- 1Lushan Botanical Garden, Jiangxi Province and Chinese Academy of Sciences, Jiujiang, Jiangxi, China
- 2Department of Horticulture, Muhammad Nawaz Shareef University of Agriculture, Multan, Pakistan
- 3Department of Plant Pathology, Faculty of Agricultural Sciences and Technology, Bahauddin Zakariya University, Multan, Pakistan
- 4Horticultural Sciences Department, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, United States
- 5Department of Plant Pathology, Muhammad Nawaz Shareef University of Agriculture, Multan, Pakistan
- 6Department of Botany and Microbiology, College of Science, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: Bacterial blight of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.), caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae (Xap), is a major constraint to pomegranate production and fruit quality. Effective management strategies are essential to mitigate yield losses and orchard decline.
Methods: Field experiments were conducted over three consecutive seasons to evaluate the efficacy of six bactericides applied at 15-day intervals (April–July) on three pomegranate cultivars such that, Sindhuri, Kalehar, and Sava using a randomized complete block design. Treatments included copper oxychloride (3000 ppm) combined with streptocycline (500 ppm) (T7) alongside other bactericides. Disease incidence, severity, marketable yield, fruit weight, aril quality, and biochemical parameters were recorded and statistically analyzed.
Results: The T7 treatment proved most effective, significantly reducing bacterial blight intensity. In the Sindhuri cultivar, mean disease incidence was lowest on leaves (3.51%), fruits (3.88%), twigs (0.58%), and trees (3.59%). Disease severity values were similarly minimized, with the highest mean disease reduction observed on leaves (77.63%), fruits (79.76%), twigs (76.10%), and whole trees (76.90%). T7 also improved productivity, with marketable yield (89.60 kg), fruit weight (245 g), and hundred-aril weight (43.30 g), while enhancing biochemical traits such as TSS (17.90 °Brix), vitamin C (36.50 mg/100 mL), antioxidants (86.40% inhibition), and enzymatic activities (CAT: 21.30 U/mg protein; POD: 1.35 U/mg protein).
Discussion: Among the cultivars, Sindhuri displayed the highest resistance, followed by Kalehar and Sava. The copper-streptocycline combination not only suppressed bacterial blight but also enhanced fruit yield, quality, and biochemical composition. These findings demonstrate the potential of optimized bactericide application in sustaining pomegranate productivity and reducing orchard losses due to Xap.
Introduction
Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) belongs to the family Lythraceae and has emerged as a marvelous fruit globally (Özcan et al., 2019). Pomegranate cultivation began in 4000 BC and has been successfully cultivated in Afghanistan, China, Iran, Iraq, Israel, India, Pakistan, South Africa, Spain, and the USA (Kahramanoglu et al., 2019; Singh et al., 2020). Pomegranate is considered an elixir of life and is declared a superfruit because of its color, refreshing juicy arils, potential antioxidants, and high medicinal and nutritional value (Arora et al., 2016). A global production of approximately 3.8 million tons has been reported, and the cultivated area for this crop is continuously increasing due to high consumer demand (Kahramanoglu et al., 2019). In Pakistan, the total cultivated area of pomegranate declined from 14,200 hectares (2003-2004) to 5,200 hectares (2020-2021), representing a 63.4% reduction. Production decreased from 0.0621 million tons to 0.042 million tons during the same period (32.4% reduction) (PBS, 2022; FAO, 2023). Despite pomegranate’s reputation as a hardy crop (tolerant of drought, poor soils, and high temperatures), growers face significant challenges in sustainable production. Key constraints include inadequate pruning practices, sunscald, fruit cracking, fruit flies, fungal diseases, and bacterial blight (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae) (Melgarejo et al., 2000).
Bacterial blight of pomegranate was first observed in 1988 at Chakwal “32.9328° N, 72.8630° E” and Islamabad “33.6995° N, 73.0363° E” in Pakistan (Akhtar and Bhatti, 1992). This disease was considered a minor issue before the 1990s, but it has now emerged as a primary constraint for pomegranate production. The causal agent Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae (XaP) has been declared a quarantine pest in various pomegranate growing areas of the world, especially in Pakistan, India, South Africa, and Turkey. This can cause serious blight disease outbreaks affecting commercial cultivation and hampering the pomegranate industry (Icoz et al., 2014; Sharma et al., 2017). XaP is a gram-negative, monotrichous, rod-shaped, and non-sporing bacterium (Sharma et al., 2017). Xap infection begins with water-soaked lesions on the abaxial side of leaves in irregular patterns, with 2.50 mm to 5.00 mm in diameter (Kumar et al., 2011; Arora, 2014). The symptoms primarily appear on the leaves and fruits, followed by chlorosis and necrotic brown to black-brown spots with dried silvery bacterial ooze, approximately 15 days after infection (Sharma et al., 2017; Maity et al., 2018). The necrotic lesion on the fruit increases with the increase in fruit size, leading to “L”, “Y”, or “Star” shaped cracks appearing on the fruit surface (Mondal and Mani, 2012).
XaP can easily survive on fallen leaves from December to mid-March. It reproduces from mid-March to the end of June as the temperature and humidity levels become favorable for multiplication (Sharma et al., 2011). This pathogen infects through wounds and stomatal openings, causing water-soaked lesions that develop into irregular spots. It spreads via airborne cells, survives in the soil for four months, and causes fresh infections on new growth (Sharma et al., 2011). Kale et al. (2012) reported that in Punjab, the pathogen survived in infected fallen leaves for up to 210 days and in canker lesions for up to 80 days. The epidemiology of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae (Xap) exhibits distinct seasonal patterns: while the pathogen remains viable year-round across broad temperature ranges (9-43 °C) at lower humidity (Jadhav and Sharma, 2011), disease severity intensifies during rainy seasons under high humidity (>80%) and moderate temperatures (25-35°C). Under these favorable conditions, Xap proliferates within lesions on leaves, stems, and fruits. Bacterial ooze emerges from lesions during wet periods and disseminates via wind-driven rain, facilitating secondary infection of new growth (Lalithya et al., 2017).
Exposure to sunlight rapidly deactivates Xap in soil and on plant surfaces, leading to rapid drying and death within a few days in the soil and a few months in the plant excretophore buried in the soil. However, Xap can persist for years in infected plant tissues if they are kept dry and free from soil contents (Yenjerappa et al., 2004, 2006; Sharma et al., 2017; Maity et al., 2018). The increased emergence trend is attributed to various primary sources, including infected planting material, insect vectors, humans, rain splashes during thunderstorms, farm equipment, and irrigation water (Sharma et al., 2013). The pathogen (XaP) enters the plant body through natural openings (stomata, hydathodes, and lenticels) and wounds made by its thorns, insects, and pruning tools (Maity et al., 2018). If proper management is not followed during the fruit development and maturation stages, the chance of disease development increases manyfold and may cause up to 100% fruit loss (Singh et al., 2015). To address this devastating disease and its impact on yield and quality, we evaluated the efficacy of six bactericides, including an optimized copper-streptocycline combination, under field conditions across three consecutive seasons.
Currently, various cultural, chemical, and biological approaches are commonly used to manage bacterial blight in pomegranate orchards. Cultural practices include the removal and destruction of infected plant material, proper pruning to improve air circulation and sunlight penetration, and avoidance of overhead irrigation to prevent bacterial spread in healthy trees. Cultural control, followed by chemical control, has proven to be effective in managing bacterial blight in pomegranates. This involves pruning diseased twigs and branches, followed by four sprays of copper oxychloride + streptocycline or copper hydroxide + streptocycline, applied at 15-day intervals from mid-June to late July. These mixtures help to reduce disease indices on fruits and leaves, likely due to their ability to reduce inoculum and fresh infections (Kumar et al., 2018). Biological control involves the use of beneficial microorganisms or natural compounds to suppress pathogenic bacteria (Chen et al., 2023; Naqvi et al., 2025b). Biopesticides containing beneficial bacteria or fungi can compete with pathogens or directly inhibit their growth (Naqvi et al., 2025a). Breeding programs aim to develop pomegranate cultivars resistant or tolerant to specific bacterial diseases, offering sustainable long-term control, though requiring time and investment. Regular orchard monitoring for signs of bacterial diseases and other abiotic issues, particularly nutritional imbalances, early detection and intervention, prevention of outbreaks, and reduction of the need for intensive control measures (Kumar et al., 2018).
The effective management and complete eradication of this disease have become a challenge for researchers because of its faster inoculum build-up rate, rapid spread, and long-term survival rate in soil and planting material (Mondal and Mani, 2012). Cultural control, followed by chemical control, has been shown to be effective in managing bacterial blight infections. Application of bactericides, such as copper oxychloride and streptocycline, could help to improve yield, weight, juice (%), peel thickness, peel content, and various biochemical attributes (Shokrollah et al., 2011; Hussain et al., 2017, 2019). In Pakistan, especially in South Punjab, growers have been facing a serious threat of bacterial blight for the last 15 to 20 years.
Therefore, considering the potential significance of bacterial blight disease in pomegranate, this study aimed to evaluate the effect of various bactericides against bacterial blight disease incidence and severity and their impact on different physical, physiological, and biochemical attributes of the pomegranate fruit, so that recommendations may be disseminated to the main stakeholders nationally and internationally.
Materials and methods
Study site and plant selection
The current study was carried out at two distantly located pomegranate orchards, i.e., Qasba Marral (29.9812° N, 71.4240° E Multan) and Ala Bad (28°56′N, 70°58′E, Rahim Yar Khan) in South Punjab (30.0174° N, 71.398° E Pakistan during 2018-2019, 2019-2020, and 2020-2021. Xap seems to infect all available pomegranate cultivars in Pakistan, and no resistant or tolerant cultivars have been reported to date. The three most cultivated cultivars in South Punjab, Kalehar, Sindhuri, and Sava, were selected for this experiment. Eight-year-old plants with homogenous vigor and size were randomly selected for the evaluation of various bactericides against bacterial blight (Table 1).
Antibacterial compound preparation and application
Antibacterial compound preparation and application followed a standardized protocol. Aqueous solutions of each treatment (concentrations detailed in Table 1) were freshly prepared by dissolving compounds in distilled water to a final volume of 3 L per replicate, followed by vigorous stirring for 5 minutes to ensure homogeneity. Prior to foliar application, infected plant material was surgically removed, and pruning wounds were coated with Bordeaux paste/mixture to eliminate inoculum reservoirs. Treatments were applied at 15-day intervals during the active growing season (April–July) using a calibrated high-density polyethylene (HDPE) knapsack sprayer (16 L capacity). Foliar spraying targeted the entire canopy, including abaxial leaf surfaces, until runoff was achieved (≈500 mL solution per tree). Bordeaux applications were reapplied to pruning sites after each surgical intervention to maintain protective coverage.
Disease assessment
The experiments were conducted in the field with a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD), comprising a total of 40 leaves per replication/plant and ten leaves from each side. Similarly, 16 twigs and 16 fruits (four twigs and four fruits randomly selected from each side of the plant) were tagged for further assessment. The data was recorded at a regular interval of 15 days regarding disease severity, disease incidence, and disease reduction on leaves, fruits, twigs, and overall trees (Wheeler, 1969). The assessment of bacterial infestations was observed following a disease rating scale (0 to 5) where every digit represents a different infestation level, that is 0= healthy, 1= <1% infection, 2 = 1-10% infestation, 3 = 11- 20% damage, 4 = 21-50% and 5= >50% infection (Naz et al., 2018). The disease incidence, severity, % reduction over control, and disease severity of trees were calculated using the following equations.
Estimation of physical and biochemical quality attributes
Marketable yield (%) was calculated using a digital weighing balance (Sanyo Digital Balance). At the same time, the weight (g) of individual fruits and the hundred arils weight were measured using an electronic weight balance (OHASU Corporation, USA). The organoleptic or palatability rating of the fruits was analyzed by a panel of ten judges (seven men and three women) aged between 20 and 35 years. The committee considered the characteristics of fruit, i.e., the appearance, taste, texture, and eating quality for their evaluation. The nine-point Hedonic scale (Amerine et al., 1965) was used to evaluate sensory attributes of pomegranate fruits, including taste, texture, aroma, and overall acceptability. The total soluble solids (TSS) of aril juice were determined using a digital refractometer (PAL-1, ATAGO, Japan), and expressed in °Brix, and titratable acidity (TA) was determined using an automatic titrator (Hannan) and expressed in % citric acid. The pH of the juice was measured using a calibrated Milwaukee MW804 pH meter.
Estimation of vitamin C, total phenolic contents, and total antioxidant activity
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) (mg/100ml) was estimated using the iodine titration method, which is based on the principle that vitamin C reduces iodine (I2) to iodide ions (I−) while being oxidized to dehydroascorbic acid. The assay was performed using a known concentration of vitamin C solution, which was prepared by accurately weighing 0.250 g of pure ascorbic acid, dissolving it in distilled water, and making up the volume to 250 mL in a volumetric flask. This standard solution (approximately 1 mg/mL) was used to standardize the iodine solution. During standardization, 25 mL of the standard vitamin C solution was taken in an Erlenmeyer flask, and about 10 drops of 0.5% starch indicator were added near the endpoint of titration. The iodine solution was then titrated until a faint blue-black color persisted for at least 20 seconds, and the volume of iodine used was recorded. For the sample analysis, 25 mL of the filtered sample solution was titrated similarly with the standardized iodine solution in the presence of starch indicator until the endpoint was reached (Hussain et al., 2017). Vitamin C concentration in the sample is calculated using the formula:
Where V is the volume of iodine solution used for the sample (mL), N is the normality of the iodine solution, 88 represents the molecular weight of ascorbic acid, and v is the volume of the sample taken (mL). This concentration may be adjusted if the sample was diluted before titration.
Total phenolic contents
Total phenolic content (TPC) was determined using the Folin–Ciocalteu colorimetric assay. An appropriate amount, 0.5 mL of the diluted sample extract was added to 2.5 mL of 10% (v/v) Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, followed by the addition of 2 mL of 7.5% (w/v) sodium carbonate solution. The reaction mixture was then incubated at room temperature in the dark for 30 minutes to allow for color development. The absorbance of the resulting, blue-colored complex was measured at 765 nm using a UV-Visible spectrophotometer. A calibration curve was prepared under identical conditions using gallic acid standard solutions at known concentrations. The total phenolic content in the samples was calculated from the gallic acid standard curve and expressed as milligrams of gallic acid equivalents (mg GAE) per 100 g of the sample. All measurements were performed in triplicate, and the results were presented as the mean ± standard deviation (Razzaq et al., 2013).
Where C is the Concentration of gallic acid determined from the calibration curve (mg/mL), V = Volume of the extract used for the assay (mL), D = Dilution factor of the sample, W = Weight of the sample extracted (g).
Antioxidant scavenging activity
The antioxidant scavenging activity of the samples was determined using the 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical scavenging assay, following the method described by Razzaq et al. (2013) with slight modifications. A freshly prepared 0.1 mM DPPH solution in methanol was used as the radical source. Briefly, 1.0 mL of the sample extract at various concentrations was mixed with 1.0 mL of DPPH solution in a test tube. The mixture was then vortexed thoroughly and incubated in the dark at room temperature for 30 minutes to allow the reaction to occur. After incubation, the absorbance of the resulting solution was measured at 517 nm using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Cecil-CE7400S, UK) against a methanol blank. A control containing methanol and DPPH solution without sample extract was also prepared (Zheng et al., 2007). The percentage of DPPH radical scavenging activity (percent inhibition) was calculated using the following formula: A0.
Where A0 = absorbance of the control (DPPH solution without sample), As = absorbance of the sample with DPPH solution, and the assay was performed in triplicate, and the results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. This method quantifies the ability of the extract to donate hydrogen atoms or electrons to neutralize the stable DPPH free radical, reflected by a decrease in absorbance. The method complements antioxidant activity measurements obtained from the Folin-Ciocalteu assay conducted at 765 nm.
Determination of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase
Sixteen fruits were harvested from each treatment, and five fruits were randomly selected for biochemical analysis. The arils were mixed, and 300 g of arils were randomly picked and stored at –80 °C. One gram of frozen sample was homogenized with 2 ml of phosphate buffer (pH 7.2) in a mortar and pestle to determine enzyme activity. The homogenized mixture was centrifuged at 12000 rpm at 4 °C for 4 min, and the supernatant was collected separately. The antioxidative enzymes, including SOD, CAT, and POD, were determined by the method of (Jin et al., 2023), with some modification using Epoch ELISA Reader (Bio-Tek Instruments, Inc., Vermont, USA).
Superoxide dismutase activity assay
Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was quantified spectrophotometrically by its ability to inhibit the photochemical reduction of nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT), a method adapted from standard protocols. The assay principle relies on superoxide radicals, generated by the photoreduction of riboflavin, reducing NBT to produce a blue formazan dye. SOD, if present, competes with NBT for these superoxide radicals, thereby inhibiting NBT reduction and consequently reducing the color intensity. The activity is thus inversely proportional to the color formed. For each assay, a total reaction volume of 3 mL was prepared. The reaction mixture contained 0.1 mM EDTA, 130 mM L-methionine, 0.75 mM NBT, and 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.8). To this mixture, 0.1 mL of the prepared enzyme extract supernatant from the pomegranate samples was added. The reaction was initiated by the addition of 0.02 mM freshly prepared riboflavin. Immediately following riboflavin addition, the tubes were exposed to a 40-watt fluorescent lamp for precisely 10 minutes. Concurrently, a series of controls and blanks were prepared: a control tube (illuminated, containing all reagents but without enzyme extract) representing 100% NBT reduction; a blank tube (non-illuminated, containing all reagents but without enzyme extract) kept in the dark to determine background absorbance; and a sample blank (non-illuminated, containing all reagents and enzyme extract) also kept in the dark to account for any intrinsic absorbance of the enzyme extract. After the 10-minute illumination period, the absorbance of all reaction mixtures, controls, and blanks was measured at 560 nm using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (e.g., UV Vis 3000, Bio-Rad Inc., Hercules, California, USA). One unit (U) of SOD activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to achieve 50% inhibition of NBT photoreduction (Jin et al., 2023). The percentage inhibition of NBT reduction for each sample was calculated using the following formula:
Catalase activity assay
Catalase (CAT) activity was assayed spectrophotometrically by measuring the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), following a modified version of the method described by previous studies. The reaction mixture consisted of 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0), 12 mM H2O2, and 50 µL of enzyme extract, brought to a final volume suitable for the measurement. The assay was initiated by adding the enzyme extract to the substrate mixture, and the decrease in absorbance of H2O2 was monitored continuously at 240 nm over a period of 3 minutes using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (e.g., Cecil CE7400S, UK) maintained at 25 °C. The decomposition of H2O2 by catalase causes a decline in absorbance, which is proportional to enzyme activity. One unit of catalase activity (U) was defined as the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the decomposition of 1 µmol of H2O2 per minute under the assay conditions (Jin et al., 2023). An extinction coefficient of 43.6 M-1 cm-1 was used to calculate the catalase activity in µmol H2O2 decomposed min-1 mg-1 protein (U mg-1 protein), according to the formula:
Peroxidase activity assay
Peroxidase (POD) activity was determined spectrophotometrically by monitoring the increase in absorbance at 470 nm, which indicates the formation of tetraguaiacol, an oxidation product of guaiacol. This method was adapted from established protocols. The reaction mixture consisted of 33 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.1), 16 mM guaiacol, 2 mM H2O2, and 200 µL of the enzyme extract. The reaction was initiated by the addition of the enzyme extract, and the increase in absorbance at 470 nm was continuously monitored for 3 minutes using a UV-visible spectrophotometer. A control reaction (without enzyme extract) was also monitored to account for any non-enzymatic oxidation. One unit (U) of POD activity was defined as the amount of enzyme that consumes 1 µmol of H2O2 per minute under the assay conditions (Jin et al., 2023). POD activity was calculated using an extinction coefficient of 26.6 mM-1 cm-1 for tetraguaiacol, and the results were expressed as µmol H2O2 decomposed min-1 mg-1 protein (U mg-1 protein) according to the formula. All measurements were performed in triplicate.
Statistical analysis
All collected datasets were analyzed using a two-factor factorial analysis of variance (ANOVA) for a Randomized Complete Block Design (RCBD) with four replicates. The factors were Bactericide Treatment (8 levels: T0-T7) and Cultivar (3 levels: Kalehar, Sindhuri, Sava). Analyses were performed using OriginPro 2024 software (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, Massachusetts, USA), following established statistical principles (Steel et al., 1997). Mean separation was conducted using Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test at a significance level of α = 0.05.
Results
Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae infection symptoms in pomegranate
The cultivars evaluated, such as Sindhuri, Kalehar, and Sava, represent regionally dominant commercial varieties in South Asian pomegranate orchards. Crucially, all three were found universally susceptible to Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae (Xap) with no documented genetic resistance, establishing them as standardized susceptibility benchmarks under field conditions. However, within this context of shared vulnerability, our results reveal significant treatment-mediated differential resilience. Sindhuri consistently demonstrated superior physiological responsiveness to copper-streptocycline application, exhibiting markedly lower disease penetration and enhanced activation of antioxidant pathways compared to Kalehar and Sava despite equivalent pathogen pressure. Field studies revealed characteristic bacterial blight symptoms on all parts of trees, wherein leaves exhibited water-soaked lesions progressing to necrotic spots, fruits developed coalescing lesions with internal discoloration, and woody tissues showed cankering and dieback (Figure 1).
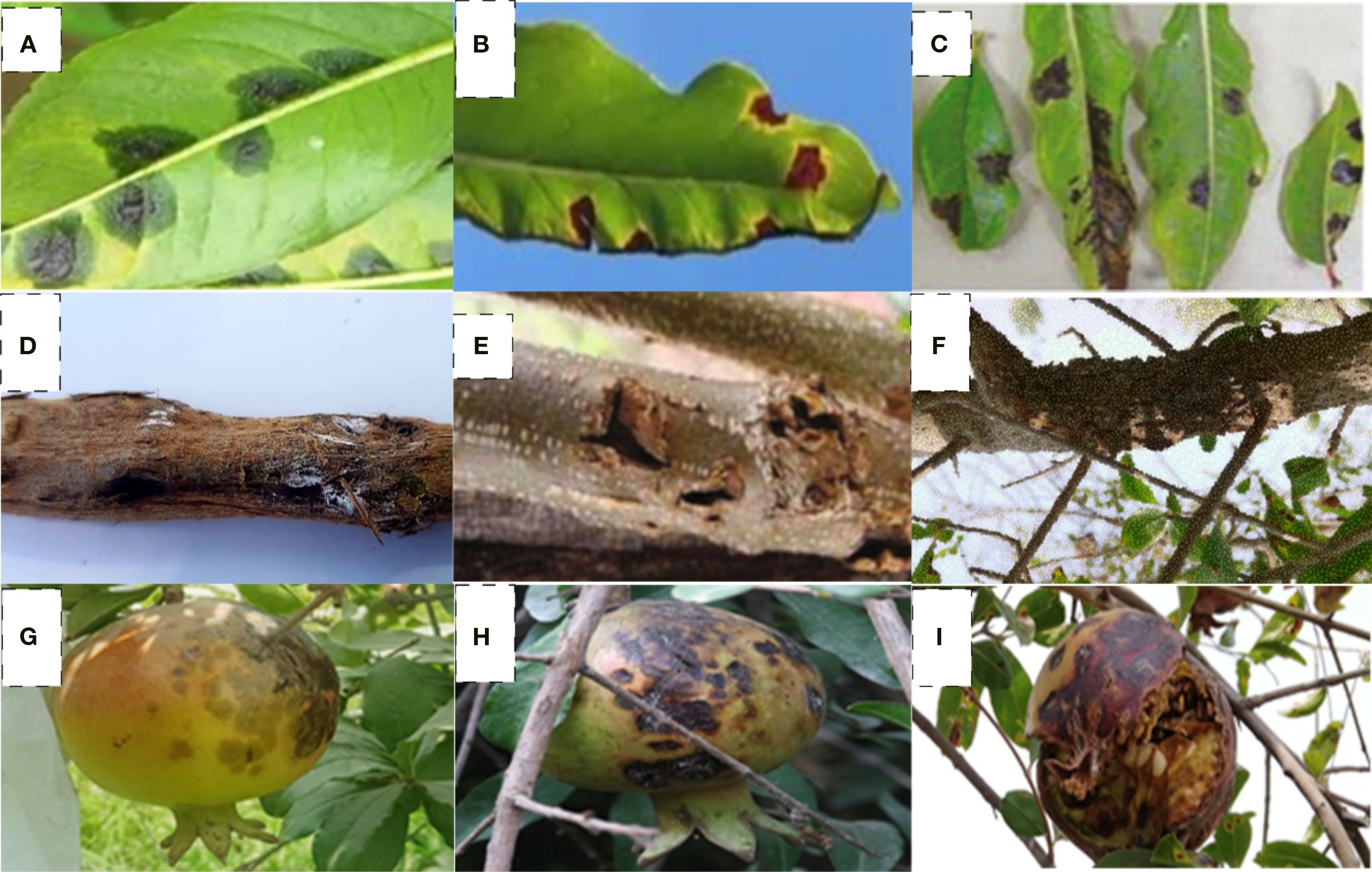
Figure 1. Progression of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae infection symptoms in pomegranate. (a–c) Leaf manifestations: initial water-soaked lesions (a), angular leaf spots (b), and severe bacterial ooze-induced necrosis (c), (d–f) Woody tissue symptoms:- twig lesions (d), branch cankers (e), and advanced branch dieback (f), (g–i) Fruit pathology:- coalescing water-soaked spots (g), persistent pathogen colonization (h), and terminal fruit rot (i).
Effect of bactericides on disease development
Disease incidence
The interactive effect of bactericides and pomegranate cultivars on disease incidence on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees was found to be statistically significant (P ≤ 0.05). The lowest disease incidence on leaves (3.51%), fruit (3.88%), twigs (0.58%), and trees (3.59%) was recorded in Sindhuri when a mixture of copper oxychloride and streptocycline (T7) was applied. Regardless of cultivar, T7 significantly reduced disease incidence by 5.11, 3.95, 3.02, and 4.06-fold on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees, respectively, as compared to the control. In Sindhuri, the disease incidence on leaves and fruits was 1.94 to 2.31 and 1.2 to 1.7-fold less than in Kalehar and Sava, respectively. The disease incidence on twigs was reduced to 1.17-1.78-fold of that in Kalehar and Sava cultivars. At the same time, on trees it was 1.77-fold and 1.38-fold of that in Sava and Kalehar, respectively, regardless of treatment effects (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Effect of various antibacterial compounds against bacterial blight incidence (%) on Leaves (A), Fruits (B), Twigs (C), and Tree (D) on three cultivars of pomegranate. The vertical bars indicate ± standard errors (S.E) of means. Means followed by the same letter in each column are not significantly different at P ≤ 0.05. LSD value for disease incidence on leaves= 2.55, disease incidence on fruits= 2.82, disease incidence on stem= 2.05, and disease incidence on tree= 0.34.
Disease severity
The interactive effect of bactericides and cultivars on disease severity on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees was significant (P ≤ 0.05). The lowest disease severity on leaves (0.56%), fruits (0.79%), twigs (0.70%), and trees (1.92%) was recorded in the Sindhuri cultivar when T7 was applied. The same treatment reduced disease severity by approximately 06.7-fold on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees compared to the control, regardless of cultivar response. The disease severity on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees on the Sindhuri cultivar was approximately 2.15 and 3.38 times reduced than that of Kalehar and Sava, respectively, irrespective of the treatment effect (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Effect of various antibacterial compounds against bacterial blight severity (%) on Leaves (A), Fruits (B), Twigs (C), and Tree (D) on three cultivars of pomegranate. The vertical bars indicate ± standard error (S.E) of means. Means followed by similar letters in each column are not statistically different at P ≤ 0.05. LSD value for disease incidence on leaves= 2.55, disease incidence on fruits= 2.82, disease incidence on stem= 2.05, and disease incidence on tree= 0.34.
Disease reduction percentage
The interactive effect of bactericides and cultivars on disease reduction percentages on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees was significant (P ≤ 0.05). Maximum disease reduction percentages on leaves (77.63%), fruits (79.76%), twigs (76.1%), and trees (76.9%) were recorded in the Sindhuri when T7 was applied, which was 4.2, 4.1, 6.8, and 4.3-fold higher that of the control on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees respectively when compared with less effective bactericides (copper hydroxide) regardless of cultivar response. The percentage of disease reduction on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees in the Sava cultivar was approximately 01.13-fold higher than that in the Kalehar and Sindhuri cultivars (Figure 4).

Figure 4. Effect of various antibacterial compounds against bacterial blight disease reduction (%) on Leaves (A), Fruits (B), Twigs (C), and Tree (D) on three cultivars of pomegranate. The vertical bars indicate ± standard error (S.E) of means. Bars showing different letters are significantly different at P ≤ 0.05.
Physical and biochemical quality attributes
Marketable yield, fruit weight, and hundred arils weight
The interactive effect of bactericides on marketable yield, fruit weight, and hundred arils weight (g) was significant (P ≤ 0.05). The maximum marketable yield (89.63%) was obtained from the Sindhuri cultivar with T7. The marketable yield received from the same treatment was 1.47 times higher than that of the control, regardless of the cultivar effect. The marketable yield from the Sindhuri cultivar was 1.1 and 1.25-fold higher than those from Kalehar and Sava, respectively. The highest fruit weight (233.1g) and hundred arils weight (42.36g) were found from the Sava cultivar when T7 was applied, 1.63 and 1.89 times more elevated than the control, respectively, irrespective of the cultivar effect. The fruit weight and hundred arils weight (g) obtained from the Sava cultivar were 1.15 and 1.04 times higher than those of the Sindhuri and Kalehar cultivars, respectively, regardless of the treatment effect.
Total soluble salts, titratable acidity, and juice pH
The interactive effects of bactericides and pomegranate cultivars related to total soluble salts and juice pH were found to be significant (P ≤ 0.05), whereas titratable acidity showed a non-significant interaction. Among the various treatment effects, the highest value of TSS (17.3 °Brix) was obtained from T7, which was 01.39-fold higher than the control, regardless of the cultivar effect. The maximum value of TSS was found by the Sava cultivar irrespective of the treatment effect, which was 1.05 and 1.02 times higher than Sindhuri and Kalehar, respectively. The highest titratable acidity value (0.72%) was obtained from the control, which was 1.28-fold higher when compared to T7, regardless of the cultivar effect. In contrast, the highest value of titratable acidity was found in the Sindhuri cultivar, irrespective of the treatment effect, which was 1.06 and 1.15-fold higher than that of the Kalehar and Sava cultivars, respectively. The highest pH value (4.14) was obtained with T7, which was 1.06-fold higher than that of the control, regardless of the cultivar effect. In contrast, the highest pH value (4.16) obtained from the Sava cultivar, irrespective of the treatment effect, was 1.04 and 1.02-fold higher than those of Sindhuri and Kalehar, respectively (Table 2).
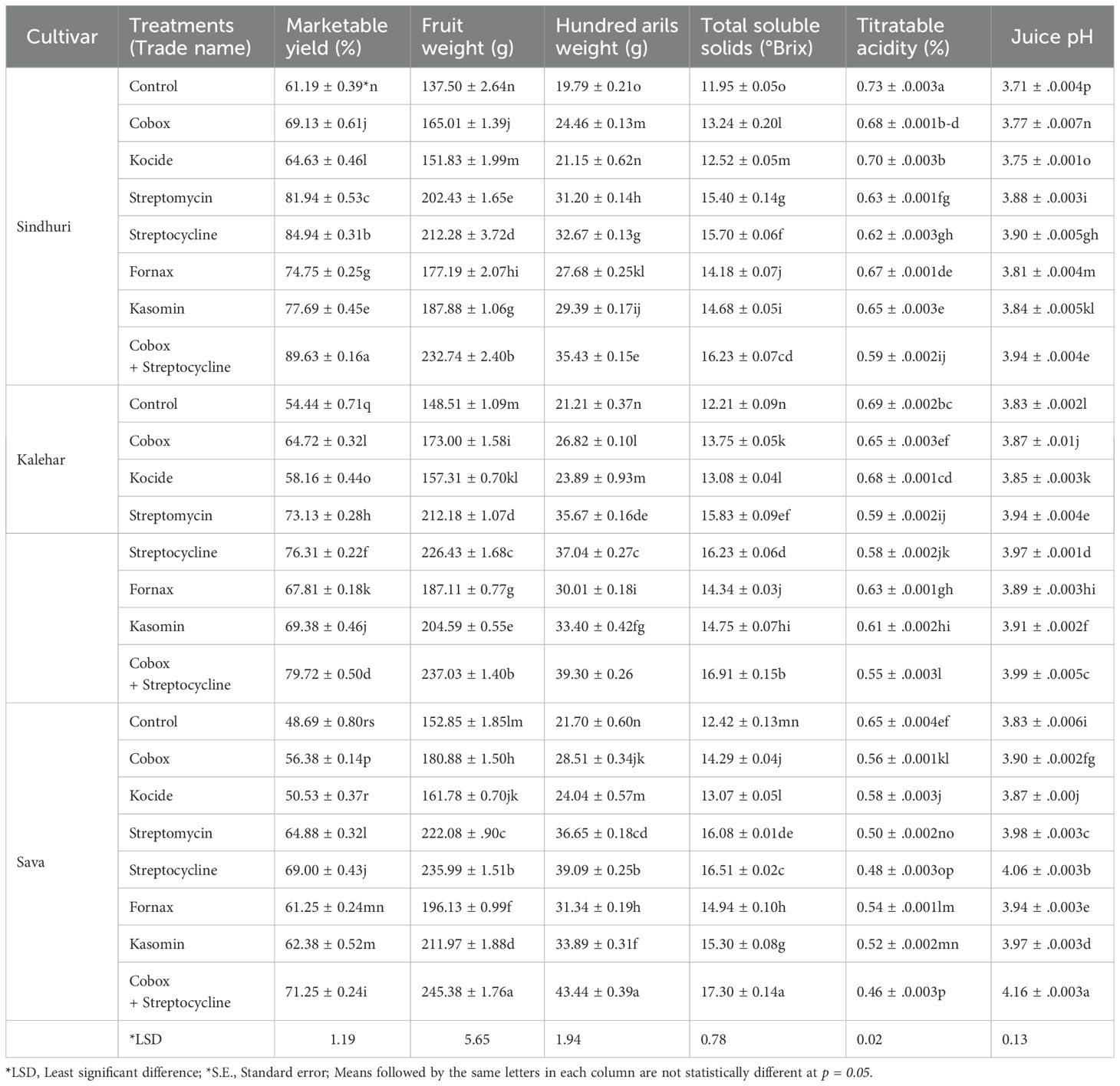
Table 2. Effect of various antibacterial compounds (Mean ± *S.E) against physical and biochemical parameters of Punica granatum.
Superoxide dismutase, catalase, and peroxidase
The impact of bactericides on total phenolic contents was significant, but it was non-significant in the case of vitamin C and total antioxidants (AO). The highest value of total phenolic contents (445.46 mg/100g of GAE) was obtained from T7, which was 1.11-fold higher than that of T0, regardless of the cultivar effect. Irrespective of the treatment effect, the total phenolic contents from the Sava cultivar were 1.16 and 1.29 times higher than Sindhuri and Kalehar, respectively. The impact of treatment on SOD was found significant (P ≤ 0.05), whereas catalase (CAT) and peroxidase (POD) showed a non-significant (P ≤ 0.05) interaction. The highest SOD value (68.30U/mg of protein) was found in the Kalehar cultivar, irrespective of the treatment effect, which was 1.18 and 1.69-fold higher than Sindhuri and Sava cultivars, respectively. The highest value of SOD was obtained from the control, which was 1.28-fold higher than T7 regardless of the cultivar effect. The highest value of POD (1.09 µ/mg of protein) was found in Sava irrespective of the treatment effect, which was 2.15 and 1.88-fold higher than that of the Sindhuri and Kalehar cultivars, respectively. In comparison, the highest value of POD was found in the control, which was 1.24-fold higher than T7, regardless of the cultivar effect (Table 3).
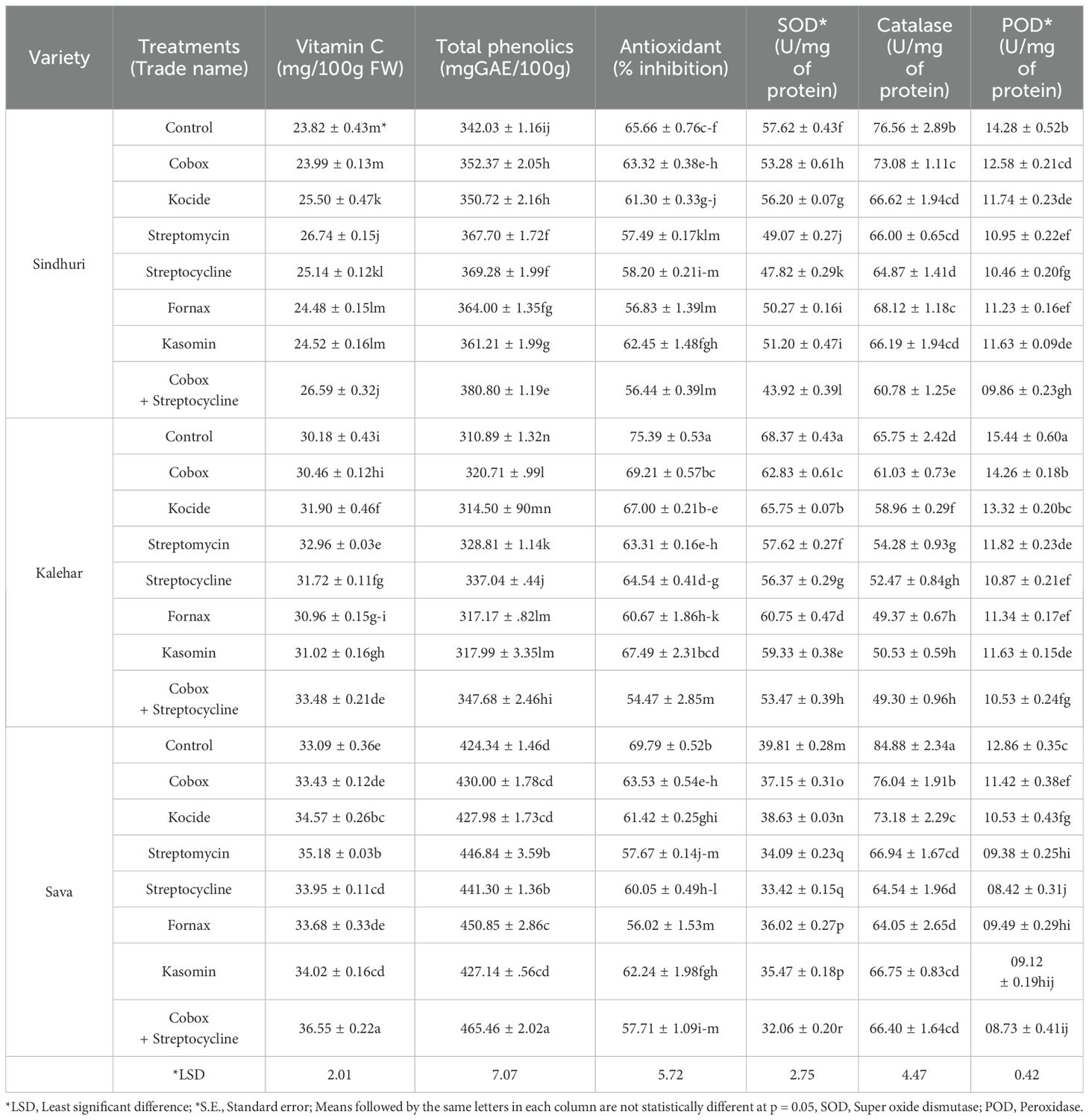
Table 3. Effect of the exogenous application of bactericides on antioxidant compounds of various pomegranate cultivars. (Mean ± *S.E).
Correlation analysis among various antibacterial treatments
The correlation analysis among various antibacterial treatments, including copper oxychloride and streptocycline, and their application as well as the incidence and severity of bacterial blight in pomegranate, and their impact on fruit quality attributes. Each panel (A, B, C, and D) illustrates the correlation between disease incidence (on leaves, fruits, twigs, and trees) and disease severity, as well as the application of different treatments across the three pomegranate cultivars (Sindhuri, Kalehar, and Sava). Positive correlations indicate treatments that effectively reduce disease symptoms, whereas negative correlations indicate minimal impact or ineffectiveness. This analysis describes the potential of certain treatments to enhance the fruit’s biochemical properties, such as TSS, vitamin C, and antioxidant content, as well as to reduce disease severity (Figure 5).

Figure 5. Correlation analysis describes the effectiveness of various antibacterial treatments on disease incidence, severity, and fruit quality attributes in pomegranate cultivars. The abbreviations show the treatments, whereas L, F, Tw, and T represent Leaves, Fruits, Twigs, and Trees, respectively.
Principal component analysis
The Principal Component Analysis (PCA) biplot describes the relationship between pomegranate cultivars, i.e., Sindhuri, Kalehar, and Sava, and among the various antibacterial treatments, for example, Copper Oxychloride, Streptomycin, and Bismerthiazole. The PC1 axis (98.3%) reported the largest portion of the variance in the data, while the PC2 axis (1.6%) captured less variation. The points on the plot represent the different treatments applied to the plants, while the vectors (arrows) indicate how each cultivar was affected by the treatments. The plot reveals that Sindhuri shows a distinct response compared to the Kalehar and Sava cultivars, particularly in terms of disease reduction or disease severity. Sindhuri was positioned along the positive side of the PC1 axis, highlighting its unique response to the antibacterial treatments. In contrast, Kalehar and Sava were positioned closer to each other in the plot, implying that these two cultivars exhibited similar patterns in response to the treatments applied. This analysis provides valuable insights into how different cultivars react to various bactericides, with Sindhuri showing significant resistance to bacterial blight, which is likely reflected in its position on the PCA biplot. The biplot describes the importance of cultivar selection for managing bacterial blight and optimizing treatment strategies (Figure 6).
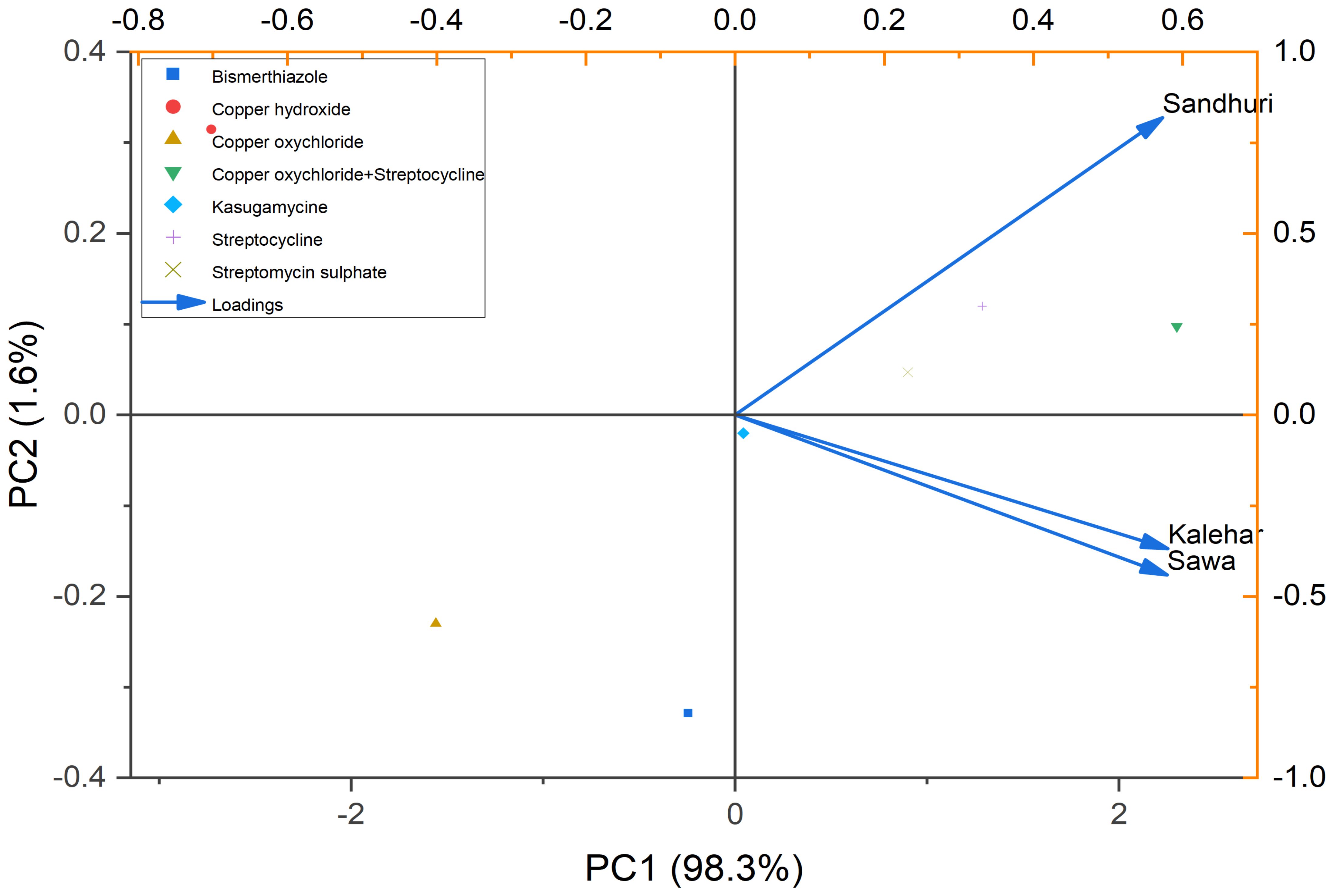
Figure 6. PCA shows the relationship among the pomegranate cultivars (Sindhuri, Kalehar, Sava) and the various antibacterial treatments (e.g., Copper Oxychloride, Streptomycin, Bismuthiazole). The plot highlights the variation in disease reduction across treatments, with PC1 (98.3%) capturing the primary variation. Sindhuri cultivar was found distinct in its response to treatments, while Kalehar and Sava exhibited similar patterns. The vectors represented the loadings of each treatment and cultivar on the principal components, illustrating their influence on bacterial blight control.
Discussion
Bacterial blight of pomegranates is a major disease in various pomegranate-producing regions, causing great qualitative and quantitative losses (Icoz et al., 2014). Removal of the primary source of inoculum, adoption of sanitation practices, and pasting and spraying pruned branches and plant canopies with effective bactericides can help control this disease. Removing the primary source of infection, followed by one spray of copper oxychloride and four sprays of streptocycline (500 ppm) + copper oxychloride (3000 ppm), has been reported to be efficient in reducing the incidence of bacterial canker in acid lime caused by (Xap) (Gopal et al., 2004).
The efficacy of treatment T7 in minimizing disease incidence and severity while maximizing disease reduction aligns with established synergistic effects of copper-streptocycline combinations (Raju et al., 2015; Naz et al., 2018). Notably, this formulation’s enhanced performance over individual applications (Lokesh et al., 2014; Yu et al., 2016) stems from complementary bactericidal mechanisms. Copper compounds (e.g., hydroxide/oxychlorides) release cuprous ions (Cu2+) that disrupt cell walls and proteins, inhibiting biofilm formation (Mondal and Mani, 2012; Munhuweyi et al., 2016). Concurrently, streptocycline’s aminoglycoside components (e.g., streptomycin) bind the 30S ribosomal S12 protein, terminating protein synthesis (Naz et al., 2017).
The minimum bacterial leaf spot incidence on the grapevine was recorded in plots sprayed with streptocycline (500 ppm) or streptomycin sulphate (500 ppm) by (Ravikumar et al., 2002). Some antibiotics kill and destroy different bacterial populations (Zhang et al., 2014). In the current study, the highest marketable yield was obtained for T7. Our results align with Raju et al (Raju et al., 2015), who recorded marketable yields of 6.12 tons/ha for streptocycline (500 ppm) + copper oxychloride (3000 ppm) and 5.91 tons/ha for streptocycline + copper hydroxide application, and both significantly exceeded control yields. These findings are corroborated by Hussain et al (Hussain et al., 2017, 2019), confirming that streptocycline-copper oxychloride combinations enhance marketable yield percentages in pomegranate.
Our findings corroborate the synergistic potential of chemical-botanical combinations reported by Meena et al. (2017) that in vitro screening identified streptocycline (250 ppm) as the most effective antibiotic against the pathogen, followed by tetracycline and neomycin. Among copper compounds, oxychloride (1000 ppm) outperformed hydroxide, while garlic extract (20%) showed superior efficacy among botanicals. Critically, in planta trials demonstrated that combined applications, particularly tetracycline (250 ppm) + copper hydroxide (1000 ppm) + garlic extract (20%), achieved significantly greater bacterial blight suppression than individual treatments during consecutive Kharif seasons. This aligns with streptocycline-copper oxychloride combinations in our study, reinforcing how integrated approaches enhance phytopathogen control (Saikia et al., 2004; Maity et al., 2018).
In a study, Tayyab et al. (2023) described four chemicals, such as streptomycin, copper oxychloride, kasugamycin, and oxytetracycline, and four plant extracts, namely Citrullus colocynthis, Calotropis gigantea, Acacia nilotica, and Moringa oleifera, which were evaluated against Xap. Under laboratory conditions, the results showed that the maximum inhibition zone of bacterial growth was expressed by streptomycin sulfate (38 mm), followed by copper oxychloride (38 mm), kasugamycin (34 mm), and oxytetracycline (24 mm) at 3% concentration after a 72-hour interval. Among the plant extracts, the maximum inhibition was observed in Moringa oleifera (27.6 mm), followed by Acacia nilotica (26.3mm), Citrullus colocynthis (16.6 mm), and Calotropis gigantea (19.3 mm) at 25%, 35%, and 45% concentrations (Mubeen et al., 2025). Under laboratory conditions, significant results were obtained for the chemical (copper oxychloride) and plant extracts (Moringa oleifera). Copper oxychloride was applied in the greenhouse and showed the lowest disease severity (23%) compared to Moringa oleifera (36%) and the positive and negative controls (Manjula et al., 2007).
Moreover, when plants were treated with antibiotics, they showed higher yield, weight, juice (%), peel thickness, peel content, and improved biochemical parameters than non-treated plants (Shokrollah et al., 2011). It was also observed that healthy or asymptomatic fruits had more weight, high juice content, less acidity, and more TSS than bacterially infected fruits (Bassanezi et al., 2009). Maximum fruit weight, juice content (%), TSS, sugar content, and low acidity were achieved with antibiotics treatment in citrus fruits compared to the control (distilled water), which had the highest total acidity, taste, and SOD (Suriachandraselvan et al., 1993; Raju et al., 2015).
However, in another study, ascorbic acid and malic acid contents showed little or no significant difference when antibiotics were applied (Baldwin et al., 2010; Liang et al., 2018). A study reported that bacterial blight of pomegranate, caused by Xap, was effectively controlled by applying paushamycin at 500 ppm combined with 0.2% copper oxychloride, administered three times at fortnightly intervals (Baldwin et al., 2010). These findings are consistent with our studies, which also demonstrate that applying bactericides at specific intervals helps reduce disease development and achieve good yields. Karn et al. (2023) found that biochemical analyses revealed a significant increase in all biochemical parameters in pomegranate plants pre-treated with resistance-inducing chemicals (Chen et al., 2022). Foliar application of salicylic acid (SA) and β-aminobutyric acid (BABA) at 300 ppm can protect Xap, the causal agent of bacterial blight. They may serve as a potential alternative to chemical pesticides (Farhan et al., 2024). Our results confirm established knowledge that copper-streptocycline combinations effectively suppress Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae in pomegranate orchards but reveal novel cultivar-specific physiological adaptations. Crucially, Sindhuri exhibited unprecedented metabolic reprogramming under treatment, characterized by enhanced antioxidant pathway activation (CAT: 21.3 U/mg protein; POX: 1.35 U/mg protein) and phytochemical accumulation (TPC: 445 mg GAE/100 mL; vitamin C: 36.5 mg/100 mL). Unexpectedly, Sindhuri’s resilience exceeded all documented benchmarks for South Asian cultivars, reducing disease incidence by >76% across organs while improving marketable yield (89.6 kg/tree). This suggests genotype-dependent optimization of defense pathways during bactericide-induced stress mitigation, a phenomenon previously unreported in pomegranate.
Conclusion
Bacterial blight is a major constraint to successful pomegranate production. Our study demonstrates that inoculum removal followed by streptocycline-copper oxychloride applications at 15-day intervals (April–August) provides robust efficacy against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae, significantly reducing disease intensity while enhancing fruit physicochemical attributes. Critical next steps should prioritize validating this protocol in diverse agroecological zones to establish scalability, assessing long-term impacts on yield stability, soil health, and resistance evolution, and exploring translational applications in other bacterial-pathogen-affected fruit crops (e.g., citrus canker, mango bacterial black spot). This framework offers a sustainable pathway for bacterial disease management in perennial horticulture.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
GM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HF: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SN: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. UK: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MI: Writing – review & editing. MA: Writing – review & editing. ME: Writing – review & editing. HM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Software, Visualization, Validation, Project administration, Funding acquisition. FL: Software, Visualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Xuncheng Talent Program (JJXC2023053 to FL), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (20224BAB215002 to FL), and Xuncheng Talent Program (JJXC2023072 to HM).
Acknowledgments
The authors extend their appreciation to the Ongoing Research Funding Program (ORF-2025-418), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University for funding through Vice Deanship of Scientific Research Chairs; Chair of Biodiversity & Bio reservation, Tilad, for environmental consultancy. The first author is also grateful to Department of Agriculture, Govt. of Punjab, Pakistan for facilitating this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The handling editor BZ declared a past co-authorship with the author SAHN.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Akhtar, M. and Bhatti, M. R. (1992). Occurrence of bacterial leaf spot of pomegranate in Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Agricultural Research. 13 (1), 95–97.
Amerine, M., Roessler, E., and Ough, C. (1965). Acids and the acid taste. I. The effect of pH and titratable acidity. Am. J. Enology viticulture 16, 29–37. doi: 10.5344/ajev.1965.16.1.29
Arora, A. (2014). Efficacy of agro-chemicals for management of bacterial blight of pomegranate. Plant Dis. Res. 29, 185–187.
Arora, A., Gill, P., and Jawandha, S. (2016). Effect of agro-chemicals on severity of bacterial blight and fruit quality in pomegranate. Int. J. Agriculture Environ. Biotechnol. 9, 1061–1067. doi: 10.5958/2230-732X.2016.00134.0
Baldwin, E., Plotto, A., Manthey, J., McCollum, G., Bai, J., Irey, M., et al. (2010). Effect of Liberibacter infection (Huanglongbing disease) of citrus on orange fruit physiology and fruit/fruit juice quality: chemical and physical analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 58, 1247–1262. doi: 10.1021/jf9031958, PMID: 20030384
Bassanezi, R. B., Montesino, L. H., and Stuchi, E. S. (2009). Effects of huanglongbing on fruit quality of sweet orange cultivars in Brazil. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 125, 565–572. doi: 10.1007/s10658-009-9506-3
Chen, D., Mubeen, B., Hasnain, A., Rizwan, M., Adrees, M., Naqvi, S. A. H., et al. (2022). Role of promising secondary metabolites to confer resistance against environmental stresses in crop plants: Current scenario and future perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 881032. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.881032, PMID: 35615133
Chen, D., Saeed, M., Ali, M. N. H. A., Raheel, M., Ashraf, W., Hassan, Z., et al. (2023). Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi combined application reveals enhanced soil fertility and rice production. Agronomy 13, 550. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13020550
FAO (2023). FAOSTAT. Pomegranate Production in Pakistan, (2000-2021) (Rome, Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization).
Farhan, M., Sathish, M., Kiran, R., Mushtaq, A., Baazeem, A., Hasnain, A., et al. (2024). Plant nitrogen metabolism: balancing resilience to nutritional stress and abiotic challenges. Phyton (0031-9457) 93. doi: 10.32604/phyton.2024.046857
Gopal, K., Reddy, M., and Babu, G. (2004). Management of bacterial canker in acid lime (Citrus aurantifolia Swingle) in Andhra Pradesh. Hyderabad, Indian Journal of Plant Protection. 32 (1), 111–113.
Hussain, S., Anjum, M., Hussain, S., Ejaz, S., and Kamran, H. (2017). Agro-climatic conditions affect fruit quality of mandarin (Citrus reticulata Blanco) cultivars. Fruits 72, 341–349. doi: 10.17660/th2017/72.6.2
Hussain, S., Rao, M. J., Anjum, M. A., Ejaz, S., Umar, U.-u., Ali, M. A., et al. (2019). Effect of different combinations of antibiotics on fruit quality and antioxidant defense system in Huanglongbing infected Kinnow orchards. AMB Express 9, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13568-019-0871-9, PMID: 31522337
Icoz, S., Polat, I., Sulu, G., Yilmaz, M., Unlu, A., Soylu, S., et al. (2014). First report of bacterial blight of pomegranate caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae in Turkey. Plant Dis. 98, 1427–1427. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-06-14-0656-PDN, PMID: 30703958
Jadhav, V. and Sharma, K. (2011). “Integrated management of diseases in pomegranate,” in Souvenir and abstracts 2nd international symposium on pomegranate and minor including Mediterranean fruits, UAS Dharwad. 23–27.
Jin, X., Liu, Z., and Wu, W. (2023). POD, CAT and SOD enzyme activity of corn kernels as affected by low plasma pretreatment. Int. J. Food Properties 26, 38–48. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2022.2151619
Kahramanoglu, I., Usanmaz, S., and Alas, T. (2019). “Advances in breeding and cultivation of pomegranate,” in Achieving sustainable cultivation of tropical fruits (Cambridge, UK: Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing), 569–596.
Kale, P., Chimote, V., Raghuwanshi, K., Kale, A., Jadhav, A., and Borkar, S. (2012). Microbial, biochemical, pathogenicity and molecular characterization of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae from pomegranate. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 6, 1699–1706.
Karn, M., Sharma, S. K., Handa, A., Sharma, A., Sharma, S., and Sharma, U. (2023). Lytic bacteriophages in preventing the bacterial blight of pomegranate caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae. Vegetos 36, 643–650. doi: 10.1007/s42535-022-00451-x
Kumar, A., Chahal, T. S., Hunjan, M. S., Kaur, H., and Srivastava, A. (2018). Studies on Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae, causing bacterial blight of pomegranate in Punjab. Int. J. Agriculture Environ. Biotechnol. 11, 537–542.
Kumar, M., Wali, S., Benagi, V., Patil, H., and Patil, S. (2011). Management of bacterial blight of pomegranate through chemicals/antibiotics. Acta Hort (ISHS) 890, 481–484.
Lalithya, K. A., Manjunatha, G., Raju, B., Kulkarni, M. S., and Lokesh, V. (2017). Plant growth regulators and signal molecules enhance resistance against bacterial blight disease of pomegranate. J. Phytopathol. 165, 727–736. doi: 10.1111/jph.12612
Liang, X., Yu, X., Pan, X., Wu, J., Duan, Y., Wang, J., et al. (2018). A thiadiazole reduces the virulence of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae by inhibiting the histidine utilization pathway and quorum sensing. Mol. Plant Pathol. 19, 116–128. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12503, PMID: 27756112
Lokesh, R., Erayya, E., Kumaranag, K. M., Chandrashekar, N., and Khan, A. N. A. (2014). 20143044956, English, Journal article, India, 2278-3202, 3, (1), Indore, International Research Journal of Biological Sciences, (31–35), International Science Congress Association, In vivo efficacy of some antibiotics against bacterial blight of pomegranate caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv.
Maity, A., Sharma, J., Sarkar, A., More, A. K., Pal, R. K., Nagane, V. P., et al. (2018). Salicylic acid mediated multi-pronged strategy to combat bacterial blight disease (Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae) in pomegranate. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 150, 923–937. doi: 10.1007/s10658-017-1333-3
Manjula, C., Khan, A., Jalikop, S., and Kumar, M. (2007). Field management of bacterial blight of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv punicae. Calcutta, Environment and Ecology. 25 (2), 385–388.
Meena, S., Chattopadhyay, A., Meena, M., Shah, R., Rawal, P., and Mali, B. (2017). Integration of chemicals and botanicals for the management of pomegranate bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae. Udaipur, Journal of Mycology and Plant Pathology. 47 (1), 27–35.
Melgarejo, P., Salazar, D. M., and Artes, F. (2000). Organic acids and sugars composition of harvested pomegranate fruits. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 211, 185–190. doi: 10.1007/s002170050021
Mondal, K. K. and Mani, C. (2012). Investigation of the antibacterial properties of nanocopper against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae, the incitant of pomegranate bacterial blight. Ann. Microbiol. 62, 889–893. doi: 10.1007/s13213-011-0382-7
Mubeen, B., Hasnain, A., Naqvi, S. A. H., Hakim, F., Naqvi, S. S. H., Hassan, M. Z., et al. (2025). Phytochemicals as multi-target therapeutic agents for oxidative stress-driven pathologies: mechanisms, synergies, and clinical prospects. Phyton-International J. Exp. Bot. 94, 1941–1971. doi: 10.32604/phyton.2025.064056
Munhuweyi, K., Lennox, C. L., Meitz-Hopkins, J. C., Caleb, O. J., and Opara, U. L. (2016). Major diseases of pomegranate (Punica granatum L.), their causes and management—A review. Scientia Horticulturae 211, 126–139.
Naqvi, S. A. H., Malik, M. T., Umar, U. U. D., Rehman, A. U., Ahmed, S., Hakim, F., et al. (2025a). Mango Tree Sudden Decline disease: 65-years global perspective of ecology, biology, epidemiology, and management-Challenge of tropical landscape pathology. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 138, 102713. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2025.102713
Naqvi, S. A. H., Rehman, A. U., and Umar, U. U. D. (2025b). Synergistic interplay of microbial probiotics in rice rhizosphere: A sustainable strategy for bacterial blight management through microbiome engineering. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 136, 102568. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2025.102568
Naz, S., Gallart-Ayala, H., Reinke, S. N., Mathon, C., Blankley, R., Chaleckis, R., et al. (2017). Development of a liquid chromatography–high resolution mass spectrometry metabolomics method with high specificity for metabolite identification using all ion fragmentation acquisition. Anal. Chem. 89(15), 7933–7942., PMID: 28641411
Naz, S., Mehboob, S., Iqbal, M., Ali, S., Niaz, Z., and Idrees, M. (2018). Antibacterial activity of commercially available chemicals against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae causing bacterial blight of pomegranate under in vivo conditions. Int. Res. J. Biosci. 12, 13–20. doi: 10.12692/ijb/12.5.13-20
Özcan, M. M., Aljuhaimi, F., Uslu, N., Mohamed Ahmed, I. A., Osman, M. A., Gassem, M. A., et al. (2019). Effect of oven drying on antioxidant activity, phenolic compounds, fatty acid composition and tocopherol contents of pomegranate aril and oils. J. Food Process. Preservation 43, e13885. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.13885
PBS (2022). Pakistan bureau of statistics. Agricultural statistics 2020-2021. Government Pakistan, 45–46.
Raju, J., Benagi, V., Jayalakshmi, K., Nargund, V., Jones Nirmalanath, J. N., Priti, S., et al. (2015). Bacterial blight of pomegranate: a menace in quality fruit production. Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology. 9 (4), 3239–3244.
Ravikumar, M., Jahagirdar, S., and Khan, A. (2002). “Management of bacterial leaf spot of grape through chemicals and antibiotics in Northern Karnataka. Paper presented,” in Ann Meet Symp Plant Disease Scenario in Southern India, Bangalore, India, December. 19–21.
Razzaq, K., Khan, A. S., Malik, A. U., and Shahid, M. (2013). Ripening period influences fruit softening and antioxidative system of ‘Samar Bahisht Chaunsa’mango. Scientia Hortic. 160, 108–114. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.05.018
Saikia, R., Kumar, R., Singh, T., Srivastava, A. K., Arora, D. K., and Lee, M.-W. (2004). Induction of defense related enzymes and pathogenesis related proteins in Pseudomonas fluorescens-treated chickpea in response to infection by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. ciceri. Mycobiology 32, 47–53. doi: 10.4489/MYCO.2004.32.1.047
Sharma, D., Chakma, J., Sharma, N., and Singh, N. (2017). Effect of different orchard management practices on the growth and production of rejuvenated of pomegranates (Punica granatum L.) cv. Kandhari Kabuli. J. Appl. Natural Sci. 9, 577. doi: 10.31018/jans.v9i1.1233
Sharma, R., De Vleesschauwer, D., Sharma, M. K., and Ronald, P. C. (2013). Recent advances in dissecting stress-regulatory crosstalk in rice. Mol. Plant 6, 250–260. doi: 10.1093/mp/sss147, PMID: 23292878
Sharma, K., Jadhav, V., and Sharma, J. (2011). Present status of pomegranate bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae and its management. Acta Hortic. 890, 513–522. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2011.890.72
Shokrollah, H., Lee Abdullah, T., Sijam, K., and Abdullah, S. N. A. (2011). Identification of physical and biochemical characteristic of mandarin (Citrus reticulata) fruit infected by huanglongbing (HLB). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 5, 181–186.
Singh, N. V., Abburi, V. L., Ramajayam, D., Kumar, R., Chandra, R., Sharma, K. K., et al. (2015). Genetic diversity and association mapping of bacterial blight and other horticulturally important traits with microsatellite markers in pomegranate from India. Mol. Genet. Genomics 290, 1393–1402. doi: 10.1007/s00438-015-1003-0, PMID: 25675870
Singh, A., Shukla, A., and Meghwal, P. (2020). Fruit cracking in pomegranate: extent, cause, and management–A Review. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 20, S1234–S1253. doi: 10.1080/15538362.2020.1784074
Steel, R. G. D., Torrie, J. H., and Dickey, D. A. (1997). Principles and procedures of statistics: a biometrical approach (New York, USA: McGraw-Hill Science, Engineering & Mathematics).
Suriachandraselvan, M., Jayasekhar, M., and Anbu, S. (1993). Chemical control of bacterial leaf and fruit spot of pomegranate. English, Journal article. 41 (4), 228–229.
Tayyab, M., Sajid, M., Mehmood, Y., Sheeraz, M., Hussain, S., Irfan, M., et al. (2023). Impact of plant extracts and chemicals against bacterial blight of pomegranate. J. Agric. Veterinary Sci. 02, 223–230. doi: 10.55627/agrivet.02.03.0584
Wheeler, B. E. J. (1969). An introduction to plant diseases. An Introduction to Plant Diseases, 374.
Yenjerappa, S., Ravikumar, M., Jawadagi, R., and Khan, N. A. (2004). “In vitro and in vivo efficacy of bactericides against bacterial blight of pomegranate,” in Proceedings of National Symposium of Crop Surveillance: Disease Forecasting and Management, New Delhi, India.
Yenjerappa, S., Srikant, K., Ravikumar, M., and Jawadagi, R. (2006). Effect of dates of pruning on the severity of bacterial blight in pomegranate. Dallimbavrutha Smaranika, 130–131.
Yu, X., Armstrong, C. M., Zhou, M., and Duan, Y. (2016). Bismerthiazol inhibits Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri growth and induces differential expression of citrus defense-related genes. Phytopathology 106 (7), 693–701., PMID: 26882850
Zhang, M., Guo, Y., Powell, C. A., Doud, M. S., Yang, C., and Duan, Y. (2014). Effective antibiotics against ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’ in HLB-affected citrus plants identified via the graft-based evaluation. PLoS One 9, e111032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111032, PMID: 25372135
Keywords: pomegranate, bacterial blight, Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae, cultivar resistance, copper oxychloride, streptocycline
Citation: Mustafa G, Rajwana IA, Faried HN, Naqvi SAH, Khalil U, Iqbal MU, Al-Ansari MM, Elshikh MS, Manghwar H and Liu F (2025) Copper-streptocycline application modulates pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) secondary metabolism and antioxidant pathways against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. punicae-induced bacterial blight. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1661602. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1661602
Received: 08 July 2025; Accepted: 11 August 2025;
Published: 15 September 2025.
Edited by:
Bingsong Zheng, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, ChinaReviewed by:
Sana Ullah, Lithuanian Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry, LithuaniaZulfiqar Ali Sahito, Zhejiang University, China
Muhammad Jawad Umer, Guangdong Academy of Agricultural Sciences (GDAAS), China
Abid Ullah, Guilin University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Mustafa, Rajwana, Faried, Naqvi, Khalil, Iqbal, Al-Ansari, Elshikh, Manghwar and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hakim Manghwar, aGFraW1AbHNiZy5jbg==; Fen Liu, bGl1ZkBsc2JnLmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ghulam Mustafa
Ghulam Mustafa Ishtiaq A. Rajwana2
Ishtiaq A. Rajwana2 Syed Atif Hasan Naqvi
Syed Atif Hasan Naqvi Hakim Manghwar
Hakim Manghwar Fen Liu
Fen Liu