- 1Department of Horticulture, College of Agriculture, Shihezi University, Shihezi, Xinjiang, China
- 2Key Laboratory of Special Fruits and Vegetables Cultivation Physiology and Germplasm Resources Utilization of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, Department of Horticulture, College of Agriculture, Shihezi University, Shihezi, Xinjiang, China
- 3Department of Horticulture, College of Agriculture, Minia University, El-Minya, Egypt
Introduction: Hydrogen-rich water (HRW) plays a crucial role in regulating plant growth and development. However, its potential involvement in modulating photosynthetic pigments, chlorophyll fluorescence (ChlF) parameters, antioxidant enzyme activities, and fruit ripening in (Vitis vinifera L.) ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes grown in a greenhouse remain unclear.
Methods: This study aimed to investigate the effects of HRW irrigation at a concentration of 1.0 mg L-1 on chlorophyll pigments, ChlF parameters, enzymatic antioxidant activities, and fruit quality.
Results: HRW irrigation induced a significant increase in carotenoid (Car) content, which was observed only on the first day after irrigation. It also significantly enhanced chlorophyll a (Chl a) and chlorophyll b (Chl b) contents, as well as ChlF parameters such as maximum quantum efficiency of photosystem II (Fv/Fm), and the photochemical quantum yield of PSII (ΦPSII), while non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) decreased, indicating enhanced PSII functionality and photosynthetic performance. Antioxidant enzyme activities, including superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), and catalase (CAT), were also enhanced, reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) accumulation and maintaining ROS homeostasis in grapevine leaves. HRW treatment promoted the accumulation of secondary metabolites such as total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), total anthocyanin content (TAC), and Car, which contributed to an improved color index of red grapes (CIRG). Additionally, fruit quality was improved by increasing total soluble solids (TSS), soluble sugars, and pH, while reducing fruit firmness and titratable acidity (TA). Berry weight and overall yield were also enhanced compared with control plants.
Discussion: These results demonstrate that HRW is a promising and sustainable approach for enhancing photosynthetic performance, antioxidant defense, secondary metabolite accumulation, and fruit quality in greenhouse-grown ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes, providing a practical basis for improving grape cultivation and production.
1 Introduction
Hydrogen gas (H2) is a sustainable energy source that reduces carbon emissions and promotes green energy (Kamshybayeva et al., 2024). H2, the most abundant element in the universe, is a small, and colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas capable of easily diffusing through cell membranes (Russell et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2023; Li et al., 2022a). It participates in atmospheric redox reactions, mainly from methane oxidation and volatile organics (Zgonnik, 2020). Produced by bacteria, algae, and plants via hydrogenases and nitrogenases (Li et al., 2022a), H2 is also released by rhizobia during nitrogen fixation (Xu et al., 2023). Although H2 treatments in crops have been shown to improve both yield and quality, its gaseous form presents challenges for practical application (Russell et al., 2020; Hu et al., 2021). Being lighter than air, H2 is difficult to retain under field conditions, making direct gaseous application impractical. Additionally, its high flammability limits its use at significant concentrations due to safety and storage concerns. A more feasible method involves using saturated forms of H2, such as HRW. Which can be directly applied to plants either through foliar spraying or soil drenching with water as demonstrated in previous (Wu et al., 2020b). HRW is commonly prepared using several techniques. One involves dissolving magnesium-based tablets in water; however, this approach may introduce residual by-products into the solution. Alternatively, HRW can be generated by bubbling or pumping H2 gas into distilled water or other irrigation media using hydrogen generators. The prepared solution can then be diluted to the desired concentration for treatment (Zulfiqar et al., 2021). HRW suppresses ROS by lowering redox potential, creating a more reducing environment that favors electron donation and directly scavenges radicals such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anions (O2•-), while simultaneously enhancing antioxidant enzyme activities and modulating gene expression to restore cellular redox balance. This integrates redox-driven reactions with enzymatic and genetic defenses, thereby mitigating oxidative stress and enhancing plant resilience (Franceschelli et al., 2016; Qazi, 2022; Ding et al., 2024a). Due to its unique climatic conditions and light-heat resources, Xinjiang Province has contributed significantly to grape culture development in China, accounting for 19% of the planting area and 24% of total grape output nationally (Cheng et al., 2021). Although Xinjiang remains a prominent agricultural region due to its sunlight-rich environment and advanced irrigation practices, sustaining long-term crop productivity and fruit quality under its intensive cultivation systems necessitates a shift toward more physiologically informed strategies (Wang et al., 2018; Han et al., 2024).
Because these antioxidant mechanisms are closely linked to photosynthetic stability, it becomes essential to monitor the functional performance of the photosynthetic apparatus under fluctuating conditions. In this context, the measurement of ChlF is a non-invasive technique used to assess the activity of photosystem II (PSII), offering valuable insights into plant responses to environmental changes, photosynthetic mechanisms, and growth (Pashkovskiy et al., 2018). This method involves high-frequency measurements using a fluorometer, where dark-adapted leaves are exposed to brief pulses of actinic light (Rochaix, 2011). The resulting fluorescence kinetics provide crucial information on parameters such as Fv/Fm, ΦPSII, the photochemical quenching coefficient (qP), the electron transport rate (ETR), and NPQ, which are fundamental for assessing light utilization efficiency in photosynthesis (Chen et al., 2021; Mvondo-She et al., 2024). These physiological indicators not only reflect the plant’s ability to cope with oxidative stress but also serve as a basis for evaluating the efficacy of agronomic interventions aimed at enhancing plant resilience. In this regard, as plants become increasingly vulnerable to both biotic and abiotic stresses, researchers are turning toward more environmentally sustainable approaches to improve productivity and fruit quality without exacerbating ecological burdens.
Under normal conditions, ROS are byproducts of essential metabolic processes, including respiration, photosynthesis, and photorespiration. However, under stress conditions, molecules such as O2•- and •H2O2 are overproduced (Yun et al., 2021). Excessive ROS accumulation, particularly under environmental stress or during senescence, can cause oxidative damage (Ali et al., 2024). To mitigate the adverse effects of these reactive molecules, plants activate specialized enzymatic defense systems that safeguard cellular function, including POD, SOD, CAT, and polyphenol oxidase (PPO), which regulate redox homeostasis and are crucial for delaying senescence and maintaining cellular integrity (Karimi et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2025).
Accordingly, grapevine (Vitis vinifera) has garnered particular attention due to its economic importance as a horticultural crop, its sensitivity to environmental stressors, and its deep-rooted association with human civilization. This species belongs to the Vitaceae family and includes two main subspecies, depending on their mode of reproduction and whether they are cultivated or wild: the wild grapevine (Vitis vinifera ssp. sylvestris), which continues to thrive in woodland ecosystems extending from Western Europe and North Africa to regions near the Himalayas, and the domesticated (Vitis vinifera ssp. vinifera, or sativa), which originated along river valleys across North America, Europe, and Asia. It is an adaptable fruit shrub that grows in hot tropical, subtropical, and temperate climates, and in a variety of soil types (Rodriguez-Izquierdo et al., 2024). Grapes rank second globally among fruit crops in terms of cultivated area and yield, following citrus (Estrada et al., 2021). They are cultivated on approximately 7.1 million hectares, yielding about 28.39 million metric tons annually, with China ranking third globally, managing around 753,000 hectares of vineyards in 2024 (OIV, 2025). Northwestern China, with long sunshine hours, sufficient light, and large diurnal temperature differences, is an excellent production area for grapes (Liang et al., 2014; Liu et al., 2025).
Within this context, ‘Flame Seedless’ has emerged as one of the most prominent and widely cultivated table grape cultivars. It is highly popular among consumers and is recognized for its seedlessness, early ripening, compact clusters, uniform berry size, and attractive bright red coloration, which is further enhanced by its elevated TAC. Moreover, it is noted for its crisp peel, juicy pulp, and distinctive flavor (Lo’ay and El-Boray, 2018; Abdel-Sattar et al., 2022). Despite these desirable characteristics, sustaining optimal productivity and fruit quality necessitates a thorough understanding of its physiological and biochemical requirements. ‘Flame Seedless’ is particularly sensitive to environmental factors such as light intensity, water availability, and temperature, all of which substantially influence photosynthetic efficiency, antioxidant activity system, and expression of defense-related genes (Lecourieux et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2022; Pei et al., 2023).
Although greenhouse cultivation provides a relatively controlled environment, microclimatic fluctuations, high planting density, and other cultivation-related stresses can still compromise photosynthetic performance, redox homeostasis, pigment stability, and overall fruit quality. Consequently, interventions that enhance intrinsic physiological and biochemical resilience are valuable even under greenhouse conditions. HRW has been demonstrated to regulate antioxidant enzyme activities, maintain ROS homeostasis, stabilize chlorophyll and PSII function, and optimize energy metabolism (Yu et al., 2023; Ferrandino et al., 2023; Dinis et al., 2024; Yu et al., 2024; Akbar et al., 2025).Moreover, HRW application can improve preharvest fruit attributes, including firmness, TSS, soluble sugars, and coloration, while reducing TA and promoting accumulation of secondary metabolites, thereby mitigating postharvest deterioration (Dong et al., 2023; Yao et al., 2024).
Despite extensive reports on HRW efficacy in laboratory and open-field conditions, its impact on greenhouse-grown ‘Flame Seedless’ grapevines remain inadequately characterized. Evaluating HRW under greenhouse conditions is essential to elucidate its potential as a practical agronomic strategy for enhancing physiological performance and fruit quality within relatively controlled cultivation systems. Accordingly, this study aims to investigate the effects of preharvest HRW application via subsurface drip irrigation on antioxidant enzyme activities, ChlF, and fruit quality of greenhouse-grown ‘Flame Seedless’ grapevines.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant material and treatments
The grape ‘Flame Seedless’ was treated in the greenhouse at the Shihezi University Base, Xinjiang, China (45°20′N, 86°03′E) from June 2023 to August 2024. To investigate the effects of HRW on grape fruit quality, ChlF, enzymatic antioxidants, and microbial communities, the treatments were arranged as follows:
1. HRW treatment at a concentration of 1.0 mg L-1 according to previous studies (Li et al., 2022b).
2. Control (water without adding H2 gas).
The greenhouse soil was sandy, with the following basic physical and chemical properties: pH 7.21, organic matter content 13.67 g·kg-1, total nitrogen 0.38 g·kg-1, rapidly available phosphorus 25.6 mg·kg-1, and rapidly available potassium 21.3 mg·kg-1. Grapevines were planted in 2018, and the vineyard was organized with vertical trellises oriented east and the grape rows in a north-south direction. Cement upright pillars were erected at two ends of each grape tree row. Four galvanized iron wires were laid on the pillars, and the trellis was approximately 1.5 m. Each row contained five grape plants with a row spacing of 2.5 m and a plant spacing of 0.8 m. During winter pruning, six fertile branches were maintained on each grape tree. All grape plants were irrigated and fertilized with Hoagland nutrient solution at 1 g/L (pH 5.8, 25°C; Coolaber Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) through an underground drip irrigation system. HRW was produced using a generator (HT-500; Beijing Zhonghuipu Analytical Technology Research Institute, Beijing, China). High-purity H2 gas (99.999% [v/v]) from the generator was infused into a 50 L plastic tank for 4 hours at a flow rate of 500 mL min-1. The container was completely filled and tightly sealed to prevent H2 loss and to enhance its dissolution in water. The concentration of dissolved H2 was approximately 1.0 mg L-1, measured using a portable dissolved H2 meter (ENH-2000; TRUSTLEX, Osaka, Japan) calibrated via gas chromatography. The residence time of H2 in the above water was more than 12 h. Once produced, HRW was piped to the trees for subsurface drip irrigation (flow rate: 4 L/h, eight drippers per grapevine) (Figure 1). HRW or water (control) was applied via subsurface drip irrigation every three days. Each grapevine received 10 liters of solution per irrigation event, delivered through the drippers at a constant flow rate. This irrigation frequency and volume were maintained consistently throughout the treatment period from June 30 (30 days after flowering) to August 10, 2024. Each treatment included six biological replicates, with one grapevine per replicate, uniformly selected based on similar growth status. Measurements were taken at four key intervals: 44, 54, 64, and 74 days after full bloom (DB44, DB54, DB64, and DB74, respectively) to estimate fruit quality traits. Additionally, measurements were conducted on the 1st, 4th, and 7th days of the same irrigation cycle (DI1, DI4, and DI7, respectively) to assess ChlF parameters and chlorophyll pigments in leaves. On the final day of the experiment (August 10), cluster and berry weights, and leaf antioxidant enzyme activity.
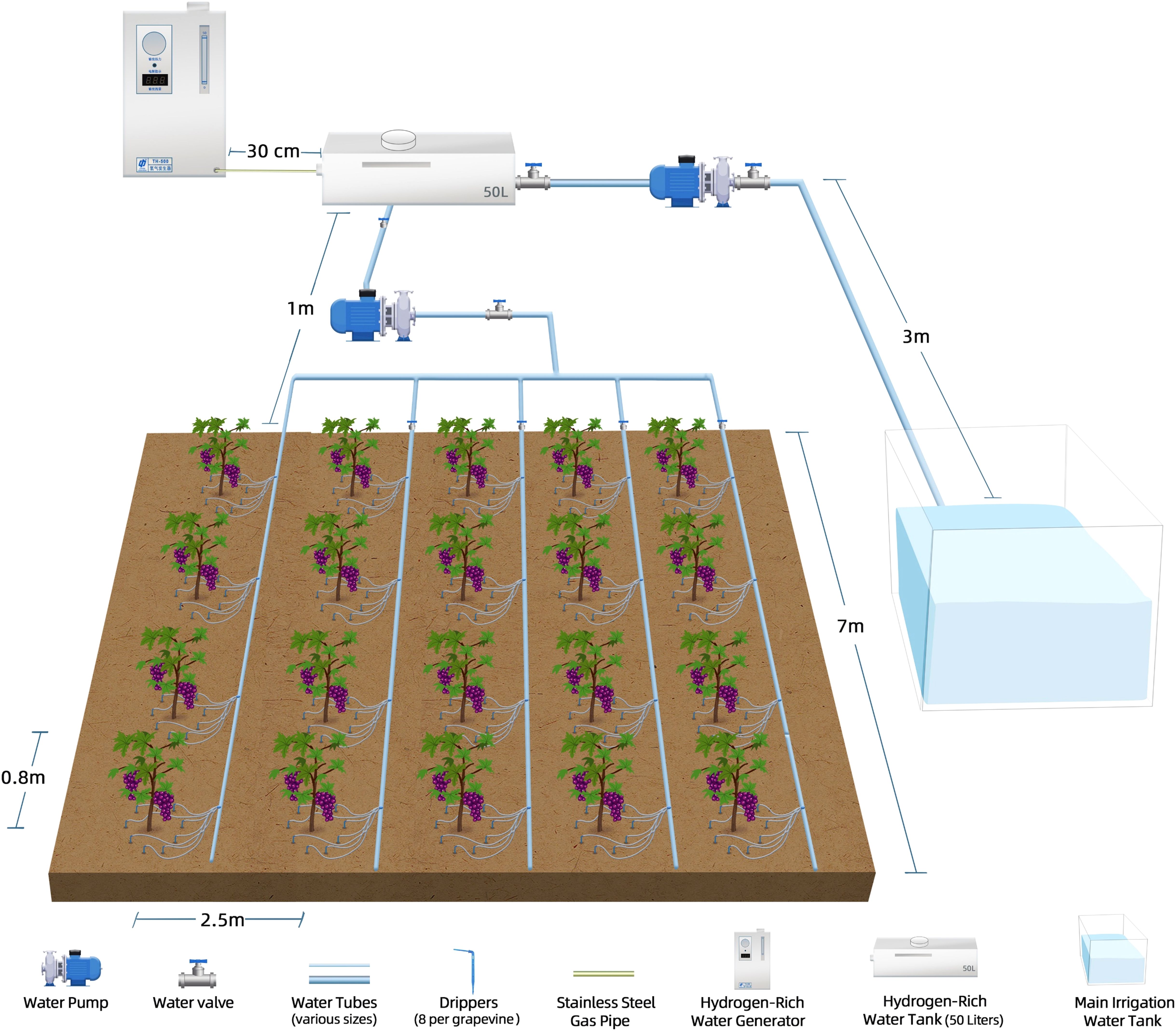
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. The irrigation system includes a main irrigation water tank, a water pump, and a series of water tubes of various sizes connected to water valves and drippers (4per grape seedlings). The HRWgeneration and delivery system consists of a HRWgenerator, a stainless steel air pipe for gas transfer, and a 50-liter HRW tank. The system ensures the precise delivery of HRW to the grape seedlings through a subsurface irrigation network designed to optimize water distribution and efficiency.
2.2 Determination of chlorophyll pigments and Car in peel and leaves
Pigment contents were determined using the methods of Li et al. (2024c). Berry peels were crushed, and fresh leaves (veins removed) were cut into small pieces. In each case, 0.1 g of sample was extracted with 10 mL of 95% ethanol in the dark for 24 hours. After centrifugation (12,000 ×g for 10 min),the absorbance of the supernatant was measured at 665, 649, and 470 nm using a UV spectrophotometer. Pigment contents were calculated based on absorbance readings, solution volume, and sample mass according to the following (Equations 1–5):
Where A665, A649, and A470 represent the absorbance values of the extracted solution at wavelengths of 665 nm, 649 nm, and 470 nm, respectively; V is the volume of the solvent mixture (mL); and W is the weight of the sample (g).
2.3 Leaf ChlF measurements
The measurement of ChlF was conducted on the 4th to 6th fully expanded leaf of each plant using a pulse-amplitude-modulation fluorometer (IMAG-CG, Walz, Germany). Leaves were dark-adapted in a humid environment for 30 minutes before measurement. Parameters recorded included: F0 (minimum fluorescence, dark-adapted), F′0 (minimum fluorescence, light-adapted), Fm (maximum fluorescence, dark-adapted), F′m (maximum fluorescence, light-adapted), and Ft (steady-state fluorescence under illumination) (Abdullaev et al., 2024). These values were used for subsequent calculations (González-Salvatierra et al., 2024) (Equations 6–10):
PPFD is the photon flux density recorded by the leaf clip sensor. 0.84 represents the proportion of light absorbed by the photosystems, and 0.5 accounts for photon distribution between them.
2.4 Determination of antioxidant enzymes activity, H2O2, and O2•-
The activity of antioxidant enzymes in the leaves, such as POD, SOD, PPO, and CAT, were measured using an assay kit (http://www.cominbio.com/index.html; Catalog Nos. POD-2-Y, SOD-2-W, PPO-2-Y, and CAT-2-Y) (Ngaffo Mekontso et al., 2021). Assay kits (http://geruisi-bio.com; Catalog Nos. G0116W for O2•- and G0168W for H2O2) were used to determine the O2•- and H2O2 content (Ruan et al., 2024). In brief, ‘Flame seedless’ grapevine leaves were removed from −80°C and immediately ground finely in liquid nitrogen. The frozen powder was weighed (0.1 g) and homogenized in 1 ml of the extraction solution. The extracts were centrifuged at 8,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C. The supernatants were collected and used for the determination of ROS and enzyme activities. The absorbance of H2O2, O2•-, SOD, POD, CAT, APX and PPO were measured by a UV spectrophotometer at 510, 540, 560, 470, 240, 290, and 525 nm, respectively. All enzymes activity and ROS were measured according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and the results were expressed as specified in these instructions.
2.5 Determination of TAC, TPC, and TFC in fruit peels
The extraction of TAC, TPC, and TFC compounds was carried out using HCl-methanol (1:99, v/v) following the method described by Xu et al. (2021) with some modifications. Peel samples were homogenized on ice, subjected to ultrasonic extraction for 30 minutes in the dark, stored at 4°C for 15 hours, and centrifuged at 8,000 × g for 3 minutes at 4°C. The tissue-to-buffer ratio was 1:40 (w/v). TAC was quantified using the pH differential spectrophotometric method Da Porto and Natolino (2018) with modifications. Absorbance was measured at 520 nm and 700 nm in buffer solutions at pH 1.0 (KCl-HCl) and pH 4.5 (NaAc-HCl) after incubating diluted samples (1 mL sample + 9 mL buffer) at room temperature for 1 hour. Results were expressed as mg cyanidin-3-glucoside per kg fresh weight (mg cyd-glu·kg-1 FW) (Equations 11, 12):
MW is the molecular mass of cyanidin 3-O-glucoside (449.2), ϵ is its molar extinction coefficient (26,900 mol-1), Df is the dilution factor, and W is the sample’s fresh weight.
TFC was determined using a colorimetric assay (Xie et al., 2015). Sample extracts and a rutin standard solution were diluted (1:4, v/v) to 5 mL with distilled water in a 10 mL flask. Then, 0.3 mL of 5% NaNO2 was added and shaken for 5 minutes, followed by 0.3 mL of 10% AlCl3 with stirring for 6 minutes. Subsequently, 2 mL of 1 M NaOH and 2.4 mL of distilled water were added and mixed thoroughly. TFC was calculated using a rutin calibration curve (0–200 mg/L) and expressed as mg rutin equivalent (RE) per 100 g fresh weight (mg RE/100 g FW). The absorbance was determined at 510 nm. TPC was determined using the modified Folin–Ciocalteu method (Vasco et al., 2008). Briefly, 0.5 mL of extract, blank, or standard solution was mixed with 0.5 mL of Folin–Ciocalteu reagent in a 25 mL volumetric flask and stirred for 3 minutes. Then, 10 mL of 75 g/L Na2CO3 solution was added, homogenized, and diluted to 25 mL with distilled water. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 1 hour, and absorbance was measured at 750 nm using a Shimadzu UV-160A spectrophotometer. Results were expressed as gallic acid equivalents (GAE) based on a standard curve (0–240 mg/L).
2.6 Determination of fruit quality-related characteristics
2.6.1 Berry and cluster weights and yield assessment
At the maturity stage (August 10, 2024), three grapevines per treatment were randomly selected. Cluster weights were measured using a precision balance (accuracy: 0.01 g). Fifty berries were randomly sampled from the upper, middle, and lower parts of clusters to determine single berry weight, with three replicates. Yield per acre (tons) was estimated by multiplying the average cluster weight, the number of clusters per vine, and the number of vines per acre based on the experimental planting density.
2.6.2 Fruit firmness and color
Fruit firmness was measured using a fruit firmness tester (GY-B, Quzhou Aipu, Co., Ltd., China) with at least three replicates (Wang et al., 2024). Berry peel color was assessed with a Minolta CR-200 colorimeter (Konica Minolta, Japan), recording L* (lightness), a* (red, green), and b* (yellow, blue) coordinates. Measurements were taken from the equator of 30 randomly selected berries, including top, middle, and bottom samples. The CIRG was calculated based on the chromaticity values (Zhou et al., 2024). The calculation formula for the CIRG is as follows (Equations 13–15):
Where:
C* = Chroma, representing color intensity
h° = Hue angle, representing the perceived color
2.6.3 TSS, pH, and TA
Grape juice was extracted by manually pressing and filtering 15–30 grapes per treatment for analysis of TA, TSS, and pH. TSS was measured using a digital refractometer (PAL-1, ATAGO, Japan) with 1 mL of the sample, following the manufacturer’s instructions (Hu et al., 2025). pH was measured with a digital pH meter (PH818, Hanoi, Vietnam), calibrated with pH 4.0 and 6.8 standard solutions (AiHaiti et al., 2025). TA was determined by titration with 0.1 M NaOH to a pH endpoint of 8.1, using phenolphthalein as the indicator, and expressed as tartaric acid equivalents per 100 g fresh berry weight, calculated using the following (Equation 16):
VI is the total extract volume (mL), N is the NaOH concentration (mol/L), VII is the NaOH volume used (mL), VIII is the extract volume used (mL), W is the sample weight (g), and f is the acid factor (0.075 for tartaric acid).
2.6.4 Total soluble sugar
Total soluble sugar was determined using the anthrone colorimetry method (Kanwal et al., 2024) with modifications. Fresh fruit tissue (1.0 g) was boiled in 10 mL distilled water for 60 minutes, filtered into a 100 mL flask, and the process was repeated to recover residues, adjusting the volume to 100 mL. A 0.5 mL extract was mixed with 1.5 mL distilled water, 0.5 mL anthrone reagent, and 5.0 mL concentrated sulfuric acid, incubated at 100°C for 1 minute, cooled, and absorbance measured at 630 nm. Glucose was used to construct the standard curve (0–100 µg/mL).
2.7 Statistical analysis
Experimental data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) (n = 3) and were analyzed using GraphPad Prism version 8.02 software (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). A multiple Student’s t-test was employed to determine significant differences between the control and treatment groups (*P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001).
3 Results
3.1 Effect of HRW treatment on berry and cluster weights
The HRW treatment influenced berry fresh weight, cluster weight, and estimated yield of ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes at different stages. Berry fresh weight increased progressively under HRW treatment, reaching the maximum value of 1.973 g at DB74, which represented an increase of 7.64% compared with the control (Table 1). This increase in berry weight was reflected in the cluster weight, with HRW-treated clusters averaging 591.67 g at DB74, compared with 551.00 g in control, corresponding to an increase of 7.38%. Similarly, the estimated yield per acre was higher in HRW-treated vines, reaching 9.94 t compared with 9.26 t in the control at DB74, indicating an increase of 7.38% (Table 1). The HRW treatment therefore consistently enhanced individual berry weight, cluster weight, and overall yield throughout the fruit development period.
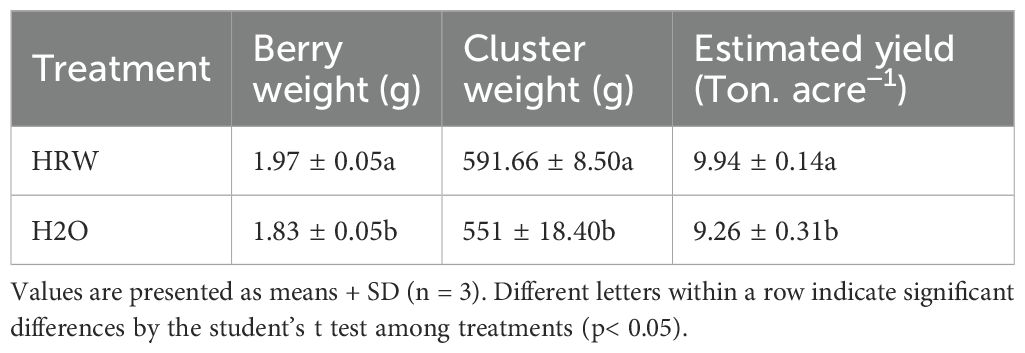
Table 1. Effect of irrigation with HRW on berry weight, cluster weight, and yield of “Flame seedless” grapes.
3.2 Effect of HRW treatment on photosynthetic pigments and ChlF parameters in the leaves of ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes
HRW treatment markedly influenced both photosynthetic pigments and ChlF parameters, reflecting enhanced PSII functionality and photosynthetic performance. As shown in Figure 2, Chl a content in HRW-treated leaves was always significantly higher than in the control (P< 0.05), with increases of 7.80%, 11.49%, and 3.16% at DI1, DI4, and DI7, respectively (Figure 2A). Similarly, Chl b also increased significantly under HRW treatment at DI1 and DI7 by 22.69% and 4.99%, respectively, compared with the control (P< 0.05), while no significant difference was detected at DI4 (Figure 2B). In contrast, the Chl a/b ratio exhibited a fluctuating trend. At DI1, HRW-treated leaves showed a significantly lower ratio than the control, with a reduction of 12.14%, whereas a significant increase of 9.23% was recorded at DI4. By DI7, only a slight change was observed, and the difference between treatments was not significant (Figure 2C). For Car content in HRW-treated leaves increased significantly at DI1 by 7.81% compared with the control (P< 0.05). The content continued to rise, reaching the highest value at DI4 for both treatments, although the difference from the control at this stage was not statistically significant. By DI7, Car levels slightly decreased compared with DI4, with a minimal and nonsignificant difference between HRW and control leaves (0.49%) (Figure 2D). These results indicate that HRW promoted Car accumulation, particularly enhancing light-harvesting potential during the early stages, with peak levels occurring at DI4, even though the difference at this point was not statistically significant. Fv/Fm in HRW-treated leaves exhibited an increase of 2.13% at DI1 (P< 0.05). By DI4, a decline was observed in both treatments; however, HRW-treated leaves retained a statistically significant enhancement of 1.43% relative to the control (P< 0.05). At DI7, Fv/Fm values increased slightly in both treatments, with HRW remaining 0.95% higher than the control, although the difference was not significant (Figure 2E). Correspondingly, ΦPSII demonstrated consistent and significant improvement under HRW, with increments of 9.76% at DI1, 7.71% at DI4, and 8.41% at DI7 (P< 0.05) (Figure 2F). This pattern was complemented by qP, which increased by 6.02% at DI1 (P< 0.05). At DI4, qP declined in both treatments. By DI7, qP rose modestly, with HRW-treated leaves exhibiting a 3.65% enhancement over the control (P< 0.05) (Figure 2G). In parallel, ETR values showed significant increases in HRW-treated leaves, being 27.41% higher than the control at DI1 (P< 0.05). On DI4, ETR decreased in both treatments, yet HRW still displayed a 10.68% improvement over the control (P< 0.05). At DI7, ETR increased moderately, with HRW exceeding the control, although the difference was not statistically significant (Figure 2H). In contrast, NPQ exhibited a progressive reduction under HRW, with decreases of 0.49% at DI1 (non-significant), 4.82% at DI4 (P< 0.05), and 12.59% at DI7 (P< 0.05) (Figure 2I).
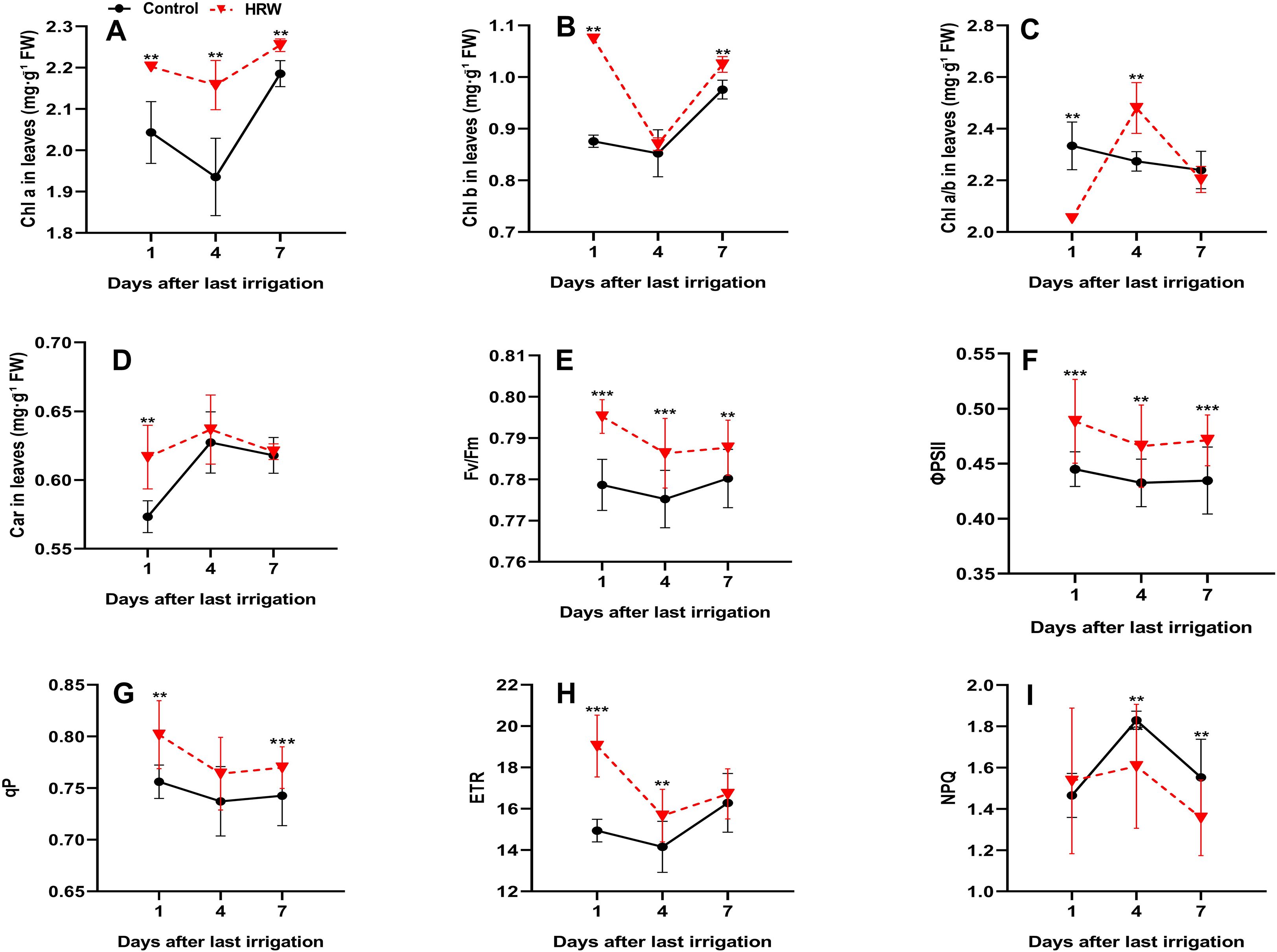
Figure 2. Effects of HRW treatment on chlorophyll a content (Chl a) (A), chlorophyll b content (Chl b) (B), chlorophyll a/b ratio (Chl a/b) (C), carotenoid content (Car) (D), maximal quantum yield of PSII (Fv/Fm) (E), photochemical quantum yield of PSII (ΦPSII) (F), photochemical quenching coefficient (qP) (G), electron transport rate (ETR) (H), and non-photochemical quenching (NPQ) (I) in ‘Flame Seedless’ grape leaves. Values (means ± SD) were from three replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences from the control (Student’s t-test; *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001).
3.3 Impact of HRW treatment on enzyme activities and ROS metabolism in ‘Flame Seedless’ grape leaves
As shown in Figure 3, HRW treatment markedly influenced ROS accumulation in grape leaves. The content of H2O2 in HRW-treated leaves was 0.519 μmol·g-1 FW, representing a significant reduction of 20.5% compared with the control, which recorded 0.652 μmol·g-1 FW (P< 0.05) (Figure 3A). Similarly, O2·- levels were lower under HRW treatment, with an average of 170.81 nmol·g-1 FW, in contrast to 222.06 nmol·g-1 FW in the control, corresponding to a decrease of 23.1% (P< 0.05) (Figure 3B). In contrast, HRW treatment significantly enhanced the activities of key antioxidant enzymes, including SOD, POD, and CAT (P< 0.05). The average activity of SOD in HRW-treated leaves reached 28.84 U·g-1 FW, compared with 25.18 U·g-1 FW in control (Figure 3C). Similarly, POD activity was markedly higher under HRW treatment, with a mean value of 1065.33 U·g-1 FW, whereas the control showed only 786.67 U·g-1 FW (Figure 3D). CAT activity also exhibited a significant elevation, averaging 2857.5 nmol·min-1·g-1 FW under HRW treatment, in contrast to 2168.2 nmol·min-1·g-1 FW in the control (Figure 3E). Notably, PPO activity was significantly reduced in HRW-treated leaves, with a mean value of 15.00 U·g-1 FW, compared to 20.40 U·g-1 FW in the control (Figure 3F).
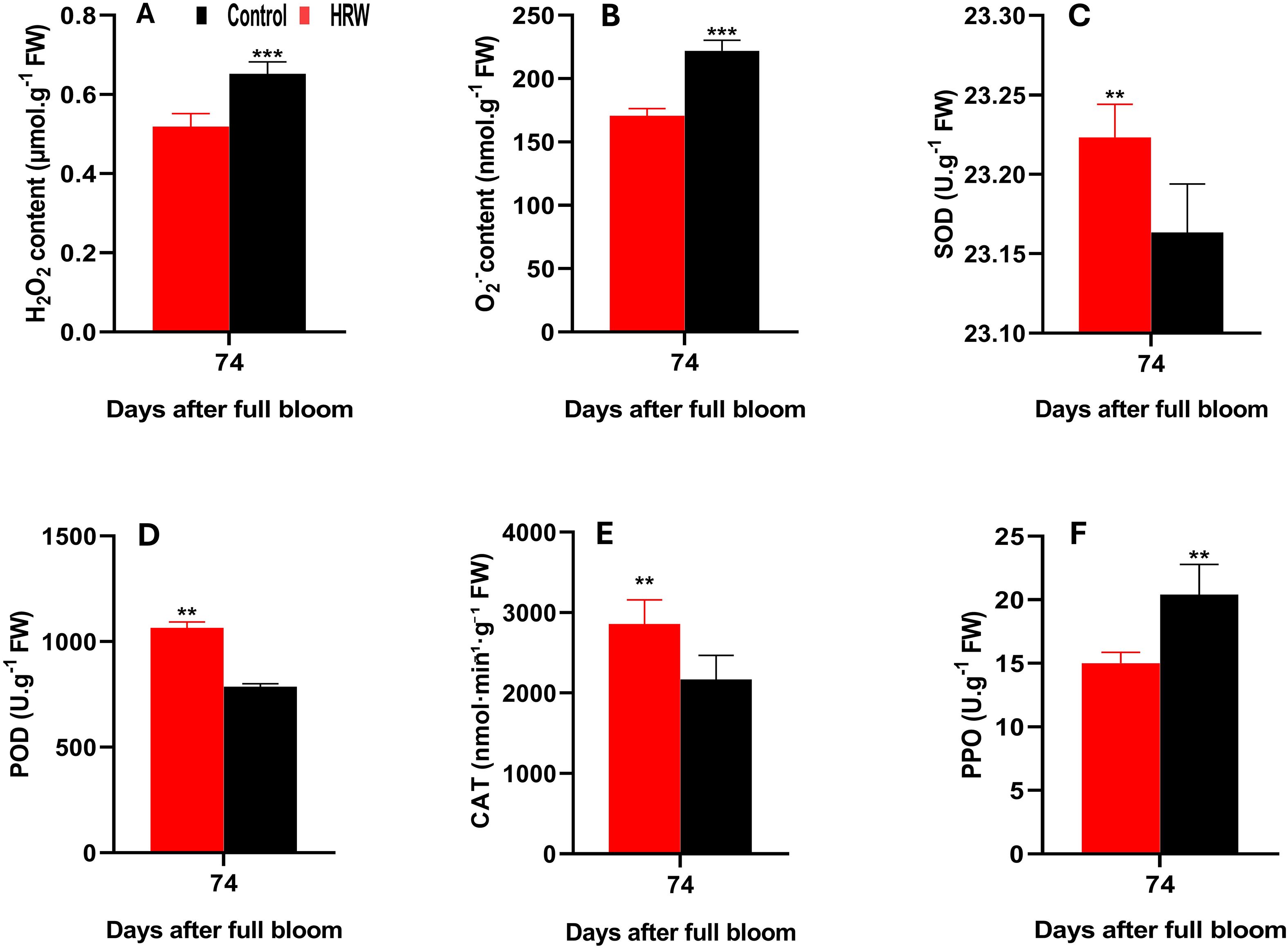
Figure 3. Effects of HRW treatment on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) content (A), superoxide anion (O2˙-) content (B), and the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) (C), peroxidase (POD) (D), catalase (CAT) (E), and polyphenol oxidase (PPO) (F) in ‘Flame Seedless’ grape leaves. Data are presented as means ± SD from three replicates. Significant differences from the control were determined by Student’s t-test (**P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001).
3.4 Effect of HRW treatment on TChl and Car in berry peels
A rapid decrease in TChl content in the berry peel was observed during fruit ripening in both treatments (Figure 4A). Compared to the control, HRW treatment reduced the TChl in berry peel at the DB44, DB54, and DB64 stages; however, the differences were not statistically significant. Notably, the control treatment showed significantly higher Car levels than HRW at DB44 and DB54, with increases of 30.77% and 12.55% (P< 0.05), respectively. By DB64, no significant differences were observed. At DB74, HRW maintained higher Car levels than the control, corresponding to an increase of 34.64% (P< 0.05) (Figure 4B).
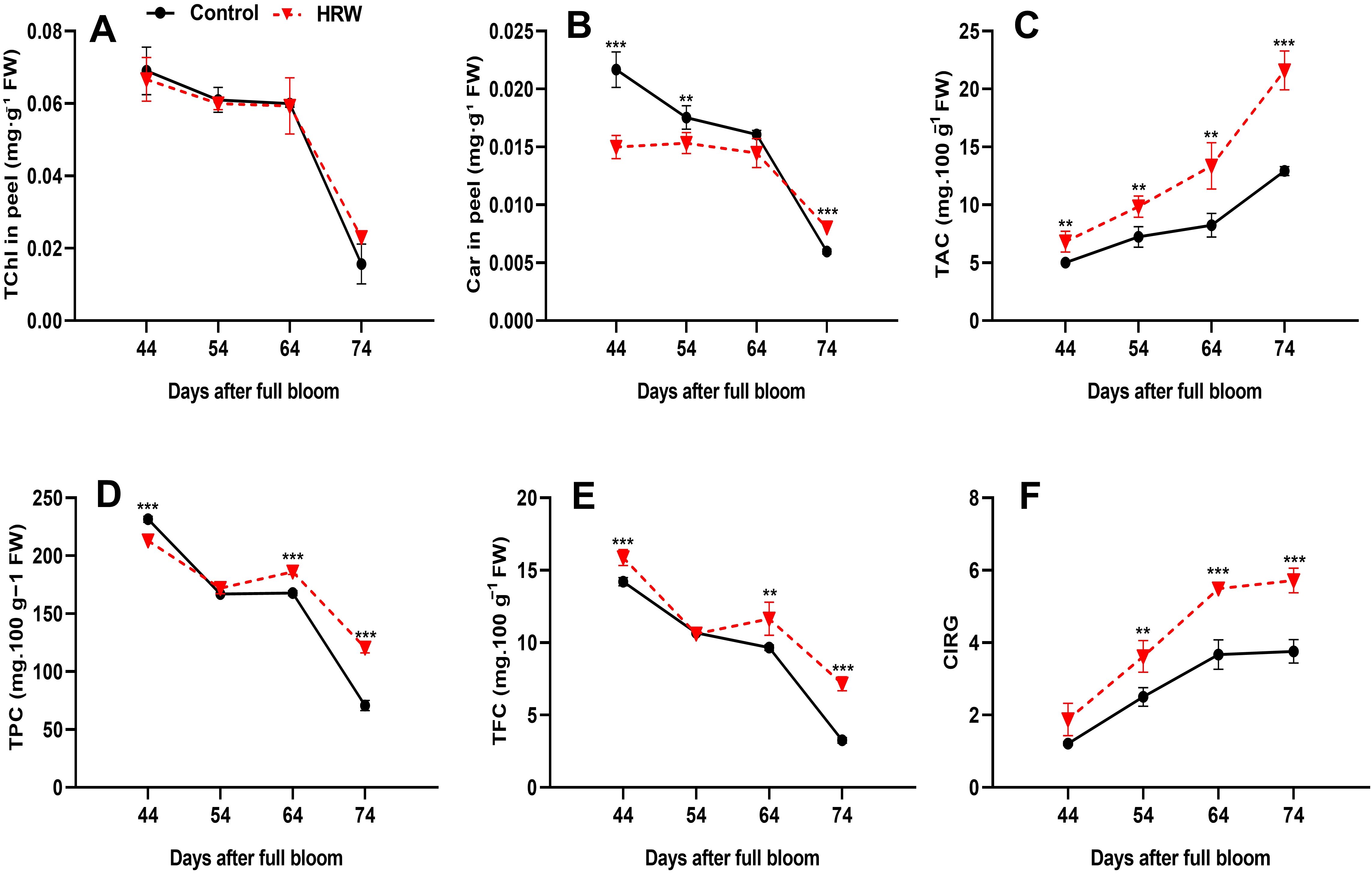
Figure 4. Effects of HRW treatment on total chlorophyll content (TChl) (A), carotenoid content (Car) (B), total anthocyanin content (mg cyanidin 3-O-glucoside 100 g-1 FW) (TAC) (C), total phenolic content (mg GAE 100 g-1 FW) (TPC) (D), total flavonoid content (mg QE 100 g-1 FW) (TFC) (E), and the color index of red grapes (CIRG) (F) in ‘Flame Seedless’ grape peel. Data are presented as means ± SD from three replicates. Significant differences from the control were determined by Student’s t-test (**P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001).
3.5 HRW improved the TAC, TPC, TFC and CIRG in berry peels
In the berry peels, TAC in both treatments showed a gradually increasing trend as the fruit matured. At all stages, the TAC levels with HRW were significantly higher than those in the control group, with values of 9.85, 13.36, and 21.60 mg 100 g-1 FW at DB54, DB64, and DB74, respectively (P< 0.05) (Figure 4C). Anthocyanins, phenolic compounds, and flavonoids are closely related antioxidant secondary metabolites, with anthocyanins considered a subclass of flavonoids. All these compounds share biosynthetic pathways and compete for common metabolic precursors, which suggest that HRW may exert a synergistic effect on their coordinated accumulation. To further understand the source of this antioxidant activity, changes in TPC and TFC were measured. The results showed that. TPC content decreased progressively from DB44 to DB74. However, TPC content was higher under HRW treatment than in the control at DB54, DB64, and DB74, with values of 172.00, 186.13, and 120.53 mg 100 g-1 FW, respectively, while it was lower at DB44 with a value of 213.07 mg 100 g-1 FW (Figure 4D). Similarly, at all stages except DB54, HRW treatment led to higher TFC content compared with the control, with values of 11.65 mg 100 g-1 FW at DB64 and 7.16 mg 100 g-1 FW at DB74, while it was slightly lower at DB54 with a value of 10.60 mg 100 g-1 FW (Figure 4E). Notably, both TPC and TFC content initially decreased to DB54 before rising again, though they followed an overall descending trend up to DB74. While TPC and TFC exhibited a descending trend, CIRG values increased consistently during fruit ripening (Figure 4F). At all-time points, CIRG values were higher under HRW treatment than in the control, with values of 3.62, 5.49, and 5.717 at DB54, DB64, and DB74, respectively (P< 0.05).
3.6 Effect of HRW treatment on fruit firmness, TA, TSS, soluble sugar content, and pH in berry fruits
The quality attributes of ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes were significantly influenced by HRW treatment compared to control. This influence is shown in Figure 5; the firmness and TA of grape fruits showed a gradually decreasing trend as the fruits matured. At DB74, fruit firmness and TA reached their lowest values, with HRW-treated grapes showing a 22.75% and 5.47%, respectively, reduction compared to the control (Figures 5A, B). Conversely, the TSS, soluble sugar content, and pH of grape fruits in each treatment gradually increased as the fruits matured. At DB54 and DB74, the content of TSS in the HRW treatment was significantly higher than control (P< 0.05), with an increase of 21.18% and 3.65%, respectively (Figure 5C). The soluble sugar content also showed a consistent rise as the fruit matured, with HRW treatment outperforming control treatment at DB44, DB54, DB64, and DB74 by 14.85%, 10.54%, 14.19%, and 3.41%, respectively (P< 0.05), and this sugar accumulation reflects improved fruit quality (Figure 5D). On the other hand, the pH of grape fruits in both treatments was not significantly different at DB54 and DB64, but at DB44 and DB74, the pH of the HRW treatment was significantly higher than the control (P< 0.05), with an increase of 3.49% and 6.09%, respectively (Figure 5E).
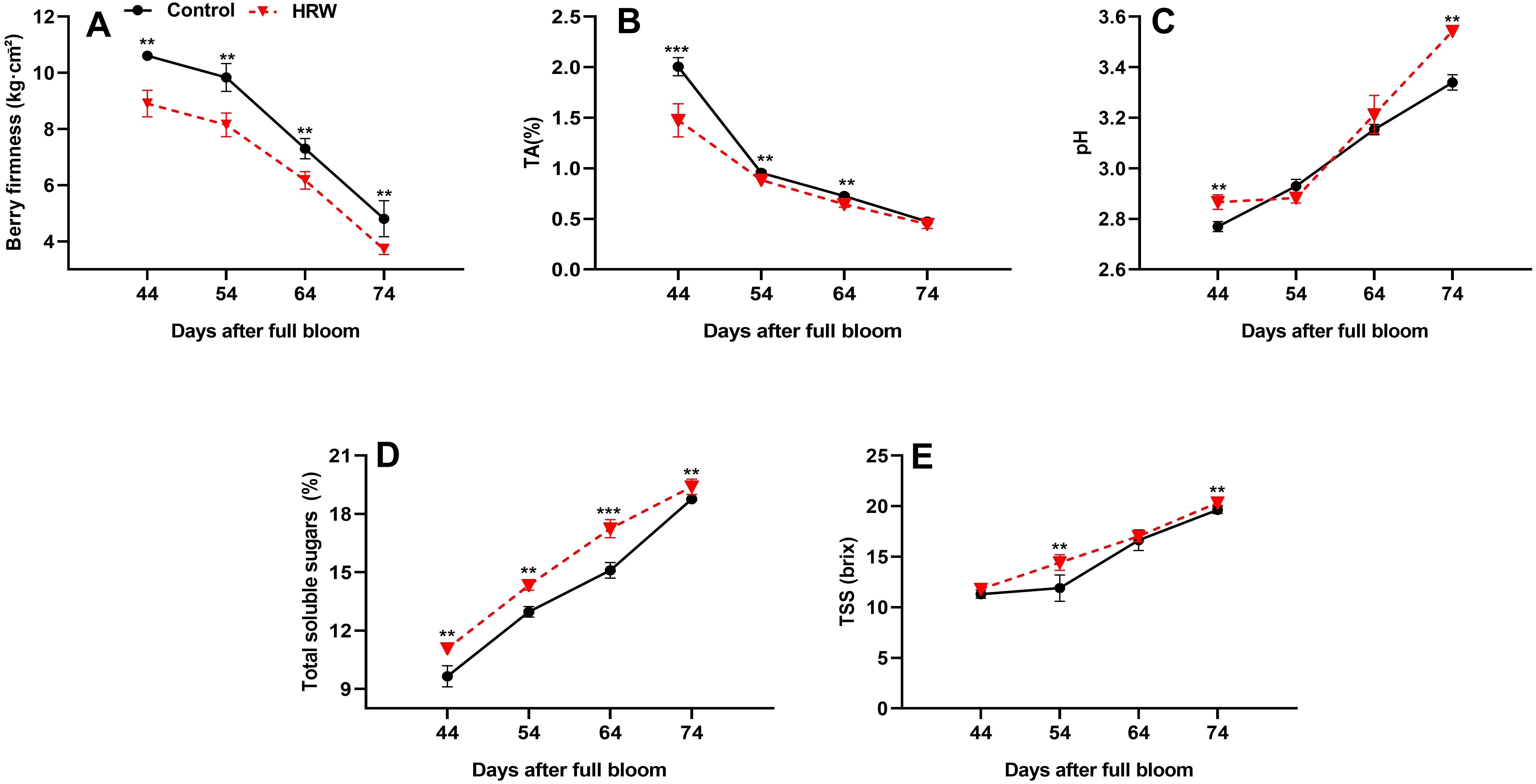
Figure 5. Effects of HRW treatment on fruit firmness (A), titratable acidity (TA) (B), pH (C), total soluble sugar (D), and total soluble solids (TSS) (E) in the berries of ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes. Values (means ± standard deviations) were calculated from three independent replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences compared to the control (Student’s t-test; **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001).
4 Discussion
4.1 HRW treatment improves yield of ‘Flame Seedless’ fruit
ChlF is a critical determinant of photosynthetic product accumulation, while the photosynthetic rate directly reflects the plant’s photosynthetic capacity (Xiong et al., 2020). Enhanced photosynthetic efficiency accelerates biomass accumulation, ultimately influencing fruit yield. In this study, HRW treatment significantly increased single berry weight, cluster weight, and estimated total yield compared with the control (Table 1). These observations are consistent with prior reports demonstrating that higher photosynthetic pigment content, improved photosynthetic parameters, and overall photosynthetic performance positively affect final plant yield (Zhang et al., 2023b).
Moreover, the observed positive correlation between HRW treatment and antioxidant enzyme activities in leaves suggests that enhanced ROS scavenging and physiological stability contribute to improved photosynthetic efficiency. Collectively, these findings indicate that HRW application promotes both fruit development and overall yield formation in ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes, highlighting its potential for improving production under greenhouse cultivation.
4.2 Impact of HRW on photosynthetic pigments, ChlF, ROS homeostasis, and antioxidant enzyme activity in ‘Flame Seedless’ grape leaves
Photosynthetic pigments and ChlF parameters are essential indicators of photosynthetic efficiency in plants. Chlorophyll, the primary pigment responsible for converting light energy into chemical energy, also serves as a key marker of both physiological and ecological status (Zhang et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022b). In our study, control plants exhibited the lowest levels of both Chl a and Chl b at DI4, while HRW-treated plants maintained higher levels across all time points, particularly at DI4 (Figures 2A, B). The lower chlorophyll pigment levels in control plants may reflect impaired chloroplast integrity and enhanced degradation of photosynthetic pigments under fluctuating soil moisture conditions. These findings highlight the potential effect of HRW on chlorophyll stability and photosynthetic efficiency, likely due to enhanced antioxidant activity and delayed chlorophyll breakdown (El-Saadony et al., 2024; Liao et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2025).
Notably, The Chl a/b ratio and Car increased at DI4 in both treatments, with HRW-treated plants showing the highest values (Figures 2C, D). This increase likely represents a photoprotective adaptation, as Car dissipate excess light energy and quench singlet oxygen, thereby stabilizing thylakoid membranes (Zgonnik, 2020; Abdel-Sattar et al., 2024; He et al., 2024; Rao et al., 2025). A higher Chl a/b ratio may also indicate selective retention of Chl a to support PSII activity under fluctuating soil moisture conditions (Xu et al., 2022b). These pigment dynamics suggest that HRW mitigates chlorophyll degradation and enhances photoprotection by regulating gene expression involved in pigment biosynthesis, thereby protecting chlorophyll while promoting Car accumulation (Zhao et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2025).
Photosynthesis relies on the absorption of light energy by light-harvesting complexes to initiate photochemical reactions (Akhlaq et al., 2025). The efficiency of PSII can be evaluated using ChlF parameters such as ΦPSII, qP, ETR, Fv/Fm, and NPQ, which are highly responsive to environmental changes, and provide insights into the functional state of the photosynthetic machinery (Abdullaev et al., 2024). Among these parameters, Fv/Fm declined at DI4 and recovered at DI7, with HRW-treated plants consistently exhibiting higher values than controls (Figure 2E). This trend indicates reduced photoinhibition and enhanced light-use efficiency, in agreement with previous findings in tomato (Hazrati et al., 2016; Akhlaq et al., 2025). Similarly, ΦPSII and qP—indicators of light energy utilization efficiency and photochemical quenching—decreased significantly at DI4 and partially recovered by DI7 after the second irrigation cycle. HRW-treated plants consistently exhibited higher values than the control group (Figures 2F, G), suggesting enhanced electron transport and improved PSII stability (Wang et al., 2022; Abdullaev et al., 2024). ETR also declined at DI4, reflecting inhibition of the electron transport chain due to soil moisture fluctuations. However, HRW-treated plants exhibited significantly higher ETR values, indicating better protection of PSII and more stable electron flow. By DI7, ETR values recovered in both groups, with HRW-treated plants maintaining superior performance. In contrast, NPQ, representing non-photochemical quenching or the thermal dissipation of excess excitation energy, increased significantly at DI4, reflecting a photoprotective mechanism (Figure 2I). Similar observations have been reported in Aloe vera, where NPQ rose under fluctuating water availability (Wang et al., 2022). Elevated NPQ is generally associated with proton accumulation in the thylakoid lumen due to transient saturation of the electron transport chain (Hazrati et al., 2016). Notably, HRW-treated plants exhibited lower NPQ levels, indicating a reduced requirement for thermal dissipation and more efficient regulation of photosynthetic activity.
The enhanced photosynthetic performance in HRW-treated plants is associated with the activation of strong antioxidant defenses that protect chloroplasts from oxidative stress. As the primary sites of photosynthesis, chloroplasts are highly sensitive to changes in the surrounding environment, which can disrupt CO2 assimilation, leading to over-reduction of the ETR and excessive ROS generation (El-Saadony et al., 2024). Accumulated ROS can impair PSII, damage thylakoid membranes, and degrade pigments, reducing photochemical efficiency as reflected by Fv/Fm and related ChlF parameters (Shah et al., 2021; Iwai et al., 2023; Rao et al., 2025). Plants mitigate such oxidative damage through a complex antioxidant system comprising both enzymatic and non-enzymatic components (Li et al., 2024b).
HRW has been shown to support redox balance by enhancing antioxidant enzyme activity and mitigating ROS levels. It directly reduces O2˙- content, forming H2O2, which is subsequently scavenged through enhanced H2O2-degrading activity (Yun et al., 2021). In the present study, ROS levels in grapevine leaves decreased markedly under HRW treatment compared with the control (Figure 3), consistent with similar reductions reported in litchi (Yun et al., 2021) and pakchoi (An et al., 2021). This decline in ROS suggests the involvement of antioxidant enzyme systems, which serve as the primary defense against oxidative stress in plant tissues and play a central role in protecting cellular structures (Wei et al., 2019).
Specifically, SOD catalyzes the dismutation of O2˙- into H2O2 and O2, while CAT and POD further degrade H2O2 into H2O and O2, preventing the harmful accumulation of ROS (Wei et al., 2019; Li et al., 2024b; Guo et al., 2025). In this study, HRW treatment significantly enhanced the activities of SOD, POD, and CAT in grapevine leaves (Figures 2C–E). Comparable responses have been observed in Hypsizygus marmoreus mushrooms (Ali et al., 2024), pakchoi (An et al., 2021), red pitaya (Ding et al., 2024a), and Chinese cabbage (Li et al., 2022a). Conversely, HRW suppressed PPO activity in grapevine leaves (Figure 2F), consistent with results reported in Lanzhou Lily (Zhang et al., 2023a).
The beneficial effects of HRW on antioxidant enzyme activity and ROS scavenging may be linked to its modulation of gene expression related to oxidative stress regulation (Yang et al., 2024). HRW enhances the expression of the transcription factor HcMYB6, which upregulates genes encoding antioxidant enzymes, thereby improving ROS scavenging capacity (Wei et al., 2019; Yun et al., 2021; Ding et al., 2024a, 2024b). In contrast, HRW suppresses the expression of the transcriptional repressor HcR2R3MYB, which is associated with PPO activity, thus reducing enzymatic browning and preserving phenolic compounds (Ding et al., 2024a). In addition to enzymatic defenses, non-enzymatic antioxidants such as Car, TFC, and TPC contribute to ROS scavenging, stabilization of thylakoid membranes, and protection of pigment–protein complexes (Hasanuzzaman et al., 2020). Car, in particular, dissipate excess excitation energy and prevent triplet chlorophyll formation, thereby reducing photoinhibition-related ROS (Hasanuzzaman et al., 2020). Collectively, these dual regulatory effects of HRW—strengthening both enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant systems—enhance the physiological integrity of leaves and fruits, maintain their quality, and support plant performance under different environmental conditions surrounding the plant.
Our results suggest that HRW application enhances both enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant responses, upregulating the expression and activity of SOD, POD, CAT, and PPO while also increasing pools of Car. These biochemical improvements correspond with observed increases in Fv/Fm, ΦPSII, qP, ETR, and a reduction in NPQ, all indicating enhanced photochemical efficiency. In addition, HRW support mitochondrial ATP synthesis, reinforcing the energy supply required for photosynthetic carbon metabolism under natural fluctuations soil water availability between irrigation cycles (He et al., 2024).Furthermore, HRW-treated plants maintained optimal Chl a/b ratios (~2.2), which are essential for efficient light harvesting and energy transfer within the photosystems. This stability is likely linked to the preservation of chloroplast ultrastructure and the efficient operation of their intrinsic antioxidant machinery, which maintains redox homeostasis and prevents oxidative damage under these conditions; such protection supports sustained photosynthetic functionality, as previously reported in wheat cultivars (Rao et al., 2025). By optimizing energy distribution and maintaining redox balance, HRW emerges as a promising strategy to improve crop resilience and productivity (Yu et al., 2023).
4.3 Influence of HRW treatment on TChl and Car in grape berry peels
Fruit ripening is characterized by chlorophyll degradation, Car accumulation, and cell wall breakdown. The transition from green to red coloration is primarily driven by the loss of chlorophyll and the biosynthesis and accumulation of pigments such as Car, TAC, and lycopene. These compounds contribute to the development of red, purple, or blue pigmentation, particularly in berries and grapes (Wu et al., 2020a; Francis and Abdulhameed, 2024). Our results showed no significant differences in TChl between HRW and control, both exhibiting a decrease in chlorophyll with ripening (Figure 4A), consistent with Fang et al. (2020), who found jasmonic acid upregulated chlorophyll degradation in broccoli. Thus, chlorophyll degradation may contribute to enhanced fruit coloration. ChlF, which reflect PSII efficiency and photoprotective capacity (Martínez-Lüscher et al., 2015), are closely linked to the balance between chlorophyll breakdown and Car synthesis during ripening. Declines in ChlF often coincide with structural changes in chloroplasts and the conversion to chromoplasts, where Car accumulate for photoprotection and antioxidant defense (Gambetta et al., 2021).
The results demonstrated that HRW treatment influenced the dynamics of Car accumulation in ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes. Car levels were lower in HRW-treated grapes compared to the control at DB44, DB54, and DB64 but surpassed the control at DB74, with both treatments showing a general decrease over time (Figure 4B). Car accumulation is regulated by redox balance, with ROS playing a key role in stimulating biosynthesis (Ali et al., 2024). Antioxidant enzymes help mitigate oxidative stress in berry tissues (Rashad et al., 2023), and their activity can indirectly modulate Car biosynthesis by controlling ROS levels that act as biosynthetic signals (El-Saadony et al., 2024).HRW-treated leaves exhibited higher antioxidant enzyme activity and lower levels of H2O2 and O2·- on the final day of the experiment, indicating enhanced ROS scavenging capacity. The reduced ROS levels during early fruit development likely led to lower Car biosynthesis stimulation, explaining the reduced accumulation at earlier stages. In contrast, the prolonged effect of HRW may have slowed Car degradation in later stages, leading to higher accumulation at DB74. Similar findings in other fruits, such as tomatoes treated with hydrogen nanobubbles(HNW) (He et al., 2024), which indicated that HRW can enhance Car levels by preventing degradation.
4.4 Enhancement of TAC, TPC, TFC, and CIRG in berry peels by HRW treatment
Plants contain low-molecular-mass antioxidant metabolites such as TAC, TPC, and TFC, which play essential roles in protecting against, and scavenging ROS, and attracting pollinators (Anić et al., 2024). Anthocyanins represent the principal pigments that confer red and blue coloration in fruits and flowers. HRW has been reported to enhance anthocyanin accumulation in plants, such as radish (Zhang et al., 2018). In our study, HRW increased TAC in grape berry peels (Figure 4C), possibly by promoting the expression of key biosynthesis genes (Zhang et al., 2019). H2 mitigates oxidative stress by scavenging excessive ROS and maintaining cellular redox homeostasis (Liu et al., 2015), thereby preventing ROS-induced inhibition of phenylpropanoid and flavonoid biosynthetic enzymes such as PAL, CHS, and COMT (Liu et al., 2022). This redox balance allows efficient TAC production by sustaining the phenylpropanoid pathway and other secondary metabolite biosynthesis routes, leading to higher accumulation of phenolics, flavonoids, and anthocyanins (Liu et al., 2022). Moreover, H2 treatment integrates with other signaling molecules, including NO, H2S, MeJA, and ethylene, to fine-tune secondary metabolite production (Sana et al., 2025). Thus, the progressive increase in TAC during ripening is not only associated with pigmentation and protection but also reflects an improved metabolic environment resulting from ROS homeostasis and enhanced transcriptional activation of key biosynthetic genes (Liu et al., 2022; Sana et al., 2025). This pattern is consistent with findings in peach, where TAC accumulation occurs during ripening (Li et al., 2023). HRW-treated grapes exhibited higher TAC levels than controls across all ripening stages, likely due to a combination of factors: suppression of PPO activity, which minimizes oxidative degradation of TAC (Zhang et al., 2023a); enhanced protection against oxidative stress, which stabilizes TAC (Ortiz et al., 2024); and modulation of secondary metabolic pathways, leading to greater anthocyanin biosynthesis and retention, as observed in bananas and pakchoi (An et al., 2021; Siddiqui et al., 2022).
TPC and TFC are critical for mitigating oxidative stress and reducing oxidative damage in fruits and vegetables (Li et al., 2024a). Recent studies have demonstrated that H2 enhances TPC, TFC, and pigments in various fruits, including dried apple (Alwazeer, 2018), and strawberries (Alwazeer and Özkan, 2022). HRW treatment also alleviates oxidative damage by boosting TPC and TFC, thereby extending the shelf life of daylily buds (Hu et al., 2021) and lychee (Yun et al., 2021).These findings collectively highlight HRW’s potential in enhancing antioxidant capacity and preserving fruits quality.
In the present study on ‘Flame Seedless’ grapevines, TPC and TFC gradually declined during ripening (Figures 4D, E), consistent with the natural oxidative processes occurring in fruit tissues. Similar decreasing trends have been reported in grapevine (Anić et al., 2024), with further reductions in overripe stages attributed to enhanced climacteric respiration (Li et al., 2023). This reduction is primarily driven by enzymatic oxidation catalyzed by PPO, which converts phenolic compounds into oxidized derivatives, thereby lowering their detectable levels (Taghipour et al., 2024). Additionally, water accumulation in berries during ripening promotes the hydrolysis of high-molecular-weight phenolics (Jediyi et al., 2019), while the decline in primary metabolic activity limits the biosynthesis of these secondary metabolites (Li et al., 2023). Over time, polyphenols may also bind to other compounds, further decreasing total phenol content (Zhao et al., 2024). Environmental conditions, particularly temperature and light intensity, can also modulate phenolic biosynthesis and degradation (Chen et al., 2025).
Notably, HRW-treated grapes maintained higher TPC and TFC than the control throughout ripening, particularly in the later stages, due to both reduced PPO activity and increased activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, POD, and CAT). These changes enhanced ROS scavenging, thereby protecting phenolic compounds from oxidative damage and delaying their degradation. This trend aligns with previous observations in daylily buds (Hu et al., 2021), banana (Siddiqui et al., 2022), and pakchoi (An et al., 2021), where HRW mitigated phenolic loss by suppressing oxidative enzyme activity.
Color is a critical quality attribute that directly influences consumer preference and marketability of grapes. In the present study, HRW-treated grapes exhibit enhanced fruit coloration, as evidenced by increased CIRG values (Figure 4F), reflecting a more desirable visual phenotype. This enhancement is closely associated with the coordinated regulation of pigment metabolism, including chlorophyll degradation and the accumulation of Car and anthocyanins. Chlorophyll degradation is a hallmark of fruit ripening, marking the transition from green to mature coloration, whereas Car and anthocyanins contribute yellow, orange, and red hues, thereby reinforcing overall color development and providing additional antioxidant benefits (Olivares et al., 2017). HRW treatment simultaneously promotes carotenoid accumulation and supports anthocyanin biosynthesis. These effects collectively enhance fruit coloration during ripening, potentially providing growers with increased flexibility in harvest timing to better align with market demands (Karimi et al., 2022).Therefore, the observed improvements in color reflect an integrated modulation of pigment metabolism and antioxidant activity, emphasizing the role of HRW in optimizing both visual quality and nutritional value of grapes.
4.5 Influence of HRW on fruit firmness, TA, pH, total soluble sugars, and TSS in grape berries
Fruit quality is determined by multiple factors, including maturity, firmness, sweetness, pH, TSS, total soluble sugars, TA, and TAC. Firmness, a key indicator of fruit texture and consumer acceptability, typically decreases during ripening due to cell wall disassembly and enzymatic activity. In this study, ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes treated with HRW exhibited reduced firmness compared to the control at all sampling points (DB44, DB54, DB64, DB72) (Figure 5A). This observation aligns with previous reports indicating that HRW promotes fruit softening during pre-harvest stages by modulating cell wall components and enhancing the activity of cell wall-degrading enzymes (Yao et al., 2024). Conversely, postharvest studies have shown that HRW preserves firmness by inhibiting cell wall degradation, as observed in okra (Dong et al., 2023). These contrasting effects may be attributed to (1) the developmental stage of the fruit, (2) HRW’s role in preserving cell wall integrity postharvest, and (3) its stimulation of ethylene biosynthesis and activation of ripening-related genes during pre-harvest. Additionally, HRW’s antioxidant properties may influence oxidative processes differently depending on the timing of application (Yao et al., 2024). HRW concentration also plays a role, with higher concentrations accelerating firmness loss (Li et al., 2021). These findings underscore the complex role of HRW in fruit texture regulation and highlight the need for further investigation into its molecular mechanisms, particularly those related to developmental timing, oxidative modulation, and phytohormonal signaling.
Organic acids are central to plant metabolism and significantly influence fruit flavor, sweetness, and overall quality (Li et al., 2023). In our study, TA levels decreased progressively as grapes matured in both treatments, with HRW-treated grapes showing significantly lower TA values than the control (Figure 5B). This result is consistent with findings in cherry tomatoes, where HRW reduced TA content (Li et al., 2024a). As ripening progressed, pH values increased, with HRW-treated grapes consistently exhibiting higher pH than the control (Figure 5C). pH serves as an indicator of fruit quality and reflects metabolic differences between treatments (Zhong et al., 2023). The observed decrease in TA and increase in pH may be attributed to the degradation of organic acids through respiratory metabolism during ripening (Shi et al., 2025). Ripening is an energy-intensive process, relying on carbon sources such as sugars, amino acids, and organic acids (Taş et al., 2021). Given the low starch content in grapes, organic acids and cell wall components are the primary contributors to soluble sugar formation during maturation (Taş et al., 2021).
Total soluble sugars increased progressively throughout ripening in both treatments, with HRW-treated grapes consistently showing higher levels than the control (Figure 5D). Similar enhancements in sugar content have been reported in strawberries treated with (HNB) (Li et al., 2024a). This increase may be linked to HRW’s ability to modulate genes involved in sucrose and starch metabolism (Hou et al., 2021), as well as its positive effects on leaf physiology improving TChl, ChlF parameters, and antioxidant enzyme activity which collectively enhance photosynthetic efficiency and assimilate production (El-Saadony et al., 2024).
TA and TSS typically exhibit an inverse relationship during fruit ripening: as acidity decreases, TSS levels rise (Subedi et al., 2025). In grapes, TSS increased steadily from immature to mature stages in both treatments, peaking at DB74, with HRW-treated grapes consistently showing higher values than the control (Figure 5E). Similar trends have been observed in HRW-treated Hypsizygus marmoreus (Ali et al., 2024). This enhancement may be attributed to HRW’s antioxidant properties (He et al., 2024), as well as natural ripening processes such as water loss and the breakdown of complex carbohydrates into water-soluble sugars (Xiao et al., 2024).
4.6 Mechanisms underlying fruit quality improvements
HRW-mediated maintenance of PSII efficiency, reflected by Fv/Fm, ΦPSII, and qP, ensured effective photochemical energy conversion, minimized photoinhibition, and supported continuous carbohydrate production, contributing to both fruit growth and sugar accumulation (Choi et al., 2016). Additionally, efficient photosynthesis facilitated a balanced acid-to-sugar ratio, moderating fruit pH and TA, thereby enhancing flavor quality (Xu et al., 2022a; Du et al., 2024).Enhanced photosynthetic activity, together with improved antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, POD, CAT), reduced ROS accumulation and oxidative degradation of pigments, preserving chlorophyll and Car and supporting biosynthesis and accumulation of phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and anthocyanins, which are key determinants of fruit color, nutritional value, and postharvest shelf-life (Arrones et al., 2022; Pérez-Labrada and Juárez-Maldonado, 2024). Moreover, stabilization of chloroplast ultrastructure and efficient energy distribution promoted sustained sugar transport to the fruit mesocarp, enhancing sweetness, and overall textural properties (Miyoshi et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2022a; Du et al., 2024).
Overall, these results demonstrate that HRW-induced improvements in photosynthesis, ChlF, and antioxidant defense collectively enhance multiple fruit quality attributes, including TSS, soluble sugars, acidity, pH, chlorophyll and Car stability, TAC, TPC, TFC, firmness, berry and cluster weight, and yield, (Figure 6) providing a comprehensive mechanistic explanation for the observed benefits in ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes (Miyoshi et al., 2021; Arrones et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2022a; Du et al., 2024; Pérez-Labrada and Juárez-Maldonado, 2024; Yin et al., 2025).In summary, the improvements in fruit quality observed under HRW treatment can be mechanistically explained by enhanced photosynthetic efficiency, stabilized ChlF, and optimized pigment composition. Increased chlorophyll content in leaves and fruits improved light-harvesting capacity and carbon assimilation, thereby enhancing photosynthate availability for sugar accumulation, leading to higher TSS and increased sweetness in fruits.
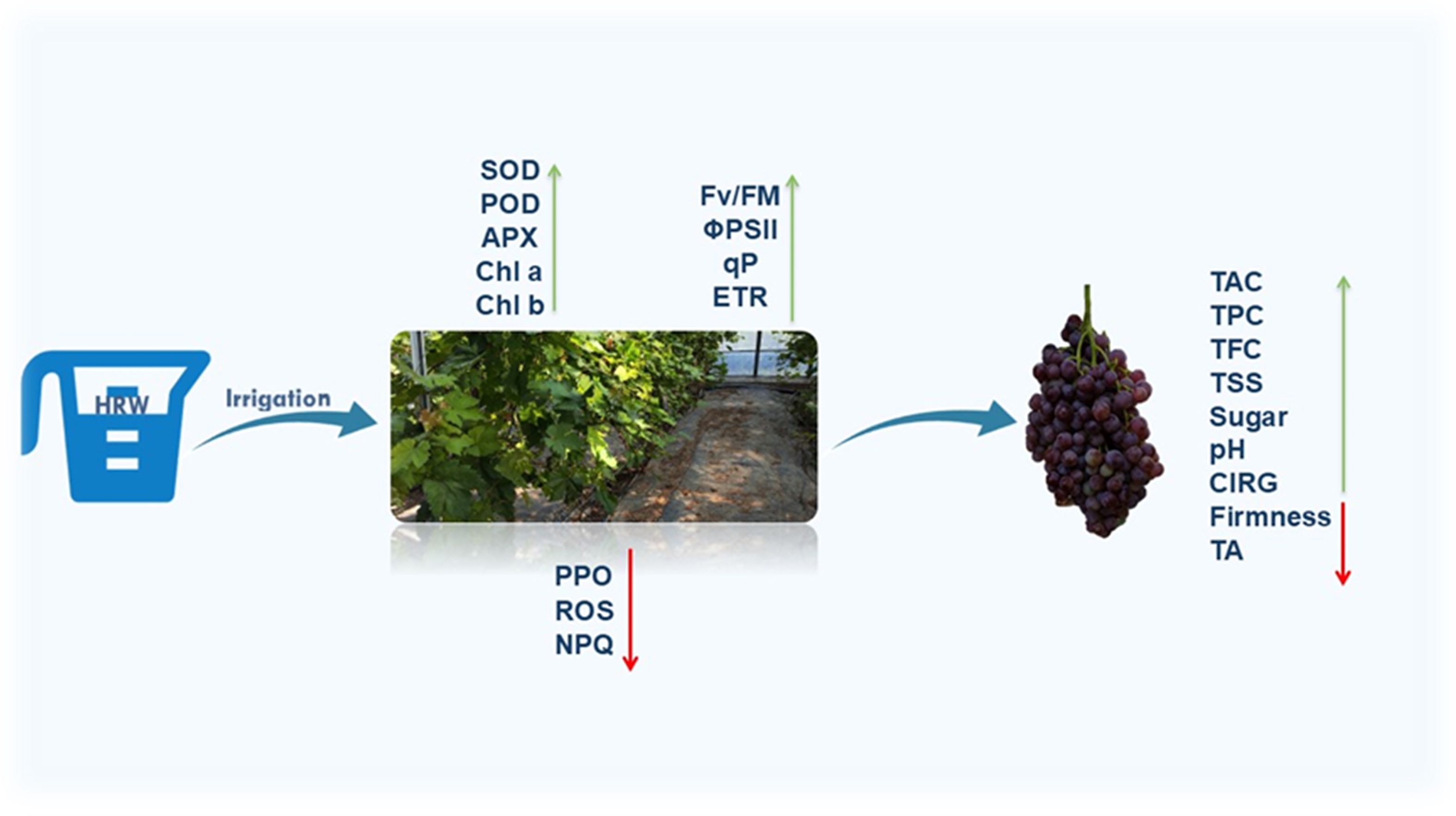
Figure 6. Proposed working model of HRW treatment in grape berry development. During berry development, HRW treatment enhanced antioxidant enzyme activities and reduced ROS levels, thereby fortifying grape leaves against oxidative stress. HRW treatment also improved photosynthetic efficiency by optimizing ChlF. Furthermore, HRW treatment promoted anthocyanin accumulation in berry peel, leading to improved fruit coloration and enhanced fruit quality by increasing total soluble solids and sugar content. HRW treatment also led to higher berry fresh weight and increased grape yield, suggesting a positive impact on resource allocation and fruit development. This suggests that HRW could lead to improvements in yield and fruit quality.
5 Conclusion
HRW treatment demonstrates a multifaceted positive impact on ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes, enhancing their physiological and biochemical characteristics. The application of HRW significantly improved the antioxidant defense system in grape leaves by increasing the activity of key enzymes like SOD, POD, and CAT while reducing ROS accumulation. This, in turn, led to improved photosynthetic efficiency, as evidenced by higher chlorophyll content, enhanced ChlF parameters (Fv/Fm, ΦPSII, ETR, and qP), and reduced NPQ. Furthermore, HRW treatment positively influenced fruit quality by promoting TAC accumulation, modulating TPC and TFC, and improving the CIRG. The treatment also resulted in increased TSS and soluble sugar content, along with enhanced berry and cluster weights, ultimately leading to a higher estimated yield. These findings suggest that HRW treatment can be a valuable strategy for improving grape production by mitigating oxidative stress, enhancing photosynthetic performance, and improving overall fruit quality and yield. Further research at the molecular level is warranted to fully elucidate the underlying mechanisms of HRW’s beneficial effects.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HA: Software, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Methodology. HZ: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Methodology. DY: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Software. LK: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. FZ: Validation, Writing – review & editing. JF: Validation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. KY: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32360718, 32460723), the Corps ‘Strong Youth’ Scientific and Technological Innovation Talent Program (2023CB008-05).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The author(s) verify and take full responsibility for the use of generative AI in the preparation of this manuscript. Generative AI was used only to check grammar and spelling and to rephrase some sentences to improve readability and language. AI tools were not used to write the manuscript independently. All content was reviewed, edited, and approved by the author(s), who take full responsibility for the content of the published article.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdel-Sattar, M., Al-Obeed, R. S., Makhasha, E., Mostafa, L. Y., Abdelzaher, R. A., and Rihan, H. Z. (2024). Improving mangoes' productivity and crop water productivity by 24-epibrassinosteroids and hydrogen peroxide under deficit irrigation. Agric. Water Manage. 298, 108860. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2024.108860
Abdel-Sattar, M., Al-Saif, A. M., Aboukarima, A. M., Eshra, D. H., and Sas-Paszt, L. (2022). Quality attributes prediction of flame seedless grape clusters based on nutritional status employing multiple linear regression technique. Agriculture 12, 1303. doi: 10.3390/agriculture12091303
Abdullaev, F., Pirogova, P., Vodeneev, V., and Sherstneva, O. (2024). Chlorophyll fluorescence in wheat breeding for heat and drought tolerance. Plants 13, 2778. doi: 10.3390/plants13192778
AiHaiti, A., Zhao, L., Maimaitiyiming, R., Wang, L., Liu, R., Mu, Y., et al. (2025). Changes in volatile flavors during the fermentation of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) juice and its storage stabilization. Food Chem. 463, 141077. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.141077
Akbar, U., Mondol, M. S. A., Abdi, G., Dash, K. K., Khan, S. A., and Dar, A. H. (2025). Hydrogen assisted technologies in food processing, preservation and safety: A comprehensive Review. Food Control 178, 111535. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2025.111535
Akhlaq, M., Miao, H., Zhang, C., Yan, H., Run, X., Chauhdary, J. N., et al. (2025). Resilience assessment of tomato crop chlorophyll fluorescence against water stress under elevated CO2 and protective cultivation. Irrigation Drainage. 74, 1234–1252. doi: 10.1002/ird.3079
Ali, M., Batool, S., Khalid, N., Ali, S., Raza, M. A., Li, X., et al. (2024). Recent trends in hydrogen-associated treatments for maintaining the postharvest quality of fresh and fresh-cut fruits and vegetables: A review. Food Control 156, 110114. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.110114
Alwazeer, D. (2018). Reducing atmosphere drying as a new technique for the preservation of the color of dried foods. J. Inst. Sci. Technol., 8, 125–131. doi: 10.21597/jist.418232
Alwazeer, D. and Özkan, N. (2022). Incorporation of hydrogen into the packaging atmosphere protects the nutritional, textural and sensorial freshness notes of strawberries and extends shelf life. J. Food Sci. Technol. 59, 3951–3964. doi: 10.1007/s13197-022-05427-y
An, R., Luo, S., Zhou, H., Zhang, Y., Zhang, L., Hu, H., et al. (2021). Effects of hydrogen-rich water combined with vacuum precooling on the senescence and antioxidant capacity of pakchoi (Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis). Scientia Hortic. 289, 110469. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110469
Anić, M., Kontić, J. K., Rendulić, N., Čarija, M., Osrečak, M., Karoglan, M., et al. (2024). Evolution of leaf chlorophylls, carotenoids and phenolic compounds during vegetation of some Croatian indigenous red and white grape cultivars. Plants 13, 971. doi: 10.3390/plants13070971
Arrones, A., Mangino, G., Alonso, D., Plazas, M., Prohens, J., Portis, E., et al. (2022). Mutations in the SmAPRR2 transcription factor suppressing chlorophyll pigmentation in the eggplant fruit peel are key drivers of a diversified colour palette. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 1025951. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1025951
Chen, P., Yang, W., Jin, S., and Liu, Y. (2021). Hydrogen sulfide alleviates salinity stress in Cyclocarya paliurus by maintaining chlorophyll fluorescence and regulating nitric oxide level and antioxidant capacity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 167, 738–747. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.09.004
Chen, T., Xu, T., Li, X., Shen, L., Hu, L., Guo, Y., et al. (2022). Transcriptional analysis of grape in response to weak light stress. Sheng wu Gong Cheng xue bao= Chin. J. Biotechnol. 38, 3859–3877. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.220289
Chen, Y., Xu, W., Han, C., Zhang, M., Chen, Y., Ma, Y., et al. (2025). Synergistic effects of ectoine and biostimulants combinations on tomato seedling growth and heat stress resilience. Plant Stress 16, 100873. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2025.100873
Cheng, P., Wang, J., Zhao, Z., Kong, L., Lou, W., Zhang, T., et al. (2021). Molecular hydrogen increases quantitative and qualitative traits of rice grain in field trials. Plants 10, 2331. doi: 10.3390/plants10112331
Choi, H. G., Moon, B. Y., and Kang, N. J. (2016). Correlation between strawberry (Fragaria ananassa Duch.) productivity and photosynthesis-related parameters under various growth conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 7, 1607. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01607
Da Porto, C. and Natolino, A. (2018). Extraction kinetic modelling of total polyphenols and total anthocyanins from saffron floral bio-residues: Comparison of extraction methods. Food Chem. 258, 137–143. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.03.059
Ding, X., Liu, S., Ma, J., Pan, X., Dong, B., and Duan, X. (2024a). Application of hydrogen-rich water maintains red pitaya fruit quality through regulation of ROS and energy metabolism. LWT 213, 117020. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2024.117020
Ding, X., Ma, J., Liu, S., Dong, X., Pan, X., and Dong, B. (2024b). Acid electrolytic water treatment improves the quality of fresh-cut red pitaya fruit by regulating ROS metabolism and phenylpropanoid pathway. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 207, 112636. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2023.112636
Dinis, L.-T., Brito, C. Q., Correia, C. M., and Moutinho-Pereira, J. (2024). “Canopy and soil management strategies: Insights to overcome abiotic stresses in grapevine,” in Advances in botanical research. (Elsevier), 71–99. doi: 10.1016/bs.abr.2024.01.002
Dong, W., Shi, L., Li, S., Xu, F., Yang, Z., and Cao, S. (2023). Hydrogen-rich water delays fruit softening and prolongs shelf life of postharvest okras. Food Chem. 399, 133997. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133997
Du, M., Zhu, Y., Nan, H., Zhou, Y., and Pan, X. (2024). Regulation of sugar metabolism in fruits. Scientia Hortic. 326, 112712. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2023.112712
El-Saadony, M. T., Saad, A. M., Mohammed, D. M., Fahmy, M. A., Elesawi, I. E., Ahmed, A. E., et al. (2024). Drought-tolerant plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria alleviate drought stress and enhance soil health for sustainable agriculture: A comprehensive review. Plant Stress 14, 100632. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2024.100632
Estrada, J. L., Arboleda, M. D. M., and Dionisio-Sese, M. L. (2021). Current status of sea grapes (Caulerpa spp.) farming and wild harvesting in the Philippines. J. Appl. Phycology 33, 3215–3223. doi: 10.1007/s10811-021-02533-w
Fang, H., Luo, F., Li, P., Zhou, Q., Zhou, X., Wei, B., et al. (2020). Potential of jasmonic acid (JA) in accelerating postharvest yellowing of broccoli by promoting its chlorophyll degradation. Food Chem. 309, 125737. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125737
Ferrandino, A., Pagliarani, C., and Pérez-Álvarez, E. P. (2023). Secondary metabolites in grapevine: crosstalk of transcriptional, metabolic and hormonal signals controlling stress defence responses in berries and vegetative organs. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1124298. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1124298
Franceschelli, S., Gatta, D. M., Pesce, M., Ferrone, A., Patruno, A., De Lutiis, M. A., et al. (2016). New approach in translational medicine: effects of electrolyzed reduced water (ERW) on NF-κB/iNOS pathway in U937 cell line under altered redox state. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 1461. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091461
Francis, D. and Abdulhameed, S. (2024). “Chapter 3 - Enzymes as a boon and a bane in the postharvest processing of fruits and vegetables,” in Enzymatic processes for food valorization. Eds. González, M. L. C., Buenrostro Figueroa, J. J., Verma, D. K., and Aguilar, C. N. (Academic Press), 37–59. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-323-95996-4.00003-4
Gambetta, J. M., Holzapfel, B. P., Stoll, M., and Friedel, M. (2021). Sunburn in grapes: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 604691. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.604691
González-Salvatierra, C., Flores, J., Díaz-Segura, O., Matías-Palafox, M. L., and Jiménez-Sierra, C. L. (2024). Seasonal chlorophyll fluorescence before and after rapid light curves in the endangered species Lophophora diffusa (Cactaceae) across two microenvironments. Flora 320, 152623. doi: 10.1016/j.flora.2024.152623
Guo, F., Sun, Y., Hu, H., Zhou, H., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., et al. (2025). Red light-emitting diode irradiation delays the senescence of postharvest pakchoi through promoting antioxidant capacity and regulating ascorbate-glutathione cycle. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 222, 113351. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2024.113351
Han, Y., Zhang, J., Chen, P., Li, H., Li, W., Liu, J., et al. (2024). Biochar improves water and nitrogen use efficiency of cotton under mulched drip irrigation in arid regions. Ind. Crops Products 222, 119830. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.119830
Hasanuzzaman, M., Bhuyan, M. B., Zulfiqar, F., Raza, A., Mohsin, S. M., Mahmud, J. A., et al. (2020). Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: Revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 9, 681. doi: 10.3390/antiox9080681
Hazrati, S., Tahmasebi-Sarvestani, Z., Modarres-Sanavy, S., Mokhtassi-Bidgoli, A., and Nicola, S. (2016). Effects of water stress and light intensity on chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and pigments of Aloe vera L. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 106, 141–148. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.04.046
He, J., Zhou, Y., Geilfus, C.-M., Cao, J., Fu, D., Baram, S., et al. (2024). Enhancing tomato fruit antioxidant potential through hydrogen nanobubble irrigation. Horticulture Res. 11, uhae111. doi: 10.1093/hr/uhae111
Hou, X., Qi, N., Wang, C., Li, C., Huang, D., Li, Y., et al. (2021). Hydrogen-rich water promotes the formation of bulblets in Lilium davidii var. unicolor through regulating sucrose and starch metabolism. Planta 254, 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03762-6
Hu, H., Li, P., and Shen, W. (2021). Preharvest application of hydrogen-rich water not only affects daylily bud yield but also contributes to the alleviation of bud browning. Scientia Hortic. 287, 110267. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2021.110267
Hu, L., Zheng, Q., Chen, Z., Qin, Y., Si, H., Ji, J., et al. (2025). Pre-harvest treatment with gibberellin (GA3) and nitric oxide donor (SNP) enhances post-harvest firmness of grape berries. Food Chemistry: Mol. Sci. 10, 100235. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2024.100235
Iwai, M., Wakao, S., and Niyogi, K. K. (2023). “Chapter 25 - photoprotection,” in The chlamydomonas sourcebook, 3rd ed. Eds. Grossman, A. R. and Wollman, F.-A. (Academic Press, London), 807–828.
Jediyi, H., Naamani, K., Ait Elkoch, A., Dihazi, A., El Fels, A. E. A., and Arkize, W. (2019). First study on technological maturity and phenols composition during the ripeness of five Vitis vinifera L grape varieties in Morocco. Scientia Hortic. 246, 390–397. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.10.052
Kamshybayeva, G. K., Kossalbayev, B. D., Sadvakasova, A. K., Kakimova, A. B., Bauenova, M. O., Zayadan, B. K., et al. (2024). Genetic engineering contribution to developing cyanobacteria-based hydrogen energy to reduce carbon emissions and establish a hydrogen economy. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 54, 491–511. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2022.12.342
Kanwal, R., Maqsood, M. F., Shahbaz, M., Naz, N., Zulfiqar, U., Ali, M. F., et al. (2024). Exogenous ascorbic acid as a potent regulator of antioxidants, osmo-protectants, and lipid peroxidation in pea under salt stress. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 247. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04947-3
Karimi, R., Gavili-Kilaneh, K., and Khadivi, A. (2022). Methyl jasmonate promotes salinity adaptation responses in two grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) cultivars differing in salt tolerance. Food Chem. 375, 131667. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131667
Lecourieux, F., Kappel, C., Pieri, P., Charon, J., Pillet, J., Hilbert, G., et al. (2017). Dissecting the biochemical and transcriptomic effects of a locally applied heat treatment on developing Cabernet Sauvignon grape berries. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 53. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00053
Li, Y., Li, L., Zhang, X., Mu, Q. E., Tian, J., Yan, J., et al. (2023). Differences in total phenolics, antioxidant activity and metabolic characteristics in peach fruits at different stages of ripening. LWT 178, 114586. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2023.114586
Li, T., Lu, C., Wei, Y., Zhang, J., Shao, A., Li, L., et al. (2024c). Chemical imaging for determining the distributions of quality components during the piling fermentation of Pu-erh tea. Food Control 158, 110234. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2023.110234
Li, L., Wang, J., Jiang, K., Kuang, Y., Zeng, Y., Cheng, X., et al. (2022b). Preharvest application of hydrogen nanobubble water enhances strawberry flavor and consumer preferences. Food Chem. 377, 131953. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131953
Li, L., Yin, Q., Zhang, T., Cheng, P., Xu, S., and Shen, W. (2021). Hydrogen nanobubble water delays petal senescence and prolongs the vase life of cut carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.) flowers. Plants 10, 1662. doi: 10.3390/plants10081662
Li, C., Yu, W., Wu, Y., and Li, Y. (2022a). Roles of hydrogen gas in plants under abiotic stress: Current knowledge and perspectives. Antioxidants 11, 1999. doi: 10.3390/antiox11101999
Li, S., Zheng, H., Sui, N., and Zhang, F. (2024b). Class III peroxidase: An essential enzyme for enhancing plant physiological and developmental process by maintaining the ROS level: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 283, 137331. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.137331
Li, M., Zhu, G., Liu, Z., Li, L., Wang, S., Liu, Y., et al. (2024a). Hydrogen fertilization with hydrogen nanobubble water improves yield and quality of cherry tomatoes compared to the conventional fertilizers. Plants 13, 443. doi: 10.3390/plants13030443
Liang, N.-N., Zhu, B.-Q., Han, S., Wang, J.-H., Pan, Q.-H., Reeves, M. J., et al. (2014). Regional characteristics of anthocyanin and flavonol compounds from grapes of four Vitis vinifera varieties in five wine regions of China. Food Res. Int. 64, 264–274. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.06.048
Liao, Z., Boubakri, H., Chen, B., Farooq, M., Yang, T., Liu, Q., et al. (2025). Pretreatment approaches for mitigating drought stress in plants. South Afr. J. Bot. 184, 709–724. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2025.06.035
Liu, F., Liu, Y. B., Li, J. S., and Huang, H. (2015). The role of hydrogen in plant stress tolerance. Zhiwu Shengli Xuebao/Plant Physiol. J. 51, 141–152. doi: 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2014.0385
Liu, Y., Pan, J., Ni, S., Xing, B., Cheng, K., and Peng, X. (2022). Transcriptome and metabonomics combined analysis revealed the defense mechanism involved in hydrogen-rich water-regulated cold stress response of tetrastigma hemsleyanum. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.889726
Liu, S., Wang, J., Li, X., Wang, X., Wang, X., Zhong, H., et al. (2025). Genetic diversity analysis and construction of a core germplasm resource bank of xinjiang’s indigenous cultivated grapes. Agriculture 15, 871. doi: 10.3390/agriculture15080871
Lo’ay, A. and El-Boray, M. (2018). Improving fruit cluster quality attributes of ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes using preharvest application of ascorbic and salicylic acid. Scientia Hortic. 233, 339–348. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.02.010
Martínez-Lüscher, J., Morales, F., Sánchez-Díaz, M., Delrot, S., Aguirreolea, J., Gomès, E., et al. (2015). Climate change conditions (elevated CO2 and temperature) and UV-B radiation affect grapevine (Vitis vinifera cv. Tempranillo) leaf carbon assimilation, altering fruit ripening rates. Plant Sci. 236, 168–176. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.04.001
Miyoshi, Y., Hidaka, K., Yin, Y.-G., Suzui, N., Kurita, K., and Kawachi, N. (2021). Non-invasive 11C-imaging revealed the spatiotemporal variability in the translocation of photosynthates into strawberry fruits in response to increasing daylight integrals at leaf surface. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 688887. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.688887
Mvondo-She, M. A., Mashilo, J., Gatabazi, A., Ndhlala, A. R., and Laing, M. D. (2024). Exogenous Silicon Application improves chilling Injury Tolerance and Photosynthetic Performance of Citrus. Agronomy 14, 139. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14010139
Ngaffo Mekontso, F., Duan, W., Cisse, E. H. M., Chen, T., and Xu, X. (2021). Alleviation of postharvest chilling injury of carambola fruit by γ-aminobutyric acid: physiological, biochemical, and structural characterization. Front. Nutr. 8. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.752583
OIV (2025). State of the world vine & Wine sector in 2024. Available online at: https://www.oiv.int/sites/default/files/2025-04/OIV-State_of_the_World_Vine-and-Wine-Sector-in-2024.pdf (Accessed July 15, 2025).
Olivares, D., Contreras, C., Muñoz, V., Rivera, S., González-Agüero, M., Retamales, J., et al. (2017). Relationship among color development, anthocyanin and pigment-related gene expression in ‘Crimson Seedless’ grapes treated with abscisic acid and sucrose. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 115, 286–297. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.04.007
Ortiz, E. P., Ospina, L. F., and Aragón, D. M. (2024). “Gastroprotective effect of the butanolic fraction from Physalis Peruviana fruits,” in Handbook of goldenberry (Physalis Peruviana) (Elsevier), 455–472. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-443-15433-1.00043-1
Pashkovskiy, P., Soshinkova, T., Korolkova, D., Kartashov, A., Zlobin, I., Lyubimov, V. Y., et al. (2018). The effect of light quality on the pro-/antioxidant balance, activity of photosystem II, and expression of light-dependent genes in Eutrema salsugineum callus cells. Photosynthesis Res. 136, 199–214. doi: 10.1007/s11120-017-0459-7
Pei, D., Ren, Y., Yu, W., Zhang, P., Dong, T., Jia, H., et al. (2023). The roles of brassinosteroids and methyl jasmonate on postharvest grape by regulating the interaction between VvDWF4 and VvTIFY 5 A. Plant Sci. 336, 111830. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111830
Pérez-Labrada, F. and Juárez-Maldonado, A. (2024). “Improving fruit quality and bioactive compounds in plants: new trends using nanocomposites,” in Nanocomposites for environmental, energy, and agricultural applications. (Elsevier), 277–314. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-443-13935-2.00009-7
Qazi, U. Y. (2022). Future of hydrogen as an alternative fuel for next-generation industrial applications; challenges and expected opportunities. Energies 15, 4741. doi: 10.37247/ADERES4EDN.4.22.6
Rao, M. J., Duan, M., Zhou, C., Jiao, J., Cheng, P., Yang, L., et al. (2025). Antioxidant defense system in plants: reactive oxygen species production, signaling, and scavenging during abiotic stress-induced oxidative damage. Horticulturae 11, 477. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae11050477
Rashad, Y. M., El-Sharkawy, H. H., El-Kenawy, M. A., and Galilah, D. A. (2023). Kaolin triggers defense-responsive genes in grapevines (cv. King Ruby seedless) to downy mildew and enhances its vegetative development, production, and berries quality standards. Scientia Hortic. 309, 111674. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111674
Rochaix, J.-D. (2011). Assembly of the photosynthetic apparatus. Plant Physiol. 155, 1493–1500. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.169839
Rodriguez-Izquierdo, A., Carrasco, D., Anand, L., Magnani, R., Catarecha, P., Arroyo-Garcia, R., et al. (2024). Epigenetic differences between wild and cultivated grapevines highlight the contribution of DNA methylation during crop domestication. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 504. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05197-z
Ruan, R., Lambers, H., and Wang, Y. (2024). Comparative responses of two maize genotypes with contrasting drought tolerance to biochar application. Biochar 6, 66. doi: 10.1007/s42773-024-00359-6
Russell, G., Zulfiqar, F., and Hancock, J. T. (2020). Hydrogenases and the role of molecular hydrogen in plants. Plants 9, 1136. doi: 10.3390/plants9091136
Sana, R., Aftab, T., Naeem, M., Jha, P. K., and Prasad, P. V. V. (2025). Production of secondary metabolites under challenging environments: understanding functions and mechanisms of signalling molecules. Front. Plant Sci. 16, 2025. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1569014
Shah, W., Ullah, S., Ali, S., Idrees, M., Khan, M. N., Ali, K., et al. (2021). Effect of exogenous alpha-tocopherol on physio-biochemical attributes and agronomic performance of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) under drought stress. PloS One 16, e0248200. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248200
Shi, Y., Li, B., Yuan, J., Qin, Y., Zhou, L., Zhong, J., et al. (2025). Controlled release active films prepared from temperature responded emulsions and their application in grape preservation. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochemical Eng. Aspects 709, 136190. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2025.136190
Siddiqui, M., Homa, F., Lata, D., Mir, H., Aftab, T., and Mishra, P. (2022). Hydrogen sulphide infiltration downregulates oxidative metabolism and extends postharvest life of banana. Plant Biol. 24, 697–703. doi: 10.1111/plb.13362
Subedi, E., Karki, P., Bhattarai, S., Pathak, R., and Poudel, P. R. (2025). Effect of botanicals and chemicals on physiochemical parameters and postharvest disease management of mango (Mangifera indica). Cogent Food Agric. 11, 2442668. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2024.2442668
Taghipour, S., Nia, A. E., Hokmabadi, H., and Martínez-Gómez, P. (2024). Physicochemical and quality characters of fresh pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) cultivars in response to chitosan/ZnO nanocomposite coating. Food Chem. 435, 137136. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137136
Taş, A., Berk, S. K., Orman, E., Gundogdu, M., Ercişli, S., Karatas, N., et al. (2021). Influence of pre-harvest gibberellic acid and post-harvest 1-methyl cyclopropane treatments on phenolic compounds, vitamin C and organic acid contents during the shelf life of strawberry fruits. Plants 10, 121. doi: 10.3390/plants10010121
Vasco, C., Ruales, J., and Kamal-Eldin, A. (2008). Total phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacities of major fruits from Ecuador. Food Chem. 111, 816–823. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.04.054
Wang, Y., Chen, X., Chen, W., Yang, Z., Shi, L., Li, X., et al. (2025). Hydrogen-rich water delays post-harvest yellowing in broccoli by inhibiting ethylene and ABA levels, thereby reducing chlorophyll degradation and carotenoid accumulation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 228, 113661. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2025.113661
Wang, H., Wu, L., Cheng, M., Fan, J., Zhang, F., Zou, Y., et al. (2018). Coupling effects of water and fertilizer on yield, water and fertilizer use efficiency of drip-fertigated cotton in northern Xinjiang, China. Field Crops Res. 219, 169–179. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2018.02.002
Wang, K., Yang, X., Liang, J., Rong, Y., Zhao, W., Ding, J., et al. (2024). Preparation, characterization, antimicrobial evaluation, and grape preservation applications of polyvinyl alcohol/gelatin composite films containing zinc oxide at quaternized chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromolecules 277, 134527. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134527
Wang, J., Zhang, X., Han, Z., Feng, H., Wang, Y., Kang, J., et al. (2022). Analysis of physiological indicators associated with drought tolerance in wheat under drought and re-watering conditions. Antioxidants 11, 2266. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112266
Wei, M., Ge, Y., Li, C., Han, X., Qin, S., Chen, Y., et al. (2019). G6PDH regulated NADPH production and reactive oxygen species metabolism to enhance disease resistance against blue mold in apple fruit by acibenzolar-S-methyl. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 148, 228–235. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2018.05.017
Wu, Q., Huang, L., Su, N., Shabala, L., Wang, H., Huang, X., et al. (2020b). Calcium-dependent hydrogen peroxide mediates hydrogen-rich water-reduced cadmium uptake in plant roots. Plant Physiol. 183, 1331–1344. doi: 10.1104/pp.20.00377
Wu, M., Xu, X., Hu, X., Liu, Y., Cao, H., Chan, H., et al. (2020a). SlMYB72 regulates the metabolism of chlorophylls, carotenoids, and flavonoids in tomato fruit. Plant Physiol. 183, 854–868. doi: 10.1104/pp.20.00156
Xiao, Y., Wu, Y., Huang, Z., Guo, M., Zhang, L., Luo, X., et al. (2024). Mechanism of induced soluble sugar accumulation and organic acid reduction in plum fruits by application of melatonin. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 1208. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05949-x
Xie, Y., Zhang, W., Duan, X., Dai, C., Zhang, Y., Cui, W., et al. (2015). Hydrogen-rich water-alleviated ultraviolet-B-triggered oxidative damage is partially associated with the manipulation of the metabolism of (iso) flavonoids and antioxidant defence in Medicago sativa. Funct. Plant Biol. 42, 1141–1157. doi: 10.1071/FP15204
Xiong, B., Qiu, X., Huang, S., Yang, Y., Sun, G., Wang, X., et al. (2020). Comparative analysis of leaf photosynthetic characteristics and fruit sugar content in trees of Citrus cultivar ‘Huangguogan’of different age. Photosynthetica 58, 902–910. doi: 10.32615/ps.2020.042
Xu, G., Li, C., Qin, S., Xiao, W., Fu, X., Chen, X., et al. (2022a). Changes in sucrose and sorbitol metabolism cause differences in the intrinsic quality of peach fruits cultivated in field and greenhouse environments. Agronomy 12, 2877. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12112877
Xu, Y., Teng, Y., Wang, X., Ren, W., Zhao, L., Luo, Y., et al. (2023). Endogenous biohydrogen from a rhizobium-legume association drives microbial biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyl in contaminated soil. Environ. Int. 176, 107962. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2023.107962
Xu, H., Wang, J., Qu, Y., Hu, L., Tang, Y., Zhou, Z., et al. (2022b). Estimating leaf chlorophyll content of moso bamboo based on unmanned aerial vehicle visible images. Remote Sens. 14, 2864. doi: 10.3390/rs14122864
Xu, J., Zhang, X., Sun, X., Lv, Q., and Zhang, Y. (2021). Red-fleshed apple anthocyanin extracts attenuate male reproductive system dysfunction caused by busulfan in mice. Front. Nutr. 8, 632483. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.632483
Yang, L., Tian, J., Zhu, M., Yu, B., and Sun, Y. (2024). Hydrogen-rich water improvement in root growth in maize exposed to saline stress. Cereal Res. Commun. 52, 581–590. doi: 10.1007/s42976-023-00413-2
Yao, Y., Zhao, Z., Ding, Z., Yao, K., Yang, Y., Hou, X., et al. (2024). Hydrogen-rich water irrigation promotes fruit ripening and nutritional composition in tomato. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 213, 112920. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2024.112920
Yin, W., Chai, Q., Fan, Z., Hu, F., Zhao, L., Fan, H., et al. (2025). Review on physiological and ecological characteristics and agronomic regulatory pathways of intercropping to delay root and canopy senescence of crops. J. Integr. Agric. 24, 1–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jia.2024.04.013
Yu, Y., Zhang, H., Xing, H., Cui, N., Liu, X., Meng, X., et al. (2023). Regulation of growth and salt resistance in cucumber seedlings by hydrogen-rich water. J. Plant Growth Regul. 42, 134–153. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1497362
Yu, P., Zheng, F., Shi, Q., Zhao, A., Peng, X., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Hydrogen-rich water treatment maintains the quality and prolongs the shelf-life of postharvest table grapes by regulating respiratory and energy metabolisms. J. Berry Res. 14, 274–286. doi: 10.1177/18785093241289212
Yun, Z., Gao, H., Chen, X., Chen, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, T., et al. (2021). Effects of hydrogen water treatment on antioxidant system of litchi fruit during the pericarp browning. Food Chem. 336, 127618. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.127618
Zgonnik, V. (2020). The occurrence and geoscience of natural hydrogen: A comprehensive review. Earth-Science Rev. 203, 103140. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103140
Zhang, Y., Hui, J., Qin, Q., Sun, Y., Zhang, T., Sun, H., et al. (2021). Transfer-learning-based approach for leaf chlorophyll content estimation of winter wheat from hyperspectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 267, 112724. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112724
Zhang, W., Li, Y., Xu, Y., Zheng, Y., Liu, B., and Li, Q. (2023b). Alternate drip irrigation with moderate nitrogen fertilization improved photosynthetic performance and fruit quality of cucumber in solar greenhouse. Scientia Hortic. 308, 111579. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2022.111579
Zhang, X., Wei, J., Huang, Y., Shen, W., Chen, X., Lu, C., et al. (2018). Increased cytosolic calcium contributes to hydrogen-rich water-promoted anthocyanin biosynthesis under UV-A irradiation in radish sprouts hypocotyls. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 1020. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01020
Zhang, X., Wei, J., Tian, J., Li, N., Jia, L., Shen, W., et al. (2019). Enhanced anthocyanin accumulation of immature radish microgreens by hydrogen-rich water under short wavelength light. Scientia Hortic. 247, 75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.11.060
Zhang, H., Wu, X., Liu, X., Yao, Y., Liu, Z., Wei, L., et al. (2023a). Hydrogen gas improves the postharvest quality of Lanzhou lily (Lilium davidii var. unicolor) bulbs. Plants 12, 946. doi: 10.3390/plants12040946
Zhao, M., Ren, H., Yan, Z., Ma, J., Feng, X., Liu, D., et al. (2024). Reusable thiol-modification Lactobacillus plantarum embedded in cellulose nanocrystals composite aerogel for efficient removal of Ochratoxin A in grape juice. Food Chemistry: X 22, 101336. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1378749
Zhao, J., Xie, X., Wang, S., Zhu, H., Dun, W., Zhang, L., et al. (2020). 1-Methylcyclopropene affects ethylene synthesis and chlorophyll degradation during cold storage of ‘Comice’pears. Scientia Hortic. 260, 108865. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.108865
Zhong, Y., Zhang, T., Zhang, W., Wang, G., Zhang, Z., Zhao, P., et al. (2023). Antibacterial castor oil-based waterborne polyurethane/gelatin films for packaging of strawberries. Food Packaging Shelf Life 36, 101055. doi: 10.1016/j.fpsl.2023.101055
Zhou, Y., Mahmoud Ali, H. S., Xi, J., Yao, D., Zhang, H., Li, X., et al. (2024). Response of photosynthetic characteristics and yield of grape to different CO2 concentrations in a greenhouse. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1378749
Keywords: hydrogen-rich water, antioxidant enzymes, chlorophyll fluorescence, Flame Seedless grapes, fruit quality, reactive oxygen species, anthocyanin accumulation
Citation: Ali HSM, Zhang H, Yao D, Kun L, Zhao F, Feng J and Yu K (2025) Hydrogen-rich water irrigation enhances fruit quality in ‘Flame Seedless’ grapes by regulating chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and antioxidant activities. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1693075. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1693075
Received: 26 August 2025; Accepted: 06 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Guoxiang Jiang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Cristina Sgherri, University of Pisa, ItalyYandong Yao, Shanxi Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Ali, Zhang, Yao, Kun, Zhao, Feng and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kun Yu, eXVrdW40MTBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Hossam Salah Mahmoud Ali1,2,3
Hossam Salah Mahmoud Ali1,2,3 Jianrong Feng
Jianrong Feng Kun Yu
Kun Yu