- 1Pepper Research Institute, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Guiyang, China
- 2Guizhou Key Laboratory of Molecular Breeding for Characteristic Horticultural Crops, Guiyang, China
- 3Guizhou Mountain Agricultural Machinery Research Institute, Guiyang, China
Introduction: Lignin biosynthesis is critical for plant structural integrity and stress response, with Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) playing a pivotal role. This study investigates the CaCCoAOMT gene family in pepper (Capsicum annuum) based on the Zunla-1 genome to elucidate their molecular characteristics and drought stress responses.
Methods: Eleven CaCCoAOMT genes (CaCCoAOMT1–CaCCoAOMT11) were identified and analyzed for physicochemical properties, phylogenetic relationships, gene structure, conserved motifs, and promoter elements. Gene expression patterns were validated using qRT-PCR under drought stress, and subcellular localization of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT2 was determined in tobacco leaves.
Results: The CaCCoAOMT genes are distributed across chromosomes 1, 2, 4, and 8, with CaCCoAOMT10 and CaCCoAOMT11 unanchored. The encoded proteins range from 143 to 380 amino acids with 2–10 exons. Phylogenetic analysis classified the genes into clades II, III, V, and VII. Ten conserved motifs were identified, with motifs 1 and 2 present in all genes. Promoter analysis revealed cis-elements responsive to light, hormones, and drought stress. Expression analysis showed tissue- and developmental stage-specific patterns, with all genes except CaCCoAOMT6 exhibiting differential expression. Under drought stress, six genes were significantly downregulated and two were upregulated in roots. CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT2 localized to both the cytoplasm and nucleus.
Discussion: These findings highlight the structural and functional diversity of the CaCCoAOMT gene family and their regulatory roles in drought stress response in pepper. The differential expression and subcellular localization suggest specific roles in lignin biosynthesis and stress adaptation, providing a foundation for further functional studies and potential applications in improving drought tolerance in pepper.
1 Introduction
Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) is a globally significant crop, but its cultivation is hindered by drought stress, which adversely impacts yield and quality (Zheng et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2024). A key plant response to drought is the alteration of lignin biosynthesis, crucial for enhancing drought tolerance (Moloi and Ngara, 2023). Lignin, a complex phenolic polymer in the plant cell wall, is vital for structural integrity, mechanical strength, efficient water transport, and environmental stress response mechanisms (Liu et al., 2018; Han et al., 2024). Studies across various species have highlighted the importance of lignin in drought tolerance. For example, in rice and grapevine, the activation of lignin biosynthetic genes enhances drought resistance by improving root structural integrity and maintaining photosynthetic efficiency (Bang et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). Similarly, in maize and cassava, lignin accumulation contributes to drought resistance by modulating stress-related pathways and oxidative stress responses (Tu et al., 2020; Bang et al., 2022). Lignin is a complex phenolic polymer deposited in plant cell walls, particularly in vascular tissues like xylem. This deposition provides structural support, allowing plants to maintain upright growth and withstand mechanical stress during drought conditions. The rigidity imparted by lignin is essential for maintaining cell wall integrity under water-deficit scenarios (Jiao et al., 2024). The hydrophobic nature of lignin decreases cell wall water permeability, thereby reducing water loss through transpiration. This property is particularly beneficial under drought stress, as it helps plants conserve water and maintain cellular hydration (Han et al., 2022). Lignin is integral to the formation of the Casparian strip in the endodermis, which regulates the uptake of water and solutes into the plant. Additionally, lignin deposition in xylem vessels enhances the plant’s ability to conduct water over long distances, ensuring adequate hydration during periods of limited water availability (Yadav and Chattopadhyay, 2023). These findings collectively highlight the importance of lignin biosynthesis in enhancing plant drought tolerance by improving cell wall structure, regulating water movement, and reducing water loss under stress conditions.
Lignin biosynthesis is a multifaceted process that involves a variety of enzymes and metabolic pathways (Choi et al., 2023; Han et al., 2024). Among these, the CCoAOMT genes are pivotal, as they participate in both lignin and flavonoid synthesis within the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway, thereby contributing to plant resistance mechanisms (Kim et al., 2007; Gu et al., 2010). Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) is a pivotal enzyme in the lignin biosynthesis pathway, catalyzing the methylation of caffeoyl-CoA to produce feruloyl-CoA, a precursor for guaiacyl (G) lignin monomers. This methylation step is crucial for the formation of lignin, a complex polymer that provides structural support and resistance to environmental stresses in plants (Yadav and Chattopadhyay, 2023). In maize, the CCoAOMT gene is essential for lignin biosynthesis, significantly influencing lignin composition and the structural integrity of the plant cell wall. Alterations in CCoAOMT genes have been shown to modify lignin content and composition, which in turn affects plant degradability and mechanical strength (AFornalé et al., 2016). In the fern Polypodiodes amoena, two CCoAOMT genes have been identified and functionally validated, demonstrating their capacity to methylate caffeoyl-CoA and contribute to lignin biosynthesis when expressed in Arabidopsis thaliana (Zhang et al., 2019). Beyond its role in lignin formation, CCoAOMT is also involved in plant defense mechanisms. In maize, CCoAOMT interacts with hydroxycinnamoyltransferase (HCT) and the NLR protein Rp1 to modulate immune responses (Wang and BalintKurti, 2016). In the hybrid species Acacia auriculiformis × Acacia mangium, the enzyme CCoAOMT plays a critical role in modulating lignin content and composition, which has significant implications for wood quality and industrial applications such as pulp production (Pang et al., 2014). Additionally, CCoAOMT is involved in regulating carbon flux between lignin and other phenylpropanoid-derived metabolites. For instance, in Asarum sieboldii, altering CCoAOMT expression shifted the metabolic balance towards increased phenylpropene production at the expense of lignin synthesis under specific conditions (Ji et al., 2023). These findings underscore the pivotal role of CCoAOMT in plant metabolism and its potential as a target for genetic engineering aimed at optimizing lignin content and composition for diverse applications (Guo et al., 2019; Lam et al., 2019). Consequently, CCoAOMT emerges as a key regulator in lignin biosynthesis and plant stress adaptation across various species.
Extensive research has been undertaken to identify and characterize the CCoAOMT gene family across a diverse range of plant species, underscoring its importance. In jute (Corchorus spp.), a comprehensive genome-wide analysis has elucidated the structural, functional, and evolutionary attributes of CCoAOMT genes, alongside their expression profiles under abiotic stress conditions (Kahie et al., 2023). Similarly, in the tea plant (Camellia sinensis), ten CCoAOMT genes have been identified, exhibiting conserved gene structures and motifs, which offer insights into their phylogenetic relationships and potential roles in lignin biosynthesis and stress responses (Wang et al., 2024). Furthermore, CCoAOMT gene families have been identified in various other plant species, including Gossypium, Solanum tuberosum, Dendrocalamus farinosus, Populus, Malus domestica, Pyrus bretschneideri, and Prunus persica (Li et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2022; Wei et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2024; Peng et al., 2024). Despite recent advances, a comprehensive identification and evolutionary analysis of CCoAOMT genes in pepper has not yet been undertaken. In this study, we utilized bioinformatics methodologies to systematically identify and characterize the CCoAOMT gene family in pepper. Our analysis encompassed the examination of protein physicochemical properties, evolutionary relationships, gene structures, cis-regulatory elements, and gene duplication events. Additionally, using qRT-PCR analysis, we identified candidate CaCCoAOMT genes that are responsive to drought stress. This research not only enhances the genomic information available for the CaCCoAOMT gene family but also lays the groundwork for future investigations into their functional roles in lignin biosynthesis, stress adaptation, and potential applications in crop improvement.
2 Results
2.1 Genome-wide identification and physicochemical analysis of the CCoAOMT family in pepper
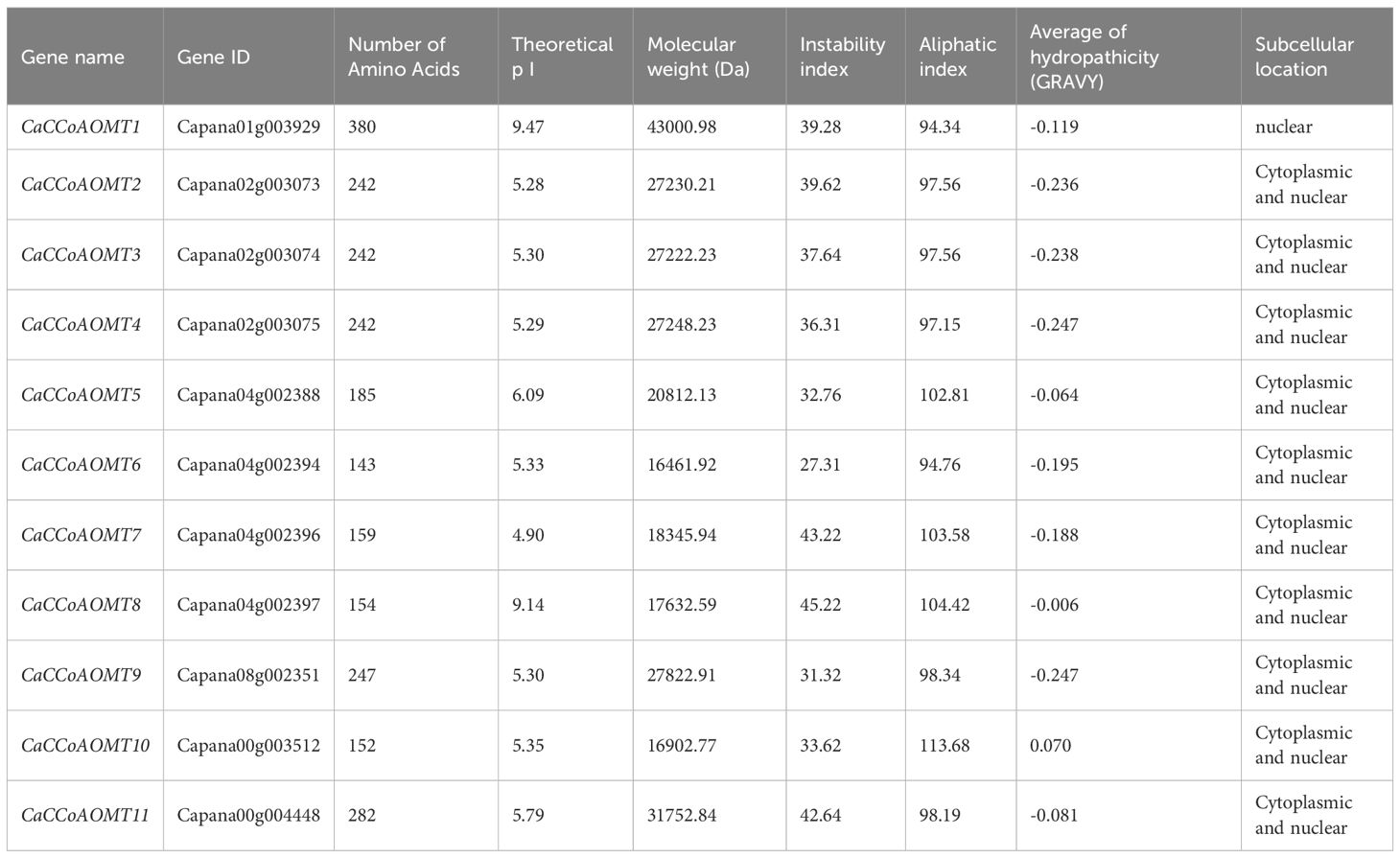
Members of the CaCCoAOMT gene family were identified in the genome of the pepper cultivar ‘Zunla 1’ using HMMER-based searches. A total of 11 CCoAOMT genes were identified in the pepper genome and were systematically designated as CaCCoAOMT1 through CaCCoAOMT11, according to their chromosomal positions (Table 1). The lengths of CaCCoAOMT proteins in pepper range from 143 to 380 amino acids. Their isoelectric points (pI) span from 4.90 to 9.47, and their molecular weights range from 16,461.92 Da to 43,000.98 Da. The instability index of these proteins varies between 27.31 and 45.22, while their aliphatic indices are between 94.34 and 113.68. The grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) values range from -0.247 to 0.070. Subcellular localization predictions indicate that CaCCoAOMT1 is localized in the nucleus, whereas the other 10 CaCCoAOMT proteins are predominantly localized to both the cytoplasm and nucleus.
2.2 Evolutionary analysis of CCoAOMTs
To elucidate the evolutionary relationships within the CCoAOMT gene family, an un-rooted neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree was constructed based on 58 CCoAOMT protein sequences from seven angiosperm species: Capsicum annuum (11 members), Arabidopsis thaliana (7), Oryza sativa (6), Camellia sinensis (10), Gossypium raimondii (6), Linum usitatissimum (6), and Solanum tuberosum (12) (Figure 1; Supplementary Table S1). The phylogenetic analysis (Figure 1) delineated the CCoAOMT proteins into seven distinct clades, each characterized by distinct species distribution patterns. Notably, members of CaCCoAOMT were absent from clades I, III, and VI. The comparative analysis revealed that CaCCoAOMT1 was grouped within clade V, alongside six rice homologs (OsCCoAOMT1–6), two Arabidopsis members (AtCCoAOMT3 and AtCCoAOMT4), two tea plant homologs (CsCCoAOMT3 and CsCCoAOMT4), and single representatives from flax (LuCCoAOMT1), cotton (GrCCoAOMT4), and potato (StCCoAOMT9). This grouping supports the hypothesis that CaCCoAOMT1 shares a closer evolutionary relationship with rice and other species in clade V. Clade IV comprised four CaCCoAOMT members (CaCCoAOMT2, CaCCoAOMT3, CaCCoAOMT4, and CaCCoAOMT10) that clustered with three potato orthologs (StCCoAOMT2, StCCoAOMT3, and StCCoAOMT4). This observation provides further insight into the evolution of these genes in Capsicum and their relationship with other Solanaceae species. Additionally, CaCCoAOMT9 formed a distinct subclade within clade II, in association with AtCCoAOMT1 and three potato paralogs (StCCoAOMT1, StCCoAOMT11, and StCCoAOMT12). This clustering suggests specific evolutionary trajectories for CaCCoAOMT9 within clade II. Notably, clade VII comprised five CaCCoAOMT proteins (CaCCoAOMT5, CaCCoAOMT6, CaCCoAOMT7, CaCCoAOMT8, and CaCCoAOMT11), which were clustered alongside three isoforms from potato (StCCoAOMT6, StCCoAOMT7, and StCCoAOMT8), a homolog from Arabidopsis (AtCCoAOMT2), two variants from the tea plant (CsCCoAOMT9 and CsCCoAOMT10), and two homologs from cotton (GrCCoAOMT3 and GrCCoAOMT6). These findings suggest a shared evolutionary origin for these CaCCoAOMT members, further supporting their potential functional similarities.
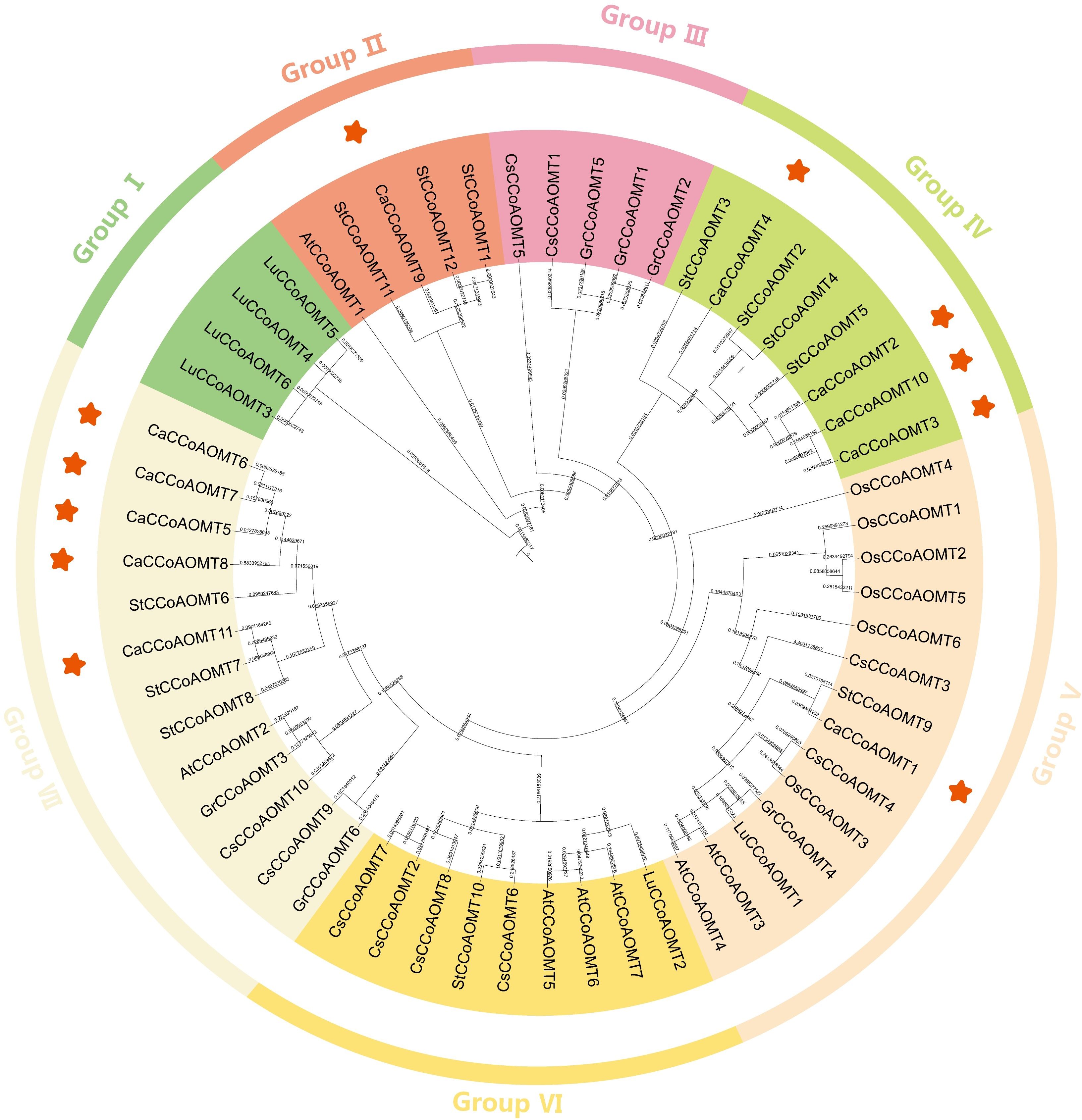
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of CCoAOMT proteins from Capsicum annuum and other selected plant species. Species abbreviations: Ca (Capsicum annuum, highlighted in red), At (Arabidopsis thaliana), Os (Oryza sativa), Cs (Camellia sinensis), Gr (Gossypium raimondii), Lu (Linum usitatissimum), and St (Solanum tuberosum). The phylogenetic tree illustrates the evolutionary relationships and divergence of CCoAOMT proteins across these representative angiosperms.
2.3 Chromosomal localization, intraspecific, and interspecific collinearity analysis of CCoAOMT genes
Chromosomal localization analysis revealed that 9 CaCCoAOMT genes were physically mapped to four chromosomes (Chr01, Chr02, Chr04, and Chr08) in Capsicum annuum, displaying distinct distribution patterns (Supplementary Figure S1). Notably, two chromosomal regions exhibited prominent gene clustering: Chr04 harbored the highest proportion of genes (36.36%, 4 out of 11), followed by Chr02 (27.27%, 3 out of 11), while Chr01 and Chr08 each contained a single gene locus. Interestingly, CaCCoAOMT10 and CaCCoAOMT11 were not anchored to any chromosomal scaffold. Intra species collinearity found a collinear relationship between CaCCoAOMT9 and CaCCoAOMT2 (Figure 2A), indicating that their positions and arrangement in the genome may have high similarity or identical structural features. Through inter species collinearity analysis, a single orthologous gene pair was identified between Capsicum annuum and Arabidopsis thaliana, indicating that these two species have low conservation in genome structure and may have significant genome rearrangements or evolutionary differentiation (Figure 2B), this is consistent with the results of phylogenetic analysis (Figure 1). Whereas five conserved syntenic pairs were found between C. annuum and Nicotiana tabacum (Figure 2B). This suggests a greater divergence of C. annuum CCoAOMTs from Brassicaceae lineage genes, possibly due to lineage-specific expansions or differential gene loss.
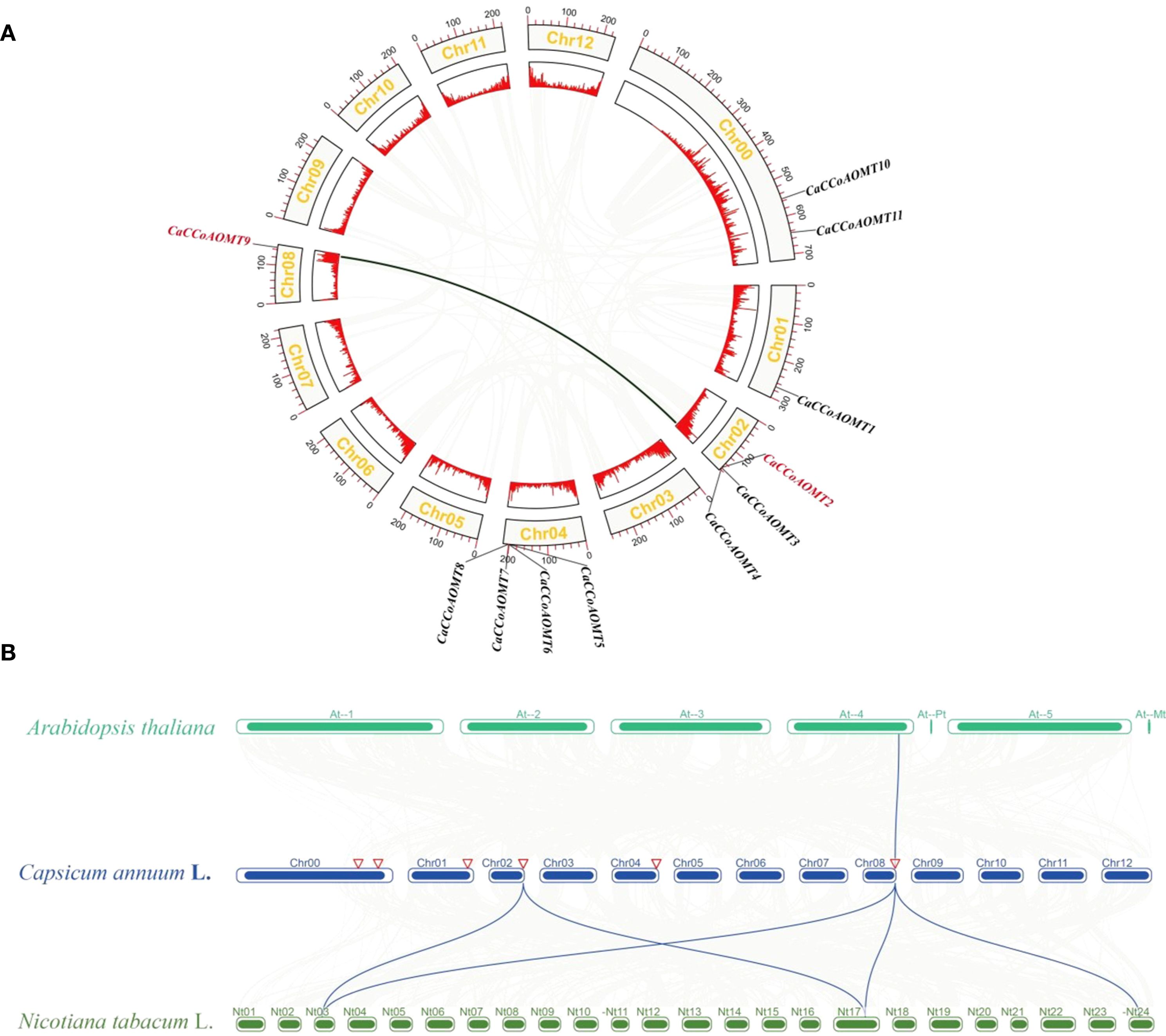
Figure 2. Collinearity analysis of C annuum and different species. (A) Intraspecific collinearity analysis of CaCCoAOMT genes. (B) Evolutionary relationship analysis between C annuum to A thaliana, and N. tabacum. Gray lines represent all synteny blocks identified between the genomes of different species.
2.4 Conserved motif composition and gene structure of CaCCoAOMT family members
To further investigate the structural characteristics of CaCCoAOMT proteins, we performed a conserved motif analysis utilizing the MEME suite. Our analysis identified ten conserved motifs, labeled Motif 1 through Motif 10, across the CaCCoAOMT family (Figure 3), with each member exhibiting a single conserved AdoMet-MTase superfamily domain. Interestingly, the number of motifs per protein varied considerably, ranging from two to seven. Despite this variation, motif composition patterns were largely consistent within phylogenetic subgroups, corresponding to their clustering in the phylogenetic tree. Exon-intron structure analysis revealed substantial diversity in gene architecture. The number of introns within CaCCoAOMT genes varied from one (in CaCCoAOMT6 and CaCCoAOMT8) to nine (in CaCCoAOMT1), with intermediate members containing two (CaCCoAOMT5, CaCCoAOMT7, CaCCoAOMT10, and CaCCoAOMT11), three (CaCCoAOMT2, CaCCoAOMT3, and CaCCoAOMT4), or four (CaCCoAOMT9) introns. The observed gradient in structural complexity, particularly the high intron content in CaCCoAOMT1, indicates that functional specialization and regulatory diversification have been influenced by evolutionary pressures within this gene family.
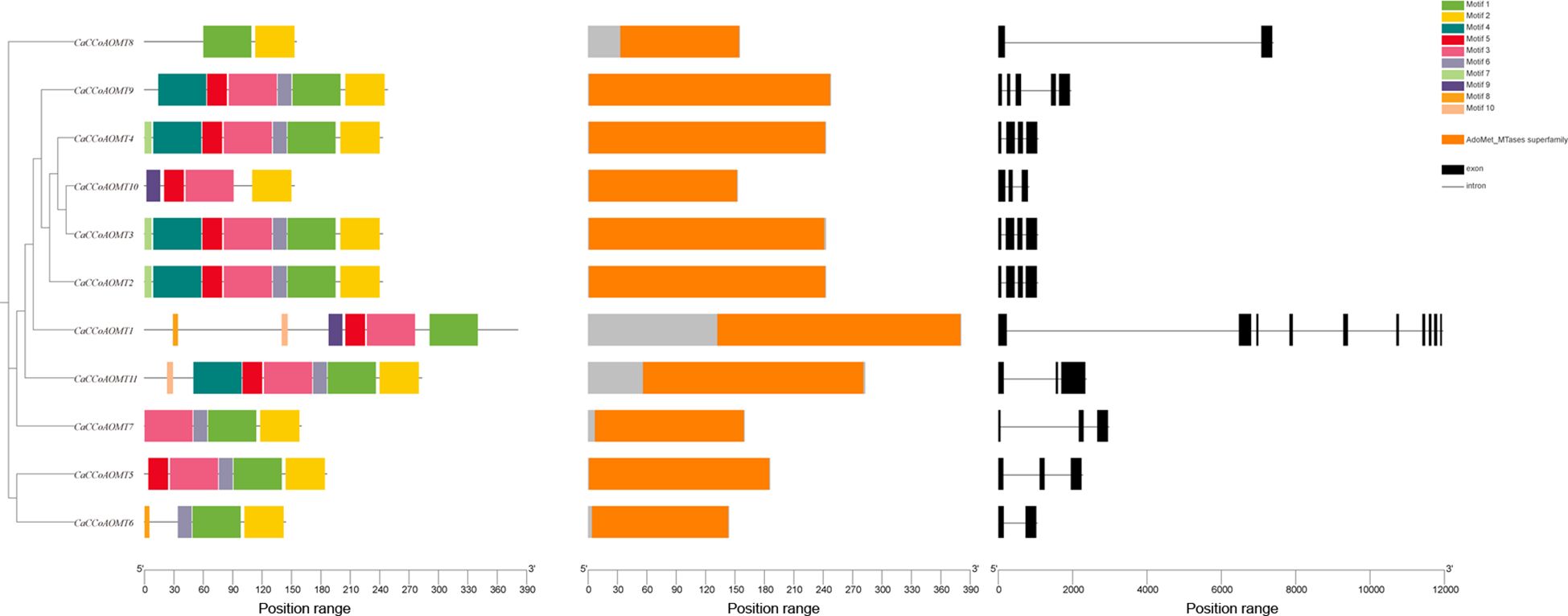
Figure 3. The phylogenetic relationship, conserved motifs, domain distribution, and exon–intron structures of the CaCCoAOMTs.
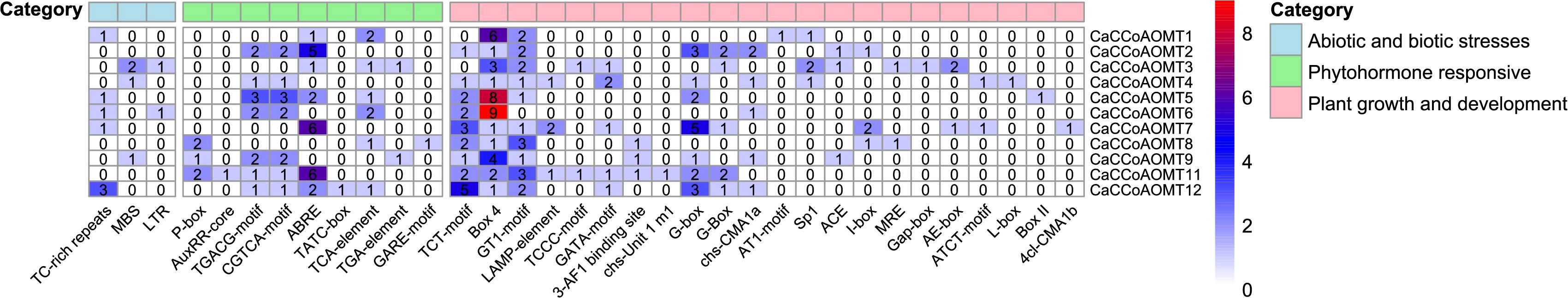
2.5 Cis-regulatory elements analysis of CaCCoAOMT genes
To elucidate the regulatory potential of the CaCCoAOMT genes, we conducted a systematic analysis of the cis-acting elements within their 2000 bp promoter regions. The ‘Plant growth and development’ category was predominantly composed of light-responsive elements, with Box4 being universally present across all CaCCoAOMT promoters. Notably, CaCCoAOMT5 and CaCCoAOMT6 exhibited the highest number of these elements. In addition to being crucial for regulating transcriptional activity under light, Box4 also play a critical role in responding to drought and salt stress, indicating that these genes may be involved in regulating plant light adaptation and stress resistance. In the ‘Phytohormone responsive’ category, ABA-responsive elements (ABRE) were identified in CaCCoAOMT2, CaCCoAOMT7, and CaCCoAOMT11. ABRE elements typically appear in the promoter regions of genes related to environmental stress response. These genes are activated by ABA signaling through the action of ABRE elements, helping plants cope with stress such as drought, salt, and low temperature. The ‘Abiotic and biotic stress’ category was the least represented, with MYB binding sites associated with drought inducibility (MBS) found in CaCCoAOMT3, CaCCoAOMT4, and CaCCoAOMT9 (Figure 4). MYB transcription factors are closely related to the response of plants to environmental stresses such as drought, salinity, pests and diseases. MBS elements play an important role in the regulation of these genes. In addition, the role of MBS components in lignin synthesis, anthocyanin synthesis, and other pathways promotes the accumulation of these important chemicals in plants during growth and development.
2.6 Expression patterns of CaCCoAOMT genes across different tissues and fruit developmental stages
To investigate the potential functional roles of the CaCCoAOMT gene family in pepper, we systematically analyzed their expression profiles across different tissues and throughout various stages of fruit development. As illustrated in Figure 5 and Table S2, CaCCoAOMT1 demonstrated elevated expression levels in leaf tissues (ZL1-Leaf) and during the initial stage of fruit development (ZL1-F-Dev1). Regarding tissue-specific expression, CaCCoAOMT2 and CaCCoAOMT3 were predominantly expressed in roots (ZL1-Root) and leaves, whereas CaCCoAOMT4 and CaCCoAOMT5 exhibited strong root-specific expression. Importantly, CaCCoAOMT6 showed no detectable expression in any of the tissues analyzed. In the context of fruit developmental stages, CaCCoAOMT7 was markedly upregulated during the late fruit maturation phase (ZL1-F-Dev8), while CaCCoAOMT8 was specifically activated at the mid-developmental stage (ZL1-F-Dev3). Furthermore, CaCCoAOMT9 and CaCCoAOMT10 displayed coordinated expression patterns in root tissues and at the fourth fruit developmental stage (ZL1-F-Dev4). CaCCoAOMT11 was expressed in both leaf and floral tissues (ZL1-Flower). Collectively, these findings indicate that CaCCoAOMT genes are subject to dynamic and finely tuned regulation across various tissues and during fruit development, suggesting their diverse roles in organogenesis and developmental processes in pepper.
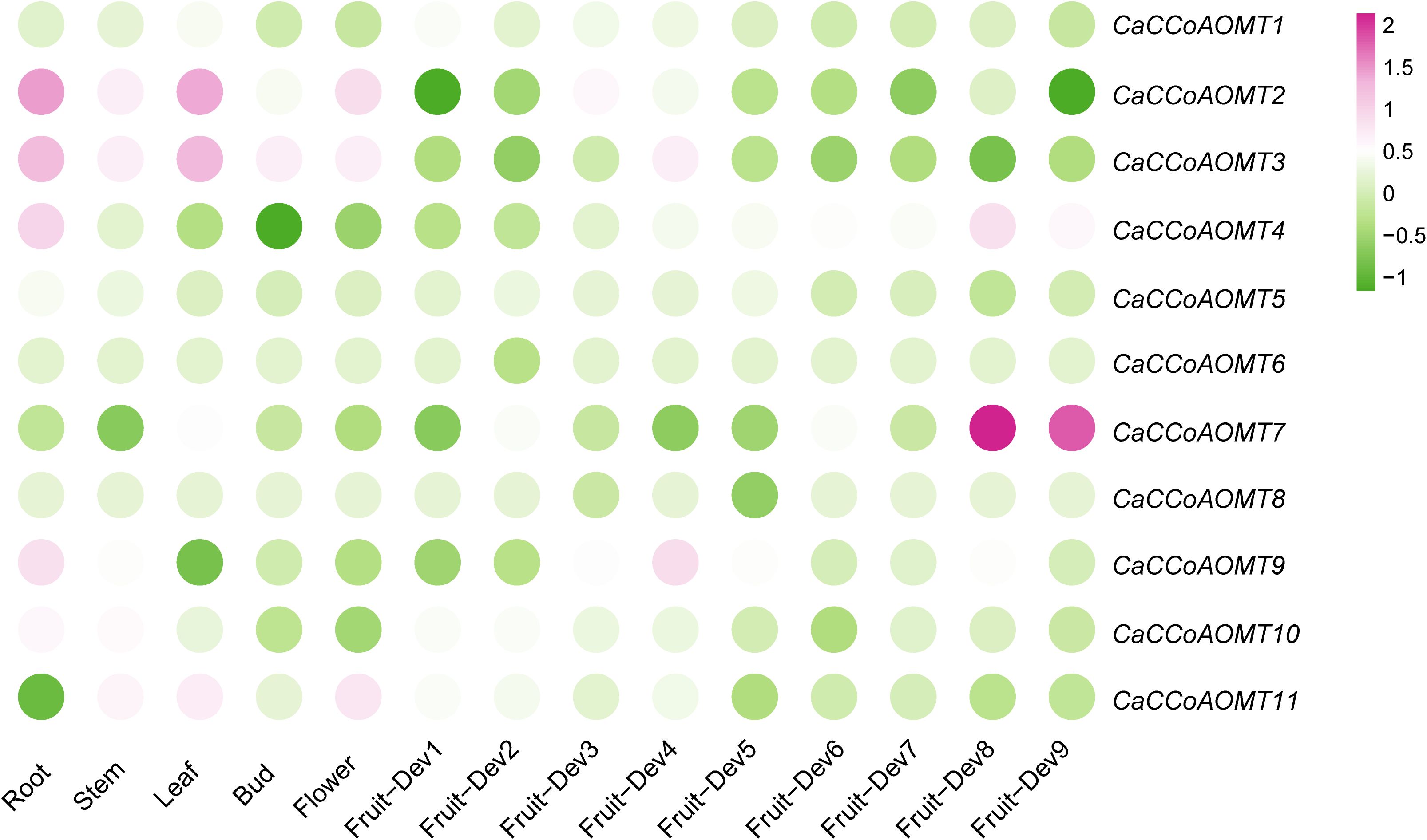
Figure 5. Heatmap representation of CaCCoAOMT gene expression across different tissues and developmental stages. Illumina RNA-seq data were used to assess CaCCoAOMT transcript levels in RNA samples from root, stem, leaf, bud, flower, and fruit tissues. The fruit developmental stages included nine phases: six pre-breaker stages (0–1 cm, 1–3 cm, 3–4 cm, 4–5 cm, and mature green fruit, ZL1-Dev1–5), the breaker stage (fruit turning red, ZL1-Dev6), and three post-breaker stages (3, 5, and 7 days after breaker, ZL1-Dev7–9). The FPKM values were log2-transformed, and the heatmap was generated using BAR Heat Mapper Plus software. The color bar at the bottom represents the log2-transformed values. Genes with high expression levels in the tissues are shown in red, while those with low expression are shown in green.
2.7 Morphology and structure of pepper under drought stress
Drought stress elicited significant adaptive morphological and cytological alterations across various organs of pepper plants. Notably, the leaves exhibited pronounced curling, whereas the stems and roots demonstrated deformation (Figure 6). Microscopic analysis of root cross-sections revealed a substantial expansion of lignified regions, identified by red staining, in the drought-treated group compared to the control group, observable under both 20× and 200× magnification. In stem cross-sections, evidence of mechanical tissue damage was apparent, including shrinkage and rupture of epidermal cells, alongside intensified red coloration of xylem vessels in longitudinal sections. Leaf curling was associated with a disorganized arrangement of palisade tissue under 20× magnification, while 200× images revealed compromised cellular membrane integrity and marked plasmolysis.
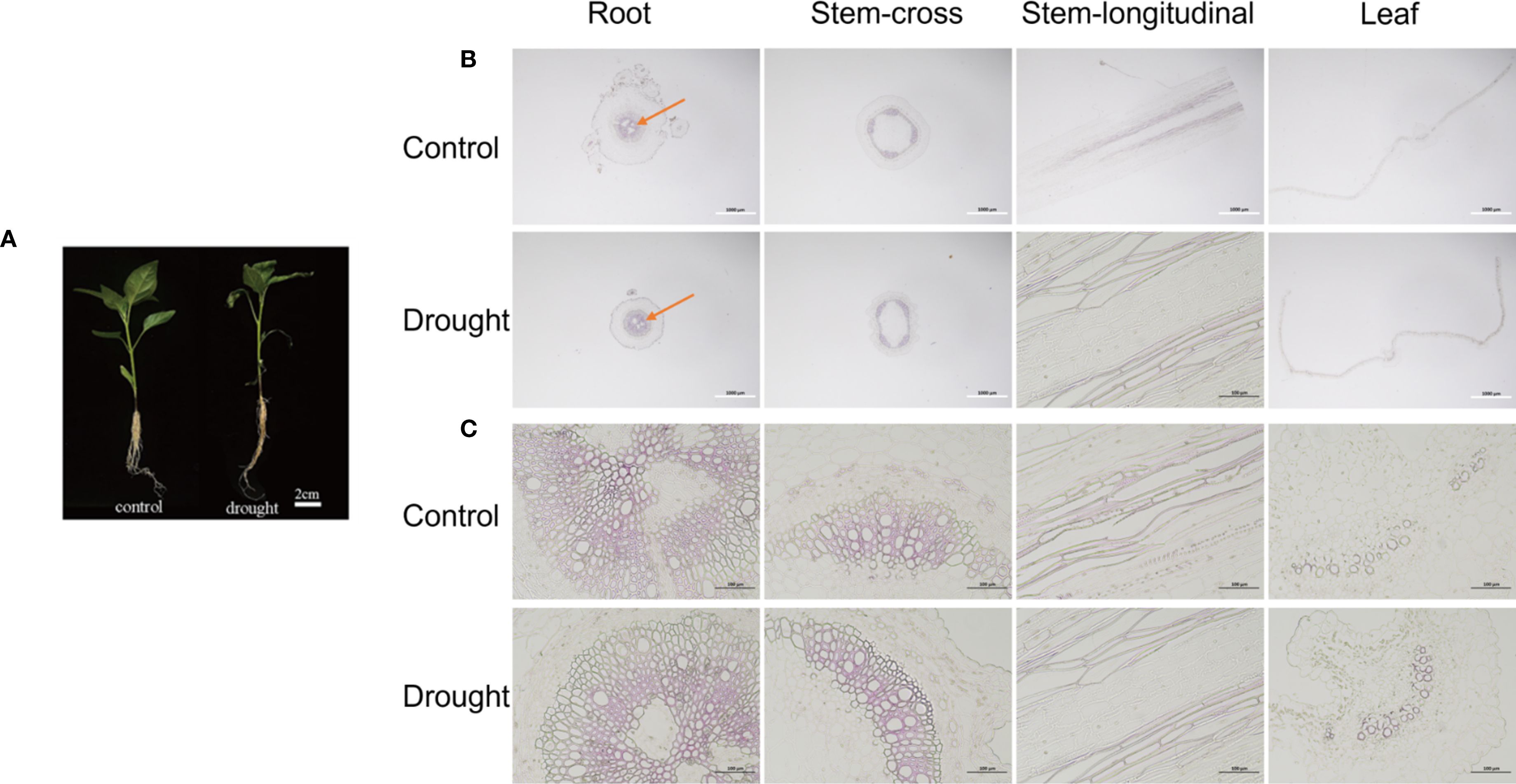
Figure 6. Morphology and structure of pepper root, stem and leaf under drought stress. (A) Morphology of pepper under control condition and drought stress. (B, C) Microstructure of root-cross section, stem-cross section, stem-longitudinal section and leaf-cross section under control condition and drought stress. The white scale is 1000 μm, and the black scale is 100 μm.
2.8 Expression patterns of CaCCoAOMTs under drought stress
We employed quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) to analyze the expression patterns of CaCCoAOMT genes under drought stress (Figure 7, Table S3). In the control group, most CaCCoAOMT genes exhibited higher basal expression levels in root tissues compared to stems and leaves. Under drought conditions, the expression of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 in roots was significantly upregulated, while CaCCoAOMT2, CaCCoAOMT3, CaCCoAOMT4, CaCCoAOMT5, CaCCoAOMT6, and CaCCoAOMT7 were markedly downregulated. In stems, drought treatment resulted in increased expression of CaCCoAOMT6 and CaCCoAOMT8, whereas CaCCoAOMT7, CaCCoAOMT9, and CaCCoAOMT11 consistently showed reduced expression. In leaf tissues, compared with the control, there was no significant change in the expression levels of 11 CaCCoAOMT induced by drought stress. The responses of CaCCoAOMT genes were consistent with phenotypic alterations under drought stress. The enhanced lignification observed in roots coincided with the significant upregulation of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 in root tissues, suggesting that these genes actively contribute to drought-induced lignin biosynthesis and reinforcement of cell walls. Such reinforcement likely improves mechanical stability and reduces water loss by limiting apoplastic permeability. Conversely, the downregulation or unchanged expression of other CaCCoAOMT members under drought stress may reflect functionally divergent paralogs, some of which could act as regulatory isoforms with tissue-specific or developmental-stage–dependent roles, rather than as primary drought response factors. Pearson correlation analysis was performed on the RNAseq and qRT-PCR datasets to illustrate their relationship. The results indicate that there may be differences, which could be caused by various factors including batch effects, sample processing, or growth conditions (Supplementary Table S4). Overall, the strong and specific induction of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 in roots after drought stress supports their identification as primary candidates for contributing to drought tolerance in pepper.
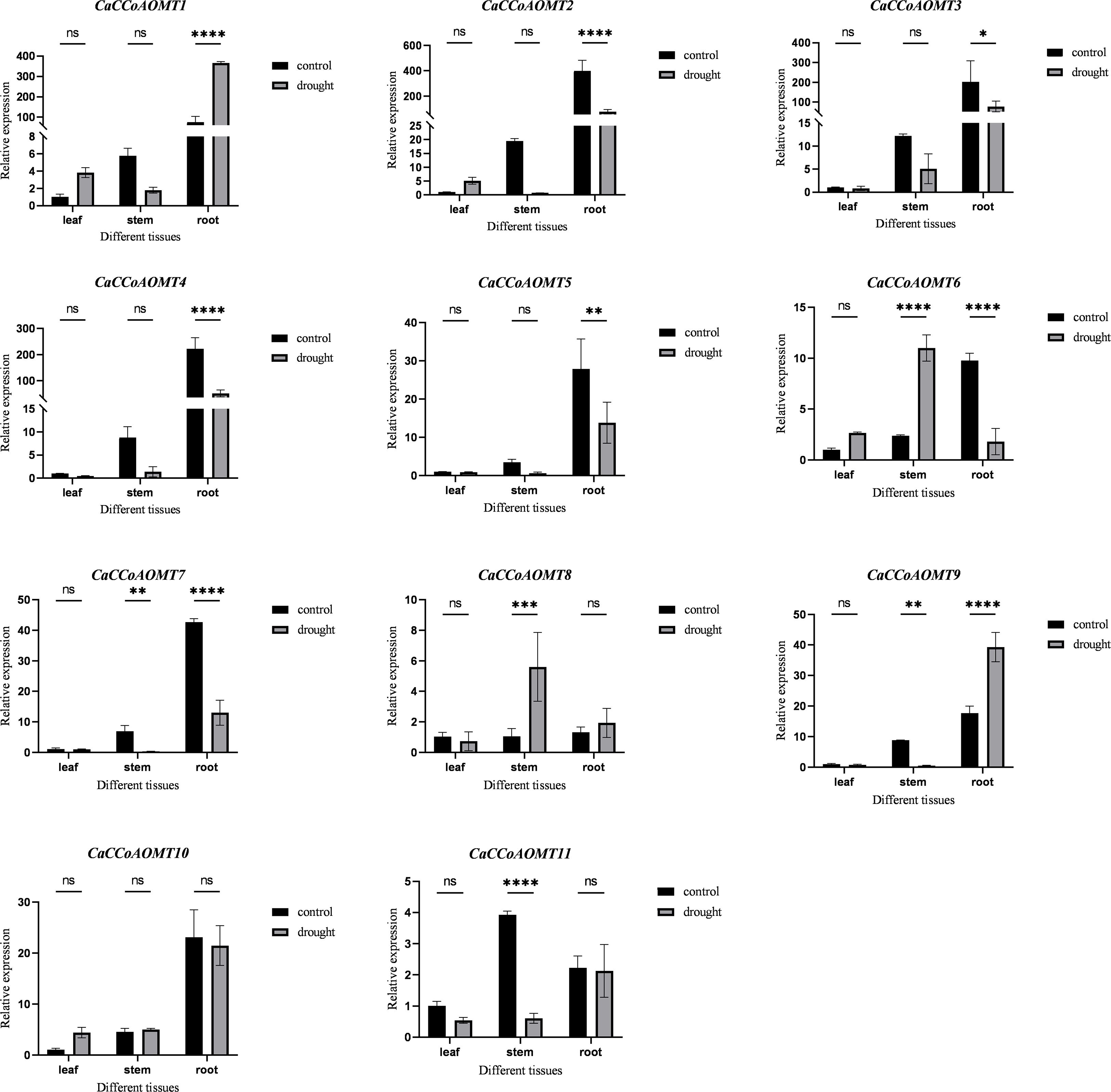
Figure 7. Expression analysis of CaCCoAOMT genes under drought stress using qRT-PCR. Plants were subjected to drought stress for two weeks. Data represent the mean ± SD of three biological replicates. "*" indicates p ≤ 0.05; "**" indicates p ≤ 0.005; "***" indicates p ≤ 0.0005; "****" indicates p ≤ 0.0001; "ns" indicates no significant difference.
2.9 Subcellular localization of the CaCCoAOMT proteins
To elucidate the subcellular localization of the CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT2 proteins in Capsicum annuum, we constructed the pCAMBIA2300-35S-CaCCoAOMT1-EGFP and pCAMBIA2300-35S-CaCCoAOMT2-EGFP plasmids (Figure 8A). These fusion proteins were transiently expressed in tobacco leaves via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. The localization of the proteins was assessed using GFP fluorescence signals. The results indicated that both CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT2 were localized in the cytoplasm as well as the nucleus (Figures 8B, C). While the prediction suggested a different localization pattern (Table 1), the experimental data clearly showed that CaCCoAOMT1 is distributed in both the cytoplasm and nucleus. Computational prediction tools often rely on amino acid sequence motifs and may not fully capture post-translational modifications, protein–protein interactions, or cell type–specific factors that affect protein localization in vivo. A GFP control, which lacked the protein fusion, was employed for comparative analysis.
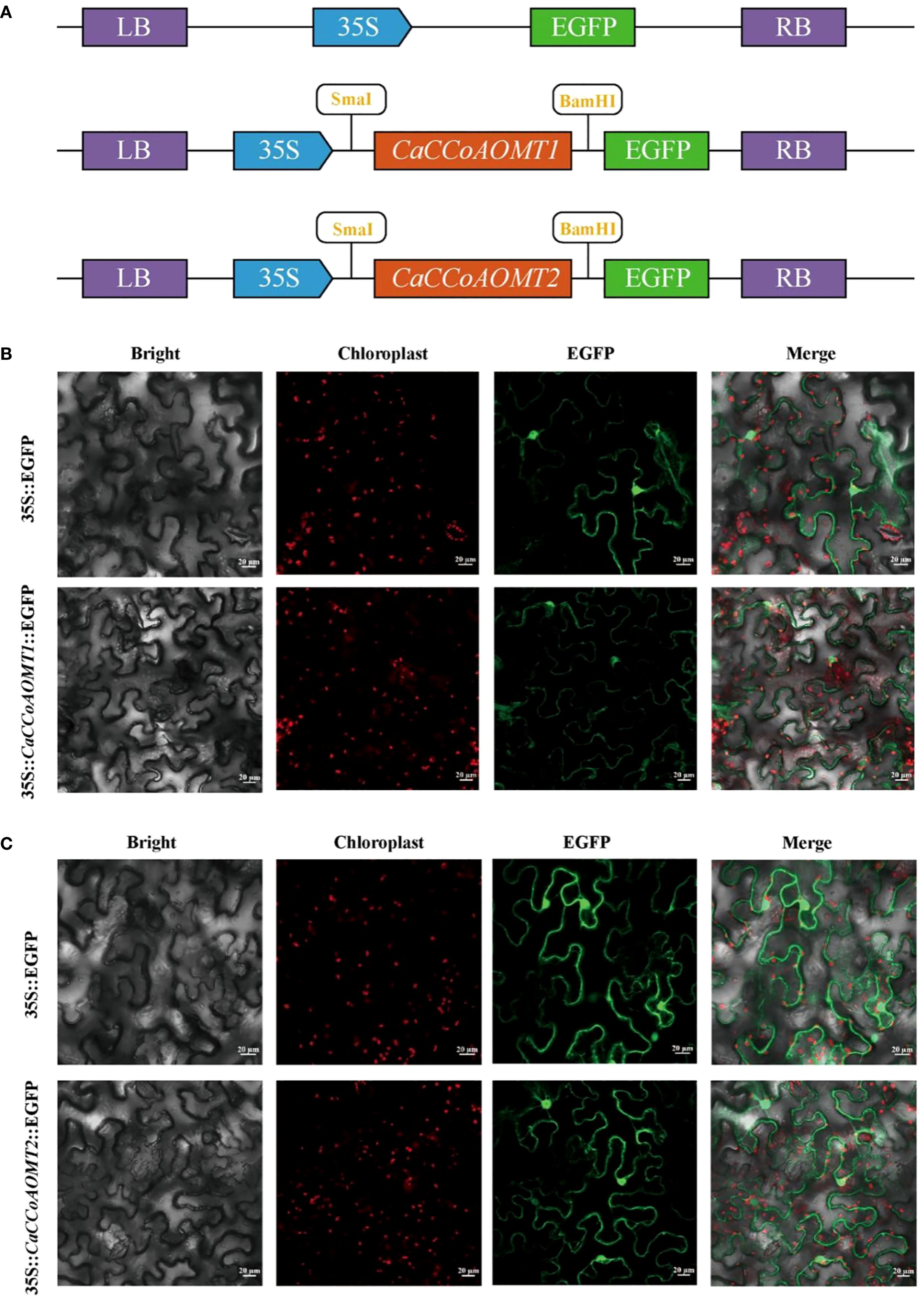
Figure 8. Subcellular localization of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT2 by transient expression in the cells of tobacco leaves. (A) Schematic diagram of the pCAMBIA2300-35S-CaCCoAOMT1-EGFP and pCAMBIA2300-35S-CaCCoAOMT2-EGFP constructs. (B) Subcellular localization of CaCCoAOMT1-GFP fusion protein. (C) Subcellular localization of CaCCoAOMT2-GFP fusion protein.
2.10 Molecular docking of the CaCCoAOMT proteins
Caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) is an important enzyme in plants, primarily involved in the methylation of caffeic acid, thereby generating a variety of crucial plant metabolites. S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), as a universal methyl donor, plays a key role in numerous methylation reactions. In this study, molecular docking analysis was performed to investigate the interactions between different CCoAOMT homologs and SAM, aiming to elucidate their potential roles in plant metabolism (Figure 9). The binding energies of CCoAOMT1, CCoAOMT3, CCoAOMT4, CCoAOMT9, and CCoAOMT11 with SAM were calculated as -6.822 kcal/mol, -6.014 kcal/mol, -5.447 kcal/mol, -6.557 kcal/mol, and -7.435 kcal/mol, respectively. These results revealed the diversity of the CCoAOMT family in their interactions with SAM, with the differences in binding energies reflecting their functional divergence in catalytic activity and metabolic processes. Members with stronger binding affinities, such as CCoAOMT1, CCoAOMT9, and CCoAOMT11, are likely to play predominant roles in lignin biosynthesis and phenylpropanoid metabolism, whereas those with weaker affinities, such as CCoAOMT4, may serve more limited regulatory functions or exhibit tissue- or condition-specific activity. This is consistent with the observation that CCoAOMT1 and CCoAOMT9 are significantly upregulated under drought stress, indicating that they not only possess high catalytic potential at the enzyme–substrate interaction level but are also transcriptionally induced under stress conditions, thereby contributing to plant stress responses. As SAM is the methyl donor for a wide range of methyltransferase reactions, the efficiency of its interaction with CCoAOMTs directly influences the biosynthesis and accumulation of metabolic products. The differential affinities among CCoAOMT family members suggest that plants may achieve fine-tuned regulation of metabolic pathways through functional diversification of these enzymes, thereby enabling dynamic modulation of metabolite synthesis during different developmental stages or under varying environmental conditions.
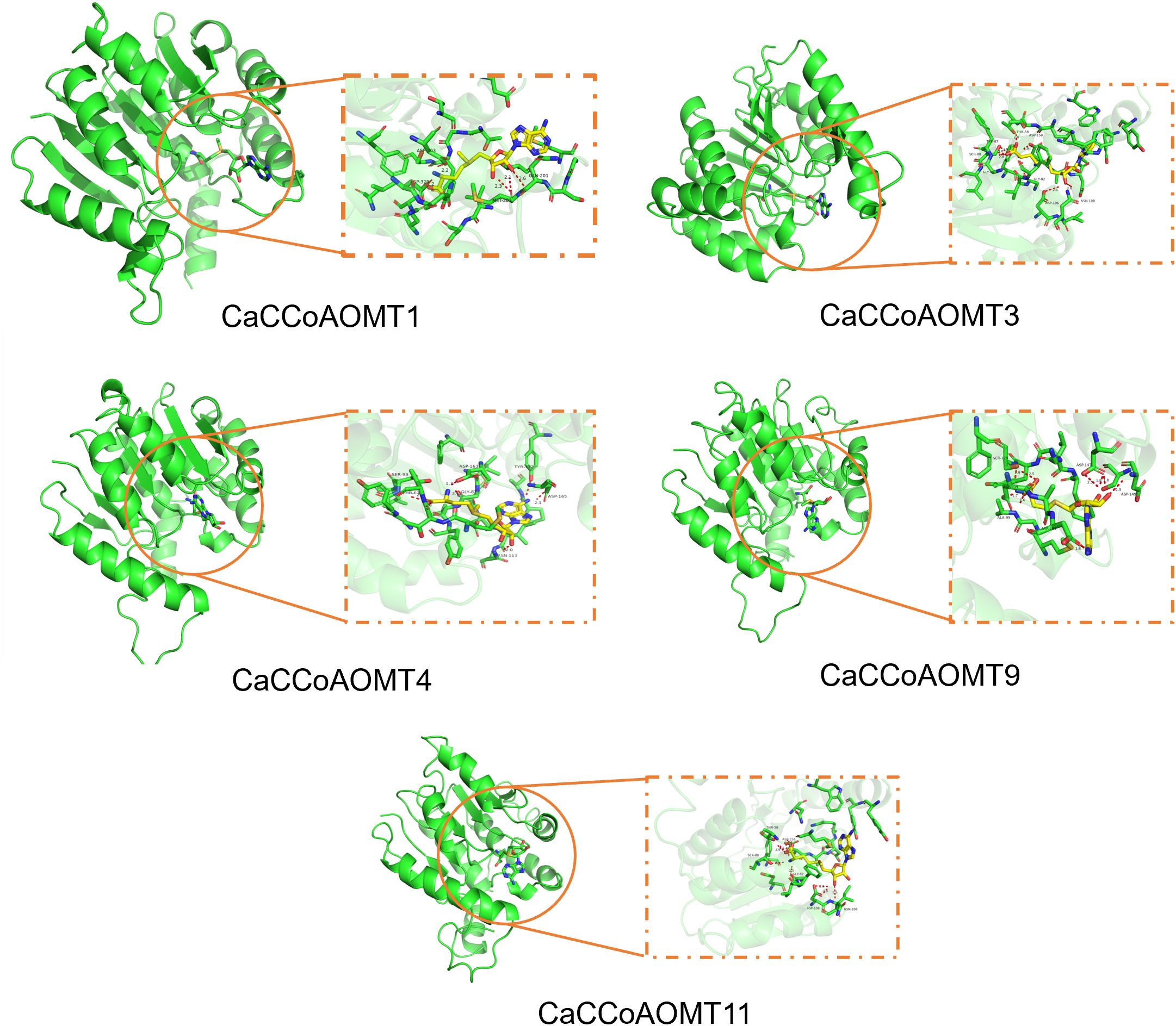
Figure 9. Docking simulations of CCoAOMT1, CCoAOMT3, CCoAOMT4, CCoAOMT9, CCoAOMT11 proteins from chili peppers with the S-adenosylmethionine molecule.
3 Discussion
Lignin is a complex phenolic polymer predominantly located in the secondary cell walls of plants, where it plays an essential role in plant growth and development. It enhances the mechanical strength and water resistance of cell walls by cross-linking with cellulose and hemicellulose (Boudet et al., 1995). The biosynthesis of lignin involves numerous enzymatic reactions, which are regulated by a sophisticated gene regulatory network. Research indicates that lignin synthesis is vital not only for normal plant growth and development but also for the plant’s adaptive responses to environmental stresses (Choi et al., 2023). The CCoAOMT gene family is integral to the lignin biosynthesis pathway and is significantly involved in key physiological processes, including cell wall formation, disease defense, and responses to abiotic stress (Li et al., 2013; Sattler and FunnellHarris, 2013; Yang et al., 2021). This gene family has been extensively studied across various plant species, such as 12 in Corchorus (Kahie et al., 2023), 17 in Camellia sinensis (Wang et al., 2024), 9 in Gossypium (Ma et al., 2024), 12 in Solanum tuberosum (Peng et al., 2024),17 in Dendrocalamus farinosus (Wei et al., 2023), 5 in Populus (Zhao et al., 2022), as well as 12 in Malus, 8 in Pyrus pyrifolia, 15 in Prunus persica (Li et al., 2021), and 7 in Sorghum bicolor (Rakoczy et al., 2018). In this study, we identified 11 CaCCoAOMT genes based on the Zunla 1 genome. This number is comparable to that found in Camellia sinensis and Solanum tuberosum, but higher than in Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, and Gossypium raimondii (Table 1, Figure 1).
The CaCCoAOMT genes demonstrate considerable variation in length, isoelectric point, molecular weight, and hydrophilicity, and such physicochemical diversity has been reported in other lignin-related O-methyltransferase families to underlie subfunctionalization and divergent expression profiles across tissues and developmental stages (Li et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2022; Kahie et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2024; Peng et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). Combining the gene expression under drought stress (Figure 7), it suggests that structural divergence within the gene family may be linked to functional specialization, with certain isoforms (e.g., CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9) preferentially induced in roots during drought stress, while others exhibit downregulation or constitutive expression, potentially reflecting roles in developmental regulation rather than abiotic stress response. The molecular weight and isoelectric point of plant proteins are known to significantly influence their biochemical functions, a phenomenon extensively documented in plant proteomics research (Mohanta et al., 2019). For example, in Arabidopsis, the PERK gene family members exhibit substantial diversity in gene length, molecular weight, and isoelectric point, suggesting specialized functions among different members (Zhang et al., 2025). Moreover, the plant antioxidant system displays variations in subcellular localization and the functional capacity of enzymes encoded by different gene copies, further highlighting the structural and functional complexity of plant proteins (Bobrovskikh et al., 2020). At the gene structure level, most CaCCoAOMT genes possess the characteristic “AdoMet_MTases” domain, which is highly conserved in comparison to known CCoAOMT sequences from other species (Sattler and FunnellHarris, 2013; Li et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2022; Kahie et al., 2023; Wei et al., 2023; Ma et al., 2024; Peng et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024).
Chromosomal localization and homology analyses indicate that the expansion of the CaCCoAOMT gene family likely occurred through tandem duplication events. Specifically, the genes CaCCoAOMT2-CaCCoAOMT4 and CaCCoAOMT5-CaCCoAOMT8 form two clusters of tandemly repeated sequences. This mode of expansion is commonly observed in plant gene families. Tandem repeats, which refer to the sequential arrangement of genes in adjacent positions on chromosomes, play a significant role in plant evolution. For instance, in rice, the expansion of the cyclic nucleotide-gated channel (CNGC) gene family is associated with chromosomal segmentation and tandem repeats, with these genes playing crucial roles in responses to hormones, pathogens, and abiotic stresses (Nawaz et al., 2014). Similarly, in Arabidopsis thaliana, the expansion of the MORC gene family is linked to tandem repeats, contributing to epigenetic regulation and immune responses in plants (Dong et al., 2018). Inter-species collinearity analysis has revealed that Capsicum annuum shares numerous conserved homologous pairs with tobacco, but exhibits weaker collinearity with Arabidopsis. This suggests a higher degree of conservation of the CCoAOMT family within Solanaceae plants.
We conducted an analysis of the 2000 base pair promoter regions of CaCCoAOMT genes, identifying the cis-acting elements. Notably, light-responsive elements (Box4) were prevalent, particularly in CaCCoAOMT5 and CaCCoAOMT6. Additionally, ABA-responsive elements (ABRE) were detected in CaCCoAOMT2, CaCCoAOMT7, and CaCCoAOMT11, while drought-related MYB binding sites (MBS) were observed in CaCCoAOMT3, CaCCoAOMT4, and CaCCoAOMT9, indicating their potential roles in stress response mechanisms. ABRE (ABA-responsive element) is a conserved cis-acting element in the promoter regions of plant genes related to ABA signal transduction, typically with the sequence PyACGTGGC. Under abiotic stresses such as drought, ABA levels increase, activating the ABRE-binding protein (AREB/ABF) family of transcription factors, which in turn promote the expression of ABA-responsive genes such as RD29B and Em. Upregulation of these genes helps plants regulate stomatal closure, synthesize osmotic adjustment substances, and produce antioxidant enzymes, thereby enhancing drought tolerance (Singh and Laxmi, 2015). The MYB transcription factor family is one of the largest in plants and plays a broad role in responses to abiotic stresses such as drought. MYB transcription factors regulate downstream gene expression by binding to MYB binding sites (MBS) in promoter regions, thereby modulating drought responses. For example, MYB44 has been shown to bind to MBS to repress the expression of the RD22 gene, thus regulating the ABA signaling pathway (Baldoni et al., 2015). These findings are consistent with previous studies on Arabidopsis thaliana AtCCoAOMT1, where expression is upregulated by ABA, MeJA, and salt stress, implicating its function in lignin biosynthesis and stress response pathways (Chun et al., 2019).
In this study, subcellular localization prediction suggested that CaCCoAOMT1 is localized exclusively in the nucleus. However, transient expression analysis in tobacco leaf epidermal cells revealed that CaCCoAOMT1 is localized in both the nucleus and cytoplasm (Table 1, Figure 8). Such discrepancies may arise because subcellular localization prediction algorithms often have inherent limitations, and their results do not always agree with experimental observations (Trofimov et al., 2019). In addition, as reported previously, subcellular localization results may vary when different receptor materials are used for transient expression assays, which can also lead to inconsistent findings (Lim et al., 2019; Zou et al., 2022).
Under drought conditions, plants generally increase lignin accumulation to enhance cell wall rigidity and minimize water loss (Bang et al., 2018; Yan et al., 2018). In this study, we found that drought stress significantly modified the anatomical structure of chili plants, particularly by increasing lignification in the roots and stems. Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) analysis revealed that CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 were upregulated in the roots, with showing especially strong induction. These findings suggest a potential role for these genes in enhancing drought tolerance through the regulation of lignin biosynthesis. In Arabidopsis, the transgenic expression of PaCCoAOMT1 and PaCCoAOMT2 from ferns promoted lignin accumulation without affecting the levels of methylated flavonols, highlighting their crucial role in lignin production (Zhang et al., 2019). Similarly, in Pinus radiata, the suppression of PrCCoAOMT expression resulted in alterations in lignin content and composition, specifically in the proportions of H, C, and G units, which ultimately influenced plant mechanical strength and growth (Wagner et al., 2011). Collectively, these findings underscore the pivotal role of CaCCoAOMT genes in lignin biosynthesis and drought stress response, offering a valuable foundation for drought-resistant breeding and further functional characterization of these genes. In tomato, curated resources annotate Solyc02g093270 as a caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT), and multiple studies report modulation of lignin-pathway genes under drought-related treatments in roots, aligning with our observation that drought enhances lignification (and CCoAOMT induction) in chili roots and stems (Xie et al., 2024). In potato, a recent genome-wide study identified 12 StCCoAOMT genes distributed on eight chromosomes, with collinearity and tandem/segmental duplications shaping the family; members were implicated in phenylpropanoid metabolism and stress-responsive regulation, consistent with lignification-linked roles under abiotic challenge (Peng et al., 2024). In addition, inter species collinearity analysis also found that CCoAOMT is more conserved among Solanaceae plants, and gene functions may also be more similar. Overall, Capsicum CaCCoAOMT genes likely share conserved, stress-responsive roles with CCoAOMTs of Solanum lycopersicum and S. tuberosum, reinforcing our inference that upregulated CaCCoAOMTs contribute to drought tolerance via lignin biosynthesis.
The results suggest that CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 are key candidates mediating lignin deposition in pepper roots under drought stress. Previous functional studies in Arabidopsis thaliana, Pinus radiata, and Polypodiodes amoena have demonstrated that altered expression of CCoAOMT genes directly modifies lignin content and composition, thereby influencing drought resistance and structural integrity. Thus, it is reasonable to hypothesize that the observed upregulation of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 enhances drought tolerance in pepper through reinforcement of cell walls and reduced water loss. Future functional validation, such as CRISPR/Cas9-mediated knockout, virus-induced gene silencing, or overexpression in transgenic pepper lines, combined with lignin quantification and drought survival assays, will be essential to confirm their mechanistic contribution.
4 Materials and methods
4.1 Plant materials and growth conditions
Seedlings of Capsicum annuum cultivar ‘ZunLa 1’, preserved in the Germplasm Resource Bank of the Pepper Research Institute, Guizhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, were used as experimental materials. The selected seeds were surface-sterilized and then cultivated in pots (20 cm diameter × 20 cm height) filled with nutrient-rich substrate. Plants were grown in a controlled greenhouse under identical environmental conditions for both treatments: a 30/26°C (day/night) temperature regime, 16/8-hour light/dark photoperiod, and ~60–65% relative humidity. After 20 days of growth, seedlings were divided into two groups, with 15 plants per treatment (three biological replicates, each replicate consisting of 5 plants). For the drought-stressed group, irrigation was withheld for 14 days to impose natural drought conditions. Drought severity was verified by measuring soil volumetric water content using a soil moisture probe, which dropped from ~75% to ~30% at the end of the treatment. For the well-watered control group, plants were maintained under the same environmental conditions but irrigated every 2 days to sustain the substrate at ~75–80% of field capacity. At the end of the 14-day treatment, roots, stems, and leaves were collected from both control and drought-stressed plants, immediately flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at –80°C for subsequent RNA extraction and expression analysis.
4.2 Identification of CaCCoAOMT genes
The pepper genome data was downloaded from the Sol Genomics Network (https://www.sgn.cornell.edu/organism/Capsicum_annuum/genome) (Qin et al., 2014), and the HMM model file (PF01596) for the CaCCoAOMT gene family in pepper was obtained from the Pfam (v 37.1) website (https://pfam.xfam.org/) (El-Gebali et al., 2019). The HMMER (v 3.3) software was used to search for CCoAOMT proteins within the pepper protein sequences (Potter et al., 2018). Domain annotation of the sequences was performed using the pfamscan tool and the SMART database, with the sequences containing the “AdoMet_MTases” domain being identified as the final candidate sequences for the CaCCoAOMT gene family.
4.3 Bioinformatic analysis of the CaCCoAOMT gene family
The online tool ExPASy (https://web.expasy.org/) was used to analyze the physicochemical properties of the proteins, while ProtComp v. 9.0 (http://linux1.softberry.com/berry.phtml) was employed to predict their subcellular localization. Multiple sequence alignment analyses of the CCoAOMT protein sequences from C. annuum and other species were performed (Wu et al., 2024). A phylogenetic tree was constructed for the CCoAOMT genes of D. farinosus using the Clustal W program in MEGA 7.0 software with the neighbor-joining (NJ) method and 1000 bootstrap replications (Li et al., 2025). The CaCCoAOMT protein sequences were uploaded to the NCBI Conserved Domain Database and the MEME Suite to obtain information on conserved domains and motif patterns (Bailey et al., 2015). The promoter regions, consisting of 2000 bp upstream of the start codon of the CaCCoAOMT genes, were extracted using the TBtools (v2.142) GXF Sequences Extract tool (Chen et al., 2023). The extracted sequences were then submitted to the PlantCARE database for analysis of cis-acting regulatory elements (Lescot et al., 2002). Based on the 11 identified CaCCoAOMT sequences and the genome annotation file of pepper (Zunla-1), collinearity analysis was performed using the TBtools (v2.142) One Step McscanX tool with the specified parameters. The homologous relationships between CaCCoAOMT genes and those in Arabidopsis thaliana and Solanum lycopersicum were analyzed using MCScanX (Wang et al., 2012). Segmental and tandem duplication events in the CaCCoAOMT genes were identified and visualized using TBtools-II v2.142. Subcellular localization prediction of CaCCoAOMT was conducted using the online website wolf-psort (https://www.genscript.com/wolf-psort.html).
4.4 Tissue expression pattern analysis of the CaCCoAOMT gene family
The transcriptome annotation files of C. annuum (Zunla-1) at different developmental stages were retrieved from the GEO database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, accession number GSE45037), including root, stem, leaf, bud, flower, and different fruit development stages. The TBtools-II v2.142 software was used to generate expression heatmaps for the CaCCoAOMT gene family in pepper.
4.5 Morphology and structure of pepper under drought stress
Roots, stems, and leaves from representative drought-treated and control pepper plants were immediately placed in FAA fixative (70% ethanol: formaldehyde: glacial acetic acid = 90:5:5) and fixed at 4°C for 24–48 h. After fixation, samples were dehydrated through a graded ethanol series and embedded in Technovit 7100 resin to prepare hard tissue sections. Embedded blocks were sectioned into 5–8 µm slices using a Leica RM2265 microtome. After de-plastification, the sections were stained with phloroglucinol to detect the distribution and degree of lignification. Sections were de-plastified and stained with 1% phloroglucinol in ethanol for 2–5 min, followed by a few drops of concentrated HCl to induce coloration. Lignified cell walls appeared red under light microscopy. Slides were temporarily mounted with neutral balsam and observed under an Olympus BX53 microscope at 20× and 200× magnification (Gritsch et al., 2015). For each treatment, three biological replicates (three independent plants per group) were processed. From each replicate, at least five sections per tissue type (root, stem, leaf) were examined, and representative images were captured.
4.6 RNA extraction and quantitative RT-PCR analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the roots, stems, and leaves of pepper plants under control and drought stress conditions using the TRIzol™ Reagent Kit (Invitrogen). cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg of RNA using the HiPro™ (H-) 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit with gDNA Eraser (Beijing PruTone). Primers for the CaCCoAOMT genes were designed based on their CDS sequences (Supplementary Table S2) and synthesized by Genewiz Biotechnology (Shanghai, China), with CaEIF5A2 used as the internal reference gene. qRT-PCR was conducted using the ProQ™ qPCR EvaGreen Master Mix (PruTone), with an ABI ViiA7 Real-Time PCR System (Life Technologies, USA) as the PCR instrument. The reaction volume was 25 μL, consisting of 2 μL cDNA, 0.5 μL of each forward and reverse primer, 10 μL of ProQ™ qPCR EvaGreen Master Mix, and ddH2O to a final volume. The PCR conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 minutes, followed by 40 cycles of 94°C for 10 seconds, 60°C for 20 seconds, and 72°C for 30 seconds. The relative expression levels of genes were calculated using the 2-ΔΔCT method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001). Gene expression levels were analyzed using Excel 2019, statistical significance was assessed using SPSS 19.0, differences between control and drought-stressed groups were tested using independent-samples t-test (p < 0.05), and graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism 8.0.
4.7 Subcellular localization of CCoAOMT proteins
To determine the subcellular localization of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT2, we constructed the pCAMBIA2300-35S-CaCCoAOMT1-EGFP and pCAMBIA2300-35S-CaCCoAOMT2-EGFP plasmids. These fusion proteins were transiently expressed in tobacco leaves via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. GFP fluorescence signals were used to observe the subcellular localization of the proteins. The localization was examined using a confocal microscope, with GFP signals visualized at an excitation wavelength of 488 nm.
4.8 Molecular docking
The PDB structure of the CCoAOMT protein was predicted using Phyre2 (https://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/~phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index). Molecular docking was performed with AutoDock software. The docking results were visualized using PyMOL.
5 Conclusions
In this study, we systematically identified and analyzed 11 CCoAOMT genes in the Capsicum annuum genome, designated CaCCoAOMT1 to CaCCoAOMT11. Analysis of their physicochemical properties, gene structures, conserved motifs, subcellular localization, and evolutionary relationships revealed the diversity and expansion of the CaCCoAOMT gene family in pepper. Transcriptome data analysis showed that these genes exhibit distinct expression patterns across different tissues and developmental stages. Furthermore, their responses to drought stress were validated by qRT-PCR. CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT11 are the most important candidate genes for pepper drought resistance. In the future, the precise functions of CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 in drought resistance response can be further revealed, especially in lignin synthesis, plant cell wall reinforcement, and plant water regulation. By utilizing the drought resistance characteristics of these genes, new varieties with stronger drought resistance can be developed. Subcellular localization experiments demonstrated that CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT2 proteins are mainly localized in both the cytoplasm and nucleus. While our results identify CaCCoAOMT1 and CaCCoAOMT9 as prime candidates for drought resistance, future studies employing functional assays (e.g., gene silencing, overexpression, lignin quantification, and drought survival tests) will be crucial to validate their mechanistic roles. This study thus lays an important foundation for subsequent functional research and offers valuable gene resources for improving drought tolerance in pepper through molecular breeding.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
DW: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation, Software, Conceptualization. CL: Data curation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. LB: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Validation. XY: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Validation. WL: Validation, Writing – review & editing, Resources. XZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LH: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Visualization, Software, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Resources, Writing – review & editing. JH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Software, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Key Research and Development Project on Core Technologies for Mountain Agriculture in Guizhou Province (GZNYGJHX-2023008), the Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects (Qiankehe Basic-ZK [2022] General 220); Qiankehepingtai ZSYS [2025]027), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2023YFD1200101), and the Innovation Fund of the Guizhou Pepper Research Institute ([2023] No. 21).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1654390/full#supplementary-material
References
AFornalé, S., Rencoret, J., GarcíaCalvo, L., Encina, A., Rigau, J., Gutiérrez, A., et al. (2016). Changes in cell wall polymers and degradability in maize mutants lacking 3- and 5-O-Methyltransferases involved in lignin biosynthesis. Plant Cell Physiol. 57, 3.9. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcw198
Bailey, T. L., Johnson, J., Grant, C. E., and Noble, W. S. (2015). The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, W39–W49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv416
Baldoni, E., Genga, A., and Cominelli, E. (2015). Plant Myb transcription factors: their role in drought response mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 15811–15851. doi: 10.3390/ijms160715811
Bang, S. W., Choi, S., Jin, X., Jung, S. E., Choi, J. W., and Seo, J. S. (2022). Transcriptional activation of rice CINNAMOYL-CoA REDUCTASE 10 by OsNAC5, contributes to drought tolerance by modulating lignin accumulation in roots. Plant Biotechnol. J. 20, 736–747. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13752
Bang, S. W., Lee, D. K., Jung, H., Chung, P. J., Kim, Y. S., Choi, Y. D., et al. (2018). Overexpression of OsTF1L, a rice HD-Zip transcription factor, promotes lignin biosynthesis and stomatal closure that improves drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 16, 1613–1626. doi: 10.1111/pbi.12951
Bobrovskikh, A., Zubairova, U., Kolodkin, A., and Doroshkov, A. (2020). Subcellular compartmentalization of the plant antioxidant system: an integrated overview. PeerJ. 8, e9489. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9451
Boudet, A. M., Lapierre, C., and GrimaPettenati, J. (1995). Biochemistry and molecular biology of lignification. New Phytol. 147, 1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.1995.tb04292.x
Chen, C. J., Wu, Y., Li, J. W., Wang, X., Zeng, Z. H., Xu, J., et al. (2023). TBtools-II: a "one for all, all for one" bioinformatics platform for biological big-datamining. Mol.Plant. 16, 1733–1742. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.09.010
Choi, S. J., Lee, Z., Kim, S., Jeong, E., and Shim, J. S. (2023). Modulation of lignin biosynthesis for drought tolerance in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1116426
Chun, H. J., Baek, D. W., Cho, H. M., Lee, S. H., Jin, B. J., Yun, D. J., et al. (2019). Lignin biosynthesis genes play critical roles in the adaptation of Arabidopsis plants to high-salt stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 14, 1625697. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2019.1625697
Dong, W., Vannozzi, A., Chen, F., Hu, Y., Chen, Z. H., Zhang, L. S., et al. (2018). and evolutionary analysis of the MORC gene family in green plants. Genome Biol. Evol. 10, 2874–2885. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evy136
El-Gebali, S., Mistry, J., Bateman, A., Eddy, S. R., Luciani, A., Potter, S. C., et al. (2019). The pfam protein families database in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D427–D432. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1002
Gritsch, C., Wan, Y. F., Mitchell, R. A. C., Shewry, P. R., Hanley, S. J., and Karp, A. (2015). G-fibre cell wall development in willow stems during tension wood induction. J. Exp. Bot. 66, 6447–6459. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv358
Gu, Z. J., Zhang, D. Q., and Huang, Q. Y. (2010). Transgenic modification on pulp plants by key genes regulating lignin biosynthesis. J. Cent. South Univ. For. Technol. 30, 67–74. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1127(10)60016-8
Guo, Z. H., Hua, H., Xu, J., Mo, J. X., Zhao, H., and Yang, J. J. (2019). Cloning and functional analysis of lignin biosynthesis genes Cf4CL and CfCCoAOMT in Cryptomeria Fortunei. Genes 10, 2.8. doi: 10.3390/genes10080619
Han, J., Wang, Z., Wu, X., Xia, J., Wang, L., Wang, Z., et al. (2024). Deciphering high-temperature induced lignin biosynthesis in wheat through comprehensive transcriptome analysis. Plants 13, 1832. doi: 10.3390/plants13131832
Han, X., Zhao, Y., Chen, Y., Xu, J., Jiang, C., Wang, X., et al. (2022). Lignin biosynthesis and accumulation in response to abiotic stresses in woody plants. Forestry Res. 2, 9. doi: 10.48130/FR-2022-0009
Ji, P. P., Lin, M. Y., Chen, M. Y., Kashif, M. H., Fan, Y. L., Ali, T. H., et al. (2023). Caffeoyl-Coenzyme A O-Methyltransferase mediates regulation of carbon flux fluctuations during phenylpropenes and lignin biosynthesis in the vegetative organ roots of Asarum Sieboldii Miq. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 188, 6.1. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.107855
Jiao, P., Jiang, Z. Z., Miao, M., Wei, X. T., Wang, C. L., Liu, S. Y., et al. (2024). Zmhdz9, an HD-Zip transcription factor, promotes drought stress resistance in maize by modulating ABA and lignin accumulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 258, 128849. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128849
Kahie, M. A., Wang, Y. J., Fang, P. P., Qi, J. M., Lei, R. J., Xu, J. T., et al. (2023). Evolution and expression analysis of the Caffeoyl-CoA 3-O-Methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) gene family in jute (Corchorus L.). BMC Genomics 24, 204. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09281-w
Kim, S. J., Kim, K. W., Cho, M. H., Franceschi, V. R., Davin, L. B., and Lewis, N. G. (2007). Expression of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenases and their putative homologues during Arabidopsis thaliana growth and development: lessons for database annotations? Phytochemistry 68, 1957–1974. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.02.032
Lam, P. Y., Tobimatsu, Y., Matsumoto, N., Suzuki, S., Lan, W., Takeda, Y., et al. (2019). OsCAldOMT1 is a bifunctional O-Methyltransferase involved in the biosynthesis of tricin-lignins in rice Cell Walls. Sci. Rep. 9, 3.8. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47957-0
Lescot, M., Déhais, P., Thijs, G., Marchal, K., Moreau, Y., Peer, Y. V. D., et al. (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Li, X. Y., Chen, W. J., Zhao, Y., Xiang, Y., Jiang, H. Y., Zhu, S. W., et al. (2013). Downregulation of Caffeoyl-CoA O-Methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) by RNA interference leads to reduced lignin production in maize straw. Genet. Mol. Biol. 37, 6.1. doi: 10.1590/S1415-47572013005000039
Li, G. M., Shi, X. Y., Lin, Q. M., Lv, M. M., Chen, J., Wen, Y. X., et al. (2025). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of heat shock transcription factors in Camellia Sinensis under abiotic stress. Plants 14, 697. doi: 10.3390/plants14050697
Li, L., Tao, S. T., Zhang, H. W., Huang, W. J., Dunwell, J. M., and Li, M. (2021). Identification and characterization of the CCoAOMT gene family in apple, chinese white pear, and peach. J. Am. Soc Hortic. Sci. 146, 184–195. doi: 10.21273/JASHS04950-20
Lim, S. D., Lee, S., Choi, W., Yim, W. C., and Cushman, J. C. (2019). Laying the foundation for crassulacean acid metabolism (CAM) Biodesign: Expression of the C4 metabolism cycle genes of CAM in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00101
Liu, Q., Luo, L., and Zheng, L. (2018). Lignins: biosynthesis and biological functions in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 335. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020335
Livak, K. J. and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of Relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT Method. Methods 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Ma, L., Wang, J., Qiao, K. K., Quan, Y. W., Fan, S. L., and Wu, L. Q. (2024). Genome-wide analysis of Caffeoyl-CoA-O-Methyltransferase (CCoAOMT) family genes and the roles of GhCCoAOMT7 in lignin synthesis in cotton. Plants 13, 2969. doi: 10.3390/plants13212969
Mohanta, T. K., Khan, A., Hashem, A., Allah, E. F. A., and Al-Harrasi, A. (2019). The molecular mass and isoelectric point of plant proteomes. BMC Genomics 20, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5983-8
Moloi, S. J. and Ngara, R. (2023). The Roles of plant proteases and protease inhibitors in drought response: a review. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1165845
Nawaz, Z., Kakar, K. U., Saand, M. A., and Shu, Q. Y. (2014). Cyclic Nucleotide-gated ion channel gene family in rice, identification, characterization and experimental analysis of expression response to plant hormones, biotic and abiotic stresses. BMC Genomics 15, 1–16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-853
Pang, S. L., Ong, S. S., Lee, H. H., Zamri, Z., Kandasamy, K. I., Choong, C. Y., et al. (2014). Isolation and characterization of CCoAOMT in interspecific hybrid of Acacia auriculiformis × Acacia mangium—a key gene in lignin biosynthesis. Genet. Mol. Res. 13, 0.6. doi: 10.4238/2014.September.5.7
Peng, Y. X., Sheng, S. A., Wang, T. T., Song, J. F., Wang, D. J., Zhang, Y. X., et al. (2024). Genome-wide characterization of solanum tuberosum CCoAOMT gene family and identification of StCCoAOMT Genes involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis. Genes 15, 1466. doi: 10.3390/genes15111466
Potter, S. C., Luciani, A., Eddy, S. R., Park, Y., Lopez, R., and Finn, R. D. (2018). HMMER web server: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, W200–W204. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky448
Qin, C., Yu, C. S., Shen, Y. O., Fang, X. D., Chen, L., Min, J. M., et al. (2014). Whole-genome sequencing of cultivated and wild peppers provides insights into Capsicum domestication and specialization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 111, 5135–5140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1400975111
Rakoczy, M., Femiak, I., Alejska, M., Figlerowicz, M., and Podkowinski, J. (2018). Sorghum CCoAOMT and CCoAOMT-Like gene evolution, structure, expression and the role of conserved amino acids in protein activity. Mol. Genet. Genomics 293, 1275–1289. doi: 10.1007/s00438-018-1441-6
Sattler, S. E. and FunnellHarris, D. L. (2013). Modifying lignin to improve bioenergy feedstocks: strengthening the barrier against pathogens? Front. Plant Sci. 4. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00070
Singh, D. and Laxmi, A. (2015). Transcriptional regulation of drought response: a tortuous network of transcriptional factors. Front. Plant Sci. 6. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00895
Trofimov, K., Ivanov, R., Eutebach, M., Acaroglu, B., Mohr, I., Bauer, P., et al. (2019). Mobility and localization of the iron deficiency-induced transcription factor bHLH039 change in the presence of FIT. Plant Direct. 3, 1–11. doi: 10.1002/pld3.190
Tu, M. X., Wang, X. H., Yin, W. C., Wang, Y., Li, Y. J., Zhang, G. F., et al. (2020). Grapevine VlbZIP30 improves drought resistance by directly activating VvNAC17 and promoting lignin biosynthesis through the regulation of three peroxidase genes. Hortic. Res. 7, 1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41438-020-00372-3
Wagner, A., Tobimatsu, Y., Phillips, L., Flint, H., Torr, K., Donaldson, L., et al. (2011). CCoAOMT suppression modifies lignin composition in Pinus Radiata. Plant J. 68, 664–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04580.x
Wang, G. F. and BalintKurti, P. J. (2016). Maize Homologs of CCoAOMT and HCT, Two Key Enzymes in lignin biosynthesis, form complexes with the NLR Rp1 protein to modulate the defense response. Plant Physiol. 172, 6.5. doi: 10.1104/pp.16.00224
Wang, Y., Gui, C., Wu, J., Gao, X., Huang, T., Cui, F., et al. (2022). Sethupathy S. Spatio-temporal modification of lignin biosynthesis in plants: a promising strategy for lignocellulose improvement and lignin valorization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.917459
Wang, Y. P., Tang, H. B., Debarry, J. D., Tan, X., Li, J. P., Wang, X. Y., et al. (2012). MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Wang, Y. Q., Wang, T., Qi, S. Y., Zhao, J. M., Kong, J. M., Xue, Z. H., et al. (2024). Genome-wide identification, expression profiling, and protein interaction analysis of the CCoAOMT gene family in the tea plant (Camellia Sinensis). BMC Genomics 25, 238. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-09972-y
Wei, L. X., Zhao, X., Gu, X. Y., Peng, J. H., Song, W. J., Deng, B., et al. (2023). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of dendrocalamus farinosus CCoAOMT gene family and the role of DfCCoAOMT14 involved in lignin synthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 8965. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108965
Wu, X. Y., Hu, X. C., Bao, Q. Y., Sun, Q., Yu, P., Qi, J. X., et al. (2024). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of NAC gene family members in Seashore Paspalum under salt stress. Plants 13, 3595. doi: 10.3390/plants13243595
Xie, J., Cao, B., and Xu, K. (2024). Uncovering the dominant role of root lignin accumulation in silicon-induced resistance to drought in tomato. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 259, 129075. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.129075
Yadav, S. and Chattopadhyay, D. (2023). Lignin: the building block of defense responses to stress in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 42, 6652–6666. doi: 10.1007/s00344-023-10926-z
Yan, J., Aznar, A., Chalvin, C., Birdseye, D. S., Baidoo, E. E., Eudes, A., et al. (2018). Increased drought tolerance in plants engineered for low lignin and low xylan content. Biotechnol. Biofuels 11, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13068-018-1196-7
Yang, G., Pan, W. Q., Zhang, R. Y., Pan, Y., Guo, Q. F., Song, W. N., et al. (2021). Genome-wide identification and characterization of Caffeoyl-Coenzyme A O-Methyltransferase genes related to the fusarium head blight response in wheat. BMC Genomics 22, 1–18. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07849-y
Zhang, Z. Y., Fu, T. Y., Zhou, C., Liu, F., Zeng, L. Y., Ren, L., et al. (2025). Genome-wide analysis of the PERK gene family in Brassica Napus L. and their potential roles in clubroot disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 1466. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062685
Zhang, X. S., Ni, R., Wang, P. Y., Zhu, T. T., Sun, C. J., Lou, H. X., et al. (2019). Isolation and functional characterization of two Caffeoyl Coenzyme A 3-O-Methyltransferases from the fern species Polypodiodes Amoena. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 140, 6.1. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2019.01.021
Zhao, H. C., Qu, C. P., Zuo, Z., Cao, L. N., Zhang, S., Xu, X. Y., et al. (2022). Genome identification and expression profiles in response to nitrogen treatment analysis of the class I CCoAOMT gene family in Populus. Biochem. Genet. 60, 656–675. doi: 10.1007/s10528-021-10112-4
Zheng, L. L., Hu, Y. F., Yang, T. Z., Wang, Z., Wang, D. Y., Jia, L. T., et al. (2024). A root cap-localized NAC transcription factor controls root halotropic response to salt stress in Arabidopsis. Food Res. Int. 15, 2061. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46482-7
Zhou, C. X., Zhang, W., Yu, B. G., Yang, H. F., Zhao, Q. Y., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). Global Analysis of spatio-Temporal variation in mineral nutritional quality of pepper (Capsicum Spp.) fruit and its regulatory variables: a meta-analysis. Food Res. Int. 193, 114855. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114855
Zou, H., Han, L., Yuan, M., Zhang, M., Zhou, L., and Wang, Y. (2022). Sequence Analysis and Functional Verification of the Effects of Three Key Structural Genes, PdTHC2'GT, PdCHS and PdCHI, on the Isosalipurposide Synthesis Pathway in Paeonia delavayi var. lutea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 5696. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105696
Keywords: Capsicum annuum, CCoAOMT gene family, drought stress, expression, whole-genome identification
Citation: Wu D, Lu C, Bai L, Yan X, Lai W, Zhang X, He L and He J (2025) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of CCoAOMT genes in Capsicum annuum L. under drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1654390. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1654390
Received: 26 June 2025; Accepted: 29 August 2025;
Published: 19 September 2025.
Edited by:
Hang Zhao, Qufu Normal University, ChinaReviewed by:
Fang Yuanyuan, Beijing Forestry University, ChinaJohn Momo, Jawaharlal Nehru University, India
Arun Kumar C. Huded, Central Coffee Research Institute, India
Yayu Guo, Beijing Forestry University, China
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Lu, Bai, Yan, Lai, Zhang, He and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei He, Y2FoZWxlaTk1NUAxMjYuY29t; Jianwen He, aGVqaWFud2VuMTAyMkAxMjYuY29t
 Di Wu
Di Wu Chen Lu2
Chen Lu2 Lei He
Lei He