- 1Department of Agriculture, Forestry and Environmental Engineering, Changzhi Vocational and Technical College, Changzhi, Shanxi, China
- 2College of Agriculture and Biotechnology, Southwest University, Chongqing, China
- 3College of Life Sciences, Leshan Normal University, Leshan, Sichuan, China
E2F/DP (Eukaryotic Transcription Factor 2/Dimerization Partner) refers to a class of protein complexes that play a pivotal role in the regulation of gene transcription in eukaryotes. In higher plants, E2F/DP transcription factors are of vital significance in mediating responses to environmental stresses. Based on differences in their conserved structural domains, they can be categorized into three subgroups: E2F, DP, and DEL (DP-E2F-like). Studies on E2F/DP in plants are relatively scarce, and no research on E2F/DP in Brassica napus has been reported to date. Utilize bioinformatics approaches to identify the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus. Construct a phylogenetic tree for evolutionary relationship analysis, and analyze the chromosomal distribution, gene structure composition, types of cis-acting elements, as well as intragenomic and interspecific collinearity. Integrate transcriptome data with real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) technology to explore the expression patterns of BnE2F/DP gene family members across various tissues. Total 29 BnE2F/DP genes were identified in Brassica napus and classified into 8 sub-families. These genes were unevenly distributed across 15 chromosomes, with enrichment on chromosomes 3 and 13. Intragenomic collinearity analysis detected 35 pairs of collinear BnE2F/DP gene pairs. Interspecific analysis revealed that there were 9 pairs of orthologous gene pairs between Brassica napus and Arabidopsis thaliana. Cis-acting element analysis showed that members of the BnE2F/DP family harbored four types of cis-acting elements, which might be involved in multiple regulatory processes, including hormonal regulation, abiotic stress responses, light reactions, and growth and development. Transcriptome and quantitative PCR data analyses indicate that members of the E2FC subfamily are likely to actively regulate seed and embryo development and positively respond to various abiotic stresses.. The conserved motifs and gene structures within each BnE2F/DP subfamily are largely consistent, which indicates that BnE2F/DP plays a crucial role in the growth and development of rapeseed seeds and embryos, as well as in the response to various abiotic stresses.
Introduction
E2F/DP (Eukaryotic Transcription Factor 2/Dimerization Partner) represents a class of protein complexes that play a pivotal role in the transcriptional regulation of genes in eukaryotes. It plays a crucial role for environmental stress responses (Mariconti et al., 2002). In eukaryotic cells, the RB/E2F signaling network orchestrates cell cycle progression, mediates mitotic division and DNA damage response, modulates cell size homeostasis, and ensures genomic integrity through dynamic phosphorylation by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs). Furthermore, this regulatory network mediates transcriptional reprogramming through sequence-specific interactions with cis-regulatory elements in target gene promoters. In planta, it plays a pivotal role in integrating photomorphogenic signaling with adaptive responses to abiotic/biotic stressors, thereby regulating spatiotemporal growth patterns, developmental transitions, and stress acclimation (Sozzani et al., 2006). In higher plants, E2F/DP transcription factors can be divided into three categories, namely E2F, DP, and DEL (DP - E2F - like), based on their conserved domains. The E2F gene group encompasses four functional domains: the retinoblastoma protein (RBR)-binding domain, the DNA-binding domain, the “mark box” domain, and the leucine-zipper dimerization domain. Typical E2Fs are able to act as either activators or repressors of gene expression. In contrast, non-typical E2Fs downregulate the expression of E2F-dependent genes by competing with typical E2Fs for DNA-binding sites. Notwithstanding recent advancements, current understanding of the E2Fs gene family evolutionary history, phylogenetic architectures, functional divergence among family members in plant species, and their roles within complex regulatory mechanism remains unclear. Currently, The E2F/DP transcription factor family in Arabidopsis thaliana represents the most comprehensively characterized member of this gene family among plant species. The Arabidopsis thaliana E2F/DP family consists of 8 members, including 3 types of canonical E2Fs (AtE2FA, AtE2FB, AtE2FC), 3 types of non-typical E2Fs (AtE2FD/DEL2, AtE2FE/DEL1, AtE2FF/DEL3), and 2 types of DP (Ramirez-Parra et al., 2004; Desvoyes et al., 2006). Functional studies have shown that E2Fs exhibit specific cooperative or antagonistic effects. The cross-regulation among various E2Fs has become part of the replication regulatory network in both animals and plants. In meristematic cells, AtE2F can activate cell-cycle genes to promote mitosis for cell proliferation. Cell proliferation in Arabidopsis thaliana depends on the transcriptional activation of E2F/DP. The deletion of the 3 typical E2F/DPs leads to plant sterility but does not affect vegetative growth (Magyar et al., 2005). The DcE2F1 factor in carrot is one of the earliest E2F factors to be studied. DcE2F1 is likely a homolog of AtE2FA in Arabidopsis thaliana. The phenotypes observed in Arabidopsis thaliana transformants with ectopic expression of DcE2F1 are highly similar to those of overexpressing AtE2FA. Conserved promotion of cell proliferation in embryonic and seedling tissues, coupled with ectopic hypocotyl formation, indicate its important role in the control of cell proliferation. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the cotyledon size of plants overexpressing AtE2FA or AtE2FB increases significantly, and the number of cells more than doubles. AtE2Fa acts downstream of the ERECTA kinase and is involved in regulating cell size and stomatal density. Studies on mammals also confirm that the E2F signaling pathway is crucial for cell growth and proliferation, demonstrating that E2F/DP plays a decisive role in the growth and development of organisms (Polager and Ginsberg, 2008). The E2F/DP gene family is extensively involved in plant growth, development, and responses to stress. Currently, E2F/DP genes have only been identified in a few plants such as Arabidopsis thaliana, moso bamboo, wheat, carrot, and tomato. There is no reported information on Brassica napus yet. For instance, salicylic acid is a key regulator in plant defense responses in Arabidopsis thaliana, the non-typical AtE2FE/DEL1 factor participates in the plant immune response and is found to inhibit the accumulation of salicylic acid to balance growth and defense. The promoters of PheE2F/DP transcription factors in moso bamboo harbor diverse cis-acting elements (Divya et al., 2024), which participate in leaf and root development, cell cycle regulation, and abiotic stresses responses. The expression of most PheE2F/DP genes is up-regulated under drought and salt stress (Li et al., 2021); The E2F/DP transcription factors in carrot regulate cell proliferation, size, and stomatal development, and are also involved in the growth and development processes of embryos and plants (Perrotta et al., 2021). Under drought stress, E2F/DP genes in wheat regulate the expression of downstream genes, maintain the balance of cell osmotic pressure, and enhance drought tolerance (Yu et al., 2022). Under drought stress, Sorbus pohuashanensis E2F/DP genes enhance the perception and response to water deficit by regulating the abscisic acid (ABA) signaling pathway, and regulate growth to adapt to a high-salt environment. Under drought stress, Medicago sativa E2F/DP genes maintain cell osmotic balance through multiple regulatory mechanisms, participate in hormone signal transduction pathways, and enhance stress tolerance, and the expression of four genes such as E2Fa is up-regulated by more than 2-fold under salt stress (Ma et al., 2014). In maize, the expression level of the ZmE2F6 gene in the stem is significantly up-regulated after 3 hours of drought treatment and down-regulated at 6, 12, and 24 hours of treatment, indicating that ZmE2F6 responds to drought stress.
Brassica napus, as an important crop with great economic value, is widely used in fields such as food production and oil processing. However, the growth of Brassica napus relatively sensitive to water deficit, and drought stress has become a key factor severely constraining the increase in its yield (Wei et al., 2022). Therefore, identifying and harnessing stress-resistant genes in rapeseed through molecular breeding techniques holds great significance for the development of the rapeseed industry. In this study, 29 BnE2F/DP genes were comprehensively identified in the Brassica napus genome. Using bioinformatics and other methods, we performed an in-depth analysis of the gene structures, physicochemical properties, chromosome locations, conserved motifs, cis-acting elements, intragenomic collinearity, and phylogenetic evolutionary characteristics of the BnE2F/DP gene family members in rapeseed. By integrating transcriptome sequencing and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) techniques, we analyzed the expression patterns of the BnE2F/DP gene family in different tissues of Brassica napus. The findings of this study not only enhance our knowledge of the biological functions of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus, but also provide important gene resources and a theoretical basis for stress-resistant molecular breeding of rapeseed. Moreover, they are anticipated to expedite the process of molecular-assisted selection for stress-resistant in rapeseed breeding.
Materials and methods
Materials
The material used in this experiment is Brassica napus “Zhongshuang 11”, which was provided by the College of Agronomy and Biotechnology, Southwest University. The seeds of Brassica napus were sown in the field. After the rapeseed entered the flowering stage, young seeds 10 to 49 days post-flowering were collected. They were rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen and then used for the qRT-PCR experiment. Three replicates were set for each treatment.
Methods
Identification of BnE2F/DP genes in the Brassica napus genome
The genomic sequences and E2F/DP protein sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana were downloaded from the TAIR database (https://www.arabidopsis.org/), and the genomic sequences, protein sequences, and gene annotation information of Brassica napus were downloaded from the BRAD (http://www.brassicadb.cn/) database (Berardini et al., 2015; Li et al., 2024). Firstly, a two-way BLAST comparison was performed between the protein sequences of Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus to preliminarily screen out the candidate genes of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus (Jia et al., 2021). Thereafter, to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the screening results, we applied a dual-screening approach using BLAST and HMMER, and finally determined the members of the BnE2F/DP gene family.
Analysis of chromosomal localization and physicochemical properties of BnE2F/DP proteins in Brassica napus
The distribution map of the BnE2F/DP genes of Brassica napus in the genome was generated using the software TBtools. We carried out prediction analysis of indicators including the amino acid length, theoretical isoelectric point, relative molecular mass, average hydrophilicity, instability coefficient, and aliphatic index of the candidate proteins of the BnE2F/DP genes in Brassica napus using the online software ExPASy (Li et al., 2022). The subcellular localization analysis of the BnE2F/DP proteins in Brassica napus was predicted using the online software CELLO v2.5 (Li et al., 2009).
Phylogenetic analysis of members of BnE2F/DP gene family
To gain an in-depth understanding of the evolutionary relationships among the members of the BnE2F/DP gene family, we used the Muscle software, a bioinformatics tool, to conduct a multiple sequence alignment analysis of the BnE2F/DP proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus (Cao et al., 2024). Subsequently, the iqtree software was employed to screen for the optimal tree-building model. Then, the raxml software was utilized to construct a phylogenetic tree (Safder et al., 2022). Finally, the visualization of the phylogenetic tree was achieved using the R software package.
Analysis of gene structures and conserved motifs of BnE2F/DP gene family
For the analysis of gene structures, the online software Gene Structure Display Server was employed to analyze the exon/intron distribution of the BnE2F/DP genes in Brassica napus and draw gene structure diagrams (Pu et al., 2020). We employed the Clustal X software to perform sequence alignment on the finally determined BnE2F/DP protein sequences in Brassica napus. Subsequently, the Jalview software was used to analyze and present the sequence features of the members of the BnE2F/DP family in Brassica napus visually (Li et al., 2014). Meanwhile, the MEME online website was utilized to analyze the conserved motifs of the BnE2F/DP proteins (Bailey et al., 2009), providing a basis for in-depth exploration of the structures and functions of this gene family.
Analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoters of BnE2F/DP gene family
We used the bedtools and seqkit software to extract the promoter region sequences of 1500 bp upstream of the start codon of the members of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus. The cis-acting elements in this promoter region were predicted through the PlantCARE5 online website (Liu et al., 2014; Biłas et al., 2016). Finally, the R software package was utilized to visually display the prediction results.
Identification of duplication events and collinearity analysis of BnE2F/DP gene family
To identify the gene duplication events of the BnE2F/DP genes in Brassica napus, we used the MCScanX software to identify the types of gene duplication (Cannon et al., 2004). Meanwhile, the orthofinder software was employed to analyze the gene collinearity between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus, and the data were output with the default parameters (Tamura et al., 2021). Finally, the circos software was utilized to visually display the gene duplication events and collinearity results for an intuitive presentation of the relevant characteristics (International Brachypodium Initiative, 2010; Hu et al., 2015).
Analysis of the expression patterns of the BnE2F/DP gene family
Based on the publicly available transcriptome data of Brassica napus, the FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads) value analysis method was employed to investigate the expression status of genes in the BnE2F/DP family of Brassica napus in different tissues and organs. Subsequently, we used the Heatmap program in the TBtools software to draw a heatmap of the expression patterns of the members of the BnE2F/DP gene family in different tissues and organs of Brassica napus, aiming to intuitively present the gene expression characteristics (Gao et al., 2014; Wai et al., 2022).
qRT-PCR analysis of BnE2F/DP gene family
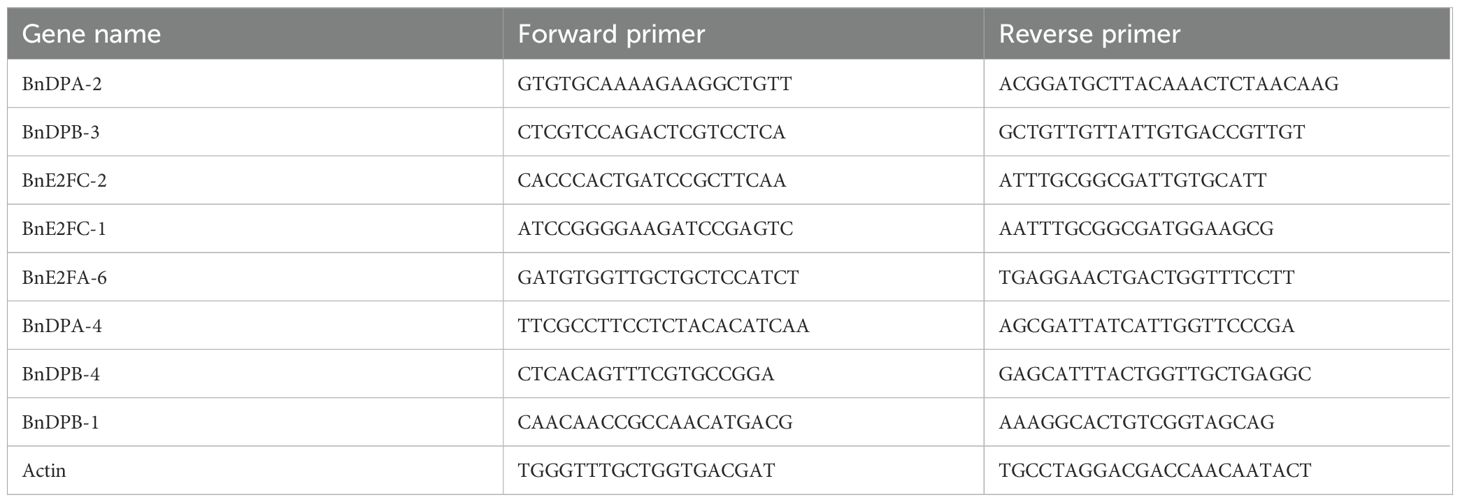
To identify the expression of the BnE2F/DP genes in different tissues of Brassica napus, RNA was extracted and then reverse-transcribed into cDNA after materials collection. Eight BnE2F/DP genes that were representative in seed expression were screened out from the heatmap. Real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR primers for the members of the BnE2F/DP gene family were designed using the Primer-BLAST tool available on NCBI (Berardini et al., 2015) (Table 1). The expression levels of these eight BnE2F/DP genes in the seeds at the above five stages were determined by real-time PCR. Bn-actin was used as an internal reference gene to calculate the expression levels of the target genes (Filichkin et al., 2010; Sharma et al., 2017).
Expression analysis and qRT-PCR validation of BnE2F/DP gene family under abiotic stress in Brassica napus
The transcriptome sequencing data of Brassica napus under salt stress, ABA stress, and drought stress were downloaded from the NCBI database. The Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads(FPKM) expression data of BnE2F/DP genes were extracted, and clustering heatmaps were drawn using TBtools software.
The Brassica napus plants were cultivated in pots in a greenhouse under a 16h/8h photoperiod at 25°C. When the plants grew to the four-leaf and one-bud stage, those with uniform growth vigor were selected as experimental materials. Drought stress was simulated by watering the substrate with 20% (w/v) polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG6000), while the control group was watered with clear water. Leaf tissues were collected at 0, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hours after treatment. Salt stress was simulated by watering the plant substrate with 200 mmol/L NaCl, while the control group was watered with clear water. After treatment, leaf tissues were collected at 0, 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours. Leaves of the plants were sprayed with 100 μmol/L ABA (abscisic acid), and leaf samples were collected at 0, 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours after treatment. All samples were stored in liquid nitrogen after collection, and stored for subsequent use. Each treatment was repeated three times.
Results
Identification and physicochemical property analysis of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus
By screening the Brassica napus database, a total of 29 members of the BnE2F/DP gene family were identified. Then, based on the phylogenetic relationships between these 29 BnE2F/DP genes in Brassica napus and those in Arabidopsis thaliana, as depicted in the phylogenetic tree, they were designated as BnE2FA-1 to BnDPA-4 in a clockwise sequence within the same subfamily.
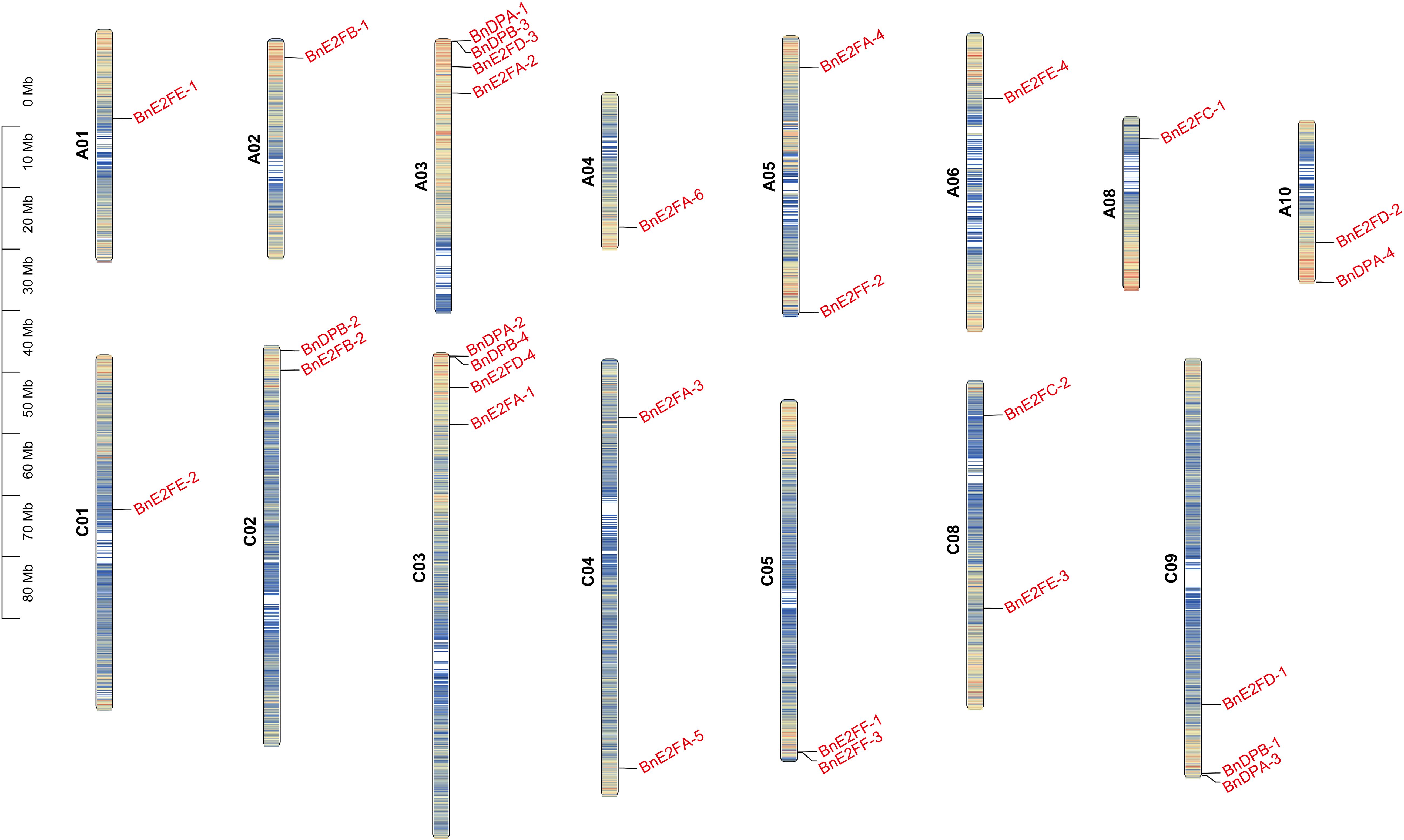
A visual analysis of the 29 BnE2F/DP family members was conducted based on chromosomal location information (Figure 1). The results revealed that these genes were unevenly distributed across the chromosomal scaffolds, which play an important role in organizing the spatial arrangement of genes. Their presence was detected on 15 chromosomes, excluding chromosomes 7, 9, 16, and 17. Both chromosome 3 and chromosome 13 harbored four genes each, and most of the genes were located at the terminal regions of the chromosomes.
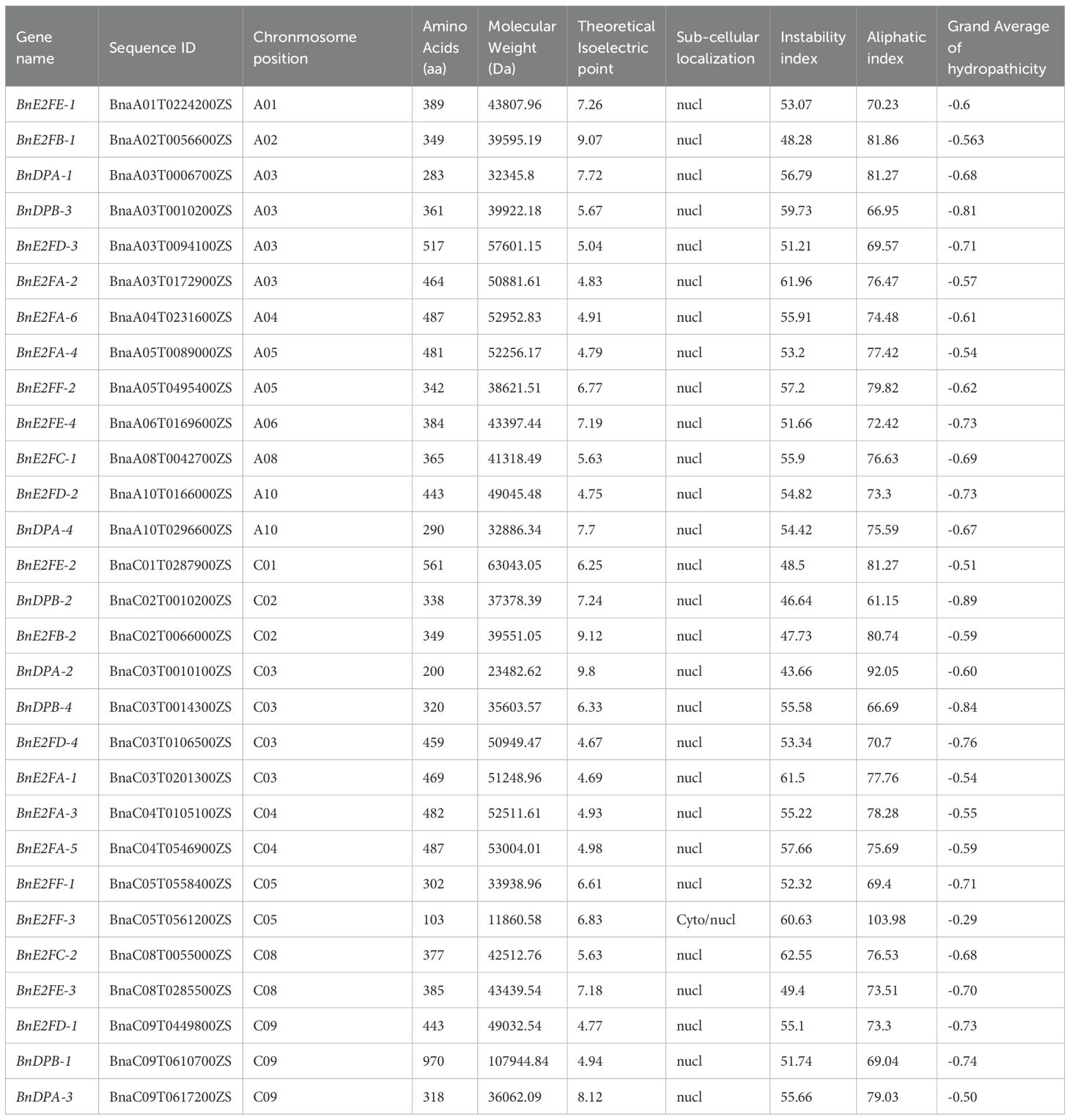
The analysis of physicochemical properties (Table 2) showed that the theoretical isoelectric points (pI) of the BnE2F/DP genes ranged from 4.67 (BnE2FD-4) to 9.8 (BnDPA-2). Moreover, the relative molecular masses of these genes exhibited a wide range, being between 11860.58 Da (BnE2FF-3) and 107944.84 Da (BnDPB-1). Additionally, the lengths of amino acids varied from 290 amino acids (aa) (BnDPA-4) to 970 aa (BnDPB-1). Subcellular localization indicated that only the BnE2FF-3 protein was located in the cytoplasm, while the rest were all in the nucleus. Furthermore, the analysis revealed that the instability coefficients of all the proteins were greater than 40, classifying them as unstable proteins. The aliphatic amino acid index ranged from 61.15 to 103.98, and the grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) values were between -0.886 and -0.289. According to the criteria that proteins with a GRAVY value below 0 are considered hydrophilic, these proteins were determined to be hydrophilic proteins.
Phylogenetic analysis of the BnE2F/DP family in Brassica napus
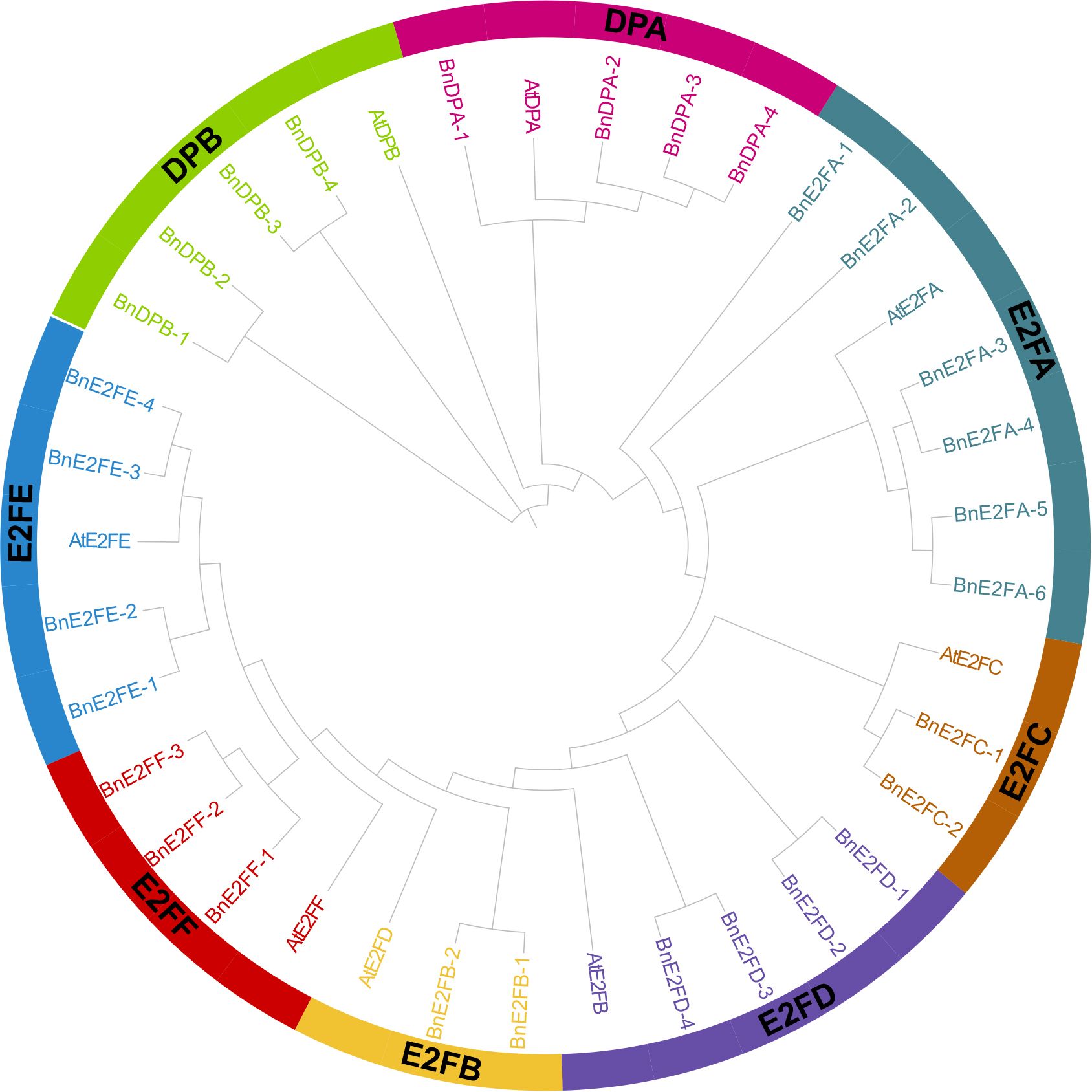
A phylogenetic tree was constructed using 29 BnE2F/DP protein sequences from Brassica napus and 8 AtE2F/DP protein sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana. Referring to the grouping rules adopted by Cubas in the research on Arabidopsis thaliana, which were mainly based on the sequence similarity and structural characteristics of the proteins, the BnE2F/DP members in Brassica napus were classified into eight sub-families, namely DPA, DPB, E2FA, E2FB, E2FC, E2FD, E2FE, and E2FF.
The results of phylogenetic tree analysis demonstrated that among the eight sub-families, the E2FA sub-family had the largest number of members, totaling seven in number. In detail, six members were from Brassica napus and one from Arabidopsis thaliana. Conversely, the E2FB and E2FC sub-families had the smallest number of members, each having only three members, comprising two from Brassica napus and one from Arabidopsis thaliana. It is postulated that the gene members of E2FA fulfill more pivotal functions in plant growth, development, and stress-tolerance responses. Furthermore, the expansion of the BnE2F/DP gene family might be attributable to the increase of gene copy numbers within this sub-family. Moreover, each clade contained E2F/DP protein members from both Brassica napus and Arabidopsis thaliana. This finding implies that there exists a definite phylogenetic affinity and a shared ancestry between the two species in the evolution of E2F/DP genes, suggesting a remarkable degree of continuity and conservation of this transcription factor family throughout the evolutionary course (Figure 2).
Analysis of gene structure and conserved motifs of BnE2F/DP genes in Brassica napus
The gene structures of BnE2F/DP in Brassica napus and the conserved motifs of their corresponding proteins were separately analyzed. As presented in Figure 3, the gene structures within the BnE2F/DP family are intricate, with the exon count ranging from 5 to 18. Members featuring similar structures mainly aggregate within the same clade. Specifically, for instance, members of both the BnE2FA and BnE2FC families consistently possess 13 exons. The number of exons in the BnDPB sub-family ranges from 9 and 18. In the BnDPA subfamily, the exon numbers are relatively smaller. Specifically, BnDPA-1 and BnDPA-4 contain 8 exons, while BnDPA-2 has 5 exons, and BnDPA-3 has 9.
Conserved motifs are highly similar sequences retained during long-term evolution. Analysis of the proteins of 29 BnE2F/DP family members in Brassica napus revealed that all contain the E2F/TDP-2 conserved domain, indicating this motif is a highly conserved and critical region within the family, preserved throughout evolution. Using MEME software, we predicted conserved regions in the amino acid sequences of the BnE2F/DP members (Figure 3), identifying six distinct motifs. Motif 1 was conserved across all family members, suggesting it corresponds to the E2F/TDP-2 domain. Notably, marked variations in motif composition were observed across subfamilies. The DPB subfamily contained Motifs 1, 3, and 6; the DPA subfamily contained Motifs 1 and 6; the E2FA, E2FC, and E2FD subfamilies contained Motifs 5, 1, 2, and 6; the E2FB and E2FE subfamilies contained Motifs 5, 1, and 4; and the E2FF subfamily contained Motifs 5 and 1. Collectively, these results indicate that the higher the sequence similarity of the BnE2F/DP genes, the more similar their structures. Members within the same subfamily shared conserved motif compositions and arrangement, supporting the hypothesis of conserved biological functions of the subfamily members (Figure 3).
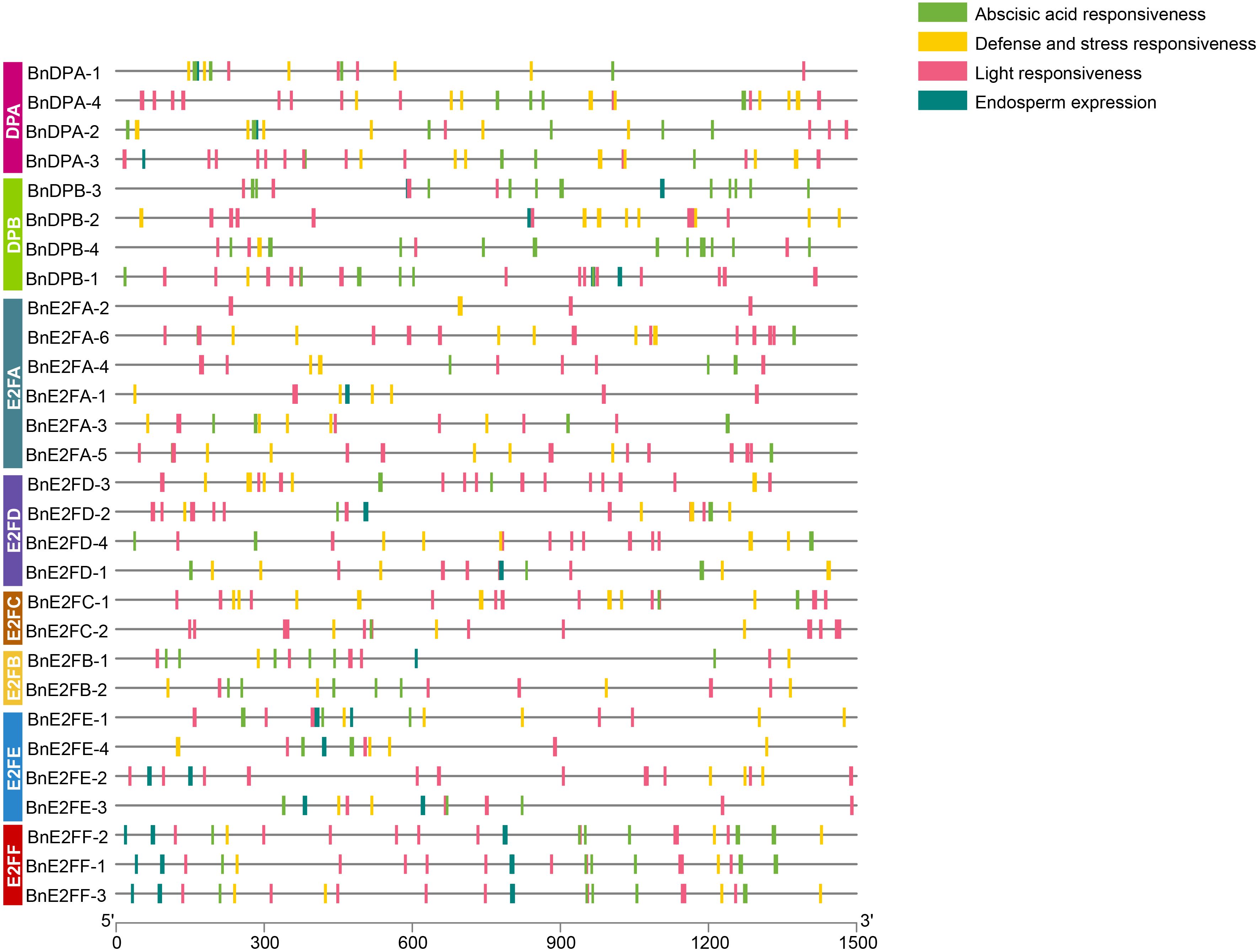
Analysis of cis-acting elements in the promoters of BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus
Cis-acting elements bind to transcription factors to regulate gene expression efficiency. Identifying and analyzing the cis-acting elements in the promoter regions of 29 BnE2F/DP genes can aid in predicting their functions. Specially, the nucleotide sequences of the promoter regions, located 1500 bp upstream of the ATG start codon for each of the 29 BnE2F/DP genes, were retrieved from the NCBI database. The PlantCARE 5, a plant cis-acting element analysis tool, was used to predict the cis-acting elements in these sequences. Subsequently, elements with potential biological functions were identified. The positional distribution patterns of each element in the sequences are detailed in Figure 4. As shown in the figure, the promoters of all BnE2F/DP genes contain multiple cis-acting elements. Among these, light response cis-elements are the most abundant, with each of the 29 genes harboring between 3-13 such elements. Except for BnDPB-2, BnE2FA-2, BnE2FA-1, and BnE2FE-2, 25 BnE2F/DP genes possess hormone-responses cis-acting elements primarily including those responsive to abscisic acid, methyl jasmonate, gibberellin, salicylic acid and auxin. Except for BnDPB-3, 28 BnE2F/DP genes contain cis-acting elements associated with abiotic stresses, including those involved in anaerobic induction, low-temperature response, drought induction, and defense and wounding stimuli. Additionally, 18 BnE2F/DP genes harbor cis-acting elements related to growth and development, primarily including those associated with endosperm-specific expression, meristematic tissue expression, flavonoid biosynthesis regulation, cell cycle regulation, and root-specific regulatory responses.
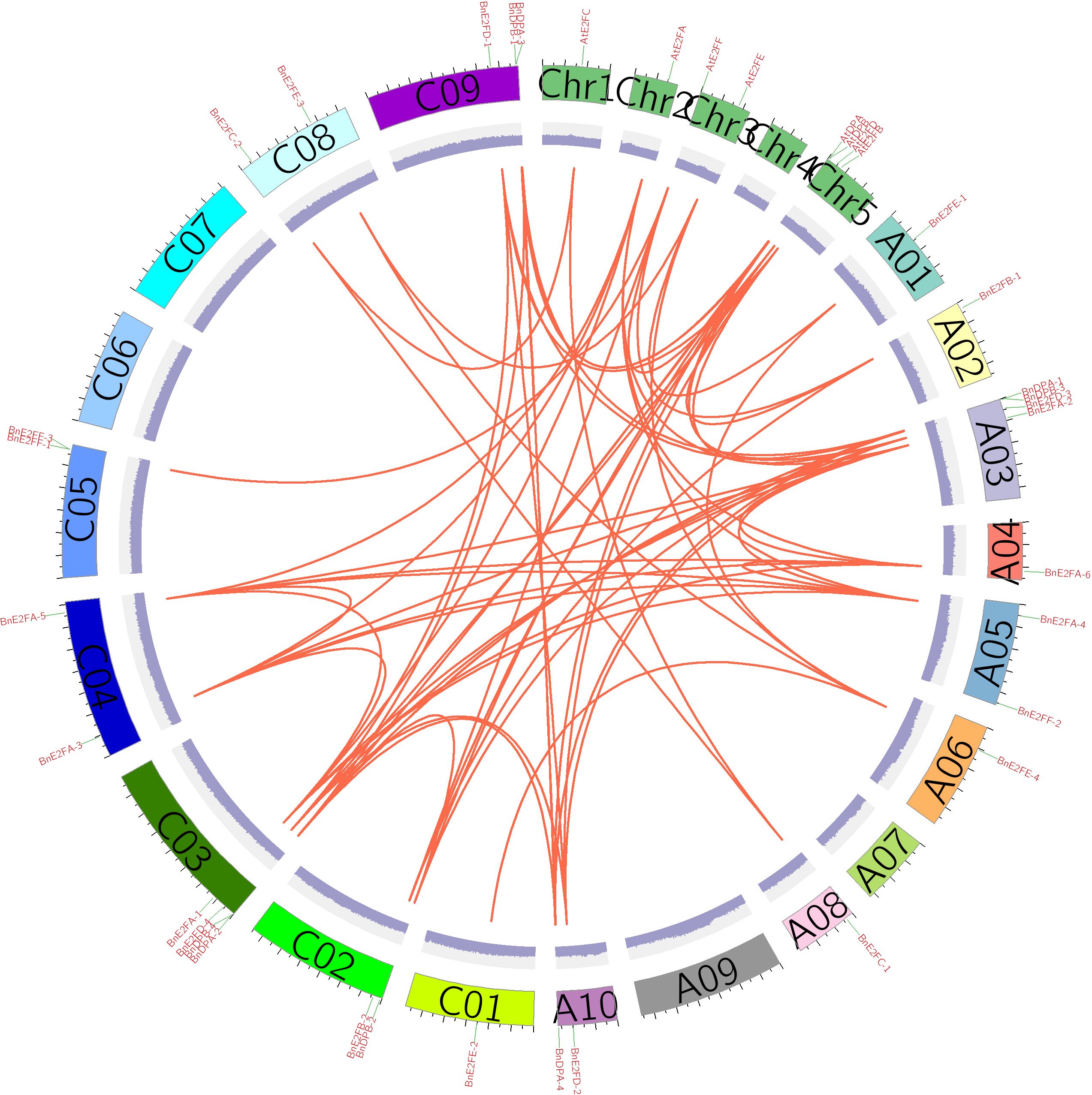
Analysis of collinearity and duplication events of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus
Gene duplication events represent a critical mechanism for the rapid expansion of plant gene families. Given that Brassica napus has undergone whole-genome duplication during its evolutionary history, the presence of duplicated genes is likely. Using the MCScanX software, we analyzed duplication patterns in the BnE2F/DP gene family and found that only one gene underwent dispersed duplication, one remained as a single copy, and 27 originated from whole-genome duplication events. This strongly indicated that whole-genome duplication plays a dominant role in the expansion process of this gene family. Specifically, BnE2FF-2 resulted from dispersed duplication, whereas BnE2FF-3 remained a single-copy gene.
To further investigate the evolutionary relationships within the BnE2F/DP gene family, TBtool was used to visualize collinear regions of the BnE2F/DP genes in Brassica napus and analyze both intraspecific and interspecific collinearities. The results revealed one pair of collinear genes within the AtE2F/DP family in Arabidopsis thaliana. In the BnE2F/DP gene family of Brassica napus, 35 pairs of intraspecific collinear gene were identified, which were distributed across 14 chromosomes. Except for BnE2FF-1, BnE2FF-3, and BnDPB-1, the remaining family members showed significant intraspecific collinearity. This result suggests that gene duplication events have occurred in the E2F/DP gene family, and it is hypothesized that the expansion of the number of family members may be accomplished through these duplication events. Additionally, examples exist where one gene is collinear with multiple genes, indicating that these genes play critical and irreplaceable roles in maintaining Brassica napus growth, development and physiological activities, with their functions being highly conserved. The prevalence of extensive collinear gene pairs within the family supports the hypothesis of functional redundancy. Gene duplication not only increase gene copy numbers but also enhance plant adaptability to environmental stresses (Figure 5).
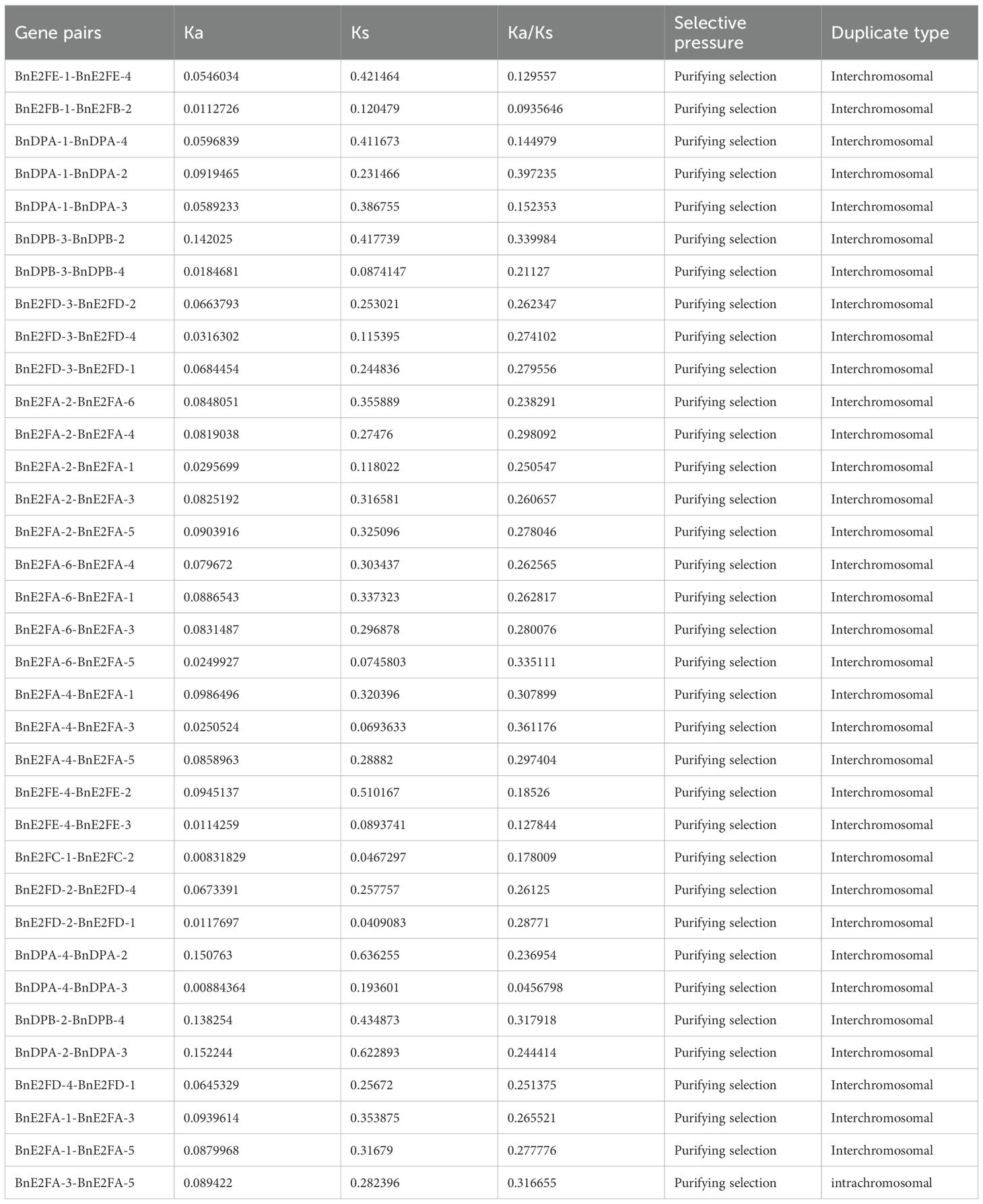
To investigate the selection pressure acting on BnE2F/DP during evolution, we performed a Ka/Ks analysis on 35 intraspecific duplicated gene pairs and analyze syntenic blocks between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus. Specifically, Ka/Ks ratios > 1 indicate positive selection driving adaptive evolution; ratios =1 reflect neutral selection, where natural selection does not influence gene evolution; ratios < 1 suggest purifying selection maintaining functional conservation. The analysis results revealed that the Ka/Ks values of the 35 duplication events in Brassica napus ranged from 0.0456798 to 0.397235 (Table 3), the analysis identify nine orthologous genes pairs between the two species, with Ka/Ks ratios ranging from 0.159425 to 0.594844 (Table 4), all of which were less than 1. This demonstrates that the duplicated genes have undergone purifying selection during evolution and the orthologous E2F/DP genes have also undergone purifying selection during interspecific evolution.
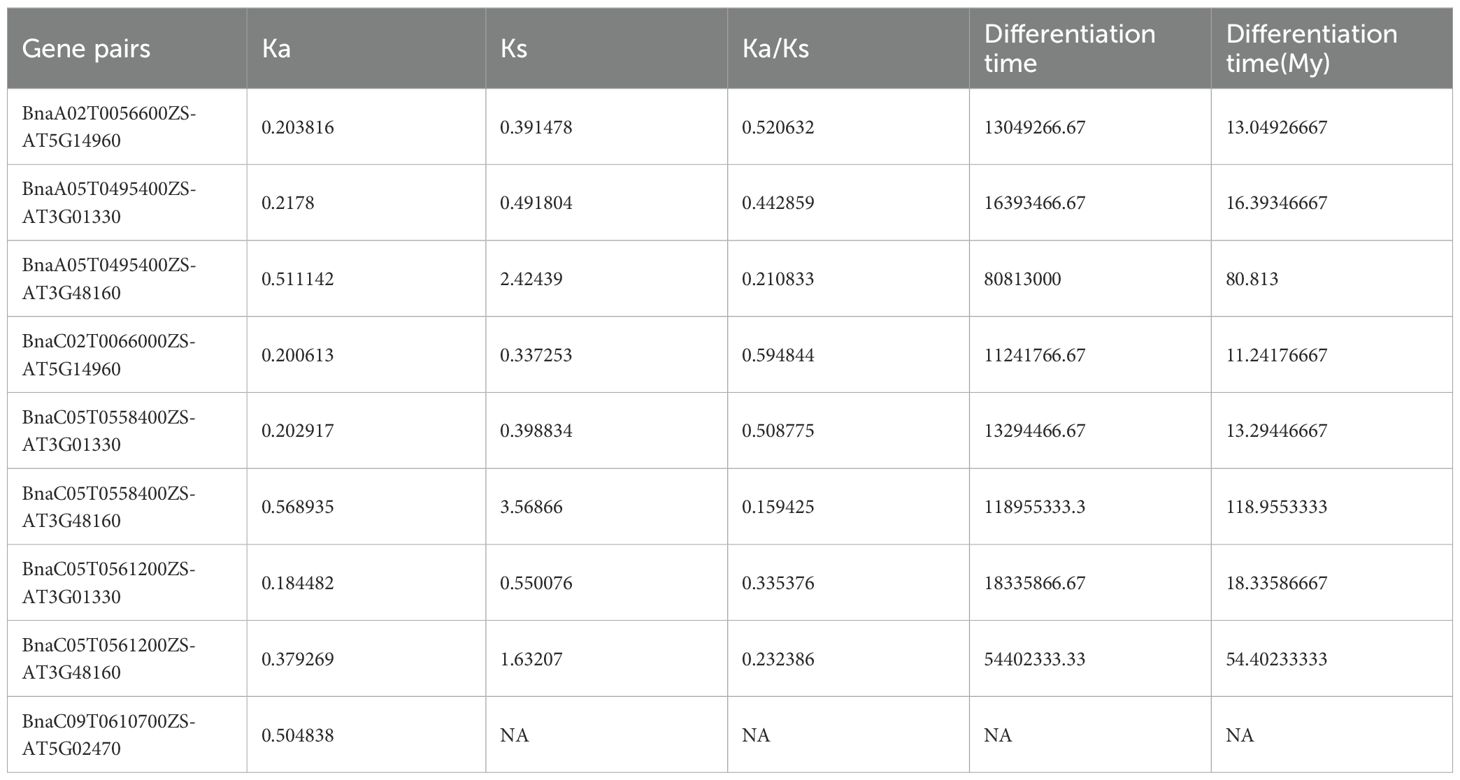
Table 4. Analysis of Ka/Ks ratio of homologous genes BnE2F/DP in Brassica napus and AtE2F/DP in Arabidopsis thaliana.
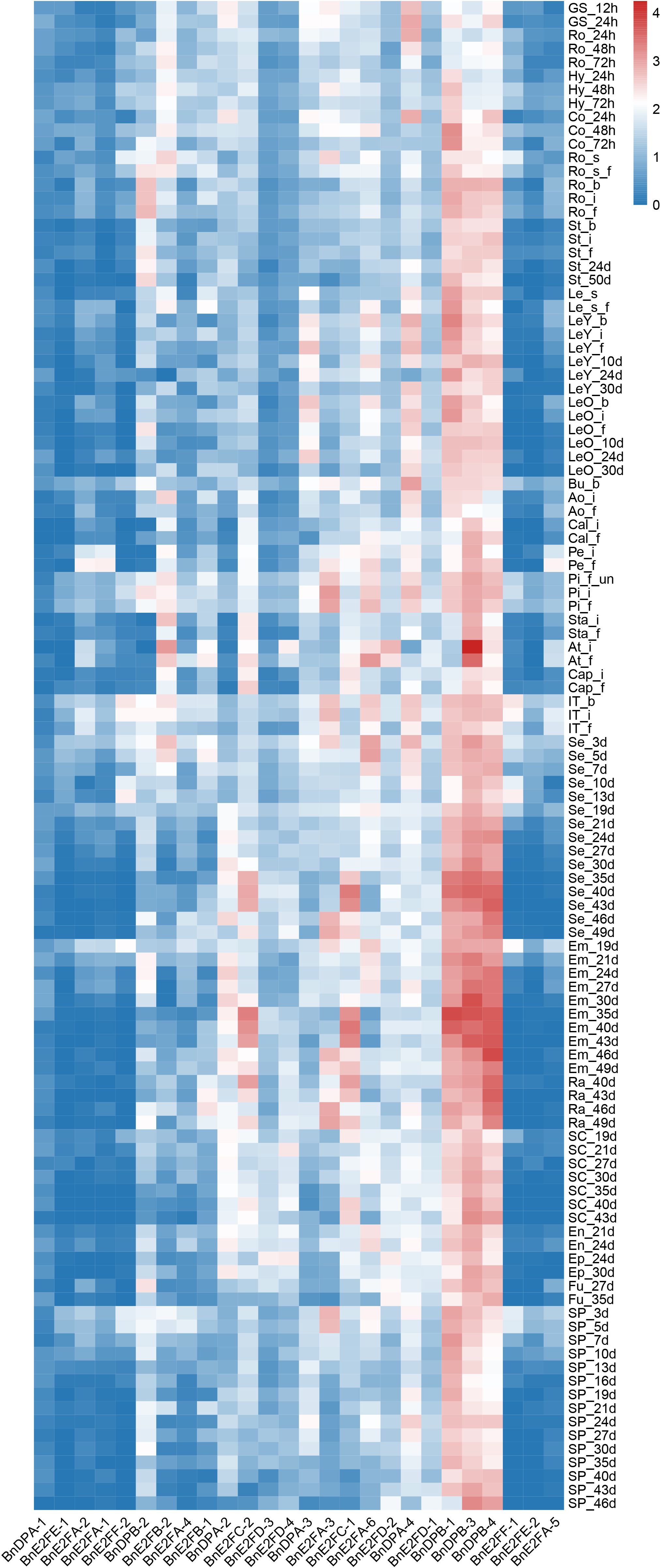
Analysis of the tissue expression patterns of members of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus
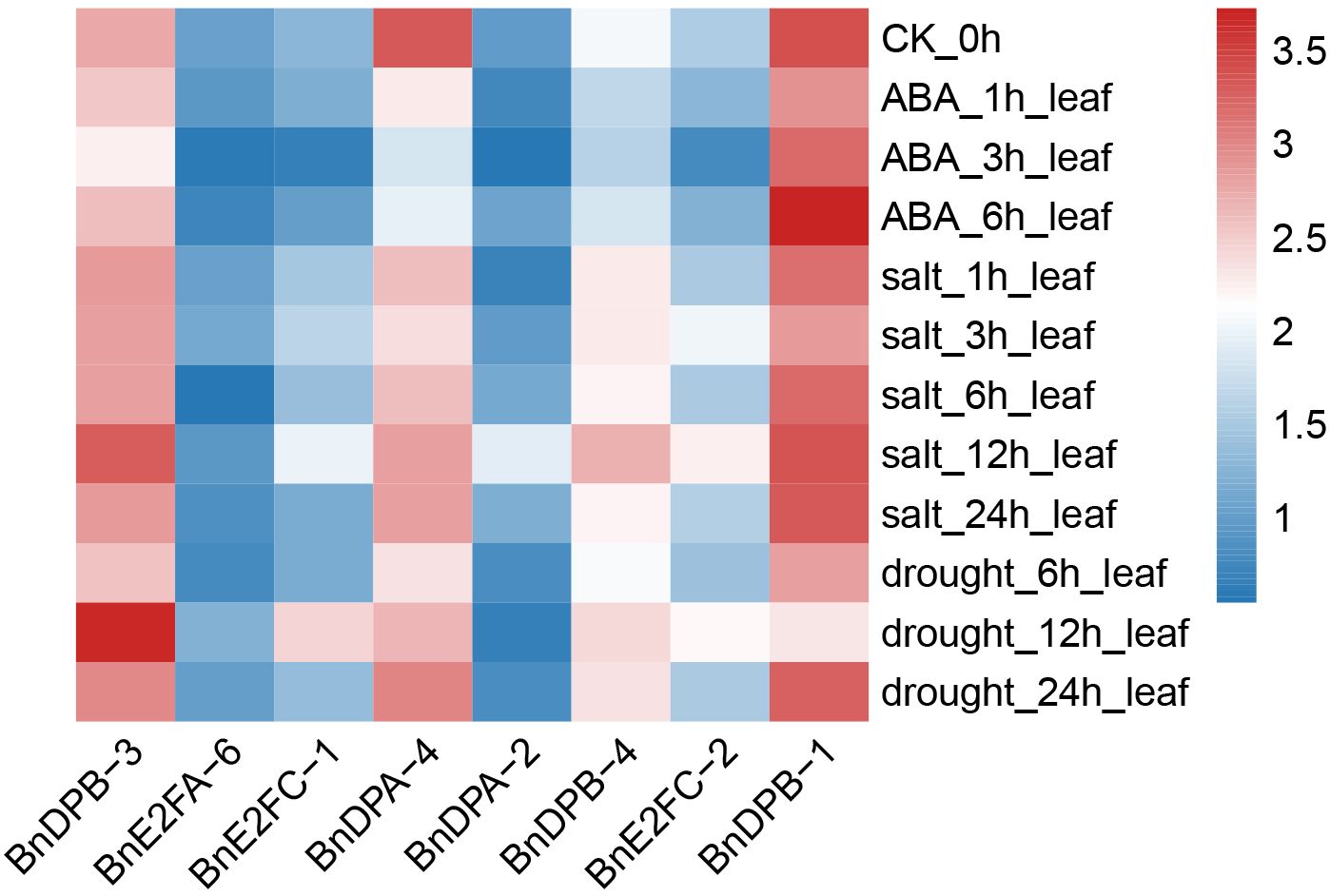
In different tissue parts of plants, various genes play distinct roles and possess different functions. To conduct an in-depth exploration of the functions roles of BnE2F/DP genes, transcriptome data from Brassica napus were analyzed to characterize the expression profiles of E2F/DP family members across 24 vegetative and reproductive tissues, including cotyledons, hypocotyls, radicles and floral organs. Expression analyses were performed across 111 distinct tissues sampled at six developmental stages (germination, seedling, bud, initial flowering stage, full-bloom, and maturity). Based on the gene FPKM (Fragments Per Kilobase of exon model per Million mapped fragments) values obtained from the transcriptome data, expression profiles of 29 BnE2F/DP genes were generated and visualized (Figure 6). The heatmap analysis revealed significant variations in transcript abundance among BnE2F/DP family members, demonstrating spatiotemporal expression patterns. Notably, BnE2FC and BnDPB subfamilies genes displayed consistently high expressions across diverse tissues and organs, whereas BnE2FA, BnE2FE, and BnE2FF subfamily members showed generally low transcript levels. The remaining BnE2F/DP genes exhibited differential expression profiles across developmental stages and tissue types in Brassica napus. Collectively, BnE2F/DP gene family members displayed elevated transcript abundance in seeds and embryos, suggesting their involvement in reproductive development. Notably, 67% (2/3) of BnE2FA subfamily genes (BnE2FA-1, BnE2FA-2, BnE2FA-4, BnE2FA-5) showed negligible expression across most tissues, with only BnE2FA-3 and BnE2FA-6 displaying detectable transcripts. In contrast, BnE2FE and BnE2FF subfamilies each contained one silent member (BnE2FE-1 and BnE2FF-1, respectively) with consistently low transcript levels (FPKM < 0.5) throughout all developmental stages analyzed. In the BnDPB subfamily, 75% (3/4) of the genes (BnDPB-1, BnDPB-3, BnDPB-4) exhibited high FPKM values in almost all tissues and organs, indicating that the members of this sub-family might play a crucial role in the entire growth cycle of Brassica napus. This inference is consistent with the known functions of homologous genes in other plant species, which are often involved in fundamental cellular processes. In the BnE2FC subfamily, both genes (BnE2FC-1, BnE2FC-2) showed the highest FPKM values in seeds and embryos, suggesting their specific roles in seeds and embryos development.
In addition, BnE2FC-1, BnE2FC-2, BnE2FA-6, BnDPB-1, BnDPA-2, BnDPB-3, and BnDPB-4 in Brassica napus showed relatively high FPKM values in seeds from 10 to 49 days after pollination and in embryos from 19 to 49 days after pollination. Given that BnE2FC-1 and BnE2FC-2, BnDPB-1 and BnDPB-3, as well as BnDPB-4 belong to the same sub-family respectively, and considering that genes within the same sub-family often share conserved functional domains and participate in similar molecular pathways according to previous studies, it is suggested that they may have similar functions in Brassica napus.
Validation of members of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus by qRT-PCR
The results (Figure 7; Supplementary Table 1) confirmed high transcript levels of all eight selected genes across seed development, with BnDPB-1, BnDPB-3, and BnDPB-4 showing peak expression at 40 days post-pollination. These results that BnE2F/DP genes play critical roles in seed development, consistent with transcriptome data and validated by qRT-PCR analysis.
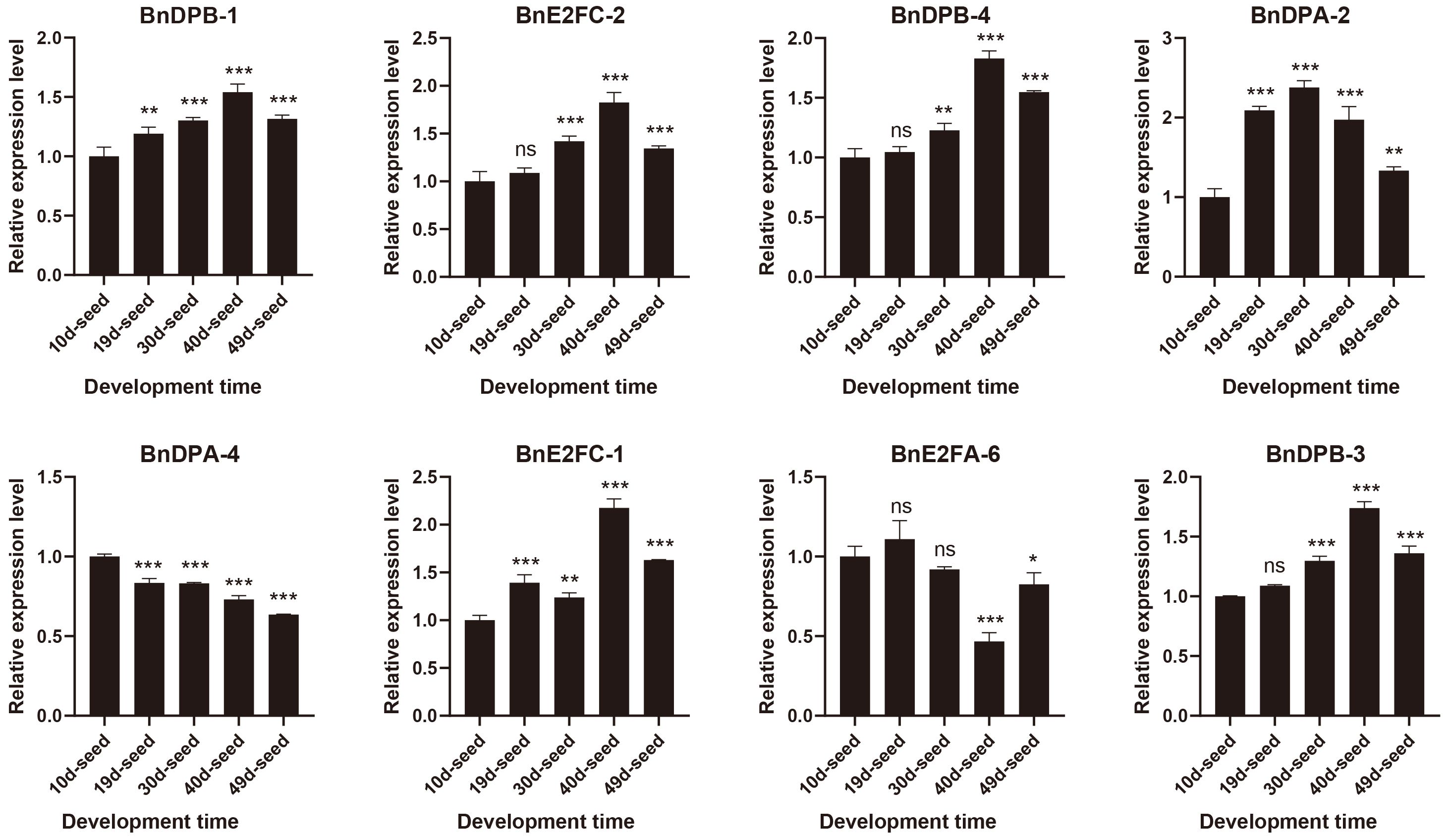
Figure 7. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression of members of the BnE2F/DP gene family in seeds from 10 to 49 days after flowering. The qRT-PCR analysis was performed in triplicate, and the quantification was normalized using the 18S RNA level as a reference. The reported values are the mean, with error bars representing the standard error. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test, where *p < 0.05, *p < 0.01, *p < 0.001, and *p < 0.0001 indicate different levels of significance, and "ns" indicates no significant difference.
qRT-PCR validation of BnE2F/DP gene family members in Brassica napus under abiotic stresses
Quantitative expression of eight genes under different treatments was detected with three replicates each. The results (Figure 8) showed that BnE2F genes were generally inhibited under ABA treatment, exhibiting a trend of first decreasing and then increasing. The gene expression levels peaked at 6 hours after treatment and then decreased, except for BnDPB-1 and BnE2FC-2. Under salt stress, the expression of most genes was inhibited but increased after 12 hours, except for BnDPA-2, BnDPA-4, and BnE2FC-1. Under drought stress, gene expression peaked at 12 hours post-treatment and then rapidly declined, except for BnDPA-2 and BnDPB-1. Notably, BnDPA-2 and BnE2FC-1 were consistently downregulated across all abiotic stress treatments and time points. The expression of BnDPB-3 and BnE2FC-2 was upregulated by more than two-fold under ABA treatment. Additionally, BnDPA-4 and BnE2FC-2 showed significant upregulation under salt stress, consistent with the expression patterns of PheE2F/DP genes in Phyllostachys edulis under salt stress (Li et al., 2021). The expression of E2FC-2 was upregulated by more than two-fold at various time points under all three stresses, whereas BnE2FC-1 was downregulated by nearly two-fold, consistent with the transcriptome data (Figure 9). These results suggest that the BnE2FC subfamily actively responds to diverse abiotic stresses, aligning with the predictions from cis-acting element analysis.
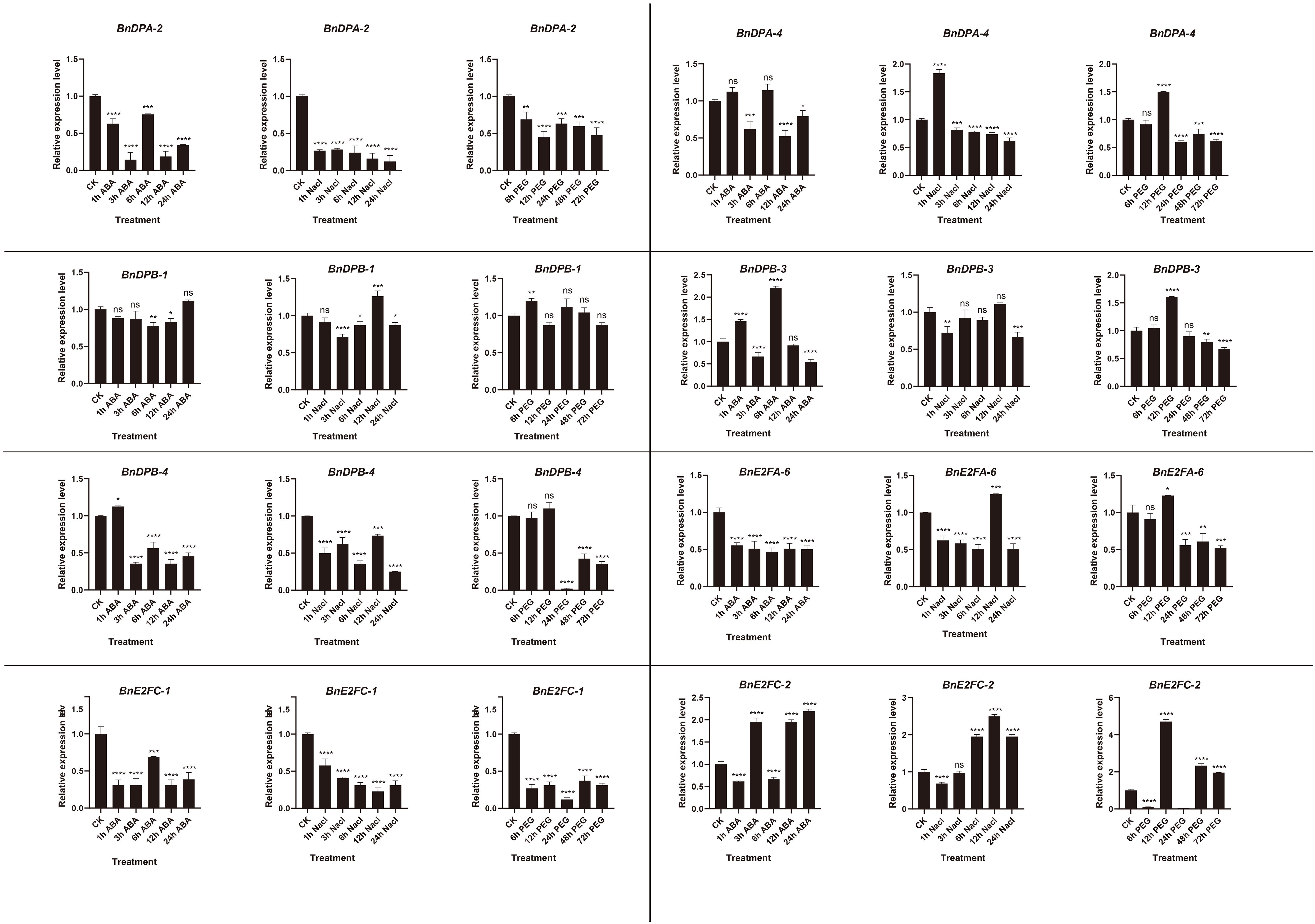
Figure 8. Real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) was used to detect the expression of BnE2F/DP gene family members at different time points under abiotic stresses induced by NaCl, ABA, and PEG.The reported values are the mean, with error bars representing the standard error. Statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test, *p < 0.05, *p < 0.01, *p < 0.001, and *p < 0.0001 indicate different levels of significance, and "ns" indicates no significant difference.
Discussion
E2F/DP transcription factors are conserved regulators of plant cell cycle progression, photoperiodic responses, and seed/embryo development, while also mediating abiotic stresses (Mariconti et al., 2002; Lammens et al., 2009; Berckmans et al., 2011). In animal systems, they play critical roles in viral replication and host cell cycle manipulation during adenovirus infection. Investigating the functional roles of E2F/DP transcription factor genes is critical for deciphering plant development regulatory circutry. Recent high-throughput genomic approaches have enabled systematic characterization of E2F/DP gene families across diverse plant species, including Phyllostachys heterocycla (Pubescens), Glycine max, and Solanum lycopersicum (Bai et al., 2018). Nevertheless, the details of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus remain poorly understood.
Genome-wide characterization of the BnE2F/DP gene family identified 29 members, representing a substantial expansion compared to other plant species: Arabidopsis thaliana (8 genes) (Xiaozhen et al., 2018), Solanum lycopersicum (8 genes) (Divya et al., 2024), Triticum aestivum (27 genes) (Yu et al., 2022), Zea mays (21 genes) (Lescot et al., 2002), Medicago sativa (Ma et al., 2014) (5 genes), Phyllostachys edulis (23 genes) (Li et al., 2021), and Daucus carota (10 genes) (Perrotta et al., 2021). The Phyllostachys edulis genome (2021 Mb) is slightly smaller than Zea mays (2300 Mb), significantly smaller than Triticum aestivum (17 Gb), and substantially larger than Brachypodium distachyon (300 Mb). The expanded PheE2F/DPs gene family in Phyllostachys edulis (23 members) suggests that gene family size correlates with genome duplication events rather than the genome size. This pattern aligns with the differential gene expansion observed across plant lineages. Notably, the Brassica napus genes arose from an additional whole-genome triplication(WGT) event subsequent to its divergence from Arabidopsis thaliana, further illustrating the role of polyploidization in shaping gene family evolution. Brassica napus is an allopolyploid formed by the interspecific hybridization of Brassica rapa (AA genome) and Brassica oleracea (CC genome). Given the paleo hexaploid nature of both progenitor species (each having undergone a whole-genome triplication event subsequent to their divergence from Arabidopsis thaliana) theoretical predictions suggest that B. napus should contain 48 E2F/DP orthologs (8 Arabidopsis genes × 3 copies in each diploid progenitor × 2 sub genomes). However, our genome-wide analysis identified only 29 E2F/DP genes, indicating significant gene loss during the evolutionary history of this allopolyploid crop. Moreover, collinearity analysis shows that the genes have undergone purifying selection during evolution, suggesting that due to functional divergence has driven the retention of critical family members in Brassica napus for environmental adaptation, while non-essential duplicates were lost through fractionation. Chromosomal localization analysis revealed that the BnE2F/DP genes are unevenly distributed across 15 of 19 chromosomes in Brassica napus.The discrepancies in genes number among different sub-families might be attributed to gene amplification and loss events that have occurred during evolution.
Gene structure dictated functional diversity, with exons number variation potentially contributing to evolutionary divergence. During evolutionary, BnE2F/DP subfamilies such as BnE2FC and BnE2FA have retained a conserved exon number, suggesting functional constraint. In contrast, the BnDPA subfamily underwent functional divergence, accompanied by exon loss, which may have enabled the acquisition of novel biological roles distinct from other subfamilies. Conserved motifs analysis revealed that all 29 BnE2F/DP genes possess the E2F-TDP domain, with additional domains present in specific subfamilies. Motif 1 is universally conserved across all BnE2F/DP proteins, indicating its critical role in the evolutionary maintenance of the gene family in Brassica napus. The high degree of motif conservation among family members suggests functional constraint, with most subfamilies sharing common regulatory modules. The presence of the conserved TDP domain (PF00207) in all members confirms their classification within the E2F/DP transcription factor family, while additional lineage-specific domains reflect subfamily diversification. Motif 1 likely corresponds to the conserved TDP domain of the BnE2F/DP genes, consistent with previous reports that all SlE2F/DP proteins in Solanum lycopersicum harbor this domain (Divya et al., 2024). Even after the evolutionary divergence of monocots and dicots within the E2F/DP gene family, these conserved motifs remain similar (Divya et al., 2024). BnE2F/DP genes within the same subfamily exhibit high sequence similarity. For example, BnE2FC and BnE2FA subfamilies share four identical motifs.
In the course of evolution, gene duplication events are a major source of new genetic traits. Segmental duplication increases the number of genes in specific gene families, thereby enhancing plants’ adaptability to various environmental stresses. Synteny analysis identified 35 duplication events among 29 BnE2F/DP genes in Brassica napus, with 28 pairs classified as segmental duplications. Moreover, the BnE2F/DP genes participated in intragenomic replication in the form of whole-genome duplication. Two duplication pairs in the tomato SlE2F/DP gene family indicate that segmental gene duplication triggered the expansion of the tomato E2F/DP gene family during evolution (Divya et al., 2024). In the wheat E2F/DP gene family, there are multiple segmental duplication events, and chromosomal segmental duplication plays a crucial role in the expansion and evolution of the E2F family (Yu et al., 2022). Twelve pairs of duplicated genes have been observed in the E2F/DP gene family of Phyllostachys edulis (moso bamboo) (Li et al., 2021). It has been reported that the functional differentiation between segmentally duplicated genes is more significant. The occurrence of multiple duplication events indicates that the BnE2F/DP gene family has been continuously expanding during the evolutionary process of the Brassica napus genome. This is consistent with the research results of Zea mays (Lescot et al., 2002) and Phyllostachys edulis (Li et al., 2021), indicating conserved E2F/DP gene family expansion patterns across plant lineages. Ka/Ks ratio analysis of the duplicated BnE2F/DP gene revealed values<1 for all pairs, indicating that the BnE2F/DP genes mainly evolved under purifying selection pressure, which is consistent with the evolutionary pattern of most gene families. Interspecific synteny analysis identified 9 orthologous genes pairs between Arabidopsis thaliana AtE2F/DP and Brassica napus BnE2F/DP, suggesting shared ancestry and functional conservation.
It has been reported that members of the E2F/DP family in some plant species actively respond to abiotic stresses. Analysis of Brassica napus BnE2F/DP promoters revealed significant variation in the number and types of cis-regulatory elements across the 29 family members. However, all members contain 3 to 13 light-responsive elements, suggesting their involvement in light signaling pathways. This finding aligns with the previous reports that most PheE2FDPs in Phyllostachys edulis are regulated by the diurnal cycle (Li et al., 2021), implying that light plays a broad and fundamental role in modulating BnE2F/DP expression. Cis-regulatory elements analysis related that 28 BnE2F/DP promoters contain abiotic stress-responsive motifs, second only to light-responsive elements in abundance. This suggested that the BnE2F/DP family plays a broad role in Brassica napus stress responses, potentially mediating mechanisms of environmental sensing, signal transduction, and adaptive responses thereby helping the plants to adapt to external stresses and maintain normal physiological functions. Twenty-five BnE2F/DP genes contain cis-acting elements related to hormone responses, mainly involving abscisic acid, methyl jasmonate, gibberellin, salicylic acid, and auxin response elements. Notably, these genes exhibited significant enrichment in ABRE (ABA-responsive element) and MeJA-responsive motifs, with additional detection of abscisic acid, auxin, salicylic acid, and gibberellin-responsive elements in specific members. This suggests that their potential involvement in integrating multiple hormonal signaling pathways under environmental stresses. QRT-PCR analysis following abiotic stress treatments revealed that most BnE2F/DP genes exhibited high expression levels under both salt and drought stress, consistent with the expression patterns observed in the transcriptome data suggesting their potential roles in abiotic stress toleranceBnDPA-4 and BnE2FC-2 showed significant up-regulation under salt stress. Previous studies have found that SlE2F/DP2, SlE2F/DP7, and SlE2F/DP8 members in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) exhibit high expression under salt stress (Divya et al., 2024); E2Fa, E2Fb, E2Fc, and E2FDPa in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) show more than two-fold up-regulation in expression under salt stress, meanwhile after 6 hours of salt stress, the expression of E2Fc increases in leaves, while in roots, its expression first rises and then declines (Ma et al., 2014). In Arabidopsis thaliana, studies report changes in expression at 6 h and 24 h under salt stress, indicating that salt stress can trigger co-expression of E2F and DP genes (Ramirez-Parra et al., 2004; Desvoyes et al., 2006; Sozzani et al., 2006). The TaDP2III-3 and TaDEL2II-27 genes in wheat (Triticum aestivum) were upregulated under salt stress, while TaE2F1I-19 and TaDP3III-15 were up-regulated under drought stress (Yu et al., 2022). These results are consistent with the findings in Phyllostachys edulis (moso bamboo), where PheE2F/DP genes exhibited upregulation at various time points in response to both drought and salt stresses (Li et al., 2021).Notably, BnE2FC-2 exhibited over two-fold up-regulation at different time points across all three stresses, while BnE2FC-1 and BnDPA-2 were repressed by nearly two-fold at various time points under the three stresses. These results suggest that the BnE2FC subfamily actively responds to diverse abiotic stresses, which is consistent with the predictions from the preceding cis-acting element analysis. The expression of BnDPB-3 and BnE2FC-2 was up-regulated by more than two-fold under ABA treatment. This observation aligns with the previous studies reporting significant enrichment in ABRE and MeJA response elements with Phyllostachys edulis PheE2F/DP genes and tomatoes SlE2F/DP genes (Li et al., 2021; Divya et al., 2024). Notably, plant genes expression is modulated not only by cis-regulatory elements but also by additional factors such as transcription factors and epigenetic modifications. Functional annotation of the BnDPB-4 promoter revealed an absence of development-related cis-regulatory elements but enrichment in hormone-responsive elements. This suggests that BnDPB-4 primarily mediates hormone signaling pathways in Brassica napus rather than participating in development process (Lescot et al., 2002).
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) validation exhibited high consistency with developmental transcriptome data. Throughout the developmental stages of Brassica napus, BnE2FA and BnE2FE subfamilies genes exhibited consistently low expression levels. This observation suggests limited or no significant roles for these genes during the growth and development. In contrast, BnE2FC and BnDPB subfamily members displayed constitutive high expressions across tissues (roots, leaves, flowers, and seeds) and developmental stages (Figure 6). This is consistent with the results that AtE2F in Arabidopsis thaliana (Xiaozhen et al., 2018) and DcE2F1 in Daucus carota (Perrotta et al., 2021) activate cell cycle genes in meristematic cells to promote cell mitotic proliferation. In tomato (Solanum lycopersicum), SlE2F/DP3, SlE2F/DP6, and SlE2F/DP8 are mainly expressed in vegetative tissues (roots), while SlE2F/DP1 and SlE2F/DP7 displayed reproductive tissue-specific expression (e.g., flowers, immature fruits). The remaining genes showed constitutive expression across both vegetative and reproductive tissues. SlE2F/DP genes play a regulatory role in the development, enlargement, and ripening processes of tomato fruits. This indicates that these genes may be involved in cell division and maturation processes (Li et al., 2021). A similar trend can be observed in the expression of E2F/DP genes in Medicago sativa (Ma et al., 2014). AtE2FC is generally regarded as a major repressor of E2F-regulated genes. Its overexpression reduces cell division and leads to an increase in endoreplication. It is hypothesized that BnE2FC may guide cells from division to differentiation in the late stage of seed maturation, thereby promoting the enlargement of seed cells and the accumulation of contents (Xiaozhen et al., 2018). In Daucus carota, DcE2F4, a homolog of AtE2FC, is reported to be well-expressed in young leaves, calli and other differentiated tissues, and is involved in regulating cell proliferation and the activities of mature cells (Perrotta et al., 2021). In summary, we speculate that the BnE2FC subfamily exhibits specific and high-level expression in seeds and embryos of rapeseed varieties, and shows a highly active response to abiotic stresses. Functional verification indicates that they play a key role in the development of seeds and embryos, and actively respond when plants are subjected to salt stress, ABA stress, and drought stress. This contrasts with previous findings in Arabidopsis thaliana (Xiaozhen et al., 2018), where overexpression of AtE2FA or AtE2FB significantly increased cotyledon size and doubled cells number. These observations suggest that during the evolution, homologous recombination events during gene duplication may have resulted in functional divergence of the BnE2FC subfamily in Brassica napus. These results suggest conserved roles for orthologous BnE2F/DP genes in regulating tissues and organ development across Brassica napus growth stages.
Conclusion
In this study, 29 members of the BnE2F/DP gene family were identified in Brassica napus and classified into 8 subfamilies based on phylogenetic analysis. Functional annotation revealed abundant cis-regulatory elements within BnE2F/DP genes, which are involved in processes including growth and development, abiotic stress responses, hormone signaling, and light perception. Notably, all 29 gene members harbored light-responsive elements, suggesting their critical roles in mediating light signaling pathways in Brassica napus. Additionally, 28 genes contained abiotic stress-responsive cis-regulatory elements, indicating their significant involvement in mediating stress tolerance mechanisms under adverse environmental conditions.
Collinearity and duplication pattern analyses revealed that genome expansion of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus occurred primarily occurred through whole-genome duplication events, with 35 collinear gene pairs identified. This finding reflects strong evolutionary conservation among family members. Ka/Ks ratio analysis further indicated that BnE2F/DP genes have undergone purifying selection during evolution. Transcriptomic analysis and qRT-PCR validation demonstrated that BnE2F/DP genes play pivotal regulatory functions across Brassica napus developmental stages, with particularly high expression during seed and embryo development. This highlights their active involvement in coordinating reproductive growth processes, including seed maturation and embryo patterning. Transcriptome prediction under stress and fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis revealed that members of the BnE2F/DP gene family exhibited upregulated or even highly expressed patterns after salt stress and drought stress treatments at different time points. BnE2FC-2 showed more than two-fold high expression under different stresses and time points, indicating that the BnE2FC subfamily actively participates in stress responses, which is consistent with the previous cis-element prediction results. We speculate that BnE2FC-2 is a candidate gene for salt and drought tolerance.
In summary, this study performed genome-wide identification and systematic bioinformatics analysis of the BnE2F/DP family in rapeseed (Brassica napus), with a focus on analyzing their expression patterns during growth and development stages and under abiotic stresses. The results provide insights for further functional studies of the BnE2F/DP gene family and identify potential candidate genes for genetic improvement of rapeseed in regulating growth and development as well as enhancing abiotic stress resistance. This study also offers new perspectives for a better understanding of the BnE2F/DP family in crops.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
MS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing CF: Formal analysis, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31701460)
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1641897/full#supplementary-material
References
Bai, Y., Kissoudis, C., Yan, Z., Visser, R. G. F., and van der Linden, G. (2018). Plant behaviour under combined stress: tomato responses to combined salinity and pathogen stress. Plant J. 93, 781–793. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13800
Bailey, T. L., Boden, M., Buske, F. A., Frith, M., Grant, C. E., Clementi, L., et al. (2009). MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W202–W208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp335
Berardini, T. Z., Reiser, L., Li, D., Mezheritsky, Y., Muller, R., Strait, E., et al. (2015). The Arabidopsis information resource: making and mining the “gold standard” annotated reference plant genome. genesis 53, 474–485. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22877
Berckmans, B., Vassileva, V., Schmid, S. P., Maes, S., Parizot, B., Naramoto, S., et al. (2011). Auxin-dependent cell cycle reactivation through transcriptional regulation of Arabidopsis E2Fa by lateral organ boundary proteins. Plant Cell 23, 3671–3683. doi: 10.1105/tpc.111.088377
Biłas, R., Szafran, K., Hnatuszko-Konka, K., and Kononowicz, A. K. (2016). Cis-regulatory elements used to control gene expression in plants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC) 127, 269–287. doi: 10.1007/s11240-016-1057-7
Cannon, S. B., Mitra, A., Baumgarten, A., Young, N. D., and May, G. (2004). The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 4, 1–21. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-4-10
Cao, Y., Wang, K., Lu, F., Li, Q., Yang, Q., Liu, B., et al. (2024). Comprehensive identification of maize ZmE2F transcription factors and the positive role of ZmE2F6 in response to drought stress. BMC Genomics 25, 465. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10369-0
Desvoyes, B., Ramirez-Parra, E., Xie, Q., Chua, N. H., and Gutierrez, C. (2006). Cell type-specific role of the retinoblastoma/E2F pathway during Arabidopsis leaf development. Plant Physiol. 140, 67–80. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.071027
Divya, D., Robin, A. H. K., Cho, L. H., Kim, D., Lee, D. J., Kim, C. K., et al. (2024). Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of E2F/DP gene family members in response to abiotic stress in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 24, 436. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05107-3
Filichkin, S. A., Priest, H. D., Givan, S. A., Shen, R., Bryant, D. W., Fox, S. E., et al. (2010). Genome-wide mapping of alternative splicing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Res. 20, 45–58. doi: 10.1101/gr.093302.109
Gao, J., Zhang, Y., Zhang, C., Qi, F., Li, X., Mu, S., et al. (2014). Characterization of the floral transcriptome of Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) at different flowering developmental stages by transcriptome sequencing and RNA-seq analysis. PloS One 9, e98910. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098910
Hu, B., Jin, J., Guo, A. Y., Zhang, H., Luo, J., Gao, G., et al. (2015). GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31, 1296–1297. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
International Brachypodium Initiative. (2010). Genome sequence analysis of the model grass Brachypodium distachyon: insights into grass genome evolution. Nature 463, 763–768. doi: 10.1038/nature08747
Jia, K., Yan, C., Zhang, J., Cheng, Y., Li, W., Yan, H., et al. (2021). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the JAZ gene family in turnip. Sci. Rep. 11, 21330. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99593-2
Lammens, T., Li, J., Leone, G., and De Veylder, L. (2009). Atypical E2Fs: new players in the E2F transcription factor family. Trends Cell Biol. 19, 111–118. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.01.002
Lescot, M., Déhais, P., Thijs, G., Marchal, K., Moreau, Y., Van de Peer, Y., et al. (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Li, D., Su, Z., Dong, J., and Wang, T. (2009). An expression database for roots of the model legume Medicago truncatula under salt stress. BMC Genomics 10, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-517
Li, D., Tang, X., Dong, Y., Wang, Y., Shi, S., Li, S., et al. (2022). Genome-wide identification and analysis of the TCP gene family in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Chin. J. Biotechnol. 38, 2974–2988. doi: 10.1007/s00299-022-02918-2
Li, J., Li, M., Shen, T., Guo, Q., Zhang, R., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). Molecular characterization of cassava zinc finger-homeodomain (ZF-HD) transcription factors reveals their role in disease resistance. Int J Biol Macromol. 27 (Pt 1), 134846. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134846
Li, L., Shi, Q., Li, Z., and Gao, J. (2021). Genome-wide identification and functional characterization of the PheE2F/DP gene family in Moso bamboo. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 1–15. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02924-8
Li, Z., Jiang, H., Zhou, L., Deng, L., Lin, Y., Peng, X., et al. (2014). Molecular wei of the HD-ZIP I gene family in legume genomes. Gene 533, 218–228. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2013.09.084
Liu, J. H., Peng, T., and Dai, W. (2014). Critical cis-acting elements and interacting transcription factors: key players associated with abiotic stress responses in plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 32, 303–317. doi: 10.1007/s11105-013-0667-z
Ma, T. Y., Li, Z. W., Zhang, S. Y., Liang, G. T., and Gao, J. (2014). Identification and expression analysis of the E2F/DP genes under salt stress in Medicago truncatula. Genes Genomics 36, 819–828. doi: 10.1007/s13258-014-0218-5
Magyar, Z., De Veylder, L., Atanassova, A., Bakó, L., Inzé, D., Bögre, L., et al. (2005). The role of the Arabidopsis E2FB transcription factor in regulating auxin-dependent cell division. Plant Cell 17, 2527–2541. doi: 10.1105/tpc.105.033761
Mariconti, L., Pellegrini, B., Cantoni, R., Stevens, R., Bergounioux, C., Cella, R., et al. (2002). The E2F family of transcription factors from Arabidopsis thaliana: novel and conserved components of the retinoblastoma/E2F pathway in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 9911–9919. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110616200
Perrotta, L., Giordo, R., Francis, D., Rogers, H. J., and Albani, D. (2021). Molecular analysis of the E2F/DP gene family of daucus carota and involvement of the DcE2F1 factor in cell proliferation. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 652570. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.652570
Polager, S. and Ginsberg, D. (2008). E2F–at the crossroads of life and death. Trends Cell Biol. 18, 528–535. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2008.08.003
Pu, X., Yang, L., Liu, L., Dong, X., Chen, S., Chen, Z., et al. (2020). Genome-wide analysis of the MYB transcription factor superfamily in Physcomitrella patens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 975. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030975
Ramirez-Parra, E., López-Matas, M. A., Fründt, C., and Gutierrez, C. (2004). Role of an atypical E2F transcription factor in the control of Arabidopsis cell growth and differentiation. Plant Cell 16, 2350–2363. doi: 10.1105/tpc.104.023978
Safder, I., Shao, G., Sheng, Z., Hu, P., and Tang, S. (2022). Genome-wide identification studies–A primer to explore new genes in plant species. Plant Biol. 24, 9–22. doi: 10.1111/plb.13340
Sharma, A., Sharma, N., Bhalla, P., and Singh, M. (2017). Comparative and evolutionary analysis of grass pollen allergens using brachypodium distachyon as a model system. PLoS One 12 (1), e0169686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169686
Sozzani, R., Maggio, C., Varotto, S., Canova, S., Bergounioux, C., Albani, D., et al. (2006). Interplay between Arabidopsis activating factors E2Fb and E2Fa in cell cycle progression and development. Plant Physiol. 140, 1355–1366. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.077990
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., and Kumar, S. (2021). MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 3022–3027. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
Wai, A. H., Rahman, M. M., Waseem, M., Cho, L. H., Naing, A. H., Jeon, J. S., et al. (2022). Comprehensive genome-wide analysis and expression pattern profiling of PLATZ gene family members in Solanum Lycopersicum L. under multiple abiotic stresses. Plants 11, 3112. doi: 10.3390/plants11223112
Wei, L., Du, H., Li, X., Fan, Y., Qian, M., Li, Y., et al. (2022). Spatio-temporal transcriptome profiling and subgenome analysis in Brassica napus. Plant J. 111, 1123–1138. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15881
Yao, X., Yang, H., Zhu, Y., Xue, J., Wang, T., Song, T., et al. (2018). The canonical E2Fs are required for germline development in arabidopsis. Front. Plant Ence 9, 638. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00638
Keywords: Brassica napus, E2F/DP, gene family, expression analysis, bioinformatics
Citation: Shen M, Wei L and Fu C (2025) Identification and expression analysis of the BnE2F/DP gene family in Brassica napus. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1641897. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1641897
Received: 06 June 2025; Accepted: 30 July 2025;
Published: 20 August 2025.
Edited by:
Lichao Zhang, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Ruchika Rajput, Oak Ridge National Laboratory (DOE), United StatesDhanasekar Divya, Sunchon National University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2025 Shen, Wei and Fu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chun Fu, NTEzMzI1ODUwQHFxLmNvbQ==; Lijuan Wei, bGlqdWFuNTI1ODg4QDE2My5jb20=
 Min Shen
Min Shen Lijuan Wei
Lijuan Wei Chun Fu
Chun Fu