- 1Industrial Crops Institute, Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Wuhan, Hubei, China
- 2Hubei University of Technology/Hubei Key Laboratory of Industrial Microbiology, Wuhan, Hubei, China
Introduction: ALOG genes encode transcription factors that control essential growth and developmental processes in various plant species. The ALOG protein domain, which is highly conserved among land plants, exhibits distinct evolutionary patterns in different plant lineages, suggesting its importance in plant adaptation and evolution. Rosa (roses), a genus of flowering plants with significant horticultural value, exhibits key traits such as floral organ differentiation and inflorescence architecture diversification. Emerging evidence suggests that ALOG genes not only modulate organogenesis but may also drive evolutionary innovations in floral organ morphology and inflorescence complexity.
Methods: We systematically identified ALOG genes in four Rosa genomes (R. chinensis, R. multiflora, R. rugosa, and R. wichurana), reconstructed their phylogenetic relationships, and cloned ALOG homologs from R. chinensis.
Results: Through integrated bioinformatic analyses including chromosomal localization, protein motif characterization, promoter cis-acting element annotation, and spatiotemporal expression profiling, we provide a comprehensive overview of ALOG gene distribution, structure, and expression patterns in Rosa.
Discussion: Our findings provide insights into the potential involvement of Rosa ALOG genes in organogenesis and inflorescence patterning, highlighting their possible roles in the evolution of floral morphology and inflorescence complexity.
1 Introduction
Roses (Rosa spp., Rosaceae), as pivotal species in ornamental horticulture and economic botany, have undergone complex reticulate hybridization events among Rosa lineages (Cui et al., 2022). These evolutionary processes have given rise to modern cultivars that are celebrated for their exceptional floral diversity, characterized by vivid pigmentation patterns and extended flowering phenology (Smulders et al., 2019). In recent years, significant progress has been made in elucidating the molecular mechanisms governing rose flower development, photoperiodic regulation of blooming, and postharvest physiology (Jing et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2024). The release of multiple Rosa genome assemblies has provided a solid foundation for functional genomic studies, facilitating deeper insights into the genetic mechanisms underlying key traits in roses (Hibrand Saint-Oyant et al., 2018; Liang et al., 2025).
Over the past three decades, researchers have identified a conserved protein family across both dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants, initially classified as DUF640 within the Pfam database (Dong et al., 2014; Takanashi et al., 2022; Upadhyaya et al., 2024). This family was subsequently designated the ALOG (Arabidopsis Light-dependent Short Hypocotyls 1 and Oryza Long Sterile Lemma) family, named after LSH1 in Arabidopsis thaliana (Lee et al., 2020) and G1 in Oryza sativa (Yoshida et al., 2009). ALOG/DUF640 proteins are classified as land plant-specific transcription factors (TFs) based on their characteristics including sequence-specific DNA binding, transcriptional regulatory activity, nuclear localization, and the ability to form homodimers (Huang et al., 2024; Iyer and Aravind, 2012). Extensive studies have characterized ALOG genes across the plant kingdom, spanning evolutionarily divergent lineages from bryophytes (Hata et al., 2024; Naramoto et al., 2020; Xiao et al., 2019) to monocotyledonous (Jiang et al., 2024) and eudicotyledonous species (Baranov et al., 2024; Lin et al., 2013; Zirkel et al., 2023). ALOG genes are involved in crucial processes of plant growth and developmental processes, including seedling photomorphogenesis, vegetative and reproductive growth, and abiotic stress responses (Liu et al., 2024; Upadhyaya et al., 2024; Vo Phan et al., 2023). AtLSH1 is the founding member of this gene family and was first characterized in A. thaliana (Zhao et al., 2004). The lsh1-D mutant exhibited light-dependent dominance, mediating photomorphogenic regulation during seedling development. This mutant exhibited hypersensitivity to sustained far-red, blue, and red light spectra, manifesting significantly reduced hypocotyl elongation compared to wild-type counterparts. Rice TAWAWA1 (TAW1) regulates inflorescence architecture by maintaining meristematic indeterminacy, which sustains inflorescence meristem activity while delaying the transition to spikelet meristem identity, thereby modulating panicle branching complexity (Beretta et al., 2023; Yoshida et al., 2013). Additional ALOG members in rice play critical roles in floral organogenesis, where loss-of-function mutations induce homeotic floral abnormalities that directly compromise grain yield (Ma et al., 2013; Peng et al., 2017; Sato et al., 2014). AtLSH8 is a novel positive regulator of the ABA signaling pathway. When its function is lost, Arabidopsis becomes insensitive to ABA treatment, primarily because of altered expression patterns of ABA-responsive proteins in the mutant (Zou et al., 2021).
As research on ALOG genes has advanced, their evolutionary trajectories and roles in plant speciation have become key topics of investigation. When OsG1 is functionally impaired, the morphology of the sterile lemma in rice undergoes significant changes and develops into a structure resembling the lemma in form and size. This phenotype, characterized by an enlarged sterile lemma equivalent to the lemma, naturally occurs in Oryza grandiglumis, and the G1 gene in O. grandiglumis exhibits distinct mutations (Yoshida et al., 2009). The tomato TERMINATING FLOWER (TMF) gene governs inflorescence determinacy through temporal suppression of floral meristem identity genes. The tmf mutant developed solitary-flowered primary inflorescences owing to the precocious activation of ANANTHA (AN) and SEPALLATA3 (SEP3) in vegetative meristems, coupled with a delayed flowering transition. Crucially, experimental modulation of AN expression timing recapitulates diverse inflorescence architectures, suggesting that this regulatory mechanism represents an evolutionary substrate for inflorescence diversification within the Solanaceae (MacAlister et al., 2012). Constitutive expression of AtLSH3 leads to abnormal fusion of the anthers and petals, suggesting that AtLSH3 is a potential modulator of sympetaly, the developmental program underlying fused corolla formation (Cho and Zambryski, 2011). During evolution, to protect flowers from various abiotic stresses, such as rain-induced damage to pollen and nectar, Torenia fournieri has developed a specialized structure known as the corolla neck (Nachev et al., 2017). TfALOG3 has been demonstrated to play a role in the evolutionary development of the corolla neck, as evidenced by its specific expression in the corolla neck and the absence of this structure in the tfalog3 mutant (Xiao et al., 2019). In legumes, which have evolved specialized root nodules, ALOG-domain genes have been shown to play key developmental roles that are not only closely associated with nodulation processes (Ahmad et al., 2024), but also contribute to the establishment of zygomorphic floral symmetry, a defining feature of legume floral architecture (He et al., 2020; Lee et al., 2024; Lei et al., 2019).
Floral morphogenesis and inflorescence patterning are key developmental processes in Rosa; however, the molecular regulators underlying these traits remain largely unexplored. Although ALOG genes are known to regulate reproductive development in diverse plant lineages, their roles in the family Rosaceae have not yet been characterized. We performed a genome-wide identification of ALOG homologs in four Rosa species and cloned the full-length coding sequences (CDSs) of ALOG genes from R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’, referred to as RcLSH genes. We further conducted phylogenetic analysis, gene structure analysis, and motif characterization, as well as investigated the conserved domain organization. Spatiotemporal expression profiling using qPCR revealed different patterns of RcLSH expression across tissues and developmental stages, offering insights into its potential functions in rose organogenesis and inflorescence development.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant materials and conditions
Seedlings of R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’ were generously provided by Professor Guogui Ning from Huazhong Agricultural University, China. The plants were grown in a greenhouse under natural photoperiod conditions, with a relative humidity of 70%–85% and a temperature range of 20–28°C.
Plant samples were collected from various tissues and developmental stages of R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’, including vegetative organs (prickles, leaves, roots, and stems), reproductive organs (0.5cm floral buds, floral receptacle, pedicel, sepals, petals, stamens, pistils, and ovaries from newly opened flowers) and shoot apices at four developmental stages (two-leaf, four-leaf, six-leaf, and eight-leaf stages). All samples were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C until use.
2.2 Identification of ALOG Genes in Rosa
Four publicly available Rosa genomes were used to identify ALOG genes, including R. chinensis, R. wichurana, R. multiflora, and R. rugosa. Candidate ALOG genes were identified using both BLASTP and Hidden Markov Model (HMM) searches. The BLASTP search was conducted in the Rosaceae genome database (Jung et al., 2019), with known ALOG proteins from A. thaliana and O. sativa as queries. In parallel, the HMM profile of the DUF640 domain (PF04852) obtained from the Pfam database was used to perform an HMMER search against annotated Rosa protein sequences. The combined results were further verified to ensure all candidates contained the conserved ALOG domain, and redundant or incomplete sequences were manually curated and removed.
2.3 Cloning of the ALOG gene in R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’
Total RNA was extracted using the RNA extraction kit (Aidlab, China). cDNA was synthesized using PrimeScript RT reagent kit with genomic DNA Eraser (Takara, Japan) from 2 μg of total RNA per sample. To validate the identified genes, gene-specific primers were designed based on the predicted CDS regions. The same primer pairs were used to amplify both the full-length CDS from cDNA and the corresponding genomic sequences (including introns) from genomic DNA. PCR amplification was performed with 2× PrimeSTAR Max Premix (Takara, Japan), a high-fidelity enzyme, and 2 μl of diluted mixture cDNA (1:20) in the PCR system. The PCR products were purified using a DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Aidlab Biotech, China) and cloned into the pMD18-T vector (Takara, Japan). The plasmids were then transformed into E. coli Top 10 via heat shock. For each gene clone, at least three positive clones were selected for sequencing (TSINGKE Biotechnology, China), and sequences with consistent results from two single clones were identified as the accurate gene sequence.
2.4 Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis
Multiple sequence alignment and phylogenetic analyses were performed using MEGA 6.0 (Tamura et al., 2013). A total of 81 ALOG proteins from nine representative species were included: 8 from R. chinensis, 7 from Fragaria vesca, 10 from A. thaliana (Zhao et al., 2004), 10 from O. sativa (Yoshida et al., 2009), 4 from Physcomitrium patens, 11 from Petunia hybrida (Chen et al., 2019), 12 from S. lycopersicum (Turchetto et al., 2023), 7 from T. fournieri (Xiao et al., 2018), and 12 from Lotus japonicus (Lei et al., 2019). Gene nomenclature was obtained from published literature, except for F. vesca.
Amino acid sequences were aligned using the MUSCLE program in MEGA 6.0. Based on the conserved ALOG domain, a maximum likelihood (ML) tree was constructed using the JTT+G+I model with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Additionally, a neighbor-joining (NJ) tree of the LSH genes in the four Rosa species was built using MEGA 6.0, with sequences aligned by MUSCLE, evolutionary distances calculated using the Poisson model, and branch support evaluated with 1,000 bootstrap replicates.
2.5 Bioinformatics analysis of ALOG genes in R. chinensis
We conducted analyses of the biological characteristics of ALOG genes in R. chinensis, including gene structure, motif analysis, promoter cis-acting element analysis, and chromosomal localization. The exon-intron structure of ALOG genes in the four Rosa species was analyzed using the Gene Structure Display Server (Hu et al., 2015). Motifs in RcLSH proteins were predicted using MEME Suite 4.12.0 with the following parameters: Minimum motif width = 6, Maximum motif width = 50, Maximum number of motifs = 20 (Bailey et al., 2009). The promoter regions, defined as 2,000 bp upstream of the start codon of ALOG genes in R. chinensis, were analyzed for cis-acting regulatory elements using the PlantCARE database (Lescot et al., 2002). Identified elements were categorized and visualized using TBtools (Chen et al., 2020). Chromosomal localization was performed using the MG2C online platform (Chao et al., 2021).
2.6 Spatiotemporal expression patterns of ALOG genes in R. chinensis
Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was performed using SYBR Premix Ex Taq (Takara, Japan) on a BIO-RAD CFX384 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, USA). The reaction was conducted in a 10 μL volume with 1 μL of 20× diluted cDNA template, 5 μL of 2× SYBR Green Master Mix, 0.2 μL of forward and reverse primers (10 μmol/μL each), and sterile water to adjust the final volume. The transcription level of RcUBC was used as the reference gene (Song et al., 2023). Each reaction was performed in three biological replicates, and the results were calculated as mean ± standard deviation. The 2−ΔΔCT method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001) was used for data analysis.
3 Results
3.1 Genome-wide identification of ALOG genes in Rosa
Using ALOG protein sequences from A. thaliana and O. sativa as queries, we conducted a genome-wide identification of ALOG homologs across four Rosa species through BLASTP and HMMER searches. Comparative genomic analysis revealed species-specific expansions (Supplementary File 1): eight ALOG genes were identified in R. chinensis, R. rugosa and R. multiflora (RcLSHs, RrLSHs and RmuLSHs), and ten in R. wichurana (RwLSHs). Notably, sequence alignment indicated 100% identity between Rw0G017960 and Rw0G022240 in R. wichurana; thus, only Rw0G017960 was retained for subsequent analyses to avoid redundancy. All identified genes were systematically numbered based on their orthology with Arabidopsis ALOG members (Supplementary File 2).
To validate the predicted coding sequences (CDS) and exon-intron architectures of Rosa ALOG genes, we designed gene-specific primers (Supplementary File 3) and amplified both the CDS and genomic DNA (gDNA) from R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’. All the predicted ALOG genes in R. chinensis were successfully amplified and validated by sequencing (Table 1).
3.2 Sequence characteristics of Rosa ALOG genes
All ALOG genes identified in the four Rosa genomes contained the conserved ALOG domain (Figure 1) but lacked introns, as demonstrated by exon–intron structure analysis (Figure 2). Comparative sequence analysis revealed a remarkable consistency in gene length among species. The CDS length of the ALOG genes ranged from 558 to 750 bp across the four Rosa species, corresponding to proteins of 185–249 amino acids. Notably, all species shared a minimum CDS length of 558 bp (185 aa). The maximum CDS length reached 744 bp (247 aa) in R. chinensis and R. rugosa, while 750 bp (249 aa) in R. wichurana and R. multiflora (Supplementary File 1).

Figure 1. Conserved ALOG domain structure in four Rosa species. The ALOG domain consists of four α-helices, a zinc ribbon insert, and a C-terminal nuclear localization signal (NLS). Residues in black are fully conserved, while purple indicates >75% sequence similarity. Species abbreviations: Rc, R. chinensis; Rmu, R. multiflora; Rw, R. wichurana; Rr, R. rugosa; At, A. thaliana.

Figure 2. Gene structures of ALOG genes in four Rosa species. All genes in R. chinensis (A), R. multiflora (B), R. wichurana (C) and R. rugosa (D) were intronless. Species abbreviations: Rc, R. chinensis; Rmu, R. multiflora; Rw, R. wichurana; Rr, R. rugosa.
3.3 Phylogenetic analysis of RcLSH proteins
To resolve the evolutionary trajectory of ALOG proteins, we constructed a phylogenetic tree using sequences from nine strategically selected species (Supplementary File 4), including P. patens (as a basal bryophyte and the root of evolution), dicotyledons (R. chinensis, A. thaliana, S. lycopersicum, P. hybrida, T. fournieri, L. japonicus, and F. vesca), and a monocot (O. sativa). The inclusion of these taxa, representing distinct evolutionary lineages with varied levels of ALOG gene characterization enabled robust functional inference of Rosa ALOG homologs. Phylogenetic reconstruction of ALOG proteins from the selected species resolved the five well-supported clades (Figure 3). Clade I, which represented the basal group of the phylogenetic tree, contained ALOG proteins from P. patens and O. sativa. Clade II (AtLSH1/2/3/4-like) included representatives of all nine species, suggesting ancestral conservation. Clades III and IV (AtLSH5/6-like) also included ALOG proteins from both monocots and dicots, but with relatively fewer members, which may indicate the loss of this gene subfamily in certain dicot species. In contrast, Clade V (AtLSH7/8/9/10-like), a type of dicot-specific radiation, consisted exclusively of ALOG proteins from dicots. To further elucidate the evolutionary relationships among R. chinensis ALOG proteins, we subdivided the R. chinensis ALOG proteins into eight distinct subgroups (G1–G8), each containing a single ALOG protein from R. chinensis. Specifically, G4 and G8 lack Arabidopsis ALOG orthologs, implying that G4 and G8 may represent a lineage-specific specialization of ALOG proteins.

Figure 3. Phylogenetic analysis of ALOG proteins from nine representative species. 81 ALOG proteins from nine representative species were aligned using MUSCLE in MEGA 6.0. A maximum likelihood (ML) tree was constructed with the JTT+G+I model and 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Branch colors indicate distinct evolutionary clades. ALOG proteins are classified into five major clades and eight subgroups. Species abbreviations: Pp, P. patens; Rc, R. chinensis; At, A. thaliana; Soly, S. lycopersicum; Ph, P. hybrida; Tf, T. fournieri; Lj, L. japonicus; Fves, F. vesca; Os, O. sativa.
3.4 Genomic dynamics and evolutionary trajectories of ALOG genes in Rosa
Genome-wide identification revealed the dynamic evolutionary patterns of ALOG genes across Rosa species, marked by interspecific variations in gene copy numbers and chromosomal distribution patterns (Supplementary File 1). To resolve the lineage-specific diversification mechanisms, we reconstructed a phylogenetic tree using CDS sequences from the four Rosa genomes. This genus-wide phylogeny demonstrates recurrent gene loss and divergence events that shape the extant ALOG repertoires (Figure 4). Notably, LSH4 homologs were exclusively absent in R. multiflora. LSH10b underwent functional diversification in R. multiflora and R. wichuriana, yielding distinct paralogs that were absent in R. chinensis and R. rugosa.
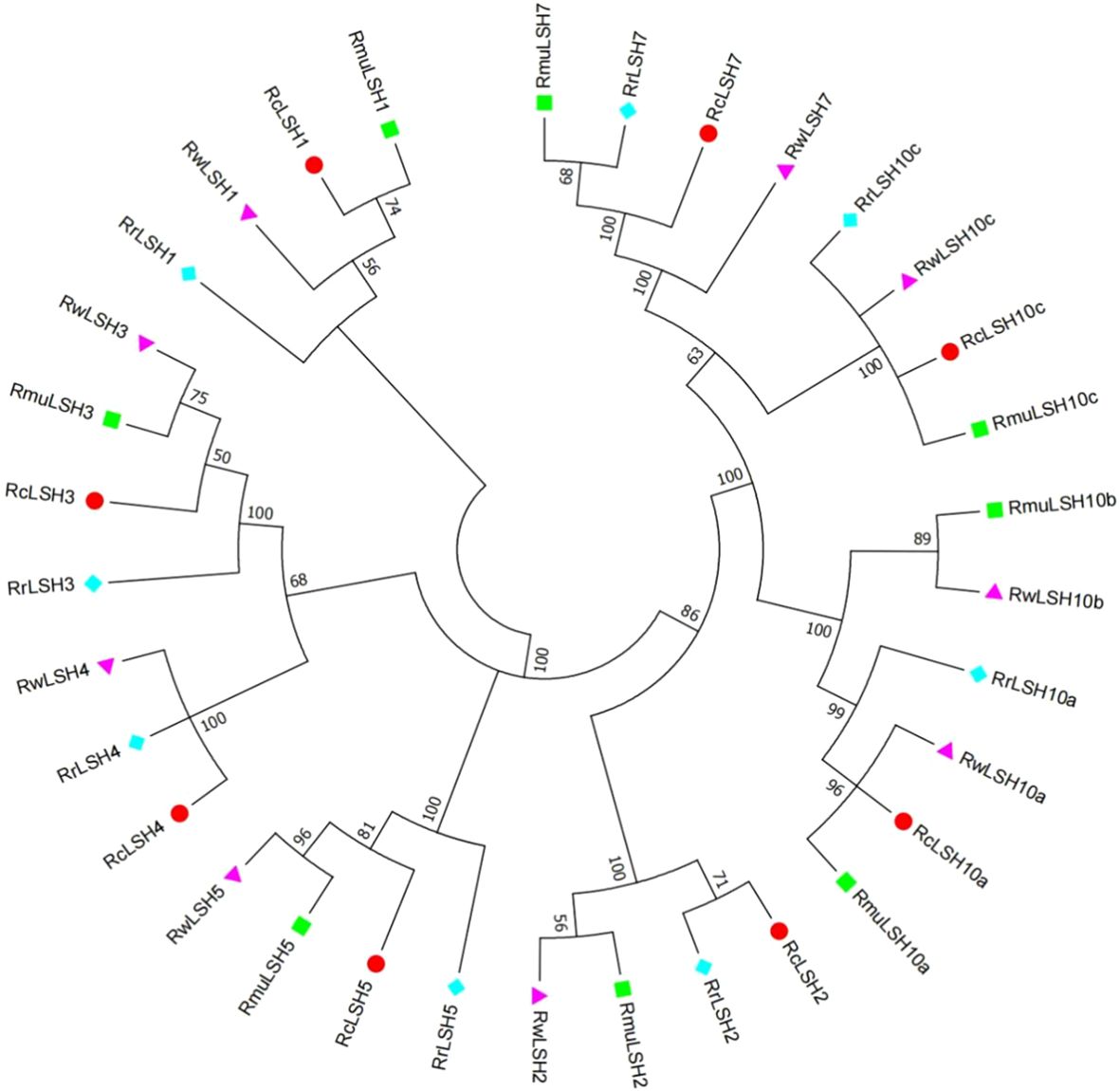
Figure 4. Phylogenetic relationships of ALOG genes among four Rosa species. Full-length CDS sequences of ALOG genes from four Rosa species were aligned using MUSCLE. A neighbor-joining (NJ) tree was generated in MEGA 6.0 with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Species abbreviations: Rc, R. chinensis; Rmu, R. multiflora; Rw, R. wichurana; Rr, R. rugosa.
3.5 Integrative analysis of chromosomal distribution, protein motifs, and regulatory elements
Chromosomal mapping revealed a non-random distribution of RcLSH genes across five of the seven chromosomes in R. chinensis (Figure 5). Notably, chromosome 5 harbored a gene cluster containing four RcLSH paralogs (RcLSH2, RcLSH5, RcLSH7, and RcLSH10c), suggesting potential tandem duplication events. Conserved motif analysis identified three functionally critical motifs within the ALOG domain (Figure 6; Supplementary File 5), that were predicted to mediate DNA-binding and protein interaction activities. Intergroup motif distribution heterogeneity among the eight RcLSH proteins aligned with their phylogenetic classification, reinforcing structure–function conservation within evolutionary subgroups. Profiling of promoter cis-elements identified 15 distinct regulatory elements in the RcLSH promoters (Figure 7; Supplementary File 6; Supplementary Table 1). Light-responsive elements were predominant, whereas hormone- and stress-responsive elements were also present.

Figure 5. Chromosomal distribution of ALOG genes in R. chinensis. Chromosomal positions were extracted from the R. chinensis ‘Old Blush’ reference genome and mapped to chromosomes.

Figure 6. Conserved motif composition of ALOG proteins in R. chinensis. Different colored boxes represent distinct predicted motifs, and the Arabic numerals above the motifs indicate their corresponding motif numbers. Motif analysis was performed in MEME.
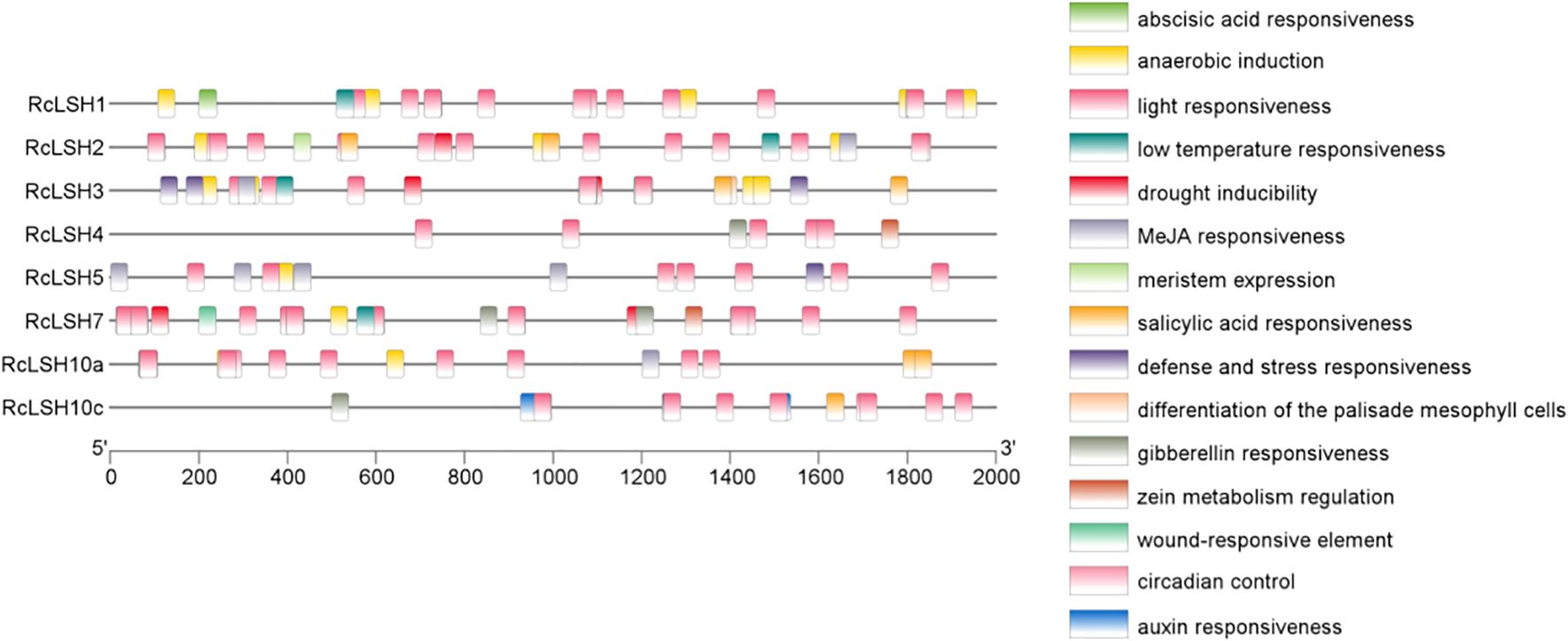
Figure 7. Cis-regulatory element analysis of ALOG gene promoters in R. chinensis. Promoter sequences (2000 bp upstream of the ATG) were extracted from the R. chinensis genome and analyzed with PlantCARE. Cis-elements were grouped by functional category and displayed with TBtools.
3.6 Spatiotemporal expression pattern of ALOG genes in R. chinensis
Gene functionality is closely linked to spatiotemporal expression dynamics. To decipher the biological roles of ALOG genes in R. chinensis, we conducted qRT-PCR analysis across 12 tissue types including prickles, leaves, roots, stems, floral buds, receptacles, pedicels, sepals, petals, stamens, pistils, and samples from different developmental stages shoot apices.
The results revealed distinct expression patterns among different ALOG genes in R. chinensis (Figure 8; Supplementary File 7). RcLSH1 is highly expressed in stems and was also significantly expressed in early stage shoot apices. RcLSH2 was predominantly expressed in prickles, followed by stems, and was notably expressed in early stage shoot apices. RcLSH3 displayed the highest expression in the shoot apices, with transcript levels gradually decreasing as the shoot apex developed. It is also expressed in various floral and vegetative organs, with the highest expression observed in the ovary. RcLSH4 exhibited the highest expression in the stem segments, followed by the prickles; however its expression was significantly up-regulated only during the mid-stage of vegetative growth in shoot apices. RcLSH5 is broadly expressed across different tissues and developmental stages, except in the petals, stamens, and pistils. Notably, the highest expression levels were observed in the ovaries. RcLSH7 was predominantly expressed in roots, stems, and prickles, whereas its expression in other tissues was relatively low. RcLSH10a and RcLSH10c exhibited similar expression patterns, characterized by low expression in floral organs but significant expression in stems, prickles, and the second stage of shoot apex development. These findings suggest that R. chinensis ALOG genes exhibit tissue- and stage-specific expression, indicating their potential roles in organ differentiation, shoot apical meristem development, and reproductive organ formation.

Figure 8. Spatiotemporal expression patterns of ALOG genes in R. chinensis. qRT-PCR was performed using SYBR Premix Ex Taq on a BIO-RAD CFX384 system. RcUBC was used as the reference gene, and expression levels were calculated with the 2−ΔΔCT method. Samples included vegetative tissues (prickles, leaves, roots, stems), reproductive organs (buds, sepals, petals, stamens, pistils, ovaries), floral receptacles, pedicels, and shoot apices at four developmental stages. Expression values were averaged across three replicates. RcLSH1 (A), RcLSH2 (B), RcLSH3 (C), RcLSH4 (D), RcLSH5 (E), RcLSH7 (F), RcLSH10a (G) and RcLSH10c (H).
4 Discussion
In this study, we systematically identified ALOG family members in four Rosa species and constructed a phylogenetic tree using ALOG genes from different species. We cloned R. chinensis genomic and CDS sequences and analyzed their gene structure, chromosomal localization, motif composition, promoter cis-elements, and spatiotemporal expression patterns. These analyses provide important insights into the evolution and potential roles of Rosa ALOG genes in growth and development. However, gene function studies typically rely on stable genetic transformation systems (such as overexpression, downregulation, or even gene knockout) that are not yet well established in Rosa and require lengthy research periods. Therefore, our study not only offers new perspectives on the systematic analysis of ALOG genes in Rosa, but also lays the foundation for identifying genes involved in the development of important traits in Rosa, especially those related to floral and specialized organ development, providing a reference for future functional studies and validation.
Compared with other dicotyledonous plants, the number of ALOG genes in the Rosa genus is moderate. For instance, strawberries, another member of the Rosaceae family, contain seven ALOG genes, whereas both A. thaliana and O. sativa each harbor ten ALOG genes (Iyer and Aravind, 2012; Zhao et al., 2004; Yoshida et al., 2009). Similar to ALOG genes in other species, Rosa ALOG genes possess a highly conserved ALOG domain characterized by four α-helices, a zinc finger insert, and a nuclear localization signal (Chen et al., 2019). These conserved structural features are essential for their role as transcription factors. Interestingly, all ALOG genes identified in Rosa lack introns, which is somewhat distinct from other species where most ALOG genes are intronless, although a few still contain introns (Chen et al., 2019). This observation suggests that the intronless structure of ALOG genes may represent a characteristic evolutionary pattern of this genus. It may also reflect structural conservation and simplification during evolution, potentially contributing to more efficient gene function in plant development. However, further studies are required to elucidate the functional and evolutionary implications of this feature in Rosa. In R. chinensis, ALOG genes were not randomly distributed across all chromosomes; notably, four genes were located on chromosome 5. This clustered arrangement likely reflects tandem duplication events, which may have contributed to the expansion and diversification of ALOG gene function within the genus. Such structural conservation and lineage-specific expansion suggest potential subfunctionalization of ALOG genes in Rosa, which is supported by their diverse expression profiles.
We were particularly interested in exploring the potential biological functions of ALOG genes in Rosa species, as ALOG genes play crucial roles in plant growth and development in other species, especially flower development (Chen et al., 2019; Li et al., 2019; Nan et al., 2018). Given that roses are a well-known ornamental flower, understanding the functions of its ALOG genes is of great significance. In this study, we constructed a phylogenetic tree of ALOG genes in R. chinensis, including species for which ALOG genes have been functionally characterized, except for F. vesca (strawberry), a representative species within the Rosaceae family, to validate the reliability of our phylogenetic analysis. Because gene expression patterns are closely related to gene function, we further analyzed the spatiotemporal expression profiles of Rosa ALOG genes. By integrating the phylogenetic clustering and expression data, we inferred the potential biological roles of these genes in growth and development.
Phylogenetic analysis classified the 81 ALOG proteins from nine different species into five well-defined clades. Clade I formed the basal lineage, exclusively comprising all P. patens ALOG proteins alongside three rice homologs. This topology aligns with broader phylogenetic analyses of 458 ALOG proteins across 61 species, which identified ancestral ALOG lineages encompassing bryophytes and selected monocots (Turchetto et al., 2023). Clades II–V exhibited angiosperm-specific diversification with pronounced lineage specialization.
Clade II comprised three subgroups (G1, G2, and G3) corresponding to the A. thaliana lineages AtLSH1/2/3/4. G1 contains the RcLSH1 gene from R. chinensis. Within this clade, AtLSH1 was the first functionally characterized ALOG involved in hypocotyl development and is regulated by different light qualities (Zhao et al., 2004). AtLSH2 is a homolog of AtLSH1 and exhibits a similar expression pattern. However, the loss of function of both LSH1 and LSH2 does not result in a visible phenotype, suggesting the possible involvement of other homologous genes, such as AtLSH9 in clade G6 (Zhao et al., 2004). The expression patterns and functional characteristics of AtLSH1 and AtLSH9 are highly similar, implying a potential functional redundancy within the ALOG gene family (Press and Queitsch, 2017). Given the highly conserved nature of the ALOG domain, this redundancy may be a common feature among ALOG family members. Therefore, the functional characterization of this gene family likely requires the generation of double or multiple mutants. In contrast, RcLSH1 was significantly expressed in the stems of Rosa and was notably expressed in the shoot apices at different developmental stages. This suggests that RcLSH1 may be involved in stem and shoot apex development, indicating functional divergence from its homolog in Arabidopsis. Similar results were observed for TfALOG1 within the same subgroup, which was highly expressed in flower buds at different stages of T. fournieri. Overexpression of TfALOG1 in T. fournieri leads to the flattening of conical cells in the petals, altered petal morphology, elongation of the yellow region in the petal tube, and changes in leaf coloration. These findings indicate that TfALOG1 plays a critical role in organ development and regulates floral organ formation, which is consistent with its expression patterns (Xiao et al., 2018). LjALOG4 and LjALOG5 were highly expressed in the stem and shoot apical meristems (SAM), similar to the expression pattern observed for RcLSH1 in Rosa. Researchers have focused on the potential roles of LjALOG4/5 in root nodule formation in L. japonicus. Although direct evidence is currently lacking, it is highly likely that LjALOG4/5 are involved in stem, shoot apex, and root nodule development (Lei et al., 2019). Notably, although the expression pattern of RcLSH1 differed from that of AtLSH1, promoter analysis revealed that all RcLSH gene promoters contained numerous light-responsive elements, suggesting that light may play a regulatory role in these genes.
In subgroup G2, AtLSH3 was specifically expressed in the SAM and the lateral organs, predominantly in the boundary regions between these structures. Functional studies have shown that overexpression of AtLSH3 alters petal number and size and leads to petal–stamen fusion, whereas ablation of AtLSH3-expressing cells results in the loss of SAM and lateral organs. The expression patterns and biological functions of AtLSH3 are largely similar to those of AtLSH4 (subgroup G4), and both genes have been proposed to function as suppressors of organ differentiation in the boundary domains (Cho and Zambryski, 2011; Rieu et al., 2024; Takeda et al., 2011). Consistently, RcLSH3 and RcLSH4 in R. chinensis exhibited pronounced expression in the shoot apex, with transcript levels displaying a dynamic pattern: initially low, then markedly elevated, and subsequently declining as the terminal bud progressed. Such temporal variations in expression are likely associated with the transition of the shoot apex from vegetative to reproductive growth, a process that is also well-characterized in tomatoes. In tomato, the TMF gene (subgroup G4) plays a crucial role in modulating the inflorescence architecture by repressing the activity of the inflorescence meristem, primarily through the regulation of its downstream gene AN.
Furthermore, several ALOG genes in tomato, including TFAM2 (SolyLSH1a) in G1, TFAM3 (SolyLSH3b) and TFAM11 (SolyLSH3a) in G2, and TFAM1 (SolyLSH2) in G4 exhibited expression dynamics comparable to TMF in the SAM. Both TFAM1 and TFAM2 have been demonstrated to interact directly with TMF to form heterodimers. These homologous and heterologous interactions among TMF, TFAM1, and TFAM2 suggest the existence of ALOG transcriptional complexes that act cooperatively to regulate shoot and early floral meristem development (MacAlister et al., 2012; Xu et al., 2016; Lippman, 2018). Notably, TFAM3 has been shown to participate in inflorescence development, whereas TFAM11 does not contribute to this process (Huang et al., 2022). Given these insights, it is reasonable to hypothesize that ALOG genes in roses play conserved yet diverse roles in regulating floral transition and inflorescence development. In support of this, we observed that RcLSH1 (G1), RcLSH4 (G3), RcLSH2 (G4), RcLSH10a (G7), and RcLSH10c (G8) displayed dynamic expression patterns at the shoot apex similar to those reported in tomatoes. Therefore, we propose that these RcLSHs are potential regulators of inflorescence architecture in roses, which warrants further functional characterization.
Clade III was characterized by the absence of A. thaliana and L. japonicus ALOG proteins. This unique lineage, corroborated by independent studies (Chen et al., 2019; Xiao et al., 2018), provides evidence of late duplication events of ALOG genes within Brassicaceae and Fabaceae. Within this clade, RcLSH2 exhibited significant expression not only in the shoot apex but also in the prickles of R. chinensis. The prickles of Rosa species represent evolutionarily specialized epidermal structures that have emerged as adaptive morphological innovations in response to environmental pressures (Zhang et al., 2024). These structures may share developmental and evolutionary connections with the ALOG-domain genes. The potential role of RcLSH2 in prickle development warrants functional validation through experimental approaches such as mutant analysis or transgenic studies. Considering the expression pattern of RcLSH2 and the fact that this subgroup also includes three rice ALOG genes—OsG1, OsG1L1 and OsG1L2—that are involved in floral organ and inflorescence development (Beretta et al., 2023; Yoshida et al., 2009), we hypothesized that RcLSH2 participates in the regulation of both inflorescence and prickle development in roses. The putative involvement of RcLSH2 in prickle formation may represent a possible neofunctionalization event within Rosa, whereby ALOG genes have been recruited into novel epidermal developmental pathways.
Clade IV contained RcLSH5 (G5), which was expressed in most tissues, with the highest expression levels in ovules, suggesting a potential role in seed development. Within the same group, TfALOG2 from T. fournieri showed high expression in leaves. Ectopic expression of TfALOG2 results in abnormal leaf development, where mesophyll cells fail to form properly at the leaf margins, indicating that TfALOG2 regulates leaf morphogenesis, which is consistent with its strong expression in leaf tissue. Moreover, 35S:TfALOG2 transgenic plants exhibited no floral phenotype compared to the wild-type, suggesting that TfALOG2 may specifically regulate leaf development (Xiao et al., 2018).
In Clade V, RcLSH7 (G6) was highly expressed in the roots, stems, and prickles. Similarly, its homologs, PhLSH7a and PhLSH7b, were predominantly expressed in the seeds of P. hybrida. However, only PhLSH7b, when ectopically expressed in Arabidopsis, strongly suppressed fruit development, implying a functional divergence between the two homologs (Chen et al., 2019). RcLSH10a (G7) and RcLSH10c (G8) exhibited similar dynamic expression patterns in shoot apices and were also strongly expressed in prickles, stems, and receptacles, suggesting that these genes may have similar biological functions in regulating organ growth and differentiation in these tissues. However, due to the lack of experimentally validated functional evidence from homologous genes, the specific roles of RcLSH10a and RcLSH10c remain uncertain and require further characterization.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
FC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. CG: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JL: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. FX: Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Hubei Provincial Technology Innovation Program Project (2024BBB022); Hubei Provincial International Scientific and Technological Cooperation Project (2024EHA022); Wuhan Knowledge Innovation Special Program-Basic Research Project (202302020101010141); Open Fund of Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Industrial Microbiology (202209KF10); Open Fund of Hubei Provincial Engineering Research Center for Specialty Flower Biological Breeding (2023ZD001); Youth Foundation Project of Hubei Academy of Agricultural Sciences (2024NKYJJ07).
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Professor Guogui Ning of Huazhong Agricultural University for generously providing the rose plant materials used in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The authors also wish to disclose that the manuscript was linguistically polished with the assistance of OpenAI’s ChatGPT (GPT-4) language model.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1690365/full#supplementary-material
References
Ahmad, M. Z., Ahmad, B., Nasir, J. A., Jamil, A., Ali, S., Gul, A., et al. (2024). Genome wide and evolutionary analysis of ALOG gene family and its role during seed development and nodulation in response to rhizobium in soybean. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 72, 5033–5050. doi: 10.1007/s10722-024-02239-1
Bailey, T. L., Boden, M., Buske, F. A., Frith, M., Grant, C. E., Clementi, L., et al. (2009). MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W202–W208. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp335
Baranov, D., Dolgov, S., and Timerbaev, V. (2024). New advances in the study of regulation of tomato flowering-related genes using biotechnological approaches. Plants (Basel). 13, 359. doi: 10.3390/plants13030359
Beretta, V. M., Franchini, E., Ud Din, I., Lacchini, E., Van den Broeck, L., Sozzani, R., et al. (2023). The ALOG family members OsG1L1 and OsG1L2 regulate inflorescence branching in rice. Plant J. 115, 351–368. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16229
Chao, J., Li, Z., Sun, Y., Aluko, O. O., Wu, X., Wang, Q., et al. (2021). MG2C: a user-friendly online tool for drawing genetic maps. Mol. Hortic. 1, 16. doi: 10.1186/s43897-021-00020-x
Chen, C., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H. R., Frank, M. H., He, Y., et al. (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 13, 1194–1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen, F., Zhou, Q., Wu, L., Li, F., Liu, B., Zhang, S., et al. (2019). Genome-wide identification and characterization of the ALOG gene family in Petunia. BMC Plant Biol. 19, 600. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2127-x
Cho, E. and Zambryski, P. C. (2011). ORGAN BOUNDARY1 defines a gene expressed at the junction between the shoot apical meristem and lateral organs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108, 2154–2159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1018542108
Cui, W. H., Du, X. Y., Zhong, M. C., Fang, W., Suo, Z. Q., Wang, D., et al. (2022). Complex and reticulate origin of edible roses (Rosa, Rosaceae) in China. Hortic. Res. 9, uhab051. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhab051
Dong, X., Lee, J., Nou, I.-S., and Hur, Y. (2014). Expression characteristics of LSH genes in Brassica suggest their applicability for modification of leaf morphology and the use of their promoter for transgenesis. Plant Breed. Biotech. 2, 126–138. doi: 10.9787/PBB.2014.2.2.126
Hata, Y., Ohtsuka, J., Hiwatashi, Y., Naramoto, S., and Kyozuka, J. (2024). Cytokinin and ALOG proteins regulate pluripotent stem cell identity in the moss Physcomitrium patens. Sci. Adv. 10, eadq6082. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adq6082
He, L., Lei, Y., Li, X., Peng, Q., Liu, W., Jiao, K., et al. (2020). SYMMETRIC PETALS 1 encodes an ALOG domain protein that controls floral organ internal asymmetry in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 4060. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114060
Hibrand Saint-Oyant, L., Ruttink, T., Hamama, L., Kirov, I., Lakhwani, D., Zhou, N. N., et al. (2018). A high-quality genome sequence of Rosa chinensis to elucidate ornamental traits. Nat. Plants. 4, 473–484. doi: 10.1038/s41477-018-0166-1
Hu, B., Jin, J., Guo, A. Y., Zhang, H., Luo, J., and Gao, G. (2015). GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31, 1296–1297. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Huang, H., Lin, M., Sun, L., Wang, R., Li, Y., and Qi, X. (2024). Screening and identification of photoresponse factors in kiwifruit (Actinidia arguta) development. Mol. Biol. Rep. 51, 112. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-09073-1
Huang, X., Xiao, N., Zou, Y., Xie, Y., Tang, L., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Heterotypic transcriptional condensates formed by prion-like paralogous proteins canalize flowering transition in tomato. Genome Biol. 23, 78. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02646-6
Iyer, L. M. and Aravind, L. (2012). ALOG domains: provenance of plant homeotic and developmental regulators from the DNA-binding domain of a novel class of DIRS1-type retroposons. Biol. Direct. 7, 39. doi: 10.1186/1745-6150-7-39
Jiang, G., Koppolu, R., Rutten, T., Hensel, G., Lundqvist, U., Tandron Moya, Y. A., et al. (2024). Non-cell-autonomous signaling associated with barley ALOG1 specifies spikelet meristem determinacy. Curr. Biol. 34, 2344–2358. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.04.083
Jing, W., Gong, F., Liu, G., Deng, Y., Liu, J., Yang, W., et al. (2023). Petal size is controlled by the MYB73/TPL/HDA19-miR159-CKX6 module regulating cytokinin catabolism in Rosa hybrida. Nat. Commun. 14, 7106. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42914-y
Jung, S., Lee, T., Cheng, C. H., Buble, K., Zheng, P., Yu, J., et al. (2019). 15 years of GDR: New data and functionality in the Genome Database for Rosaceae. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, D1137–D1145. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1000
Lee, M., Dong, X., Song, H., Yang, J. Y., Kim, S., and Hur, Y. (2020). Molecular characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana LSH1 and LSH2 genes. Genes Genomics 42, 1151–1162. doi: 10.1007/s13258-020-00985-x
Lee, T., Orvosova, M., Batzenschlager, M., Bueno Batista, M., Bailey, P. C., Mohd-Radzman, N. A., et al. (2024). Light-sensitive short hypocotyl genes confer symbiotic nodule identity in the legume Medicago truncatula. Curr. Biol. 34, 825–840. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2024.01.018
Lei, Y., Su, S., He, L., Hu, X., and Luo, D. (2019). A member of the ALOG gene family has a novel role in regulating nodulation in Lotus japonicus. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 61, 463–477. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12711
Lescot, M., Dehais, P., Thijs, G., Marchal, K., Moreau, Y., Van de Peer, Y., et al. (2002). PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 325–327. doi: 10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Li, N., Wang, Y., Lu, J., and Liu, C. (2019). Genome-wide identification and characterization of the ALOG domain genes in rice. Int. J. Genomics 2019, 2146391. doi: 10.1155/2019/2146391
Liang, Z., Miao, J., Deng, H., Jiao, R., Li, L., Li, S., et al. (2025). A chromosomal-scale reference genome for Rosa hugonis. Sci. Data. 12, 272. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-04526-7
Lin, T., Sharma, P., Gonzalez, D. H., Viola, I. L., and Hannapel, D. J. (2013). The impact of the long-distance transport of a BEL1-like messenger RNA on development. Plant Physiol. 161, 760–772. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.209429
Lippman, B. (2018). Control of flowering and inflorescence architecture in tomato bysynergistic interactions between ALOG transcription factors. J. Genet. Genomics 45, 557–560. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2018.03.008
Liu, Z., Fan, Z., Wang, L., Zhang, S., Xu, W., Zhao, S., et al. (2024). Expression profiling of ALOG family genes during inflorescence development and abiotic stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Front. Genet. 15. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1381690
Livak, K. J. and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2–ΔΔCT method. Methods 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu, J., Zhang, G., Ma, C., Li, Y., Jiang, C., Wang, Y., et al. (2024). The F-box protein RhSAF destabilizes the gibberellic acid receptor RhGID1 to mediate ethylene-induced petal senescence in rose. Plant Cell. 36, 1736–1754. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae035
Ma, X., Cheng, Z., Wu, F., Jin, M., Zhang, L., Zhou, F., et al. (2013). BEAK LIKE SPIKELET1 is required for lateral development of lemma and palea in rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 31, 98–108. doi: 10.1007/s11105-012-0480-0
MacAlister, C. A., Park, S. J., Jiang, K., Marcel, F., Bendahmane, A., Izkovich, Y., et al. (2012). Synchronization of the flowering transition by the tomato TERMINATING FLOWER gene. Nat. Genet. 44, 1393–1398. doi: 10.1038/ng.2465
Nachev, V., Stich, K. P., Winter, C., Bond, A., Kamil, A., and Winter, Y. (2017). Cognition-mediated evolution of low-quality floral nectars. Science 355, 75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.aah4219
Nan, W., Shi, S., Jeewani, D. C., Quan, L., Shi, X., and Wang, Z. (2018). Genome-wide identification and characterization of wALOG family genes involved in branch meristem development of branching head wheat. Genes (Basel). 9, 510. doi: 10.3390/genes9100510
Naramoto, S., Hata, Y., and Kyozuka, J. (2020). The origin and evolution of the ALOG proteins, members of a plant-specific transcription factor family, in land plants. J. Plant Res. 133, 323–329. doi: 10.1007/s10265-020-01171-6
Peng, P., Liu, L., Fang, J., Zhao, J., Yuan, S., and Li, X. (2017). The rice TRIANGULAR HULL1 protein acts as a transcriptional repressor in regulating lateral development of spikelet. Sci. Rep. 7, 13712. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14146-w
Press, M. O. and Queitsch, C. (2017). Variability in a short tandem repeat mediates complex epistatic interactions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 205, 455–464. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.193359
Rieu, P., Beretta, V. M., Caselli, F., Thevenon, E., Lucas, J., Rizk, M., et al. (2024). The ALOG domain defines a family of plant-specific transcription factors acting during Arabidopsis flower development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 121, e2310464121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2310464121
Sato, D. S., Ohmori, Y., Nagashima, H., Toriba, T., and Hirano, H. Y. (2014). A role for TRIANGULAR HULL1 in fine-tuning spikelet morphogenesis in rice. Genes Genet. Syst. 89, 61–69. doi: 10.1266/ggs.89.61
Smulders, M. J. M., Arens, P., Bourke, P. M., Debener, T., Linde, M., Riek, J., et al. (2019). In the name of the rose: a roadmap for rose research in the genome era. Hortic. Res. 6, 65. doi: 10.1038/s41438-019-0156-0
Song, J., Chen, F., Lv, B., Guo, C., Yang, J., Huang, L., et al. (2023). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the TIR-NBS-LRR gene family and its response to fungal disease in rose (Rosa chinensis). Biol. (Basel). 12, 426. doi: 10.3390/biology12030426
Takanashi, H., Kajiya-Kanegae, H., Nishimura, A., Yamada, J., Ishimori, M., Kobayashi, M., et al. (2022). DOMINANT AWN INHIBITOR encodes the ALOG protein originating from gene duplication and inhibits AWN elongation by suppressing cell proliferation and elongation in Sorghum. Plant Cell Physiol. 63, 901–918. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcac057
Takeda, S., Hanano, K., Kariya, A., Shimizu, S., Zhao, L., Matsui, M., et al. (2011). CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON1 transcription factor activates the expression of LSH4 and LSH3, two members of the ALOG gene family, in shoot organ boundary cells. Plant J. 66, 1066–1077. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04571.x
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., and Kumar, S. (2013). MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 30, 2725–2729. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197
Turchetto, C., Silverio, A. C., Waschburger, E. L., Lacerda, M. E. G., Quintana, I. V., and Turchetto-Zolet, A. C. (2023). Genome-wide identification and evolutionary view of ALOG gene family in Solanaceae. Genet. Mol. Biol. 46, e20230142. doi: 10.1590/1415-4757-GMB-2023-0142
Upadhyaya, G., Sethi, V., Modak, A., and Gangappa, S. N. (2024). ALOG/LSHs: a novel class of transcription factors that regulate plant growth and development. J. Exp. Bot. 76, erae409. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae409
Vo Phan, M. S., Keren, I., Tran, P. T., Lapidot, M., and Citovsky, V. (2023). Arabidopsis LSH10 transcription factor and OTLD1 histone deubiquitinase interact and transcriptionally regulate the same target genes. Commun. Biol. 6, 58. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-04424-x
Xiao, W., Su, S., Higashiyama, T., and Luo, D. (2019). A homolog of the ALOG family controls corolla tube differentiation in Torenia fournieri. Development 146, dev177410. doi: 10.1242/dev.177410
Xiao, W., Ye, Z., Yao, X., He, L., Lei, Y., Luo, D., et al. (2018). Evolution of ALOG gene family suggests various roles in establishing plant architecture of Torenia fournieri. BMC Plant Biol. 18, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12870-018-1431-1
Xu, C., Park, S. J., Van Eck, J., and Lippman, Z. B. (2016). Control of inflorescence architecture in tomato by BTB/POZ transcriptional regulators. Genes Dev. 30, 2048–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.288415.116
Yoshida, A., Sasao, M., Yasuno, N., Takagi, K., Daimon, Y., Chen, R., et al. (2013). TAWAWA1, a regulator of rice inflorescence architecture, functions through the suppression of meristem phase transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, 767–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1216151110
Yoshida, A., Suzaki, T., Tanaka, W., and Hirano, H. Y. (2009). The homeotic gene long sterile lemma (G1) specifies sterile lemma identity in the rice spikelet. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 106, 20103–20108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907896106
Zhang, Y., Zuo, M., Li, R., Huang, J., Cheng, W., Shi, C., et al. (2024). Morphology, structure and development of glandular prickles in the genus Rosa. Scientia Horticulturae. 326, 112763. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2023.112763
Zhao, L., Nakazawa, M., Takase, T., Manabe, K., Kobayashi, M., Seki, M., et al. (2004). Overexpression of LSH1, a member of an uncharacterized gene family, causes enhanced light regulation of seedling development. Plant J. 37, 694–706. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.2003.01993.x
Zirkel, J., Hulse-Kemp, A. M., and Storm, A. R. (2023). Gossypium hirsutum gene of unknown function, Gohir.A02G039501.1, encodes a potential DNA-binding ALOG protein involved in gene regulation. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000670
Keywords: rose, ALOG domain gene, phylogenetic relationships, bioinformatics characteristics, expression patterns, gene function
Citation: Chen F, Lv B, Guo J, Song J, Guo C, Yang J, Lin J, Yang Y and Xiang F (2025) Genome-wide identification and characterization of ALOG domain genes in Rosa. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1690365. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1690365
Received: 21 August 2025; Accepted: 30 October 2025;
Published: 20 November 2025.
Edited by:
Jiedan Chen, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Aminu Shehu Abubakar, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaQiong Wang, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences (JAAS), China
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Lv, Guo, Song, Guo, Yang, Lin, Yang and Xiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fayun Xiang, eGZ5MzIzQGhiYWFzLmFjLmNu; Jianguo Lin, Smlhbmd1b2xpbkBoYnV0LmVkdS5jbg==; Yuanyuan Yang, eWFuZ3l5QGhiYWFzLmFjLmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Feng Chen
Feng Chen Bo Lv1†
Bo Lv1† Jurong Song
Jurong Song Cong Guo
Cong Guo Fayun Xiang
Fayun Xiang