- 1College of Forestry, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
- 2Key Laboratory of State Forestry and Grassland Administration on Biodiversity Conservation in Southwest China, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
- 3Key Laboratory for Forest Resources Conservation and Use in the Southwest Mountains of China, Ministry of Education, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming, China
Introduction: Anthracnose poses a significant threat to the sustainable development of the Camellia oleifera industry. In this study, we aimed to assess the efficacy of melatonin-induced Bacillus tequilensis DZY6715 (MT-DZY 6715) in controlling C. oleifera anthracnose caused by Colletotrichum siamense.
Methods: The antifungal activity of MT-DZY6715 against C. siamense was systematically evaluated in vitro dual-culture assays and in planta infection trials. Furthermore, we analyzed the impact of MT-DZY 6715 on the anatomical features of C. oleifera leaves using histological sectioning. Additionally, transcriptome and enzymatic assays were employed to assess the expression of secondary metabolism-related genes and the activity of cell wall-degrading enzymes.
Results: The application of MT-DZY 6715 effectively controls the growth of C. siamense, markedly reducing the incidence of C. oleifera anthracnose and delaying the spread of pathogens on the leaves. Furthermore, MT-DZY 6715 treatment enhanced leaf thickness, palisade mesophyll, as well as elevated the ratio of palisade mesophyll to spongy mesophyll (PS) and tissue compactness (CTR), while simultaneously decreasing tissue looseness (SR). Meanwhile, the leaf stomata undergo a reduction in size and a decrease in their openness. In addition, MT-DZY 6715 promoted the expression of secondary metabolism-related genes, such as PAL, CAL, Laccase, HCT, and CHI, and inhibited the activity of enzymes related to cell wall degradation (pectinase and cellulase), thereby coordinating and enhancing the accumulation of secondary metabolites and strengthening the mechanical properties of the cell wall.
Discussion: The results of this study demonstrate that MT-DZY 6715 enhances the resistance of C. oleifera to anthracnose by modulating leaf morphology, regulating stomatal function, and promoting the accumulation of secondary metabolites. These findings provides a scientific foundation for deploying MT-DZY6715 as an eco-friendly alternative to chemical fungicides in anthracnose management.
1 Introduction
Camellia oleifera, widely known as the tea oil tree, is an evergreen shrub or small tree of the genus Camellia in the Theaceae family. It stands out as one of the four primary woody oil seed plants, earning the esteemed title of “Oriental Olive Oil” owing to its remarkable economic and culinary value (Yang et al., 2024). Additionally, C. oleifera is acclaimed for its medicinal benefits and holds vital ecological significance. However, as the cultivation area of C. oleifera expands, anthracnose has gradually emerged as a major obstacle to the industry’s development. Anthracnose, caused by Colletotrichum species (Hao et al., 2023; Jeyaraj et al., 2023), is characterized by its rapid spread, wide incidence, and high virulence, posing a grave threat to the health of C. oleifera (Chen et al., 2023). In the field, leaves infected by the anthracnose pathogen initially exhibit dark brown or yellowish-brown semicircular spots. As the disease advances, these spots gradually expand and turn into grayish-white patches adorned with black fruiting bodies (Jiang and Li, 2018). The damage of anthracnose is not limited to leaves, it also impacts fruits, branches, and other parts of the plant, ultimately leading to defoliation, fruit drop, and even the death of the entire plant (Muntala et al., 2020). These severe consequences not only significantly impact the yield and quality of C. oleifera but also result in huge economic losses.
In the face of this challenge, although traditional chemical control methods can provide some suppression of the disease, they also bring drawbacks such as pathogen resistance, chemical residues, and ecological impacts that cannot be overlooked ignored (Martinez et al., 2020; Xia et al., 2023). Thus, the pursuit of green, safe, and eco-friendly biological control measures has become a primary focus (Kumar Ahirwar et al., 2019). Microbial preparations are known for their low toxicity, minimal residue, and environmental friendliness (Ashraf et al., 2014), making them an ideal alternative to chemical pesticides for controlling diseases in the C. oleifera industry. Their application may promote the green and sustainable development of the C. oleifera industry, helping to achieve a harmonious balance of economic, ecological, and social benefits. Bacillus species is often regarded as ideal candidates for biological control due to their ability to enhance plant resistance by producing antagonistic compounds that inhibit pathogen growth and inducing systemic resistance, as reported in several studies (Fira et al., 2018; Miljaković et al., 2020; Ongena et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2018). However, the efficacy of Bacillus is inferior to that of chemical fungicides, so it is necessary to develop methods to improve its biological efficiency.
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, MT) is a versatile small molecule substance widely distributed in both animals and plants. It is a natural compound, serving as a potent antioxidant and free radical scavenger, playing a crucial role in enhancing plant disease resistance (Hernández-Ruiz et al., 2023). Bisquert et al. (2018) suggested under oxidative stress conditions, Saccharomyces cerevisiae treated with MT exhibited significantly modulated gene expression related to stress protection, leading to an increased cell viability of up to 35% compared to control group. Peter et al. (2024) discovered that MT and Bacillus sp. IPR-4 co-inoculation significantly enhanced soybean resistance to drought stress by promoting growth, optimizing nutrient absorption, regulating redox homeostasis, and upregulating drought-responsive genes. Furthermore, studies have confirmed that melatonin can enhance resistance in litchi fruit cell walls by modulating membrane lipid and energy metabolisms, thereby retarding browning, senescence, and lesion expansion caused by pathogens (Wang et al., 2020a; Zhang et al., 2021). Plant-produced secondary metabolites, including phenolics, flavonoids, and lignin, work together with the cell wall to construct a defensive system, while melatonin further promotes the synthesis of these disease-resistant metabolites, significantly boosting the plant’s disease resistance (Anjali et al., 2023). Additionally, Liu et al. (2019) reported that melatonin enhances tomato fruit resistance to Botrytis cinerea by modulating H2O2 levels and the jasmonic acid (JA) signaling pathway. MT enhances plants’ disease resistance by activating defense signaling pathways, such as ROS scavenging, MAPK activation, and crosstalk with SA/JA (Tiwari et al., 2022). Song et al. (2022) discovered that Melatonin improves the postharvest quality of eggplant fruits by inhibiting the activity and gene expression of cell wall-degrading enzymes (PME, PG, and Cel).
Currently, there is limited information available on the application of melatonin induced Bacillus sp. in enhancing disease resistance in C. oleifera, especially regarding the mechanisms underlying the induction of physical defense at both genetic and physiological levels. Thus, in this study, melatonin was employed to induce B. tequilensis DZY 6715 (MT-DZY 6715), with the aims of exploring: 1) the inhibitory effects of MT-DZY 6715 on Colletotrichum siamense in vitro; 2) the influence of MT-DZY 6715 on the structural characteristics of C. oleifera leaves; 3) the relevant disease-resistance genes through transcriptome analysis following MT-DZY 6715 treatment; and 4) the enzymatic activities associated with cell wall and phenylpropanoid metabolism in C. oleifera plants induced by MT-DZY 6715 treatment. The findings of this study offer novel insights into the molecular mechanisms that enhance disease resistance in C. oleifera through the induction of MT-DZY 6715.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant, pathogen, bacterial strain and melatonin
Two-year-old C. oleifera seedlings (‘Changlin No. 53’) sourced from Yingjiang Linli Oil Tea Co., Ltd. in Yunnan, China, were housed in a greenhouse at Southwest Forestry University. The greenhouse conditions were maintained at a controlled temperature of 25°C and humidity of 80%, with regular irrigation using sterile water.
The pathogenic fungus, C. siamense, was isolated from C. oleifera leaves affected by anthracnose. Identification was confirmed through sequencing of the Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) region using universal primers ITS1 and ITS4. The pathogenic fungus was maintained on the slope of a Potato Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium at a temperature of 4°C for preservation.
The B. tequilensis DZY 6715 strain was isolated from C. oleifera and cultured in Luria-Bertani (LB) medium at the College of Forestry, Southwest Forestry University, located in Kunming, Yunnan Province, China.
MT (CAS: 73-31-4) was obtained from Merck (Sigma-Aldrich Shanghai Trading Co., Ltd.) and stored under 4°C conditions.
2.2 Preparation of MT-DZY 6715 suspension
Based on our previous research (Liu et al., 2023), an MT concentration of 50 μmol L-1 was selected. Regarding the determination of culture time, B. tequilensis DZY 6715 reaches its peak viable cell count and biofilm-forming capability after being cultured for 72 h when induced by MT at a concentration of 50 μmol L-1. Consequently, a culture period of 72 h was selected for further investigation.
2.3 Effect of MT-DZY 6715 against C. siamense in vitro
The antifungal test was conducted utilizing the plate confrontation method (Zhou et al., 2022). Five-day-old viable cultures of C. siamense, each with a diameter of 6 mm, served as the indicator pathogen and were placed at the center of 90 mm petri dishes filled with PDA medium. Treatment groups were established by injecting the following solutions 3 cm away from the center of each dish: (1) 50 μmol L-1 MT, (2) 72-h DZY 6715 suspension at a concentration of 1×107 CFU mL-1, and (3) DZY 6715 suspension that had been induced with 50 μmol L-1 MT for 72 h (MT-DZY 6715), at a concentration of 1×107 CFU mL-1. The control group consisted of petri dishes with the pathogen inoculated alone. All petri dishes were then placed in an incubator at 28°C. Adopted from Al Farraj and Elshikh (2023), the inhibition rate (R) was calculated was calculated as follows: R = (R1 - R2)/R1, where R1 and R2 represent the diameters of the pathogen colonies in the control and treatment groups, respectively. Each treatment was replicated three times, and the experiment was conducted twice.
2.4 Effect of MT-DZY 6715 against C. siamense on C. oleifera
Healthy, uniform, and mechanical damage-free C. oleifera seedlings were selected. The leaves were sanitized with 75% ethanol for 30 s, rinsed three times with sterile water. Then the selected seedlings following treatments with MT, DZY 6715, MT-DZY 6715, and sterile water as a control. Each seedling received 20 mL of the respective solution applied evenly with a spray bottle, ensuring no droplets fell off, and the leaves were allowed to dry before reapplying. Twenty-four hours post-inoculation, created on either side of the central vein of the leaves using a sterile inoculation needle. Subsequently,10 μL of conidial suspension of C. siamense, at a concentration of 1 × 105 CFU mL-1 was applied to the wounded area of each leaf. The seedlings were cultivated at room temperature with a controlled humidity of 80%. Finally, the lesion size on the leaves and the incidence rate (M) were calculated based on the Xie et al. (2021) ‘s approach, as formulated:
where M1 and M2 represent the number of infected leaves and the total number of leaves, respectively. Each treatment had nine replicates, and the experiment was repeated twice.
2.5 Effects of MT-DZY 6715 on the leaf structure of C. oleifera
The treatment for C. oleifera seedlings was conducted as described in section 2.4. Each seedling received 20 mL of the respective solution, which was applied evenly to ensure no droplets fell off. Leaf samples from the C. oleifera seedlings were collected 30 days post-treatment for further analysis.
2.5.1 Scanning electron microscopy
The method for the scanning electron microscope was adapted from the previous description by Lubna et al. (2019) with appropriate modifications. Specifically, collected leaf samples were promptly immersed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde for overnight fixation, then rinsed with 0.1M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) at a pH of 7.4, followed by dehydration with increasing concentrations of ethanol. After freeze-drying, the surfaces of the samples were coated with gold to enhance their visibility. Finally, the samples were observed under a Hitachi Regulus 8100 SEM.
2.5.2 Stomata characteristics
The stomatal characteristics on the leaf surface were analyzed based on the method described by Ayala-Ramos et al. (2024), with slight modifications. Fully expanded and well-grown leaves were selected, and samples were collected between 8–9 am to ensure consistent physiological conditions. The lower epidermis of each leaf was meticulously peeled off using a fine dissecting knife, gently rinsed with sterile distilled water to remove any contaminants, and promptly transfer to phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) solution to maintain cell integrity. Stomatal characteristics, including the horizontal axis of stomata (HAS), vertical axis of stomata (VAS), stomatal area (SA), and stomatal perimeter (SP), were measured. For each observation, ten random fields of view were examined to ensure comprehensive assessment of the stomatal characteristics. Each treatment was repeated three times.
2.5.3 Leaf tissue structure
The anatomical structure of the leaf was analyzed using the paraffin sectioning method (Yao et al., 2023). Specifically, collected samples were cut into 1x1 cm pieces using a dissecting knife and preserved in FAA solution (a mixture of formaldehyde, acetic acid, and 70% ethanol). Then, the samples were dehydrated in a series of ethanol solutions and ethanol/xylene mixtures, embedded in paraffin, and then sectioned using a Leica RM 2016 rotary microtome (Leica, Nussloch, Germany), the sections were stained with safranine O-fast green staining (Hu et al., 2022). Images of the stained sections were captured using a Zeiss MC 80 Axiolab optical microscope. The NDP view 2.9.22 RUO software was utilized to measure anatomical structures, including leaf thickness (Ln), the thickness of the upper (Tup) and lower epidermises (Tep), spongy mesophyll (Tsp), palisade mesophyll (Tpa), the ratio of palisade mesophyll to spongy mesophyll (PS). Additionally, tissue compactness (CTR) was calculated as the ratio of leaf thickness to palisade mesophyll thickness, and tissue looseness (SR) was assessed by the ratio of spongy mesophyll thickness to leaf thickness. Each treatment group consisted of three leaves, and the experiment was repeated twice.
2.6 Transcriptome analysis of C. oleifera induced by MT-DZY 6715
2.6.1 RNA extraction, RNA-sequencing and differentially expressed gene identification
Samples of C. oleifera leaves, treated with MT, DZY 6715, and MT-DZY 6715 for 24 h, as well as a control group (CK) treated with sterile water, were collected and promptly frozen in liquid nitrogen for RNA extraction. The quality of the extracted RNA was evaluated using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. Subsequently, sequencing of the RNA libraries was conducted on the Illumina HiSeq platform. Low-quality reads were excluded from the raw sequencing data, resulting in a set of high-quality, filtered reads. These reads were then aligned to the reference genome of C. oleifera which was obtained from a designated website (https://zenodo.org/record/5768785#.ywrqgnzbwdu). Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified using the DESeq2 software package. The functional annotation of these DEGs was conducted using the KEGG database (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). To identify DEGs, we applied thresholds of |log2FC|>1 and a P <0.05.
2.6.2 RNA-seq verification by quantitative real-time PCR
To verify DEGs expression, RT-qPCR was conducted, utilizing primers specifically designed for DEGs with Primer Express Software v2.0 (Supplementary Table S1), in accordance with the transcriptional analysis.
2.7 Effect of MT-DZY 6715 of on the defense enzymes activity and substances related to the cell wall in C. oleifera
The treatment method for C. oleifera remains consistent with that described in section 2.4. Leaf samples of C. oleifera, collected on the 30th day post-treatment, were used to evaluate the following indicators. The activity of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) was assessed as described by Zhu et al. (2021). The activities of cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase (C4H) and 4-coumarate: coenzyme A ligase (4CL) were investigated according to the method described by Yin et al. (2023). Laccase and cinnamyl-alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD) activities were measured in accordance with the protocol established by Khedr and Khedr (2024). The content of lignin and cellulose were examined as illustrated by Sun et al. (2023). Additionally, cellulase activities was examined utilizing the methodology detailed by Abu-Goukh and Bashir (2003). Protopectin content was determined based on Shinga and Fawole (2023) method. Pectinase activity was determined as described by Dal Magro et al. (2019). The results for the activities of PAL, 4CL, C4H, CAD, laccase, cellulase, and pectinase are expressed in units per gram of protein concentration (U g-¹), while the content of lignin, cellulose, and protopectin is indicated as milligrams per gram of fresh leaf weight (mg g-¹).
2.8 Statistical analyses
Statistical comparisons of the data were performed using independent t-test or Duncan’s multiple range test in SPSS 20.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA), with statistical significance determined at P <0.05.
3 Result
3.1 Inhibitory effect of MT-DZY 6715 against C. siamense in vitro
After inducing DZY 6715 with 50 μmol L-1 MT (MT-DZY 6715), the inhibitory effect on C. siamense was the best, during the 24–120 h of cultivation, MT-DZY6715 treatment showed an inhibition rate of 58.67% -76.33% against C. siamense, and the highest inhibition rate was observed at 72 h, which was 26.86% higher than the DZY 6715 treatment (Figure 1).
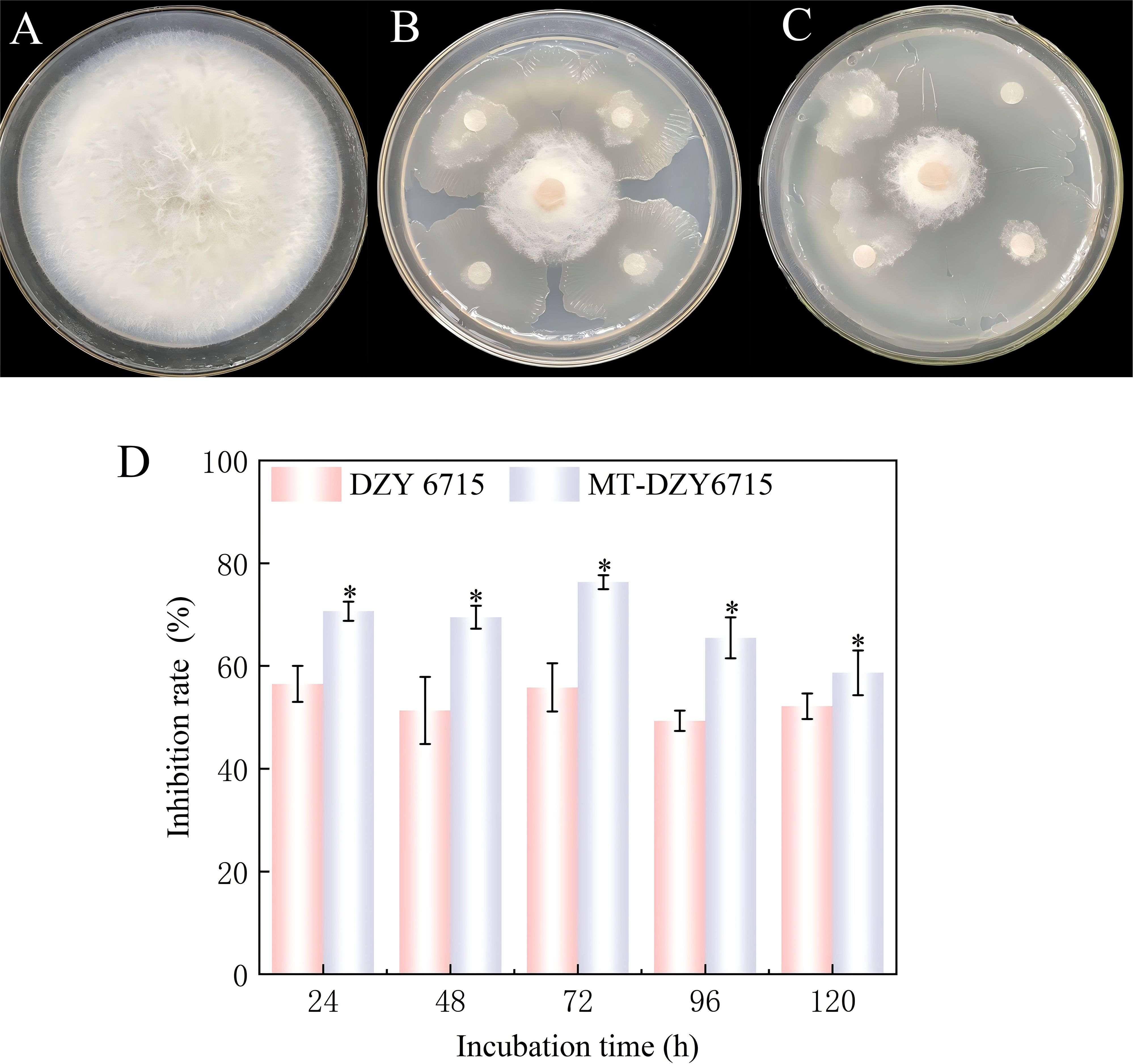
Figure 1. Representative photos demonstrating the antagonistic activity of MT-DZY 6715 on the growth of C. siamense. (A) represents the treatment with the pathogen alone; (B) shows the treatment with DZY 6715 suspension; (C) displays the treatment with MT-DZY 6715; and (D) illustrates the inhibitory effect on the pathogen in vitro. The data presented are expressed as the mean ± standard error (SE). * represents significant differences based on P <0.05.
3.2 The impact of MT-DZY 6715 aganist C. siamense on C. oleifera
Figure 2A showed that as the treatment time increased, the disease incidence rate in all treatment groups rises linearly. At the 9th day, the disease incidence rate in the control group reached 100%, which is significantly higher than that of the DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 treatment groups by 22.22%, 8.89%, and 35.56%, respectively. In addition, the lesion diameter on the leaves of each treatment group also gradually increase with prolonged treatment time. However, from the 4th to 10th day of treatment, the leaf lesion diameters of the DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 treatment are significantly lower by 40.24-52.66%, 13.83-31.17%, and 54.88-63.83%, respectively, compared to the control group (Figure 2B). The above indicated that the MT-DZY 6715 treatment exhibited the highest inhibitory activity against C. oleifera anthracnose caused by C. siamense.
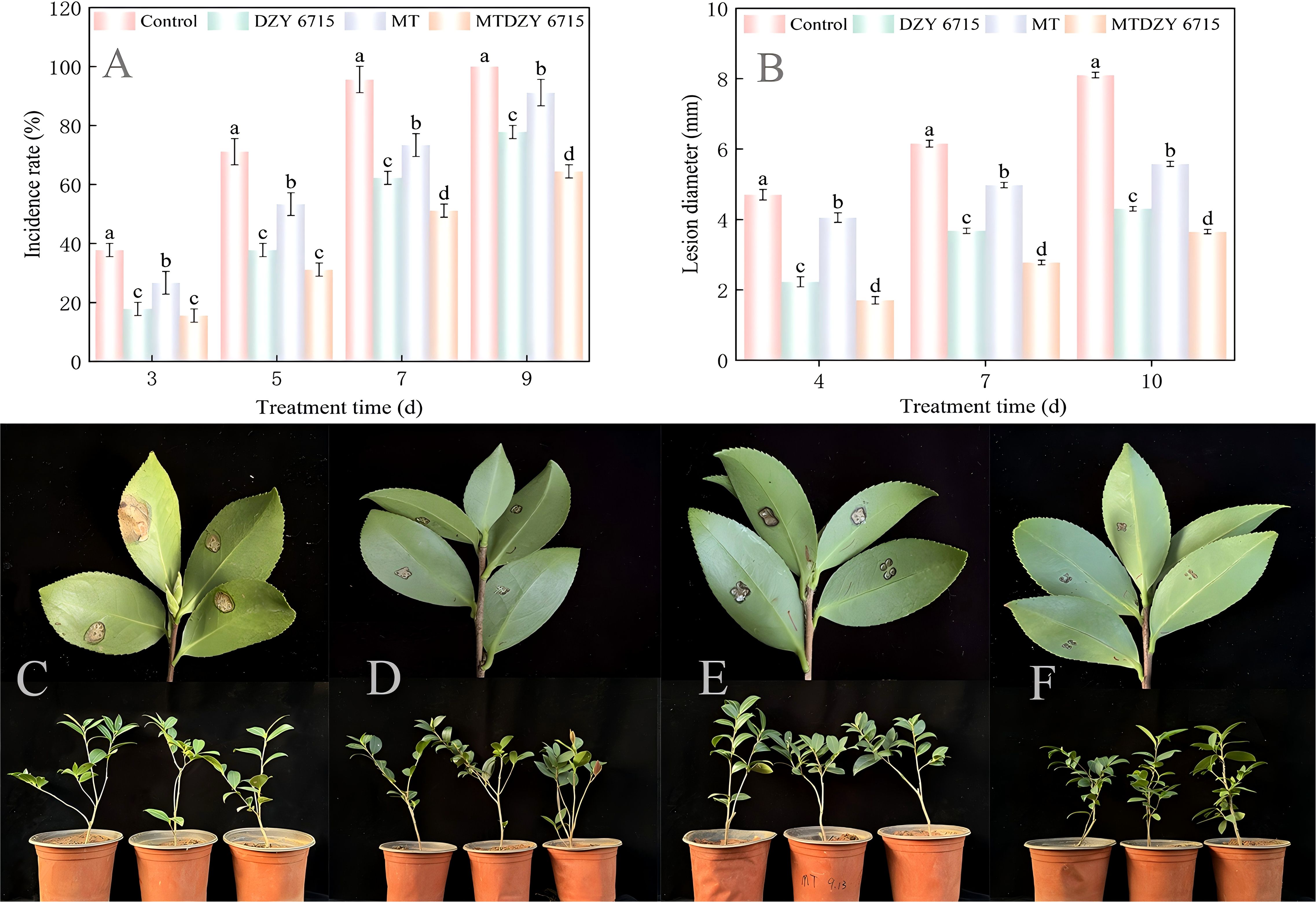
Figure 2. The incidence rate (A) and lesion diameter (B) of C. siamense on C. oleifera leaves during the cultivation period. Representative images illustrate the effect of MT-DZY 6715 on lesion development in C. oleifera leaves resulting from 10 days post-pathogen inoculation (C-F). (C-F) represent treatments with C. siamense, DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715, respectively. Data are represented as mean ± standard error (SE). Diverse letters are used to denote significantly differences among the different timepoints as determined through a Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
3.3 Impact of MT DZY 6715 on the leaf structure of C. oleifera
3.3.1 Surface structure and stomata of C. oleifera leaves
Figure 3 showed that on the 30th day post-treatment, the MT-DZY 6715 treatment group exhibited stomatal dimensions with horizontal axis of stomata (HAS) of 17.59 μm, a vertical axis of stomata (VAS) of 16.51 μm, a stomatal area (SA) of 163.12 μm2, and a stomatal perimeter (SP) of 47.03 μm. These values were significantly (P<0.05) lower compared to the CK, MT, and DZY 6175 treatment groups. Furthermore, the stomata in the MT-DZY 6715 treated group were nearly fully closed, meanwhile, the stomata in the control and MT groups were larger and more open. In addition, after 30 days of treatment, the epidermal surfaces of C. oleifera leaves showed varying amounts of solid particulate matter. It is worth noting that compared with the control group, DZY 6715, and MT, the leaves treated with MT-DZY 6715 showed notably more solid particles. These particles comprised the waxy layer of the leaf epidermis. Furthermore, MT-DZY 6715 treatment resulted in reduced epidermal folding and a wax layer with dense, fragmented protrusions.
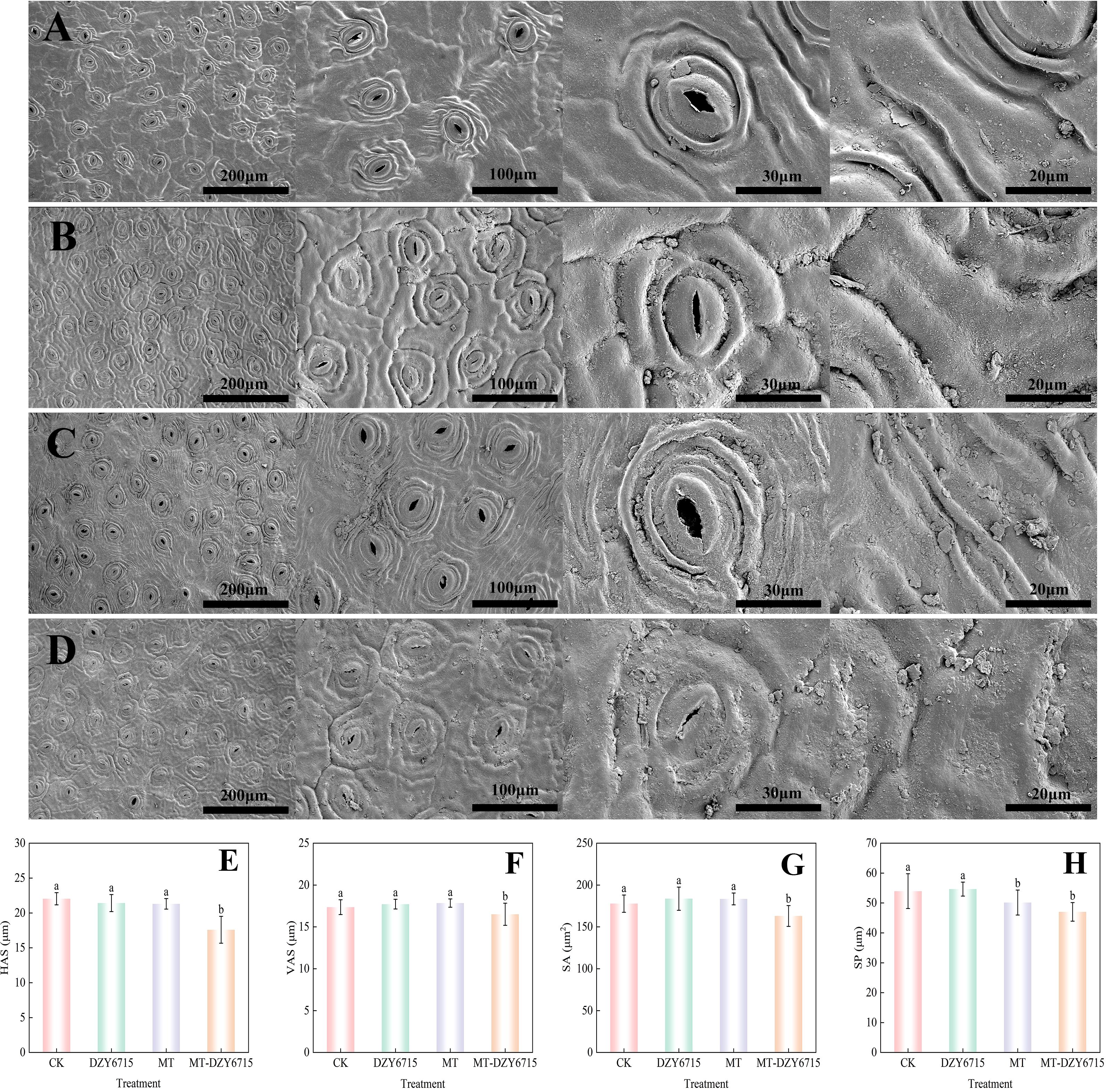
Figure 3. Scanning electron microscope assessment of the effects of CK (A), DZY 6715 (B), MT (C), and MT-DZY 6715 (D) treatments on the stomata of C. oleifera leaves, and stomatal structure characteristic parameters of leaves under different treatments at 30 d: HAS (E), VAS (F), SA (G), and SP (H). Data are represented as mean ± standard error (SE). Different letters indicate significant differences between the different treatments as determined by a Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
3.3.2 Leaf anatomical structure
Figure 4 exhibited the structural features of the cross-section of C. oleifera leaves. Both the upper and lower epidermal layers are composed of a single layer cell. Adjacent to the upper epidermis is the palisade mesophyll, characterized by its tightly packed arrangement of elongated, columnar cells in 2–3 layers. Spongy mesophyll, situated next to the palisade mesophyll, consists of irregularly shaped cells arranged loosely with expansive intercellular spaces. Figure 5 showed that there are differences in the anatomical characteristics of C. oleifera leaves following various treatments. Compared to the control, leaves treated with DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 exhibited an increase in leaf thickness (Ln) and palisade mesophyll thickness (Tpa). No significant difference was observed in the upper/lower epidermal thickness (Tup/Tep) between the MT-DZY 6715 treatment and the control. The sponge tissue thickness (Tsp) in the MT-DZY6715 treatment group was significantly reduced compared to the control, MT and DZY 6715 treatment groups. Additionally, leaves treated with MT-DZY 6715 exhibited a significantly higher ratio of palisade mesophyll to spongy mesophyll (PS) and a greater degree tissue compactness (CTR) than the control, MT, and DZY 6715 groups. Conversely, the tissue looseness (SR) in the MT-DZY6715 treatment group was significantly lower than that in the other three groups.
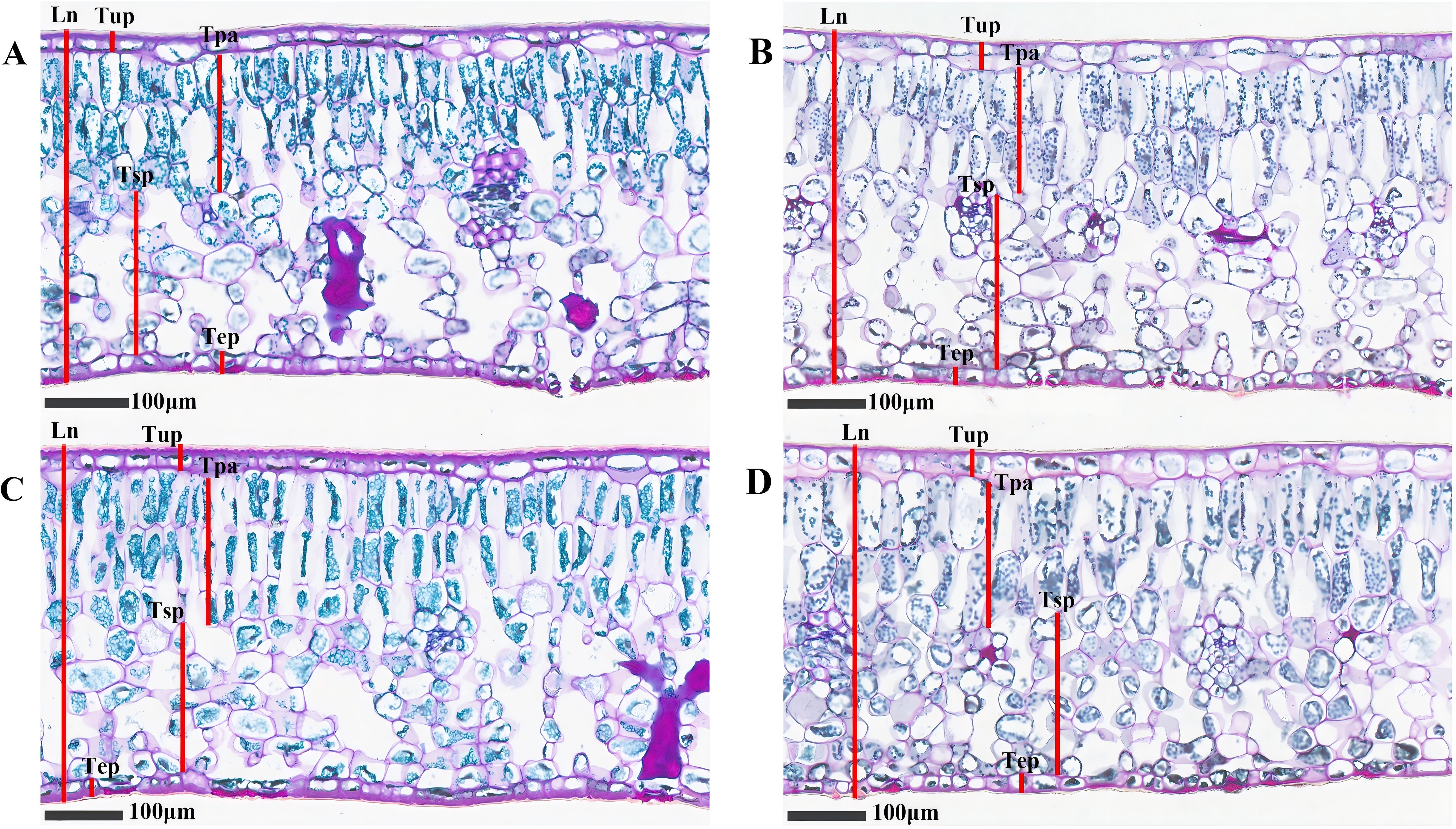
Figure 4. Microscopic analysis of C. oleifera leaf anatomical structures at ×20 magnification after treated with CK (A), DZY 6715 (B), MT (C), MT-DZY 6715 (D).
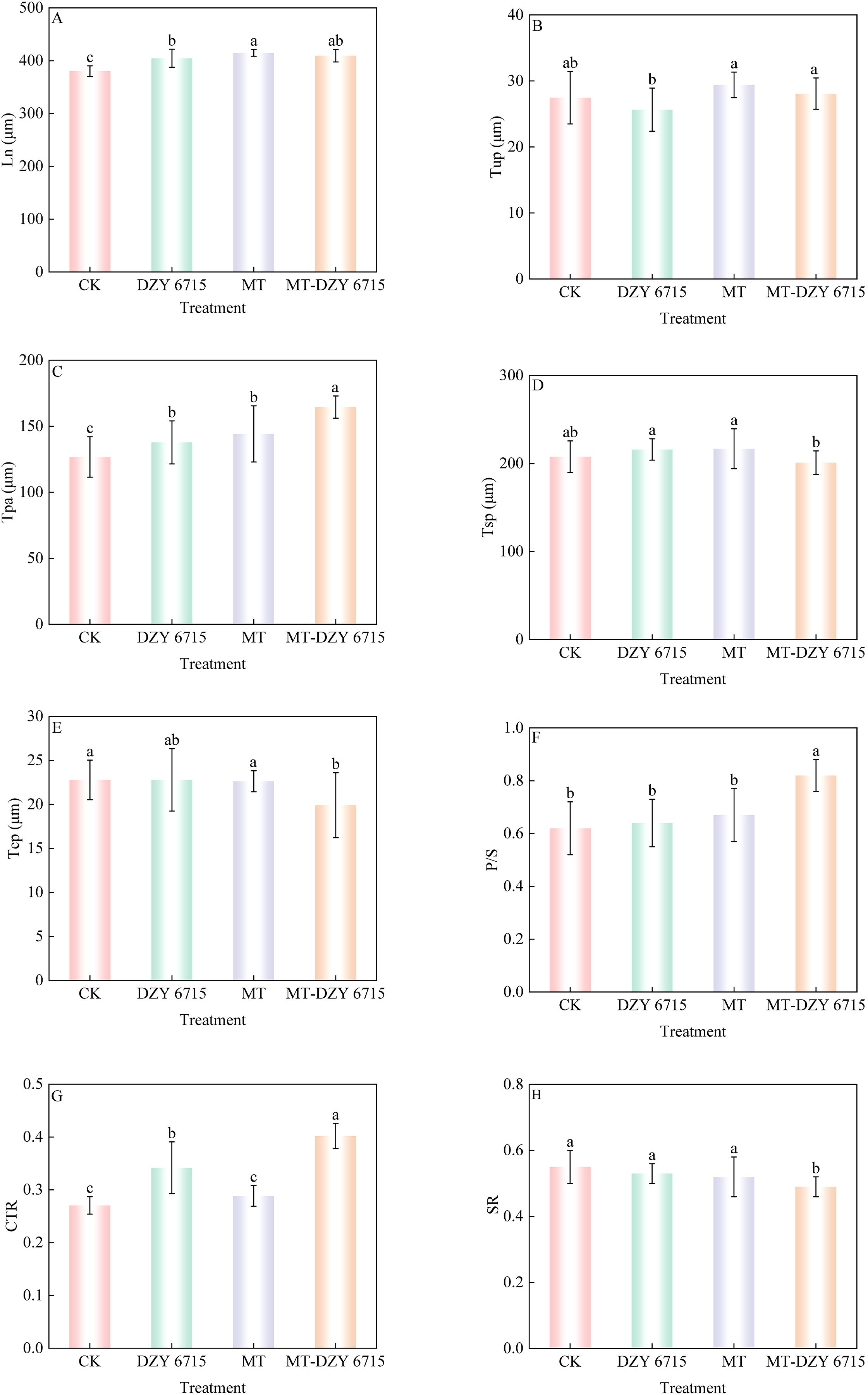
Figure 5. Morpho-anatomical traits of C. oleifera leaf of different treatments at 30(d) (A) Ln, leaf thickness; (B) Tup, thickness of the upper epidermises; (C) Tpa, thickness of the palisade mesophyll; (D) Tsp, thickness of the spongy mesophyll; (E) Tep, thickness of the lower epidermises; (F) P/S: the ratio of palisade mesophyll to spongy mesophyll; (G) CTR (tissue compactness), the ratio of leaf thickness to palisade mesophyll thickness; (H) SR (tissue looseness), the ratio of spongy mesophyll thickness to leaf thickness. Vertical bars indicate the standard errors of the mean. Different letters denote a significant difference among various treatments, as determined by one-way ANOVA at P < 0.05. Values are the mean ± SE.
3.4 Transcriptomic analysis of C. oleifera treated with MT-DZY 6715
3.4.1 DEGs identified by transcriptome analysis
In the present study, the R2 values between biological replicates fell within the range of 0.98 to 1.00, signifying the high reliability of the transcriptome data, thereby validating it for subsequent downstream analyses (Figure 6A). In the comparison CK-vs-DZY 6715, 1,142 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were detected, with 442 upregulated and 700 downregulated. In CK-vs-MT, 924 DEGs were identified, including 558 upregulated and 366 downregulated genes. A total of 1,372 DEGs were detected in CK-vs-MT-DZY 6715, among which 620 were upregulated and 752 were downregulated. The identification of a higher number of DEGs in CK-vs-MT-DZY 6715 suggests that the MTDZY 6715 treatment has a more significant impact on C. oleifera (Figure 6B).
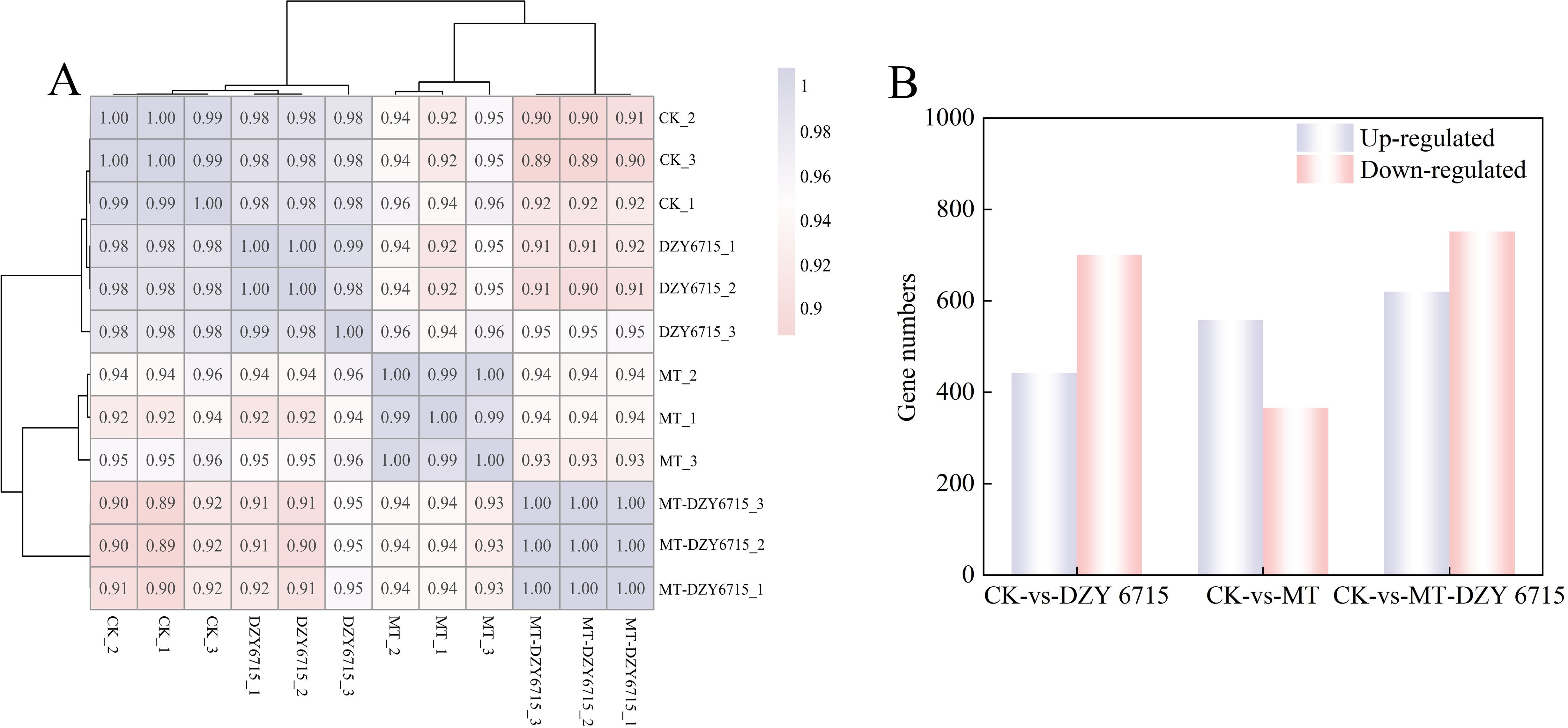
Figure 6. Sample correlation test chart (A), and DEGs in CK-vs-DZY 6715, CK-vs-MT, and CK-vs-MT-DZY 6715 (B).
3.4.2 Effects of different treatments on the transcriptome of C. oleifera
To further elucidate gene functions, KEGG enrichment analysis was conducted on the DEGs. The results revealed that the 1,142, 924, and 1,372 DEGs identified in CK-vs-DZY 6715, CK-vs-MT, and CK-vs-MTDZY 6715, respectively, were enriched into 92, 85, and 108 KEGG pathways, with the top 20 pathways shown in the Figure 7. Among these top 20 KEGG pathways, Phenylpropanoid biosynthesis exhibited the highest number of enrichments in both CK-vs-DZY 6715 (Figure 7A) and CK-vs-MT-DZY 6715 (Figure 7B), whereas Plant-pathogen interaction was the most enriched in CK-vs-MT (Figure 7C). The application of DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 altered the differential gene expression (DEGs) link to disease resistance in C. oleifera. These DEGs were subsequently analyzed and categorized into four functional groups: transcription factors, plant hormone signal transduction, cell wall and phenylpropanoid metabolism.
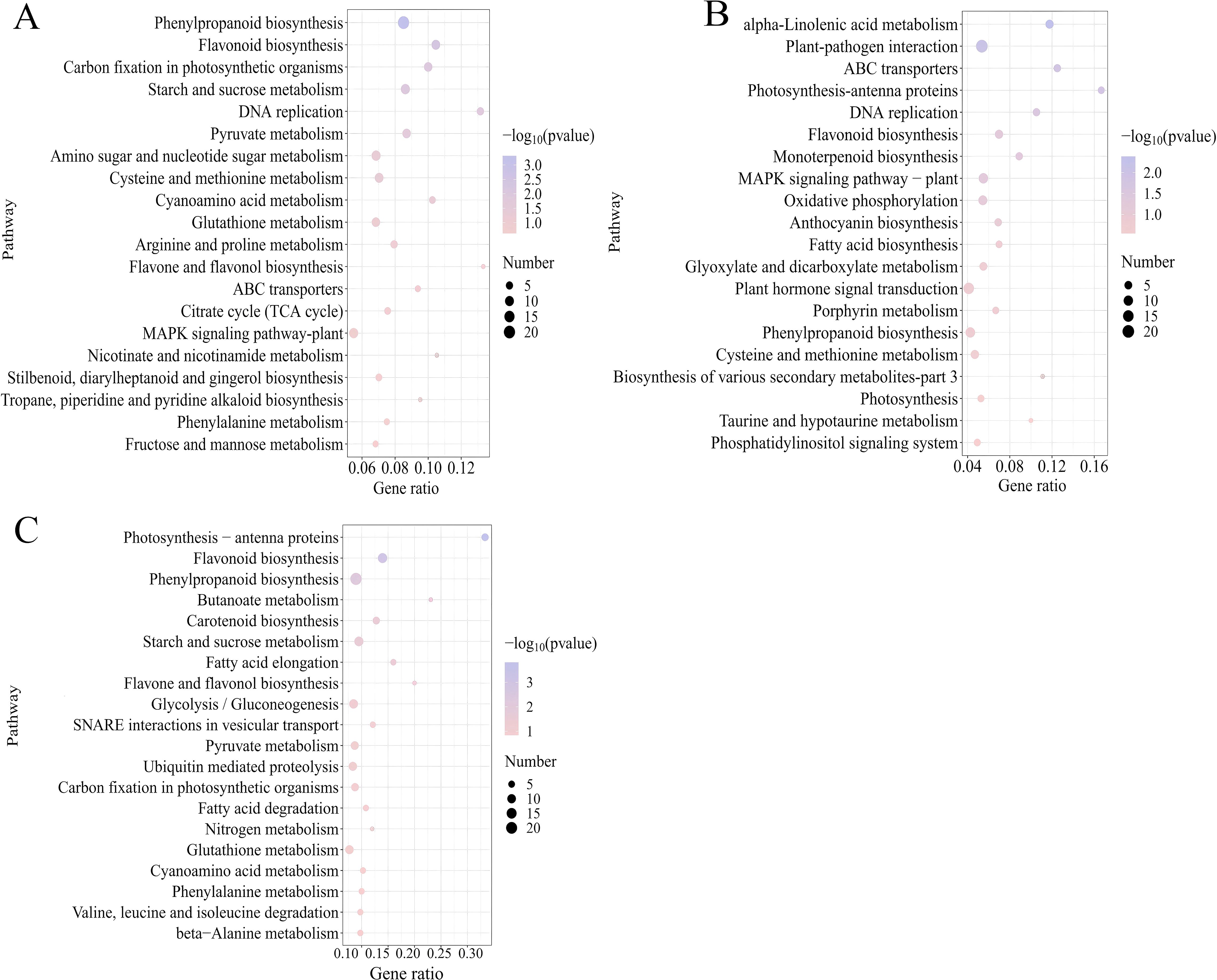
Figure 7. The 20 most significantly associated KEGG pathways identified in comparisons of CK-vs-DZY 6715 (A), CK-vs-MT (B), CK-vs-MT-DZY 6715 (C) in C. oleifera.
For transcription factors (Figure 8A), compared to the control group, after DZY 6715 application, a total of 13 genes were up-regulated, including TAF10, MYBP, U2AF1, ERF1, PTI5, UAF30, 2 AP2, 3 EREBPs, and 2 WRKY33, while 5 genes were down-regulated, encompassing HD-ZIP, HSPP, WRKY33, 2 MYBPs, and ARF. Following the MT application, 6 genes experienced up-regulated, including AP2, MYC2, WRKY33, ARF, UAF30 and RNF38_44, while 7 genes were down-regulated, including EREBP, HD-ZIP, HSFF, WRKY33, and 3 MYBPs. The application of MT-DZY 6715, 16 genes exhibited up-regulation, such as TAF10, AP2, U2AF1, RAV, ERF1, HSFF, UAF30, RNF38_44, along with 3 EREBPs, 3 MYBP and 2 WRKY33, while 5 genes were down-regulated, including HD-ZIP, WRKY33, ARF. For plant hormone signal transduction (Figure 8B), compared to the control group, after DZY 6715 was applied, 11 genes were affected, with 3 up-regulated (including AOC, IAA, SAUR), and 8 genes down-regulated (BHMT, SMG1, AMD1, SAUR, PIN, GH3, PYL, and SLC15A3_4). And the MT application, 9 genes exhibited changes, with 4 up-regulated, such as IAA, GH3, SAUR, AUX1, and 5 down-regulated, including BHMT, CYP26A, SAUR and 2 PYL. Meanwhile, MT-DZY6715 treatment led to alterations in 13 genes. Among these, 7 genes were up-regulated, including GA2ox, CYP707A, IAA, SAUR, AOG and 2 AOCs, while 6 genes down-regulated like BHMT, SMG1, PIN, GH3, PYL, SLC15A3_4. For cell wall metabolism (Figure 8C), compared to the control group, after DZY 6715 was applied, 29 genes were affected, among these, 6 genes were up-regulated, including otsB, SEC61G, PIP, ANXA7_11 and 2 CHI. At the same time, 23 genes were down-regulated, such as PE, CHI, PREP, 2 ATP2C, PPC, 3 PEL, CFL, CDC45, YCG1, TUBA, 3 CESA, 2 GAUT, CSLA, SCPL-IV, NEDD1, SACS, EXOC6. Following MT application, 18 genes exhibited changes, with 8 up-regulated (PIP5K, PE, cynT, 2 AOS, PEL, TUBA, CESA) and 10 down-regulated (PPC, PEL, CFL, CDC45, UGT75C1, GAUT, NEDD1, ECOC6 and 2 CHI). Meanwhile, MT-DZY6715 treatment led to alterations in 34 genes. Among these, 13 genes were up-regulated, such as PE, otsB, 2 CHI, TUBA, 4 PIP, TIP, CESA, GAUT, SCPL-IV. While 21 genes were down-regulated, including PIP5K, CHI, PREP, ATP2C, PPC, 3 PEL, APR, CDC45, YCG1, TUBA, TRIP12, 2 CESA, KPC1, UGT75C1, UTP20, NEDD1, SACS, EXOC6. In the phenylpropanoid metabolism (Figure 8D), the application of DZY6715 resulted in the differential expression of 22 genes compared to the control group. Specifically, 8 genes were up-regulated, including 6 peroxidases (PODs) and 2 hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA shikimate/quinate hydroxycinnamoyltransferases (HCTs), while 14 genes were down-regulated, comprising 5 PODs, 5 laccases (LAs), 2 leucoanthocyanidin reductases (LARs), and 2 cinnamoyl-CoA reductases (DCRs). Upon the application of MT, 14 lignin-associated genes exhibited altered expression, with 9 genes up-regulated, including 7 PODs and 2 HCTs, and 5 genes down-regulated, specifically 2 PODs, 2 LARs, and chalcone synthase (CHS). The application of MT-DZY6715 led to changes in the expression of 15 phenylpropane metabolism-related genes, with 15 genes up-regulated, including 7 PODs, CHS, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL), LA, 3 phenylalanine ammonia-lyases (PALs), and 2 HCTs, while 5 genes were down-regulated, including POD, 3 LAs, and DCR.
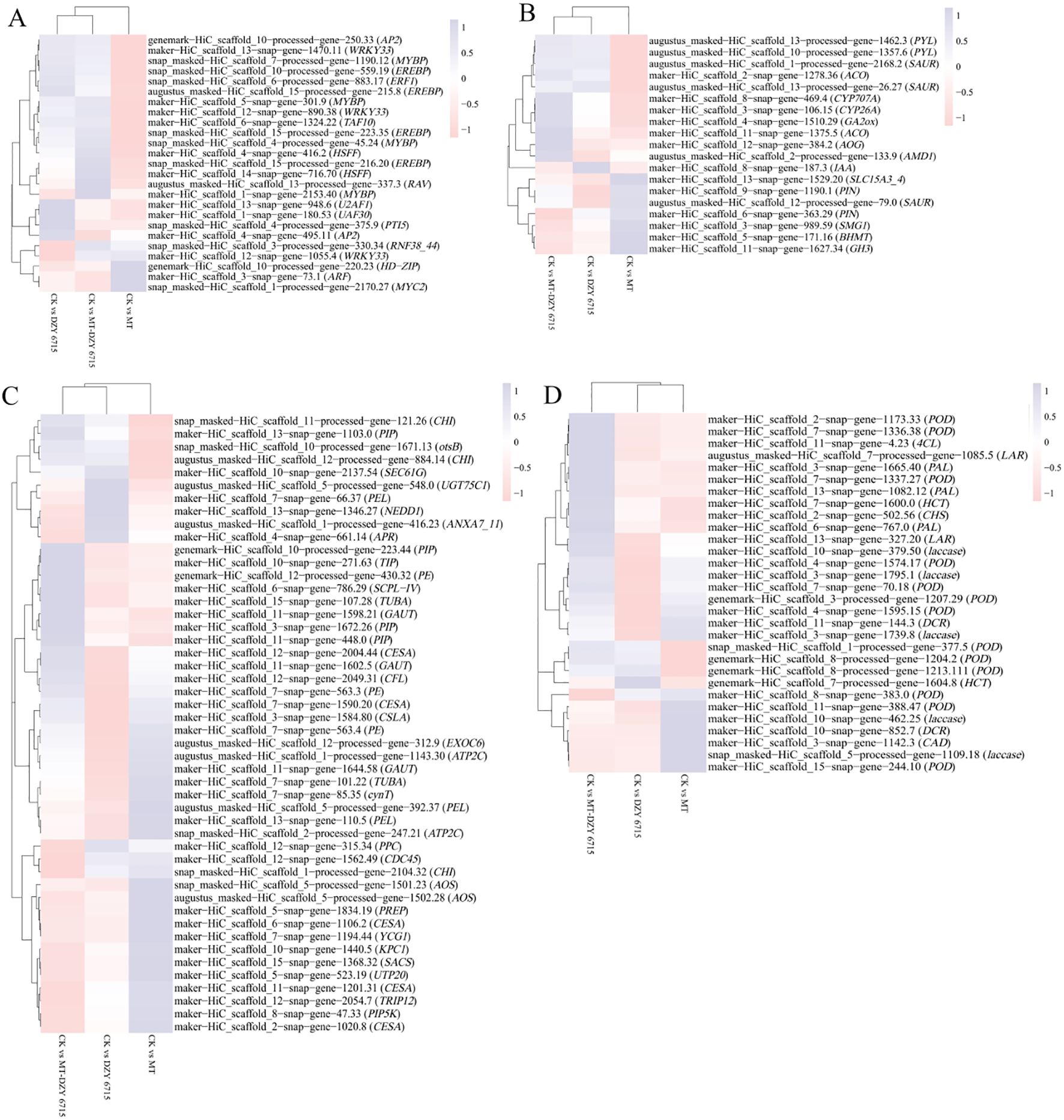
Figure 8. presents cluster analyses of the expression profiles of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) related to transcription factors (A), plant hormone signal transduction (B), cell wall metabolism (C), and phenylpropanoid metabolism (D) following treatment with DZY 6715, MT, MT-DZY6715.
3.4.3 qRT-PCR assay
To verify the accuracy of the transcriptome data, we performed qRT-PCR analysis on six randomly selected differentially expressed genes. The results, as illustrated in Figure 9, demonstrate that the expression levels of these genes in the CK, DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 samples align with the trends observed in the transcriptome data, indicating the reproducibility and consistency of the RNA-seq data.
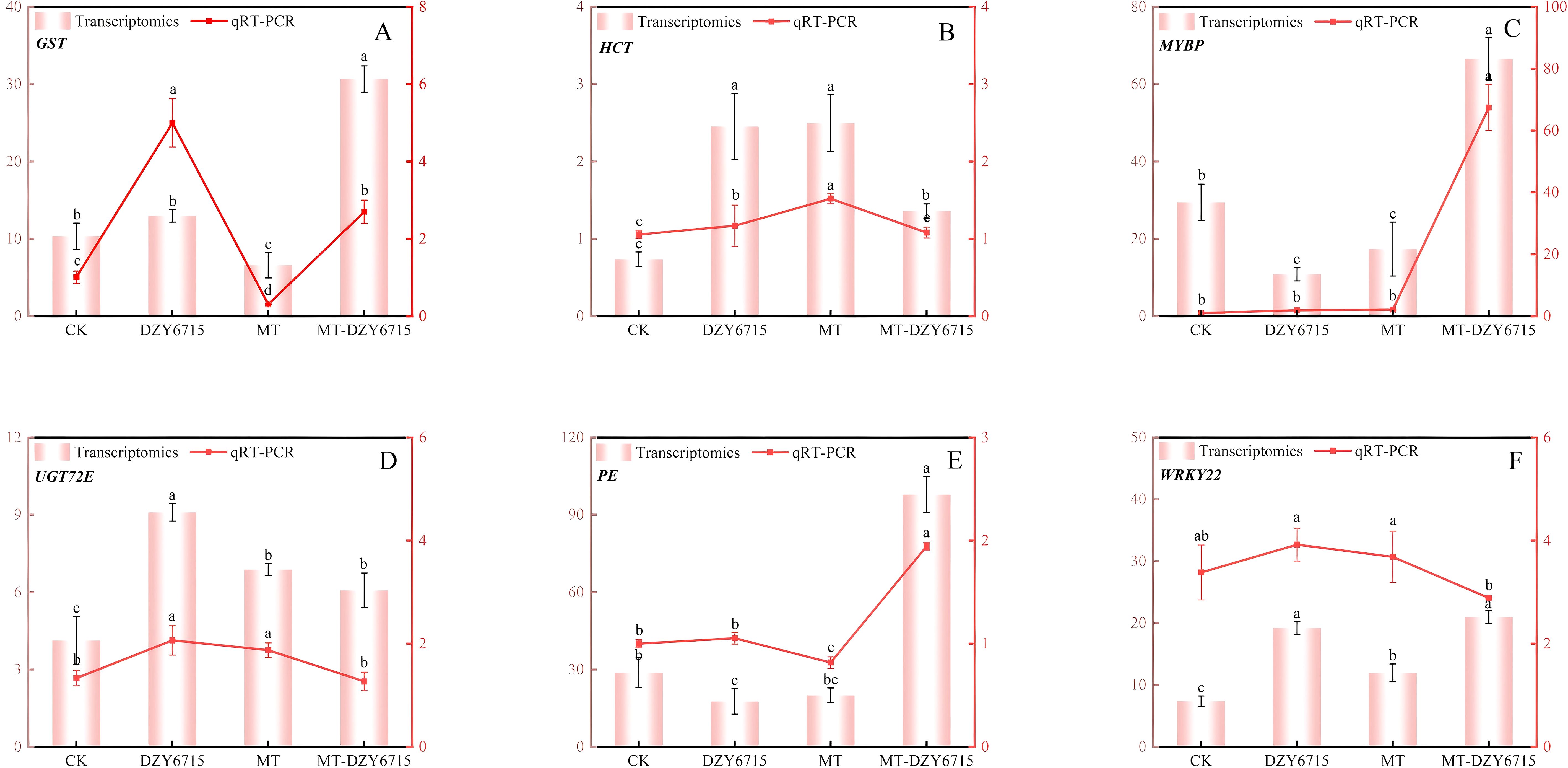
Figure 9. qRT-PCR assay performed to validate the DEGs GST (A), HCT (B), MYBP (C), UGT72E (D), PE (E), WRKY22 (F). The vertical bars indicate the SD from three replicates. Different letters indicate significant differences among the different treatment groups, as determined by Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
3.5 Defense enzyme activities and substances in C. oleifera after MT-DZY 6715 treatment
After 30 days of treatment with DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY6715, the PAL activity in C. oleifera significantly increased by 59.50%, 32.11%, and 59.86%, respectively, compared to the control group (Figure 10A). Similarly, the 4CL activity in the groups treated with DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY6715 was significantly elevated compared to the control. Specifically, the 4CL activity was 344.97 U g-1 (10.99% higher), 330.29 U g-1 (5.65% higher), and 386.0 U g-1 (24.20% higher) in the DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 groups, respectively (Figure 10B). Additionally, after 30 days of treatment with DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715, the C4H activity significantly rose by 30.04%, 17.60%, and 43.28%, respectively, compared to the control group (Figure 10C). On the 30th day of treatment, the CAD activity in the DZY 6715-treated group was reduced to 1.08- times that of the control group, whereas the CAD activity in the MT and MT-DZY 6715 treatment groups was elevated to 1.06- times and 1.38- times that of the control group, respectively (Figure 10D). As shown in Figure 10E, the laccase activity in the treatment groups with DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 was 2.73-, 2.16-, and 3.06- times higher, respectively, compared to that of the control group. Figure 10F exhibited that after 30 days of treatment, the lignin content in the DZY 6715 and MT treatment groups was 3.02% and 3.22% lower, respectively, compared to the control group. In contrast, the lignin content in the MT-DZY6715 treatment group was 6.96% higher than that of the control group. On the 30th day, the cellulase activities in the DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY6715 treatment groups were 781.88, 881.96, and 754.85 U g-1, respectively, which were 23.94%, 9.88%, and 28.38% lower than those in the control (Figure 10G). As shown in Figure 10H, the cellulose content in the DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 treatment groups significantly increased to 1.32- times, 1.13- times, and 1.41- times higher than that of the control group, respectively. On the 30th day of treatment, the pectinase activity in the control group was 1.20-, 1.13-, and 1.27- times higher than that in the DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY 6715 treatment groups, respectively (Figure 10I). Figure 10J showed that on the 30th day, the protopectin content in the DZY 6715, MT, and MT-DZY6715 treatment groups was markedly higher than that in the control group, with increases of 5.60%, 21.14%, and 37.92%, respectively.
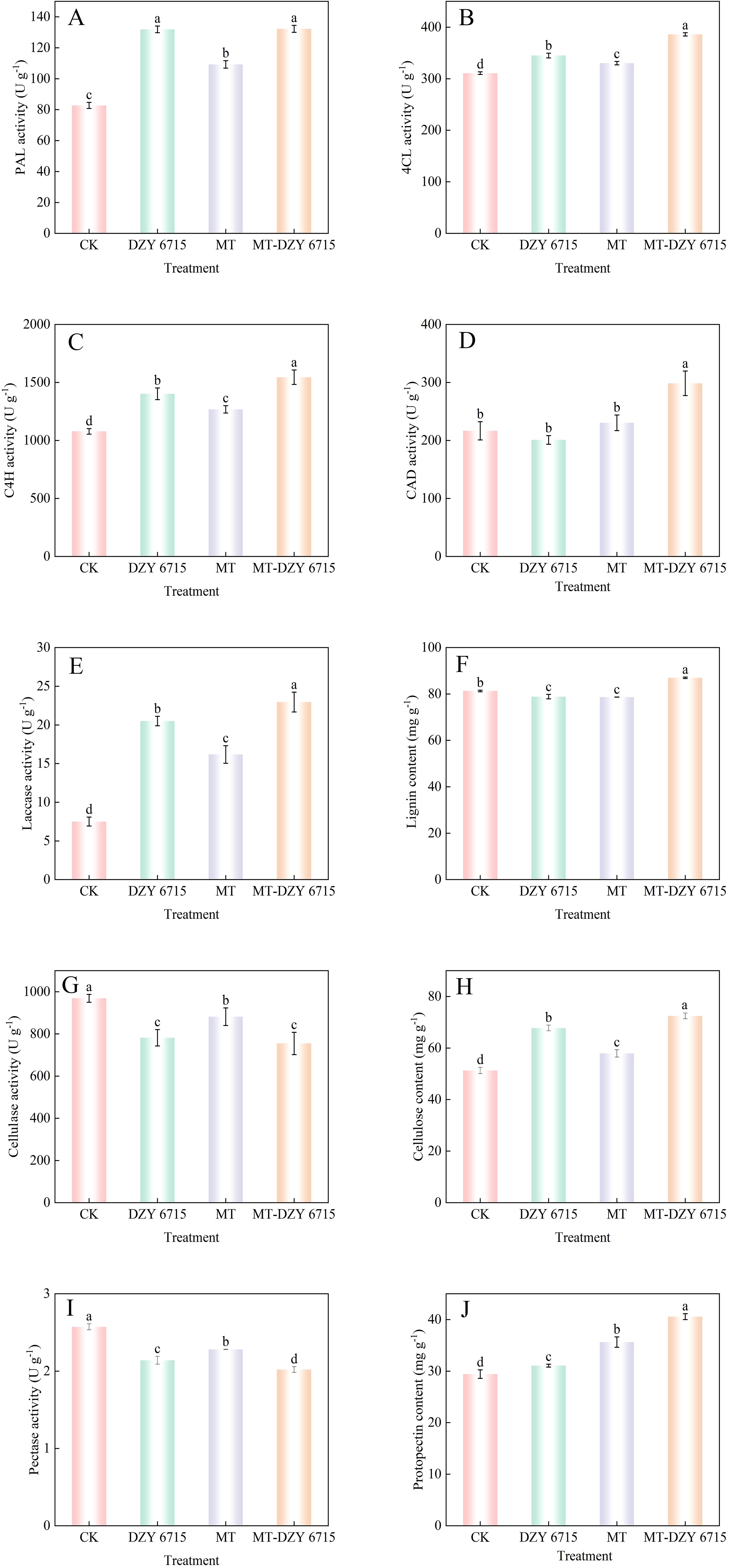
Figure 10. Effect of MT-DZY 6715 on the PAL (A), 4CL (B), C4H (C), CAD (D), laccase (E) cellulase (G), pectinase (I) activities and the content of lignin (F), cellulose (H), protopectin (J) in C. oleifera. Diverse letters stand for significantly different at the different treatment groups as determined through a Duncan’s multiple range test (P < 0.05).
4 Discussion
Anthracnose, a disease primarily caused by Colletotrichum species like C. gloeosporioides, C. fructicola, C. siamense, and C. boninense, poses as a significant threat to C. oleifera (Jeyaraj et al., 2023). This disease results in substantial yield losses, ranging between 20% and 50% (Zhu and He, 2023). In response to the growing emphasis on environmental protection, the application of Bacillus species for microbial control has emerged as a more sustainable and efficacious alternative (Elnahal et al., 2022; Lastochkina et al., 2019). Research has shown that Bacillus species effectively inhibit the growth and invasion of pathogen through a combination of mechanisms, including nutrients spatial niche competition (Caulier et al., 2018; Lastochkina et al., 2019), secretion of antibiotic substances, production of antibacterial proteins (Liu et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2017), and induction of enhanced activity of plant disease resistance-related enzymes (Bai et al., 2023; Fan et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2019). Although Bacillus sp. exhibit considerable potential for biological control, they are generally less effective than chemical fungicides. MT, as a naturally occurring small molecule substance widely present in organisms, functions as a biological stimulant capable of counteracting various biotic and abiotic stresses (Ahammed et al., 2020; Arnao and Hernández-Ruiz, 2014; Zhao et al., 2019). As reported by Liu et al. (2024), the combined application of MT and fungal metabolites enhances disease resistance in tomato plants against bacterial wilt by regulating the expression of plant hormone-related genes, increasing the contents of jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA), decreasing ethylene (ET) levels, and augmenting antioxidant enzyme activity within the plants. Chen et al. (2019) indicated that compared to the control, MT significantly inhibited the growth of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc), reduced its pathogenicity, as evidenced by a decrease in lesion length by over 23% and a reduction in bacterial population by 45%. Additionally, MT effectively suppressed Xoc’s biofilm formation, motility, and extracellular protease activity, ultimately leading to a 17% decrease in the incidence of rice bacterial leaf streak disease. In the present work, MT was used as the elicitor for the induced culture of B.tequilensis DZY 6715. According to our results, MT-DZY 6715 exhibited enhanced antibacterial activity compared to DZY 6715, achieving a maximum inhibition rate of 76% against C. siamense in vitro. Furthermore, MT-DZY 6715 treatment effectively suppressed the growth of the anthracnose pathogen and controlled its spread on leaves of C. oleifera.
Leaves, being highly sensitive to environmental changes and possessing significant plasticity, provide an important perspective through the study of their anatomical structures for analyzing the physical defense mechanisms and disease resistance against pathogens (Accioly et al., 2024). Specifically, leaf epidermis serves as the first barrier between plants and the external environment. It often contains structures such as wax layer and cuticle layer, which are crucial in resisting pathogen invasion (Wang et al., 2020b; Ziv et al., 2018). The wax layer, as a protective barrier outside the cuticle, endows plants with natural defense capabilities, as its hydrophobic properties can effectively prevent pathogen spores from adhering to the leaf surface, thus hindering their penetration into plant tissues (Li et al., 2019; Reina-Pinto and Yephremov, 2009; Sharma et al., 2018; Tafolla-Arellano et al., 2018). C. oleifera anthracnose belongs to an air-borne disease, with the pathogen producing a large number of conidia that spreads through media like wind and rain. In the current research, compared to the control, the epidermal wax of leaves treated with MT-DZY 6715 showed dense, fragmented, and more tightly packed protrusions. These changes indicated that the MT-DZY 6715 treatment altered the structure of the wax crystals on the C. oleifera leaves, forming a stronger defensive barrier, and thus more effectively resisting pathogen invasion. In addition, thicker leaves provide plants with a more solid physical barrier, which not only effectively blocks pathogen entry into plant tissues, mitigating disease incidence, and aiding in water conservation by reducing transpiration, thereby maintaining the plant’s water balance (Guo et al., 2017; Ma et al., 2012). As the same time, thicker leaves exhibit heightened efficiency in utilizing light energy to synthesize organic matter (Jinwen et al., 2009; Murchie et al., 2005), which helps accumulate more nutrients and enhance the plant’s resistance to diseases. The palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll are crucial mesophyll tissues. Palisade mesophyll is primarily responsible for efficiently conducting photosynthesis, thereby accumulating energy and nutrients for the plant (Zhang et al., 2022). Meanwhile, the spongy mesophyll features large cell gaps and primarily functions to store water and facilitate gas exchange, maintaining water balance and gas circulation within the plant (Tamang et al., 2023). Their synergistic effect is vital in maintaining leaf stability and enhancing plant’s disease resistance. For example, Wang et al. (2022b) found that the decreased expression of CmNF-YB8 leads to improved drought resistance in chrysanthemum by altering leaf anatomy. Specifically, this modification includes a decrease in stomatal opening and the development of a thicker epidermal cuticle. Walnuts exhibit enhanced disease resistance against Xanthomonas arboricola pv. juglandis through altered leaf anatomy, characterized by reduced stomatal length and area, as well as an increased thickness ratio of spongy to palisade mesophyll (Yang et al., 2021). In our study, leaves treated with MT-DZY 6715 exhibited increased leaf thickness (Ln), palisade mesophyll thickness (Tpa) compared to the control group, and the treated leaves had a significantly higher ratio of palisade mesophyll to sponge tissue (PS) and tissue compactness (CTR), as well as reducing tissue looseness (SR) (Figure 5). Furthermore, the stomata of the leaves treated with MT-DZY6715 decrease in stomatal opening, and the stomatal characteristic index was also significantly lower compared to the control, MT, and DZY 6715 treatment (Figure 3). These structural changes further suggested that C. oleifera leaves treated with MT-DZY 6715 enhanced resistance to the infiltration of pathogens.
To further investigate the mechanism by which MT-DZY 6715 treatment enhances the disease resistance of C. oleifera, we analysis the molecular mechanisms underlying MT-DZY 6715-induced resistance enhancement using transcriptome. In this study, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis indicated that the secondary metabolites biosynthesis played a pivotal role in C. oleifera when treated with MT-DZY 6715. Previous studies have demonstrated that the synthesis of secondary metabolites in plants is significantly influenced by a range of transcription factors (TFs), including WRKY (Chen et al., 2017), MYB (Zhao et al., 2022b), AP2/ERF (Mizoi et al., 2012), NAC (Danielsson et al., 2011), bHLH (Sun et al., 2018). Among these, WRKY transcription factors play a pivotal role in regulating the biosynthesis of various secondary metabolites, like phenols, lignin, flavonoids, tannins, etc. For instance, Tang et al. (2023) research revealed that Paeonia lactiflora can regulate its secondary cell wall thickness to enhance stem strength through modulation by TF PlWRKY41a. Wang et al. (2022a) have demonstrated that group IIc WRKY TFs directly binds to the promoter of GhMKK2, regulating its expression and triggering a novel mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade involving GhMKK2, GhNTF6, and GhMYC2. By upregulating various flavonoid biosynthesis-related genes expressed by GhMYC2, the accumulation of flavonoids was increased, thereby enhancing cotton’s resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum. Similarly, HvWRKY23 regulates the expression of genes such as PAL, C4H, 4CL, HCT, Laccase15, and UDPGT, promoting the biosynthesis of favonoid glycoside and Hydroxycinnamic acid amides, which strengthens cell walls and enhances barley resistance to Fusarium head blight (Karre et al., 2019). In potatoes, StNAC43 activates the StMYB8, and subsequently, StMYB8 directly regulates the expression of secondary cell wall biosynthesis genes such as HCT, PHT, and CHS, enhancing the structure and function of cell wall, thereby increasing potato resistance to late blight (Yogendra et al., 2017). In addition, GbERF1-like, acting as a positive regulator of lignin synthesis, enhances lignin accumulation in cotton plants by promoting the expression of genes-related to plant secondary metabolism, including PAL, C4H, C3H, HCT, CCR, and F5H. Consequently, this strengthens the cotton plants’ resistance to Verticillium wilt, a disease induced by Verticillium dahlia (Guo et al., 2016). Furthermore, according to Li et al. (2020) reported that the enhancement of rice disease resistance is attributed to the thickening of sclerenchyma cells near the epidermis due to OsMYB30-induced lignin accumulation, which inhibits pathogen penetration and augments rice immunity. In this study, the expression of transcription factors such as MYBP, AP2, MYBP, WRKY33, WRKY22, and ERF1 was activated after treatment with MT-DZY6715, which induced the expression of genes associated with the secondary metabolic pathways in C. oleifera, including PAL, CAL, Laccase, HCT, and CHI. Furthermore, the expression of these genes activated the secondary metabolic pathways, leading to the accumulation of secondary metabolites and ultimately enhancing the disease resistance of C. oleifera.
Lignin biosynthesis is a core branch of plant secondary metabolism, with its foundation rooted in three primary hydroxycinnamyl alcohols: p-coumaryl alcohol, coniferyl alcohol, and sinapyl alcohol (Yao et al., 2021). These alcohols undergo radical coupling reactions to synthesize lignin. During the process of lignin biosynthesis, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL), 4-coumarate:CoA ligase (4CL), and cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) play crucial roles (Ma et al., 2023). The process initiates with phenylalanine, which is converted into cinnamic acid under the action of PAL. Subsequently, cinnamic acid undergoes hydroxylation catalyzed by C4H, producing p-coumaric acid (Yao et al., 2021). Then, p-coumaric acid is hydroxylated at C3 position catalyzed by coumarate 3-hydroxylase (C3H), generating caffeic acid. The hydroxyl group at the C3 position of caffeic acid is further methylated by cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (COMT), resulting in the production of ferulic acid (Choi et al., 2023; Marchiosi et al., 2020). This series of transformations provides the necessary intermediates for subsequent lignin monomer synthesis. Next, p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid undergo consecutive catalysis by enzymes, including 4CL, cinnamoyl-CoA reductase (CCR), cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD), quinate/shikimate p-hydroxycinnamoyltransferase (HCT), p-coumaroylshikimate 3’-hydroxylase (C3’H), and caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase (CCoAOMT), forming monolignols—the precursors of lignin (Liu et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2022a). Finally, these monolignol precursors, catalyzed by lignin-forming enzymes, particularly peroxidases (PRX) and laccases (LACs), undergo polymerization through radical reactions on the cell wall, resulting in the formation of lignin (Blaschek and Pesquet, 2021; Jalal et al., 2025; Peracchi et al., 2024). This process enhances the stability and mechanical strength of plant cell walls, thereby improving the plant’s resistance to external environmental and biological stresses (Han et al., 2022; Yadav and Chattopadhyay, 2023). In our research, compared to the control group, the application of MT-DZY 6715 significantly increased the activity of PAL, C4H, 4CL, CAD, and laccase. This synergistic enhancement of these enzyme activities that associated with disease resistance defense, promoted the synthesis and accumulation of lignin, thereby effectively enhanced the resistance of C. oleifera to anthracnose.
The plant cell wall, comprising intricate components such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, stands as a formidable physical barrier, crucial for safeguarding plants against pathogen invasion (Lorrai and Ferrari, 2021). Within this structure, cellulose molecules coalesce into microfibrils, forming the foundational scaffold of the cell wall. Pectin, on the other hand, plays a pivotal role in maintaining the structural integrity and mechanical properties of the cell wall, while also participating in plant defense mechanisms by modulating cell wall permeability and signaling pathways (Bidhendi and Geitmann, 2016). Lakshmesha et al. (2005) reported that the decreased activities of cellulase and pectinase hindered the degradation of cell walls, and effectively delaying the spread of anthracnose on pepper fruits. Similarly, Li et al. (2018) found that intercropping potato onion with tomato stimulates the roots to reduce the activities of cellulase and pectinase, thereby inhibiting the growth of the soil-borne pathogen Verticillium dahliae and enhancing tomato’s resistance to Verticillium wilt. According to Xiang et al. (2025), MT effectively enhanced mango resistance to anthracnose by inducing the expression of the IF MiWRKY45, which in turn activated the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway, and promoted the synthesis of lignin and other defense compounds. Similarly, research by Sun et al. (2021) suggested that to a single treatment, the combined application of MT and Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1 markedly hinders the invasion and spread of Botrytis cinerea by enhancing defense-related enzyme activities, such as POD, PAL and PPO, as well as accumulating total phenolics and lignin content. Consequently, this combination fortifies the mechanical strength of fruit cell walls, thereby enhancing apple fruit resistance to gray mold disease. According to our experimental results, treatment with MT-DZY 6715 effectively inhibited both cellulase and pectinase activities, maintaining elevated levels of cellulose and protopectin in the leaves of C. oleifera, which better preserved the mechanical properties of C. oleifera cell walls and ultimately enhanced its disease resistance.
5 Conclusion
In summary, the application of MT-DZY 6715 effectively inhibits the growth of C. siamense, consequently decreasing the incidence of C. oleifera anthracnose. The structural characteristics of C. oleifera leaves were fortified, resulting in an elevated disease resistance, after being treated with MT-DZY 6715. Additionally, MT-DZY 6715 treatment stimulates the expression of genes associated with secondary metabolic pathways, increasing the activities of enzymes like PAL, 4AL, C4H, and CAD, while simultaneously suppressing the activities of cellulase and pectinase. These combined effects synergistically promote the accumulation of secondary metabolites, maintain the mechanical integrity of cell walls, and enhance the resistance of C. oleifera against anthracnose. Therefore, MT-DZY 6715 emerges as a promising biological control agent for managing C. oleifera anthracnose. However, future research is still needed to comprehensively evaluate the long-term prevention and control effects of MT-DZY 6715 under different environmental conditions through field trials. Additionally, the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between MT-DZY 6715 and C. oleifera should be explored in depth using transcriptomics and proteomics. Furthermore, exploring potential synergistic effects between MT-DZY 6715 and other biocontrol agents or chemical pesticides to enhance the integrated disease control efficacy. Collectively, these future research paths hold significant potential for promoting the sustainable management of C. oleifera anthracnose, offering novel technological support and solutions for the healthy development of the C. oleifera industry.
Data availability statement
The transcriptome data presented in this study have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) with the accession number PRJNA1268391.
Author contributions
FW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Project administration. ZA: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Validation, Visualization, Methodology. HZ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. RP: Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis. DL: Writing – original draft, Visualization. JW: Visualization, Writing – original draft, Methodology. JD: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 32160395, 32160394, 32460409), Joint Special Project for Agriculture of Yunnan Province (202301BD070001-102, 202301BD070001-155), and “High-level Talents Training Support Program” of Yunnan Province (XDYC-QNRC-2022-0226, YNWR-QNBJ-2020-205), Southwest Forestry University Forestry Science in Yunnan Province First-class Construction Discipline (LXXK-2024Z08).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1593369/full#supplementary-material
References
Abu-Goukh, A. B. A. and Bashir, H. A. (2003). Changes in pectic enzymes and cellulase activity during guava fruit ripening. Food Chem. 83, 213–218. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(03)00067-0
Accioly, A., do, N., Farias, R., and Arruda, E. C. P. (2024). Plants in the caatinga possess multiple adaptative leaf morphoanatomical traits concurrently, a pattern revealed from a systematic review. J. Arid Environ. 222, 105162. doi: 10.1016/j.jaridenv.2024.105162
Ahammed, G. J., Wu, M., Wang, Y., Yan, Y., Mao, Q., Ren, J., et al. (2020). Melatonin alleviates iron stress by improving iron homeostasis, antioxidant defense and secondary metabolism in cucumber. Sci. Hortic. 265, 109205. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2020.109205
Al Farraj, D. A. and Elshikh, M. S. (2023). Biocontrol of Fusarium wilt disease by endophytic Bacillus xiamenensis BS10 isolated from the root nodules of Brassica nigra (mustard plant) and analysis of defence molecular biomarkers in the greenhouse and field trial. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 128, 102169. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2023.102169
Anjali, K., Korra, T., Thakur, R., Arutselvan, R., Kashyap, A. S., Nehela, Y., et al. (2023). Role of plant secondary metabolites in defence and transcriptional regulation in response to biotic stress. Plant Stress 8, 100154. doi: 10.1016/j.stress.2023.100154
Arnao, M. B. and Hernández-Ruiz, J. (2014). Melatonin: Plant growth regulator and/or biostimulator during stress? Trends Plant Sci. 19, 789–797. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2014.07.006
Ashraf, M. A., Ullah, S., Ahmad, I., Qureshi, A. K., Balkhair, K. S., and Abdur Rehman, M. (2014). Green biocides, a promising technology: Current and future applications to industry and industrial processes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 94, 388–403. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6371
Ayala-Ramos, M. A., Montaño-Arias, S. A., Terrazas, T., and Grether, R. (2024). Ecological implications of stomatal density and stomatal index in the adult stage of Mimosa L. (Leguminosae, Caesalpinioideae). Protoplasma 261, 477–486. doi: 10.1007/s00709-023-01909-8
Bai, X., Li, Q., Zhang, D., Zhao, Y., Zhao, D., Pan, Y., et al. (2023). Bacillus velezensis Strain HN-Q-8 Induced Resistance to Alternaria solani and Stimulated Growth of Potato Plant. Biol. (Basel) 12, 856. doi: 10.3390/biology12060856
Bidhendi, A. J. and Geitmann, A. (2016). Relating the mechanics of the primary plant cell wall to morphogenesis. J. Exp. Bot. 67 (2), 449–461. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv535
Bisquert, R. J., Muñiz-Calvo, S., and Guillamón, J. M. (2018). Protective role of intracellular melatonin against oxidative stress and UV radiation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Front. Microbiol. 9, 318. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00318
Blaschek, L. and Pesquet, E. (2021). Phenoloxidases in plants—How structural diversity enables functional specificity. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 754601. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.754601
Caulier, S., Gillis, A., Colau, G., Licciardi, F., Liépin, M., Desoignies, N., et al. (2018). Versatile antagonistic activities of soil-borne Bacillus spp. and Pseudomonas spp. against Phytophthora infestans and other potato pathogens. Front. Microbiol 9, 143. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00143
Chen, X., He, Y., Wang, Z., Niu, A., Xue, Y., Zhou, D., et al. (2023). Research progress and management strategies of fungal diseases in Camellia oleifera. Front. Microbiol. 14, 1215024. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1215024
Chen, F., Hu, Y., Vannozzi, A., Wu, K., Cai, H., Qin, Y., et al. (2017). The WRKY transcription factor family in model plants and crops. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 36 (5-6), 311–335 doi: 10.1080/07352689.2018.1441103
Chen, X., Sun, C., Laborda, P., He, Y., Zhao, Y., Li, C., et al. (2019). Melatonin treatments reduce the pathogenicity and inhibit the growth of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Plant Pathol. 68, 288–296. doi: 10.1111/ppa.12954
Choi, S. J., Lee, Z., Kim, S., Jeong, E., and Shim, J. S. (2023). Modulation of lignin biosynthesis for drought tolerance in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1116426. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1116426
Dal Magro, L., de Moura, K. S., Backes, B. E., de Menezes, E. W., Benvenutti, E. V., Nicolodi, S., et al. (2019). Immobilization of pectinase on chitosan-magnetic particles: Influence of particle preparation protocol on enzyme properties for fruit juice clarification. Biotechnol. Rep. 24, e00373. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00373
Danielsson, M., Lundén, K., Elfstrand, M., Hu, J., Zhao, T., Arnerup, J., et al. (2011). Chemical and transcriptional responses of Norway spruce genotypes with different susceptibility to Heterobasidion spp. infection. BMC Plant Biol. 11, 154. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-11-154
Elnahal, A. S. M., El-Saadony, M. T., Saad, A. M., Desoky, E. S. M., El-Tahan, A. M., Rady, M. M., et al. (2022). The use of microbial inoculants for biological control, plant growth promotion, and sustainable agriculture: A review. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 162 (4), 759–792. doi: 10.1007/s10658-021-02393-7
Fan, Y., He, X., Dai, J., Yang, N., Jiang, Q., Xu, Z., et al. (2023). Induced resistance mechanism of bacillus velezensis S3–1 against pepper wilt. Curr. Microbiol 80, 367. doi: 10.1007/s00284-023-03470-2
Fira, D., Dimkić, I., Berić, T., Lozo, J., and Stanković, S. (2018). Biological control of plant pathogens by Bacillus species. J. Biotechnol. 285, 44–55. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2018.07.044
Guo, W., Jin, L., Miao, Y., He, X., Hu, Q., Guo, K., et al. (2016). An ethylene response-related factor, GbERF1-like, from Gossypium barbadense improves resistance to Verticillium dahliae via activating lignin synthesis. Plant Mol. Biol. 91, 305–318. doi: 10.1007/s11103-016-0467-6
Guo, C., Ma, L., Yuan, S., and Wang, R. (2017). Morphological, physiological and anatomical traits of plant functional types in temperate grasslands along a large-scale aridity gradient in northeastern China. Sci. Rep. 7, 40900. doi: 10.1038/srep40900
Han, X., Zhao, Y., Chen, Y., Xu, J., Jiang, C., Wang, X., et al. (2022). Lignin biosynthesis and accumulation in response to abiotic stresses in woody plants. Forestry Res. 2, 9. doi: 10.48130/FR-2022-0009
Hao, Y., Zhou, L., Guo, J., Jin, C., and Guo, K. (2023). Antagonistic microbes isolated from fermentation broth of plant wastes against anthracnose of Camellia oleifera caused by Colletotrichum siamense. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 1–20. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3351177/v1
Hernández-Ruiz, J., Giraldo-Acosta, M., El Mihyaoui, A., Cano, A., and Arnao, M. B. (2023). Melatonin as a possible natural anti-viral compound in plant biocontrol. Plants. 12 (4), 781. doi: 10.3390/plants12040781
Hu, Y., Yang, L., Gao, C., Liao, D., Long, L., Qiu, J., et al. (2022). A comparative study on the leaf anatomical structure of Camellia oleifera in a low-hot valley area in Guizhou Province, China. PloS One 17, e0262509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262509
Jalal, A., Wang, Y., Cai, C., Ayaz, A., Alabbosh, K. F., Khan, K. A., et al. (2025). The architecture of adaptive lignin biosynthesis navigating environmental stresses in plants. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 211 (1), e70012. doi: 10.1111/jac.70012
Jeyaraj, A., Elango, T., Chen, X., Zhuang, J., Wang, Y., and Li, X. (2023). Advances in understanding the mechanism of resistance to anthracnose and induced defence response in tea plants. Mol. Plant Pathol. 24 (10), 1330–1346. doi: 10.1111/mpp.13354
Jiang, S. Q. and Li, H. (2018). First Report of Leaf Anthracnose Caused by Colletotrichum karstii on Tea-Oil Trees (Camellia oleifera) in China. Plant Dis. 102, 674. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-08-17-1195-PDN
Jinwen, L., Jingping, Y., Pinpin, F., Junlan, S., Dongsheng, L., Changshui, G., et al. (2009). Responses of rice leaf thickness, SPAD readings and chlorophyll a/b ratios to different nitrogen supply rates in paddy field. Field Crops Res. 114, 426–432. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2009.09.009
Karre, S., Kumar, A., Yogendra, K., Kage, U., Kushalappa, A., and Charron, J. B. (2019). HvWRKY23 regulates flavonoid glycoside and hydroxycinnamic acid amide biosynthetic genes in barley to combat Fusarium head blight. Plant Mol. Biol. 100, 591–605. doi: 10.1007/s11103-019-00882-2
Khedr, E. H. and Khedr, N. (2024). Enhancing productivity, modifying biochemical parameters, and regulating the phenylpropanoid pathway in “Le-Conte” pears through optimal protocatechuic acid treatments. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 50. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04715-9
Kumar Ahirwar, N., Singh, R., Chaurasia, S., Chandra, R., Prajapati, S., and Ramana, S. (2019). Effective role of beneficial microbes in achieving the sustainable agriculture and eco-friendly environment development goals: A review. Front. Environ. Microbiol. 5, 111. doi: 10.11648/j.fem.20190506.12
Lakshmesha, K. K., Lakshmidevi, N., and Mallikarjuna Aradhya, S. (2005). Changes in pectinase and cellulase activity of Colletotrichum capsici mutants and their effect on Anthracnose disease on capsicum fruit. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 38, 267–279. doi: 10.1080/03235400500094100
Lastochkina, O., Seifikalhor, M., Aliniaeifard, S., Baymiev, A., Pusenkova, L., Garipova, S., et al. (2019). Bacillus spp.: Efficient biotic strategy to control postharvest diseases of fruits and vegetab les. Plants. 8 (4), 97. doi: 10.3390/plants8040097
Li, L., Du, Y., He, C., Dietrich, C. R., Li, J., Ma, X., et al. (2019). Maize glossy6 is involved in cuticular wax deposition and drought tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 70, 3089–3099. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz131
Li, W., Wang, K., Chern, M., Liu, Y., Zhu, Z., Liu, J., et al. (2020). Sclerenchyma cell thickening through enhanced lignification induced by OsMYB30 prevents fungal penetration of rice leaves. New Phytol. 226, 1850–1863. doi: 10.1111/nph.16505
Li, H. Y., Zhou, X. G., and Wu, F. Z. (2018). Effects of root exudates from potato onion on Verticillium dahliae. Allelopathy J. 43, 217–222. doi: 10.26651/allelo.j/2018-43-2-1142
Liu, B., Chen, W., Geng, H., You, L., Qu, X., and Zhou, Y. (2024). Melatonin and fungal metabolites synergistically enhance tomato tolerance to Cd and disease resistance by regulating phytohormones. Sci. Hortic. 327, 112845. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2024.112845
Liu, C., Chen, L., Zhao, R., Li, R., Zhang, S., Yu, W., et al. (2019). Melatonin induces disease resistance to botrytis cinerea in tomato fruit by activating jasmonic acid signaling pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. 67, 6116–6124. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b00058
Liu, W., Jiang, Y., Jin, Y., Wang, C., Yang, J., and Qi, H. (2021). Drought-induced ABA, H2O2 and JA positively regulate CmCAD genes and lignin synthesis in melon stems. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02869-y
Liu, Y., Teng, K., Wang, T., Dong, E., Zhang, M., Tao, Y., et al. (2020). Antimicrobial Bacillus velezensis HC6: production of three kinds of lipopeptides and biocontrol potential in maize. J. Appl. Microbiol 128, 242–254. doi: 10.1111/jam.14459
Liu, D., Yang, K., Du, Q. J., Zhou, H. Q., Wu, J. R., and Wang, F. (2023). The mechanism of enhancing biocontrol efficacy of bacillus tequilensis DZY 6715 induced by melatonin against anthracnose disease in Camellia oleifera. J. West China Forestry Sci. 52, 94–102. doi: 10.16473/j.cnki.xblykx1972.2023.06.013
Lorrai, R. and Ferrari, S. (2021). plants host cell wall damage during pathogen infection: mechanisms of perception and role in plant-pathogen interactions. Plants 10 (2), 399. doi: 10.3390/plants
Lubna, Z., Ahmad, M., Shaheen, S., Sultana, S., Rehman, S., and Amina, H. (2019). Micromorphological investigation of leaf epidermis and seeds of Vitaceae from Pakistan using light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Microsc Res. Tech 82, 335–344. doi: 10.1002/jemt.23102
Ma, J. J., Ji, C. J., Han, M., Zhang, T. F., Yan, X. D., Hu, D., et al. (2012). Comparative analyses of leaf anatomy of dicotyledonous species in Tibetan and Inner Mongolian grasslands. Sci. China Life Sci. 55, 68–79. doi: 10.1007/s11427-012-4268-0
Ma, J., Li, X., He, M., Li, Y., Lu, W., Li, M., et al. (2023). A joint transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the regulation of shading on lignin biosynthesis in asparagus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 1539. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021539
Marchiosi, R., dos Santos, W. D., Constantin, R. P., de Lima, R. B., Soares, A. R., Finger-Teixeira, A., et al. (2020). Biosynthesis and metabolic actions of simple phenolic acids in plants. Phytochem. Rev. 19, 865–906. doi: 10.1007/s11101-020-09689-2
Martinez, J., Gomez, A., Ramirez, C., Gil, J., and Durango, D. (2020). Controlling anthracnose by means of extracts, and their major constituents, from Brosimum rubescens Taub. Biotechnol. Rep. 25, e00405. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00405
Miljaković, D., Marinković, J., and Balešević-Tubić, S. (2020). The significance of bacillus spp. In disease suppression and growth promotion of field and vegetab le crops. Microorganisms. 8 (7), 1037. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8071037
Mizoi, J., Shinozaki, K., and Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. (2012). AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 1819 (2), 86–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.08.004
Muntala, A., Norshie, P. M., Santo, K. G., and Saba, C. K. S. (2020). Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex: pathogen causing anthracnose, gummosis and die-back diseases of cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) in Ghana. Eur. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2, 1–10. doi: 10.24018/ejfood.2020.2.6.146
Murchie, E. H., Hubbart, S., Peng, S., and Horton, P. (2005). Acclimation of photosynthesis to high irradiance in rice: Gene expression and interactions with leaf development. J. Exp. Botany. 56 (411), 449–460. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri100
Ongena, M., Jourdan, E., Adam, A., Paquot, M., Brans, A., Joris, B., et al. (2007). Surfactin and fengycin lipopeptides of Bacillus subtilis as elicitors of induced systemic resistance in plants. Environ. Microbiol 9, 1084–1090. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.01202.x
Peracchi, L. M., Panahabadi, R., Barros-Rios, J., Bartley, L. E., and Sanguinet, K. A. (2024). Grass lignin: biosynthesis, biological roles, and industrial applications. Front. Plant Sci. 15, 1343097. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1343097
Peter, O., Imran, M., Shaffique, S., Kang, S. M., Rolly, N. K., Felistus, C., et al. (2024). Combined application of melatonin and Bacillus sp. strain IPR-4 ameliorates drought stress tolerance via hormonal, antioxidant, and physiomolecular signaling in soybean. Front. Plant Sci. 15, 1274964. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1274964
Reina-Pinto, J. J. and Yephremov, A. (2009). Surface lipids and plant defenses. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 47 (6), 540–549. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.01.004
Sharma, P., Kothari, S. L., Rathore, M. S., and Gour, V. S. (2018). Properties, variations, roles, and potential applications of epicuticular wax: A review. Turk J. Botany. 42 (2), 135–149. doi: 10.3906/bot-1702-25
Shinga, M. H. and Fawole, O. A. (2023). Opuntia ficus indica mucilage coatings regulate cell wall softening enzymes and delay the ripening of banana fruit stored at retail conditions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 245, 125550. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125550
Song, L., Zhang, W., Li, Q., Jiang, Z., Wang, Y., Xuan, S., et al. (2022). Melatonin alleviates chilling injury and maintains postharvest quality by enhancing antioxidant capacity and inhibiting cell wall degradation in cold-stored eggplant fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 194, 112092. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.112092
Sun, C., Huang, Y., Lian, S., Saleem, M., Li, B., and Wang, C. (2021). Improving the biocontrol efficacy of Meyerozyma guilliermondii Y-1 with melatonin against postharvest gray mold in apple fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 171, 111351. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2020.111351
Sun, J., Hui, K., Guo, Z., Li, Y., and Fan, X. (2023). Cellulose and lignin contents are negatively correlated with starch accumulation, and their correlation characteristics vary across cassava varieties. J. Plant Growth Regul. 42, 658–669. doi: 10.1007/s00344-022-10573-w
Sun, X., Wang, Y., and Sui, N. (2018). Transcriptional regulation of bHLH during plant response to stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 503 (2), 397–401. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.123
Tafolla-Arellano, J. C., Báez-Sañudo, R., and Tiznado-Hernández, M. E. (2018). The cuticle as a key factor in the quality of horticultural crops. Sci. Hortic. 232, 145–152. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2018.01.005
Tamang, B. G., Zhang, Y., Zambrano, M. A., and Ainsworth, E. A. (2023). Anatomical determinants of gas exchange and hydraulics vary with leaf shape in soybean. Ann. Bot. 131, 909–920. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcac118
Tang, Y., Lu, L., Huang, X., Zhao, D., and Tao, J. (2023). The herbaceous peony transcription factor WRKY41a promotes secondary cell wall thickening to enhance stem strength. Plant Physiol. 191, 428–445. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiac507
Tiwari, R. K., Lal, M. K., Kumar, R., Mangal, V., Altaf, M. A., Sharma, S., et al. (2022). Insight into melatonin-mediated response and signaling in the regulation of plant defense under biotic stress. Plant Mol. Biol. 1–15. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01202-3
Wang, L., Guo, D., Zhao, G., Wang, J., Zhang, S., Wang, C., et al. (2022a). Group IIc WRKY transcription factors regulate cotton resistance to Fusarium oxysporum by promoting GhMKK2-mediated flavonoid biosynthesis. New Phytol. 236, 249–265. doi: 10.1111/nph.18329
Wang, T., Hu, M., Yuan, D., Yun, Z., Gao, Z., Su, Z., et al. (2020a). Melatonin alleviates pericarp browning in litchi fruit by regulating membrane lipid and energy metabolisms. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 160, 111066. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2019.111066
Wang, X., Kong, L., Zhi, P., and Chang, C. (2020b). Update on cuticular wax biosynthesis and its roles in plant disease resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (15), 5514. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155514
Wang, T., Wei, Q., Wang, Z., Liu, W., Zhao, X., Ma, C., et al. (2022b). CmNF-YB8 affects drought resistance in chrysanthemum by altering stomatal status and leaf cuticle thickness. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 64, 741–755. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13201
Wang, X. Q., Zhao, D. L., Shen, L. L., Jing, C. L., and Zhang, C. S. (2018). Application and mechanisms of Bacillus subtilis in biological control of plant disease, in: Role of Rhizospheric Microbes in Soil: Stress Management and Agricultural Sustainability. Springer Singapore, 225–250. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8402-7_9
Wu, Z., Huang, Y., Li, Y., Dong, J., Liu, X., and Li, C. (2019). Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani via Induction of the Defense Mechanism and Antimicrobial Compounds Produced by Bacillus subtilis SL-44 on Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front. Microbiol 10, 2676. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02676
Xia, Y., Liu, J., Wang, Z., He, Y., Tan, Q., Du, Z., et al. (2023). Antagonistic Activity and Potential Mechanisms of Endophytic Bacillus subtilis YL13 in Biocontrol of Camellia oleifera Anthracnose. Forests 14, 886. doi: 10.3390/f14050886
Xiang, Y., Zhu, L., Liu, J., Liu, G., Meng, L., Xu, X., et al. (2025). Melatonin induces resistance against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides in mango fruit via regulation of defense-related genes by MiWRKY45 transcription factor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol 287, 138606. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138606
Xie, Z., Li, M., Wang, D., Wang, F., Shen, H., Sun, G., et al. (2021). Biocontrol efficacy of Bacillus siamensis LZ88 against brown spot disease of tobacco caused by Alternaria alternata. Biol. Control 154, 104508. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2020.104508
Yadav, S. and Chattopadhyay, D. (2023). Lignin: the building block of defense responses to stress in plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 42 (10), 6652–6666. doi: 10.1007/s00344-023-10926-z
Yang, H., Han, S., He, D., Jiang, S., Cao, G., Wan, X., et al. (2021). Resistance evaluation of walnut (Juglans spp.) against Xanthomonas arboricola and the correlation between leaf structure and resistance. For Pathol. 51, e12659. doi: 10.1111/efp.12659
Yang, G., Qi, Z., Shan, S., Xie, D., and Tan, X. (2024). Advances in separation, biological properties, and structure-activity relationship of triterpenoids derived from camellia oleifera abel. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72 (9), 4574–4586. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09168
Yao, T., Feng, K., Xie, M., Barros, J., Tschaplinski, T. J., Tuskan, G. A., et al. (2021). Phylogenetic occurrence of the phenylpropanoid pathway and lignin biosynthesis in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 12, 704697. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.704697
Yao, X. C., Meng, L. F., Zhao, W. L., and Mao, G. L. (2023). Changes in the morphology traits, anatomical structure of the leaves and transcriptome in Lycium barbarum L. under salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 14, 1090366. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1090366
Yin, Y., Hu, J., Yang, Z., Fang, W., and Yang, J. (2023). Effects of methyl jasmonate and NaCl treatments on the resveratrol accumulation and defensive responses in germinated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 194, 664–673. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.12.012
Yogendra, K. N., Sarkar, K., Kage, U., and Kushalappa, A. C. (2017). Potato NAC43 and MYB8 mediated transcriptional regulation of secondary cell wall biosynthesis to contain phytophthora infestans infection. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 35, 519–533. doi: 10.1007/s11105-017-1043-1
Zhang, Y., Chen, C., Jin, Z., Yang, Z., and Li, Y. (2022). Leaf anatomy, photosynthesis, and chloroplast ultrastructure of Heptacodium miconioides seedlings reveal adaptation to light environment. Environ. Exp. Bot. 195, 104780. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2022.104780
Zhang, Z., Wang, T., Liu, G., Hu, M., Yun, Z., Duan, X., et al. (2021). Inhibition of downy blight and enhancement of resistance in litchi fruit by postharvest application of melatonin. Food Chem. 347, 129009. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129009
Zhang, J., Xie, J., Zhou, Y., Deng, L., Yao, S., and Zeng, K. (2017). Inhibitory effect of Pichia membranaefaciens and Kloeckera apiculata against Monilinia fructicola and their biocontrol ability of brown rot in postharvest plum. Biol. Control 114, 51–58. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2017.07.013
Zhao, X., Li, P., Liu, X., Xu, T., Zhang, Y., Meng, H., et al. (2022a). High temperature increased lignin contents of poplar (Populus spp) stem via inducing the synthesis caffeate and coniferaldehyde. Front. Genet. 13, 1007513. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1007513
Zhao, D., Yu, Y., Shen, Y., Liu, Q., Zhao, Z., Sharma, R., et al. (2019). Melatonin synthesis and function: Evolutionary history in animals and plants. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 10, 441357. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2019.00249
Zhao, Y., Zhang, G., Tang, Q., Song, W., Gao, Q., Xiang, G., et al. (2022b). EbMYBP1, a R2R3-MYB transcription factor, promotes flavonoid biosynthesis in Erigeron breviscapus. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 946827. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.946827
Zhou, J., Xie, Y., Liao, Y., Li, X., Li, Y., Li, S., et al. (2022). Characterization of a Bacillus velezensis strain isolated from Bolbostemmatis Rhizoma displaying strong antagonistic activities against a variety of rice pathogens. Front. Microbiol 13, 983781. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.983781
Zhu, H. and He, C. (2023). Identification and characterization of Colletotrichum species causing tea-Oil Camellia (Camellia oleifera C.Abel) anthracnose in Hainan, China. Forests 14, 1030. doi: 10.3390/f14051030
Zhu, L., Yang, R., Sun, Y., Zhang, F., Du, H., Zhang, W., et al. (2021). Nitric oxide maintains postharvest quality of navel orange fruit by reducing postharvest rotting during cold storage and enhancing antioxidant activity. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 113, 101589. doi: 10.1016/j.pmpp.2020.101589
Keywords: melatonin, Bacillus tequilensis, anthracnose, enzyme activity, transcriptome analysis
Citation: Zhou A, Zhou H, Peng R, Liu D, Wu J, Deng J and Wang F (2025) Melatonin-induced Bacillus tequilensis enhanced the disease resistance of Camellia oleifera against anthracnose by modulating cell wall and phenylpropanoid metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1593369. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1593369
Received: 14 March 2025; Accepted: 19 May 2025;
Published: 09 June 2025.
Edited by:
Esther Menendez, University of Salamanca, SpainReviewed by:
Katarzyna Otulak-Kozieł, Warsaw University of Life Sciences, PolandBeimi Cui, University of Edinburgh, United Kingdom
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Zhou, Peng, Liu, Wu, Deng and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fang Wang, ZmFuZ2VyZnJpZW5kQHN3ZnUuZWR1LmNu; Jia Deng, ZGVuZ2ppYTE5ODNAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Aiting Zhou
Aiting Zhou Huiqin Zhou1,2
Huiqin Zhou1,2 Jia Deng
Jia Deng Fang Wang
Fang Wang