- Department of Plant Breeding, Justus Liebig University, Giessen, Germany
Faba bean is a valuable legume crop desired globally for its high nutritional composition. However, the seed vicine and convicine (v-c) content reduces the nutritional quality of faba bean protein and can induce favism in susceptible individuals. Recently, VC1 gene, encoding a bi-functional riboflavin protein, was reported to initiate the v-c biosynthetic pathway in V. faba. In low v-c cultivars, a 2 bp insertion in this gene disrupts its function by causing a frameshift and premature stop codon. However, because v-c biosynthesis is only partially reduced, this suggests that additional genes may also be involved in the pathway. Here, we identify and investigate multiple tandem gene duplications at the VC1 locus. Our findings reveal that VC1 exhibits multiple structural variants and copy number variations, but its expression is independent of copy number. Low v-c genotypes carry both variants of the gene — with and without the 2 bp insertion — but only the variant with the insertion is expressed. In contrast, high v-c genotypes consistently express the variant lacking the insertion. Although some high v-c genotypes also carry the insertion, it is found in a non-expressed variant, while the expressed variant lacks the insertion, resulting in the high v-c phenotype. We also report a novel diverging VC1 homolog, RIBA2, which shares expression domains with VC1. This homologous gene encodes GTP cyclohydrolase II, a critical enzyme in the v-c pathway. Expression of this gene contributes ~5-10% of riboflavin gene transcripts in immature seeds suggesting it as a minor-effect candidate locus in v-c biosynthesis. Moreover, two SNPs within the coding sequence of RIBA2 segregated with v-c content, offering a reliable alternative for marker-assisted selection in faba bean breeding. In conclusion, this study contributes to the elucidation of the complex genetic regulation of v-c biosynthesis and provides valuable insights to facilitate further efforts in its reduction in faba bean.
1 Introduction
Faba bean (Vicia faba L.) is a grain legume which is globally important for its highly nutritious, protein-rich seeds. The global production of faba bean stands at 5.7 million tons in 2020 (FAOSTAT, 2022), making it the sixth most produced pulse crop and the highest yielding legume after soybean (Adhikari et al., 2021). It is reported to have originated from the Mediterranean basin and subsequently spread to be cultivated across nearly all continents worldwide (Duc et al., 2010; Caracuta et al., 2016). It has become increasingly popular, especially in cool-season climates where other protein crops perform poorly. Faba bean seeds contain up to 37% protein and are rich in micronutrients, making them a suitable source of food for humans and feed for their livestock (Duc et al., 1999; Karkanis et al., 2018; Warsame et al., 2020). In addition to its nutritional benefits, faba bean can improve soil fertility in association with rhizobium bacteria by fixing a significant quantity of nitrogen in the soil, which reduces the need for application of inorganic nitrogen fertilizer in subsequent seasons (Karkanis et al., 2018; Adhikari et al., 2021). This feature is leveraged in many agricultural systems by incorporating faba bean into crop rotation or mixed cropping with others crops such as cereals (Stagnari et al., 2017; Carrillo-Perdomo et al., 2020). This ecological importance of faba bean and its roles in food and feed has increased its global reputation significantly.
However, the agronomic relevance of faba bean is limited by the presence of significant quantities of vicine and convicine (v-c) in all parts of the plants (Luzzatto and Arese, 2018; Choudhary and Mishra, 2019; Badjona et al., 2023). The metabolic products of vicine and convicine—divicine and isouramil—release free radicals that cause oxidative damage to red blood cells in people with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency, leading to acute hemolytic anemia, a condition also known as favism (Badjona et al., 2023; Björnsdotter et al., 2021). Therefore, to enhance faba bean usage and its general acceptability, reducing the v-c content to the barest minimum safe for food and feed is essential. However, the genetic basis of v-c accumulation remains to be fully elucidated, and all low v-c cultivars still carry baseline v-c levels.
Previous studies have highlighted a bimodal pattern in the v-c phenotype, primarily influenced by a major quantitative trait locus (QTL) on chromosome 1 of the faba bean genome (Duc et al., 1989; Ramsay et al., 1995; Gutierrez et al., 2006; Khazaei et al., 2015). Molecular markers flanking this locus were identified by Khazaei et al. (2015); however, the gene RIBA1 was only recently discovered within this region by Björnsdotter et al. (2021). RIBA1, named VC1, encodes a bi-functional riboflavin protein responsible for catalyzing the pivotal step in the v-c biosynthetic pathway. The gene has two functional domains, RibA and RibB, encoding GTP cyclohydrolase II (GCHII) and 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone-4-phosphate synthase (DHBPS), respectively. However, it is the GTP cyclohydrolase II domain that directly catalyzes v-c biosynthesis, via conversion of purine nucleoside triphosphate GTP into the unstable intermediates leading to v-c (Björnsdotter et al., 2021). A 2 bp insertion in the GCHII domain leads to loss of function in low v-c cultivars. This frameshift mutation inactivates VC1 by causing a premature stop codon, hindering the correct synthesis of GTP cyclohydrolase II. However, this mutation does not eliminate v-c completely, although it causes a significant reduction. This suggests a potential involvement of other genes or gene copies, necessitating further research to comprehensively understand the genetic factors that control v-c biosynthesis in faba bean. Recently completed V. faba genome assemblies and gene annotations for low and high v-c cultivars (Jayakodi et al., 2023) provide an excellent basis to advance knowledge in this regard. Therefore, the objectives of this study were to elucidate the genetic regulation of v-c content by identifying active bi-functional riboflavin genes and polymorphisms corresponding to changes in v-c content. Due to the residual v-c content in seeds of low v-c genotypes, we hypothesize that at least one additional locus controls v-c biosynthesis. To study this, we identified RIBA protein-coding genes by homology mapping of the RIBA1 protein sequence to two faba bean reference genomes with high and low v-c content, respectively. All similar protein-encoding genes were identified and functionally analyzed across a set of well-characterized low and high v-c cultivars using bioinformatic predictions, gene expression and transcript analyses, and phenotype correlation analysis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant materials and cultivation
The study utilized a diverse set of well-characterized faba bean lines consisting of nine low v-c and nine high v-c genotypes with different genetic backgrounds (Supplementary Table S1). These lines represent a set of carefully selected genotypes with known characteristics and performances. They were obtained from Norddeutsche Pflanzenzucht Hans-Georg Lembke KG (NPZ, Hohenlieth, Germany) and comprise both commercial cultivars and lines inbred beyond the fifth generation of selfing. Vicine content for each genotype was measured from a sample of two faba bean seeds using spectrophotometry as described by Sixdenier et al. (1996).
Two seeds from each genotype were planted in 4-liter plastic pots within a pollinator-proof chamber in the greenhouse. Fresh leaves at 21 days after planting were collected from the first fully opened leaves for DNA isolation. For RNA extraction for gene expression and transcript analyses, a subset of ten genotypes was selected, including five with low and five with high seed v-c content. The plants were manually tripped during flowering to ensure pod-set (Kambal et al., 1976). Fresh and immature seeds were collected from this subset for RNA isolation at two stages during seed development: early seed filling stage (ESF) (stage four) and late seed filling stage (LSF) (stage six). Specifically, seeds aged 13–16 days and 20–25 days after tripping were selected, respectively. At the ESF stage, the cleft between the cotyledons is broad, with a spherical chalazal chamber. The embryo has a butterfly-shaped appearance and is surrounded by endosperm. In contrast, at LSF, the intense green cotyledons are closely positioned and have a curved axis (Borisjuk et al., 1995).
2.2 DNA extraction
Fresh leaves collected from each genotype were immediately flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and lysed using Qiagen Tissue Lyser II (Qiagen, Düsseldorf, Germany). Genomic DNA was isolated from the leaf powder following the Doyle and Doyle (1990) method.
2.3 RNA extraction and cDNA synthesis
Immature seeds were immediately flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and then manually ground into powder using a mortar and pestle. RNA was isolated from 100 mg of the powdered samples using the Zymo RNA miniprep kit (Zymo Research, Freiburg, Germany) following the manufacturer’s manual. DNaseI treatment was performed to remove genomic DNA, following the procedure outlined in the Zymo RNA kit manual. RNA concentration and quality were determined using Qubit RNA assay kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Germany) and agarose gel (1%), respectively. First-strand cDNA was synthesized using the RevertAid cDNA synthesis kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, Germany). Initially, 1 µl of Random Hexamer primer was added to 1 µg of RNA, incubated for 5 minutes at 65°C, and subsequently cooled on ice. The cDNA reaction master mix was prepared by adding 4 µl of Reaction buffer (5x), 2 µl of dNTP mix (10mM), 1 µl of Ribolock RNase inhibitor (20 U/µl), and 1 µl of RevertAid H Minus Reverse Transcriptase (200 U/µl). Reactions were carried out in a thermal cycler at the following temperature conditions: 25°C for 5 minutes, 42°C for 60 minutes, 70°C for 5 minutes, and then held at 4°C. The resulting cDNA was utilized for gene expression analysis and Sanger sequencing of VC1 and RIBA2 genes.
2.4 Homology-based gene identification
Custom databases for faba bean were established from the reference assemblies of the high v-c cultivar, Hedin, and the low v-c cultivar, Tiffany (Jayakodi et al., 2023), using ncbi-blast 2.12.0+. RIBA1 protein sequence was aligned to these databases using the tblastn function to identify all RIBA genes in both genomes. Genes exhibiting sequence similarity were identified and filtered to retain only those with over 85% protein sequence similarity to RIBA1, and were then functionally analyzed in this study.
2.5 Phylogenetic and sequence analysis
Alignments were performed using MAFFT tool in Jalview (version 2.11.3.0). Phylogenetic analysis was conducted using the phylogeny.fr platform. The maximum likelihood method, implemented in the PhyML program (v3.1/3.0 aLRT), was employed to reconstruct the phylogenetic tree while TreeDyn (v198.3) was used for tree rendering. Amino acid sequences of RIBA proteins for chickpea (XP_004485599), lupin (KAE9591829), grass pea (CAK6822722), lotus (XP_057429064), Medicago (XP_003593237) and pea (XP_050880829) were downloaded from NCBI database (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Functional domains of RIBA proteins were predicted using PsiPred workbench (http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred/).
2.6 Primer design and synthesis
All primers for the experiments were designed using Primer3 plus (https://www.primer3plus.com/index.html) and subsequently synthesized by Microsynth AG (Balgach, Switzerland). For each primer, gene sequences from the two reference genomes, Hedin and Tiffany (Jayakodi et al., 2023), were aligned to identify conserved regions with priming efficiency, as predicted by Primer3 Plus.
2.7 PCR Validation of VC1 and RIBA2 genes in faba bean
All VC1 variants and RIBA2 were validated in faba bean genotypes using selective PCR amplification. PCR reactions were set up in a final volume of 25 µl, including 12.5 µl of GoTaq Hot Start Green Master Mix, (Promega, Madison, WI, United States), 1.25 µl of 10 µM forward and reverse primers (Supplementary Table S2), 1.5 µl of genomic DNA and 8.5 µl of MilliQ water. The reactions were carried out in a T100 Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, United States) with the following conditions: 94°C for 2 minutes, 35 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 30 seconds, annealing at 60°C for 30 seconds and extension at 72°C for 40 to 90 seconds depending on the size of amplicon, followed by final extension for 5 minutes at 72°C. Amplicons were separated on a 1% agarose gel and visualized under UV light.
2.8 VC1 copy number determination by quantitative PCR
VC1 copy number was determined by quantitative PCR in 10 µl final volume, containing 5 µl 2x SYBR Green master mix (ThermoFisher Scientific, Germany), 1 µl 10 µM forward primer and 1 µl 10 µM reverse primer (Supplementary Table S2), 1 µl of DNA and 2 µl of MilliQ water. ELF1A was used as the reference gene for normalization (Gutierrez et al., 2011). There were two biological and three technical replicates for each genotype, as well as triplicates of water samples serving as no-template controls. Quantitative PCR was done using StepOneplus (ThermoFisher Scientific, Germany) with the following temperature conditions: 95°C for 10 minutes, 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 seconds followed by 60°C for 1 minute. Relative quantification was determined by delta-delta CT (ΔΔCt) method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001).
2.9 Relative quantification of VC1 and RIBA2 expression levels by reverse-transcription quantitative PCR
The expression levels of VC1 and RIBA2 were determined from cDNA synthesized from the previous step. The reaction mixture consisted of 5 µl of 2x SYBR Green master mix (ThermoFisher Scientific, Germany), 1 µl of 10 µM forward primer and 1 µl of 10 µM reverse primer (Supplementary Table S2), 1 µl of cDNA, and 2 µl of MilliQ water. The reference genes, CYP2 and ELF1A, were used for normalization as they were previously reported to be stably expressed in faba bean (Gutierrez et al., 2011). As controls, three water samples were included as no-template controls and each sample had two biological and three technical replicates. Quantitative PCR was done using StepOneplus (ThermoFisher Scientific, Germany) as described above for copy number quantification and relative transcript levels were determined by delta-delta CT (ΔΔCt) method (Livak and Schmittgen, 2001).
2.10 VC1 and RIBA2 cDNA sequencing
The cDNA samples, synthesized as described above, were used for selective amplification of VC1 and RIBA2. Forward and reverse primer pairs specific to VC1 and RIBA2 were used (Supplementary Table S2). The PCR conditions were as described previously in the gene validation section, except that the annealing temperature was set at 58°C. Subsequently, the resulting amplicons were sent for Sanger sequencing at Microsynth AG (Balgach, Switzerland). For each genotype, samples from the two developmental stages were sequenced.
2.11 KASP marker assay development and SNP genotyping
Genotyping was performed using Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR (KASP) assay technique for polymorphisms within VC1 gene. VC1 genes from the two reference assemblies were aligned to identify possible single nucleotide polymorphisms. For identified variants, allele-specific primers were designed. To detect the presence of 2 bp insertion in VC1 (SNP08) within our faba bean set, primers were designed where A1 binds to the wild-type variant, and A2 binds to the mutant variant. The common primer used was C1. Detailed information on all KASP markers can be found in Supplementary Table S3. The KASP marker assay procedure was conducted according to the methodology outlined in the study by Makhoul and Obermeier (2022).
2.12 Data analysis
All experiments, including PCR, sequencing, copy number quantification, gene expression analysis, and KASP genotyping, were repeated at least twice. The resulting qPCR data from copy number quantification and gene expressions were analyzed using Microsoft Excel and R (version 4.3.2). The library packages ggpubr and ggplot2 were used to generate plots using R studio. Statistical differences were inferred using t-test for two groups or one-way ANOVA for more than two groups.
3 Results
3.1 Multiple gene models encode RIBA proteins in the Vicia faba genome
In this study, we investigated the role of the different genes that encode bifunctional RIBA enzymes responsible for catalyzing the initial step in the v-c biosynthetic pathway. We employed a homology-based method to align RIBA1 protein to the recently assembled faba bean reference genomes, Hedin— a high v-c cultivar— and Tiffany— a low v-c cultivar (Jayakodi et al., 2023). Our analysis revealed the presence of multiple gene models encoding RIBA protein in the faba bean genome. In Hedin, we identified four such genes on chromosome 1 and contig_8341, namely Vfaba.Hedin2.R1.1g485480, Vfaba.Hedin2.R1.1g485520, Vfaba.Hedin2.R1.1g485560, and Vfaba.Hedin2.R1.Ung108560. Tiffany, on the other hand, had five genes on chromosome 1, including Vfaba.Tiffany.R1.1g399960, Vfaba.Tiffany.R1.1g400000, Vfaba.Tiffany.R1.1g400040, Vfaba.Tiffany.R1.1g400120, and Vfaba.Tiffany.R1.1g400280 (Figure 1a; Supplementary Table S4). Comparative analysis indicated that three of these genes from Hedin and four from Tiffany shared significant identity (>96%) with the RIBA1 (VC1) gene previously reported by Björnsdotter et al. (2021) (Figure 1b). Therefore, we classified these genes as genetic variants of VC1. These VC1 variants exhibited contrasting structural variations that grouped into three major variants, defined by their structural characteristics. VC1A had a tandem duplication of a 65 bp in intron 3 and VC1B had a partial deletion in this intron, while VC1C lacked the entire intron (Figure 1c). There were three copies of VC1A in the Hedin assembly and two copies each of VC1B and VC1C in Tiffany. As expected, one copy each of VC1B and VC1C carried a 2 bp frameshift insertion in exon 6, as reported by Björnsdotter et al. (2021), which renders the gene product non-functional. This insertion was absent in VC1A. The modification in intron 3 is associated with a three-nucleotide difference in exon 3 and can distinguish VC1C/vc1c from VC1A and VC1B/vc1b. Beside these variations, vc1b and VC1C share similar alleles at most SNP positions. Additionally, there are SNPs within exon 4 and 5 that can distinguish other VC1 variants (Supplementary Figure S1).
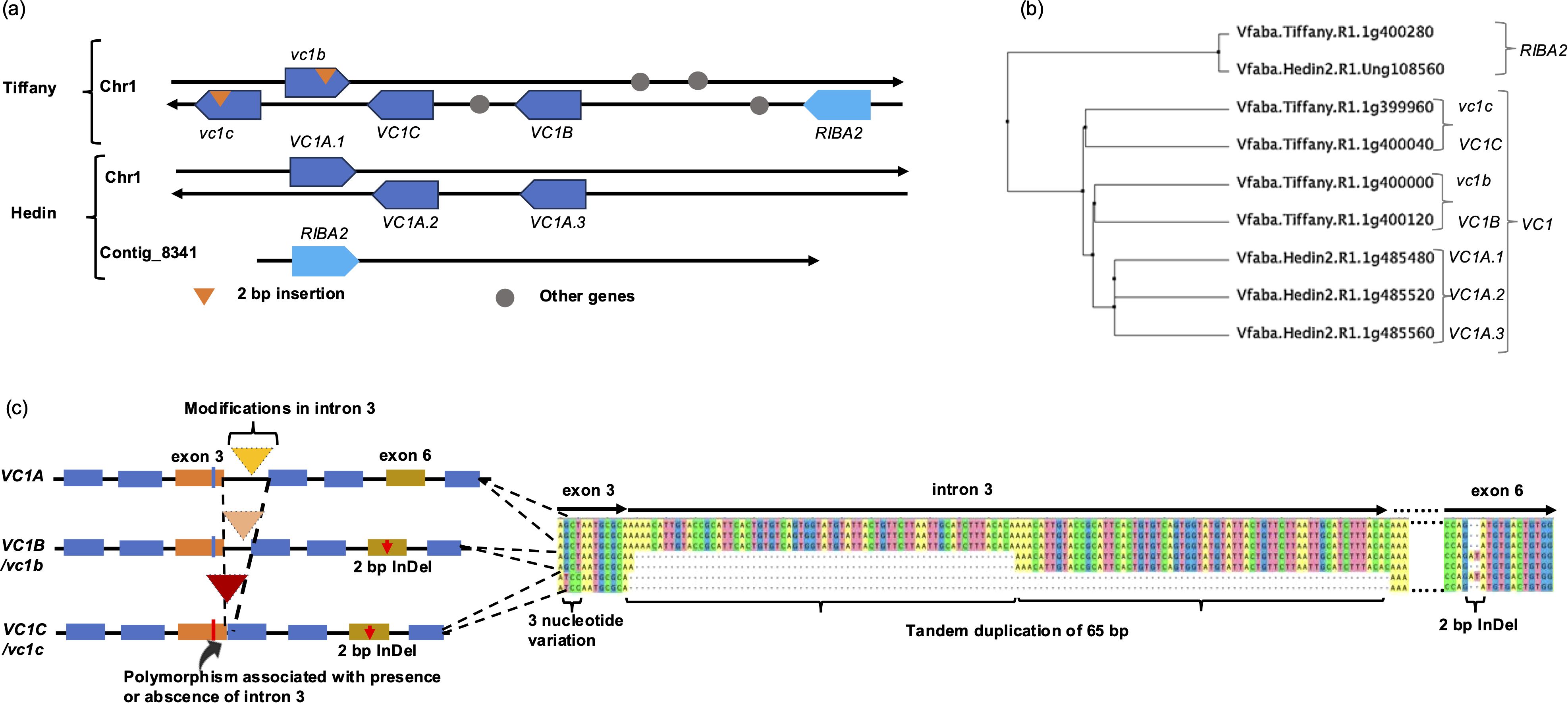
Figure 1. Identification and analysis of RIBA genes. (a) Configurations of RIBA genes from two reference assemblies. The direction of arrows shows the orientation of the genes on the top and bottom strand of chromosome 1 and Contig_8341. (b) Phylogenetic tree showing the genetic relationship among RIBA genes in V. faba. (c) Major structural variations in VC1 genes. VC1 variants were structurally differentiated by modifications in intron 3. These modifications are associated with a 3-nucleotide variation in exon 3.
The fourth and fifth gene models identified in Hedin and Tiffany, respectively, shared only approximately 65% sequence similarity with VC1 and 99% sequence similarity with each other, suggesting that they represent a newly discovered VC1-like gene. While there were structural variations between VC1 and this homolog, these differences occurred primarily in non-coding regions, with the coding regions displaying a high degree of similarity (>87%). As a result, they shared over 90% similarity in their predicted protein sequences.
Analysis of the protein sequence of this homologous gene showed presence of two functional domains, RibA and RibB, as in other bifunctional riboflavin proteins, and highly identical to VC1 protein domains. Subsequently, we analyzed bifunctional RIBA protein homologs from other legume crops in the Fabaceae family including chickpea, lupin, grass pea, lotus, Medicago and pea. Comparison of the amino acid sequence encoded by this newly identified V. faba gene to those of VC1 and RIBA genes from other legumes revealed high similarity among these RIBA proteins and conservation of all key amino acid residues required for catalytic activity. All the proteins shared a high identity in the two catalytic domains, except vc1b and vc1c which differed significantly in the second domain due to a 2 bp insertion, altering the reading frame and causing a premature stop codon (Figures 2a, b). Hence, the high degree of similarity among these proteins, especially within their functional domains, suggests that their roles as RIBA proteins are well conserved. We therefore denominated this novel homolog as RIBA2, since it represents a second RIBA locus in V. faba.
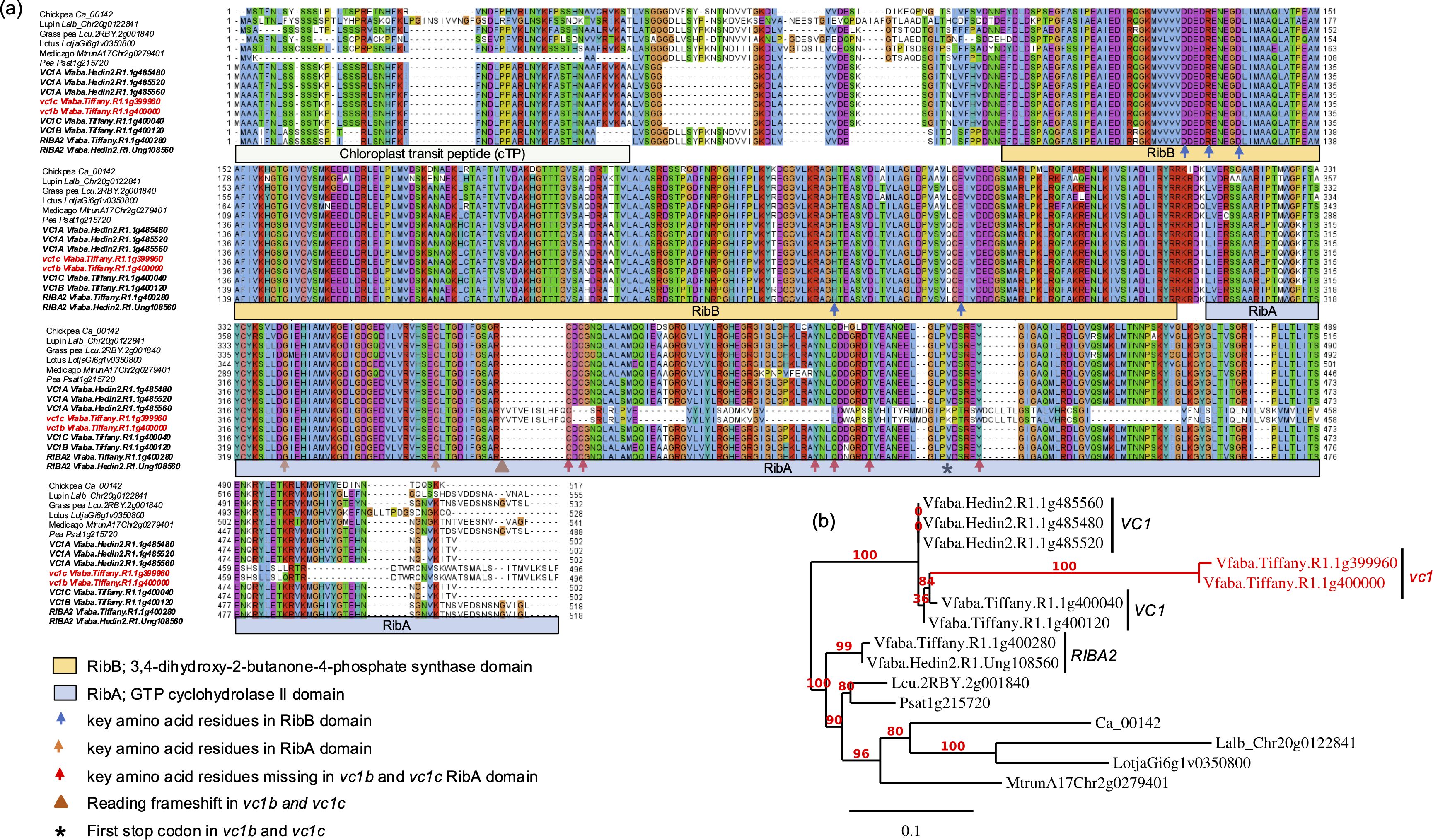
Figure 2. Comparison of amino acid sequences and phylogeny of RIBA proteins. (a) Alignment of amino acid sequences and (b) phylogenetic tree of RIBA proteins from V. faba and related legume crops in Fabaceae family, including chickpea, lupin, grass pea, lotus, Medicago and pea. Major variations lie within the domain encoding chloroplast transit peptide (cTP). RibB and RibA domains of the proteins show high similarity, except the protein sequences encoded by vc1b and vc1c which show variations in the RibA domain due to a frameshift mutation. The functional domains are shown underneath the alignment as predicted using PsiPred workbench. Predicted key residues based on Björnsdotter et al. (2021) are indicated with different colors of arrows.
We validated the existence of all the genes in a set of 18 faba bean genotypes. First, we selectively amplified the genes using PCR. The results indicated that RIBA2 was present in all faba bean genotypes. VC1A was present in most high v-c genotypes, while VC1B and VC1C were found in all low v-c genotypes but were also carried by some high v-c genotypes (Figure 3a). It was also observed that all three VC1 variants could be present in a single genotype, as observed in the low v-c genotype, NPZ-FB-73, and the high v-c genotype, NP-FB-143. Secondly, the presence of active and inactive copies of VC1B and VC1C in the Tiffany genome assembly suggests that low v-c genotypes may still carry functional copies of VC1. To confirm the hypothesis that both active and inactive copies of VC1 are carried by low v-c genotypes, we employed a KASP assay targeting the 2 bp insertion in exon 6. KASP primers were designed such that allele 1-specific primers bind to the active variants while allele 2-specific primers bind to the mutated variants. Subsequently, it was observed that most high v-c genotypes (7 out of 9) were homozygous for the assay indicating the presence of only active variants, whereas all nine genotypes with low v-c and two high v-c genotypes were heterozygous, indicating the presence of both active and mutated variants (Figures 3b, c). There was no homozygous genotype call for only the mutant, revealing that no faba bean genotype carried only the mutant gene copies. However, since a set of 18 faba bean genotypes is too small to draw definitive conclusions, we extended our analysis to a larger and more diverse panel of 97 genotypes to test this hypothesis. This diversity panel included breeding lines and cultivars exhibiting a wide range of seed v-c content, obtained from Norddeutsche Pflanzenzucht Hans-Georg Lembke KG (NPZ, Hohenlieth, Germany). We observed that all low v-c genotypes, as well as some high v-c genotypes, carried a functional VC1 variant in addition to the non-functional vc1 allele (Figure 3d; Supplementary Table S5), confirming the hypothesis that all low v-c faba beans carry multiple VC1 variants, including gene variants with and without the inactivating insertion. Additionally, some high v-c faba beans exhibit the same characteristic.
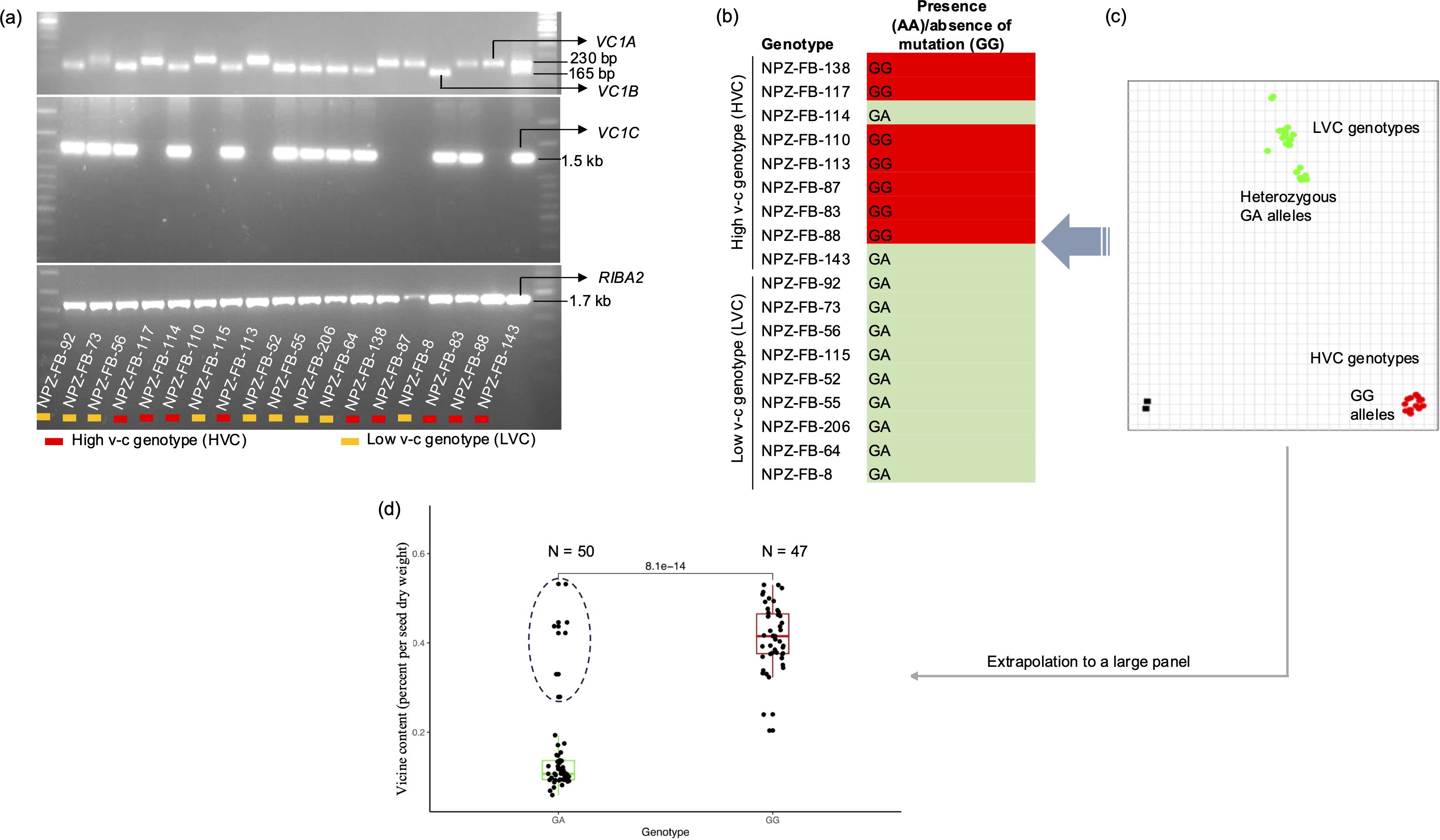
Figure 3. Validation of the presence of RIBA genes and the mutation in VC1. (a) Selective amplification by PCR showing the presence of VC1 and RIBA2 variants in a set of 18 faba bean lines. (b) Allele calls and (c) allelic discrimination plot for the 2 bp insertion in exon 6 of VC1. Allele GG represents the absence of insertion (wild type variants), while allele AA represents the presence of insertion (mutant). Heterozygous cluster (GA) indicates the presence of both the wild type and mutant variants. (d) Boxplot illustrating the v-c contents for two groups: VC1 wildtypes (GG) and genotypes carrying both the mutant and wildtype (GA) gene variants in a panel of 97 genotypes. High v-c genotypes carrying GA alleles are enclosed within a circle.
3.2 VC1 exhibits copy number variations and is dosage-insensitive
The presence of multiple copies of VC1 in faba bean reference genomes suggests a potential variable copy number for the gene. As a result, we determined VC1 copy number through relative quantification by qPCR. The result confirmed that VC1 shows copy number variations, with gene copies ranging from 2 to 5 across 18 faba bean genotypes (Figure 4a). Unexpectedly, low v-c genotypes tended to carry higher copy numbers than high v-c genotypes. This observation could mean that some of the gene variants are not functional or not expressed as was observed for the faba bean hilum color locus (Jayakodi et al., 2023). Therefore, we assessed the transcription activity of VC1 and RIBA2 genes by quantifying their relative expression levels using RT-qPCR in a subset of ten faba bean cultivars with varying v-c contents. These cultivars, selected to reflect the diversity in seed v-c levels, included genotypes representing all known VC1 haplotypes. Furthermore, our focus was on whole seeds at the early stage of seed development, in which VC1 expression is known to be the highest (Björnsdotter et al., 2021).
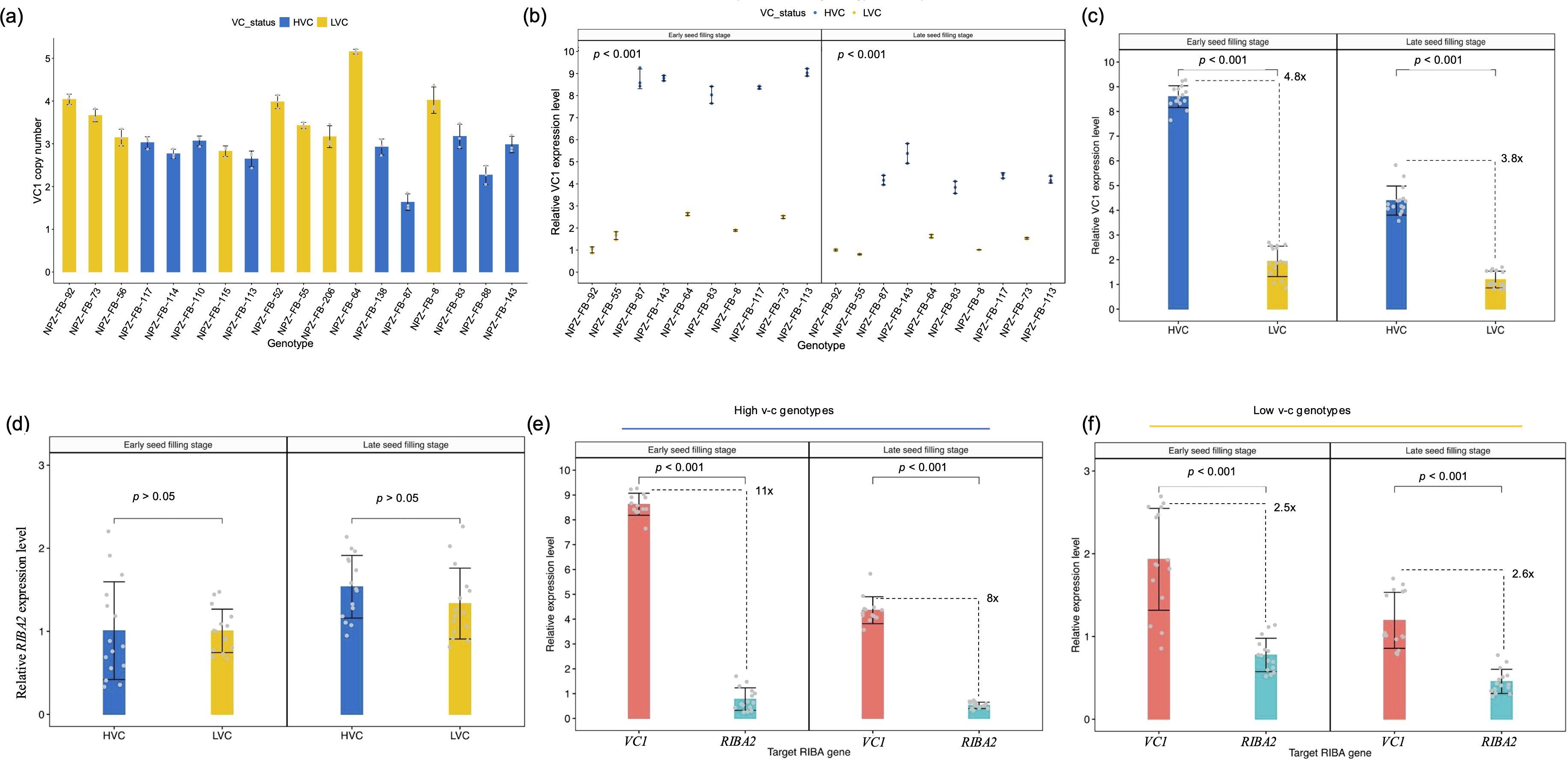
Figure 4. Copy number variation and transcription activities of RIBA genes. (a) VC1 copy numbers across 18 faba bean genotypes, comprising high (HVC) and low vicine-convicine (LVC) lines (means ± SD, n = 3). (b) VC1 relative expression levels during seed development (means ± SD, n = 3). (c) Comparisons of the relative expression levels between high and low v-c genotypes at early and late seed filling stages (means ± SD, n = 15). (d) Comparisons of relative levels of RIBA2 transcripts between high and low v-c (means ± SD, n = 15). (e) Comparisons of VC1 and RIBA2 expression levels within high v-c genotypes (means ± SD, n = 15). (f) Comparison of VC1 and RIBA2 expression levels within low v-c genotypes (means ± SD, n = 15). Significance for comparisons between groups were determined using t-test.
Expression analysis revealed significantly (P < 0.001) higher VC1 expression levels in high v-c genotypes at early and late seed filling stages compared to low v-c genotypes (Figure 4b). High v-c genotypes showed about 5-fold and 4-fold more expression (P < 0.001) than low v-c genotypes at ESF and LSF, respectively (Figure 4c). In contrast to VC1 differential expression, RIBA2 displayed relatively consistent expression levels between high and low v-c genotype groups at both stages (Figure 4d). However, VC1 expression was significantly higher than RIBA2 expression. Within high v-c genotypes, VC1 exhibited up to 11-fold more expression than RIBA2 (Figure 4e), compared to 2.6-fold within low v-c genotypes (Figure 4f).
Importantly, despite fewer copy numbers in high v-c genotypes, the elevated expression of VC1 suggests that it may not be sensitive to dosage. To validate this, we conducted a correlation analysis between VC1 gene copy number and gene expression. Subsequently, we observed a negative correlation (Supplementary Figure S2A), indicating that higher copy number correlated with lower expression level. This negative correlation seems to be attributed to a shared genetic origin among low v-c genotypes, rather than interactive effects of variants resulting from antisense regulation. To verify this observation, we used a SNP genotyping dataset to trace the lineage of our low v-c lines across a broader panel of 347 faba bean genotypes. These genotypes were genotyped using the faba bean 50k Affymetrix chip. After filtering for missing data, minimum allele frequency, and heterozygosity, 13k polymorphic SNPs remained and were used for population structure analysis. The principal component analysis plot depicted a close clustering of the low v-c lines (Supplementary Figure S2B). This clustering pattern confirms a common genetic origin among low v-c genotypes, elucidating the observed negative correlation between VC1 gene copy number and expression.
However, this observed correlation between high copy number and low expression suggests that not all VC1 copies are expressed, potentially due to some regulatory mechanisms. To identify the functional variants, we sequenced cDNA fragments of VC1. As VC1 variants can be differentiated by the mutations in exon 3 and 6, and SNPs within exon 4 and 5, we designed primers flanking this region and subsequently sequenced amplicons from four low v-c and five high v-c genotypes.
The analysis of cDNA sequences showed that three VC1 gene variants were expressed across genotypes, namely, high v-c genotypes can express VC1A or VC1C, while vc1b was detected in low v-c genotypes (Figures 5a, b; Supplementary Table S6). Surprisingly, only one gene variant was expressed per genotype, regardless of the total number of variants present. For instance, low v-c genotype NPZ-FB-92 carried four VC1 gene copies, two each of VC1B and VC1C, but only vc1b mutant was expressed, as in all other low v-c genotypes. Similarly, high v-c genotype NPZ-FB-143 carried multiple gene copies including all three variants but expressed only VC1A. This demonstrates and explains why VC1 was found dosage insensitive.
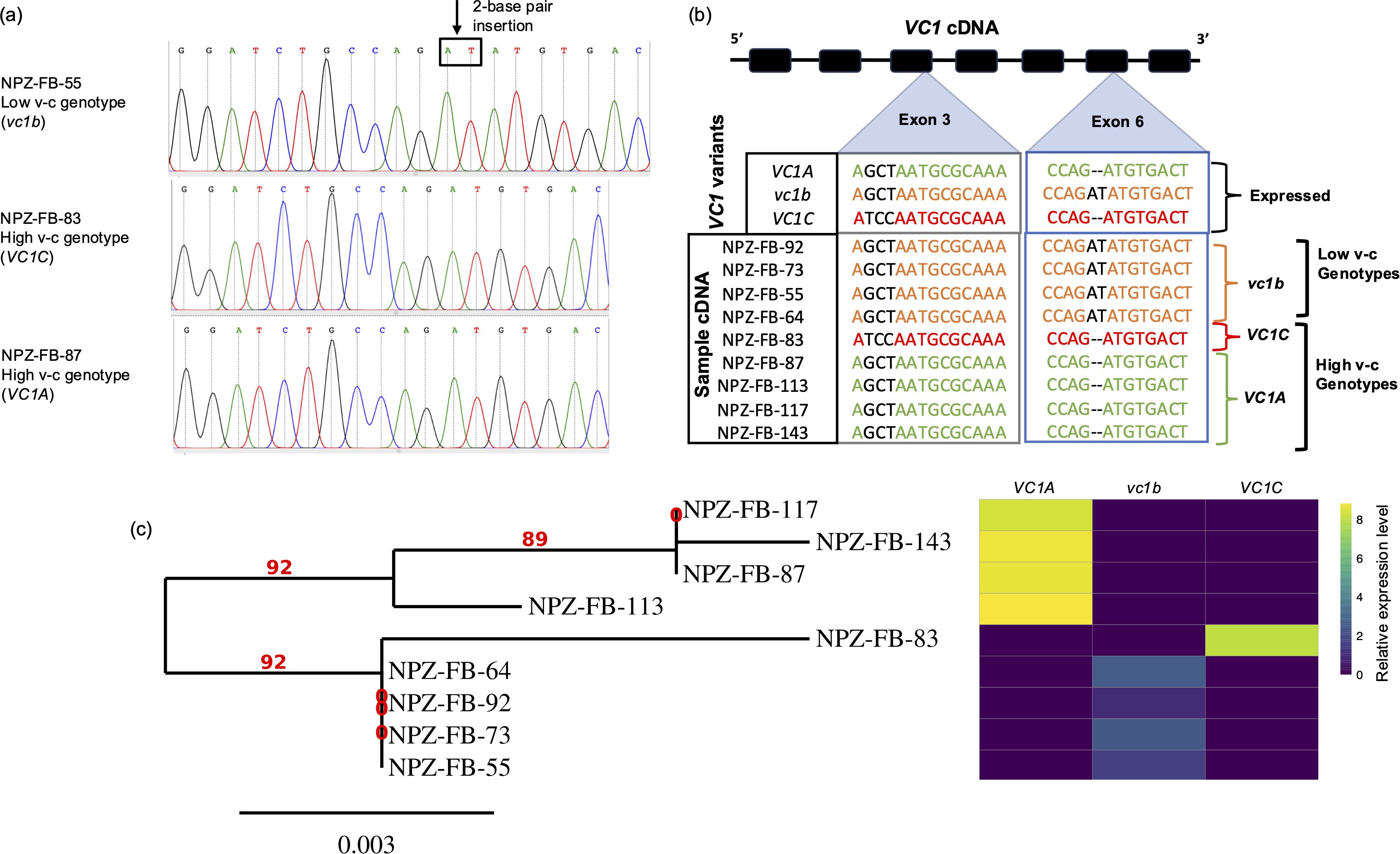
Figure 5. Identification of functional VC1 variants. (a) Chromatograms obtained by Sanger sequencing of PCR fragments of VC1 cDNA show single peaks corresponding to only one variant of the gene. The position of the 2-base pair insertion is indicated by the arrow, and the nucleotides are enclosed in a box. (b) VC1 cDNA analysis showing the expressed VC1 variants. For each genotype, cDNA samples from two developmental stages were sequenced. In addition to the mutations shown here, single nucleotide polymorphisms in exons 4 and 5 were used to distinguish the variants (see Supplementary Table S6). (c) Phylogenetic tree showing the genetic relationships among the faba bean lines using maximum likelihood method, alongside a heatmap illustrating expression profiles for VC1 variants.
Additionally, we constructed a phylogenetic tree using VC1 cDNA sequences for the sequenced subset. The genotypes clustered into two major groups (Figure 5c). The first group comprised only high v-c genotypes expressing VC1A, while the second group comprised two subgroups: low v-c genotypes expressing vc1b and high v-c genotypes expressing VC1C. This distinction within the second subgroup was primarily attributed to the presence or absence of the 2 bp insertion, suggesting it as a functional polymorphism within VC1 capable of distinguishing genotypes based on v-c contents. We additionally sequenced RIBA2 cDNA which overlaps with this VC1 region, particularly within the GCHII domain. RIBA2 cDNA sequences from both low v-c and high v-c genotypes did not carry any inactivating insertion (Supplementary Table S6).
3.3 RIBA2 gene is a candidate v-c locus with localized SNPs that segregate with v-c phenotypes
It is evident that VC1 is not the only locus controlling v-c biosynthesis in faba bean. We identified a diverging homolog of VC1 which may also be involved in v-c regulation. As earlier noted, analysis of protein sequences of this homologous gene revealed two functional domains, RibA and RibB, similar to the functional VC1 protein domains, which are conserved across related legumes like chickpea, lupin, and pea. This high similarity and conservation of key amino acid residues among these proteins indicates that their roles as RIBA proteins are well conserved (see Figure 2a), suggesting that RIBA2 is another functional RIBA locus in faba bean. Notable differential expressions were evident among individual faba bean lines for this gene, with observed variations tending to correlate with differences in v-c contents (Figure 6a).
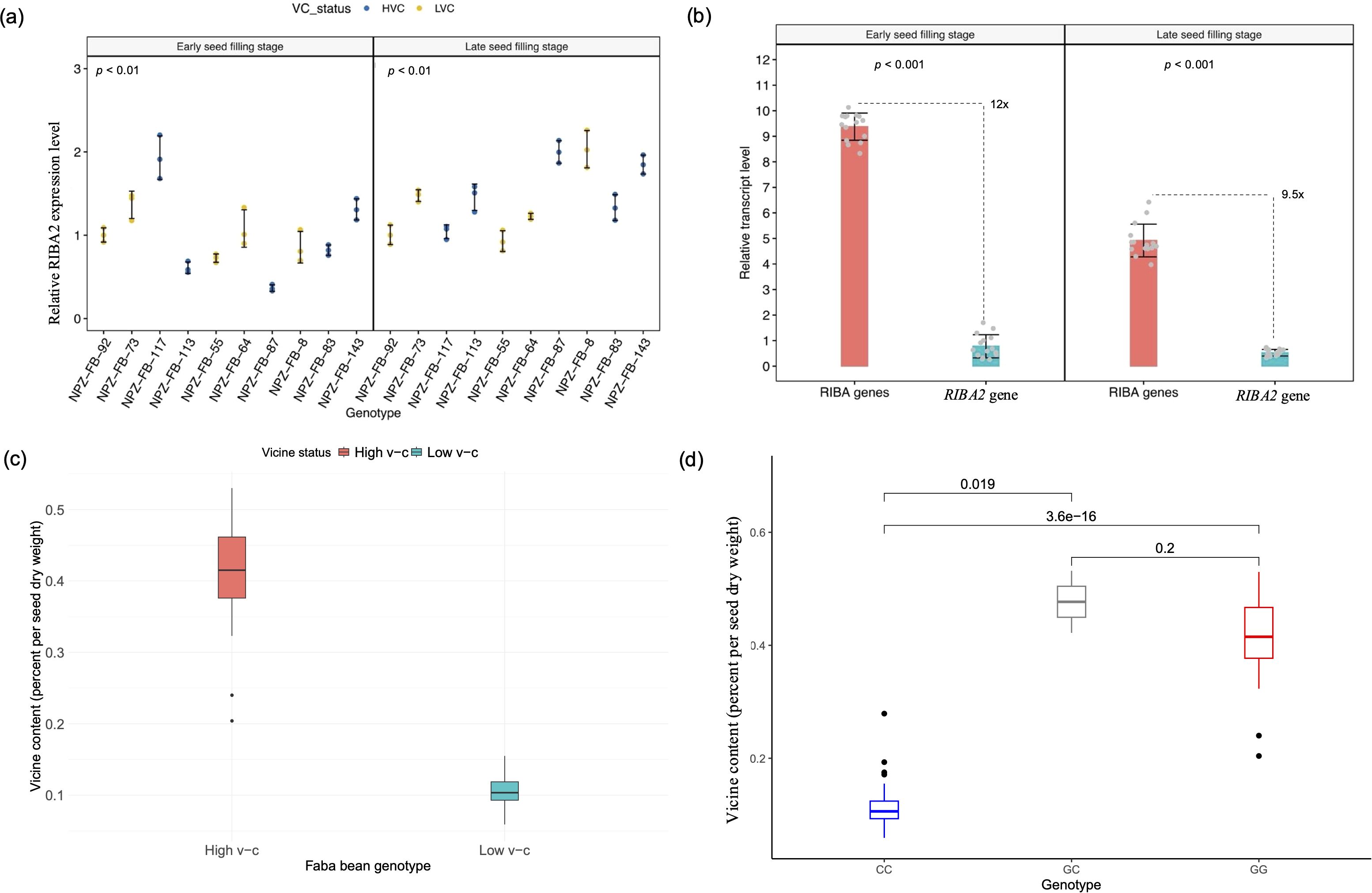
Figure 6. Analysis of RIBA2 activity on vicine and convicine biosynthesis. (a) Relative expression levels of RIBA2 across faba bean lines (means ± SD, n = 3). (b) Proportion of RIBA2 expression relative to the combined RIBA gene (VC1 and RIBA2) expression in high v-c lines at early and late seed filling stages (means ± SD, n = 15). Significance for comparisons between groups were determined using t-test. (c) Phenotypic differences in vicine content between high and low v-c faba bean genotypes (d) Allelic effects of a single nucleotide polymorphism within exon 6 of RIBA2 gene in a panel of 97 diverse faba bean genotypes.
Furthermore, when comparing the proportion of RIBA2 expression relative to the combined expression of both RIBA genes in high v-c cultivars, we observed an average transcript level at least 9.5-fold lower, ranging up to 20-fold (Figure 6b). This would represent about 5-10% of v-c content relative to high v-c cultivars and corresponds to the observed phenotypic differences between low and high v-c cultivars (Figure 6c). These results suggest that this neighboring homolog of VC1 is a candidate locus with minor effect in v-c regulation.
Additionally, two neighboring single nucleotide polymorphisms within exon 6 of the RIBA2 gene segregate with v-c phenotypes. We evaluated the segregation pattern of a SNP in exon 6 of this gene in a diversity panel of 97 genotypes. The results showed that this polymorphism can differentiate low v-c from high v-c genotypes, where allele C segregated with low v-c phenotype while allele G segregated with high v-c phenotype (Figure 6d; Supplementary Table S5), demonstrating that the SNPs are tightly linked to v-c phenotypes and can be utilized for marker-assisted selection in v-c breeding.
3.4 Genetic variations in v-c contents involve polymorphisms associated with differential expression of VC1 and RIBA2 genes
It is commonly observed that high v-c faba beans exhibit substantial variations in v-c content, whereas low v-c faba beans show much narrower variation, significantly below this threshold (Khamassi et al., 2013; Puspitasari et al., 2022). This pattern suggests that the 2 bp inactivating insertion in VC1, although critical, may not fully explain the observed phenotypic diversity. Based on our findings, we propose that polymorphisms influencing the expression levels of VC1 and RIBA2, in addition to the 2 bp insertion, contribute to the variations in v-c content (Supplementary Figure S3). Specifically, VC1 expression levels can vary up to five-fold among faba bean genotypes, potentially accounting for much of the variability within high v-c group. In contrast, the 2 bp mutation in VC1 appears to be the primary determinant of the sharp phenotypic difference between high and low v-c genotypes. Although RIBA2 generally exhibits low expression and may play a minor role, it could be the sole contributor to v-c biosynthesis in low v-c lines lacking functional VC1. This may explain the narrow v-c variation observed in these genotypes, which remains substantially lower than in high v-c lines.
3.5 Implications of multiple VC1 gene variants in molecular breeding for low vicine-convicine faba bean
It was observed that three different variants of VC1 can be expressed. High v-c genotypes can express either VC1A or VC1C, while low v-c genotypes consistently express vc1b. Notably, VC1C shared close similarity with vc1b, having similar alleles at most SNP positions. This similarity caused genotypes expressing these variants to cluster under a major branch as observed in Figure 5c. Consequently, the existence of multiple VC1 variants may present a significant challenge for marker-assisted selection of v-c content in faba bean breeding. Issues such as false heterozygous calls or incomplete segregation may arise due to the presence of multiple gene variants. To investigate this, we conducted genotyping assays using well-characterized low and high v-c genotypes. These assays involved single nucleotide polymorphic markers located within VC1 gene, including some previously developed for v-c breeding. Since genomic DNA (gDNA) contains all gene variants, while complementary DNA (cDNA) only contains the expressed variant, we performed KASP genotyping assays with gDNA and cDNA as templates.
Our results revealed two key findings. Firstly, the presence of multiple variants could lead to bias in allele calls (Figures 7a, b; Table 1). In most cases, low v-c genotypes consistently exhibited false heterozygous signals when gDNA was used as a template. A similar trend can also occur in a few high v-c genotypes. However, when cDNA was used as the template, these genotypes were correctly identified as homozygous individuals. Likewise, in the assay targeting the 2 bp insertion, all low v-c genotypes were initially called as heterozygous when gDNA was used as the template, due to the presence of multiple copies, including both wild-type and mutant variants. However, these genotypes were correctly called as homozygous when cDNA was used as the template. Additionally, this observation further confirms that only one copy of VC1 is expressed in each genotype analyzed.
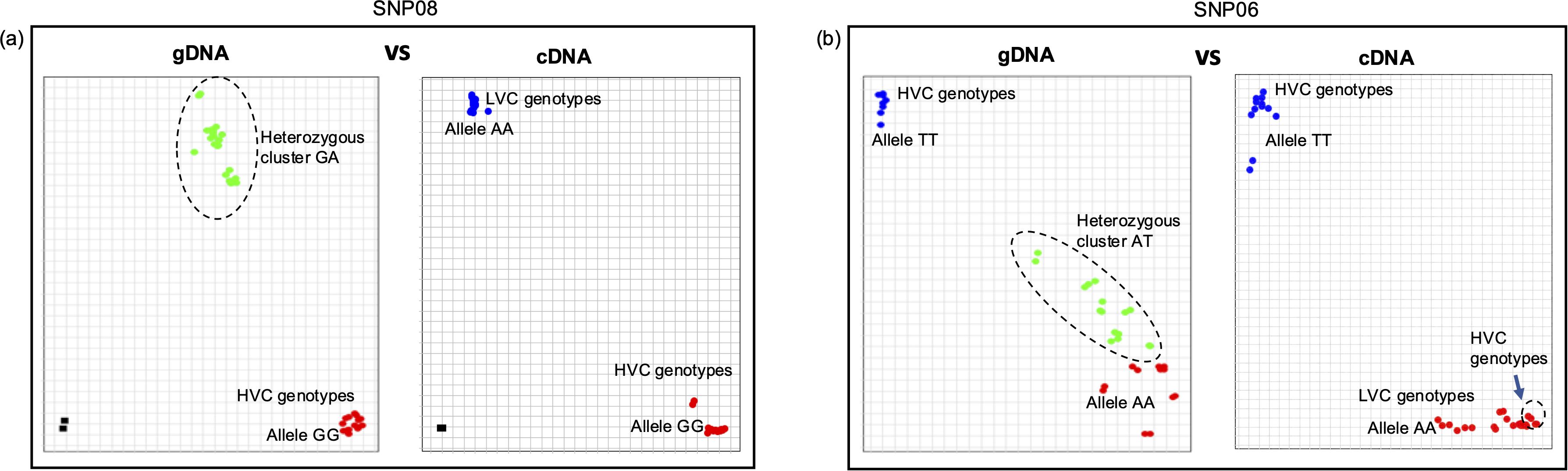
Figure 7. Multiple VC1 copies can cause bias during marker analysis. Allelic discrimination plots for (a) 2 bp insertion in exon 6 and (b) an SNP within exon 5 of VC1. In both cases, the plots exhibited false heterozygous calls for all or most low vicine-convicine (v-c) (LVC) genotypes and some high v-c (HVC) genotypes when gDNA was employed as the template. In contrast, clear homozygous calls were observed with cDNA. Additionally, some high v-c genotypes expressing VC1C variant can cluster with low v-c genotypes, as observed in b (see arrow).
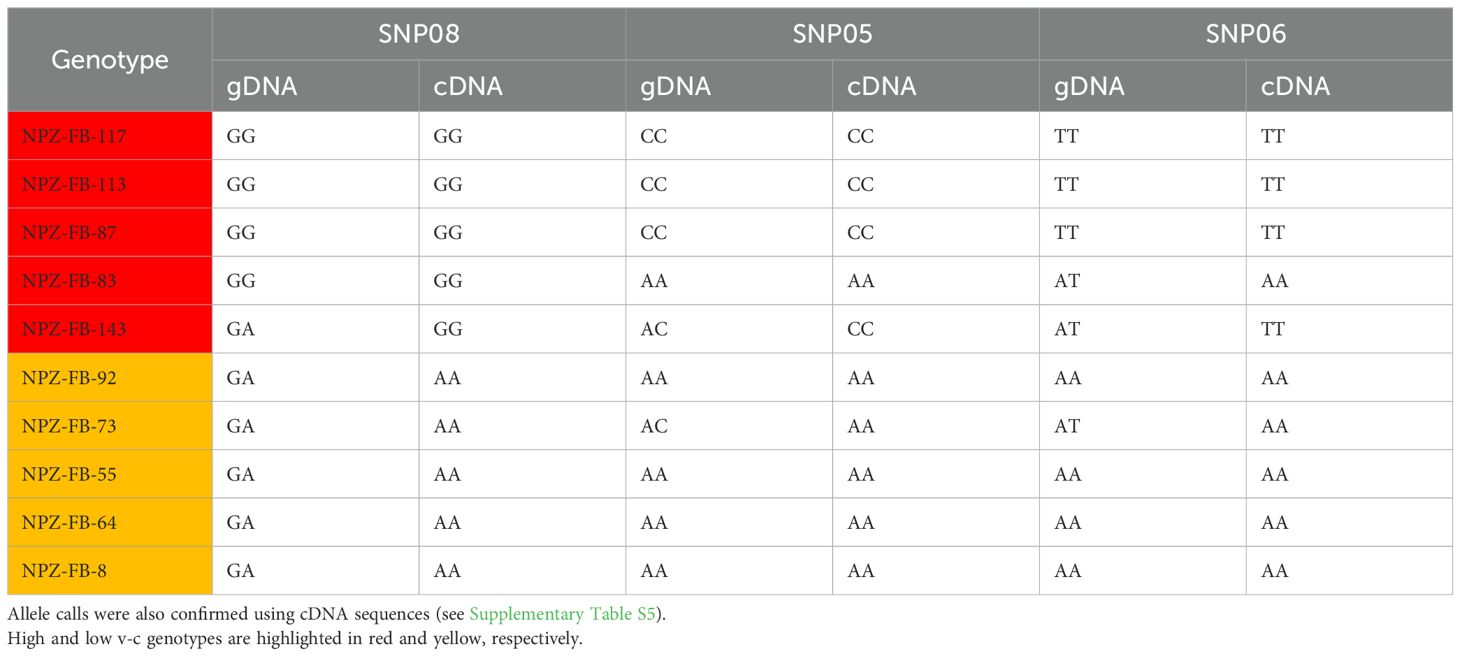
Table 1. Comparison of allele calls between gDNA and cDNA for SNPs detected by KASP Assays showed that multiple copies of VC1 often lead to inaccurate allele calls.
Secondly, we observed that SNP alleles do not always segregate completely with the v-c phenotype. Low v-c alleles often segregate with some high v-c genotypes expressing VC1C variant. This results in the false clustering of these high v-c genotypes with low v-c genotypes, leading to inaccurate predictions of the v-c phenotype. (Figure 7b). This pattern was consistent with other VC1-based SNPs, except for the 2 bp insertion, which can efficiently distinguish the cultivars based on v-c contents. Beside this polymorphism, other SNPs within VC1 were ineffective in predicting v-c contents in a diverse genetic background.
4 Discussion
4.1 VC1 is multiallelic but exhibits single-copy expression
Until recently, the elucidation of genetic mechanisms underlying important traits in faba bean has been hindered by the unavailability of genomic tools for this crop, which has an enormous genome in which the largest chromosome is bigger than the entire human genome. This constraint equally impeded early endeavors to identify genes responsible for v-c biosynthesis in faba bean. In the absence of reference genomes, previous investigations relied on molecular markers generated by mapping mRNA contigs from faba bean to the genomes of closely related crops, such as Medicago truncatula, to identify regions controlling v-c content (Khazaei et al., 2015; Tacke et al., 2022). However, the involvement of VC1 gene in v-c biosynthesis in faba bean was established recently and a frameshift mutation in this gene results in a loss-of-function, leading to a low v-c phenotype (Björnsdotter et al., 2021).
The availability of recently assembled V. faba reference genomes with functional gene annotations (Jayakodi et al., 2023) enabled us to map RIBA1 protein to these assemblies and identify all relevant RIBA genes associated with v-c biosynthesis. Our study revealed multiple VC1 variants, primarily characterized by mutations in intron 3, exon 3 and 6. We found that VC1 is affected by copy number variations, and that all low v-c genotypes carry both functional and non-functional variants, although only the non-functional variant is expressed. Previously, only two allelic forms of VC1 were known, where low v-c faba beans carried only mutant vc1, while high v-c faba beans carried the wild-type variant (Björnsdotter et al., 2021). These wild-type and mutant alleles correspond to VC1A and vc1b variants, respectively. Our identification of an additional variant, VC1C, expressed by some high v-c lines, underscores the diversity of VC1 genes and highlights the significance of utilizing multiple genotypes in our study. However, a major structural variation in intron 3 across the three VC1 variants did not appear to have functional relevance as it did not associate with the expression pattern.
We observed a differential expression of VC1, consistent with previous reports between high and low v-c genotypes (Björnsdotter et al., 2021). Surprisingly, copy number did not correlate with phenotypic expression. Although we observed a negative correlation between copy number and gene expression, this was due to the influence of low v-c genotypes sharing a single genetic source. These genotypes exhibited high copy numbers but lower expression levels. This observation was supported by cDNA sequencing which showed that each genotype expressed only one VC1 variant despite having multiple variants in the genome. Previous reports on the transformation of hairy roots of Hedin with an additional copy of functional VC1 did not result in increased vicine accumulation (Björnsdotter et al., 2021). This confirms that despite copy number variation, VC1 is not sensitive to dosage.
The mechanisms involved in VC1 dosage compensation are unclear; however, certain mechanisms have been proposed for genes with multiple copies. These mechanisms could involve complex processes at different transcription stages (Vaquerizas et al., 2009; Woodwark and Bateman, 2011), including microRNAs (miRNAs) that can activate or repress the transcription of duplicated or copy number variable (CNV) genes (Vasudevan et al., 2007; Li et al., 2008; Bartel, 2009; Woodwark and Bateman, 2011; Chang and Liao, 2012), imprinted or monoallelically expressed genes (Pauler et al., 2007), and DNA methylation (Suzuki and Bird, 2008; Law and Jacobsen, 2010).
The regulation of VC1 differential expression between low and high v-c genotypes and the impact of the 2 bp insertion carried by low v-c genotypes on expression levels remain unclear. Differences in the expression of VC1 genes can also stem from variations within the regulatory elements. Elements like enhancers and silencers have the potential to amplify or suppress the gene expression of the target gene (Bulger and Groudine, 2011; Kolovos et al., 2012). Upstream and downstream of VC1 are various variants, such as short tandem repeats, InDels and SNPs. Structural differences within this region could potentially affect one or more regulatory elements. The interaction among these diverse regulatory components, their interplay with target promoters, and the involvement of epigenetic modifications can intricately regulate the expression of this gene (Bulger and Groudine, 2011; Kolovos et al., 2012; Cremer and Cremer, 2001; Maeda and Karch, 2011; Yang and Corces, 2011).
4.2 RIBA2 is a functional RIBA locus in faba bean and a candidate for a minor effect v-c locus
The variation in VC1 expression alone does not correlate with observed phenotypic differences among faba bean genotypes. Subsequent analysis of VC1 cDNA in this study aligns with findings reported by Björnsdotter et al. (2021), that all low v-c cultivars express vc1b variant carrying 2 bp insertion in exon 6 which results in a non-functional protein. This implies that VC1 is not active in low v-c genotypes. However, as previously mentioned, this mutation only causes a significant reduction in v-c content but does not entirely eliminate it. For instance, the seed v-c content of the first low v-c genotype, initially reported by Duc et al. (1989) is approximately 0.04%, which is about 1/10 to 1/20 of high v-c contents. This substantial reduction in v-c content due to a single gene mutation highlights the major effect of VC1 locus in v-c phenotype regulation and equally suggests the involvement of another gene with a minor effect.
In addition to the already known VC1, we identified a homologous gene, RIBA2, encoding putative bi-functional riboflavin proteins in faba bean genome. The distinct structure of the RIBA2 gene compared to VC1 suggests that it represents a second RIBA locus in faba bean. RIBA2 is a bi-functional riboflavin gene with two catalytic domains, RibB and RibA, encoding DHBPS and GCHII enzymes, respectively. RIBA enzymes are known for their involvement in the riboflavin biosynthetic pathway in plants (Hiltunen et al., 2012). However, Björnsdotter et al. (2021) demonstrated that RIBA enzymes are also involved in v-c production in faba bean where v-c are synthesized in a three-step pathway that starts from the GTP cyclohydrolase II function of RIBA proteins. While VC1 and RIBA2 share nearly identical functional domains, RIBA2 lacks the inactivating insertion present in vc1b mutant. Detailed analysis of VC1 and RIBA2 amino acid sequences showed conservation in all key amino acid residues necessary for catalytic activities, including those required for binding zinc ions essential for GCHII activity as demonstrated by Kaiser et al. (2002). These key amino acid residues are well conserved in VC1 and RIBA2 and other RIBA proteins within Fabaceae family but lacking in vc1b.
Subsequent analysis shows that RIBA2 is expressed at much lower levels than VC1 in seeds. Similarly, there was a significantly lower expression level relative to the combined riboflavin gene transcripts in high v-c genotypes, aligning with the observed phenotypic differences between low and high v-c genotypes. Previous studies consistently emphasize the VC1 locus as a major determinant in v-c regulation (Ramsay et al., 1995; Gutierrez et al., 2006; Khazaei et al., 2015; Tacke et al., 2022). Our study substantiates this hypothesis, indicating several-fold higher expression of VC1 relative to the homolog, RIBA2. These findings suggest that this homologous gene is a candidate for a minor effect locus for v-c content. The expression of this minor effect gene may explain why mutation in vc1 does not eliminate v-c completely in affected genotypes. Tacke et al. (2022) used a transcript-based annotation method to identify a differentially expressed contig associated with v-c contents, as well as another, non-differentially expressed contig which mapped to the VC1 locus. However, they could not fully decipher the locus due to the lack of genomic data.
It is essential to validate the involvement of RIBA2 in v-c biosynthesis through mutant analysis, particularly in a vc1 background. However, the lack of reliable transformation methods and mutant resources in faba bean significantly hinders functional gene validation through knockouts (O’Sullivan and Angra, 2016). Moreover, given that riboflavin biosynthesis is essential for fundamental cellular processes and overall plant development, it remains uncertain whether simultaneous loss-of-function mutations in both VC1 and RIBA2 would be viable.
4.3 The complexity of VC1 locus limits the efficiency of localized SNPs for marker-assisted selection in v-c breeding
Various molecular markers have been developed to facilitate breeding of low v-c faba beans (Tacke et al., 2022; Khazaei et al., 2017). However, most existing v-c markers target polymorphisms within VC1 genes. While these markers have proven valuable in some contexts, their efficiencies may be limited due to complex nature of VC1. Our research revealed that multiple VC1 copies can lead to inaccurate allele calls, resulting in false clusters during marker analysis. This often happens because of the existence of closely homologous sequences in the genome (Makhoul et al., 2020). Consequently, conventional KASP assays may require optimization to improve accuracy (Makhoul et al., 2020). Nevertheless, the applicability of these SNPs might be confined to specific genetic backgrounds. In a diverse genetic background, comprising all expressed VC1 variants, SNPs often do not segregate fully with the phenotype. Hence, these polymorphisms may not be efficient for MAS of v-c in faba bean breeding. Therefore, we strongly advise caution when utilizing VC1-based molecular markers for v-c content selection in breeding programs. Overreliance on only these markers for selection may inadvertently lead to incorrect prediction of v-c contents.
However, our study highlights the functional significance of the 2 bp insertion in exon 6 as a reliable polymorphism in VC1 that effectively distinguishes genotypes based on the v-c phenotype. Optimizing the KASP assay targeting this polymorphism could significantly enhance its efficiency and specificity, particularly given the potential for inaccurate clustering due to multiple gene copies. Moreover, we have shown that SNPs within RIBA2 show consistent segregation with v-c contents. These SNPs can accurately predict v-c content without bias and will be valuable for faba bean breeding.
5 Conclusion
We have demonstrated that VC1 exists in multiple copies and shows CNV. However, copy number does not correlate with gene expression and suggests a tight regulation of the gene. Multiple VC1 variants were expressed among low and high v-c genotypes which complicates molecular marker development for breeding. We also identified a diverging homolog of VC1, RIBA2, which shares nearly identical RIBA domains with VC1. Our results show that RIBA2 has two functional domains similar to the active VC1 genes, with highly conserved key amino acid residues, indicating well-conserved roles as RIBA proteins. Our findings suggest that this homologous gene is a candidate minor effect v-c locus, and its involvement can be validated using gene editing knockouts.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
SU: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MM: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. AG: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing. CO: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. RS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work was supported by DFG grant 469336000 to RJS from the German Research Society (DFG) for the International Research Training Group IRTG 2843 Accelerating Crop Genetic Gain. DFG grant 497667402 to AAG.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Stavros Tzigos and Annette Plank for their valuable technical assistance with nucleic acid extraction and plant management in the greenhouse, respectively. We thank Erick Owuor Mikwa for his insightful comments and suggestions. We also express our gratitude to Norddeutsche Pflanzenzucht Hans-Georg Lembke KG (NPZ, Hohenlieth, Germany) for providing the faba bean seeds used in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1565210/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
cDNA, Complementary DNA; CNV, Copy number variation; DHBPS, 3,4-Dihydroxy-2-Butanone-4-Phosphate Synthase; DNA, Deoxyribonucleic Acid; ESF, Early Seed Filling; G6PD, Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase; GCHII, Guanosine Triphosphate Cyclohydrolase II; gDNA, Genomic DNA; GTP, Guanosine Triphosphate; HVC, High Vicine-Convicine; KASP, Kompetitive Allele-Specific PCR; LSF, Late Seed Filling; LVC, Low Vicine-Convicine; miRNA, MicroRNA; NCBI, National Center for Biotechnology Information; PCR, Polymerase Chain Reaction; qPCR, Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction; QTL, Quantitative Trait Locus; RNA, Ribonucleic Acid; RT-qPCR, Reverse Transcription Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction; SNP, Single Nucleotide Polymorphism; v-c, Vicine and Convicine.
References
Adhikari, K., Khazaei, H., Ghaouti, L., Maalouf, F., Vandenberg, A., Link, W., et al. (2021). Conventional and molecular breeding tools for accelerating genetic gain in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.744259
Badjona, A., Bradshaw, R., Millman, C., Howarth, M., and Dubey, B. (2023). Faba bean flavor effects from processing to consumer acceptability. Foods 12, 2237. doi: 10.3390/foods12112237
Bartel, D. P. (2009). MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136, 215–233. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Björnsdotter, E., Nadzieja, M., Chang, W., Escobar-Herrera, L., Mancinotti, D., Deepti Angra, D., et al. (2021). VC1 catalyses a key step in the biosynthesis of vicine from GTP in faba bean. Nat. Plants 7, 923–931. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-00950-w
Borisjuk, L., Weber, H., Panitz, R., Manteuffel, R., and Wobus, U. (1995). Embryogenesis of V. faba L.: Histodifferentiation in relation to starch and storage protein synthesis. Plant Physiol. 147, 203–218. doi: 10.1016/S0176-1617(11)81507-5
Bulger, M. and Groudine, M. (2011). Functional and mechanistic diversity of distal transcription enhancers. Cell 144, 327–339. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.01.024
Caracuta, V., Weinstein-Evron, M., Kaufman, D., Yeshurun, R., Silvent, J., and Boaretto, E.. (2016). 14,000-year-old seeds indicate the Levantine origin of the lost progenitor of faba bean. Sci. Rep. 6, 37399. doi: 10.1038/srep37399
Carrillo-Perdomo, E., Vidal, A., Kreplak, J., Duborjal, H., Leveugle, M., Duarte, J., et al. (2020). Development of new genetic resources for faba bean (Vicia faba L.) breeding through the discovery of gene-based SNP markers and the construction of a high-density consensus map. Sci. Rep. 10, 6790. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63664-7
Chang, A. Y. and Liao, B. Y. (2012). DNA methylation rebalances gene dosage after mammalian gene duplications. Mol. Biol. Evol. 29, 133–144. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msr174
Choudhary, D. K. and Mishra, A. (2019). In vitro and in silico interaction of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) seed extract with xanthine oxidase and evaluation of antioxidant activity as a therapeutic potential. Nat. Prod. Res. 33, 2689–2693. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1460831
Cremer, T. and Cremer, C. (2001). Chromosome territories, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in mammalian cells. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2, 292–301. doi: 10.1038/35066075
Duc, G., Bao, S., Baum, M., Redden, B., Sadiki, M., Suso, M. J., et al. (2010). Diversity maintenance and use of Vicia faba L. genetic resources. Field Crops Res. 115, 270–278. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2008.10.003
Duc, G., Marget, P., Esnault, R., Le Guen, J., and Bastianelli, D. (1999). Genetic variability for feeding value of faba bean seeds (Vicia faba): comparative chemical composition of isogenics involving zero-tannin and zero-vicine genes. J. Agric. Sci. 133, 185–196. doi: 10.1017/S0021859699006905
Duc, G., Sixdenier, G., Lila, M., and Furstoss, V. (1989). “Search of genetic variability for vicine and convicine content in V. faba L.: A first report of a gene which codes for nearly zero-vicine and zero-convicine contents,” in International Workshop on ‘Antinutritional Factors (ANF) in Legume Seeds’ (Pudoc, Wageningen).
FAOSTAT (2022). Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online at: http://faostat.fao.org (Accessed November 22, 2022).
Gutierrez, N., Avila, C. M., Duc, G., Marget, P., Suso, M. J., Moreno, M. T., et al. (2006). CAPs markers to assist selection for low vicine and convicine contents in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 114, 59–66. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0410-3
Gutierrez, N., Giménez, M. J., Palomino, C., and Avila, C. M. (2011). Assessment of candidate reference genes for expression studies in Vicia faba L. by real-time quantitative PCR. Mol. Breed. 28, 13–24. doi: 10.1007/s11032-010-9456-7
Hiltunen, H.-M., Illarionov, B., Hedtke, B., Fischer, M., and Grimm, B. (2012). Arabidopsis RIBA proteins: two out of three isoforms have lost their bifunctional activity in riboflavin biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 13, 14086–14105. doi: 10.3390/ijms131114086
Jayakodi, M., Golicz, A. A., Kreplak, J., Fechete, L. I., Angra, D., Bednář, P, et al. (2023). The giant diploid faba genome unlocks variation in a global protein crop. Nature 615, 652–659. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-05791-5
Kaiser, J., Schramek, N., Eberhardt, S., Puttmer, S., Schuster, M., and Bacher, A. (2002). Biosynthesis of vitamin B2. Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 5264–5270. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03239.x
Kambal, A. E., Bond, D. A., and Toynbee-Clarke, G. (1976). A study on the pollination mechanism in field beans (Vicia faba L.). J. Agric. Sci. 87, 519–526. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600033128
Karkanis, A., Ntatsi, G., Lepse, L., Fernández, J. A., Vågen, I. M., Rewald, B., et al. (2018). Faba bean cultivation–revealing novel managing practices for more sustainable and competitive European cropping systems. Front. Plant Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01115
Khamassi, K., Ben Jeddi, F., Hobbs, D., Irigoyen, J., Stoddard, F., O'Sullivan, D. M, et al. (2013). A baseline study of vicine–convicine levels in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) germplasm. Plant Genet. Resour. 11, 250–257. doi: 10.1017/S1479262113000105
Khazaei, H., O’Sullivan, D. M., Jones, H., Pitts, N., Sillanpää, M. J., Pärssinen, P., et al. (2015). Flanking SNP markers for vicine-convicine concentration in faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Mol. Breed. 35, 38. doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0214-8
Khazaei, H., Purves, R. W., Song, M., Stonehouse, R., Bett, K. E., Stoddard, F. L., et al. (2017). Development and validation of a robust, breeder-friendly molecular marker for the vc - locus in faba bean. Mol. Breed. 37, 140. doi: 10.1007/s11032-017-0742-5
Kolovos, P., Knoch, T. A., Grosveld, F. G., Cook, P. R., and Papantonis, A. (2012). Enhancers and silencers: an integrated and simple model for their function. Epigenet. Chromatin 5, 1. doi: 10.1186/1756-8935-5-1
Law, J. A. and Jacobsen, S. E. (2010). Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 204–220. doi: 10.1038/nrg2719
Li, J., Musso, G., and Zhang, Z. (2008). Preferential regulation of duplicated genes by microRNAs in mammals. Genome Biol. 9, R132. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-8-r132
Livak, K. J. and Schmittgen, T. D. (2001). Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2ΔΔC(T) Method. Methods 25, 402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Luzzatto, L. and Arese, P. (2018). Favism and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. N Engl. J. Med. 378, 60–71. doi: 10.1056/nejmra1708111
Maeda, R. K. and Karch, F. (2011). Gene expression in time and space: additive vs hierarchical organization of cis-regulatory regions. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 21, 187–193. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.01.021
Makhoul, M. and Obermeier, C. (2022). Development of breeder-friendly KASP markers from genome-wide association studies results. Methods Mol. Biol. 2481, 287–310. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2237-7_17
Makhoul, M., Rambla, C., Voss-Fels, K. P., Hickey, L. T., Snowdon, R. J., and Obermeier, C. (2020). Overcoming polyploidy pitfalls: a user guide for effective SNP conversion into KASP markers in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 133, 2413–2430. doi: 10.1007/s00122-020-03608-x
O’Sullivan, D. M. and Angra, D. (2016). Advances in faba bean genetics and genomics. Front. Genet. 22. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00150
Pauler, F. M., Koerner, M. V., and Barlow, D. P. (2007). Silencing by imprinted noncoding RNAs: is transcription the answer? Trends Genet. 23, 284–292.
Puspitasari, W., Allemann, B., Angra, D., Appleyard, H., Ecke, W., Möllers, C., et al. (2022). NIRS for vicine and convicine content in faba bean seeds enabled a GWAS in preparation for a marker-assisted adjustment of seed quality of German winter faba beans. J. für Kulturpflanzen 74, 1–10. doi: 10.5073/JfK.2022.01-02.01
Ramsay, G., van de Ven, W., Waugh, R., Griffi ths, D. W., and Powel, W. (1995). “Mapping quantitativetrait loci in faba beans,” in AEP (ed) 2nd Eur Conf on Grain Legume (Copenhagen, AEP, Paris, France), 444—445.
Sixdenier, G., Cassecuelle, F., Guillaumin, L., and Duc, G. (1996). Rapid spectrophotometric method for reduction of vicine and convicine in faba bean seed. FABIS Newslett. 38, 42–44.
Stagnari, F., Maggio, A., Galieni, A., and Pisante, M. (2017). Multiple benefits of legumes for agriculture sustainability: an overview. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 4, 2. doi: 10.1186/s40538-016-0085-1
Suzuki, M. M. and Bird, A. (2008). DNA methylation landscapes: provocative insights from epigenomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 465–476. doi: 10.1038/nrg2341
Tacke, R., Ecke, W., Höfer, M., Sass, O., and Link, W. (2022). Fine-mapping of the major locus for vicine and convicine in faba bean (Vicia faba) and marker-assisted breeding of a novel, low vicine and convicine winter faba bean population. Plant Breed 141, 644–657. doi: 10.1111/pbr.13039
Vaquerizas, J. M., Kummerfeld, S. K., Teichmann, S. A., and Luscombe, N. M. (2009). A census of human transcription factors: function, expression and evolution. Nat. Rev. Genet. 10, 252–263. doi: 10.1038/nrg2538
Vasudevan, S., Tong, Y., and Steitz, J. A. (2007). Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 318, 1931–1934. doi: 10.1126/science.1149460
Warsame, A. O., Michael, N., O’Sullivan, D. M., and Tosi, P. (2020). Identification and quantification of major faba bean seed proteins. J. Agri Food Chem. 68, 8535–8544. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02927
Woodwark, C. and Bateman, A. (2011). The characterisation of three types of genes that overlie copy number variable regions. PLoSONE 6, e14814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0014814
Keywords: VC1 gene, structural variation, KASP markers, Vicia faba, convicine
Citation: Ugwuanyi S, Makhoul M, Golicz AA, Obermeier C and Snowdon RJ (2025) Multiple copy number variants of VC1 gene reveal single-copy expression as a key determinant of vicine content. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1565210. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1565210
Received: 22 January 2025; Accepted: 19 May 2025;
Published: 13 June 2025.
Edited by:
Elisabetta Mazzucotelli, Council for Agricultural Research and Economics- Research Centre for Genomics and Bioinformatics, ItalyReviewed by:
Ragupathi Nagarajan, CTC Genomics, United StatesAna Luisa Garcia-Oliveira, Alliance Bioversity & CIAT, Colombia
Copyright © 2025 Ugwuanyi, Makhoul, Golicz, Obermeier and Snowdon. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Samson Ugwuanyi, c2Ftc29uLnVnd3VhbnlpQGFncmFyLnVuaS1naWVzc2VuLmRl
†ORCID: Samson Ugwuanyi, orcid.org/0000-0002-1537-4748
Manar Makhoul, orcid.org/0000-0003-4970-209X
Christian Obermeier, orcid.org/0000-0001-5605-9106
Rod J. Snowdon, orcid.org/0000-0001-5577-7616
 Samson Ugwuanyi
Samson Ugwuanyi Manar Makhoul
Manar Makhoul Agnieszka A. Golicz
Agnieszka A. Golicz Christian Obermeier
Christian Obermeier Rod J. Snowdon
Rod J. Snowdon