided temporal insights into the expression of key miRNAs. Future studies using sequencing at individual time points will be essential to capture fine-scale, transient regulatory dynamics. Moreover, exploring the role of pathogen-derived sRNAs and their possible cross-kingdom effects on wheat defense responses will provide a more comprehensive understanding of this interaction. Overall, the present study enhances the wheat miRNA library and serves as an important foundational work in understanding miRNA-mediated regulation in wheat during B. sorokiniana infection, providing potential candidate genes to develop spot blotch-resistant wheat varieties through resistance breeding and gene editing.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
NK: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. PB: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. XC: Software, Writing – review & editing. LM: Software, Writing – review & editing. AK: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JK: Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing. RA: Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing. MS: Formal Analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing. SP: Data curation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. We acknowledge the financial support received from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR)-Consortium Research Platform on Genomics-Pathogenomics (ICARG/CRP-Genomics/2015-2720/IARI-12-151), National Agricultural Higher Education Project-Overseas Training program.
Acknowledgments
The first author is grateful to ICAR-Senior Research Fellowship and the University of Southern Queensland’s Strategic Research Scheme on Crop Molecular Genetics for the opportunity to undertake this project. We are highly thankful to the Director, Joint Director (Research), ICAR-IARI, New Delhi, for providing guidance and facilities for investigation. We sincerely acknowledge Dr. Barsha Poudel at the Centre for Crop Health, University of Southern Queensland, Australia, for her valuable assistance in learning and understanding the Cytoscape software.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1640327/full#supplementary-material
References
Aggarwal, R., Sharma, S., Singh, K., Gurjar, M. S., Saharan, M. S., Gupta, S., et al. (2019). First draft genome sequence of wheat spot blotch pathogen Bipolaris sorokiniana BS_112 from India, obtained using hybrid assembly. Microbiol. Res. Announc. 8, e00308–e00319. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00308-19
Aggarwal, R., Singh, V. B., Gurjar, M. S., Gupta, S., and Srinivas, P. (2009). Intraspecific variations in Indian isolates of Bipolaris sorokiniana infecting wheat based on morphological, pathogenic, and molecular characters. Indian Phytopathol. 62, 449–460.
Al-Sadi, A. M. (2016). Variation in resistance to spot blotch and the aggressiveness of Bipolaris sorokiniana on barley and wheat cultivars. J. Plant Pathol. 98, 97–103. Available online at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/24892627d
Anders, S. and Huber, W. (2010). Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 11, R106. doi: 10.1186/gb-2010-11-10-r106
Arvey, A., Larsson, E., Sander, C., Leslie, C. S., and Marks, D. S. (2010). Target mRNA abundance dilutes microRNA and siRNA activity. Mol. Syst. Biol. 6, 363. doi: 10.1038/msb.2010.24
Asadi, M. and Millar, A. A. (2024). Review: Plant microRNAs in pathogen defense: A panacea or a piece of the puzzle? Plant Sci. 341, 111993. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.111993
Basak, P., Gurjar, M. S., Kumar, T. P. J., Kashyap, N., Singh, D., Jha, S. K., et al. (2024). Transcriptome analysis of Bipolaris sorokiniana–Hordeum vulgare provides insights into mechanisms of host-pathogen interaction. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1360571
Boccara, M., Sarazin, A., Thiebeauld, O., Jay, F., Voinnet, O., Navarro, L., et al. (2015). The Arabidopsis miR472-RDR6 silencing pathway modulates PAMP- and effector-triggered immunity through the post-transcriptional control of disease resistance genes. PloS Pathog. 11, e1004814. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004814
Chand, R., Sen, D., Prasad, K. D., Singh, A. K., Bashyal, B. M., Prasad, L. C., et al. (2008). Screening for disease resistance in barley cultivars against Bipolaris sorokiniana using callus culture method. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 46, 249–253.
Chaurasia, S., Chand, R., and Joshi, A. K. (2000). Relative dominance of Alternaria triticina Pras. et Prab. & Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc.) Shoemaker in different growth stages of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). J. Plant Dis. Prot. 107, 176–181.
Cohen, P. (2000). The regulation of protein function by multisite phosphorylation – a 25-year update. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 596–601. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)01712-6
Cui, X., Fan, B., Scholz, J., and Chen, Z. (2007). Roles of Arabidopsis cyclin-dependent kinase C complexes in Cauliflower mosaic virus infection, plant growth, and development. Plant Cell 19, 1388–1402. doi: 10.1105/tpc.107.051375
Devi, H. M., Mahapatra, S., and Das, S. (2018). Assessment of yield loss of wheat caused by spot blotch using regression model. Indian Phytopathol. 71, 291–294. doi: 10.1007/s42360-018-0036-9
Eisa, M., Chand, R., and Joshi, A. K. (2013). Biochemical and histochemical parameters associated with slow blighting of spot blotch (Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc.) Shoem.) in wheat (Triticum spp.). Zemdirbyste Agric. 100, 191–198. doi: 10.13080/z-a.2013.100.025
Friedländer, M. R., Mackowiak, S. D., Li, N., Chen, W., and Nikolaus, R. (2012). miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, 37–52. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr688
Goyal, R. K., Tulpan, D., Chomistek, N., González-Peña Fundora, D., West, C., Ellis, B. E., et al. (2018). Analysis of MAPK and MAPKK gene families in wheat and related Triticeae species. BMC Genomics 19, 178. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4545-9
Griffiths-Jones, S., Saini, H. K., van Dongen, S., and Enright, A. J. (2008). miRBase: tools for microRNA genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, D154–D158. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm952
Gupta, P. K., Chand, R., Vasistha, N. K., Pandey, S. P., Kumar, U., Mishra, V. K., et al. (2018). Spot blotch disease of wheat: the current status of research on genetics and breeding. Plant Pathol. 67, 508–531. doi: 10.1111/ppa.12781
Gurjar, M. S., Bhardwaj, N. R., Jain, S., Sharma, S., Gupta, S., and Aggarwal, R. (2018). Identification of resistance sources and expression level of defense-related genes in wheat against Bipolaris sorokiniana. Indian Phytopathol. 71, 127–134. doi: 10.1007/s42360-018-0020-4
Inal, B., Türktaş, M., Eren, H., Ilhan, E., Okay, S., Atak, M., et al. (2014). Genome-wide fungal stress responsive miRNA expression in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Planta 240, 1287–1298. doi: 10.1007/s00425-014-2153-8
Islam, W., Qasim, M., Noman, A., Adnan, M., Tayyab, M., Farooq, T. H., et al. (2018). Plant microRNAs: front line players against invading pathogens. Microb. Pathol. 118, 9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.03.008
Jaiswal, S., Iquebal, M. A., Arora, V., Sheoran, S., Sharma, P., Angadi, U. B., et al. (2019). Development of species-specific putative miRNA and its target prediction tool in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Sci. Rep. 9, 3790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40333-y
Jiang, L., Zhang, S., Su, J., Peck, S. C., and Luo, L. (2021). Protein kinase signaling pathways in plant-Colletotrichum interaction. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.829645
Jin, S. B., Fu, H. T., Jiang, S. F., Xiong, Y. W., Qiao, H., Zhang, W. Y., et al. (2015). Identification of androgenic gland microRNA and their target genes to discover sex-related microRNA in the oriental river prawn Macrobrachium nipponense. Genet. Mol. Res. 14, 18396–18406. doi: 10.4238/2015.December.23.27
Jin, J., Yang, L., Fan, D., Li, L., and Hao, Q. (2024). Integration analysis of miRNA-mRNA pairs between two contrasting genotypes reveals the molecular mechanism of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) response to high-temperature stress. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 612. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05304-0
Jones, D. A. and Jones, J. D. G. (1997). “The role of leucine-rich repeat proteins in plant defenses,” in Adv. Bot. Res. Eds. Andrews, J. H., Tommerup, I. C., and Callow, J. A.. Advances in Botanical Research. London, UK: Academic Press. 89–167.
Kanehisa, M. and Goto, S. (2000). KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 27–30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Kramer, M. F. (2015). “STEM-LOOP RT-qPCR for miRNAs,” in Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. Ed. Ausubel, F. M., New York, NY: John Wiley & Sons. 95. doi: 10.1002/0471142727.mb1510s95
Kumar, D., Dutta, S., Singh, D., Prabhu, K. V., Kumar, M., and Mukhopadhyay, K. (2016). Uncovering leaf rust responsive miRNAs in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using high-throughput sequencing and prediction of their targets through degradome analysis. Planta 245, 161–182. doi: 10.1007/s00425-016-2600-9
Langmead, B., Trapnell, C., Pop, M., and Salzberg, S. L. (2009). Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10, R25. doi: 10.1186/gb-2009-10-3-r25
Li, Y., Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., Wu, L., Qi, Y., and Zhou, J. (2010). Identification of microRNAs involved in pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered plant innate immunity. Plant Physiol. 152, 2222–2231. doi: 10.1104/pp.109.151803
Liu, J., Cheng, X., Liu, D., Xu, W., Wise, R., Shen, Q. H., et al. (2014). The miR9863 family regulates distinct Mla alleles in barley to attenuate NLR receptor-triggered disease resistance and cell-death signaling. PloS Genet. 10, e1004755. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004755
Navarro, L., Dunoyer, P., Jay, F., Arnold, B., Dharmasiri, N., Estelle, M., et al. (2006). A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 312, 436–439. doi: 10.1126/science.1126088
Ouyang, S., Park, G., Atamian, H. S., Han, C. S., Stajich, J. E., Kaloshian, I., et al. (2014). MicroRNAs suppress NB domain genes in tomato that confer resistance to Fusarium oxysporum. PloS Pathog. 10, e1004464. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004464
Sahu, R., Sharaff, M., Pradhan, M., Sethi, A., Bandyopadhyay, T., Mishra, V. K., et al. (2016). Elucidation of defense-related signaling responses to spot blotch infection in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant J. 86, 35–49. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13149
Schwab, R., Palatnik, J. F., Riester, M., Schommer, C., Schmid, M., and Weigel, D. (2005). Specific effects of microRNA on the plant transcriptome. Dev. Cell 8, 517–527. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2005.01.018
Šečić, E., Kogel, K. H., and Ladera-Carmona, M. J. (2021). Biotic stress-associated microRNA families in plants. J. Plant Physiol. 263, 153451. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2021.153451
Shannon, P., Markiel, A., Ozier, O., Baliga, N. S., Wang, J. T., Ramage, D., et al. (2003). Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13, 2498–2504. doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303
Sharma, P., Gupta, O. P., Gupta, V., Singh, G., and Singh, G. P. (2021). Differential expression profiling of microRNAs and their target genes during wheat-Bipolaris sorokiniana pathosystem. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 27, 2567–2577. doi: 10.1007/s12298-021-01092-1
Singh, P. K., He, X., Sansaloni, C. P., Juliana, P., Dreisigacker, S., and Duveiller, E. (2018). Resistance to spot blotch in two mapping populations of common wheat is controlled by multiple QTL of minor effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 4054. doi: 10.3390/ijms19124054
Singh, P. S., Singh, P. K., Rutkoski, J., Hodson, D. P., He, X., Jørgensen, L. N., et al. (2016). Disease impact on wheat yield potential and prospects of genetic control. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 54, 303–322. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080615-095835
Su, Y., Li, H., Wang, Y., Li, S., Wang, H., Yu, L., et al. (2018). Poplar miR472a targeting NBS-LRRs is involved in effective defense against the necrotrophic fungus Cytospora chrysosperma. J. Exp. Bot. 69, 5519–5530. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery304
Su, Y., Peng, Q., Ling, H., You, C., Wu, Q., Xu, L., et al. (2022). Systematic identification of miRNA-regulatory networks unveils their potential roles in sugarcane response to Sorghum mosaic virus infection. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 247. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03641-6
Su, Y. C., Xiao, X. H., Ling, H., Huang, N., Liu, F., Su, W. H., et al. (2019). A dynamic degradome landscape on miRNAs and their predicted targets in sugarcane caused by Sporisorium scitamineum stress. BMC Genomics 20, 57. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5400-8
Tembo, B., Sibiya, J., and Tongoona, P. (2018). Genetic variability among wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) germplasm for resistance to spot blotch disease. J. Agric. Rural Dev. Trop. Subtrop. 119, 85–93. doi: urn:nbn:de:hebis:34-2018022754656
Vaish, S. S., Ahmed, S. B., and Prakash, K. (2011). First documentation on status of barley diseases from the high-altitude cold arid trans-Himalayan Ladakh region of India. Crop Prot. 30, 1129–1137. doi: 10.1016/j.cropro.2011.04.015
Varkonyi-Gasic, E., Wu, R., Wood, M., Walton, E. F., and Hellens, R. P. (2007). Protocol: a highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 3, 12. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-3-12
Vasistha, N. K., Tandon, A., Pal, S., Sharma, S., Mishra, V. K., and Gupta, P. K. (2025). Transcriptome analysis for the identification of spot blotch responsive genes and miRNAs in wheat. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 135, 102485. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2024.102485
Wang, B., Song, N., Zhang, Q., Wang, N., and Kang, Z. (2018). TaMAPK4 acts as a positive regulator in defense of wheat stripe-rust infection. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00152
Wang, Z., Xia, Y., Lin, S., Wang, Y., Guo, B., Song, X., et al. (2018). Osa-miR164a targets OsNAC60 and negatively regulates rice immunity against the blast fungus Magnaporthe oryzae. Plant J. 95, 584–597. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13972
Zhang, H., Xu, X., Wang, M., Wang, H., Deng, P., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). A dominant spotted leaf gene TaSpl1 activates endocytosis and defense-related genes causing cell death in the absence of dominant inhibitors. Plant Sci. 310, 110982. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110982
Zhu, Q., Fan, L., Liu, Y., Xu, H., Llewellyn, D., and Wilson, I. (2013). miR482 regulation of NBS-LRR defense genes during fungal pathogen infection in cotton. PloS One 8, e84390. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084390
Keywords: wheat, spot blotch, Bipolaris sorokiniana, miRNA, defense, host-pathogen interaction
Citation: Kashyap N, Gurjar MS, Basak P, Sun X, Ma L, Kumar A, Kumari J, Aggarwal R, Saharan MS and Periyannan S (2025) Genome-wide identification, expression, and regulatory network analysis of wheat microRNAs responsive to Bipolaris sorokiniana. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1640327. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1640327
Received: 03 June 2025; Accepted: 06 November 2025; Revised: 03 November 2025;
Published: 27 November 2025.
Edited by:
Udai B. Singh, National Bureau of Agriculturally Important Microorganisms (ICAR), IndiaReviewed by:
Sudhir Navathe, Agharkar Research Institute, IndiaMehi Lal, ICAR-Central Potato Research Institute, India
Sajad Un Nabi, Central Institute of Temperate Horticulture (ICAR), India
Copyright © 2025 Kashyap, Gurjar, Basak, Sun, Ma, Kumar, Kumari, Aggarwal, Saharan and Periyannan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Malkhan Singh Gurjar, bWFsa2hhbl9pYXJpQHlhaG9vLmNvbQ==; Sambasivam Periyannan, c2FtYmFzaXZhbS5wZXJpeWFubmFuQHVuaXNxLmVkdS5hdQ==
†ORCID: Malkhan Singh Gurjar, orcid.org/0000-0002-4292-1882
 Natasha Kashyap
Natasha Kashyap Malkhan Singh Gurjar
Malkhan Singh Gurjar Poulami Basak
Poulami Basak Xizhe Sun2
Xizhe Sun2 Lisong Ma
Lisong Ma Rashmi Aggarwal
Rashmi Aggarwal Mahender Singh Saharan
Mahender Singh Saharan Sambasivam Periyannan
Sambasivam Periyannan