- 1Crop Stress Molecular Biology Laboratory, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqin, Heilongjiang, China
- 2Quality and Safety Institute of Agricultural Products, Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Quality and Safety of Cereals and Their Products, State Administration for Market Regulation, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 4Food Processing Institute, Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
- 5Heilongjiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China
Introduction: Maize is a crucial source of nutrition, and the quality traits such as starch content, oil content, and lysine content are essential for meeting the demands of modern agricultural development. Understanding the genetic basis of these quality traits significantly contributes to improving maize yield and optimizing end-use quality. While previous studies have explored the genetic basis of these traits, further investigation into the quantitative trait loci (QTL) responsible for variations in starch content, oil content, and lysine content still requires additional attention.
Methods: Double haploid (DH) populations were developed via a nested association mapping (NAM) design. Phenotypic data for starch, oil, and lysine content were collected using near-infrared spectroscopy and analyzed via ANOVA. Genotyping employed a 3K SNP panel, and genetic maps were constructed using QTL IciMapping. QTL analysis integrated single linkage mapping (SLM) and NAM approaches, with candidate genes identified via maizeGDB annotation and transcriptome data.
Results: The broad-sense heritability of the populations with a range of 63.98-80.72% indicated the majority of starch content, oil content and lysine content variations were largely controlled by genetic factors. The genetic maps were constructed and a total of 47 QTLs were identified. The phenotypic variation explained (PVE) of the three traits is in a range of 2.60-17.24% which suggested that the genetic component of starch content, oil content and lysine content was controlled by many small effect QTLs. Five genes encoding key enzymes in regulation of starch, oil and lysine synthesis and metabolism located within QTLs were proposed as candidate genes in this study.
Discussion: The information presented herein will establish a foundation for the investigation of candidate genes that regulate quality traits in maize kernels. These QTLs will prove beneficial for marker-assisted selection and gene pyramiding in breeding programs aimed at developing high-quality maize varieties.
Introduction
Maize (Zea mays L.) is one of the most significant crops globally, contributing to 43% of total cereal production worldwide (Žilić et al., 2022). Beyond yield improvement, enhancing kernel quality traits-starch, oil, and lysine has emerged as a priority to meet rising demands for nutrient-dense crops and sustainable biorefineries (Planta and Messing, 2017; Mishra et al., 2025). Starch, constituting 70%–80% of kernel dry weight, directly determines caloric output and industrial utility, while oil (4%–5%) and lysine (0.13%–0.30%) are pivotal for nutritional value, particularly in livestock and human diets (Moro et al., 1996; Comparot-Moss and Denyer, 2009; Ranum et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2019). This composition varies across genotypes and environments, highlighting the genetic complexity underlying carbohydrate and lipid allocation in kernels. Despite decades of genetic research, the interplay between these traits and their genetic networks remains poorly resolved, limiting holistic breeding strategies.
To elucidate the genetic variation in starch, oil, and lysine biosynthesis and metabolism, a multitude of QTL studies have been conducted over the past few years employing various mapping methods and diverse populations. These investigations have successfully identified numerous QTLs associated with quality traits in maize kernels. For instance, six QTLs associated with starch content in maize kernel were identified within a RIL population. Following the application of the bin-map method to refine the QTL intervals, seven genes emerged as candidate genes. Three of these genes encode enzymes are involved in non-starch metabolism, while four genes may function as direct regulators of starch biosynthesis (Wang et al., 2015). Subsequently, a total of 50 QTLs were identified, including 18 novel QTLs, through the integration of single linkage mapping (SLM), joint linkage mapping (JLM), and GWAS within a multi-parent population comprising six recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations (Hu et al., 2021). Many QTLs have been shown to regulate seed oil accumulation in a randomly mated F2:3 population derived from the cross between IHO and ILO (Alrefai et al., 1995; Laurie et al., 2004). These studies have demonstrated that oil content was controlled by numerous genes with individually small effects and mainly additive gene action (Yang et al., 2010). An important high-oil QTL, designated as qHO6, has been successfully cloned from chromosome 6. The candidate gene identified encodes an acyl-CoA:diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT1-2), which is responsible for catalyzing the final step in oil synthesis (Zheng et al., 2008). The major QTL Pal9, which accounts for 42% of the phenotypic variation in palmitic acid content, was identified on maize chromosome 9 within a bi-parental segregating population. The candidate gene Zmfatb, which encodes acyl-ACP thioesterase, is associated with this QTL (Li et al., 2011b). In order to enhance breeding strategies aimed at achieving a balanced amino acid composition in maize kernels, several QTLs associated with lysine content or quality protein maize (QPM)-related traits have been examined in previous studies, including o2 modifiers on chromosomes 5, 7, and 9 (Holding et al., 2011; Wu and Messing, 2014). Recent multi-parent population studies reveal that natural allelic diversity beyond o2 (e.g., o7 and fl2) significantly impacts lysine biosynthesis, as observed in wheat and rice grain quality research (Hung et al., 2017; Kumar et al., 2020).
However, maize exhibits considerable phenotypic and genetic diversity (Ansaf et al., 2024). The molecular diversity in maize is estimated to be two- to fivefold greater than that found in other domesticated grass crops (Buckler et al., 2001). This extensive genetic variation has led to the observation that QTLs are often specialized within distinct populations and parent lines. Consequently, it motivates us to conduct further investigations using relevant germplasm to enhance our understanding of the genetic basis underlying quality traits. In this study, we constructed three DH populations using a NAM design with four quality parents. The genetic maps were developed and conducted subsequent analyses to investigate the genetic basis and identify QTLs associated with starch content, oil content, and lysine content. Additionally, we proposed key genes involved in related biosynthetic pathways within the QTL regions as candidate genes, which may provide valuable insights into the genetic foundation of quality traits in maize kernels and facilitate marker-assisted breeding for high-quality maize.
Materials and methods
Plant materials and growing environment
Four maize inbred lines (X987F, AJ5001, AJ7001, and AJ9010) from Maize Yufeng Biotechnology LLC were collected to construct three DH populations with X987F as the common parent, forming a NAM population. The plants were cultivated using a randomized complete block design across three different locations in 2022: Beijing (BJ, 40°08′N, 116°10′E), Neimeng (NM, 40°31′N, 107°05′E), and Liaoning (LN, 40°82’N, 123°56’E). Each line was grown in single-row plots, 250 cm in length, with 11 plants per row and 60 cm spacing between rows, under natural field conditions. The 11 plants in each row were self-pollinated, and 300 kernels were bulk-sampled from five moderate-sized ears, with an equal number of kernels collected from each ear. These bulk kernels were then used for phenotyping.
Collection and analysis of phenotypic data
Phenotypic data were collected on three phenotypic quality traits of maize, including starch content, oil content, and lysine content. Specifically, a near-infrared reflectance (NIR) spectrometer (DA 7250, Perten Instruments Inc., Sweden) was utilized to assess the quality traits in maize kernels. Each sample underwent scanning three times to obtain an average value. The phenotypic variation of the quality traits was analyzed using R software version 4.0.1 with the “AOV” function (ANOVA). The ANOVA model employed is expressed as y = μ + αg + βe + ϵ, where αg is the effect of the gth line, βe is the effect of the eth environment, and ϵ is the error. All of the effects were considered to be random. These variance components were used to calculate the broad-sense heritability as h2 = σg2/(σg2 + σϵ2/e), where σg2 is the genetic variance, σϵ2 is the residual error, and e is the number of environments. To eliminate the influence of environmental effects, the best linear unbiased predictor (BLUP) value for each line was calculated using a linear mixed model that considered both genotype and environment as random effects in the R function “LME4,” and the trait BLUP values were used for subsequent analyses.
Genotyping and construction of genetic linkage map
The genotype of the three DH populations with their parents was obtained by utilizing the GenoBaits Maize 1K marker panel (Mol Breeding Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shijiazhuang, China). A total of 4,589 SNP markers were identified based on genotyping using a target sequencing platform. The minor allele frequency (MAF) and missing rate were estimated for each population, with SNPs exhibiting MAF < 0.1 or a missing rate > 0.6 being filtered out (Purcell et al., 2007). Following quality control measures, the polymorphic SNPs between the two parental lines were utilized to construct genetic linkage maps through the functions est.rf and est.map from the R/qtl package, employing the Kosambi mapping method (Broman et al., 2003). A joint linkage map for the three DH populations was developed using the CMP module in QTL IciMapping software (version 4.2).
QTL mapping for maize kernel quality traits
Using the genetic linkage maps derived from three DH populations, SLM was conducted utilizing composite interval mapping as previously described (Zeng, 1994; Hu et al., 2021), which was implemented in Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5, according to the methodology of Wang et al. (2010) for each DH population. Model 6 of the Zmapqtl procedure (Basten et al., 1997) in the Composite Interval Mapping module was employed to identify QTLs across the genome by surveying intervals of 1.0 cM between markers within a window size of 10 cM. Forward–backward stepwise regression with five controlling markers was used to account for background contributions from adjacent markers. To determine the threshold logarithm of odds (LOD) value for putative QTLs, 1,000 permutations were performed for each trait in each DH population, and the resulting LOD score threshold ranged from 2.76 to 3.27 (α = 0.05). For simplification purposes, a LOD score threshold of 3.0 was adopted globally. The confidence interval concerning the position of the QTL was estimated using the 1.5-LOD support interval method as articulated in Liu’s study (Liu et al., 2017). Additionally, we utilized the R function “LM” to calculate total PVE by significant individual QTLs.
The NAM module in QTL IciMapping (version 4.2) was used to conduct the nested association mapping. The mapping approach employed was ICIM-ADD (Li et al., 2011a), with a step size set at 1.0 cM. In the same way, 1,000 permutations were performed for each trait. The resulting LOD score threshold ranged from 4.84 to 5.36 (α = 0.05), and we adopted a LOD score of 5.0 as the global threshold.
Identification of candidate genes
All genes located within the QTL support interval were extracted based on their physical position using the Zea mays L. B73 reference genome version 4.0. The functional annotation of genes and information on starch, oil, and lysine metabolism pathways were obtained from the maizeGDB database (http://www.maizegdb.org/). The expression levels of candidate genes in different tissues are derived from public transcriptome data (Yi et al., 2019).
Results
Phenotypic variation and correlation analysis among three traits
Four inbred lines exhibiting starch content ranging from 70.99% to 74.22%, oil content between 4.01% and 5.04%, and lysine content varying from 0.27% to 0.35% were collected for the development of three DH populations. The three DH populations, namely, DHPop1, DHPop2, and DHPop3, comprised 163, 219, and 320 lines, respectively (Table 1). The distributions of all traits within the DH populations showed continuous normality without significant skewness (Figures 1A–C). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed that genotype variance exceeded environmental variance across almost all populations (Table 1), indicating that phenotypic variations were predominantly controlled by genetic factors. In addition, starch content, oil content, and lysine content exhibited average broad-sense heritabilities of 78.40%, 71.69%, and 74.89%, respectively (Table 1). Therefore, the abundant phenotypic variation along with high heritability observed in maize kernel quality traits across the three DH populations provides a solid genetic foundation for identifying new QTLs in maize.
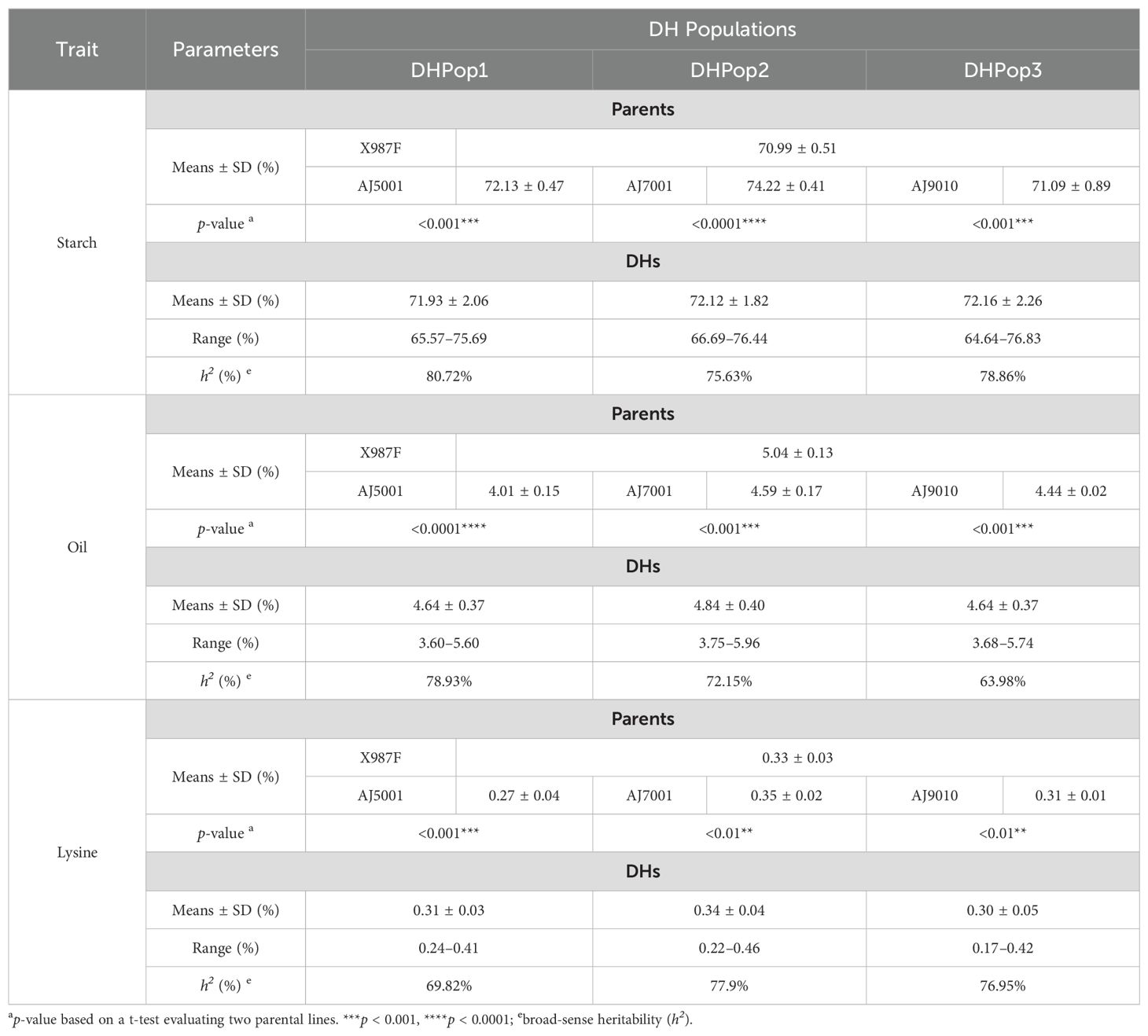
Table 1. The phenotypic performance of four parents, variance and broad-sense heritability of starch content, oil content, and lysine content in the three DH populations.
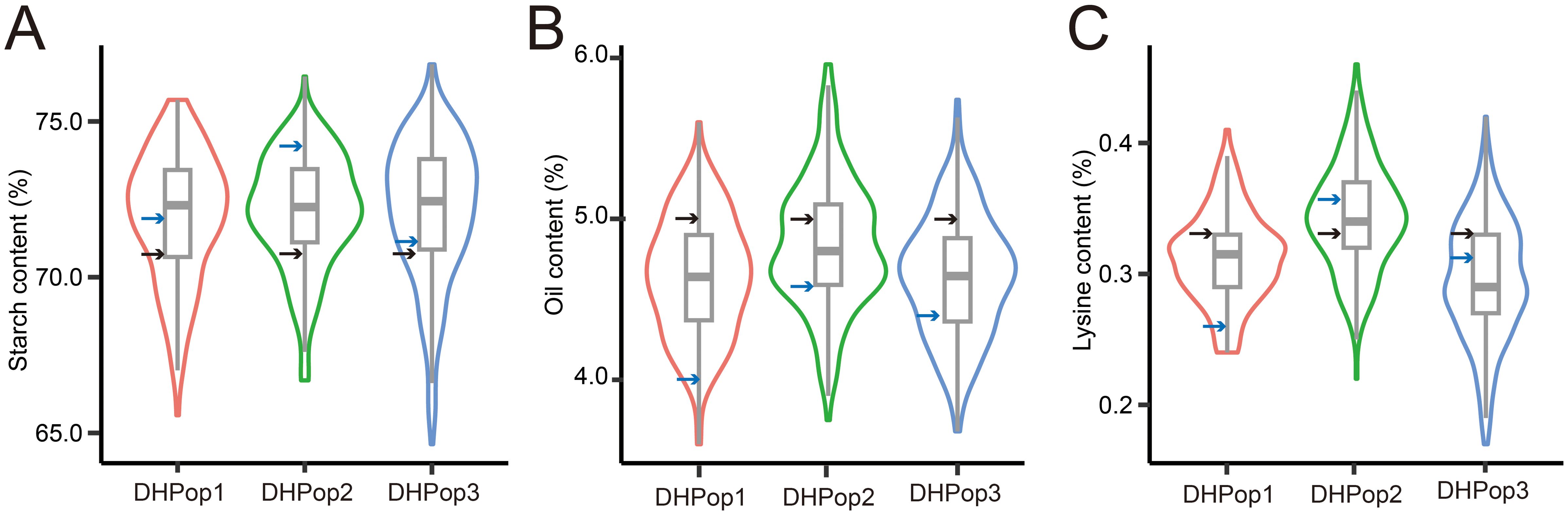
Figure 1. Phenotypic variation analysis of three traits. (A–C) Phenotypic variation in related to starch content, oil content, and lysine content among the three DH populations. The black arrows indicated the values for the common parent line X987F, while the blue arrows represented the values for the unique parent lines.
Genotyping and genetic linkage map
The three DH populations were genotyped by using the GenoBaits Maize 1K marker panel including 4,589 SNP markers. After quality control, DHPop1, DHPop2, and DHPop3 contained 1,266, 1,210, and 1,249 high-quality SNP markers, respectively, and covered all ten maize chromosomes. Based on the reference parental polymorphic loci, three linkage maps were independently constructed, with genetic map lengths of 728, 734, and 749 cM (Supplementary Figure S1). The average genetic distance between adjacent markers was 0.58, 0.61, and 0.62 cM in each DH population, respectively. The combined linkage map for the three DH populations using the CMP module in QTL IciMapping, included 1,993 SNP markers spanning a total genetic distance of 1,343 cM.
Genetic architecture of quality traits dissected via two methods
We performed SLM analysis in each DH population with the composite interval mapping method (Zeng, 1994). In total, 37 QTLs for quality traits were detected, including 14 QTLs for starch content, 13 QTLs for oil content, and 10 QTLs for lysine content (Supplementary Table S1, Supplementary Figure S2). The 1.5-LOD supporting QTL interval averaged 46.26 cM, with a range of 1.7–168.2 cM. The total PVE by all identified QTLs in a population ranged from 20.67% to 53.51% for starch content, 28.71% to 33.98% for oil content, and 7.53% to 37.13% for lysine content (Supplementary Table S1). The PVE for the three traits showed far less than broad-sense heritability (Figure 2A), which suggested that some minor QTLs for these traits cannot be detected in bi-parent populations. Of these QTLs, 75.68% had the PVE <10% (Supplementary Table S1). For starch content, the PVE for each QTL ranged from 3.97% (qSC14 in DHPop3) to 17.24% (qSC04 in DHPop1), and only 28.57% (4/14) of the QTLs had large effects with PVE ≥ 10% (Figure 2A, Supplementary Table S1). For oil content, the PVE for each QTL ranged from 3.16% (qOiL13 in DHPop3) to 14.27% (qOiL07 in DHPop2), and only 23.08% (3/13) of the QTLs had large effects with PVE ≥ 10% (Figure 2A, Supplementary Table S1). For lysine content, the PVE for each QTL ranged from 5.14% (qLys05 in DHPop3) to 12.06% (qLys08 in DHPop3), and only 20.00% (2/10) of the QTLs had large effects with PVE ≥ 10% (Figure 2A, Supplementary Table S1). For each DH population, both parents in each DH population contained the alleles that increased starch content, oil content, and lysine content, respectively (Figures 2B–D, Supplementary Table S1). In addition, the QTL co-localization analysis among these three populations showed partial overlaps among more than two populations. Moreover, 10 QTLs uniquely detected in a given population underscored the genetic diversity of the founders of the DH populations (Figure 2E).
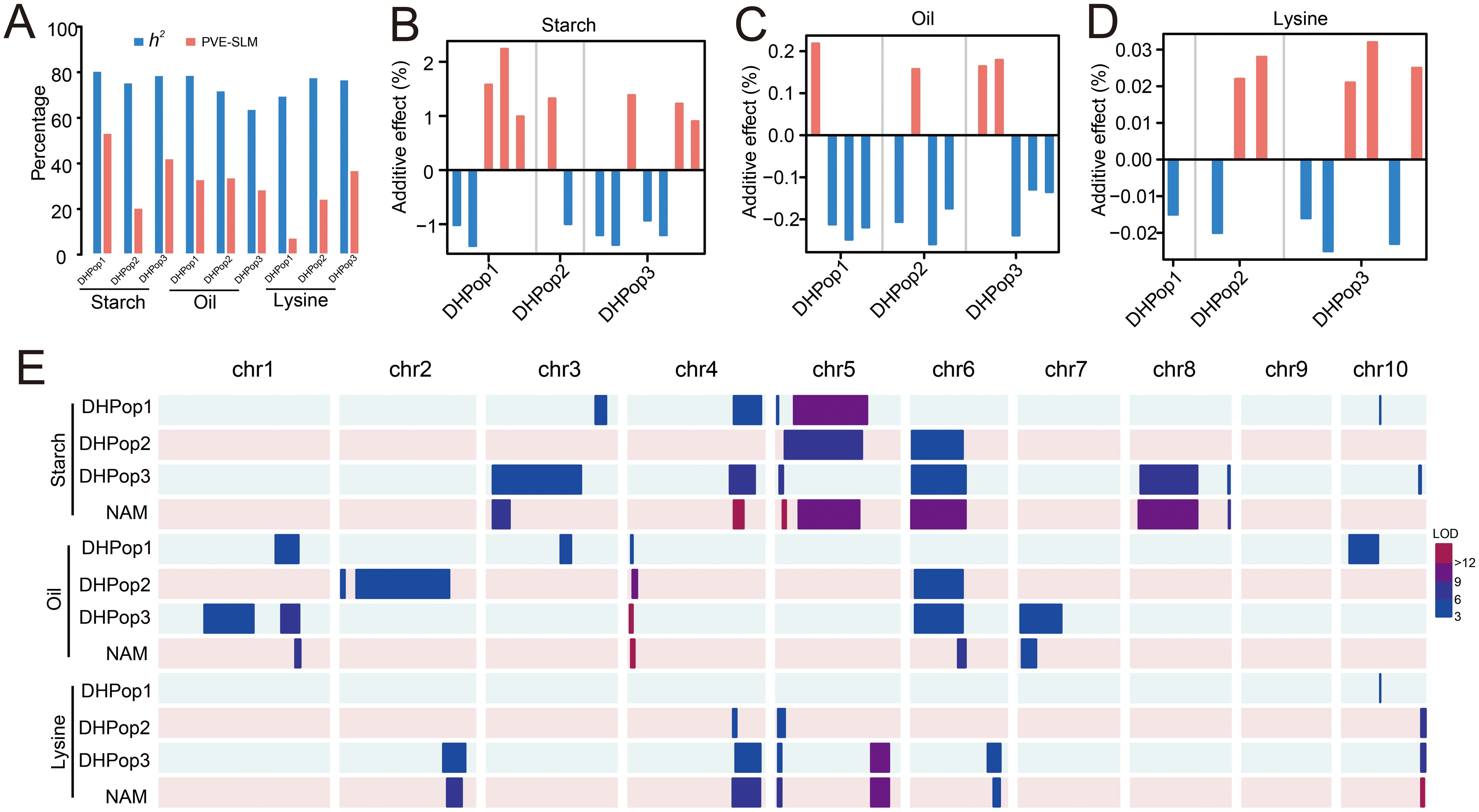
Figure 2. Summary of single QTLs for starch content, oil content, and lysine content identified by SLM and NAM analysis. (A) Broad-sense heritability (h2) and total PVE for single QTLs in each population. (B–D) Effect size and the origin of the increasing alleles of the identified single QTLs. Orange bars indicated that increasing alleles come from the unique parent lines, while blue bars indicated that increasing alleles come from the common parent. (E) Distribution of single QTLs on chromosomes.
Subsequently, we identified a total of 17 QTLs using the NAM analysis, including seven QTLs for starch content, four QTLs for oil content, and six QTLs for lysine content (Table 2, Supplementary Table S2). The total PVE averaged 5.42%, with a range of 2.60%–9.72% in all populations for the three traits. Compared with the SLM results, the QTL interval was expectedly small, with 82.35% (14/17) of the QTL intervals falling within 50 Mb. The QTL co-localization analysis showed that almost all QTL from NAM were overlapping intervals with these from SLM, which indicates that the QTLs mined from the three DH populations established are representative (Figure 2E).
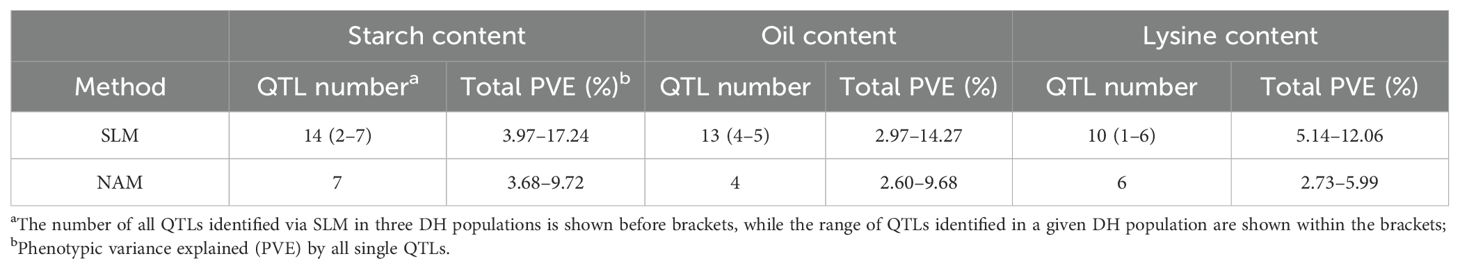
Table 2. Summary of QTLs for starch content, oil content, and lysine content identified via two methods.
Identification of candidate genes underlying the detected QTLs
The genes located within the QTL support interval were extracted, resulting in the identification of 20,367 genes (Supplementary Table S3). According to the annotation in the MaizeGDB database (www.maizegdb.org), genes with the most relevant functional annotation information was nominated as the candidate genes. Phosphoglucomutase2 protein-coding gene pgm2 was the most abundant annotations gene for starch content positioned in 11,195,010–11,201,017 interval of chromosome 5 (Figure 3A, Supplementary Table S3). Expression pattern analysis showed that pgm2 was expressed in all tissues of maize, and the expression levels were relatively the same except in pollen (Figure 3B). There were two annotations genes for oil content. Acyl carrier protein coding gene ACP was positioned in 252129992–252138538 interval of chromosome 1 and expressed in all tissues (Figures 3C, D; Supplementary Table S3). Acyl-coenzyme A oxidase coding gene ACOX was positioned in 7209473–7214489 interval of chromosome 4 (Figure 3E, Supplementary Table S3). ACOX was also expressed in almost all tissues of maize except in pollen (Figure 3F). In addition, the expression levels in the embryo and endosperm vary with different developmental stages (Figure 3F). For lysine content, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 4 coding gene gpc4 and Acyl-activating enzyme-like protein coding gene o7 were positioned in 186104976–186109690 interval of chromosome 5 and 149382212–149384169 interval of chromosome 10, respectively (Figure 3G, I; Supplementary Table S3). gpc4 was expressed in all tissues of maize, and the expression level of o7 was significantly lower in the shoot apical meristem (SAM), ear, cob, and embryo tissues compared to other tissues (Figures 3H, J).
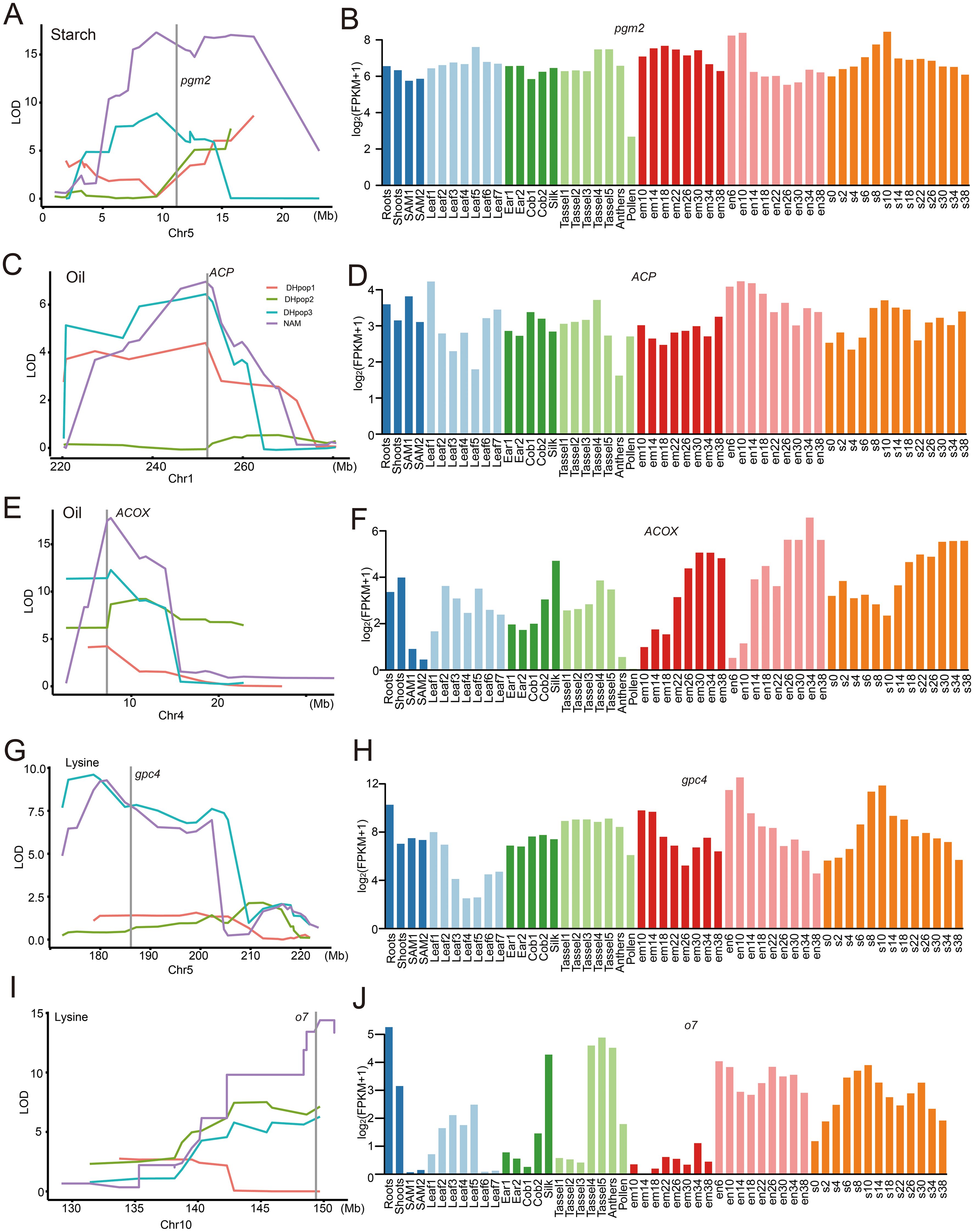
Figure 3. Co-localization of candidate genes (A, C, E, G, I) and their expression levels in different tissues from the public transcriptome data (Yi et al., 2019) (B, D, F, H, J). SAM (shoot apical meristem) 1 and 2 : Vegetative Stages (V1 and V2); Leaf 1-7: the leaves of V1-V7; Ear 1-2: the ear of V1-V2; Cob 1-2: Reproductive Stages (R1-R2); Tassel 1-5: the tassel of V13-V18; em 10-38: the embryo of DAP (days after pollination) 10-38; en 6-38: the endosperm of DAP 6-38; s 0-38: the seed of DAP 6-38.
Discussion
QTL mapping precision
SNP markers represent the most prevalent variations within genomes, and their application in plant breeding has significantly enhanced the precision of QTL mapping and genetic analysis (Bhattramakki et al., 2002; Mammadov et al., 2012; Kaur et al., 2021). By conditioning linked markers during testing, the sensitivity of the test statistic to the positions of individual QTLs is heightened, thus improving the accuracy of QTL mapping (Zeng, 1994). With advancements in sequencing technology, an increasing array of molecular markers has been utilized for QTL mapping, leading to substantial improvements in its accuracy (Schnable et al., 2009; Chia et al., 2012; Bukowski et al., 2018; Fang et al., 2021). In this study, the average physical intervals of the QTLs were 42.11 Mb; 29.79% (14/47) spanned physical intervals of <10 Mb, and 68.09% (32/47) spanned <50 Mb. These findings indicate a considerable enhancement in resolution due to both the large number of employed markers and the suitable population type used in this research. The resolution is likely on the order of 2–3 cM, since pairs of markers that are farther apart rarely exhibit significant levels of linkage disequilibrium.
Genetic basis of maize kernel quality traits in the DH and NAM populations
The maize kernel quality traits including starch content, oil content, and lysine content are complex quantitative traits, and the genetic basis are still unresolved issues at present (Holding et al., 2008; Huang et al., 2021). A set of parameters that elucidates the genetic component underlying trait variation within or among populations will influence the genetic architecture of quantitative traits. Mapping populations represent one of the critical parameters capable of capturing genetic diversity and possessing the power to detect QTLs with small effects (Odell et al., 2022). DH populations have the advantages of retaining homozygosity and genetically identical replicates (Bordes et al., 2006; Foiada et al., 2015; Yan et al., 2017; Chaikam et al., 2019) and nested association mapping simultaneously exploits the advantages of both linkage and association mapping and has been successfully applied to investigate the genetic basis of complex quantitative traits in maize (Yu et al., 2008; Gage et al., 2020). In this study, we developed a NAM population formed by three DH populations for detection of QTLs and identification of candidate genes. The results of the phenotypic and genetic detection showed that there was a wide phenotypic variation extent in starch content (64.64%–76.83%), oil content (3.60-5.96%), and lysine content (0.17-0.46%) and high broad-sense heritability in the DH populations. It illustrated that these traits were mainly controlled by genetic factors. Totally, 47 QTLs were found in the three DH populations and distributed on chromosomes 1–10. Among the identified QTLs, three QTLs (qSC02 in DHPop1 and qSC09 in DHPop3 for starch content, qLys06 in DHPop3 for lysine content) spanned a 104.93 Mb physical interval on chromosome 4. Four QTLs (qSC07 in DHPop2 and qSC11 in DHPop3 for starch content, qOiL08 in DHPop3 and qOiL12 in DHPop3 spanned 86.51 Mb physical interval on chromosome 6. These results indicated that there is cross-over in the regulatory network of starch content, oil content, and lysine content in maize kernel. The average PVE per QTL was 7.89% using SLM in each DH population, whereas it was 5.42% using NAM method across three DH populations. Similar to previous studies, our findings align with the quantitative nature of these quality traits, which are acknowledged to be governed by a multitude of genes and QTLs with minor effects.
Candidate genes underlying quality traits QTLs
For starch content, pgm2 (Zm00001d013428) located in qSC10 was the most abundant annotations among the annotated genes (Figure 3A), which encoded phosphoglucomutase 2. Phosphoglucomutase (PGM) is a phosphoenzyme (EC 5.4.2.2) and catalyzes an important trafficking point in carbohydrate metabolism in cells of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms (Manjunath et al., 1998). In maize, cytosolic isozymes of PGM are encoded by pgm1 and pgm2 (Goodman et al., 1980; Stuber and Goodman, 1983), and the existing levels of PGM are sufficient to maintain the flux of Glc-1-phosphate into glycolysis under O2 deprivation (Manjunath et al., 1998).
There were three most abundant annotations genes for oil content (Figure 3A). ACP (Zm00001d033149) in qOiL10 interval was annotated to be one of the important acyl carrier protein encoding gene. ACP is linked to the malonyl group via a transacylation reaction when acetyl-CoA is carboxylated to malonyl-CoA and participates in de novo fatty acid synthesis in plants and prokaryotes (Kalinger and Rowland, 2023). In qOiL03 interval, there were two abundant annotations genes both related to lipid synthesis metabolic pathways. ACOX (Zm00001d048890) was identified as acyl-coenzyme oxidase encoding gene that involved in the fatty acid β-oxidation pathway in plant peroxisomes (Li et al., 2024; Ruan et al., 2024). ACOX family members may specifically recognize distinct chain lengths of fatty acids and catalyze the first step of peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation to converse fatty acyl-CoAs to trans-2-enoyl CoAs (Chu et al., 1994). This step is thought to be critical the rate of carbon flux in the β-oxidation pathway (Pinfield-Wells et al., 2005).
Zm00001d017121 in qLys08 is one of the small multi-gene family, which encoded a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. In maize cytoplasm, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase protein is synthesized in roots during anoxic conditions and is known to be one of the “anaerobic polypeptides” (Manjunath and Sachs, 1997). In plants, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), a key enzyme in the glycolytic pathway, reversibly converts the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate by coupling with the reduction in NAD1 to NADH (Sirover, 1997) and plays an important role in several cellular processes, including plant hormone signaling, plant development, and transcriptional regulation (Kim et al., 2024). Zm00001d026649 in qLys04 was annotated as opaque endosperm7 (o7) gene. o7 is one of the three most important high-lysine mutants in maize, alongside opaque2 (o2) and floury2 (fl2) (Misra et al., 1972; Miclaus et al., 2011). The o7 mutant endosperm was characterized as having significantly more lysine due to a general reduction in zein levels and an increase in other lysine-rich proteins like the albumins and globulins (Misra et al., 1972; Azevedo et al., 2004).
Conclusion
In this study, four maize inbred lines were used in a NAM design to establish three DH populations. The kernel starch content, oil content, and lysine content exhibited continuously and approximately normal distribution. The analysis of broad-sense heritability indicated that the majority of the three quality traits variations were largely controlled by genetic factors. Nine major and 38 minor effect QTLs were identified based on the genetic linkage map with LOD threshold of 3.00 with PVE in the range of 2.60%–17.24%, which suggested that the genetic component of starch content, oil content, and lysine content was controlled by many small effect QTLs. Furthermore, five main genes that were involved in starch, oil, and lysine synthesis and metabolism pathways were the causal candidate genes underlying the identified QTLs. These QTLs in this study will facilitate the exploration of candidate genes that regulate the quality characteristics of maize kernels. The advancement will also benefit molecular breeding programs that utilize marker-assisted selection to develop maize varieties with optimal quality traits.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Author contributions
ZH: Methodology, Formal Analysis, Data curation, Writing – original draft. JW: Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Software. JLL: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. JWL: Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. LC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Data curation. XZ: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Project administration, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201798) to XZ, the Opening Project of Key Laboratory of Quality and Safety of Cereals and Their Products, State Administration for Market Regulation to XZ, the Talent Introduction Project of Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University (XYB202203), and Daqing City Guiding Science and Technology Plan Project (zd-2024-22) to JL.
Acknowledgments
We thank all members of our laboratories for the helpful discussion and assistance during this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2025.1599530/full#supplementary-material
References
Alrefai, R., Berke, T. G., and Rocheford, T. R. (1995). Quantitative trait locus analysis of fatty acid concentrations in maize. Genome 38, 894–901. doi: 10.1139/g95-118
Ansaf, H., Yobi, A., and Angelovici, R. (2024). High-throughput protein-bound amino acid quantification from maize kernels. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot108632
Azevedo, R. A., Lea, P. J., Damerval, C., Landry, J., Bellato, C. M., Meinhardt, L. W., et al. (2004). Regulation of lysine metabolism and endosperm protein synthesis by the opaque-5 and opaque-7 maize mutations. J. Agric. Food Chem. 52, 4865–4871. doi: 10.1021/jf035422h
Basten, C. J., Weir, B. S., and Zeng, Z. B. (1997). QTL cartographer: a reference manual and tutorial for QTL mapping (Raleigh: Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University).
Bhattramakki, D., Dolan, M., Hanafey, M., Wineland, R., Vaske, D., Register, J. C., et al. (2002). Insertion-deletion polymorphisms in 3’ regions of maize genes occur frequently and can be used as highly informative genetic markers. Plant Mol. Biol. 48, 539–547. doi: 10.1023/a:1014841612043
Bordes, J., Charmet, G., de Vaulx, R. D., Pollacsek, M., Beckert, M., and Gallais, A. (2006). Doubled haploid versus S1 family recurrent selection for testcross performance in a maize population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 112, 1063–1072. doi: 10.1007/s00122-006-0208-3
Broman, K. W., Wu, H., Sen, S., and Churchill, G. A. (2003). R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19, 889–890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg112
Buckler, E. S., Thornsberry, J. M., and Kresovich, S. (2001). Molecular diversity, structure and domestication of grasses. Genet. Res. 77, 213–218. doi: 10.1017/s0016672301005158
Bukowski, R., Guo, X., Lu, Y., Zou, C., He, B., Rong, Z., et al. (2018). Construction of the third-generation Zea mays haplotype map. Gigascience 7, 1–12. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/gix134
Chaikam, V., Molenaar, W., Melchinger, A. E., and Boddupalli, P. M. (2019). Doubled haploid technology for line development in maize: technical advances and prospects. Theor. Appl. Genet. 132, 3227–3243. doi: 10.1007/s00122-019-03433-x
Chia, J. M., Song, C., Bradbury, P. J., Costich, D., de Leon, N., Doebley, J., et al. (2012). Maize HapMap2 identifies extant variation from a genome in flux. Nat. Genet. 44, 803–807. doi: 10.1038/ng.2313
Chu, C., Mao, L. F., and Schulz, H. (1994). Estimation of peroxisomal beta-oxidation in rat heart by a direct assay of acyl-CoA oxidase. Biochem. J. 302, 23–29. doi: 10.1042/bj3020023
Comparot-Moss, S. and Denyer, K. (2009). The evolution of the starch biosynthetic pathway in cereals and other grasses. J. Exp. Bot. 60, 2481–2492. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erp141
Fang, H., Fu, X., Ge, H., Zhang, A., Shan, T., Wang, Y., et al. (2021). Genetic basis of maize kernel oil-related traits revealed by high-density SNP markers in a recombinant inbred line population. BMC Plant Biol. 21, 344. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-03089-0
Foiada, F., Westermeier, P., Kessel, B., Ouzunova, M., Wimmer, V., Mayerhofer, W., et al. (2015). Improving resistance to the European corn borer: a comprehensive study in elite maize using QTL mapping and genome-wide prediction. Theor. Appl. Genet. 128, 875–891. doi: 10.1007/s00122-015-2477-1
Gage, J. L., Monier, B., Giri, A., and Buckler, E. S. (2020). Ten years of the maize nested association mapping population: impact, limitations, and future directions. Plant Cell 32, 2083–2093. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00951
Goodman, M. M., Stuber, C. W., Newton, K., and Weissinger, H. H. (1980). Linkage relationships of 19 enzyme Loci in maize. Genetics 96, 697–710. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.697
Holding, D. R., Hunter, B. G., Chung, T., Gibbon, B. C., Ford, C. F., Bharti, A. K., et al. (2008). Genetic analysis of opaque2 modifier loci in quality protein maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 117, 157–170. doi: 10.1007/s00122-008-0762-y
Holding, D. R., Hunter, B. G., Klingler, J. P., Wu, S., Guo, X., Gibbon, B. C., et al. (2011). Characterization of opaque2 modifier QTLs and candidate genes in recombinant inbred lines derived from the K0326Y quality protein maize inbred. Theor. Appl. Genet. 122, 783–794. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1486-3
Hu, S., Wang, M., Zhang, X., Chen, W., Song, X., Fu, X., et al. (2021). Genetic basis of kernel starch content decoded in a maize multi-parent population. Plant Biotechnol. J. 19, 2192–2205. doi: 10.1111/pbi.13645
Huang, L., Tan, H., Zhang, C., Li, Q., and Liu, Q. (2021). Starch biosynthesis in cereal endosperms: An updated review over the last decade. Plant Commun. 2, 100237. doi: 10.1016/j.xplc.2021.100237
Hung, Q. D., Byrne, P. F., Reid, S. D., and Haley, S. D. (2017). Validation of quantitative trait loci for grain quality-related traits in a winter wheat mapping population. Euphytica 213, 5. doi: 10.1007/s10681-016-1793-0
Kalinger, R. S. and Rowland, O. (2023). Determinants of substrate specificity in a catalytically diverse family of acyl-ACP thioesterases from plants. BMC Plant Biol. 23, 1. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-04003-y
Kaur, G., Pathak, M., Singla, D., Chhabra, G., Chhuneja, P., and Kaur Sarao, N. (2021). Quantitative trait loci mapping for earliness, fruit, and seed related traits using high density genotyping-by-sequencing-based genetic map in bitter gourd (Momordica charantia L.). Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.799932
Kim, J.-Y., Lee, Y.-J., Lee, H.-J., Go, J.-Y., Lee, H.-M., Park, J.-S., et al. (2024). Knockout of osGAPDHC7 gene encoding cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase affects energy metabolism in rice seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (22), 12470. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212470
Kumar, A., Saripalli, G., Jan, I., Kumar, K., Sharma, P. K., Balyan, H. S., et al. (2020). Meta-QTL analysis and identification of candidate genes for drought tolerance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 26, 1713–1725. doi: 10.1007/s12298-020-00847-6
Laurie, C. C., Chasalow, S. D., LeDeaux, J. R., McCarroll, R., Bush, D., Hauge, B., et al. (2004). The genetic architecture of response to long-term artificial selection for oil concentration in the maize kernel. Genetics 168, 2141–2155. doi: 10.1534/genetics.104.029686
Li, H., Bradbury, P., Ersoz, E., Buckler, E. S., and Wang, J. (2011a). Joint QTL linkage mapping for multiple-cross mating design sharing one common parent. PloS One 6, e17573. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017573
Li, L., Li, H., Li, Q., Yang, X., Zheng, D., Warburton, M., et al. (2011b). An 11-bp insertion in Zea mays fatb reduces the palmitic acid content of fatty acids in maize grain. PloS One 6, e2469. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024699
Li, L., Liu, Z., Pan, X., Yao, K., Wang, Y., Yang, T., et al. (2024). Genome-wide identification and characterization of tomato fatty acid β-oxidase family genes KAT and MFP. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (4), 2273. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042273
Liu, J., Huang, J., Guo, H., Lan, L., Wang, H., Xu, Y., et al. (2017). The conserved and unique genetic architecture of kernel size and weight in maize and rice. Plant Physiol. 175, 774–785. doi: 10.1104/pp.17.00708
Mammadov, J., Aggarwal, R., Buyyarapu, R., and Kumpatla, S. (2012). SNP markers and their impact on plant breeding. Int. J. Plant Genomics 2012, 728398. doi: 10.1155/2012/728398
Manjunath, S., Lee, C. H., VanWinkle, P., and Bailey-Serres, J. (1998). Molecular and biochemical characterization of cytosolic phosphoglucomutase in maize. Expression during development and in response to oxygen deprivation. Plant Physiol. 117, 997–1006. doi: 10.1104/pp.117.3.997
Manjunath, S. and Sachs, M. M. (1997). Molecular characterization and promoter analysis of the maize cytosolic glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene family and its expression during anoxia. Plant Mol. Biol. 33, 97–112. doi: 10.1023/a:1005729112038
Miclaus, M., Wu, Y., Xu, J.-H., Dooner, H. K., and Messing, J. (2011). The maize high-lysine mutant opaque7 is defective in an acyl-CoA synthetase-like protein. Genetics 189, 1271–1280. doi: 10.1534/genetics.111.133918
Mishra, S. J., Gopinath, I., Muthusamy, V., Zunjare, R. U., Chand, G., Venkatesh, A. K. T., et al. (2025). Unraveling the interactive effect of opaque2 and waxy1 genes on kernel nutritional qualities and physical properties in maize (Zea mays L.). Sci. Rep. 15, 3425. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87666-5
Misra, P. S., Jambunathan, R., Mertz, E. T., Glover, D. V., Barbosa, H. M., and McWhirter, K. S. (1972). Endosperm protein synthesis in maize mutants with increased lysine content. Science 176, 1425–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.176.4042.1425
Moro, G. L., Habben, J. E., Hamaker, B. R., and Larkins, B. A. (1996). Characterization of the variability in lysine content for normal and opaque2 maize endosperm. Crop Sci. 36, 1651–1659. doi: 10.2135/cropsci1996.0011183X003600060039x
Odell, S. G., Hudson, A. I., Praud, S., Dubreuil, P., Tixier, M.-H., Ross-Ibarra, J., et al. (2022). Modeling allelic diversity of multiparent mapping populations affects detection of quantitative trait loci. G3 (Bethesda). 12 (3), jkac011. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkac011
Pinfield-Wells, H., Rylott, E. L., Gilday, A. D., Graham, S., Job, K., Larson, T. R., et al. (2005). Sucrose rescues seedling establishment but not germination of Arabidopsis mutants disrupted in peroxisomal fatty acid catabolism. Plant J. 43, 861–872. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02498.x
Planta, J. and Messing, J. (2017). Quality protein maize based on reducing sulfur in leaf cells. Genetics 207, 1687–1697. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300288
Purcell, S., Neale, B., Todd-Brown, K., Thomas, L., Ferreira, M. A. R., Bender, D., et al. (2007). PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 559–575. doi: 10.1086/519795
Ranum, P., Peña-Rosas, J. P., and Garcia-Casal, M. N. (2014). Global maize production, utilization, and consumption. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1312, 105–112. doi: 10.1111/nyas.12396
Ruan, D., Jiang, J., Huang, W., Fouad, A. M., El-Senousey, H. K., Lin, X., et al. (2024). Integrated metabolomics and microbiome analysis reveal blended oil diet improves meat quality of broiler chickens by modulating flavor and gut microbiota. Anim. Nutr. (Zhongguo xu mu shou yi xue hui) 19, 453–465. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.04.024
Schnable, P. S., Ware, D., Fulton, R. S., Stein, J. C., Wei, F., Pasternak, S., et al. (2009). The B73 maize genome: complexity, diversity, and dynamics. Science 326, 1112–1115. doi: 10.1126/science.1178534
Sirover, M. A. (1997). Role of the glycolytic protein, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, in normal cell function and in cell pathology. J. Cell. Biochem. 66, 133–140. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4644(19970801)66:2<133::AID-JCB1>3.0.CO;2-R
Stuber, C. W. and Goodman, M. M. (1983). Inheritance, intracellular localization, and genetic variation of phosphoglucomutase isozymes in maize (Zea mays L.). Biochem. Genet. 21, 667–689. doi: 10.1007/BF00498915
Wang, S., Basten, C. J., and Zeng, Z. B. (2010). Windows QTL Cartographer V2.5_011 (Raleigh: Dep. Stat. North Carolina State University).
Wang, T., Wang, M., Hu, S., Xiao, Y., Tong, H., Pan, Q., et al. (2015). Genetic basis of maize kernel starch content revealed by high-density single nucleotide polymorphism markers in a recombinant inbred line population. BMC Plant Biol. 15, 288. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0675-2
Wu, Y. and Messing, J. (2014). Proteome balancing of the maize seed for higher nutritional value. Front. Plant Sci. 5. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00240
Yan, G., Liu, H., Wang, H., Lu, Z., Wang, Y., Mullan, D., et al. (2017). Accelerated generation of selfed pure line plants for gene identification and crop breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01786
Yang, X., Guo, Y., Yan, J., Zhang, J., Song, T., Rocheford, T., et al. (2010). Major and minor QTL and epistasis contribute to fatty acid compositions and oil concentration in high-oil maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 120, 665–678. doi: 10.1007/s00122-009-1184-1
Yi, F., Gu, W., Chen, J., Song, N., Gao, X., Zhang, X., et al. (2019). High temporal-resolution transcriptome landscape of early maize seed development. Plant Cell. 31, 974–992. doi: 10.1105/tpc.18.00961
Yu, J., Holland, J. B., McMullen, M. D., and Buckler, E. S. (2008). Genetic design and statistical power of nested association mapping in maize. Genetics 178, 539–551. doi: 10.1534/genetics.107.074245
Zeng, Z. B. (1994). Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136, 1457–1468. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.4.1457
Zhang, X., Hong, M., Wan, H., Luo, L., Yu, Z., and Guo, R. (2019). Identification of key genes involved in embryo development and differential oil accumulation in two contrasting maize genotypes. Genes 10, 993. doi: 10.3390/genes10120993
Zheng, P., Allen, W. B., Roesler, K., Williams, M. E., Zhang, S., Li, J., et al. (2008). A phenylalanine in DGAT is a key determinant of oil content and composition in maize. Nat. Genet. 40, 367–372. doi: 10.1038/ng.85
Keywords: maize, starch, oil, lysine, QTLs, genetic analysis
Citation: He Z, Wang J, Li J, Li J, Chen L and Zhang X (2025) QTL-based dissection of three key quality attributes in maize using double haploid populations. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1599530. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1599530
Received: 25 March 2025; Accepted: 23 April 2025;
Published: 16 May 2025.
Edited by:
Jun Fang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), ChinaReviewed by:
Hongjun Liu, Shandong Agricultural University, ChinaLovepreet Singh, Michigan State University, United States
Zhenhai Cui, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China
Jincheng Long, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2025 He, Wang, Li, Li, Chen and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianwei Li, bGp3X3BsYW50QHllYWgubmV0; Lei Chen, Y2hlbmd6NTI1MUAxNjMuY29t; Xiaolei Zhang, enhsbnl6QDEyNi5jb20=
 Zitian He1
Zitian He1 Jianwei Li
Jianwei Li Xiaolei Zhang
Xiaolei Zhang