- 1State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Adaptation and Improvement, College of Agriculture, Henan University, Kaifeng, Henan, China
- 2School of Life Sciences, Henan University, Kaifeng, China
- 3Kaifeng Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences, Kaifeng, China
- 4Plant Breeding and Genetics Division, (NIAB), Faisalabad, Pakistan
The Glu-D1 locus is known to contribute the most to gluten quality in common wheat. Aegilops tauschii, as a donor species of the common wheat D genome, is of great significance for improving wheat flour processing quality by exploring and utilizing its excellent quality-related genes. In this study, high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit (HMW-GS) compositions of 173 Aegilops tauschii accessions from the Middle East, Central Asia, and Xinjiang were analyzed using sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) technology. A total of 13 subunit types were detected at the Glu-D1 t locus, including the unique subunit types absent in common wheat. Unexpectedly, all these Ae. tauschii accessions lacked the extra cysteine residue at position 118 in their Glu-1Dx subunits detected by a specific functional marker, dCAPS5. To determine whether other sites of Glu-D1t subunits in Ae. tauschii contains the extra cysteine residue, the grain RNA of Ae. tauschii accessions with rare subunit types at different days post-anthesis (6th, 9th, 12th, 15th, 18th, 21st, and 24th days) were mixed and sequenced using third-generation (PacBio) transcriptome sequencing technology. A total of 12 new HMW-GS genes were obtained, including 6 genes each for Glu-D1x and Glu-D1y. Sequence alignment analysis revealed the extra cysteine residue was not observed in the protein sequences deduced by 12 new HMW-GS genes. Interestingly, HMW-GS of Ae. tauschii accessions AY16 and AY49 had longer repetitive domain insertions, while those of AY16 and AY53 exhibited higher α-helix and β-strand contents, which may positively influence dough properties. Additionally, the relative content of HMW-GS in AY11, AY32, and AY49 was significantly higher than that of the Glu-D1 subunits in wheat variety Xinmai 26 with the strong gluten quality, favoring the formation of larger glutenin polymers. From this point of view, Ae. tauschii, as a potentially valuable germplasm resource, can provide rich subunit gene resources for quality breeding in common wheat.
Introduction
As a donor species of the common wheat D genome, Aegilops tauschii (2n = 2x = 14, DD) contains beneficial genes for disease resistance, insect resistance, and abiotic stress resistance (Sukhwinder et al., 2012; Savary et al., 2019). The Fertile Crescent is considered the origin and genetic diversity center of Ae. tauschii, which is widely distributed from west to east along the Caspian Sea coast (Wang et al., 2013). According to morphological characteristics, Ae. tauschii is classified as two subspecies, namely, Ae. tauschii ssp. tauschii and ssp. strangulata. Due to that, only a few Ae. tauschii genotypes in specific regions (mainly Ae. tauschii ssp. strangulata subspecies) are involved in the origin of the common wheat D genome, the genetic diversity of Ae. tauschii is significantly higher than that of the common wheat D genome (Hao et al., 2020; Gaurav et al., 2022). Therefore, Ae. tauschii is considered an important genetic resource for improving common wheat. Some beneficial genes from Ae. tauschii have been transferred to common wheat through direct hybridization and indirect methods using tetraploid wheat-Ae. tauschii artificial synthetic lines (Zhang et al., 2018, 2017; Zhou et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2022).
The flour processing quality of wheat is significantly correlated with its seed storage proteins (SSPs), which are divided into globulin, albumin, gliadin, and glutenin based on their solubility characteristics (Khalid et al., 2023). Among them, glutenin and gliadin are the main components, accounting for about 90% of the total wheat SSPs. It is generally believed that glutenin, composed of HMW-GS and low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit (LMW-GS), determines the dough elasticity, while gliadin endows the fluidity and extensibility of dough (Guo et al., 2021).
As a structural scaffold for interactions with other glutenin subunits and gliadins, HMW-GS serves as the primary determinant of flour processing quality, critically influencing dough strength and elasticity (Li et al., 2021; Yazar et al., 2017). The HMW-GS of common wheat are composed of a large central repetitive domain flanked by short non-repetitive N- and C-terminal domains, which are named as Ax1 or Ax2* at the Glu-A1 locus, Bx7 + By8, Bx17 + By18, Bx13 + By16, and Bx14 + By15 at the Glu-B1 locus, and Dx2 + Dy12 and Dx5 + Dy10 at the Glu-D1 locus based on their mobility in SDS-PAGE, respectively (Zhang et al., 2016). The Glu-D1 locus is a key genetic determinant of wheat dough strength and bread-making quality compared with Glu-A1 and Glu-B1. Studies on the contributions of Glu-1 alleles to flour processing quality have demonstrated that Dx5 and Dy10 subunits were regarded as the most favorable combination (Ma et al., 2005; Blechl et al., 2007; Ren et al., 2022).
Studies have shown that glutenin subunits in Ae. tauschii have positive effects on the flour processing quality of wheat (Hsam et al., 2001; Delorean et al., 2021). Moreover, allelic variations of HMW-GS in Ae. tauschii exhibit extensive polymorphism, most of which, however, is yet to be discovered in the D genome of common wheat. Therefore, Ae. tauschii is regarded as a valuable genetic resource for improving the flour processing quality in wheat (Tahernezhad et al., 2013). In this study, HMW-GS of 173 Ae. tauschii accessions from the Middle East, Central Asia, and Xinjiang regions were detected utilizing SDS-PAGE technology. The molecular characterization and relative content of their rare HMW-GS were analyzed, and the results will provide a theoretical basis and genetic resources for wheat quality breeding.
Materials and methods
Plant materials
A total of 173 Ae. tauschii accessions used in this study were shown in Supplementary Table S1. Accessions from the Middle East and Central Asia were provided by the US National Plant Germplasm Center and Institute of Genetics (National Plant Germplasm System, https://www.usda.gov/taxonomy/term/7820), while accessions from Xinjiang were collected and cultivated by the Plant Germplasm Resources and Genetic Engineering Laboratory, Henan University. Common wheat Chinese Spring (null, Bx7 + By8, Dx2 + Dy12) and Xinmai 26 (Ax1, Bx7 + By8, Dx5 + Dy10) were used as standard glutenin subunit controls.
Glutenin extraction, SDS-PAGE
Glutenin was extracted according to the method described by Zhang et al. (2008a). Half-seeds without embryos were crushed and used for HMW-GS extraction. The flour (20 mg) was first washed with distilled water by stirring for 1h at room temperature to remove the water-soluble proteins. After centrifuging at 5,000g for 15 min, the supernatant was discarded and the residue washed with 50% (v/v) propan-1-ol by stirring for 30 min at 60°C. After centrifuging at 5,000g for 15 min, the supernatant was discarded. This step was repeated three times to remove gliadins completely. The pellet was extracted with 50% (v/v) propan-1-ol, 0.08 M Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) containing freshly added 1% (w/v) DTT by stirring for 1h at 60 °C. After centrifuging at 12,000g for 30 min, the supernatant was precipitated with 1-propanol (final concentration 60% v/v) at 4 °C overnight. The resultant precipitate was collected by centrifuging at 12,000g for 15 min and dried by vacuum centrifugation. Samples were separated by SDS-PAGE with a discontinuous system of 4% (w/v) stacking gel and 10% (w/v) separating gel. Eight microliter samples were separately loaded onto lanes of the gel and electrophoresed at approximately 15°C and 12 mA for 18h.
Genotyping
Genomic DNA was extracted from young leaves according to the approach reported by Su et al. (2020). PCR amplification of the Dx5 subunit in Ae. tauschii was performed with marker dCAPS5 using the method described by Ren et al. (2022) (P1: 5 ‘- GCAGCAAACTCCAACGTA-3’ and P2: 5 ‘- GATAGTATGAAACCTGCTGTCGA-3’). The 25 μl PCR reaction volume contained 50 ng of genomic DNA, 1× Taq DNA polymerase buffer, 0.5 μM of each primer, 200 μM of each dNTP, and 1 U of Taq DNA polymerase (Takara, Japan). The program for PCR amplification was as follows: initial denaturation at 94°C for 3 min, 30 cycles of 94°C for 25 s, 58°C for 25 s, 72°C for 15 s, and a final extension at 72°C for 10 min. The PCR products were digested with restriction enzyme Sal I (Takara, Japan). The 10 μl reaction volume consisted of 5 μl of the PCR product, 1 U of the restriction enzyme, and 1× buffer. The reaction was performed at 37°C for 3h, and the digested products were detected with a 3.0% agarose gel. The Dx5 subunit (containing cysteine residues) of the strong-gluten wheat variety Xinmai 26 was used as a control. The amplification products were digested with restriction enzyme Sal I, and the digestion products were analyzed by 3% agarose gel electrophoresis.
PacBio RNA sequencing and data analysis
The timing of anthesis and grain development was inspected and recorded after heading. The grain samples were similarly collected on the 6th, 9th, 12th, 15th, 18th, 21st, and 24th days after flowering (DAF). A total amount of 2 µg RNA was used as input material for the RNA sample preparation. The first-strand cDNA synthesis (reverse transcription and template switching) and PCR amplification were performed utilizing the NEBNext Single Cell/Low Input cDNA Synthesis & Amplification Module (NEB, E6421). HMW-GS genes were obtained through PacBio RNA sequencing and data analysis as described by Ren et al. (2022). Due to the highly complex sequence structure of the HMW-GS genes, a custom pipeline was used to remove redundant sequences to acquire HMW-GS genes in IsoSeq3. Briefly, as queries from the nucleotide sequences of the published glutenin genes in NCBI, the own redundant sequences were first removed utilizing CD-hit software with parameter “-c 0.9.” The obtained nonredundant sequences were merged with those of the annotated glutenin genes in Chinese Spring (RefSeq v1.0) to form query sequences. Then, Blat software (Kent, 2002) was used to search for the FLNC sequence generated by IsoSeq3 based on the query sequences, in which those with coverage and identity greater than 70% were retained, followed by error correction and removal of redundant reads using IsoCon software (Sahlin et al., 2018). Thus, obtained sequences were aligned by MAFFT software (Katoh and Standley, 2013) and manually removed again in redundant ones according to the support score acquired by IsoCon.
Sequence alignment and secondary structure prediction
The open reading frame (ORF) of the target gene was translated into an amino acid sequence using the NCBI ORF Finder program (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The alignment of sequences was carried out using the Clustal X 2.0 software (Larkin et al., 2007). Secondary structure prediction of deduced amino acid sequences was performed by PSIPRED server 4.0 (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred/). Default parameters were used in these analyses.
Detection of glutenin subunit relative quantities
Equal weights (100 mg each) of sieved flour from Ae. tauschii accessions, Xinmai 26, and Chinese Spring were used for glutenin extraction following the method described by Zhang et al. (2016). The extracted glutenin was separated by SDS-PAGE with 20 μl per sample and visualized by Coomassie Blue staining. Bovine serum albumin (BSA) at 0.4 μg/μl was used as a reference control. Densitometric analyses of glutenin subunits were performed using Image J software (Bio-Rad, http://www.bio-rad.com). The value of the optical density multiplication area was used to quantify HMW-GS abundance. Student’s t-test was used to determine the significance of differences (P < 0.05) between Ae. tauschii and Xinmai 26.
Results and discussion
Composition and allelic variation of HMW-GS in 173 Ae. tauschii accessions
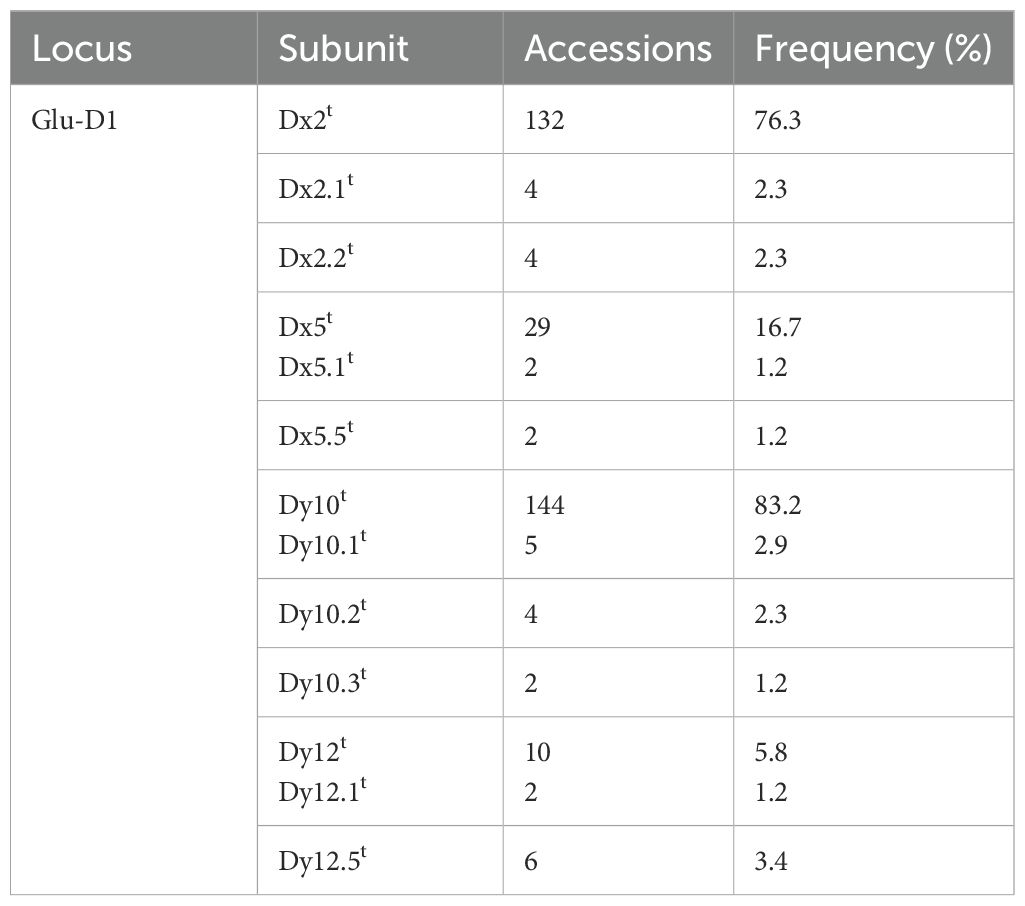
HMW-GS compositions of 173 Ae. tauschii accessions were analyzed based on their mobility in SDS-PAGE, with Chinese Spring (null, Bx7 + By8, Dx2 + Dy12) and Xinmai 26 (Ax1, Bx7 + By8, Dx5 + Dy10) as standards (Figure 1; Supplementary Table S1; Supplementary Figure S1). The results showed that HMW-GS combinations of Ae. tauschii exhibited high diversity, and a total of 16 distinct types were identified. The most frequent subunit combination was Dx2t + Dy10t, accounting for 68.2% of accessions, followed by Dx5t + Dy10t (13.3%). The other subunit combinations included Dx5t + Dy12t, Dx2.1t + Dy10.1t, Dx5t + Dy12.5t, Dx5.5t + Dy12.1t, Dx2.2t + Dy10t, Dx2t + Dy10.2t, Dx2t + Dy10.1t, and Dx2t + Dy12.5t, and so forth. Allelic variation and subunit frequency analysis at the Glu-Dx1 locus revealed that the Dx2t subunit has the highest frequency (76.3%), followed by the Dx5t subunit (16.7%) (Table 1). In addition, several rare subunits in common wheat were detected, including Dx2.1t, Dx2.2t, Dx5.1t, and Dx5.5t, with frequencies of 2.3%, 2.3%, 1.2%, and 1.2%, respectively. At the Glu-Dy1 locus, Dy10t was the most prevalent subunit (83.2%), while Dy12t occurred at 5.8%. Five rare subunits in common wheat were also identified, including Dy10.1t, Dy10.2t, Dy10.3t, Dy12.1t, and Dy12.5t, with frequencies of 2.9%, 2.3%, 1.2%, 1.2%, and 3.4%, respectively.
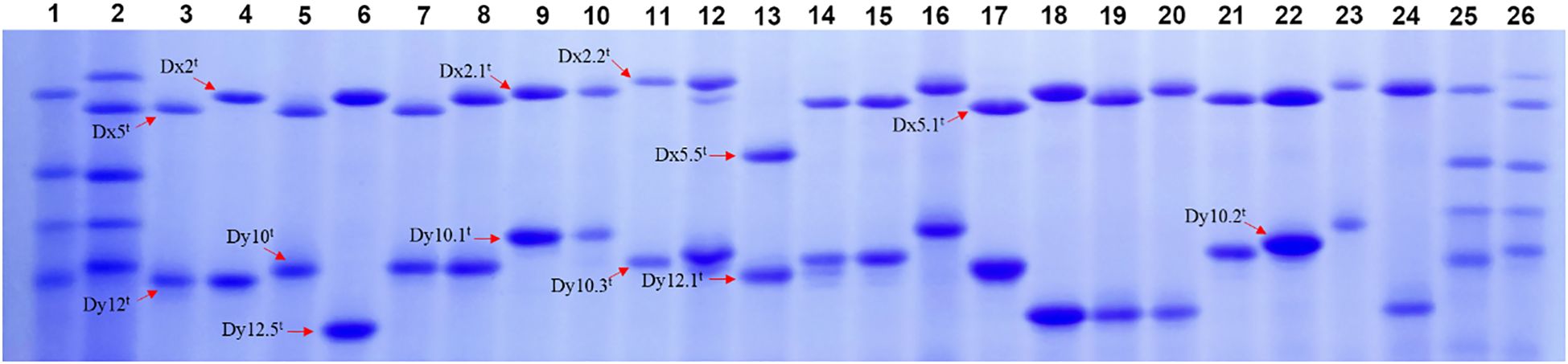
Figure 1. SDS-PAGE patterns of HMW-GS in partial Ae. tauschii accessions. (1, Chinese spring; 2, Xinmai 26; 3, AY1; 4, AY34; 5, AY27; 6, AY6; 7, AY33; 8, AY23; 9, AY79; 10, AY37; 11, AY73; 12, AY9; 13, AY32; 14, AY38; 15, AY15; 16, AY11; 17, AY16; 18, AY60; 19, AY55; 20, AY61; 21, AY8; 22, AY29; 23, AY24; 24, AY53;25, Chinese spring; 26, Xinmai 26).
The Dx5 + Dy10 subunit combination is considered a superior type for bread-making quality in wheat. As the donor species of the common wheat D genome, Ae. tauschii possesses more diverse HMW-GS combinations and allelic variation at the Glu-D1 locus. Tahernezhad et al.19 identified eight novel subunit combinations in 28 Ae. tauschii accessions from Iran, including Dx1.5t + Dy10t, Dx3t + Dy11t, Dx2t + Dy10.1t, Dx3t + Dy12t, Dx3t + Dy12.3t, Dx1.5t + Dy12t, Dx3t + Dy12.2t, and Dx1.5t + Dy12.1*t. These results demonstrate that HMW-GS compositions of Ae. tauschii has abundant genetic diversity, which could provide valuable subunit gene resources for common wheat quality breeding.
It is widely accepted that the Dx5 subunit, as a superior high-quality strong glutenin subunit, has been extensively utilized in wheat quality breeding since it contains an extra cysteine residue (codon: TGT) at the 118th position of the amino acid sequence. This residue can form additional disulfide bonds with other HMW-GS or LMW-GS, generating larger glutenin polymers that positively influence dough viscoelasticity (Sun et al., 2024). It is natural to know whether the extra cysteine residue in wheat Dx5 subunit directly originates from Ae. tauschii. To address this issue, 173 Ae. tauschii accessions were analyzed utilizing the specific functional marker dCAPS5, which was developed to target the extra cysteine residue in the wheat Dx5 subunit (Ren et al., 2022). Among them, accessions AY01, AY06, AY08, AY09, AY16, AY40, AY49, AY55, AY60, AY61, and AY80 belong to the L2E family (Li et al., 2022), which has been identified as the direct donor of the wheat D genome (Wang et al., 2013, 2024; Cavalet-Giorsa et al., 2024). Unexpectedly, none of the Ae. tauschii accessions carried the extra cysteine residue at position 118 in their Dx5t subunits (Supplementary Table S1). Similar results were reported by Dong et al. (2013), in which none of the Glu-Dx5t subunits with the extra cysteine residue at position 118 were found in 355 Ae. tauschii accessions from over 20 countries using seven molecular markers linked to the wheat Dx5 subunit. Additionally, alignment analysis of the amino acid sequence deduced by the cloned Dx5t subunit gene showed that none of the extra cysteine residue was observed except for four conserved cysteine residues (Yan et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2008b). Furthermore, Pflüger et al. (2001) found that the two subunits exhibited significant differences in surface hydrophobicity compared with Ae. tauschii Dx5t subunit and wheat Dx5 subunit using reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC), attributing this difference primarily to the extra cysteine residue in the wheat Dx5 subunit. All these findings demonstrated that the wheat Dx5 subunit might not originate directly from theDx5t subunit in Ae. tauschii. Wang et al. (2024) proposed that the wheat D genome predominantly accumulated novel mutations derived from Ae. tauschii rather than direct introgression through analyzing genomic structural variations of 292 wheat and 400 Ae. tauschii accessions, where the relative importance of novel mutation accumulation was much higher for the genetic diversity of the D genome. This contrast can be partially attributed to frequent interploidy introgression from tetraploid wheat into hexaploid wheat, while rare introgressions from Ae. tauschii to hexaploid wheat. The multi-layered genetic diversity of the D genome was caused by the accumulation of variations, and key genetic loci such as TaBTR-D1, TaPPD-D1, and TaGlu-D1 acquired genetic diversity through this featured structure, thereby facilitating the adaptation and agronomic utilization of hexaploid wheat (Wang et al., 2024). Thus, current evidence suggests the extra cysteine residue in wheat 1Dx5 might arise from mutational events during the evolutionary process from Ae. tauschii to common wheat.
Molecular characterization of HMW-GS genes from Ae. tauschii
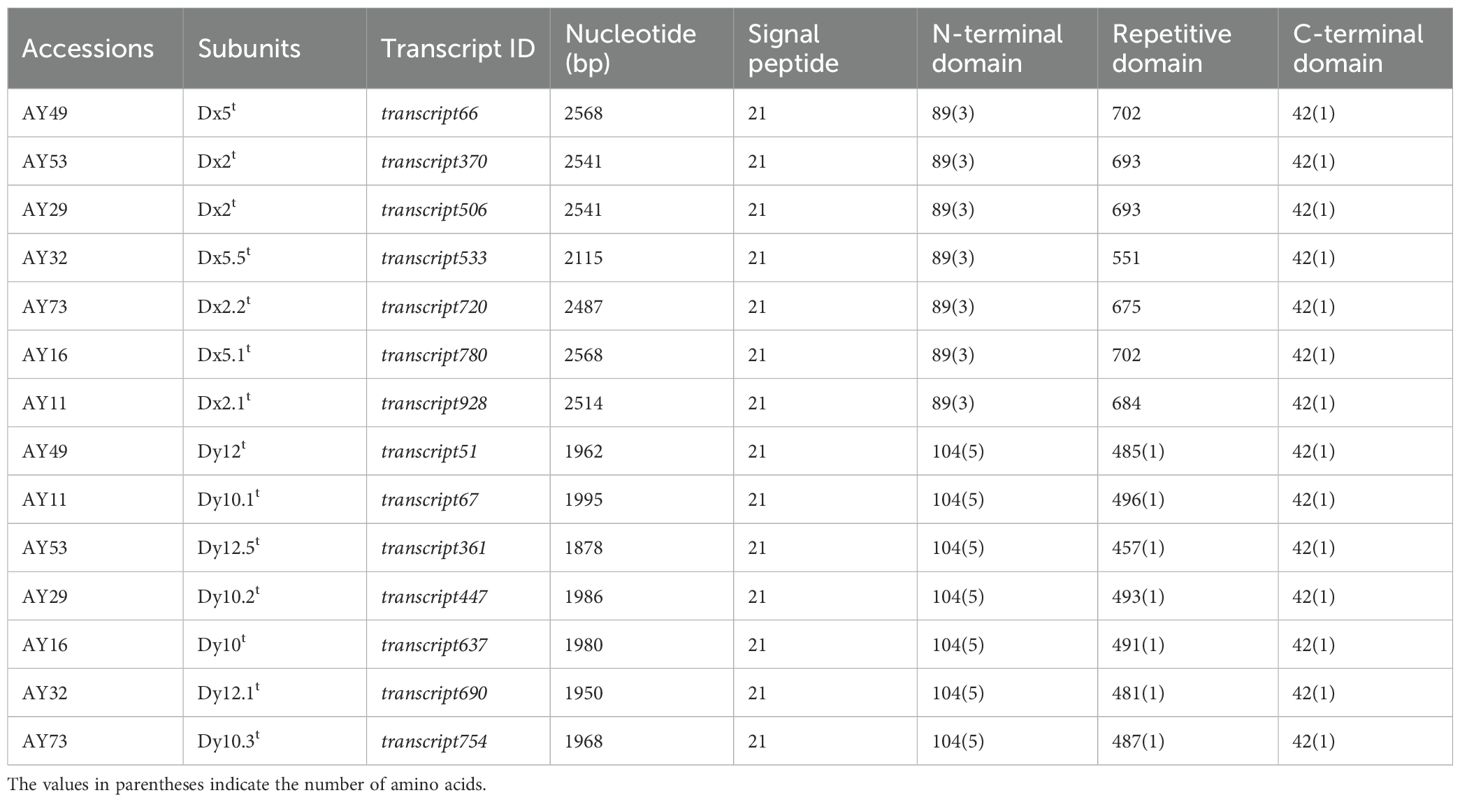
To determine whether other sites of Glu-D1t subunits in Ae. tauschii contain the extra cysteine residue except for the Dx5t subunit; the accessions AY11, AY16, AY29, AY32, AY49, AY53, and AY73, containing all subunits (Dx2t, Dx2.1t, Dx2.2t, Dx5t, Dx5.1t, Dx5.5t, Dy10t, Dy10.1t, Dy10.2t, Dy10.3t, Dy12t, Dy12.1t, and Dy12.5t) in this study, were selected for the third-generation transcriptome sequencing through the PacBio Sequel II platform. A total of 164,696,323 subreads with a mean length of 1,818 bp were generated, from which the 3,358,335 reads of a circular consensus sequence (CCS) were extracted. The 3,162,107 full-length nonchimeric sequences (FLNCs) were acquired after refining by the IsoSeq3 pipeline. Due to the highly complex sequence structure of HMW-GS, the redundant sequences were further removed utilizing a custom pipeline in FLNCs. Thus, the obtained sequences were further aligned, and manually removed again in redundant ones. Finally, fourteen transcripts of HMW-GS genes were identified based on the alignment with the published glutenin genes from Triticeae (Table 2; Supplementary Table S2).
Sequence alignment with published HMW-GS genes in GenBank revealed that transcript928 and transcript67 showed complete identity to the previously reported Dx subunit gene (Accession: AF480486) and Dy subunit gene (Accession: FJ008134), respectively. Consequently, six novel Dx subunit genes (transcript720, transcript66, transcript533, transcript370, transcript506, and transcript780) and six novel Dy subunit genes (transcript637, transcript51, transcript361, transcript447, transcript754, and transcript690) were identified. All these Ae. tauschii HMW-GS gene sequences initiated with the start codon ATG and terminated with the double stop codon TGATAG.
Sequences of the seven identified Dx subunit genes ranged from 2115 to 2568 bp in length, encoding 703–854 amino acids (Table 2; Supplementary Table S2). Notably, the 1Dx5.5t subunit exhibited a 426-bp deletion in the central repetitive domain, resulting in the shortest variant of only 703 amino acids. Sequence alignment analysis with the reference Dx5 subunit in wheat variety Xinmai 26 with the strong gluten demonstrated that all seven Dx subunits in Ae. tauschii only contained four conserved cysteine residues located at positions 10, 25, and 40 in the N-terminal domain and position 30 in the C-terminal domain (Figure 2). The central repetitive domains (containing 551 to 702 amino acids) emerged as the primary source of molecular diversity among these subunits. Particularly, the Dx5.1t subunit of AY16 and the Dx5t subunit of AY49 had a six-amino-acid insertion (SGQGQQ) at positions 146–151 within the central repetitive region. Compared with other subunits, the two subunits displayed higher sequence similarity with the high-quality subunit Dx5, implying their potential values for wheat quality improvement.
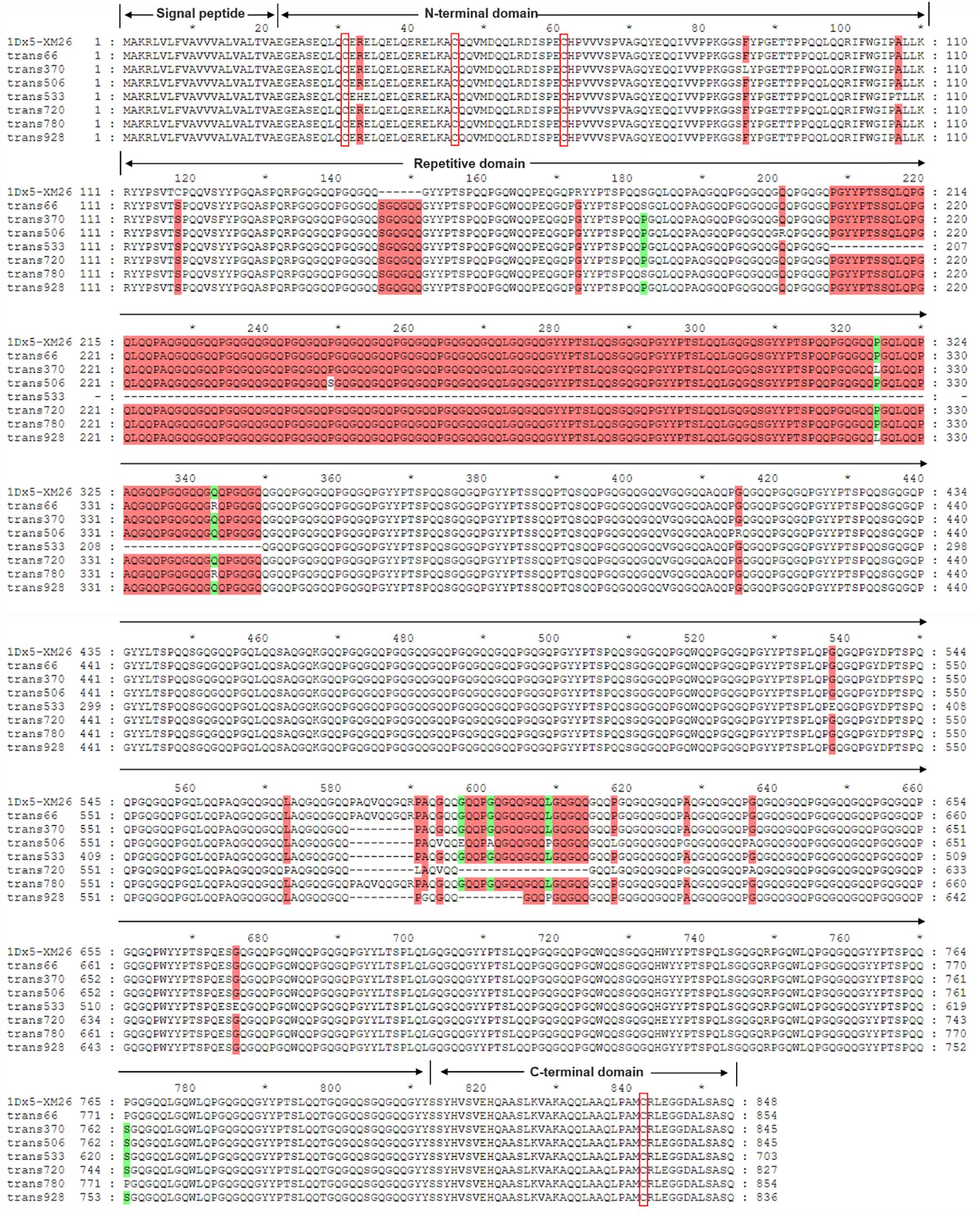
Figure 2. Sequence alignment of 7 identified Dx subunits in Ae. tauschii and the Dx5 subunit in Xinmai 26. (The red boxes indicate the conserved cysteine residues).
The full lengths of seven Dy subunit genes ranged from 1878 to 1995 bp, encoding 624 to 663 amino acids (Table 2). The positions of the seven cysteine residues contained in the Dy subunit sequence are very conserved, with five in the N-terminal domain (at positions 10, 22, 44, 45, and 55), one in the central repetitive domain (at position 418), and one in the C-terminal domain (at position 32) (Supplementary Figure S2). Compared with the Dy10 subunit in wheat variety Xinmai 26, the 1Dy10t subunit in AY16 has two identical six-peptide insertions (QIGQGQ) at positions 202–207 and 229–234 within its central repetitive region (Supplementary Figure S2). The longer repetitive region may have positive effects on dough properties and consequently possess high potential for wheat quality improvement (Wang et al., 2012).
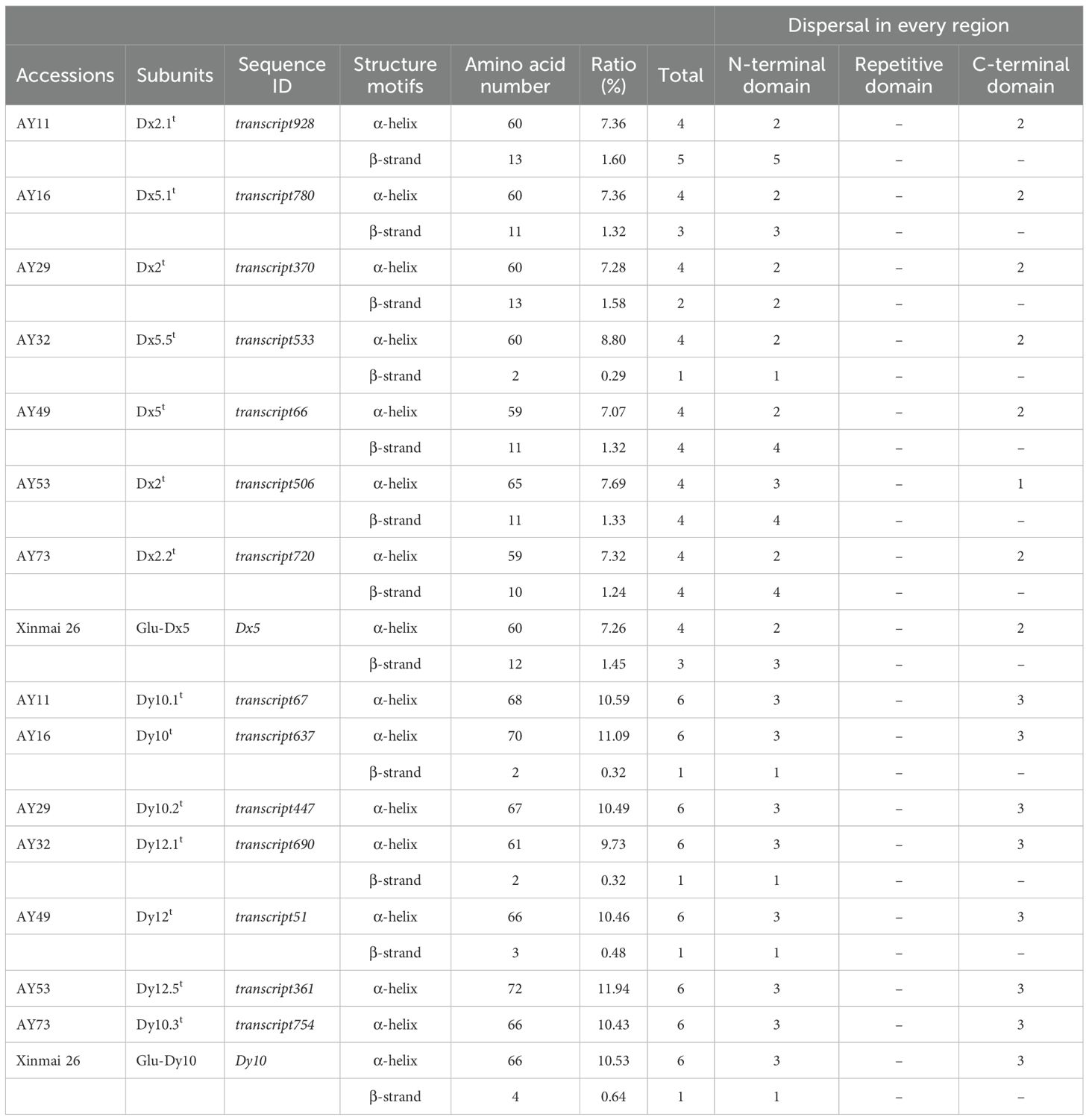
The secondary structure of HMW-GS, primarily composed of α-helices and β-strands in wheat gluten, forms the structural foundation for its complex spatial conformation. According to Masci et al. (1998), helix–helix interactions were critical for intramolecular disulfide bond formation. The increased α-helix content is likely to play a significant role in enhancing dough quality, and the β-strands are believed to be positively correlated with dough elasticity and resistance to distortion capability (Jiang et al., 2008). The secondary structures of all subunits in this study were predicted and compared with previously reported Glu-D1 subunits of wheat Xinmai 26 with strong gluten (Table 3). As a result, the α-helices of HMW-GS in Ae. tauschii and Xinmai 26 were predominantly localized in both N-terminal and C-terminal domains, while β-strands were exclusively confined to the N-terminal domains. The Dx2t subunit of AY53 exhibited significantly higher α-helix and β-strand content than the Dx5 subunit of Xinmai 26, containing 65 and 11 amino acid residues, respectively. The Dy subunits of Ae. tauschii generally have fewer β-strands, with the Dy subunits of AY11, AY29, AY53, and AY73 even lacking β-strands. In comparison, the Dy10t subunit of AY16 shows significantly higher α-helix and β-strand content than those of Xinmai 26, containing 70 and 2 amino acid residues, respectively.
The results of HMW-GS sequence composition and secondary structure content revealed that the Dx5.1t + Dy10t subunit combination of accession AY16 possesses the longer repetitive domain and higher α-helix and β-strand content compared to the other Ae. tauschii accessions, which makes it potentially a valuable germplasm resource for improving wheat quality.
Relative content of HMW-GS in Ae. tauschii
The viscoelastic properties of dough are influenced not only by glutenin subunit composition but also by glutenin content in the grain. Higher glutenin content can promote the formation of larger glutenin macropolymers, which in turn stabilizes the structural integrity and enhances the dough elasticity (Gao et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2023). The HMW-GS of 7 Ae. tauschii accessions (AY11, AY16, AY29, AY32, AY49, AY53, and AY73) were separated by SDS-PAGE, with Xinmai 26 and Chinese Spring as controls at equivalent amounts. As shown in Figure 3A, the band of the most Ae. tauschii accessions displayed significantly larger volume and more intense staining than Xinmai 26. This reveals that the content of HMW-GS in these Ae. tauschii accessions are higher than the Glu-D1 subunit in common wheat.
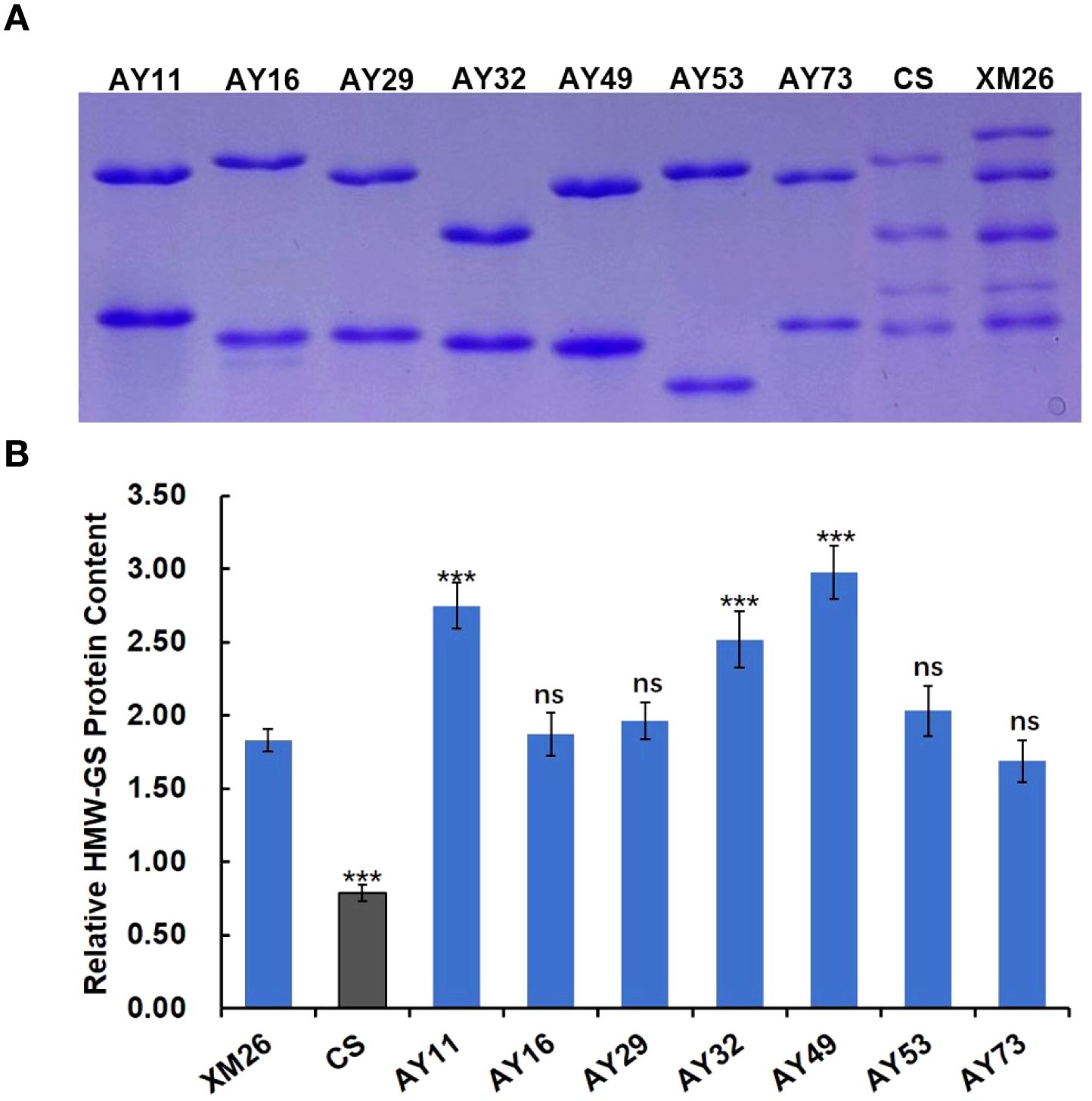
Figure 3. HMW-GS content in AY11, AY16, AY29, AY32, AY49, AY53, AY73, Xinmai 26 and Chinese Spring. (A, electrophoresis patterns of HMW-GS in the same amount of flour. B, the relative content of HMW-GS. XM26, Xinmai 26; CS, Chinese Spring; ns, no significance. ***indicate significantly different from Xinmai 26 at P = 0.001).
The relative content of HMW-GS in Ae. tauschii and wheat was quantified based on optical density using Image J software, with BSA as the reference protein (Figure 3b). The results showed that relative HMW-GS content in all Ae. tauschii accessions exhibited higher than that in Chinese Spring. Notably, the relative content of HMW-GS in AY11, AY32, and AY49 was significantly higher than that of the Glu-D1 subunits in the wheat variety Xinmai 26 with strong gluten, which indicated that these three accessions could be valuable germplasm resources for wheat quality improvement.
In conclusion, HMW-GS compositions of Ae. tauschii exhibited remarkable genetic diversity. However, none of the Glu-D1t subunits in Ae. tauschii contained the extra cysteine residue at position 118, suggesting that the extra cysteine of the Dx5 subunit in wheat might have arisen from mutational events during the evolution of hexaploid wheat from its progenitors. Additionally, the longer repetitive domains and higher α-helix and β-strand contents in HMW-GS of Ae. tauschii may have positive effects on dough properties. Furthermore, the higher HMW-GS content in some Ae. tauschii accessions, such as AY11, AY32, and AY49, may facilitate the formation of larger glutenin macropolymers. Therefore, Ae. tauschii could be used as a valuable germplasm resource for enriching the genetic basis of wheat quality breeding.
Data availability statement
All raw data of the PacBio RNA sequencing in this study were deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under BioProject number PRJNA1307214.
Author contributions
HP: Formal Analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft. LL: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Data curation. QL: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Data curation. GZ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision. JR: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Data curation. MA: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RC: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Supervision. DZ: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was partially supported by Key Technology R&D Program of Henan Province of China (231111112900, 225200810024, 241111110900), Key Technology Program of Henan Province of China (242103810025), Key Scientific Research Projects of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province (25A210002), Kaifeng City Science and Technology Development Plan Project (2202005). We also thank the US National Plant Germplasm Center for providing the test materials.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1658088/full#supplementary-material
References
Blechl, A., Lin, J., Nguyen, S., Chan, R., Anderson, O. D., and Dupont, F. M. (2007). Transgenic wheats with elevated levels of Dx5 and/or Dy10 high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits yield doughs with increased mixing strength and tolerance. J. Cereal Sci. 45, 172–183. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2006.07.009
Cavalet-Giorsa, E., González-Munoz, A., Athiyannan, N., Holden, S., Salhi, A., Gardener, C., et al. (2024). Origin and evolution of the bread wheat D genome. Nature 633, 848–855. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07808-z
Delorean, E., Gao, L., Lopez, J. F. C., Wulff, B. B. H., Ibba, M. I., Poland, J., et al. (2021). High molecular weight glutenin gene diversity in Aegilops tauschii demonstrates unique origin of superior wheat quality. Commun. Biol. 4, 1242. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02563-7
Dong, Z., Yang, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, K., Lou, H., An, X., et al. (2013). Haplotype variation of glu-D1 locus and the origin of glu-D1d allele conferring superior end-use qualities in common wheat. PloS One 8, e74859. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074859
Gao, Y., An, K., Guo, W., Chen, Y., Zhang, R., Zhang, X., et al. (2021). The endosperm-specific transcription factor TaNAC019 regulates glutenin and starch accumulation and its elite allele improves wheat grain quality. Plant Cell 33, 603–622. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaa040
Gaurav, K., Arora, S., Silva, P., Sánchez-Martín, J., Horsnell, R., Gao, L., et al. (2022). Population genomic analysis of Aegilops tauschii identifies targets for bread wheat improvement. Nat. Biotechnol. 40, 422–431. doi: 10.1038/s41587-021-01058-4
Guo, J., Wang, F., Zhang, Z., Wu, D., and Bao, J. (2021). Characterization of gluten proteins in different parts of wheat grain and their effects on the textural quality of steamed bread. J. Cereal Sci. 102, 103368. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2021.103368
Hao, C., Jiao, C., Hou, J., Li, T., Liu, H., Wang, Y., et al. (2020). Resequencing of 145 landmark cultivars reveals asymmetric sub-genome selection and strong founder genotype effects on wheat breeding in China. Mol. Plant 13, 1733–1751. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.09.001
Hsam, S. L. K., Kieffer, R., and Zeller, F. J. (2001). Significance of Aegilops tauschii glutenin genes on breadmaking properties of wheat. Cereal Chem. 78, 521–525. doi: 10.1094/CCHEM.2001.78.5.521
Jiang, C., Pei, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, X., Yao, D., Yan, Y. M., et al. (2008). Molecular cloning and characterization of four novel LMW glutenin subunit genes from Aegilops longissima, Triticum dicoccoides and T.zhukovskyi. Hereditas 145, 92–98. doi: 10.1111/j.0018-0661.2008.02035.x
Katoh, K. and Standley, D. M. (2013). MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 772–780. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010
Kent, W. J. (2002). BLAT-the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 12, 656–664. doi: 10.1101/gr.229202
Khalid, A., Hameed, A., and Tahir, M. F. (2023). Wheat quality: A review on chemical composition, nutritional attributes, grain anatomy, types, classification, and function of seed storage proteins in bread making quality. Front. Nutr. 10, 1053196. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1053196
Larkin, M. A., Blackshields, G., Brown, N. P., Chenna, R., McGettigan, P. A., McWilliam, H., et al. (2007). Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23, 2947–2948. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Li, Y., Fu, J., Shen, Q., and Yang, D. (2021). High-molecular-weight glutenin subunits: genetics, structures, and relation to end use qualities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 184. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010184
Li, H., Nie, F., Zhu, L., Mu, M., Fan, R., Li, J., et al. (2022). New insights into the dispersion history and adaptive evolution of taxon Aegilops tauschii in China. J. Genet. Genomics 49, 185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.11.004
Ma, W., Appels, R., Bekes, F., Larroque, O., Morell, M. K., and Gale, K. R. (2005). Genetic characterisation of dough rheological properties in a wheat doubled haploid population: additive genetic effects and epistatic interactions. Theor. Appl. Genet. 111, 410–422. doi: 10.1007/s00122-005-2001-0
Masci, S., D’ovidio, R., Lafiandra, D., and Kasarda, D. D. (1998). Characterization of a low-molecular-weight glutenin subunit gene from bread wheat and the corresponding protein that represents a major subunit of the glutenin polymer. Plant Physiol. 118, 1147–1158. doi: 10.1104/pp.118.4.1147
Pflüger, L. A., D’ovidio, R., Margiotta, B., Peña, R., Mujeeb-Kazi, A., and Lafiandra, D. (2001). Characterisation of high- and low-molecular weight glutenin subunits associated to the D genome of Aegilops tauschii in a collection of synthetic hexaploid wheats. Theor. Appl. Genet. 103, 1293–1301. doi: 10.1007/s001220100704
Ren, J., Jiang, Z., Li, W., Kang, X., Bai, S., Yang, L., et al. (2022). Characterization of glutenin genes in bread wheat by third-generation RNA sequencing and the development of a glu 1Dx5 marker specific for the extra cysteine residue. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 7211–7219. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c02050
Sahlin, K., Tomaszkiewicz, M., Makova, K. D., and Medvedev, P. (2018). Deciphering highly similar multigene family transcripts from Iso-Seq data with IsoCon. Nat. Commun. 9, 4601. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-06910-x
Savary, S., Willocquet, L., Pethybridge, S. J., Esker, P., McRoberts, N., and Nelson, A. (2019). The global burden of pathogens and pests on major food crops. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 3, 430–439. doi: 10.1038/s41559-018-0793-y
Su, Y., Zou, M., Zhu, Y., Han, X., Li, Y., Zhang, D., et al. (2020). Analysis of population structure and origin in Aegilops tauschii Coss. from China through SNP markers. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 67, 923–934. doi: 10.1007/s10722-020-00890-y
Sukhwinder, S., Chahal, G. S., Singh, P. K., and Gill, B. S. (2012). Discovery of desirable genes in the germplasm pool of Aegilops tauschii Coss. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 72, 271–277. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-12-126
Sun, N., Mu, Y., Wang, D., Li, J., Yuan, T., Liu, W., et al. (2024). Allelic variations of HMW-GS and LMW-GS and quality analysis in Yannong series wheat cultivars/derivative lines. Front. Genet. 15, 1465540. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1465540
Tahernezhad, Z., Musavi, Z., Zamani, M. J., Aghaei, M. J., and Foroudi, B. R. (2013). Allelic diversity of high molecular weight glutenin subunits (HMW-GS) in Iranian Aegilops tauschii Coss. accessions by sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 60, 905–911. doi: 10.1007/s10722-012-9887-6
Wang, K., An, X. L., Pan, L. P., Dong, K., Gao, L. Y., Wang, S. L., et al. (2012). Molecular characterization of HMW-GS 1Dx3t and 1Dx4t genes from Aegilops tauschii and their potential value for wheat quality improvement. Hereditas 149, 41–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.2011.02215.x
Wang, J., Luo, M. C., Chen, Z., You, F. M., Wei, Y. M., Zheng, Y., et al. (2013). Aegilops tauschii single nucleotide polymorphisms shed light on the origins of wheat D-genome genetic diversity and pinpoint the geographic origin of hexaploid wheat. New Phytol. 198, 925–937. doi: 10.1111/nph.12164
Wang, Z., Wang, W., He, Y., Xie, X., Yang, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). On the evolution and genetic diversity of the bread wheat D genome. Mol. Plant 17, 1672–1686. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2024.09.007
Yan, Z. H., Guo, Z. F., Liu, D. C., Dai, S. F., Wei, Y. M., and Zheng, Y. L. (2008). Characterization of HMW-GS genes Dx5t and Dy12t from Aegilops tauschii accession with subunit combination Dx5t+Dy12t. Cereal Res. Commun. 36, 477–487. doi: 10.1556/CRC.36.2008.3.12
Yang, T., Wang, Y., Jiang, J., Wang, P., Zhong, Y., Zhou, Q., et al. (2023). Influence of high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit on components and multiscale structure of gluten and dough quality in soft wheat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 71, 4943–4956. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c07958
Yang, F., Zhang, J., Liu, Q., Liu, H., Zhou, Y., Yang, W., et al. (2022). Improvement and re-evolution of tetraploid wheat for global environmental challenge and diversity consumption demand. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 2206. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042206
Yazar, G., Duvarci, O. C., Tavman, S., and Kokini, J. L. (2017). LAOS behavior of the two main gluten fractions: Gliadin and glutenin. J. Cereal Sci. 77, 201–210. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2017.08.014
Zhang, Q., Dong, Y., An, X., Wang, A., Zhang, Y., Li, X., et al. (2008a). Characterization of HMW glutenin subunits in common wheat and related species by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS). J. Cereal Sci. 47, 252–261. doi: 10.1016/j.jcs.2007.04.013
Zhang, D., He, J., Huang, L., Zhang, C., Zhou, Y., Su, Y., et al. (2017). An advanced backcross population through synthetic octaploid wheat as a “Bridge”: development and QTL detection for seed dormancy. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 2123. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.02123
Zhang, D. L., He, T. T., Liang, H. H., Huang, L. Y., Su, Y. Z., Li, Y. G., et al. (2016). Flour quality and related molecular characterization of high molecular weight glutenin subunit genes from wild emmer wheat accession TD-256. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 5128–5136. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b01547
Zhang, Y., Li, X., Wang, A., An, X., Zhang, Q., Pei, Y., et al. (2008b). Novel x-type high-molecular-weight glutenin genes from Aegilops tauschii and their implications on the wheat origin and evolution mechanism of Glu-D1–1 proteins. Genetics 178, 23–33. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.077412
Zhang, D., Zhou, Y., Zhao, X., Lv, L., Zhang, C., Li, J., et al. (2018). Development and Utilization of Introgression Lines Using Synthetic Octaploid Wheat (Aegilops tauschii x Hexaploid Wheat) as Donor. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01113
Keywords: Aegilops tauschii, high molecular weight glutenin subunit, RNA sequencing, protein secondary structure prediction, SDS-PAGE
Citation: Peng H, Lv L, Lu Q, Zhao G, Ren J, Rehman Arif MA, Su Y, Cheng R and Zhang D (2025) Molecular characterization of novel high-molecular-weight glutenin subunit genes from Aegilops tauschii. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1658088. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1658088
Received: 02 July 2025; Accepted: 03 September 2025;
Published: 19 September 2025.
Edited by:
Yunfeng Xu, Kansas State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Huagang He, Jiangsu University, ChinaLiqiang Song, Hebei Agricultural University, China
Tongde Bie, Yangzhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, China
Copyright © 2025 Peng, Lv, Lu, Zhao, Ren, Rehman Arif, Su, Cheng and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ruiru Cheng, Y2hlbmdydWlydUBoZW51LmVkdS5jbg==; Dale Zhang, emhhbmdkYWxlQGhlbnUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Huijun Peng1,2†
Huijun Peng1,2† Ruiru Cheng
Ruiru Cheng