- 1New Quality Productivity Research Center, Guangdong ATV College of Performing Arts, Deqing, China
- 2Institute of Biophysics, Math & Physics College, Jinggangshan University, Ji’an, China
- 3School of Life Sciences, Nantong University, Nantong, China
- 4State Key Laboratory of Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology, Research Center for Eco-Environmental Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 5School of Foreign Languages, Guangdong Baiyun University, Guangzhou, China
- 6College of Bioscience and Engineering, Jiangxi Agriculture University, Nanchang, China
- 7School of Life Sciences, Jinggangshan University, Ji’an, China
- 8Wenzhou Key Laboratory of Early-Maturing Tea Tree Breeding, Wenzhou Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Wenzhou, Zhejiang, China
Accurate determination of photosynthetic parameters is essential for understanding how plants respond to environmental changes. In this study, we evaluated the performance of the Farquhar-von Caemmerer-Berry (FvCB) model and introduced a novel model to fit photosynthetic rates against ambient CO2 concentration (An–Ca) and intercellular CO2 concentration (An–Ci) curves for Lolium perenne and Triticum aestivum under 2% and 21% O2 conditions. We observed significant discrepancies in the FvCB model’s fitting capacity for An–Ca and An–Ca curves across different oxygen regimes, particularly in estimates of key parameters such as the maximum carboxylation rate (Vcmax), the day respiratory rate (Rday), and the maximum electron transport rate for carbon assimilation (JA-max). Notably, under 2% and 21% O2 conditions, the values of Vcmax and Rday derived from An–Ca curves using the FvCB model were 46.98%, 44.37%, 46.63%, and 37.66% lower than those from An–Ci curves for L. perenne, and 47.10%, 44.30%, 47.03%, and 37.36% lower for T. aestivum, respectively. These results highlight that the FvCB model yields significantly different Vcmax and Rday values when fitting An–Ca versus An–Ci curves for these two C3 plants. In contrast, the novel model demonstrated superior fitting capabilities for both An–Ca and An–Ci curves under 2% and 21% O2 conditions, achieving high determination coefficients (R2≥ 0.989). Key parameters such as the maximum net photosynthetic rate (Amax) and the CO2 compensation point (Γ) in the presence of Rday, showed no significant differences across oxygen concentrations. However, the apparent photorespiratory rate (Rpa0) and photorespiratory rate (Rp0) derived from An–Ci curves consistently exceeded those from An–Ca curves for both plant species. Furthermore, Rpa0 values derived from An–Ca curves closely matched observed values, suggesting that An–Ca curves more accurately reflect the physiological state of plants, particularly for estimating photorespiratory rates. This study underscores the importance of selecting appropriate CO2-response curves to investigate plant photosynthesis and photorespiration under diverse environmental conditions, thereby ensuring a more accurate understanding of plant responses to changing environments
1 Introduction
In the context of ongoing global climate change and the persistent increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations, studying the response models of plant photosynthesis to intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) (see Supplementary Table S1 for the list of abbreviations) and ambient CO2 concentration (Ca) is of critical importance. Photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert CO2 into organic matter using light energy, plays a crucial role in the carbon cycle and the energy flow within ecosystems (Sergio et al., 2015; Kolari et al., 2014; Roberta et al., 2024). This process is influenced by both light intensity and CO2 concentrations, making the development of accurate photosynthesis models essential for predicting plant growth and ecosystem changes (Eric et al., 2019; Pleban et al., 2020; Taylor et al., 2024).
The response models of photosynthesis to Ci (An–Ci model, where An represents the net photosynthetic rate) and to Ca (An–Ca model) are fundamental for understanding plant photosynthesis, each addressing different aspects. The An–Ci model primarily describes the relationship between the internal CO2 concentration within plant leaves and An. This model incorporates internal gas exchange and biochemical processes, such as the carboxylation reaction of Rubisco (Kelly et al., 2016; Ye et al., 2024). Ci denotes the CO2 concentration in the air space around mesophyll cells, which is influenced by stomatal conductance (Miner and Bauerle, 2017; Taylor et al., 2024). This model is typically used to analyze photosynthetic performance under various environmental conditions, including changes in light, temperature, and CO2 concentrations (De Kauwe et al., 2016; Yiotis et al., 2021; Xiong et al., 2022). Conversely, the An–Ca model focuses on the relationship between ambient CO2 concentration and plant photosynthesis. This model evaluates the impact of changes in atmospheric CO2 on photosynthesis, particularly in the context of global climate change and rising CO2 levels (Eric et al., 2019; Qiu and Katul, 2020). It helps predict future impacts on plant growth and ecosystem dynamics. In practical applications, the An–Ci model provides insights into the biochemical mechanisms of photosynthesis, while the An–Ca model is more frequently used in ecological and climate change research (Kelly et al., 2016; Miner and Bauerle, 2017; Xiong et al., 2022). Both models are invaluable tools in plant physiology and global change biology.
As we explore the complex ways in which plant photosynthesis responds to variations in CO2 levels, a plethora of models has been developed by scientists. These models can be broadly categorized into two types: empirical and biochemical. Among the empirical models, the Michaelis-Menten (M-M) model stands out due to its foundation in enzyme kinetics, while the exponential equation model provides a mathematical framework for describing the photosynthetic response (Watling et al., 2000; Sharkey et al., 2007; Silva-Pérez et al., 2017), offering a refined method for fitting photosynthetic curves. These empirical models are utilized to fit the An–Ca or An–Ci curves of plants, enabling the extraction of key parameters such as the maximum net photosynthetic rate (Amax), which indicates the upper limit of photosynthetic capacity, the CO2 compensation point with day respiratory rate (Γ), which reveals the CO2 level at which photosynthesis balances respiration, and the apparent photorespiratory rate (Rpa0) at CO2 concentration approaching 0 μmol mol−1, a measure of the energy invested in photorespiration (Leuning, 1995; Medlyn et al., 2011; Morfopoulos et al., 2014). These three pivotal photosynthetic parameters are quantifiable (Medlyn et al., 2011; Morfopoulos et al., 2014; Burnett et al., 2019). Consequently, regardless of the model used and whether it is for the An–Ca or An–Ci curve, the parameters derived from these models should closely match the observed data without significant discrepancies. It is only under these conditions that we can deem a model to be effective. Apparently, the M-M model and the exponential equation model, though both being asymptotic functions, can’t always accurately depict net CO2 assimilation rates reductions beyond the TPU-limitation phase in some plant species (Watling et al., 2000; Silva-Pérez et al., 2017). Furthermore, these two models are unable to directly estimate the critical transition point from Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP)-limited to TPU-limited conditions (CTPU).
Among the biochemical models, the one developed by Farquhar et al. (1980) and its subsequent modifications (Harley and Sharkey, 1991) are central. The model introduced by Farazdaghi and Edwards (1988) also contributes to the field. The Farquhar model, widely known as the FvCB model, has been extensively analyzed for its biochemical mechanisms and is used to fit the An–Ci curve of C3 plants (Dubois et al., 2007; Fan et al., 2011; Busch and Sage, 2017; Rogers et al., 2017; Walker et al., 2017; Yin et al., 2021). This model provides five crucial parameters: the maximum electron transport rate (JA-max) for photosynthesis, the maximum carboxylation rate (Vcmax), triose phosphate utilization rate (VTPU), day respiratory rate (Rday), CO2 compensation point (Γ*) in absence of Rday and mesophyll conductance (gm) (Long and Bernacchi, 2003; Norby et al., 2017; Xiao et al., 2021). Despite its extensive use in studying the photosynthetic response of C3 plants to environmental changes such as light, temperature, CO2 concentration, and nitrogen (N) nutrition (Bellasio et al., 2015; Sharkey, 2016; Busch and Sage, 2017; Anderegg et al., 2018; Cheah and The, 2020; Han et al., 2020; Yin et al., 2021; Yin and Amthor, 2024), the FvCB model has limitations. It cannot directly estimate parameters like Amax, Γ, and Rpa0, as well as is specific to C3 plants.
In the current research field, the An–Ci curves of plants are typically analyzed using biochemical models to derive key photosynthetic parameters (Farquhar et al., 1980; Harley and Sharkey, 1991; Fan et al., 2011; Vijayakumar et al., 2024). However, research on fitting the An–Ca curve is limited, probably because Ci is directly involved in photosynthetic carboxylation while ambient Ca only indirectly affects Ci (Long and Bernacchi, 2003). Moreover, there is a paucity of studies examining whether significant differences exist between important photosynthetic parameters (e.g., Amax, Γ, and Rpa0) derived from the An–Ca and An–Ci curves and the observed data (Busch and Sage, 2017). Similarly, the consistency of parameters such as JA-max, Vcmax, Γ*, VTPU, and Rday, obtained from fitting gas exchange data (i.e., An–Ca and An–Ci curves) with biochemical models, remains underexplored (Medlyn et al., 2011; Morfopoulos et al., 2014; Yin et al., 2021; Smith et al., 2023). Accurately determining these parameters is essential for understanding plant responses to ambient CO2 variations, evaluating carbon assimilation efficiency, and assessing adaptability to climate change. Thus, a comparative analysis of model predictions and measured data is particularly critical.
In this study, we begin with a clear and concise explanation of the FvCB model, initially introduced by Farquhar et al. in 1980. Subsequently, we introduce a new model. This model describes the CO2-response curve of photosynthesis and incorporates an explicit term for Rday. Additionally, we also introduce another version of the model that does not explicitly define Rday. Then, we showcase how to apply both the FvCB model and our newly developed model to fit An–Ca and An–Ci curves, respectively, in order to estimate key photosynthetic and biochemical parameters. Finally, we utilize a modeling-observation intercomparison approach to assess the photosynthetic parameters derived from An–Ca and An–Ci curves for both the FvCB model and our newly developed model. For the FvCB model, these parameters include Vcmax, JA-max, Γ*, VTPU, and Rday. For the new model, they encompass Amax, CTPU, Γ, CO2 compensation point (Γ*) in the absence of Rday and Rpa0. We then determine which parameters exhibit different values when derived from the An–Ca and An–Ci curves. Ultimately, we evaluate whether there are significant differences in the estimated parameters obtained from these two types of curves. Through this methodological exploration, we aim to provide novel insights and tools to enhance research in plant photosynthesis.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 FvCB model description
The FvCB model considers that the carbon assimilation process of C3 plants includes: the Rubisco enzyme activity limitation stage, the RuBP regeneration limitation stage, and the triose phosphate utilization (VTPU) limitation stage.
In the Rubisco limitation stage (Farquhar et al., 1980; Dubois et al., 2007; Sharkey et al., 2007; Miao et al., 2009; Ellsworth et al., 2015; Yin et al., 2021), the following equation is used:
where Vc,max is the maximum velocity of the carboxylase (μmol·m−2·s−1); Ci is the intercellular CO2 concentration; Kc and Ko are the Michaelis-Menten constants for CO2 and O2, respectively (Farquhar et al., 1980; Silva-Pérez et al., 2017); O is the partial pressure of oxygen at the site of Rubisco. Rday is the day respiratory rate.
During the RuBP-limited phase of photosynthesis, if the regeneration of RuBP is predominantly constrained by the availability of NADPH, then the following equation can be applied:
where Aj is the carbon assimilation rate limited by RuBP regeneration capacity. At light saturation, J is equal to JA-max in Equation 2 (Farquhar et al., 1980; Gu et al., 2010; von Caemmerer, 2013; Farquhar and Busch, 2017; Yin et al., 2021).
When RuBP regeneration is co-determined by the availability of both NADPH and ATP, the equation assumes a slightly modified form:
At light saturation, J is equal to JA-max in Equation 3 (von Caemmerer, 2000; Long and Bernacchi, 2003; Yin et al., 2004; Yin et al., 2009; Lenz et al., 2010; Bernacchi et al., 2013).
In the TPU limitation stage, we have:
where Ap is the carbon dioxide assimilation rate when the utilization of phosphate glucose is limited. αG is the proportion of glycolic acid not returned to chloroplasts and is related to the release of phosphate (Dubois et al., 2007). αG is between [0, 1]. While is equal to 0, Equation 4 is expressed as (Long and Bernacchi, 2003; Bernacchi et al., 2013).
Based on the analysis above, it can be inferred that fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves separately using the FvCB model should yield different values for Vcmax, JA-max, and Rday, while the values for VTPU and Γ* should be the same. For VTPU and Γ*, it is not possible for their values to change simply because Ca or Ci is altered. This should be consistent with the actual situation.
On the other hand, experimental methodologies facilitate the accurate quantification of whole-chain electron transport, represented by Jf, through the application of fluorescence techniques. As elucidated by von Caemmerer (2000) and Long and Bernacchi (2003), Jf is partitioned among several pivotal processes, with photosynthesis being a principal recipient and denoted by JA. Beyond photosynthesis, Jf contributes to other synthetic and electron-consuming pathways, including photorespiration (JO), the reduction of nitrate to ammonium (JNit), and the light-driven oxygen uptake via the Mehler ascorbate peroxidase (MAP) reaction (JMAP). Consequently, the relationship can be encapsulated as Jf = JA + JO + JNit + JMAP. The analysis underscores a critical correlation between Jf and JA: the magnitude of Jf must necessarily surpass that of JA. This inference arises from the understanding that Jf encompasses not only the electrons associated with JA. It also includes those in other synthetic and metabolic pathways, such as JO, JNit, and JMAP. Consequently, it can be deduced that the maximum rate of photosynthesis (JA-max) as determined by the FvCB model must be inherently lower than the maximum rate of whole-chain electron transport (Jf-max).
In recent years, significant progress has been made in the field of plant photosynthesis models. Among them, the FvCB model has also achieved remarkable advancements in aspects such as dynamic light response expansion and multi-scale coupling models. Under dynamic light environments, stomatal conductance also changes dynamically and interacts with photosynthesis. Previous studies have coupled the dynamic stomatal model with the FvCB model (Zhang et al., 2017; Yin and Amthor, 2024). They found that by using an improved version of the Ball-Berry stomatal model, the dynamic effects of factors such as light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and air humidity on stomatal conductance can be considered. Stomatal conductance (gs) can be expressed as: gs = g0 + m × An/Ca × hs, where g0 is the minimum stomatal conductance, m is an empirical coefficient, An is the net photosynthetic rate, Ca is the atmospheric CO2 concentration, and hs is the relative humidity of the air at the leaf surface. Under dynamic light environments, changes in light intensity affect the photosynthetic rate, which in turn dynamically adjusts the stomatal conductance through the stomatal model and then feedback-affects photosynthesis. This enables the model to more realistically simulate the photosynthesis-stomatal coupling process of plants under dynamic light environments.
2.2 A new model for describing the CO2–response curve of photosynthesis with an explicit Rday
In order to estimate key photosynthetic parameters such as Amax, CTPU and Γ*, we have developed a new model describing CO2-resposne curves of photosynthesis (An–C curves) (hereafter referred to Model I). The new model can be written as follows:
where An is the net photosynthetic rate; Γ* is the CO2 compensation point in the absence of Rday. αc, βc and γc are three coefficients that depend on plant characteristics and environmental conditions, and they are independent of C. C can represent both ambient CO2 concentration (Ca) and intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci).
In addition, Equation 5 can be rearranged as:
In contrast to Equation 1, the initial term represents the gross rate of photosynthesis, while the subsequent term denotes the actual rate of photorespiration (Rp), assuming no contribution from Rday Equation 6. Consequently, Rp can be expressed as follows:
In Equation 7, Rp will decrease with C. Therefore, it can be used to investigate the relationship between Rp and C under different environmental factors. Specially, while C = 0 μmol mol−1, Rp0 = . In this scenario, theoretically, Rp0 will take on two different values when either Ca or Ci is at 0 μmol mol−1. In practice, there is only a single value that defines the CO2-response curve for photosynthesis. Consequently, the Rp0 value serves as a benchmark to assess the plausibility of different response types. Specifically, the proximity of the Rp0 values derived from fitting An–Ca and An–Ci curves to the actual measured data is one of the criteria used to evaluate which response type is more justifiable.
Supposing that Rday approximates a constant or is independent of C, the first derivative of Equation 5 is expressed as follows:
where dAn/dC is the slope of the An–C curve, and dAn/dC decreases with increasing C. As C tends to zero in Equation 8, dAn/dC equals , and it is referred to as the initial slope of the An–C curve (α0 = ). When dAn/dC equals zero, CTPU can be calculated, then dAn/dC will be negative when C surpasses CTPU. Therefore, Equation 5 is a non-asymptotic function.
When dAn/dC= 0, CTPU can be calculated Equation 9:
And Amax can be calculated Equation 10:
In addition, when An equals zero in Equation 5, Γ can be calculated Equation 11:
Indeed, in practical terms, there is but a single set of values for Amax and Γ that characterizes the CO2-response curve of photosynthesis. These values are pivotal as they provide a reference point to evaluate the reasonableness of various response types. Notably, the closeness of the Amax and Γ values, as determined by fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves, to the observed data obtained serves as a critical criterion. This comparison helps in ascertaining which response type is more rational and aligned with the actual physiological processes of photosynthesis.
2.3 A new model for describing the CO2–response curve of photosynthesis without an explicit Rday
Since precisely measuring Rday in plants remains a challenging (Atkin and Tjoelker, 2003; Yin et al., 2009) (see Tcherkez et al., 2017 for a comprehensive review), we have developed an alternative model. It can not only accurately fit the CO2–response curve of photosynthesis (An–C curve) but also minimize potential fitting discrepancies due to different choices of Rday (hereafter referred to Model II). The model is expressed as follows:
where αc1, βc1, and γc1 are three coefficients that depend on plant characteristics and environmental conditions; Γ is the photorespiratory CO2 compensation point in presence of Rday (Farquhar et al., 1980; Long and Bernacchi, 2003). Furthermore, considering the influence of Rday, it is anticipated that the coefficients of αc1, βc1, and γc1 in Equation 12 will differ from those of αc, βc and γc in Equation 5.
In addition, Equation 12 can be rearranged as:
In Equation 13, the first term is the gross photosynthetic rate, and the second term is the apparent photorespiration rate (Rpa) including Rday. Therefore, Rpa can be expressed as:
In Equation 14, Rpa decreases as C increases. Therefore, it can be utilized to explore the relationship between Rp and C for all plant species under any environmental conditions. Indeed, when C is exactly 0 μmol mol−1, Rpa0 takes on a particular value. Theoretically, one might expect Rpa0 to have two different values corresponding to either Ca or Ci being at 0 μmol mol−1. However, in actuality, there is but a single value that delineates the CO2-response curve for photosynthesis. This singular Ca or Ci value thus becomes an essential criterion for assessing the plausibility of various response types. Notably, the closeness of the Rpa0 values, derived from fitting An–Ca and An–Ci curves, to the observed data is a pivotal factor in judging which response type is more reasonable.
The first derivative of Equation 12 may be expressed as follows:
where dAn/dC is the slope of the An–C curve, and dAn/dC decreases with increasing C. As C tends to zero in Equation 15, dAn/dC equals , and it is referred to as the initial slope of the An–C curve (i.e., α0 = ). dAn/dC equals zero when C equals to CTPU, then dAn/dC will be negative when C surpasses CTPU. It is important to acknowledge that the new model, distinguishes between two distinct values for the An–C curve: one is Ci,TPU, which represents An–Ci, and the other is Ca,TPU, which corresponds to the An–Ca curve. This distinction is crucial for accurately modeling and understanding the photosynthetic responses in plants.
Therefore, while the , CTPU is calculated by:
And Amax can be obtained as:
Besides CTPU and Amax can be calculated by Equations 16, 17, respectively, Γ can also be estimated by Equation 12. Indeed, in practical applications, there is but one definitive set of values for Amax and Γ that characterizes the CO2-response curve of photosynthesis. These values are crucial as they serve as a benchmark against which the reasonableness of different response types can be assessed. Importantly, the proximity of the Amax and Γ values, derived from fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves, to the actual observed data is a key criterion. This comparison is essential for determining which response type is more rational and in accordance with the true physiological mechanisms of photosynthesis.
Furthermore, it is important to acknowledge that Equations 5, 12 are fundamentally equivalent when it comes to determining photosynthetic parameters like Amax and Γ, irrespective of whether An–Ca curves or An–Ci curves are being fitted.
2.4 Plant materials
In this study, two typical C3 plants, namely Lolium perenne L. (Zhongxin 830) and Triticum aestivum L. (Jimai 22), were selected as the experimental materials. As two important crops, their photosynthetic characteristics display the typical carbon assimilation process of C3 plants. Their photosynthesis is highly sensitive to environmental conditions such as light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration, and water supply (Höglind et al., 2011; Pshenichnikova et al., 2019). Therefore, these two crops are highly suitable for a comparative study of the differences between the FvCB model (applicable only to C3 plants) and the new model in fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves and estimating key photosynthetic parameters under different oxygen concentration conditions. The two experimental materials were sown in mid-October 2022 and managed conventionally in the field. Data were collected on sunny days from April 28 to May 10, 2023. T. aestivum was at the booting stage to the initial flowering stage, with a plant height of 60–70 cm, and its flag leaf was selected for measurement. L. perenne was at the booting stage, with a plant height of about 1.3 m, and the first leaf below its flag leaf was selected for measurement.
2.5 Gas exchange data measurement
A portable photosynthesis system (LI-6400-40, LI-COR INC., USA) was used to collect data on sunny days from 9:00 to 11:30 and 14:00 to 17:00, with air temperatures at 30.3 ± 2.5°C and maximum midday light intensity of about 1,600 μmol·m-2·s-1. After a 1.5- to 2-hour induction under natural light, the device was turned on for preheating and checked. The oxygen concentration in the fluorescence leaf chamber is controlled by connecting external gas cylinders filled with different gas mixtures. The oxygen concentrations are set at 2% (2% oxygen and 98% nitrogen; under this concentration, the plant’s photorespiration can be neglected, and this serves as the treatment group) and 21% (21% oxygen and 79% nitrogen; this is the atmospheric oxygen concentration, and it serves as the control group). The high-pressure gas cylinders are first connected to a self-made buffer bag. A small amount of water is injected into the buffer bag to simulate the relative humidity in the atmosphere. After passing through the buffer bag, the mixed gas enters the leaf chamber through the intake pipe of the photosynthesis instrument, ensuring the stability of the oxygen concentration and appropriate humidity. Currently, this buffer device has been granted a Chinese national utility model patent (ZL 2015 2 0174847.1). The CO2 injection system was calibrated using an open gas path with a flow rate of 500 μmol·s-1. Before measuring the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of the two plants, the light response curves of photosynthesis (An–I curves, where I is light intensity) for these two plants were measured first. When measuring the An–I curve, the CO2 injection system provided a stable CO2 concentration. Based on measurements of atmospheric CO2 concentration, the CO2 concentration in the instrument chamber was set to 420 μmol·mol-1, and the light intensity gradient was set to: 2,000, 1,800, 1,600, 1,400, 1,200, 1,000, 800, 600, 400, 200, 150, 100, 80, 50, 0 μmol·m-2·s-1. All measurements used an automatic measurement program, simultaneously recording leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters. During automatic measurement, the minimum waiting time for each recording was 2 minutes, and the maximum waiting time was 3 minutes. Before data recording, the instrument automatically performed matching between the reference chamber and the sample chamber. After the data were measured, the “Photosynthesis Model Fitting Software (PMSS)” at http://photosynthetic.sinaapp.com/calc.html (Shenzhen Baoying Technology Computing Co., Ltd., China) was used to fit the An–I curves of the two plants in accordance with the photosynthesis light-response model (Ye et al., 2013). The saturated light intensity for both plants was found to be 2,000 μmol·m-2·s-1.
While measuring the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of the two plants, the light intensity was set to 2,000 μmol·m-2·s-1, and the O2 concentrations were 2% and 21%, respectively. The CO2 injection system provided different external CO2 gradients (Ca): 1,600, 1,400, 1,200, 1,000, 800, 600, 420, 300, 200, 100, 50, and 0 μmol·mol-1. All measurements used an automatic measurement program, simultaneously recording leaf gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence parameters. During the process of automatic measurement, the waiting time for each recording ranged from a minimum of 2 minutes to a maximum of 3 minutes. Before data recording, the instrument automatically performed matching between the reference chamber and the sample chamber. For the FvCB model, the An–Ci curves of the two plant species were meticulously fitted using a method developed by Sharkey et al. (2007) to estimate parameters such as Vcmax, JA-max, VTPU, Γ*, and Rday. In particular, the Rday value is derived under the assumption that it equals 0.015 Vcmax. This method developed by Sharkey et al. is integrated into the Photosynthesis Model Simulation Software (PMSS) platform, which can be accessed at http://photosynthetic.sinaapp.com/calc.html (Shenzhen Baoying Technology Computing Co., Ltd., China). Moreover, to determine the Jf-max, which represents the maximum electron transport rate associated with Photosystem II (PSII), a comprehensive analysis of the J–Ci curves obtained though measurements is necessary. The Jf-max, identified as the uppermost threshold of electron transport rate within these curves, is a crucial parameter for assessing the photosynthetic potential of plants. Its significance becomes particularly pronounced after the J–Ci curves have been meticulously quantified and analyzed.
Additionally, the parameters Amax, CTPU, Γ, Rpa0, Rp0, Γ*, and Rp can be determined using Model I and Model II with the assistance of the PMSS platform. The PMSS platform offers a user-friendly interface for conducting simulations and extracting key parameters that are essential for analyzing the photosynthetic performance of plants. It is a valuable tool for researchers and students alike. Please be aware that there might be temporary network issues that could prevent the webpage from loading.
2.6 Statistical analysis
All variables were presented as mean values and standard error (mean ± standard error, n = 3) with three replicates. Data were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). A paired-sample t-test was used to compare whether there was a significant difference between the fitting results and the corresponding observed values at the 5% significance level (p < 0.05). The data analysis was performed using the SPSS 18.5 statistical software package (SPSS, Chicago, Illinois, USA). One paired-sample t test was employed to compare whether there were significant differences between the fitting results and corresponding observed values at the 5% level of significance (p < 0.05) using the statistical package of SPSS 18.5 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, United States). Graphs were created using Origin 2021, and final graphic processing was performed with Adobe Illustrator CS5. The determination coefficient (R2) was used to indicate the degree of fit between the model and observed points, which was calculated as R2 = 1 – SSE/SST, where SST is the total sum of squares and SSE is the sum of squared errors.
3 Results
3.1 An–Ca and An–Ci curves and their fitting with the FvCB model at 21% O2 concentration
Figure 1 shows the An–Ca curves and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum under the conditions of 21% O2 concentration. As analyzed in Figure 1, the FvCB model shows significant differences when fitting the An–Ca curves and An–Ci curves of these two plants.
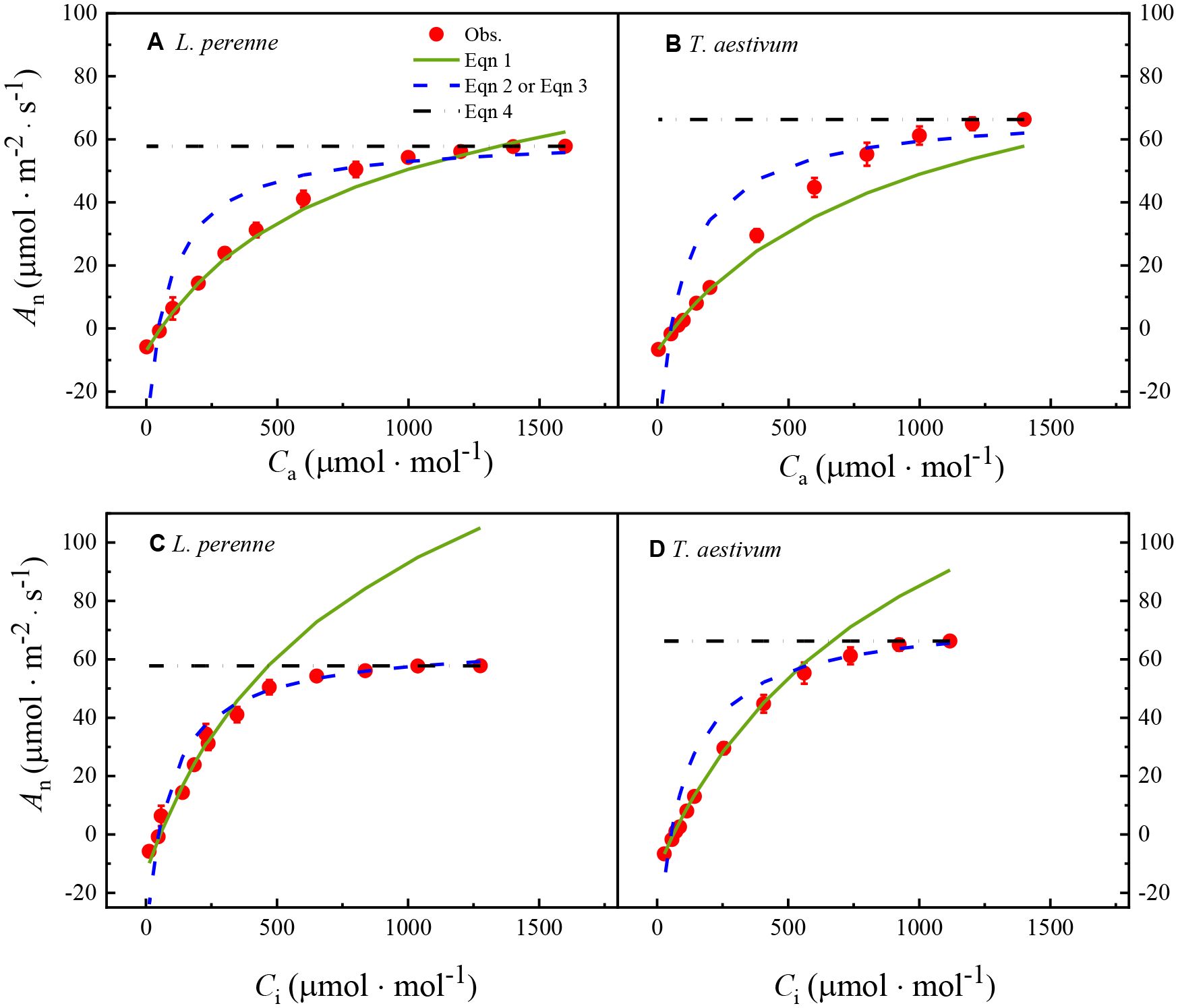
Figure 1. The An–Ca and An–Ci curves for L. perenne and T.aestivum under atmospheric conditions with an oxygen concentration of 21%. The curves have been fitted with the FvCB model, a comprehensive model that describes the photosynthetic process in C3 plants, taking into account the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco, the rate of electron transport, and the triose phosphate utilization. The solid red dots on the curves represent the observed experimental data, which are the actual measurements obtained from the plants under controlled conditions. Each data point is expressed as the mean ± standard error (SE), and the experiments were conducted with three replicates (n = 3) to ensure the robustness and reproducibility of the results.
Specifically, (1) after fitting the An–Ca curve of T. aestivum with Equations 1, 2, the obtained curve has a large deviation from the actual observed data (Figure 1B); (2) as showed in Figure 1A, the transition point from Rubisco limitation to RuBP limitation (Ci,tr) is approximately 1,200 μmol·mol-1, which is significantly higher than the currently accepted empirical range of 300-600 μmol·mol-1, while the curve of T. aestivum does not show Ci,tr (Figure 1B), indicating a significant discrepancy from the theory that Ci,tr must exist. Furthermore, when the FvCB model fits the An–Ci curves of the two plants, it reveals three key processes affecting C3 plant carbon assimilation: Rubisco limitation, RuBP regeneration limitation, and TPU limitation (Figures 1C, D).
Table 1 shows the key parameters obtained by fitting the An–Ca curves and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum with the FvCB model, including JA-max, Vcmax, VTPU, Γ*, and Rday. According to the results in Table 1, the Vcmax and VTPU predicted by the FvCB model are two indirect parameters that currently cannot be directly measured by experiments; Γ* and Rday are two parameters that are difficult to accurately measure in experiments, so there are no corresponding observed values in this study. Among these parameters, only the model predicted value of Jmax can be directly compared with the actual observed value.
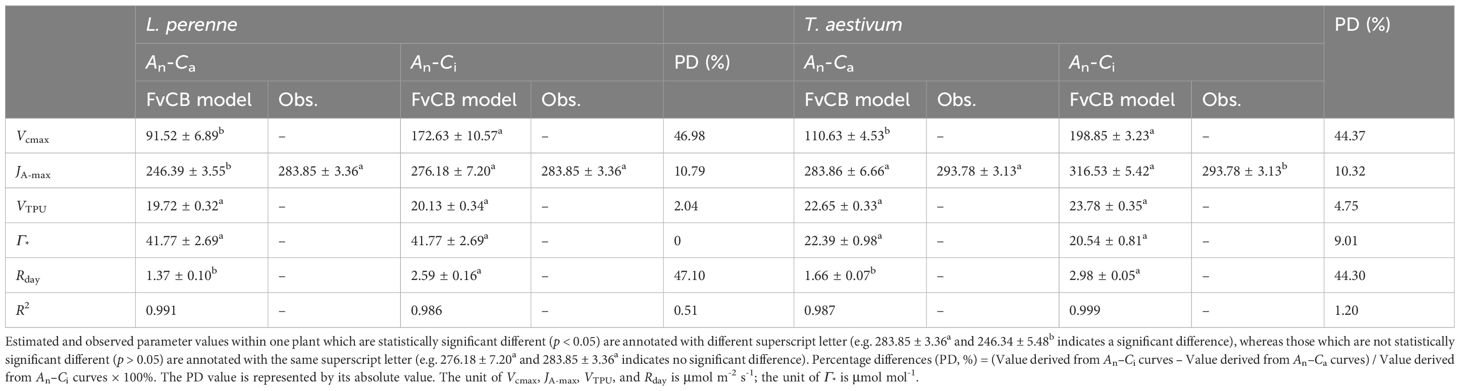
Table 1. Observed data and results estimated by FvCB model for two C3 species at 21% O2 concentration (mean ± SE, n = 3).
However, the data presented in Table 1 indicate that the JA-max values derived from fitting the An–Ca curve of L. perenne using the FvCB model is considerably lower than the observed Jf-max value. In contrast, the JA-max value obtained by fitting the An–Ci curve of L. perenne aligns closely with the observed Jf-max value, with no significant discrepancy between the estimated and observed data. Conversely, for T. aestivum, the JA-max value obtained from fitting the An–Ca curve is close to the observed Jf-max value.
In addition, the results in Table 1 show that the Vcmax values obtained by fitting the An–Ca curves with the FvCB model are smaller than the values obtained by fitting the An–Ci curves with the model by 46.98% and 44.37% for L. perenne and T. aestivum, respectively. A similar pattern is observed for the estimation of Rday. That is, the Rday values obtained by fitting the An–Ca curves with the FvCB model are significantly smaller than those obtained by fitting the An–Ci curves with the same model, with reductions of 47.10% and 44.30% for L. perenne and T. aestivum, respectively.
3.2 An–Ca and An–Ci curves and their fitting with the FvCB model at 2% O2 concentration
Figure 2 shows the An–Ca curves and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum under the conditions of 2% O2 concentration. As the data presented in Figure 2, it can be observed that the fitted curves using the FvCB model show significant differences in the values of Ci,tr. Specifically, the FvCB model predicts significantly higher Ci,tr values when fitting the An–Ca curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum compared to when fitting their An–Ci curves (Figure 2). Furthermore, the fitting results of the FvCB model reveal three key biochemical processes affecting C3 plant carbon assimilation: Rubisco enzyme limitation process, RuBP regeneration limitation, and TPU limitation. These processes play a crucial role in plant photosynthesis under varying oxygen concentration conditions (Figures 2C, D). At 2% O2 concentration, these limitation processes may differ from those at 21% O2 concentration, possibly due to plant’s adaptive regulation in low-oxygen environments. For example, Rubisco enzyme limitation may be more prominent as oxygen competes with CO2 for Rubisco’s active site, and this competition may be intensified in low-oxygen conditions. At the same time, the regeneration of RuBP and TPU limitation may also be affected by the reduction of oxygen concentration, thereby affecting the overall efficiency of photosynthesis.
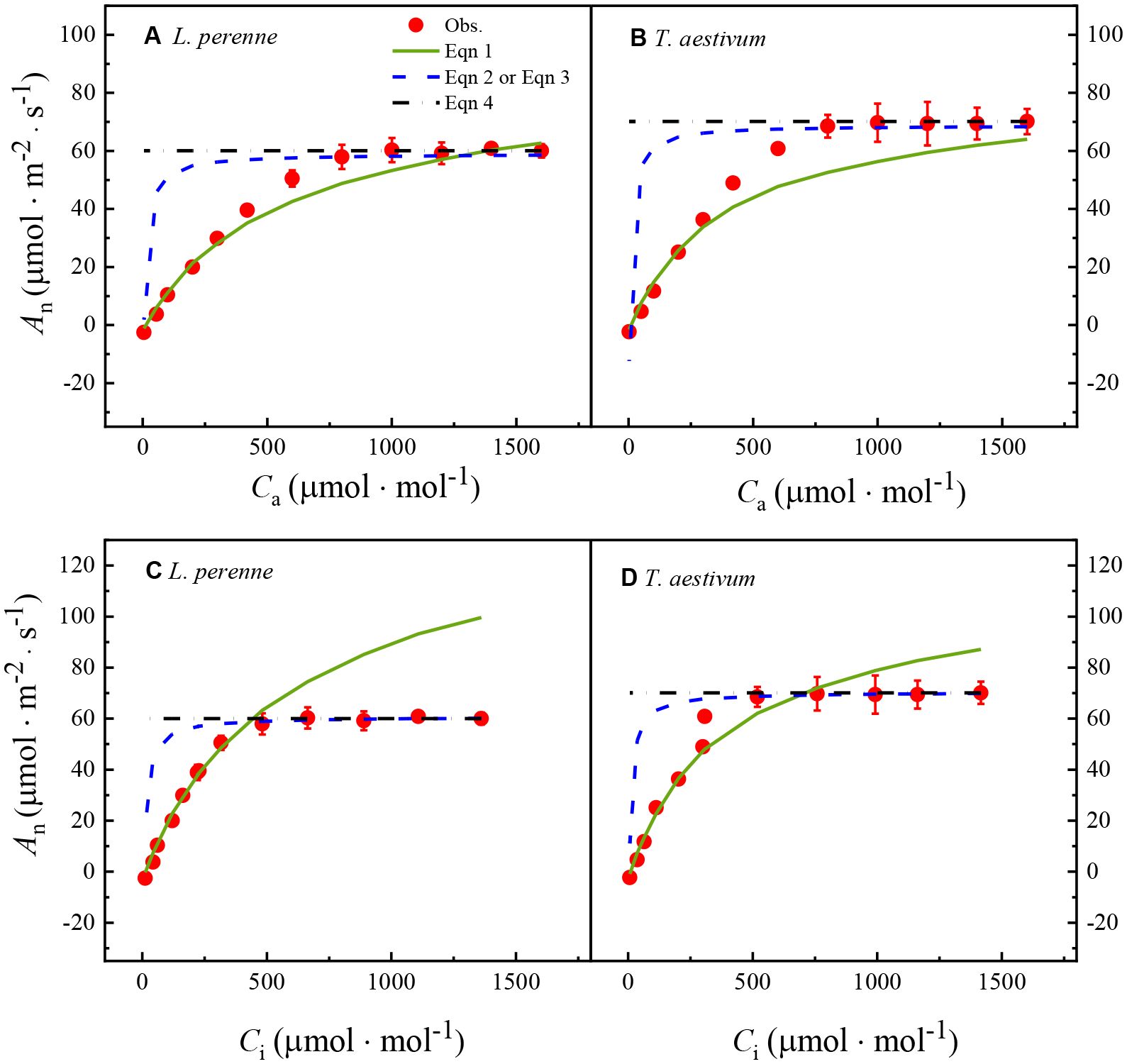
Figure 2. The An–Ca and An–Ci curves for L. perenne and T. aestivum under a reduced oxygen concentration of 2%. The curves have been fitted with the FvCB model, a comprehensive model that describes the photosynthetic process in C3 plants, taking into account the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco, the rate of electron transport, and the triose phosphate utilization. The solid red dots on the curves represent the observed experimental data, which are the actual measurements obtained from the plants under controlled conditions. Each data point is expressed as the mean ± standard error (SE), and the experiments were conducted with three replicates (n = 3) to ensure the robustness and reproducibility of the results.
Table 2 shows the key parameters obtained by fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum with the FvCB model, including JA-max, Vcmax, VTPU, Γ*, and Rday. Similar to the results in Table 1, the four parameters Vcmax, VTPU, Γ*, and Rday have no corresponding observed values. Only the model-predicted value of JA-max can be directly compared with the observed Jf-max value. Furthermore, as showed in Table 2, regardless of whether it is the An–Ca curves or the An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum fitted with the FvCB model, the derived JA-max values closely approximate the observed Jf-max value, and there is no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the estimated values and the observed data (Table 2).
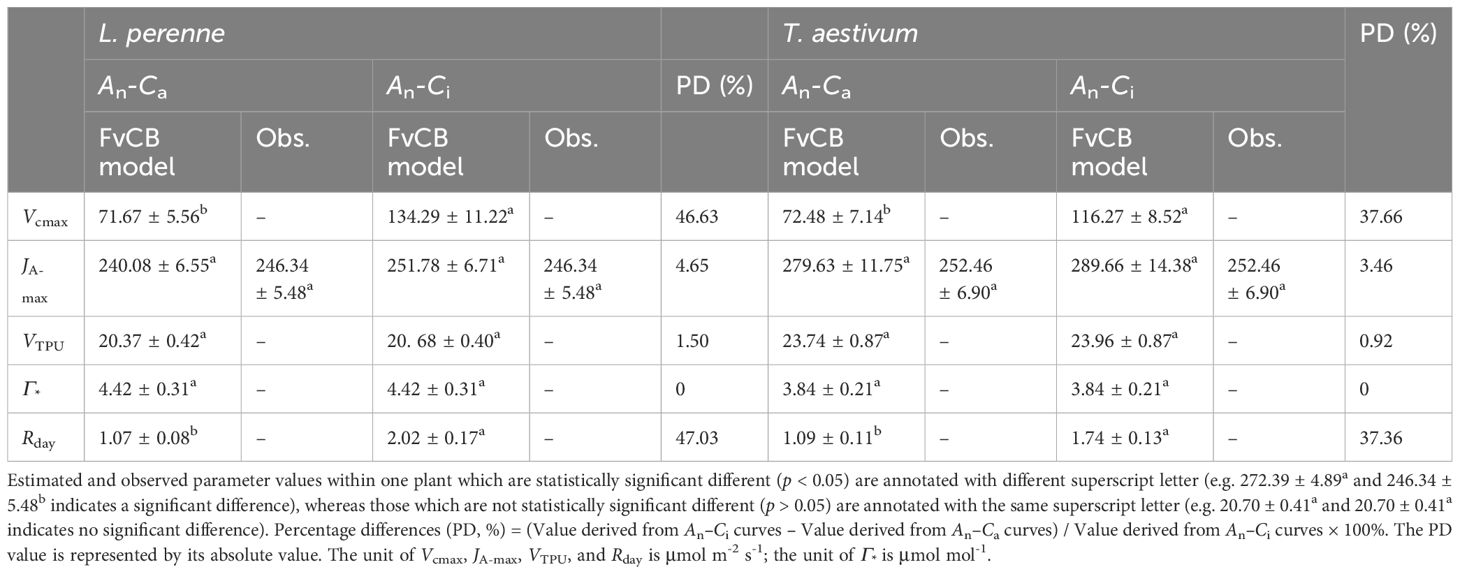
Table 2. Observed data and results estimated by FvCB model for two C3 species at 2% O2 concentration (mean ± SE, n = 3).
In addition, the results in Table 2 also show that the Vcmax values obtained by fitting the An–Ca curves with the FvCB model are significantly smaller (p < 0.05) than the values obtained by fitting the An–Ci curves with the model by 46.63% and 37.66% for L. perenne and T. aestivum, respectively. A similar situation applies to the estimation of Rday. That is, the Rday values derived by fitting the An–Ca curves with the FvCB model are significantly lower (p < 0.05) than those obtained by fitting the An–Ci curves with the same model, with reductions of 47.03% and 37.36% for L. perenne and T. aestivum, respectively. This discrepancy underscores the importance of the curve types in fitting, as it can influence estimated parameters and, in turn, our understanding of the photosynthetic responses in different plant species. Furthermore, the Γ* values estimated by the FvCB model for both plant species appear to be underestimated (Table 2).
3.3 An–Ca and An–Ci curves and their fitting using the Model I or Model II at 21% O2 concentration
Figure 3 shows the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum, along with the fitting curves generated by Model I or Model II. As shown in Figure 3, both models can accurately reproduce these plant’s An–Ca and An–Ci curves at 21% O2 concentration, with the determination coefficient (R2) at least 0.995.
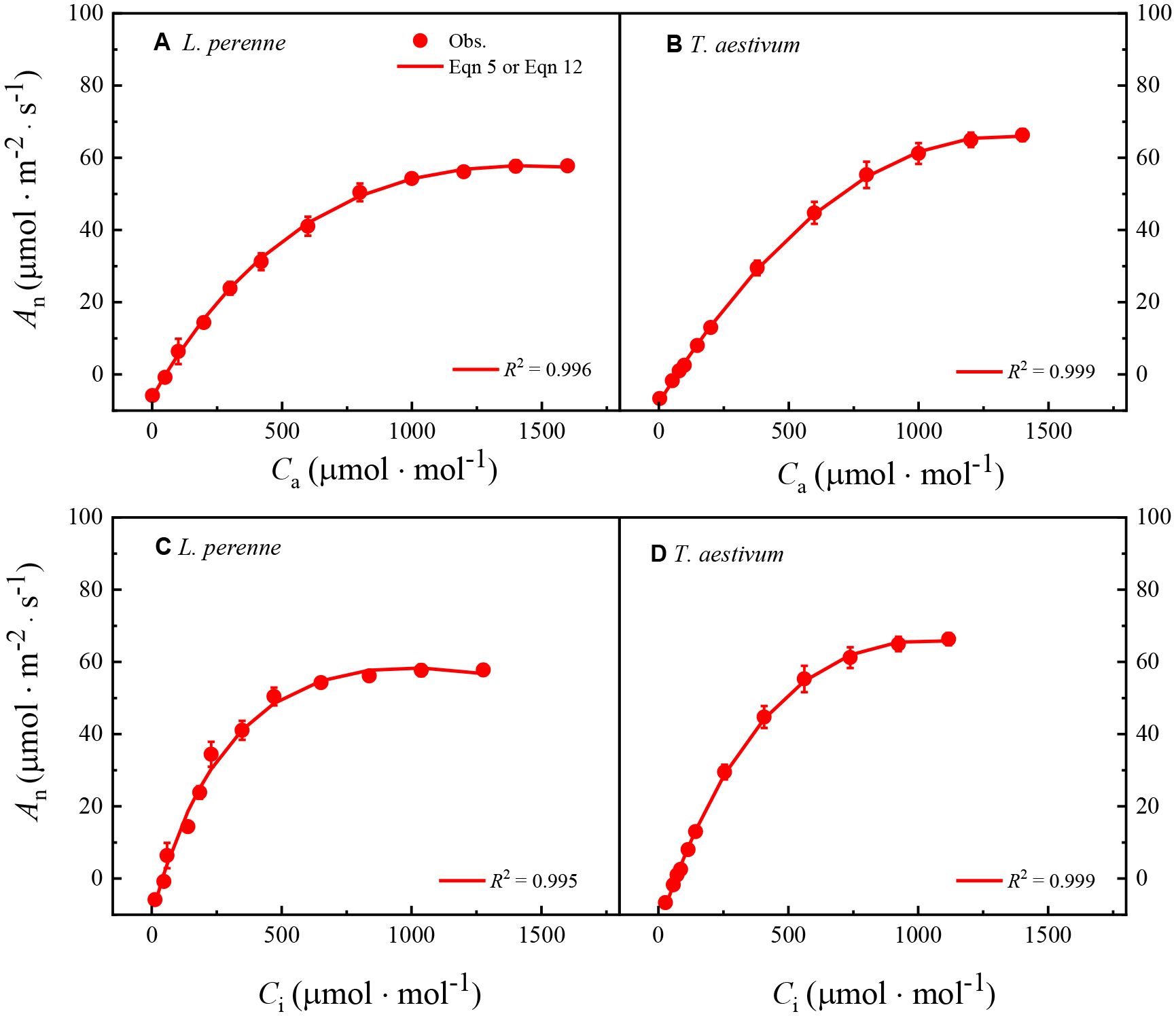
Figure 3. The An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum at an ambient oxygen concentration of 21%. These curves are derived from the photosynthetic response to varying carbon dioxide concentrations, which is a critical parameter in understanding plant carbon assimilation capabilities. The curves have been precisely fitted using either Equations 5 or 12, which are two new models designed to capture the relationship between photosynthesis, internal and external carbon dioxide concentrations. The solid red dots scattered across the graphs represent the observed experimental data points, each carefully measured to ensure accuracy and reliability. These data points are presented as the mean value ± standard error (SE), with each measurement being replicated three times (n = 3) to ensure statistical significance and to account for biological variability.
Table 3 presents several parameters derived from fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum using Model I or Model II, including α0, Amax, Ci,TPU, Γ*, Γ, Rp0, and Rpao. The data in Table 3 indicate that the Amax and Γ values obtained by fitting the An–Ca curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum with both models do not significantly differ (p > 0.05) from those obtained from the An–Ci curves. The Rpa0 values derived from fitting the An–Ca curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum with Model I or Model II are close to their respective observed values, with no significant difference (p > 0.05) between them (Table 3). However, the Rpa0 values obtained by fitting the An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum with either Model I or Model II are considerably higher than the corresponding observed values, exhibiting a significant discrepancy (p < 0.05, Table 3). Furthermore, for L. perenne and T. aestivum at 21% O2 conditions, the values of α0 derived from An–Ca curves estimated by Model I were 57.09% and 52.26% lower than those obtained by fitting their An–Ci curves (Table 3).
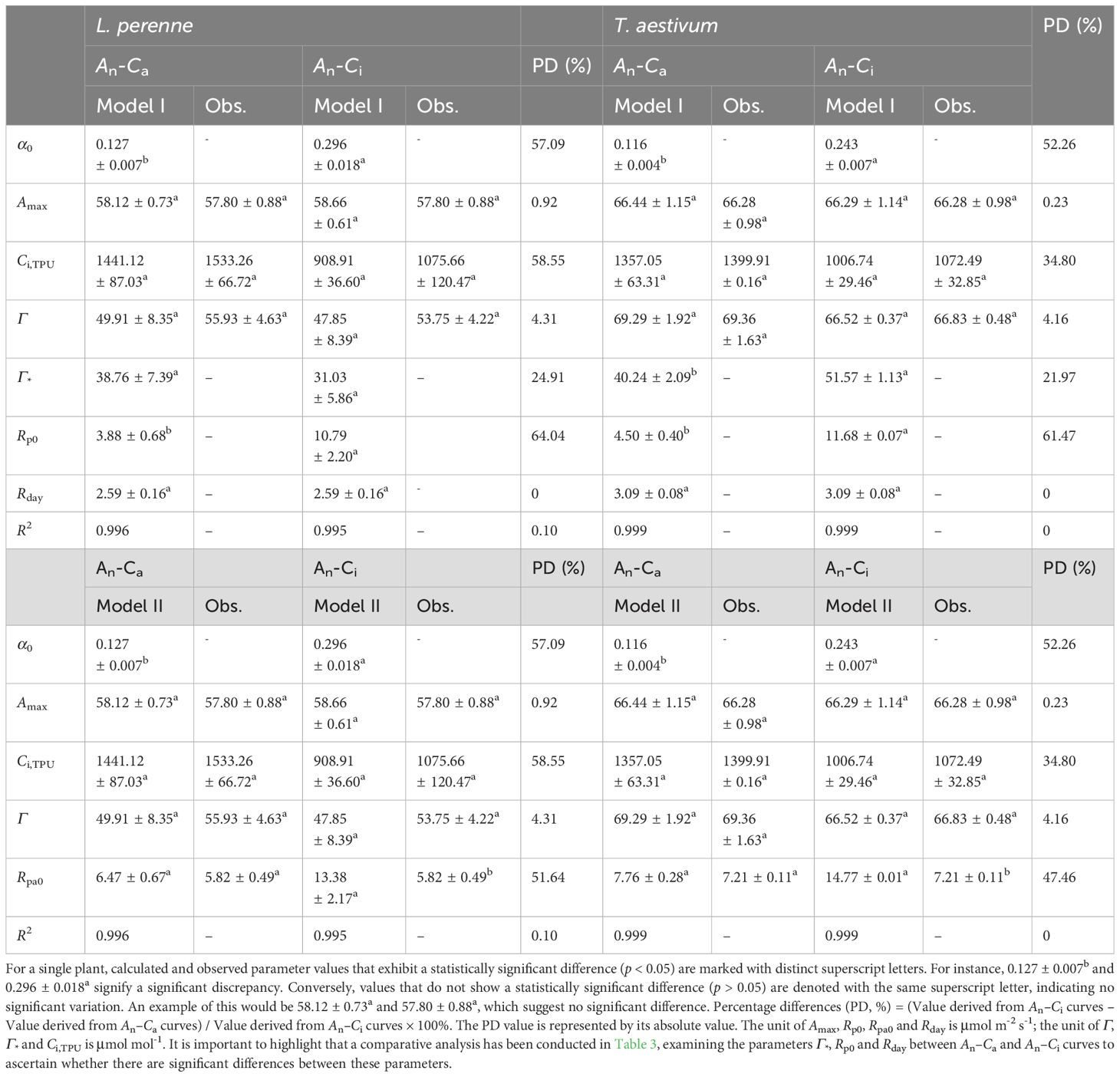
Table 3. The observed data and the outcomes generated by Model I and Model II for the two C3 species at a 21% O2 concentration for An-Ca and An-Ci curves are presented (mean ± SE, n = 3).
3.4 An–Ca and An–Ci curves and their fitting using the Model I or Model II at 2% O2 concentration
Figure 4 shows the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum at 2% O2 concentration, along with the fitting curves generated by Model I or Model II, with the R2 at least 0.989. As showed in Figure 4, both models can accurately reproduce the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of these two plants at 2% O2 concentration.
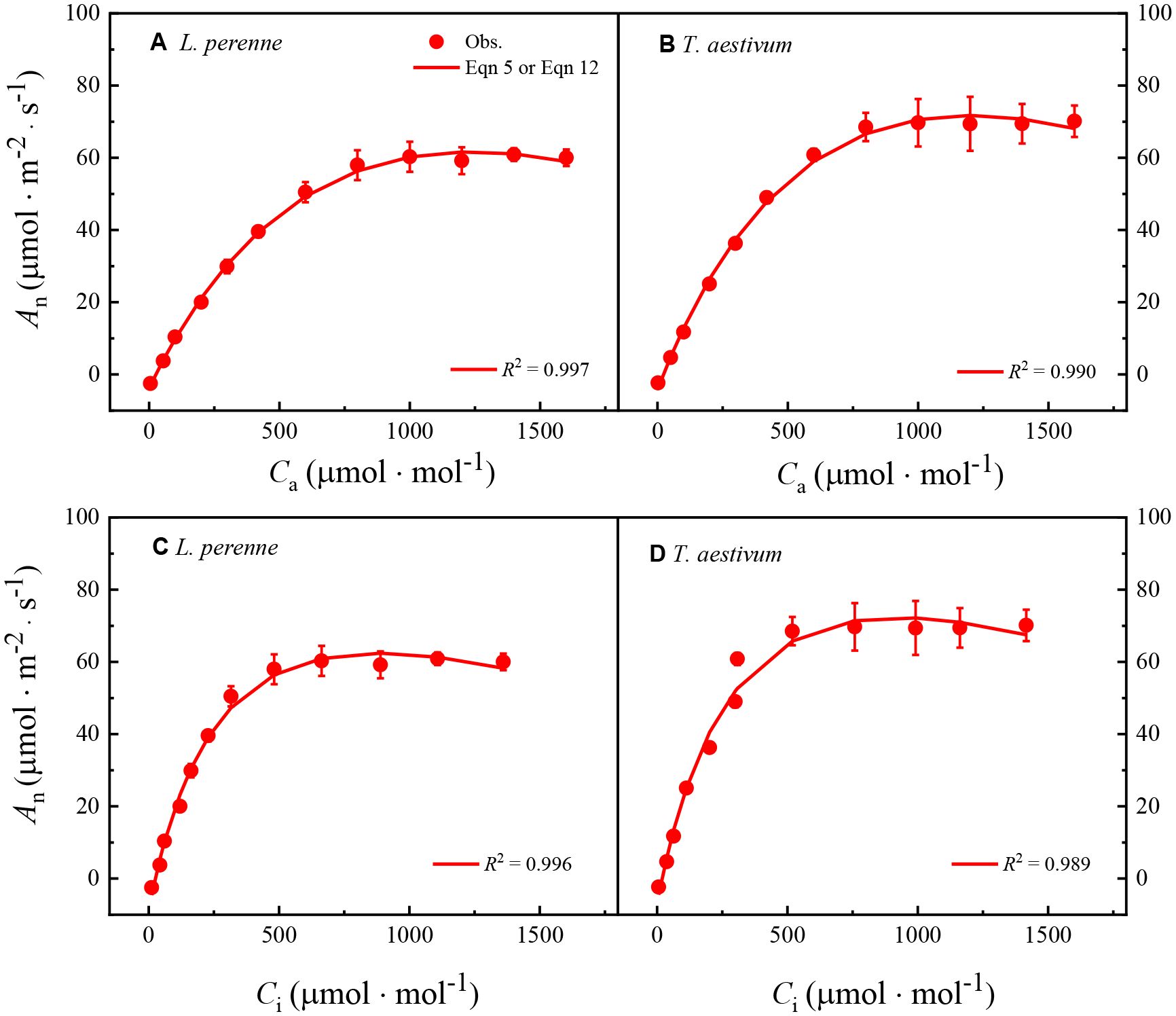
Figure 4. The An–Ca and An–Ci response curves for both L. perenne and T. aestivum under an oxygen concentration of 2%. These curves have been meticulously fitted using either Equations 5 or 12, which is indicated in the respective graphs. The solid red dots scattered across the curves correspond to the observed experimental data points, providing a visual representation of the actual measurements taken during the study. Each data point is presented as the mean value, with error bars indicating the standard error of the mean (SEM) to convey the variability within the dataset. It is important to note that the data are based on three replicates (n = 3), ensuring a robust statistical foundation for the analysis.
Table 4 shows the parameters obtained by fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum with Model I and Model II at 2% O2 concentration, including α0, Amax, Ci,TPU, Γ, Γ*, Rp0, and Rpa0. The data in Table 4 indicate that, similar to the results in Table 3, for both the An–Ca and An–Ci curves, the Amax and Γ values obtained from fitting with the two models do not significantly differ (p > 0.05) from the corresponding observed values (except for the Γ values of T. aestivum obtained from the An–Ca curve fitting with Model II). In addition, for L. perenne, the Rpa0 value obtained by fitting the An–Ca curve with Model II is close to the observed value, and there is no significant difference (p > 0.05) between the two (Table 4). On the contrary, when Model II is employed to fit the An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum, the Rpa0 value obtained is significantly higher (p < 0.05) than the corresponding observed value (Table 4). Moreover, we found that there is a significant difference (p < 0.05) between the Rpa0 value calculated by Model II and the observed data at 2% O2 concentration for T. aestivum. To avoid potential issues with the results, we opted to use Model II for fitting the An–Ca curve within the range of 0 to 300 μmol·mol−¹. By doing this, the Rpa0 value calculated with Model II is (2.45 ± 0.15) μmol·m−²·s−¹, which shows no significant difference when compared to the observed value of (2.31 ± 0.17) μmol·m−²·s−¹. In this instance, the coefficient of determination (R2) exceeds 0.9995, signifying an exceptionally high level of agreement between the fitted and observed data points. For L. perenne, following the same procedures, we determined the Rpa0 value using Model II to be (3.09 ± 0.38) μmol·m−²·s−¹. This value is in close proximity to the observed value, which is (3.03 ± 0.23) μmol·m−²·s−¹, with no significant divergence between them. When compared with the initial value of (3.68 ± 0.41) μmol·m−²·s−¹ presented in Table 4, the calculated value of (3.09 ± 0.38) μmol·m−²·s−¹ is more closely aligned with the observed values. Here as well, with an R2 value surpassing 0.9977, we observe a remarkable alignment between the model’s predictions and the empirical data, reinforcing the model’s efficacy and reliability.
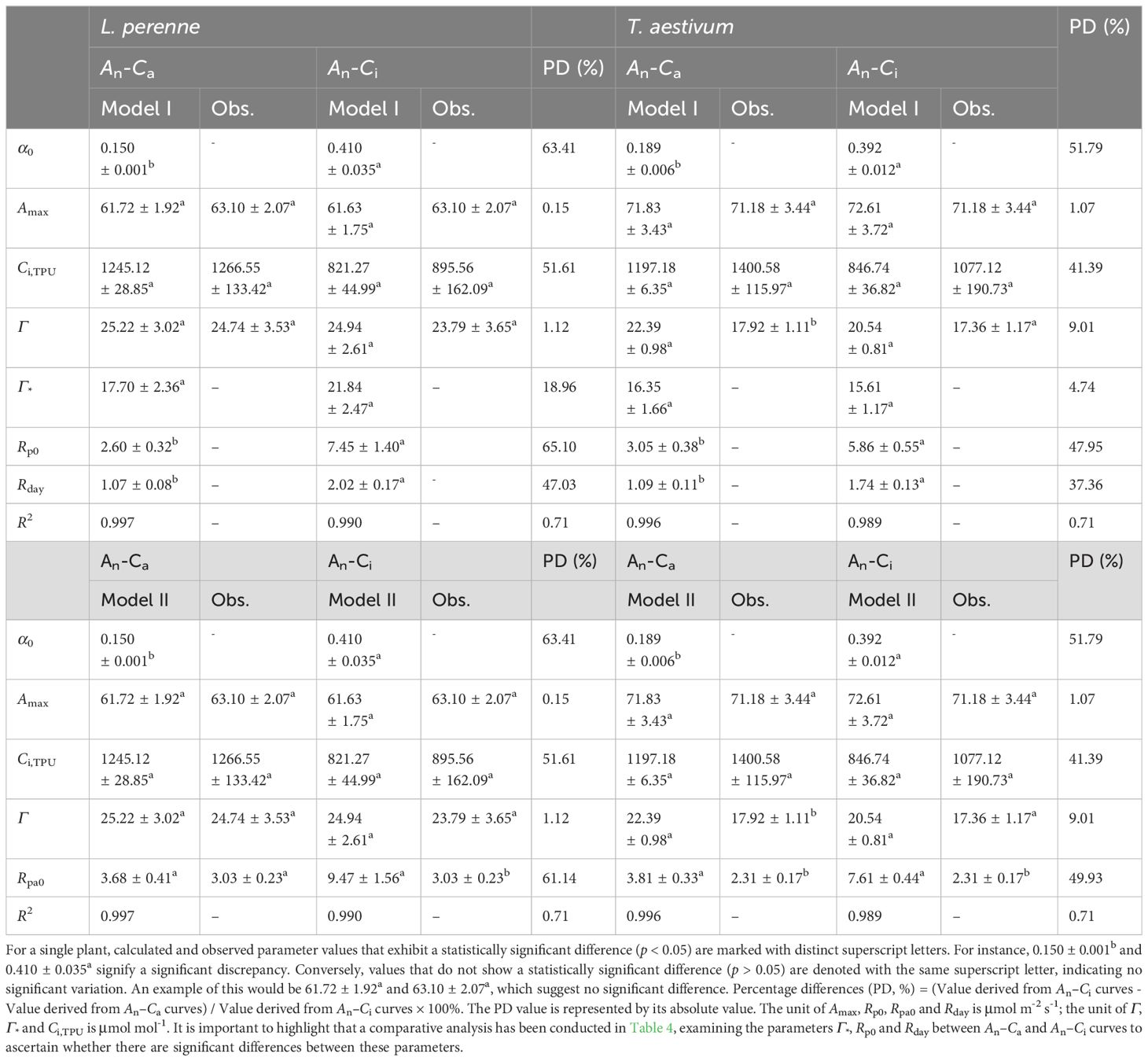
Table 4. The observed data and the outcomes generated by Model I and Model II for the two C3 species at a 2% O2 concentration for An-Ca and An-Ci curves are presented (mean ± SE, n = 3).
It is noteworthy that there is a significant difference (p < 0.05) in the α0 values obtained by fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum with the Model I. The values of α0 derived from An–Ca curves estimated by Model I were 63.41% and 51.79% lower than those obtained by fitting their An–Ci curves for L. perenne and T. aestivum at 2% O2 conditions. This finding may indicate that the model is sensitive to different CO2 response curves. Furthermore, when comparing Tables 2, 4, it can be observed that the Γ* values derived from Model I are higher than those estimated by the FvCB model for both plant species.
4 Discussions
4.1 The FvCB model in fitting CO2-response curve of photosynthesis and estimating photosynthetic parameters
In this study, the application of the FvCB model and Model I highlighted the importance of model selection in simulating the process of photosynthesis in C3 plant species. The differences in the performance of the two models across different oxygen concentrations provided valuable information about the applicability and parameter sensitivity of these models.
The FvCB model is a widely used photosynthesis model in plant physiological research, based on the photosynthetic biochemical mechanism proposed by Farquhar et al. (1980). This model predicts the photosynthetic rate of plants under different environmental conditions by simulating key biochemical processes in photosynthesis, such as the carboxylation reaction of Rubisco, the regeneration of RuBP, and photorespiration. The FvCB model is particularly suitable for analyzing the photosynthetic performance of C3 plant species under changing environmental conditions, such as different CO2 concentrations, temperatures, and light intensities (von Caemmerer and Farquhar, 1981; Walker et al., 2017; Miyazawa et al., 2020; Xiao et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2021). In practical applications, the FvCB model has been used to assess the potential impact of climate change on crop yields (Long and Bernacchi, 2003; Fan et al., 2011) and to study plant adaptability to environmental changes (Morfopoulos et al., 2014; Han et al., 2020). For example, by simulating photosynthesis under different CO2 concentrations, researchers can predict the future impact of increasing atmospheric CO2 concentrations on plant growth and ecosystem carbon cycling (Ainsworth and Long, 2005, 2021). In addition, the FvCB model has also been used to optimize agricultural management practices, such as irrigation and fertilization, to improve the light energy utilization efficiency and yield of crops (Zhu et al., 2010; De Kauwe et al., 2016; Vijayakumar et al., 2024).
Although the FvCB model holds significant value in plant physiological ecology research, its accuracy and applicability are still constrained by the model parameterization method and changes in environmental conditions. For example, in this study, fitting the An–Ca curves or An–Ci curves of plants with the model produced five important photosynthetic parameters: JA-max, Vcmax, VTPU, Γ*, and Rday (Tables 1, 2). However, only the estimated parameter JA-max can be directly compared with the observed Jf-max value (Tables 1, 2). At the same time, under normal conditions, the distribution of the electron flow from Photosystem II clearly indicates that the JA-max allocated for carbon assimilation is significantly lower than the Jf-max. In the FvCB model, this parameter is not obtained by fitting the electron transport rate to the CO2 response (J–Ci) data, but is indirectly estimated by fitting the An–Ca curve or An–Ci curve. This may lead to the model overestimating or underestimating the JA-max in plants. In this study, it was found that the JA-max value obtained by fitting the An–Ca curve of L. perenne with the FvCB model was significantly lower (p < 0.05) than the observed value at 21% O2 concentration (Table 1), whereas the JA-max value obtained by fitting the An–Ci curve of L. perenne was close to the observed value (Table 1). In contrast, the JA-max values obtained by fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of T. aestivum with the FvCB model showed the opposite trend (Table 1). However, the JA-max value derived from fitting the An–Ci curve of T. aestivum is markedly higher than the observed Jf-max value, indicating a significant divergence between the estimated value and the empirical data (Table 1). Given the starkly contrasting outcomes for JA-max when fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves with the FvCB model, it remains uncertain which response curve is more justified. This phenomenon may be related to the inaccurate simulation of the carboxylation reaction of the key enzyme Rubisco in photosynthesis by the model. Under the condition of 21% O2 concentration, the oxygenation of Rubisco may be overestimated, resulting in the model’s prediction of JA-max being either too high or too low.
On the other hand, as explained by von Caemmerer (2000) and Long and Bernacchi (2003), under 21% O2 conditions, Jf supports not only JA but also JO, JNit, and JMAP. This relationship can be expressed as Jf = JA + JO + JNit + JMAP. Consequently, JA-max must be less than Jf-max. Under 2% O2 conditions, JO can be neglected. In this case, the relationship can be expressed as Jf = JA + JNit + JMAP, and JA-max must still be less than Jf-max. Based on this criterion, we observed that under 21% O2 concentration the JA-max estimated by the FvCB model when fitting the An–Ci curve of T. aestivum exceeds the Jf-max (Table 1). Taking into account that JNit and JMAP are non-zero, we further found that the JA-max estimated by the FvCB model when fitting both the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum also surpasses the Jf-max under 2% O2 concentration (Table 2).
Furthermore, the findings in Table 1 reveal a pattern in the Vcmax values derived from the FvCB model when it is applied to the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum. Specifically, the Vcmax values obtained from fitting the An–Ca curves are consistently lower than those derived from fitting the An–Ci curves for both plant species. A similar trend is observed for the estimation of Rday; that is, the Rday values derived from the An–Ca curve fits are also consistently lower than those from the An–Ci curve fits using the FvCB model for L. perenne and T. aestivum. Despite these observations, it remains challenging to discern which set of values—those from the An–Ca or An–Ci curve fits—provides a more accurate representation of the true Vcmax and Rday values for these two plant species. This uncertainty highlights the complexity of accurately modeling photosynthetic parameters. Thus, there is a need for further investigation to refine our understanding of how different models perform across various plant species and under different physiological conditions.
It is noteworthy that the choice between An–Ca and An–Ci curve fitting may be influenced by factors such as the atmospheric CO2 concentration, the specific photosynthetic pathway of the plant, and the presence of other environmental stressors. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis considering these factors and more experimental data may be necessary to determine the most appropriate model for accurately predicting Vcmax and Rday values. This could involve comparing the FvCB model’s predictive power with other models, examining its sensitivity to initial conditions, and assessing its robustness under varying environments.
At 2% oxygen concentration, the FvCB model’s fitting results differ significantly from those at the typical atmospheric concentration of 21% O2 (Figures 1, 2; Tables 1, 2). This discrepancy may indicate the plant’s adaptive responses in its photosynthetic machinery under hypoxic conditions. Notably, the model’s estimations of JA-max for both L. perenne and T. aestivum closely approximate the actual observations, regardless of whether the An–Ca curve or the An–Ci curve is fitted (Table 2). It is important to highlight that the JA-max value predicted by the FvCB model exceeds the observed Jf-max value for T. aestivum when either the An–Ca curve or the An–Ci curve is modeled. This outcome is perplexing given the prevailing photosynthetic theory as articulated by von Caemmerer (2000), which posits that JA-max should be less than Jf-max. Consequently, the findings are currently challenging to interpret.
Under hypoxic conditions of 2% O2, the carboxylation efficiency of Rubisco is likely impeded, and photorespiration gains prominence, as indicated by Busch and Sage (2017). The FvCB model reveals that Rubisco limitation, RuBP regeneration limitation, and TPU limitation, which are all pivotal to the photosynthetic process in C3 plants. Under low O2 environments, these limitations may become more pronounced and dampen the overall photosynthetic efficiency, as supported by Zhu et al. (2010). Furthermore, at 21% O2 (normoxic condition), the FvCB model-calculated Vcmax values for the An–Ca curve are systematically lower than those for the An–Ci curve when analyzing the two plant species (Table 1). This suggests that photosynthetic parameters are sensitive to oxygen levels, and the FvCB model may require refinements to accurately estimate them under different environmental conditions.
4.2 Model I and Model II in fitting CO2-response curve of photosynthesis and estimating photosynthetic parameters
In this study, both Model I and Model II exhibited a high R2 when fitting the An–Ca and An–Ci curves of L. perenne and T. aestivum, indicating that the two models have high accuracy in simulating the photosynthesis curves under varying oxygen concentrations (Figures 3, 4). This result may be attributed to the advantages of the Model I and Model II in parameterization and model structure, enabling them to better capture the photosynthetic response of plants under different environmental conditions. Moreover, both models effectively capture the An–Ca and An–Ci curves, demonstrating the reduction in carbon assimilation rates under elevated CO2 concentrations. They also enable the direct calculation of CTPU (Tables 3, 4). The results of our study show that the models’ estimation of the Amax and Γ values for L. perenne and T. aestivum under the two O2 concentrations does not show significant differences from the corresponding observed values (Tables 3, 4). Indeed, a notable discrepancy is observed between the Rpa0 values derived from fitting the An–Ca curves and those derived from fitting the An–Ci curves, as shown in Tables 3, 4. Despite this, the scientific community has not yet reached a definitive conclusion on which of these Rpa0 values—obtained from the An–Ca curve or the An–Ci curve—more accurately represents the true Rpa0 value. However, considering the nuances of measurement technology, it is plausible to suggest that the Rpa0 value obtained from the An–Ca curve may be closer to the actual Rpa0 value. This assumption is based on the belief that the Rpa0 values, particularly those fitted for L. perenne and T. aestivum using Model II, reflect the true Rpa0 values for these plant species. This belief is further supported by the An–Ca curve’s more direct measurement of CO2 assimilation and its lesser influenced by internal CO2 concentration changes compared to the An–Ci curve. Therefore, the Rpa0 derived from the An–Ca curve is often considered to be more representative of the plant’s true photorespiratory rate at CO2 concentrations approaching zero.
Furthermore, the rationale behind this preference is rooted in the technology used in plant photosynthesis measurement instruments. These instruments utilize non-diffusive infrared CO2 analysis technology to measure CO2 concentrations. This method takes advantage of the significant absorption of CO2 at a specific wavelength of infrared light, a characteristic not shared by O2. Consequently, it is advisable to use the An–Ca curves derived from such measurements for quantitative studies of plant Rpa0. Given this, when conducting research on Rpa0 in plants, it is more logical to fit the An–Ca curves using Model II rather than the An–Ci curves. Model II’s curve- fitting approach better matches the capabilities of non-diffusive infrared CO2 analysis technology, making it a more suitable choice for accurate and reliable Rpa0 assessments. In this study, another notable finding is that once Model I can determine the value of Rday, it can also compute the value of Rp0 (Tables 3, 4). However, the precision of determining Rday presents a challenge, which in turn affects the accuracy of the derived Rp0. Nevertheless, our research suggests that when Rday can be accurately ascertained, our methodology offers a viable approach for estimating Rp0.
4.3 Comparative analysis of the FvCB model and the new models
The FvCB model and Model I/II represent fundamentally divergent paradigms in photosynthetic modeling. As a biochemical mechanistic framework, the FvCB model simulates enzymatic processes governing carbon assimilation (Farquhar et al., 1980), whereas Model I/II adopts an empirical approach emphasizing practical parameterization. This dichotomy reflects their core objectives: the FvCB model prioritizes biochemical fidelity, while Model I/II emphasizes operational simplicity and environmental adaptability.
Our comparative analysis demonstrates that the superior predictive performance of Models I/II in estimating Rpa0 and critical photosynthetic parameters (Amax, Γ, and CTPU) across oxygen gradients stems from their distinct structural architectures. The FvCB model’s dependence on rigid biochemical constraints–including fixed Rday/Vcmax ratios (von Caemmerer, 2013; De Kauwe et al., 2016), stoichiometric electron requirements (4 e- per CO2; Long and Bernacchi, 2003), and invariant photorespiratory CO2 release (0.5 mol/RuBP oxygenation; Farquhar et al., 1980)–introduces systematic biases. In contrast, Model I dynamically parameterizes Rday (Equation 5), while Model II integrates photorespiration into an apparent rate (Rpa; Equation 14), effectively decoupling photorespiratory flux from predefined biochemical ratios. This innovation enables direct empirical estimation of Rpa0 from gas exchange data, especially under hypoxic conditions (e.g., 2% O2) where photorespiration suppression exposes the FvCB model’s limitations. Specifically, the fixed Rday/Vcmax assumption the FvCB model (von Caemmerer, 2013) leads to 46%-47% underestimation of respiratory activity compared to experimental data (Tables 1, 2), whereas the new models’ dynamic parameterization achieves precise alignment with observations.
Methodologically, the FvCB model’s indirect estimation of JA-max via An–Ci curve fitting propagates errors from uncertain electron transport partitioning (Sharkey et al., 2007). Models I/II circumvent this limitation through direct quantification of Amax, Γ, CTPU, and Rpa0, eliminating error accumulation inherent to multi-step biochemical approximations. This distinction explains their robust performance across 2% and 21% O2 environments (Figures 3, 4), demonstrating adaptability to oxygen fluctuations in both agricultural and natural ecosystems.
The FvCB model’s systematic underestimation of Vcmax and Rday during An–Ca curve fitting further highlights its sensitivity to stomatal conductance dynamics—a confounding factor absent in An–Ci analyses. Models I/II address this through unified Ca-Ci treatment within a single analytical framework (Equations 5, 12), minimizing stomatal-induced artifacts. This proves critical under 2% O2, where stomatal closure amplifies discrepancies in FvCB-derived parameters. Additionally, the non-asymptotic formulation of Models I/II (Equations 5, 12) better captures CTPU inflection points than the FvCB model’s segmented approach (Figures 3, 4), which struggles to resolve RuBP- versus TPU-limited transitions under dynamic conditions.
However, these advancements come with trade-offs: Models I/II cannot estimate Vcmax or JA-max—parameters critical for Rubisco kinetic analyses (Farquhar et al., 1980; Bernacchi et al., 2013). This reflects the inherent tension between empirical accuracy and biochemical interpretability, necessitating context-specific model selection. Future hybrid frameworks could integrate Model I/II’s empirical strengths with the FvCB model’s biochemical resolution, particularly to disentangle photorespiratory and respiratory fluxes—a capability demonstrated in low-O2 environments where traditional partitioning assumptions fail (Xiong et al., 2022).
Enhanced predictive accuracy comes with increased parameterization complexity. Determining nuanced parameters like Rday requires high-precision gas exchange measurements and measured method under controlled conditions (Medlyn et al., 2011; Yin and Amthor, 2024), posing challenges for resource-limited studies. Furthermore, while coefficients αc/αc1, βc/βc1 and γc/γc1 in Models I/II are environment-dependent (Equations 5, 12), their biochemical basis—particularly regarding Rubisco carboxylation- oxygenation kinetics—remains unresolved. Clarifying these relationships through multi-omics approaches (e.g., concurrent chlorophyll fluorescence and metabolomic profiling) could bridge empirical models with photosynthetic biochemistry (Smith et al., 2023), transforming them into mechanistically robust tools for climate resilience research.
Furthermore, the limited sample size in our study may compromise the generalizability of our findings. Our experiments focused exclusively on two C3 plant species, L. perenne and T. aestivum. As such, additional validation is essential to establish the broader applicability of the new models to other plant species, particularly those with distinct photosynthetic pathways, such as C4 and CAM plants. Moreover, the models were evaluated under specific environmental conditions (2% and 21% O2 concentrations), and their performance under other stressors—such as high temperature, drought, or elevated CO2 levels—has yet to be fully explored. Additionally, to enhance the accuracy of Rpa0 estimation, we recommend incorporating several additional measurement points at low CO2 concentrations (below 200 μmol·mol−¹), specifically at 30, 80, and 150 μmol·mol−¹. This refinement, however, necessitates increased time and effort to obtain comprehensive An–Ca or An–Ci curves.
5 Conclusions
In conclusion, this study underscores the essential requirement for accurate model parameters and their relevance when selecting photosynthesis models. It also highlights the significance of ongoing efforts to enhance these models to improve predictions of plant photosynthesis under diverse environmental conditions. Further exploration into the molecular mechanisms underlying Rubisco-catalyzed reactions and photorespiration is crucial, as it will not only refine model accuracy but also bolster our predictive capabilities in the face of environmental changes. Such advancements are pivotal to optimizing agricultural strategies and ecological preservation.
Moreover, both Model I and Model II have shown remarkable performance, particularly under varying oxygen levels, positioning them as valuable tools for analyzing C3 plant photosynthesis. Their consistent and reliable estimation of key parameters such as Amax, Γ, and Rpa0, coupled with their proficiency in fitting both An–Ca and An–Ci curves, offers a more precise depiction of plant photosynthetic mechanisms. As research progresses, future research should focus on validating these models across a broader range of temperatures, light intensities, and CO2 levels to enhance their robustness. Additionally, adapting these models for C4 and CAM plants by incorporating their unique biochemical pathways, such as PEPCase activity in C4 plants and temporal CO2 uptake in CAM plants, would significantly expand their applicability. Extensive validation across multiple species and conditions is essential to refine the models and ensure their accuracy. Comparative studies across different photosynthetic pathways will highlight areas for improvement and contribute to the development of generalized frameworks applicable across diverse plant types. Integrating these models into ecosystem models could also provide valuable insights into carbon cycling and ecosystem dynamics. Overall, although the new models are promising, more adaptation and validation are required to fully tap their potential in predicting photosynthetic responses among different plant species under various environmental conditions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
ZY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – original draft. XY: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZY: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft. TA: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. SD: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. HK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. FW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32260063 and 32060428), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20202BAB205008 and 20224BAB205020).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1575217/full#supplementary-material
References
Ainsworth, E. A., Long, S. P. (2005). What have we learned from 15 years of free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE)? A meta-analytic review of the responses of photosynthesis, canopy properties and plant production to rising CO2. New Phytol. 165, 351–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01224.x
Ainsworth, E. A., Long, S. P. (2021). 30 years of free-air carbon dioxide enrichment (face): What have we learned about future crop productivity and its potential for adaptation? Global Change Biol. 27, 27–49. doi: 10.1111/gcb.15375
Anderegg, W. R. L., Wolf, A., Arango-Velez, A., Choat, B., Chmura, D., Jansen, S., et al. (2018). Woody plants optimize stomatal behavior relative to hydraulic risk. Ecol. Lett. 21, 968–977. doi: 10.1111/ele.12962
Atkin, O. K., Tjoelker, M. G. (2003). Thermal acclimation and the dynamic response of plant respiration to temperature. Trends Plant Sci. 8, 343–351. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(03)00136-5
Bellasio, C., Beerling, D. J., Griffiths, H. (2015). An Excel tool for deriving key photosynthetic parameters from combined gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence: Theory and practice. Plant Cell Environ. 39, 1180–1197. doi: 10.1111/pce.12560
Bernacchi, C. J., Bagley, J. E., Serbin, S. P., Ruiz-Vera, U. M., Rosenthal, D. M., VanLoocke, A. (2013). Modelling C3 photosynthesis from the chloroplast to the ecosystem. Plant Cell Environ. 36, 1641–1657. doi: 10.1111/pce.12118
Burnett, A. C., Davidson, K. J., Serbin, S. P., Rogers, A. (2019). The “one-point method” for estimating maximum carboxylation capacity of photosynthesis: a cautionary tale. Plant Cell Environ. 42, 2472–2481. doi: 10.1111/pce.13574
Busch, F. A., Sage, R. F. (2017). The sensitivity of photosynthesis to O2 and CO2 concentration identifies strong Rubisco control above the thermal optimum. New Phytol. 213, 1036–1051. doi: 10.1111/nph.14258
Cheah, S. S., The, C. (2020). Parameterization of the Farquhar-von Caemmerer-Berry C3 photosynthesis model for oil palm. Photosynthetica 58, 769–779. doi: 10.32615/ps.2020.020
De Kauwe, M. G., Lin, Y. S., Wright, I. J., Medlyn, B. E., Crous, K. Y., Ellsworth, D. S., et al. (2016). A test of the ‘one-point method’ for estimating maximum carboxylation capacity from field-measured, light-saturated photosynthesis. New Phytol. 212, 792. doi: 10.1111/nph.13815
Dubois, J. J. B., Fiscus, E. L., Booker, F. L., Flowers, M. D., Reid, C. D. (2007). Optimizing the statistical estimation of the parameters of the Farquhar-von Caemmerer-Berry model of photosynthesis. New Phytol. 176, 402–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02182.x
Ellsworth, D. S., Crous, K. Y., Lambers, H., Cooke, J. (2015). Phosphorus recycling in photorespiration maintains high photosynthetic capacity in woody species. Plant Cell Environ. 38, 1142–1156. doi: 10.1111/pce.12468
Eric, D. M., Duarte, A. G., Way, D. A. (2019). Plant carbon metabolism and climate change: elevated CO2 and temperature impacts on photosynthesis, photorespiration and respiration. New Phytol. 221, 32–49. doi: 10.1111/nph.15283
Fan, Y. Z., Zhong, Z. M., Zhang, X. Z. (2011). Determination of photosynthetic parameters Vcmax and Jmax for a C3 plant (spring hulless barley) at two altitudes on the Tibetan Plateau. Agr For. Meteorol. 151, 1481–1487. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2011.06.004
Farazdaghi, H., Edwards, G. E. (1988). A mechanistic model for photosynthesis based on the multisubstrate ordered reaction of ribulose 1,5 bisphosphate carboxylase. Plant Cell Environ. 11, 789–798. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.1988.tb01904.x
Farquhar, G. D., Busch, F. A. (2017). Changes in the chloroplastic CO2 concentration explain much of the observed Kok effect: a model. New Phytol. 214, 570–584. doi: 10.1111/nph.14512
Farquhar, G. D., von Caemmerer, S., Berry, J. A. (1980). A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species. Planta 149, 78–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00386231
Gu, L. H., Pallardy, S. G., Tu, K., Law, B. E., Wullschleger, S. D. (2010). Reliable estimation of biochemical parameters from C3 leaf photosynthesis–intercellular carbon dioxide response curves. Plant Cell Environ. 33, 1852–1874. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02192.x
Han, T., Zhu, G., Ma, J., Wang, S., Zhang, K., Liu, X., et al. (2020). Sensitivity analysis and estimation using a hierarchical Bayesian method for the parameters of the FvCB biochemical photosynthetic model. Photosyn Res. 143, 45–66. doi: 10.1007/s11120-019-00684-z
Harley, P. C., Sharkey, T. D. (1991). An improved model of C3 photosynthesis at high CO2: reversed O2 sensitivity explained by lack of glycerate reentry into the chloroplast. Photosyn Res. 27, 169–178. doi: 10.1007/BF00035838
Höglind, M., Hanslin, H. M., Mortensen, L. M. (2011). Photosynthesis of Lolium perenne L. at low temperatures under low irradiances. Environ. Exp. Bot. 70, 297–304. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2010.10.00
Kelly, J. W. G., Duursma, R. A., Atwell, B. J., Tissue, D. T., Medlyn, B. E. (2016). Drought × CO2 interactions in trees: a test of the low-intercellular CO2 concentration (Ci) mechanism. New Phytol. 209, 1600–1612. doi: 10.1111/nph.13715
Kolari, P., Chan, T., Porcar-Castell, A., Bäck, J., Nikinmaa, E., Juurola, E. (2014). Field and controlled environment measurements show strong seasonal acclimation in photosynthesis and respiration potential in boreal scots pine. Front. Plant Sci. 5. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00717
Lenz, K. E., Host, G. E., Roskoski, K., Noormets, A., Sôber, A., Karnosky, D. F. (2010). Analysis of a Farquhar-von Caemmerer-Berry leaf–level photosynthetic rate model for Populus tremuloides in the context of modeling and measurement limitations. Environ. pollut. 158, 1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2009.08.004
Leuning, R. (1995). A critical appraisal of a coupled stomatal–photosynthesis model for C3 plants. Plant Cell Environ. 18, 339–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.1995.tb00370.x
Long, S. P., Bernacchi, C. J. (2003). Gas exchange measurements, what can they tell us about the underlying limitations to photosynthesis? Procedures and sources of error. J. Exp. Bot. 54, 2393–2401. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erg262
Medlyn, B. E., Duursma, R. A., Eamus, D., Ellsworth, D. S., Prentice, I. C., Barton, C. V. M., et al. (2011). Reconciling the optimal and empirical approaches to modelling stomatal conductance. Global Change Biol. 17, 2134–2144. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02375.x
Miao, Z., Xu, M., Lathrop, R. G., Wang, Y. (2009). Comparison of the A–Cc curve fitting methods in determining maximum ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase carboxylation rate, potential light saturated electron transport rate and leaf dark respiration. Plant Cell Environ. 32, 109–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2008.01900.x
Miner, G. L., Bauerle, W. L. (2017). Seasonal variability of the parameters of the Ball–Berry model of stomatal conductance in maize (Zea mays L.) and sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) under well-watered and water-stressed conditions. Plant Cell Environ. 40, 1874–1886. doi: 10.1111/pce.12990
Miyazawa, S. I., Tobita, H., Ujino-Ihara, T., Suzuki, Y. (2020). Oxygen response of leaf CO2 compensation points used to determine Rubisco specificity factors of gymnosperm species. J. Plant Res. 133, 205–215. doi: 10.1007/s10265-020-01169-0
Morfopoulos, C., Sperlich, D., Peñuelas, J., Filella, I., Llusià, J., Medlyn, B. E., et al. (2014). A model of plant isoprene emission based on available reducing power captures responses to atmospheric CO2. New Phytol. 203, 125–139. doi: 10.1111/nph.12770
Norby, R. J., Gu, L. H., Haworth, I. C., Jensen, A. M., Turner, B. L., Walker, A. P., et al. (2017). Informing models through empirical relationships between foliar phosphorus, nitrogen and photosynthesis across diverse woody species in tropical forests of Panama. New Phytol. 215, 1425–1437. doi: 10.1111/nph.14319
Pleban, J. R., Guadagno, C. R., Mackay, D. S., Weinig, C., Ewers, B. E. (2020). Rapid chlorophyll a fluorescence light response curves mechanistically inform photosynthesis modeling. Plant Physiol. 183, 602–619. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.00375
Pshenichnikova, T. A., Doroshkov, A. V., Osipova, S. V., Permyakov, A. V., Afonnikov, D. A. (2019). Quantitative characteristics of pubescence in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) are associated with photosynthetic parameters under conditions of normal and limited water supply. Planta 249, 839–847. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-3049-9
Qiu, R., Katul, G. G. (2020). Maximizing leaf carbon gain in varying saline conditions: an optimization model with dynamic mesophyll conductance. Plant J. 101, 543–554. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14553
Roberta, C., Elizabete, C. S., Cho, Y. B., Maria, E., Jeremy, H., Tracy, L., et al. (2024). Perspectives on improving photosynthesis to increase crop yield. Plant Cell. 36, 3944–3973. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae132
Rogers, A., Serbin, S. P., Ely, K. S., Sloan, V. L., Wullschleger, S. D. (2017). Terrestrial biosphere models underestimate photosynthetic capacity and CO2 assimilation in the Arctic. New Phytol. 216, 1090–1103. doi: 10.1111/nph.14740
Sergio, T., Alberto, P., Stefano, P., Daniela, F. (2015). Influence of light and shoot development stage on leaf photosynthesis and carbohydrate status during the adventitious root formation in cuttings of Corylus avellana L. Front. Plant Sci. 6. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00973
Sharkey, T. D. (2016). What gas exchange data can tell us about photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 39, 1161–1163. doi: 10.1111/pce.12641
Sharkey, T. D., Bernacchi, C. J., Farquhar, G. D., Singsaas, E. L. (2007). Fitting photosynthetic carbon dioxide response curves for C3 leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 30, 1035–1040. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01710.x
Silva-Pérez, V., Furbank, R. T., Condon, A. G., Evans, J. R. (2017). Biochemical model of C3 photosynthesis applied to wheat at different temperatures. Plant Cell Environ. 40, 1552–1564. doi: 10.1111/pce.12953
Smith, E. N., Aalst, M. V., Tosens, T., Niinemets, L., Stich, B., Morosinotto, T., et al. (2023). Improving photosynthetic efficiency toward food security: strategies, advances, and perspectives. Mol. Plant 16, 1547–1563. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2023.08.017
Taylor, G., Walter, J., Kromdijk, J. (2024). Illuminating stomatal responses to red light: establishing the role of Ci-dependent versus -independent mechanisms in control of stomatal behavior. J. Exp. Bot. 75, 6810–6822. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae093
Tcherkez, G., Gauthier, P., Buckley, T. N., Busch, F. A., Barbour, M. M., Bruhn, D., et al. (2017). Leaf day respiration: low CO2 flux but high significance for metabolism and carbon balance. New Phytol. 216, 986–1001. doi: 10.1111/nph.14816
Vijayakumar, S., Wang, Y., Lehretz, E. L. S. (2024). Kinetic modeling identifies targets for engineering improved photosynthetic efficiency in potato (Solanum tuberosum cv. Solara). Plant J. 117, 561–572. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16512
von Caemmerer, S. (2000). Biochemical models of leaf photosynthesis (Victoria, Australia: CSIRO Publishing). doi: 10.1071/9780643103405
von Caemmerer, S. (2013). Steady-state models of photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 36, 1617–1630. doi: 10.1111/pce.12098
von Caemmerer, S., Farquhar, G. D. (1981). Some relationships between the biochemistry of photosynthesis and the gas exchange of leaves. Planta 153, 376–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00384257
Walker, A. P., Quaife, T., Bodegom, P. V., Kauwe, M., Keenan, T. F., Joiner, J., et al. (2017). The impact of alternative trait–scaling hypotheses for the maximum photosynthetic carboxylation rate (Vcmax) on global gross primary production. New Phytol. 215, 1370–1386. doi: 10.1111/nph.14623
Watling, J. R., Press, M. C., Quick, W. P. (2000). Elevated CO2 induces biochemical and ultrastructural changes in leaves of the C4 cereal sorghum. Plant Physiol. 123, 1143–1152. doi: 10.1104/pp.123.3.1143
Xiao, Y., Sloan, J., Hepworth, C., Osborne, C. P., Fleming, A. J., Chen, X., et al. (2021). Estimating uncertainty: A Bayesian approach to modelling photosynthesis in C3 leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 44, 1436–1450. doi: 10.1111/pce.13995
Xiong, Z., Xiong, D., Cai, D., Wang, W., Cui, K., Peng, S. B., et al. (2022). Effect of stomatal morphology on leaf photosynthetic induction under fluctuating light across diploid and tetraploid rice. Environ. Exp. Bot. 194, 104757. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2021.104757
Ye, Z., He, J., An, T., Duan, S., Kang, H., Wang, F. (2024). Influences of residual stomatal conductance on the intrinsic water use efficiency of two C3 and two C4 species. Agric. Water Manage. 306, 109136. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2024.109136
Ye, Z., Suggett, D., Robakowski, P., Kang, J. (2013). A mechanistic model for the photosynthesis–light response based on the photosynthetic electron transport of photosystem II in C3 and C4 species. New Phytol. 199, 110–120. doi: 10.1111/nph.12242
Yin, X., Amthor, J. S. (2024). Estimating leaf day respiration from conventional gas exchange measurements. New Phytol. 241, 52–58. doi: 10.1111/nph.19330
Yin, X., Busch, F. A., Struik, P. C., Sharkey, T. D. (2021). Evolution of a biochemical model of steady-state photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 44, 2811–2837. doi: 10.1111/pce.14070
Yin, X., Struik, P. C., Romero, P., Harbinson, J., Evers, J. B., van der Putten, P. E. L., et al. (2009). Using combined measurements of gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence to estimate parameters of a biochemical C3 photosynthesis model: a critical appraisal and a new integrated approach applied to leaves in a wheat (Triticum aestivum) canopy. Plant Cell Environ. 32, 448–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2009.01934.x
Yin, X., van Oijen, M., Schapendonk, A. H. C. M. (2004). Extension of a biochemical model for the generalized stoichiometry of electron transport limited C3 photosynthesis. Plant Cell Environ. 27, 1211–1222. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2004.01224.x
Yiotis, C., McElwain, J. C., Osborne, B. A. (2021). Enhancing the productivity of ryegrass at elevated CO2 is dependent on tillering and leaf area development rather than leaf-level photosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 72, 1962–1977. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eraa584
Zhang, N. Y., Li, G., Yu, S. X., An, D. S., Sun, Q., Luo, W. H., et al. (2017). Can the responses of photosynthesis and stomatal conductance to water and nitrogen stress combinations be modeled using a single set of parameters? Front. Plant Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00328
Keywords: photosynthesis models, C 3 plants, FvCB model, parameter estimation, CO 2 -response to photosynthesis, apparent photorespiratory rate
Citation: Ye Z-P, Yang X-L, Ye Z-W-Y, An T, Duan S-H, Kang H-J and Wang F-B (2025) Evaluating photosynthetic models and their potency in assessing plant responses to changing oxygen concentrations: a comparative analysis of An–Ca and An–Ci curves in Lolium perenne and Triticum aestivum. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1575217. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1575217
Received: 12 February 2025; Accepted: 04 April 2025;
Published: 29 April 2025.
Edited by:
Aoxue Wang, Northeast Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zhouping Sun, Shenyang Agricultural University, ChinaDongliang Wang, Anhui Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Ye, Yang, Ye, An, Duan, Kang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hua-Jing Kang, a2FuZ2h1YWppbmdAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Fu-Biao Wang, d2ZiMTk4NzI4NTZAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zi-Piao Ye
Zi-Piao Ye Xiao-Long Yang
Xiao-Long Yang Zi-Wu-Yin Ye5
Zi-Wu-Yin Ye5 Ting An
Ting An Shi-Hua Duan
Shi-Hua Duan Hua-Jing Kang
Hua-Jing Kang Fu-Biao Wang
Fu-Biao Wang