- 1School of Life Sciences and Medicine, Shandong University of Technology, Zibo, China
- 2School of Basic Medicine, Qilu Medical University, Zibo, China
Eggplant (Solanum melongena), an important crop for food supply, can suffer from severe gray mold rot caused by Botrytis cinerea, resulting in huge postharvest damage every year. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades, important to the signal transduction pathway, were identified in many species and proved to be involved in plant growth, development, and immune response, although our knowledge of this cascade in eggplant is scarce. In this work, based on the state-of-art genome sequencing data, the MAPK cascades of eggplant were identified. The result showed that there were 117 MAP3Ks, 5 MAP2Ks, and 16 MAPKs in the eggplant genome. All the proteins possessed traditional MAPK domains. Phylogenetic and collinear analysis showed that eggplant MAPKs was homologous with Arabidopsis and tomato. Cis-acting element analysis indicated that eggplant MAPKs may participate in defense and stress responsiveness. Meanwhile, transcriptomic analysis of postharvest eggplant after Botrytis cinerea infection showed that most of the MAPK genes had altered expression; further functional assays indicate that SmMAP3K38 likely operates as a negative regulator of eggplant immunity against Botrytis cinerea infection, which provides us new insights into the molecular basis of this important crop in disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea and gives us new potential targets for the prevention and control of gray mold.
1 Introduction
Eggplant (Solanum melongena), a widely grown and consumed vegetable around the world, is the third most cultivated Solanaceae crop after tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) and potato (Solanum tuberosum), especially in India and China, where it is a component in the daily diet (Barchi et al., 2021). With an abundance of vitamins, phenolics, and antioxidants, eggplant provides significant nutritive benefits to human health (Gürbüz et al., 2018). Gray mold is a fungal disease mainly caused by Botrytis cinerea, resulting in an annual economic loss of up to US $10–100 billion globally, ranking among the top ten plant fungal diseases (Dean et al., 2012). Botrytis cinerea is a necrotrophic fungus that can infect more than 1400 plants, including important economic crops such as tomato, eggplant, strawberry, and grape (Fillinger and Elad, 2016). Because of its convenience and low price, chemical control is still the most widely used method for the prevention and control of gray mold. However, the long-term use of chemical agents has caused problems such as pesticide residues and environmental pollution, which seriously endanger human health (De Miccolis Angelini et al., 2014; Lamichhane et al., 2016). Therefore, locating target genes that regulate plant resistance and susceptibility to pathogens and using targeted genetic manipulation to control gray mold would be an environmentally friendly way to combat this disease (AbuQamar et al., 2017).
Plants have evolved two sets of innate immune mechanisms in the course of long-term interaction with pathogens: pattern-triggered immunity (PTI) and effector triggered immunity (ETI) (Jones and Dangl, 2006). PTI refers to the pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) located on the surface of cells, which recognize conserved MAMPs/DAMPs (Microbe-/Damage-associated molecular patterns), initiate downstream immune responses (including intracellular Ca2+ signal transduction, reactive oxygen species (ROS) burst, and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade activation), and express corresponding immune genes (Yu et al., 2017; Zhang and Zhang, 2022). This layer of defense constitutes the first line. In order to avoid immune processes triggered by conserved molecular patterns, pathogens have evolved effectors that inhibit plant PTI processes to achieve successful plant infection (Jones and Dangl, 2006). Plants further evolved resistance proteins that recognize effectors directly or indirectly, activating the ETI process, which induce local programmed cell death (PCD) or a hypersensitive response (HR) (Boller and He, 2009). After immune receptors recognize MAMPs/DAMPs signals, they typically transmit the signal through a MAPK cascade pathway, which transfers the signal from the receptor to a specific effector to regulate gene expression and cellular activities (Han et al., 2010; Meng and Zhang, 2013). A typical MAPK cascade usually included three components: a MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K/MEKK/MAPKKK/MKKK), a MAP kinase kinase (MAP2K/MKK/MAPKK/MEK), and a MAP kinase (MAPK/MPK) (Zhang and Zhang, 2022). As a close relative of eggplant, there have been several reports on the involvement of the MAPK pathway genes in response to Botrytis cinerea in tomato. The tomato genome contains 89 MAP3Ks, 5 MAP2Ks, and 16 MAPKs (Wu et al., 2014). Some of them were reported to be involved in the immune response to Botrytis cinerea. Transient silencing of SlMKK2 or SlMKK4 could decrease the resistance of tomato plants to Botrytis cinerea, increase the accumulation of reactive oxygen species, and reduce the expression of defense genes in tomato (Li et al., 2014). The downstream signaling component of MKK was MPK, and silencing of tomato SlMPK1/2/3/4 could block the defense signaling pathway of tomato fruits and enhance the sensitivity of tomato to Botrytis cinerea (Virk et al., 2013; Zheng et al., 2015). After further knocking out SlMPK3 via CRISPR/Cas9, the slmpk3 mutant showed reduced activities of immunity-related enzymes, accumulated more reactive oxygen species, and became more susceptible to Botrytis cinerea compared with the wild type (Zhang et al., 2018). A recent study revealed that overexpression of SlMPK8 enhances fruit resistance to Botrytis cinerea, whereas the slmpk8 mutant fruit exhibits increased sensitivity to this pathogen (Deng et al., 2024a). Another result showed that overexpression of SlMKK2 and SlMKK4 caused cell death of tomato leaf cells and activation of SlMPK2/3 (Pedley and Martin, 2004). Meanwhile, in vitro kinase experiments showed that SlMKK2 and SlMKK4 can phosphorylate SlMPK1/2 (Pedley and Martin, 2004). The above results provide a new way for us to use MAPK as a molecular target for the prevention and control of gray mold.
As the third most cultivated Solanaceae crop, little is known about the MAPK family and the role of MAPK in Botrytis cinerea infection of eggplant. In this study, through the comprehensive use of a variety of bioinformatics approaches, 117 MAP3Ks, 5 MAP2Ks, and 16 MAPKs were identified in the eggplant genome, and transcriptomic analysis of this family in postharvest eggplant after Botrytis cinerea infection provided us new insights and potential targets for the prevention and control of this important fungus.
2 Results
2.1 Identification of eggplant MAPK family
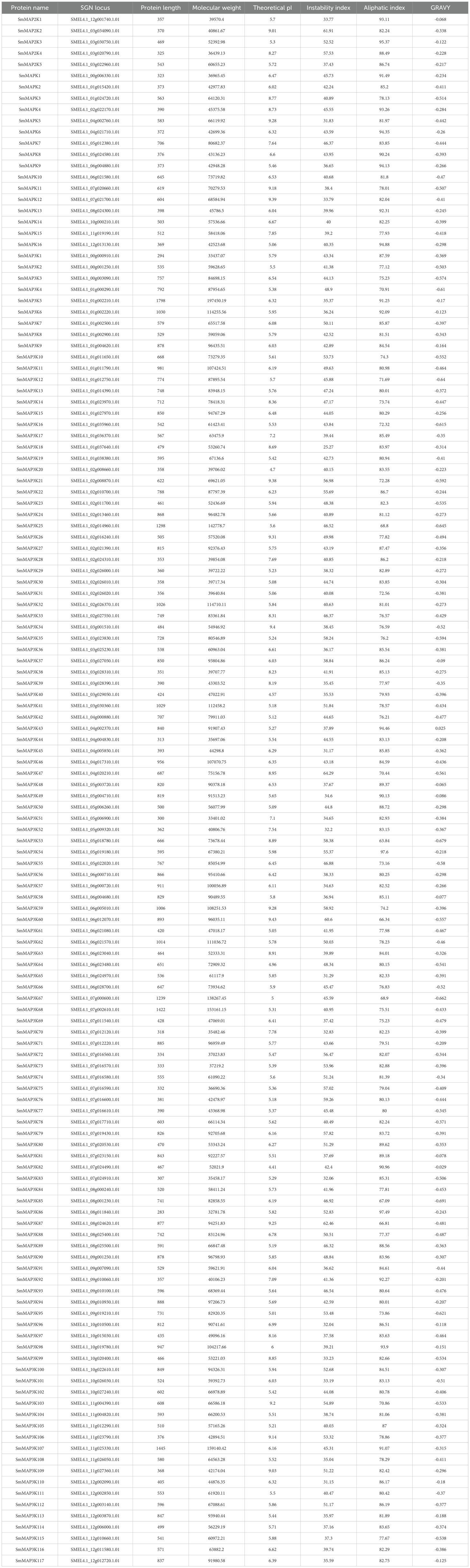
The identification of the eggplant MAPK family used the local blast programmer from TBtools (Chen et al., 2020). Previously reported MAPK protein sequences from tomato (Kong et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2014) were used as seeds to search for eggplant protein data. As shown in Table 1, 117 MAP3Ks, 5 MAP2Ks, and 16 MAPKs were identified in the eggplant genome. MAP3Ks and MAPKs were named according to their location on the chromosome, and MAP2Ks were named based on tomato MAP2Ks. The physicochemical property of the eggplant MAPK family, including protein length (unit: amino acid, aa), molecular weight (unit: Da), theoretical isoelectric point (pI), instability index, aliphatic index, and grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY), were then analyzed. The results showed that the largest protein was SmMAP3K5, which was composed of 1798 aa, and the smallest protein was SmMAP3K86, consisting of 283 aa.
2.2 Phylogenetic analysis of the eggplant MAPK family
To explore the relationships among eggplant, tomato, and Arabidopsis MAPKs, the phylogenetic analyses using these protein sequences were conducted. The results showed that the three species of MAP2Ks could be divided into four groups (group I to IV, Figure 1A). In group I, there was only one member, Arabidopsis AtMKK10, while Group II to IV had 4, 5, and 10 eggplant, tomato, and Arabidopsis members respectively. This result indicates that eggplant MAP2Ks and tomato share a close phylogenetic relationship. As for MAPKs, all the eggplant, tomato, and Arabidopsis MAPKs were divided into two groups according to their conserved protein domain, TEY (Thr-Glu-Tyr) and TDY (Thr-Asp-Tyr) (Figure 1B). MAP3Ks were the largest MAPKs. The phylogenetic analysis showed that eggplant MAP3Ks also had three subgroups: MEKK, ZIK, and Raf (Figure 1C). Consistent with previous reports in tomato, the Raf subfamily constitutes the largest proportion of MAP3K members.
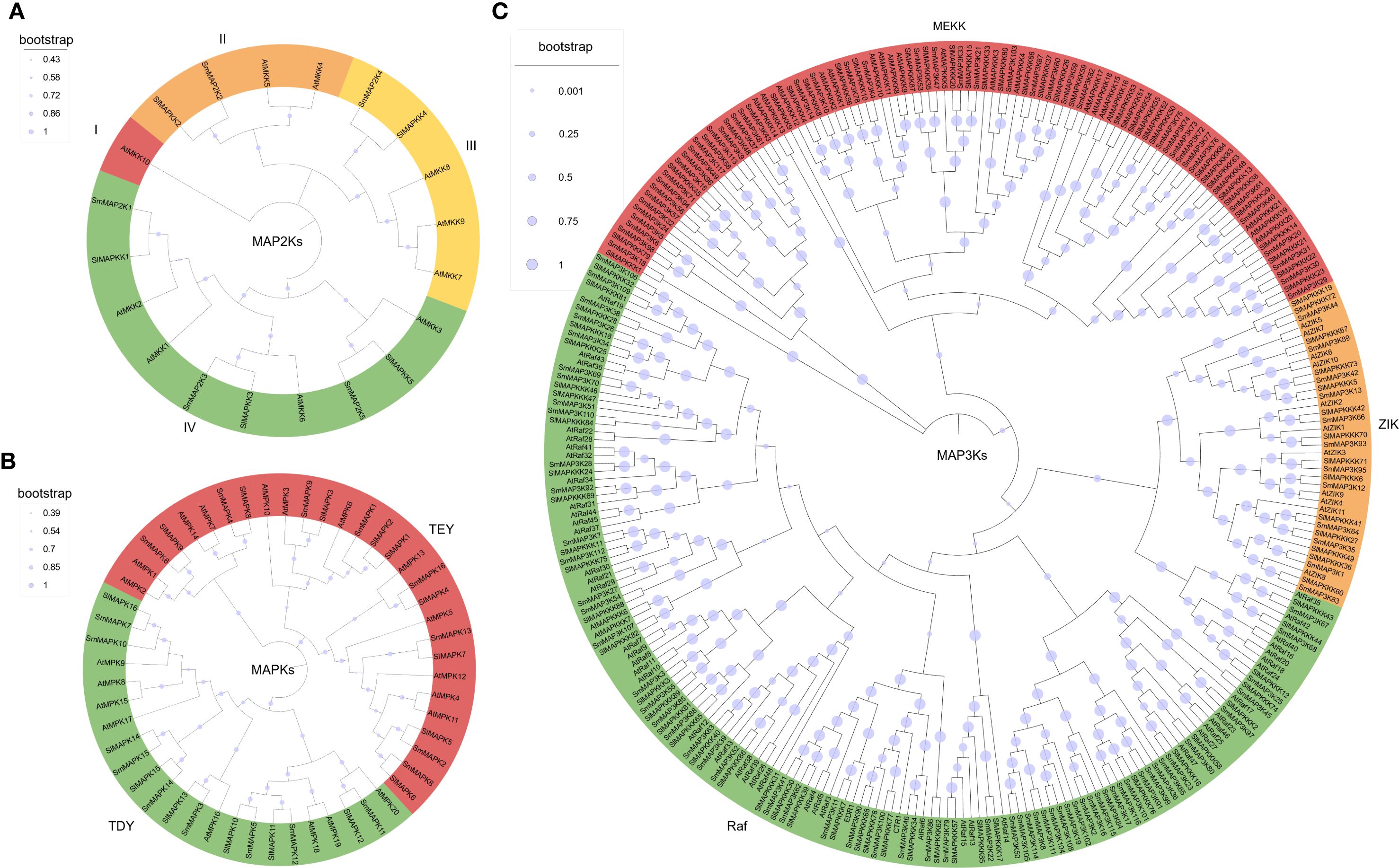
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of the eggplant MAPK family. The phylogenetic analysis of eggplant MAP2Ks (A), MAPKs (B), and MAP3Ks (C).
2.3 The gene collinearity of the eggplant MAPK family.
To gain a deeper insight into the genetic duplication occurrences within the eggplant MAPKs gene family, their collinearity was examined utilizing the One Step MCScanX tool available in TBtools. The analysis revealed that there were 50 pairs of SmMAPK genes exhibiting collinearity, indicating the presence of intraspecific duplication events (Figure 2A, Supplementary Table S1). Additionally, a detailed investigation was conducted to explore the collinearity between eggplant MAPKs genes and those of Arabidopsis and tomato. This additional analysis aimed to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the genetic relationships and potential duplication events across these species. This led to the identification of 94 and 156 pairs of collinear genes between eggplant and those of Arabidopsis and tomato, respectively (Figures 2B, C, Supplementary Table S1). These findings hint at the possibility of interspecific duplication events having taken place during their evolutionary history.
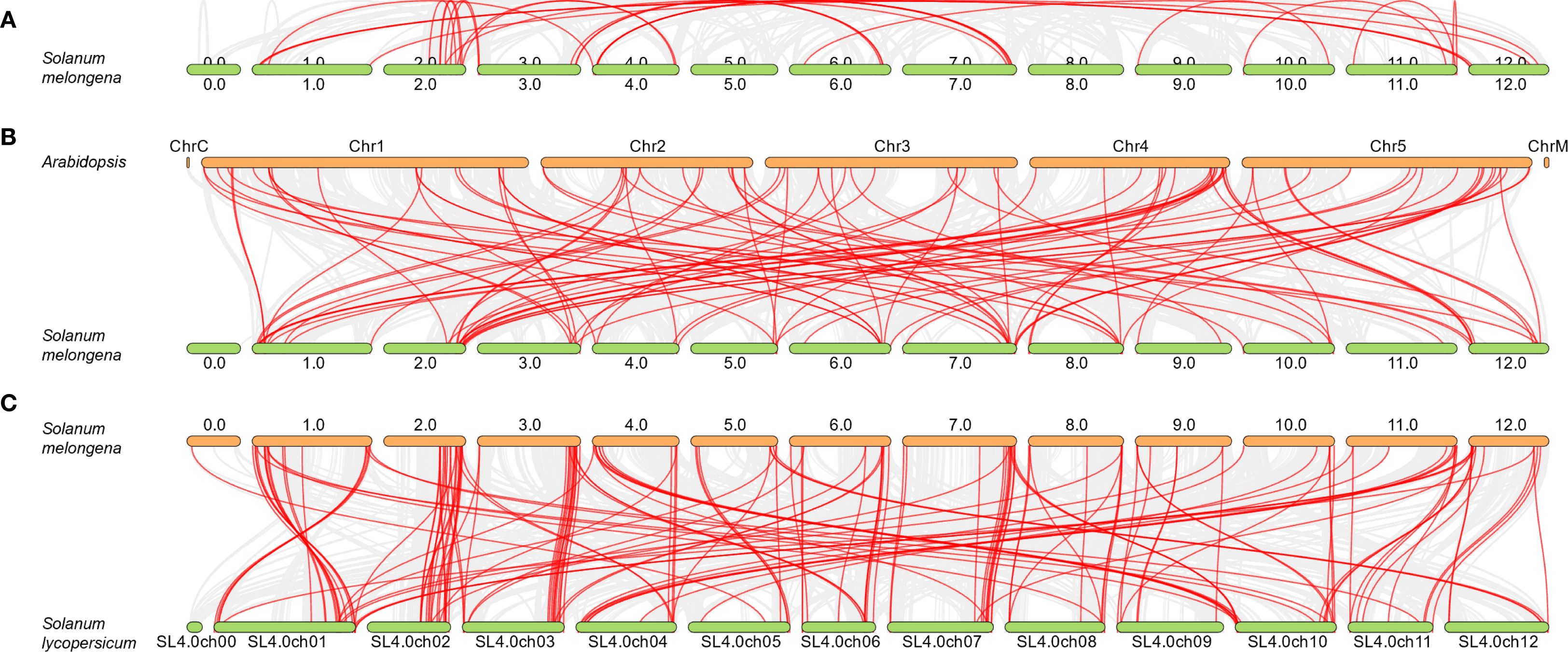
Figure 2. Gene collinearity analysis of the eggplant MAPK genes. Collinearity analysis of MAPK genes among eggplant itself (A), eggplant versus Arabidopsis (B), and eggplant versus tomato (C).
2.4 Chromosome location of the eggplant MAPK family
The 138 eggplant MAPKs genes were anchored on the eggplant chromosomes, as shown in Figure 3. Among them, SmMAPKs genes were distributed across all chromosomes except chromosomes 3 and 9, while SmMAP2Ks genes were mainly distributed on chromosomes 3 and 12. Members of the eggplant MAP3K family were conspicuously clustered along the chromosomes.
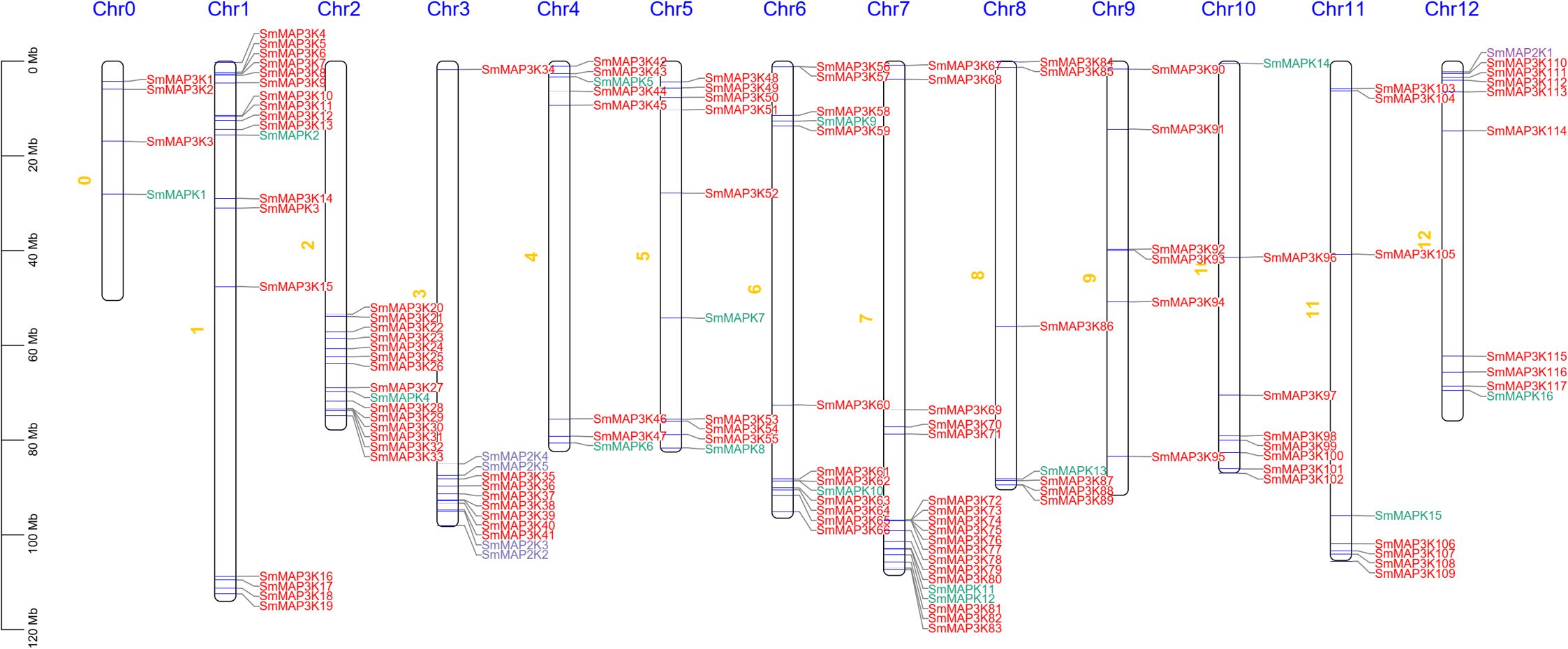
Figure 3. The chromosome location of the eggplant MAPK family. The MAP3Ks, MAP2Ks, and MAPKs were marked with red, blue, and green respectively. Scale bar indicates chromosome length. Scar bar = 20 Mb.
2.5 Gene structure and protein domain analysis of the eggplant MAPK family
Using the Batch-CD search tool from NCBI, the conserved protein domains of eggplant MAPKs were acquired. As shown in Supplementary Figure S1 and Supplementary Table S2, the SmMAPKs mainly included STKc_TEY_MAPK or STKc_TDY_MAPK domains, the SmMAP2Ks mainly consisted of PKc_MAPKK_plant_like domains, and the SmMAP3Ks mainly contained STKc_ MAPKKK, STKc_MEKK1_plant, or STKc_MAP3K_like domains, which further confirmed the accuracy of these identified proteins. Otherwise, the distribution of these domains was varied in different proteins. They could be located in the N-terminal, middle space, or C-terminal. In addition, with the help of gene annotation file, the gene structures of eggplant MAPKs were acquired and visualized. Most of the eggplant MAPK genes owned one or more introns, while some of them had a complete CDS that was not interrupted by introns (Supplementary Figure S1).
2.6 Cis-acting element analysis of the eggplant MAPK family
MAPKs were reported to be involved in plant growth, development, and stress responses (Meng and Zhang, 2013; Xu and Zhang, 2015; Zhang and Zhang, 2022). Cis-acting elements can give us information about the possible functions of genes. In order to preliminarily analyze whether eggplant MAPKs also participated in the above process, the promoters of these 138 genes were extracted by TBtools and analyzed by PlantCARE to test the cis-acting elements. The results showed that all the promoters of eggplant MAPKs genes held diverse cis-acting elements, including light response, hormone response, and defense and stress response, indicating that eggplant MAPK genes might participate in these biological progresses (Supplementary Figure S2, Supplementary Table S3).
2.7 Transcriptomic analysis of the eggplant MAPK family genes in response to Botrytis cinerea infection
Cis-acting elements analysis indicated that eggplant MAPK genes might participate in defense response. Gray mold is a severe disease of eggplant caused by Botrytis cinerea. In order to further explore the function of MAPKs family genes in eggplant, transcriptome sequencing technology was used to detect the gene expression levels of MAPK family genes before and after the fruit was infected with Botrytis cinerea (Figure 4A). The results were as follows.
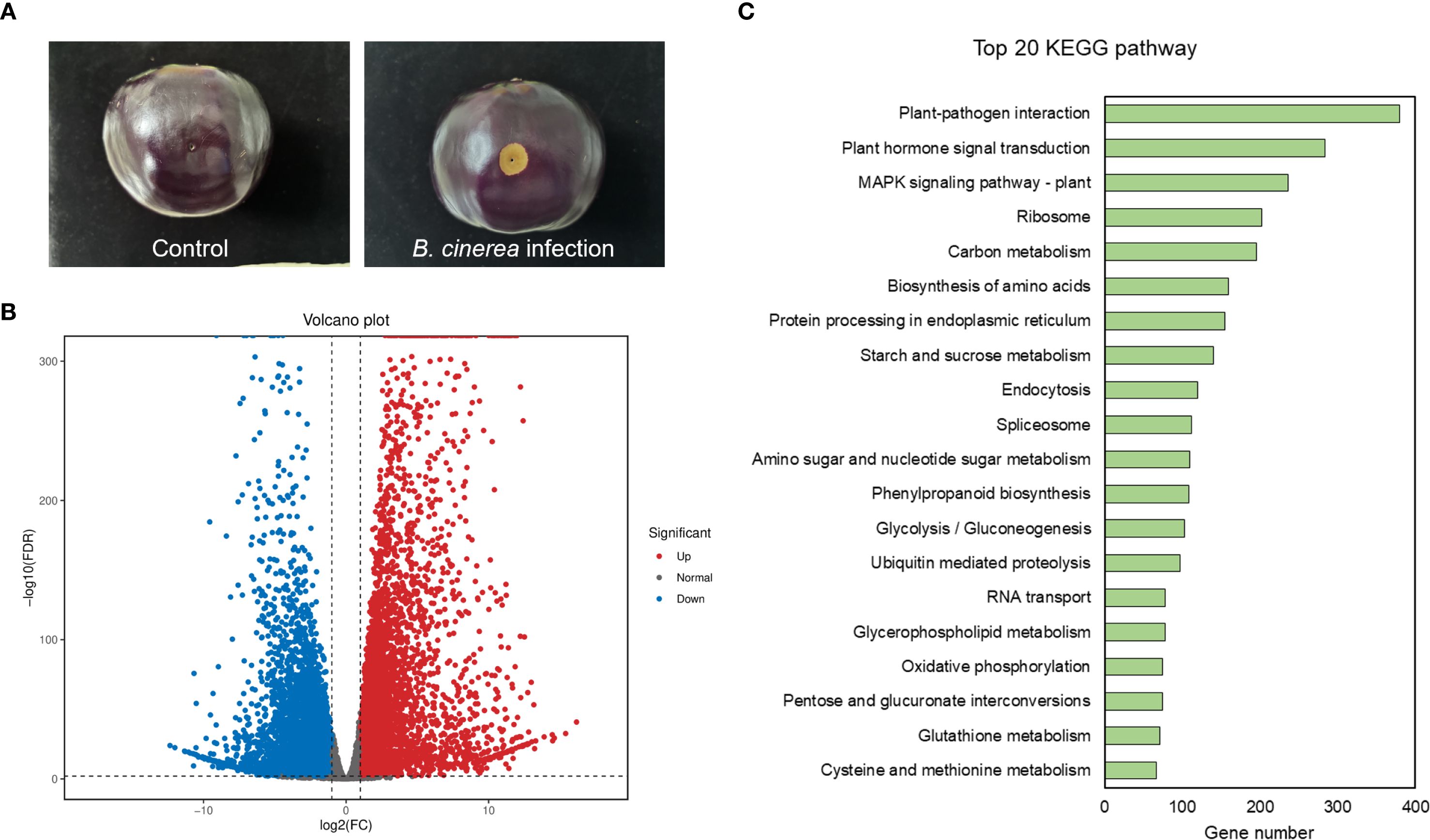
Figure 4. Transcriptomic analysis of the eggplant genes in response to Botrytis cinerea infection. (A) The representative images depict the eggplant samples used in the transcriptome experiment. (B) Volcano plot of up- and down-regulated genes in eggplant before and after infection by Botrytis cinerea. Red indicates up-regulation, blue indicates down-regulation, and gray indicates no significant difference. (C) KEGG pathway analysis of the DEGs. Categories are ranked according to the number of genes obtained by clustering.
To validate the reliability of our transcriptomic experiment, we first mined the literature for well-established disease-resistance marker genes in tomato (PR1a1, GRAS4.1, WRKY28, PTI5, LRR22, and GRAS2) (Nguyen et al., 2010; Taylor et al., 2012; Harel et al., 2014; Topalović et al., 2020). Their eggplant orthologs were then retrieved by reciprocal BLAST searches. Expression profiling confirmed that these orthologous genes were markedly up-regulated following Botrytis cinerea infection, corroborating the robustness of our experimental treatment (Supplementary Figure S3). Then, differential expression analysis revealed that there were 10496 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between the Botrytis cinerea infection group and control group. After Botrytis cinerea infection, 5531 genes were down-regulated and 4965 genes were up-regulated (Figure 4B). For functional classification of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs), KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was performed (Figure 4C). Interestingly, 236 DEGs were enriched in the MAPK signaling pathway-plant term of KEGG, indicating that MAPK signaling pathway genes might play important roles in eggplant to Botrytis cinerea infection. The gene expression of the 138 newly identified eggplant MAPKs were analyzed by transcriptomic sequencing. As shown in Supplementary Figure S4 and Supplementary Table S4, most of the genes were up-regulated and some of the genes were down-regulated after Botrytis cinerea infection. However, 26 genes had no available data due to the limitation of sequencing technology or the low expression level.
2.8 SmMAP3K38 is involved in the response of eggplant to Botrytis cinerea
Transcriptome profiling revealed that MAPK cascade components across multiple tiers displayed marked expression shifts following Botrytis cinerea challenge. To corroborate these findings, we selected the SmMAP2Ks, SmMAPKs, and SmMAP3Ks exhibiting the most pronounced transcriptional changes and re-examined their transcript abundance by qPCR. The resulting expression patterns were fully concordant with the RNA-seq data, providing independent confirmation of the reliability of our transcriptomic dataset (Figure 5A). As the first signaling component of the MAPK cascade, MAP3K usually receives upstream pathogen signals directly and plays a key role within the MAPK module. Our previous work demonstrated that tomato SlMAP3K18 perceives upstream immune cues and precisely modulates the fruit’s response to Botrytis cinerea (Ji et al., 2023). The present transcriptomic data reveal SmMAP3K38 as the MAPK-family gene exhibiting the greatest down-regulated expression change. It belongs to the Raf clade, clusters closely with SlMAP3K18 in phylogenetic analysis, and shares similar genes and protein architectures (Figure 5B). SmMAP3K38 is therefore highly likely to participate in eggplant’s defense against Botrytis cinerea, and its expression profile suggests it acts as a negative regulator. To test this hypothesis, we constructed expression vectors to express EGFP (control) and SmMAP3K38-EGFP (experimental) in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana (Figure 5C), followed by inoculation with Botrytis cinerea spore suspension. Lesion diameters were significantly larger in SmMAP3K38-expressing leaves than in controls (Figures 5D, E), supporting our hypothesis. These results indicate that SmMAP3K38 serves as a negative regulator of the eggplant defense response to Botrytis cinerea.
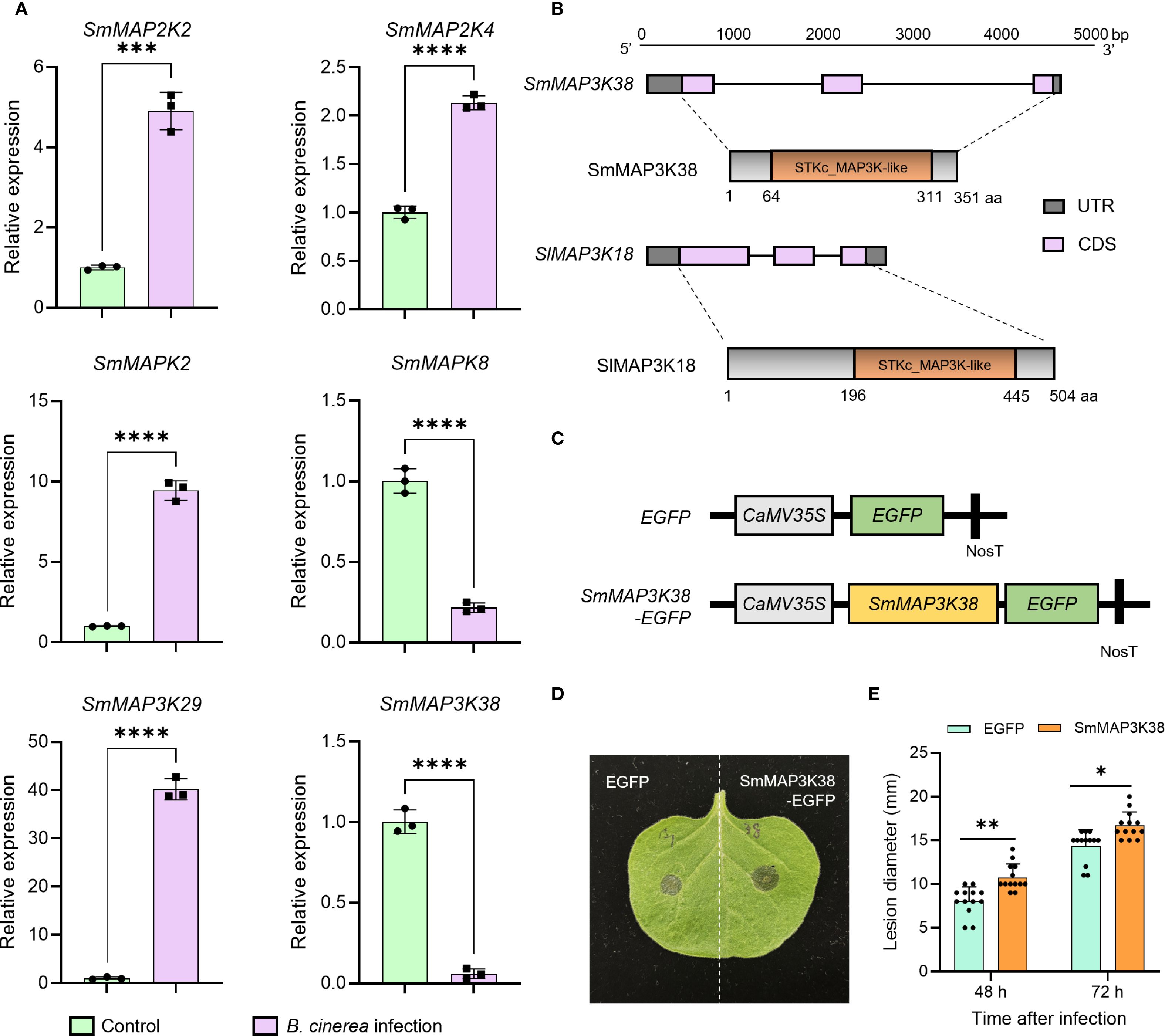
Figure 5. SmMAP3K38 is involved in response to Botrytis cinerea infection. (A) qPCR confirms the expression trends of six MAPK-component genes (SmMAP2K2, SmMAP2K4, SmMAPK2, SmMAPK8, SmMAP3K29 and SmMAP3K38) identified in the transcriptome. (B) The comparison of gene and protein structure between SmMAP3K38 and SlMAP3K18. (C) Schematic diagram of the SmMAP3K38 expression vector construction. (D) Representative photograph of gray mold lesions on tobacco leaves 48 h after inoculation with Botrytis cinerea spore suspension following transient expression of SmMAP3K38. (E) Statistical analysis of gray mold lesion diameters on tobacco leaves transiently expressing SmMAP3K38. Data were mean values ± SD. Asterisks indicate significant difference (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001; Student’s t-test).
3 Methods
3.1 Plant and fungi materials
Eggplant fruit (Solanum melongena var. esculentum) was purchased in Zibo City, Shandong Province Zhangdian District supermarket. The Botrytis cinerea was isolated from naturally infected strawberry fruits and preserved in the laboratory. The Botrytis cinerea was routinely maintained on potato dextrose agar (PDA) and incubated at 23 ± 2°C for 7–10 days until profuse sporulation. Conidia were gently dislodged by flooding each plate with sterile distilled water, and the resulting suspension was filtered through four layers of sterile cheesecloth to remove mycelial debris. A hemocytometer count adjusted the final spore density to 2 × 105 spores per mL.
3.2 Gene family identification and phylogenetic analysis
The eggplant and tomato protein sequences were extracted from SGN (Sol Genomics Network, https://solgenomics.net/) (Fernandez-Pozo et al., 2015). The tomato MAPK, MAP2K, and MAP3K protein sequences were set as reference sequences to conduct blast analysis in eggplant protein database using TBtools. The results were filtered by E-value=0. The Arabidopsis MAPK protein sequences were downloaded from TAIR (https://www.arabidopsis.org/) (Berardini et al., 2015). All candidate eggplant sequences were submitted to the NCBI Batch-CD database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi)?. Among the returned results (Batch CD hitdata-full), sequences with clear MAPK, MAP2K, or MAP3K annotations were selected for subsequent analysis.
Then, these sequences were sent to ClustalW to align. The neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree were constructed by MEGA, version 11 (Tamura et al., 2021) (State College, PA, USA), with 1,000 bootstrap replicates, a pairwise deletion, and a Poisson model. The tree file was optimized by iTOL, version 6 (Letunic and Bork, 2024) (https://itol.embl.de/) (Heidelberg, Germany).
3.3 Chromosome location
The chromosomal locations of the MAPK, MAP2K, and MAP3K genes in eggplant were retrieved from the SGN and visualized using TBtools.
3.4 Gene structure and protein domain analysis
Protein domain analysis was performed by submitting the amino acid sequences to the Batch CD-Search tool under default parameters, with only hits meeting the significance threshold (E-value < 1×10−10) retained for further analysis.
For gene structure analysis, the corresponding gene annotation files were retrieved from the Solanaceae Genomics Network (SGN) database and subsequently visualized using the Gene Structure View module in TBtools.
3.5 Cis-acting element analysis
The 2,000 base pair (bp) region located upstream of the coding sequence start sites for SmMAPK, SmMAP2K, and SmMAP3K was extracted from the eggplant genome utilizing the GXF Sequence Extract function within TBtools. Following this extraction, the sequence was subjected to analysis using PlantCARE (available at http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) (Lescot, 2002), with the aim of identifying cis-acting elements under standard parameters. The outcomes of this analysis were subsequently visualized employing the Simple BioSequence Viewer feature of TBtools version 1.108.
3.6 Gene collinearity analysis
The genomic data of eggplant, tomato, and Arabidopsis were downloaded from SGN and TAIR. These sequence data were used to conduct gene collinearity analysis using TBtools.
3.7 Transcriptomic analysis
For inoculation, the eggplant fruits were washed with sterile water three times, then disinfected with 2% sodium hypochlorite and washed again with sterile water three times. The eggplants were subjected to a standardized incision process: a sterilized scalpel created wounds on the fruits’ equatorial region, each 2 mm in width and 5 mm in depth, prior to inoculation. Each incision received a 5 μL application of a spore suspension, with a concentration of 2 × 105 spores per mL. For comparison, a set of fruits was treated with water and served as the control group. All fruits were then placed in plastic containers, maintaining a high humidity level of approximately 95%, and were kept at an ambient temperature of 23 ± 2°C for a duration of four days. Both the control and Botrytis cinerea treatment groups comprised three biological replicates.
For transcriptome sequencing, total RNA were extracted and sent to Biomarker Technologies (Qingdao, China). Raw FASTQ reads were trimmed with in-house Perl scripts to remove adapters, poly-N tails, and low-quality bases; adapter- and quality-filtered reads were discarded. High-quality reads were aligned to the reference genome with HISAT2, keeping only uniquely mapped reads with ≤1 mismatch. Differential expression between groups was determined with DESeq2 (negative-binomial model, FDR < 0.01, |log2 Fold Change (log2FC)| ≥ 1). Statistical enrichment of differentially expressed genes in KEGG pathways was assessed with KOBAS (Mao et al., 2005) and clusterProfiler.
3.8 RT-qPCR
Total RNA was reverse-transcribed into first-strand cDNA using the Hifair® III 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis SuperMix for qPCR (gDNA digester plus) according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Yeasen Biotech, Shanghai, China). RT-qPCR was performed on a LightCycler 480 Instrument II platform (Roche) with Hieff UNICON Universal Blue SYBR Green Master Mix (Yeasen) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Primer pairs specific to each target (Supplementary Table S5) were designed with TBtools, and SmACTIN (Deng et al., 2024b) served as the reference gene. Data are presented as means ± SD of three replicates.
3.9 Gene clone and pathogen inoculation
SmMAP3K38 CDS was amplified from eggplant fruit cDNA and ligated into the pEAQ-EGFP backbone downstream of the CaMV 35S promoter and upstream of the NOS terminator. Sequence-verified plasmids were introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens GV3101. Transformed bacteria were cultured overnight at 28°C in LB supplemented with kanamycin and rifampicin and resuspended in infiltration buffer (10 mM MES, pH 5.7, 10 mM MgCl2, 200 µM acetosyringone) to an OD600 of 0.5. After 2 h incubation, the suspension was pressure-infiltrated into the abaxial surface of 4-week-old Nicotiana benthamiana leaves with a needleless 1 mL syringe. Leaves were harvested 48 h post-infiltration for pathogen challenge, following the protocol described previously (Ji et al., 2023). The primers used in this study are listed in Supplementary Table S5.
4 Discussion
The present study provides a comprehensive genome-wide identification and transcriptomic analysis of the MAPK family genes in eggplant, elucidating their potential roles in the molecular basis of disease resistance against Botrytis cinerea postharvest. This investigation offers valuable insights into the complex regulatory mechanisms underlying the defense responses in eggplant, a crucial horticultural crop.
Through a systematic genome-wide approach, we identified a total of 138 MAPK family genes in eggplant. The uneven distribution of these genes across the chromosomes suggests the occurrence of gene duplication events, which may have contributed to the functional diversification of the MAPK family in eggplant. The conserved domain analysis revealed a high degree of evolutionary conservation among MAPK family genes, implying that they may share similar functions across different plant species. This conservation is essential for understanding the fundamental roles of MAPKs in plant stress and pathogen responses and provides a basis for comparative studies with other species.
The transcriptomic analysis unveiled dynamic expression patterns of MAPK family genes during the postharvest infection of eggplant by Botrytis cinerea. Transcriptome analysis revealed that the majority of genes exhibited upregulation trends, while a subset showed downregulation. Excluding genes with undetectable expression levels, all SmMAP2K genes were upregulated, whereas some SmMAPK genes displayed minimal expression changes. Notably, SmMAP3K genes demonstrated diverse expression patterns. Of particular interest, following Botrytis cinerea infection, SmMAP3K29 showed the highest upregulation fold-change while SmMAP3K38 exhibited the most significant downregulation. As the primary signaling components in the MAPK cascade, MAP3Ks may be associated with the specificity of infection signal recognition. This differential expression pattern highlights the multifaceted functions of MAPK family genes in the resistance of eggplant to Botrytis cinerea, encompassing early pathogen recognition, signal transduction, and downstream defense response regulation.
In our previous work, we demonstrated that tomato SlMAP3K18 acts as a molecular bridge linking receptor-like kinases to downstream MAP2Ks and thereby modulates the fruit’s response to Botrytis cinerea (Ji et al., 2023). The eggplant ortholog SmMAP3K38 shares extensive sequence and structural similarity with SlMAP3K18, and pathogen challenge assays reveal that SmMAP3K38 likewise functions as a negative regulator of immunity against Botrytis cinerea. These findings suggest that this clade of MAP3Ks performs a conserved role across Solanaceous species. Nevertheless, functional divergence is evident. SlMAP3K18 is transcriptionally up-regulated upon Botrytis cinerea infection, yet transient silencing of SlMAP3K18 in tomato does not alter disease susceptibility, implying that its primary contribution lies in signal transmission via phosphorylation rather than in modulating transcript abundance. MAPK cascades operate through sequential phosphorylation events, and their output is likely conditioned by the abundance of each signaling component, which are themselves subject to transcriptional control. Our current data indicate that transcriptional regulation of SmMAP3K38 contributes—at least in part—to its functional output. Comparable scenarios have been reported for other MAPK constituents. Botrytis cinerea infection induces SlMKK2 (SlMAP2K2) and SlMKK4 (SlMAP2K4) expression in tomato and transient silencing of either gene enhances susceptibility, while over-expression reduces it (Li et al., 2014). Silencing or knockout of SlMPK1/2/3/4/8 renders tomato markedly more susceptible to Botrytis cinerea infection (Virk et al., 2013; Zheng et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2018; Deng et al., 2024a). Collectively, these results underscore a nuanced interplay between transcriptional control and post-translational phosphorylation in shaping the strength and specificity of MAPK-mediated defense responses.
Based on the expression patterns and existing literature, we propose that MAPK family genes may function through multiple molecular mechanisms in the resistance of eggplant to Botrytis cinerea. Initially, the MAPK signaling pathway is likely involved in the recognition of PAMPs by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on the plant cell surface, triggering early immune responses (Yu et al., 2017; Zhang and Zhang, 2022; Ji et al., 2023). This process may activate a cascade of downstream signaling components, including calcium ion signaling, transcription factors, and hormone signaling pathways. The eggplant MAPK family genes may participate in and regulate the synthesis and signaling of plant hormones such as salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and auxin, thereby influencing the plant’s defense responses, as shown in the cis-acting element analysis of this family. Additionally, MAPK family genes may be involved in the signaling of cell wall-related pathways, reinforcing the structural integrity of the cell wall to restrict pathogen invasion and spread (Meng and Zhang, 2013). This multi-layered regulatory mechanism provides significant clues for understanding the molecular basis of disease resistance in eggplant.
This study significantly advances our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying postharvest disease resistance in eggplant by providing a detailed characterization of the MAPK family genes and their potential roles in defense against Botrytis cinerea. The findings not only offer valuable genetic resources for developing new disease-resistant strategies but also contribute to the broader field of plant pathology and molecular biology. Future research should focus on functional validation of these MAPK family genes using techniques such as CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing, overexpression analyses, and single-cell and spatial RNA sequencing (Deng et al., 2024a; Dong et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024) to elucidate their specific roles and molecular mechanisms in disease resistance. Additionally, integrating protein-protein interaction network analyses and metabolomics studies could provide a holistic understanding of the complex regulatory networks involving the MAPK signaling pathway in plant defense responses.
Data availability statement
The raw sequence data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive (Chen et al., 2021) in National Genomics Data Center (CNCB-NGDC Members and Partners et al., 2025), China National Center for Bioinformation/Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GSA: CRA029243) that are publicly accessible at https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa.
Author contributions
WZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DJ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by project ZR2022QC256, supported by Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, and by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 32402640).
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank Dr. Jing Gao for her invaluable assistance with the qPCR experiments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1680931/full#supplementary-material
References
AbuQamar, S., Moustafa, K., and Tran, L. S. (2017). Mechanisms and strategies of plant defense against Botrytis cinerea. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 37, 262–274. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2016.1271767
Barchi, L., Rabanus-Wallace, M. T., Prohens, J., Toppino, L., Padmarasu, S., Portis, E., et al. (2021). Improved genome assembly and pan-genome provide key insights into eggplant domestication and breeding. Plant J. 107, 579–596. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15313
Berardini, T. Z., Reiser, L., Li, D., Mezheritsky, Y., Muller, R., Strait, E., et al. (2015). The arabidopsis information resource: Making and mining the “gold standard” annotated reference plant genome: Tair: Making and Mining the “Gold Standard” Plant Genome. genesis 53, 474–485. doi: 10.1002/dvg.22877
Boller, T. and He, S. Y. (2009). Innate immunity in plants: an arms race between pattern recognition receptors in plants and effectors in microbial pathogens. Science 324, 742–744. doi: 10.1126/science.1171647
Chen, C., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H. R., Frank, M. H., He, Y., et al. (2020). TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 13, 1194–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen, T., Chen, X., Zhang, S., Zhu, J., Tang, B., Wang, A., et al. (2021). The genome sequence archive family: toward explosive data growth and diverse data types. Genomics Proteomics Bioinf. 19, 578–583. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2021.08.001
CNCB-NGDC Members and Partners, Bao, Y., Bai, X., Bu, C., Chen, H., Chen, H., et al. (2025). Database resources of the national genomics data center, China national center for bioinformation in 2025. Nucleic Acids Res. 53, D30–D44. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae978
Dean, R., Van Kan, J. A. L., Pretorius, Z. A., Hammond-Kosack, K. E., Di Pietro, A., Spanu, P. D., et al. (2012). The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 13, 414–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x
De Miccolis Angelini, R. M., Rotolo, C., Masiello, M., Gerin, D., Pollastro, S., and Faretra, F. (2014). Occurrence of fungicide resistance in populations of Botryotinia fuckeliana ( Botrytis cinerea ) on table grape and strawberry in southern Italy. Pest. Manage. Sci. 70, 1785–1796. doi: 10.1002/ps.3711
Deng, J., Feng, C., Zhang, L., and Yang, X. (2024b). Screening of Eggplant qRT-PCR Internal Reference Genes under Different Tissues and Adversity Stresses. China Vegetables 1, 37–46. doi: 10.19928/j.cnki.1000-6346.2024.2019
Deng, H., Pei, Y., Xu, X., Du, X., Xue, Q., Gao, Z., et al. (2024a). Ethylene-MPK8-ERF.C1-PR module confers resistance against Botrytis cinerea in tomato fruit without compromising ripening. New Phytol. 242, 592–609. doi: 10.1111/nph.19632
Dong, X., Lv, H., Zhao, L., He, B., Zhang, J., Zhao, B., et al. (2024). SlMAPKKK43 regulates tomato resistance to gray mold. Acta Hortic. Sin. 51, 309–320. doi: 10.16420/j.issn.0513-353x.2023-0757
Fernandez-Pozo, N., Menda, N., Edwards, J. D., Saha, S., Tecle, I. Y., Strickler, S. R., et al. (2015). The Sol Genomics Network (SGN)—from genotype to phenotype to breeding. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D1036–D1041. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1195
Fillinger, S. and Elad, Y. (2016). Botrytis – the fungus, the pathogen and its management in agricultural systems. Eds. Fillinger, S. and Elad, Y. (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing). doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-23371-0
Gürbüz, N., Uluişik, S., Frary, A., Frary, A., and Doğanlar, S. (2018). Health benefits and bioactive compounds of eggplant. Food Chem. 268, 602–610. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.06.093
Han, L., Li, G. J., Yang, K. Y., Mao, G., Wang, R., Liu, Y., et al. (2010). Mitogen-activated protein kinase 3 and 6 regulate Botrytis cinerea-induced ethylene production in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 64, 114–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04318.x
Harel, Y. M., Mehari, Z. H., Rav-David, D., and Elad, Y. (2014). Systemic resistance to gray mold induced in tomato by benzothiadiazole and trichoderma harzianum T39. Phytopathology 104, 150–157. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-02-13-0043-R
Ji, D., Liu, W., Cui, X., Liu, K., Liu, Y., Huang, X., et al. (2023). A receptor-like kinase SlFERL mediates immune responses of tomato to Botrytis cinerea by recognizing BcPG1 and fine-tuning MAPK signaling. New Phytol. 240, 1189–1201. doi: 10.1111/nph.19210
Jones, J. D. G. and Dangl, J. L. (2006). The plant immune system. Nature 444, 323–329. doi: 10.1038/nature05286
Kong, F., Wang, J., Cheng, L., Liu, S., Wu, J., Peng, Z., et al. (2012). Genome-wide analysis of the mitogen-activated protein kinase gene family in Solanum lycopersicum. Gene 499, 108–120. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.01.048
Lamichhane, J. R., Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S., Kudsk, P., and Messéan, A. (2016). Toward a reduced reliance on conventional pesticides in European agriculture. Plant Dis. 100, 10–24. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-05-15-0574-FE
Lescot, M. (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Letunic, I. and Bork, P. (2024). Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 52, W78–W82. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae268
Li, X., Li, B., Gu, S., Pang, X., Mason, P., Yuan, J., et al. (2024). Single-cell and spatial RNA sequencing reveal the spatiotemporal trajectories of fruit senescence. Nat. Commun. 15, 3108. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47329-x
Li, X., Zhang, Y., Huang, L., Ouyang, Z., Hong, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2014). Tomato SlMKK2 and SlMKK4 contribute to disease resistance against Botrytis cinerea. BMC Plant Biol. 14, 1–17. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-14-166
Mao, X., Cai, T., Olyarchuk, J. G., and Wei, L. (2005). Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 21, 3787–3793. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430
Meng, X. and Zhang, S. (2013). MAPK cascades in plant disease resistance signaling. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 51, 245–266. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-082712-102314
Nguyen, H. P., Chakravarthy, S., Velásquez, A. C., McLane, H. L., Zeng, L., Nakayashiki, H., et al. (2010). Methods to study PAMP-triggered immunity using tomato and nicotiana benthamiana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 23, 991–999. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-23-8-0991
Pedley, K. F. and Martin, G. B. (2004). Identification of MAPKs and their possible MAPK kinase activators involved in the pto-mediated defense response of tomato. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 49229–49235. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M410323200
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., and Kumar, S. (2021). MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 38, 3022–3027. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
Taylor, K. W., Kim, J.-G., Su, X. B., Aakre, C. D., Roden, J. A., Adams, C. M., et al. (2012). Tomato TFT1 is required for PAMP-triggered immunity and mutations that prevent T3S effector xopN from binding to TFT1 attenuate xanthomonas virulence. PloS Pathog. 8, e1002768. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002768
Topalović, O., Bredenbruch, S., Schleker, A. S. S., and Heuer, H. (2020). Microbes attaching to endoparasitic phytonematodes in soil trigger plant defense upon root penetration by the nematode. Front. Plant Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00138
Virk, N., Liu, B., Zhang, H., Li, X., Zhang, Y., Li, D., et al. (2013). Tomato SlMPK4 is required for resistance against Botrytis cinerea and tolerance to drought stress. Acta Physiol. Plant 35, 1211–1221. doi: 10.1007/s11738-012-1160-2
Wu, J., Wang, J., Pan, C., Guan, X., Wang, Y., Liu, S., et al. (2014). Genome-wide identification of MAPKK and MAPKKK gene families in tomato and transcriptional profiling analysis during development and stress response. PloS One 9, 19–21. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103032
Xu, J. and Zhang, S. (2015). Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in signaling plant growth and development. Trends Plant Sci. 20, 56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.10.001
Yu, X., Feng, B., He, P., and Shan, L. (2017). From chaos to harmony: responses and signaling upon microbial pattern recognition. Annu. Rev. Phytopathology. 55, 109–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev-phyto-080516-035649
Zhang, S., Wang, L., Zhao, R., Yu, W., Li, R., Li, Y., et al. (2018). Knockout of SlMAPK3 reduced disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato plants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 66, 8949–8956. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02191
Zhang, M. and Zhang, S. (2022). Mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades in plant signaling. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 64, 301–341. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13215
Keywords: MAPK, eggplant, Botrytis cinerea, gene family, transcriptomic analysis
Citation: Zhang W, Ming Y and Ji D (2025) Genome-wide identification and transcriptomic analysis of the MAPK family provides insights into the molecular basis of disease resistance of postharvest eggplant in response to Botrytis cinerea. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1680931. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1680931
Received: 06 August 2025; Accepted: 05 September 2025;
Published: 24 September 2025.
Edited by:
Guoxiang Jiang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Zhengke Zhang, Hainan University, ChinaLijuan Chen, Sun Yat-sen University, China
Heng Deng, Southwest University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Ming and Ji. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dongchao Ji, amlkb25nY2hhb0BzZHV0LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Wenxuan Zhang1†
Wenxuan Zhang1† Dongchao Ji
Dongchao Ji