- 1Guangxi Key Laboratory of Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicine, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, China
- 2The Development and Industrialization of Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicinal Materials of Guangxi Universities Engineering Research Center, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, China
- 3The Collaborative Innovation Center of Zhuang and Yao Ethnic Medicine, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, China
- 4Guangxi Engineering Research Center of Ethnic Medicine Resources and Application, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, China
Secondary metabolites are low-molecular-weight organic compounds produced by plants under specific conditions. While they are not directly involved in fundamental growth and developmental processes, they play crucial roles in plant defense, protection, and regulation. These compounds mainly include phenolics, terpenoids, alkaloids, flavonoids, and others. Light, as a key environmental factor regulating the synthesis of plant secondary metabolites, influences their production and accumulation through multidimensional regulatory mechanisms. Different light qualities activate or suppress specific metabolic pathways via signal transduction networks mediated by specialized photoreceptors. Light intensity dynamically modulates secondary metabolite accumulation by affecting photosynthetic efficiency, while photoperiod coordinates metabolic rhythms through circadian clock genes. These light responsive mechanisms constitute a chemical defense strategy that enables plants to adapt to their environment, while also providing critical targets for the directed regulation of medicinal components and functional nutrients. This study provides a review of recent research on the effects of light on plant secondary metabolites, aiming to deepen the understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying light-regulated secondary metabolism. The findings may offer an insight for enhancing bioactive compounds in medicinal plants and developing functional agricultural products.
1 Introduction
During the long evolutionary process, plants have developed a series of secondary metabolites with unique physiological functions, primarily including flavonoid (Ma et al., 2024), terpenoid (Pichersky and Raguso, 2018), alkaloid (Gu et al., 2025) and phenolic (Sheteiwy et al., 2023) compounds. These specialized metabolites not only help plants cope with environmental stresses but also play pivotal roles in fields such as medicine and health, nutritional food, and agricultural production (Brosset and Blande, 2022; Ahmed et al., 2024; Jahan et al., 2025). Among various environmental factors affecting plant growth, the light environment - with its unique spatial distribution, spectral properties, irradiation intensity, photoperiod, and circadian rhythms - elicits distinct physiological responses in plants and profoundly influences the biosynthesis and accumulation of secondary metabolites (Morales et al., 2025). Breakthroughs in modern photobiological research and metabolomics analysis techniques have increasingly elucidated the molecular mechanisms by which light signals regulate plant secondary metabolism, paving innovative pathways for using optical regulation technologies to enhance the content of functional plant compounds.
The regulatory effects of light environment on plant secondary metabolism exhibit multi-dimensional characteristics. From the perspective of spectral properties, specific wavelengths of light can achieve differential biological regulation through specialized photoreceptor systems. UV, for instance, activates the HY5 transcription factor signaling pathway via the UVR8 receptor, enhancing the biosynthesis efficiency of phenolics, flavonoids, and anthocyanins (Shamala et al., 2020; Morales et al., 2025). Blue light, mediated by cryptochrome and phototropin protein complexes, influences the phenylpropanoid metabolism process by acting on transcriptional regulatory networks such as HY5 and MYB (Rai et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020a; Zhang et al., 2025b). Red light, on the other hand, modulates the production of terpenoids through phytochrome mediated hormonal signaling pathways, altering the levels of endogenous hormones (Holalu et al., 2020; Escobar-Bravo et al., 2024). The interactions between these specific light wavelengths and photoreceptors elucidate the response mechanisms of photoreceptors to light signals. In terms of light intensity, it regulates the expression of metabolism-related genes by modifying photosynthetic efficiency, energy allocation, and stress responses, ultimately affecting the accumulation of metabolic products (Borbély et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2024). However, excessive light may induce photoinhibition, disrupting normal metabolic activities (Alsharafa et al., 2014). On the temporal scale, the circadian rhythm system coordinates the synthesis of plant secondary metabolites by perceiving changes in photoperiod (Hoffman et al., 2010). Thus, Understanding the molecular regulatory mechanisms of light signals on plant secondary metabolism holds significant scientific importance and practical value. On one hand, it can reveal the molecular regulatory networks by which plants adapt to their external environment; on the other hand, it provides theoretical support for developing light-based technologies to improve crop quality (Zhang et al., 2024c). This review summarizes the effects of different light characteristics (light quality, intensity, and photoperiod) on plant secondary metabolites and their underlying mechanisms, highlights the progress in the application of light-control technologies in agriculture and medicine, and explores future research directions in this field. The aim is to provide insights for both fundamental research and industrial applications of light-mediated regulation in plant secondary metabolism.
2 Effects of light quality on plant secondary metabolites
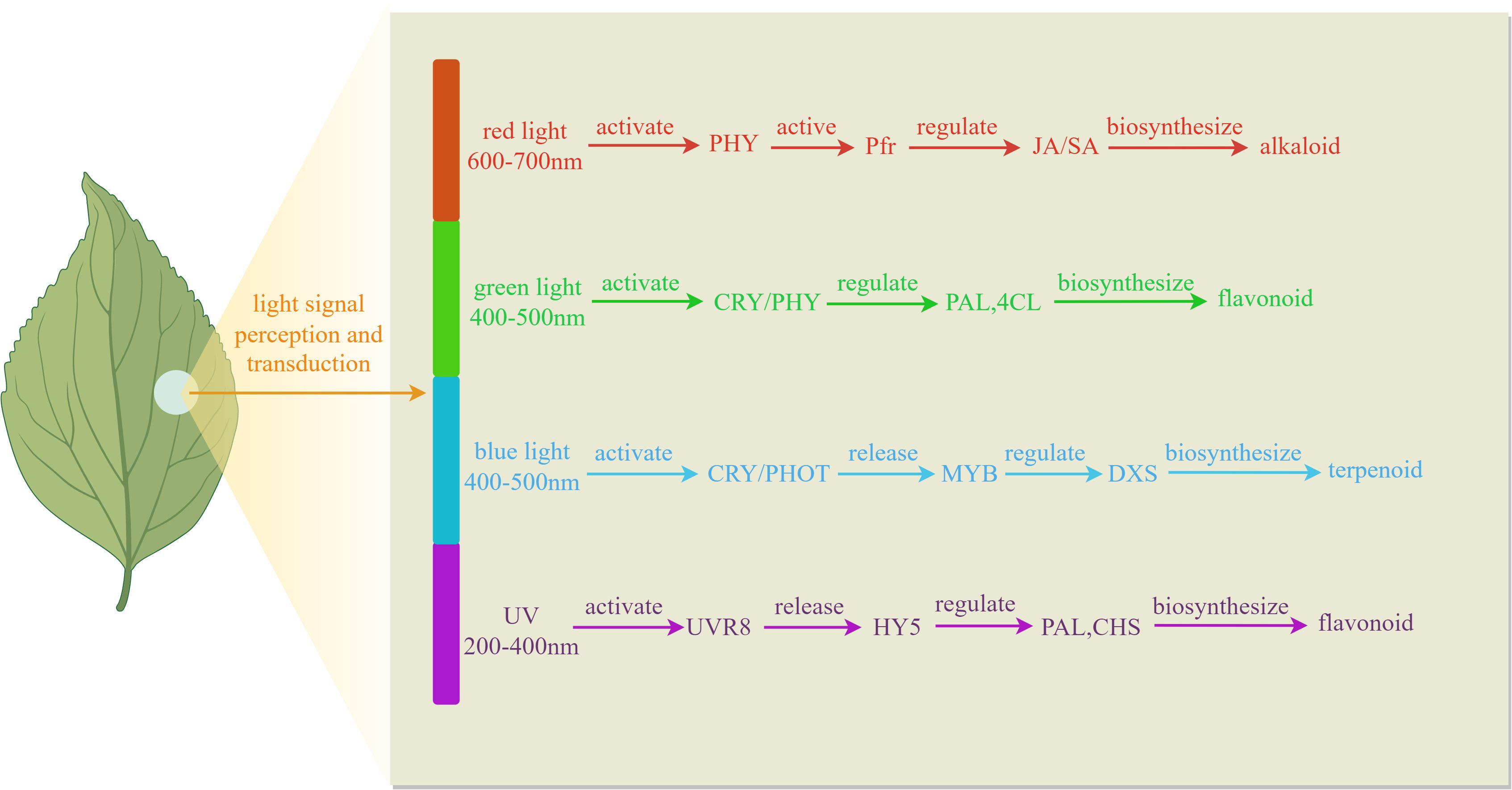
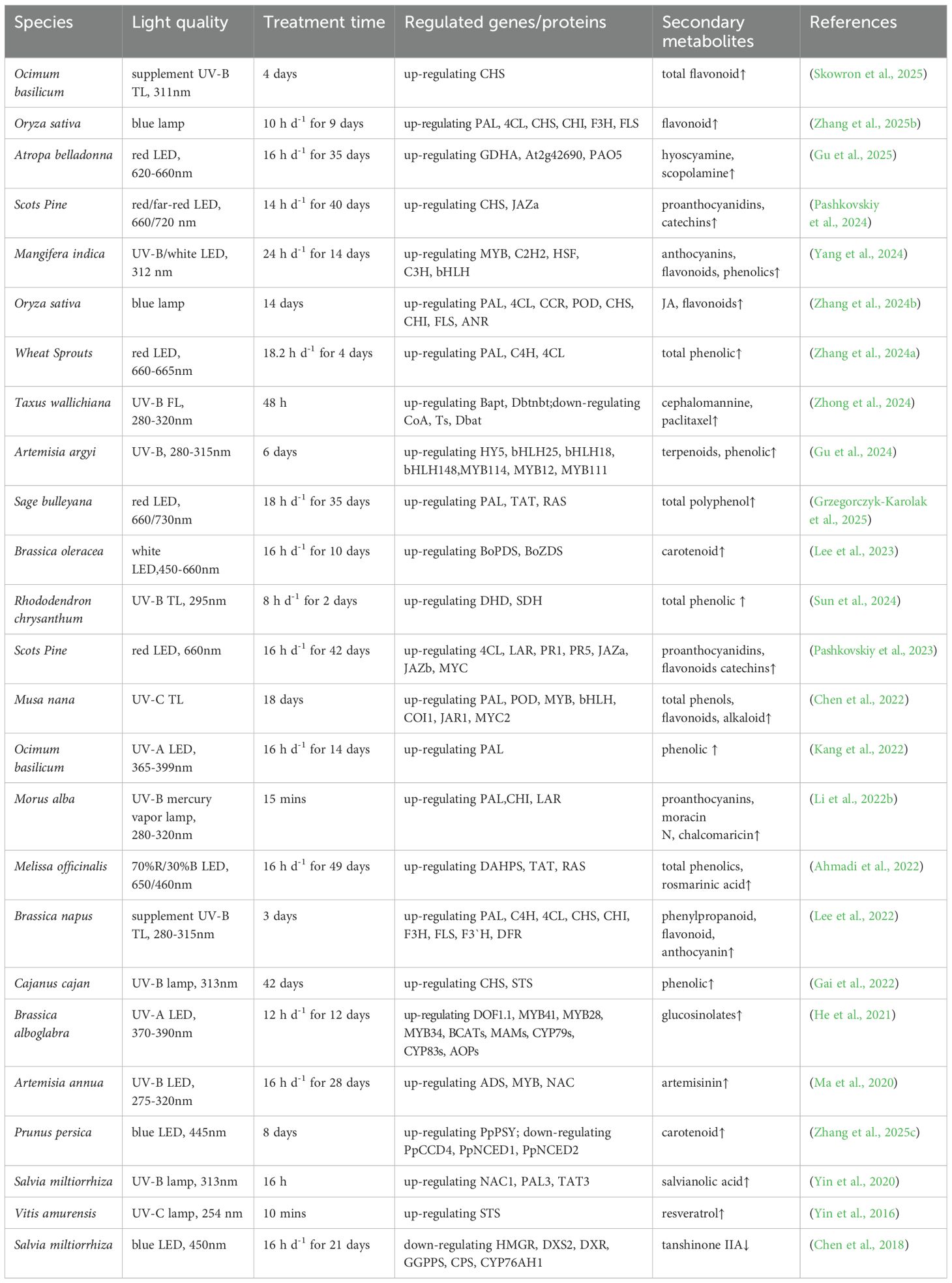
Light quality, as a crucial parameter of the light environment, exerts multidimensional regulatory effects on plant growth, development, and physiological metabolism through specific wavelength combinations. In plant physiology and facility agriculture, light sources can be categorized into visible light, infrared light, and ultraviolet light based on their wavelengths. Among these, visible light can be further divided into various colors such as red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet, which play a regulatory role in plant growth, development, and the accumulation of metabolic products. As illustrated in Figure 1, different wavelengths of light signals are selectively recognized by the plant photoreceptor system, triggering distinct physiological responses that regulate the synthesis of secondary metabolites. As shown in Table 1, differential light treatments influence the expression of different genes.
2.1 UV light
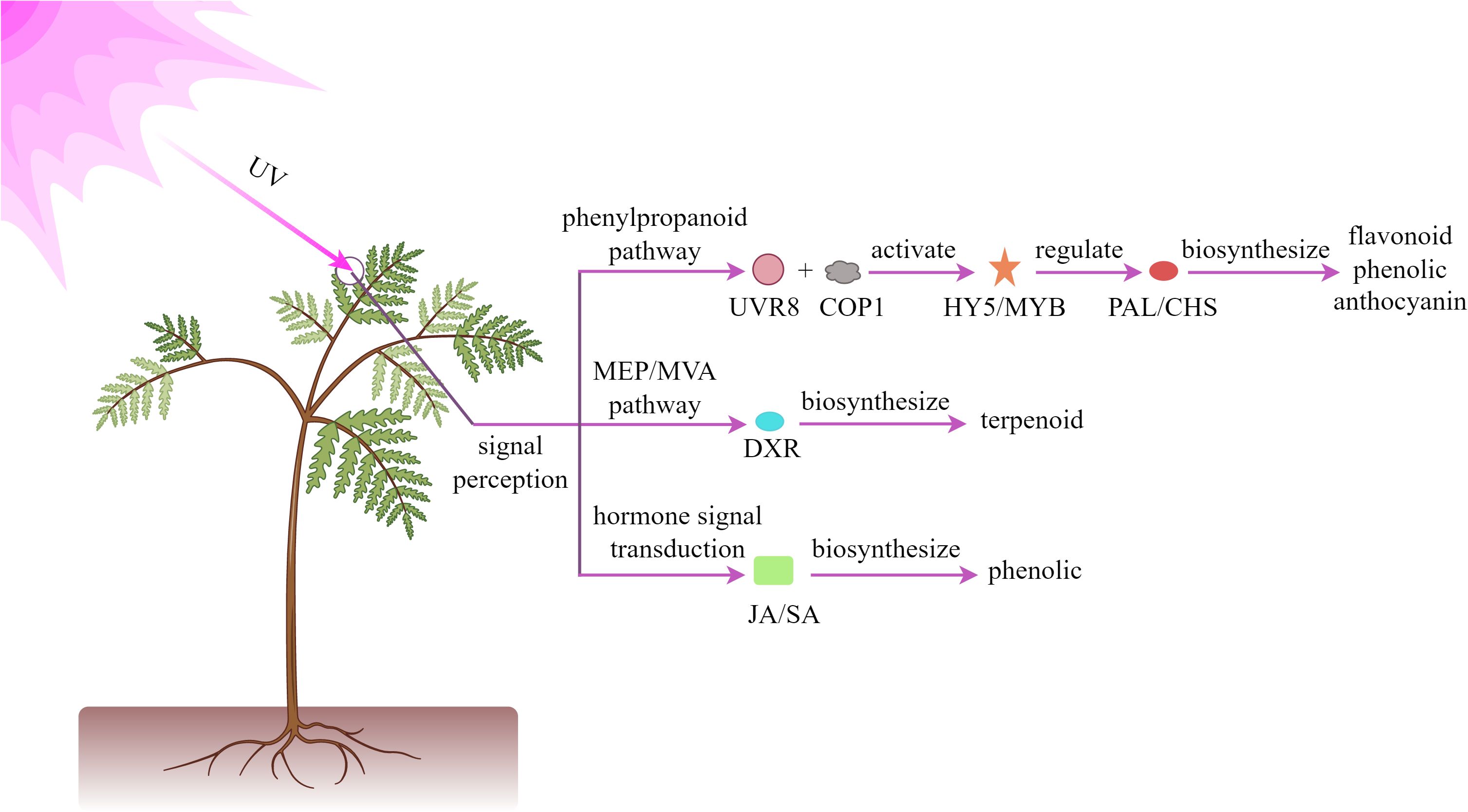
UV radiation, as a significant component of the solar spectrum, can be classified into three primary bands based on wavelength range: UV-A (315–400 nm), UV-B (280–315 nm), and UV-C (200–280 nm). When plants are exposed to UV radiation, they activate a series of defense mechanisms, primarily manifested through the enhanced biosynthesis of specific secondary metabolites, including flavonoids, phenolics, and terpenoids. These substances play crucial roles in plant responses to environmental stresses (Vanhaelewyn et al., 2020; Kivimäenpä et al., 2022). As illustrated in Figure 2, at the molecular level, UV radiation can specifically activate photoreceptor system in plants, promoting the combination of UVR8 photoreceptors with COP1, activating HY5 transcription factor. This subsequently induces the expression of key enzymes in the phenylpropanoid pathway, such as PAL and CHS, thereby enhancing the synthesis and accumulation of anthocyanins and flavonoids. These biochemical responses significantly improve the plant’s resistance to oxidative stress (Shamala et al., 2020; Jaiswal and Agrawal, 2021). Moreover, the terpenoid biosynthetic gene network is dynamically regulated through both the MEP and MVA pathways, ultimately modulating terpenoid diversity and yield (Contreras-Avilés et al., 2024; Zha et al., 2024). Regarding signal transduction, ultraviolet radiation influences the biosynthesis of defensive compounds such as phenolic acids by regulating phytohormone JA and SA pathways (Gai et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2024; Zhou et al., 2025).
Different UV treatments can improve the nutritional quality of agricultural products and the component content of medicinal plants, while their light signals also vary in regulating the biosynthetic genes and hormonal signaling mechanisms in plants. UV-A treatment of Ocimum basilicum upregulates PAL enzyme activity, increasing total phenolic concentration and antioxidant capacity (Kang et al., 2022). UV-A significantly enhances the content of gallotannins and ellagitannins in Eucalyptus camaldulensis by altering the expression of phenolic compounds (Khanal et al., 2025). Under UV-A exposure, the shikimate and MEP pathways are modulated to promote the synthesis of flavonoids and phenolic acids in Lactuca sativa, while the MVA pathway is suppressed, reducing the biosynthesis of sesquiterpenes and triterpenes (Zha et al., 2024). Under UV-B exposure, the total flavonoid and phenolic content is increased in Mangifera indica (Yang et al., 2024), Stevia rebaudiana (Semenova et al., 2024), Lactuca sativa (Skowron et al., 2024), Pelargonium graveolens (Jadidi et al., 2023), Eucommia ulmoides (Xiao et al., 2023), and Oryza sativa (Aimvijarn et al., 2023), enhancing their antioxidant activity. In Vitis vinifera, in addition to boosting secondary metabolite levels, also improves flavor (Narra et al., 2023). UV-B acts on Pennisetum glaucum to increase the content of phytosterols and triterpenoids (Singh and Choudhary, 2025).
Furthermore, UV-B treatment modulates the gene expression involved in plant secondary metabolism. For instance, upon UV-B irradiation, genes such as PAL, C4H, 4CL, CHS, and CHI in Brassica napus are rapidly upregulated within 24 hours, promoting the accumulation of phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, and anthocyanins (Lee et al., 2022). After 48 hours of UV-B exposure in Taxus wallichiana, the expression of Bapt and Dbtnbt genes is upregulated, while CoA, Ts, and Dbat genes are downregulated, leading to increased synthesis of paclitaxel and cephalomannine (Zhong et al., 2024). Through the shikimate and MEP pathways, genes including HY5, bHLH25, bHLH18, bHLH148, MYB114, MYB12, and MYB111 in Artemisia argyi are upregulated, enhancing the production of terpenoid and phenolic compounds (Gu et al., 2024). A 15-minute UV-B irradiation followed by 36 hours of dark incubation upregulates PAL, CHI, and LAR gene expression in Morus alba, promoting the accumulation of proanthocyanins, moracin N, and chalcomaricin, which indicated that appropriate dark incubation under stress conditions facilitates secondary metabolite biosynthesis (Takshak and Agrawal, 2019; Li et al., 2022b). Additionally, in Salicornia europaea, the ABA pathway under UV-B is regulated by ROS, resulting in reduced ABA levels and increased carotenoid content, thereby improving nutritional quality (Fitzner et al., 2023). Regarding UV-C, it upregulates the expression of genes such as PAL, POD, MYB, bHLH, COI1, JAR1, and MYC2 by modulating flavonoid and phenylpropanoid biosynthetic pathways and activating phytohormones, thereby enhancing the accumulation of alkaloids, flavonoids, and phenolics in Musa nana (Chen et al., 2022). Plant responses to UV radiation exhibit significant species-specificity and developmental stage-dependence. Tolerance thresholds to UV radiation vary markedly across plant families and even within the same species at different growth stages (Kang et al., 2022). This characteristic holds crucial implications for modern agricultural practices, particularly in controlled-environment agriculture systems where precise light quality management must be tailored to crop varieties and growth phases. Notably, UV intensities exceeding plant tolerance thresholds can cause photosystem damage and inhibit normal growth, exemplifying the biphasic “low-dose stimulation, high-dose inhibition” response typical of UV-induced physiological effects.
2.2 Blue light
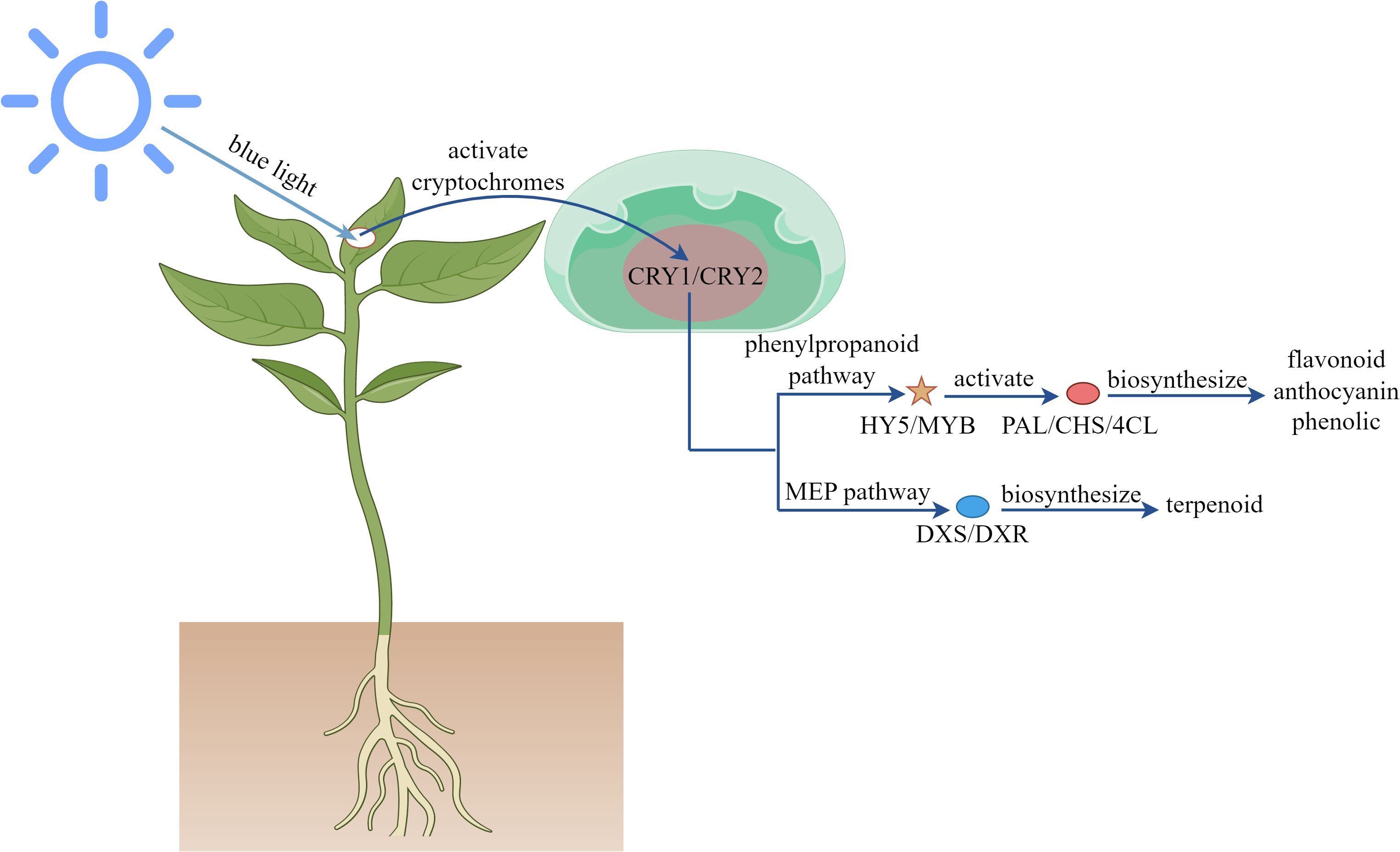
As a vital component of the visible spectrum, blue light plays a crucial regulatory role in plant growth and development. As shown in Figure 3, this specific wavelength activates the plant photoreceptor system, including cryptochromes and phototropins, to mediate photomorphogenesis-inhibiting hypocotyl elongation while promoting leaf expansion and stomatal opening (Wang et al., 2017; Gao et al., 2022; Li et al., 2022a). At the metabolic level, blue light upregulates the expression of transcription factors such as HY5 and MYB, which specifically activated the expression of key enzymes of phenylpropanoid pathway PAL, CHS and 4CL, promoted the accumulation of flavonoids, anthocyanins and phenolics, and enhanced the antioxidant capacity of plants (Wang et al., 2020a; Zhang et al., 2025b). Additionally, blue light modulates the activity of DXS and DXR rate-limiting enzymes by regulating MEP pathway, influencing terpenoid biosynthesis (Lopes et al., 2020; Xie et al., 2021; Cheng et al., 2023). Molecular studies reveal that blue light stabilizes COP1 protein, altering the expression patterns of secondary metabolism-related genes (Liu et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2017; Miao et al., 2022). Optimizing blue light exposure can thus enhance bioactive compound production in medicinal plants and improve the nutritional quality of fruits and vegetables. Empirical studies demonstrate that blue light increases total flavonoids and phenolics in Ocimum basilicum (Fayezizadeh et al., 2024a), Artemisia argyi (Su et al., 2024), Capsicum annuum (Darko et al., 2022), Rhodiola imbricata (Kapoor et al., 2018), and Brassica oleracea (Lee et al., 2023), alongside elevated antioxidant activity. It also promotes JA (Zhang et al., 2023), terpenoid (Morello et al., 2022; Le et al., 2023), and alkaloid (Moranska et al., 2023) accumulation. In Oryza sativa, blue light upregulates PAL, 4CL, CHS, CHI, F3H, and FLS genes, enhancing enzyme activity and flavonoid biosynthesis (Zhang et al., 2025b).
In addition, blue light can interact with selenium nanoparticles(SeNPs) through specific photoreceptors, and the interaction between nano-materials and light environment can be used to regulate plant physiological and biochemical processes. For instance, Mazhar et al. (2024) treated Santalum album with SeNPs under blue LED light, significantly increasing total phenolics, saponins, terpenoids, and flavan-3-ols. In modern controlled-environment agriculture, blue LED lighting is widely adopted for tissue culture, leafy vegetable quality enhancement, and medicinal plant cultivation. However, optimal spectral parameters must be tailored to crop species and growth stages to maximize efficacy while avoiding photoinhibition.
2.3 Red light
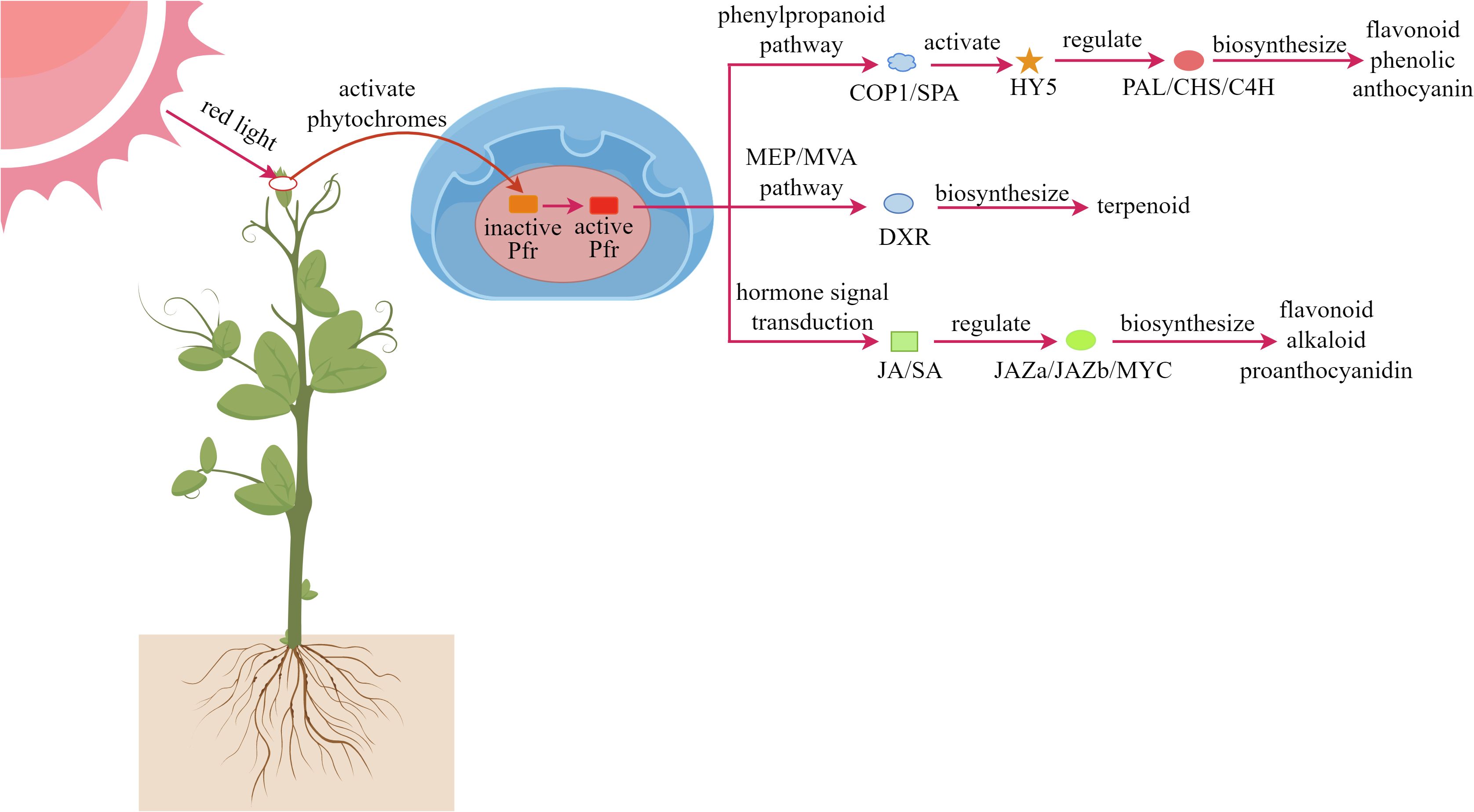
Phytochrome, as a light-sensitive protein complex, is widely distributed in plant cells. Red light can regulate physiological processes in plants through the phytochrome system, triggering a series of complex signal transduction pathways (De Wit et al., 2016; Holalu et al., 2020). As shown in Figure 4, When plants are exposed to red light, photoreceptors such as phytochromes are activated, and these signals are transmitted to the nucleus, triggering a cascade of molecular responses (Viczián et al., 2017; Kwon et al., 2024; Péter et al., 2024). First, the activated Pfr form can interfere with the function of the COP1/SPA protein complex, thereby stabilizing the expression of the HY5 transcription factor (Sweere et al., 2001; Oh et al., 2020). Second, red light upregulates PAL and CHS key enzyme genes in the phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway, promoting the synthesis of antioxidant compounds such as anthocyanins, flavonoids, and phenolics (Pashkovskiy et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024a). Within the MEP/MVA metabolic pathways, red light enhances the expression of the DXR gene, increasing terpenoid production (Lopes et al., 2020; Sankhuan et al., 2022b; Mokhtari et al., 2025). Additionally, red light signaling can synergize with plant hormone systems, particularly the JA and SA pathways, to coordinately regulate the biosynthesis of various defensive secondary metabolites, including anthocyanins and alkaloids (Li et al., 2014; Zhang et al., 2023).
These physiological changes collectively enhance the plant’s ability to cope with environmental stress. Pashkovskiy et al. (2023) demonstrated that under red and far-red light, the content of proanthocyanidins and catechins in Scots Pine are increased and the possible mechanism is to promote the expression of CHS gene. In Triticum aestivum treated with red light for four days, the activity and relative gene expression levels of PAL, C4H, and 4CL were upregulated, effectively stimulating the synthesis of total phenolics and enhancing antioxidant capacity (Zhang et al., 2024a). Under red light, polyphenol accumulation in sage shoot was promoted, accompanied by upregulated PAL, TAT, and RAS gene expression, leading to increased rosmarinic acid content (Grzegorczyk-Karolak et al., 2025). Red light also stimulated the accumulation of catechins, flavonoids, and proanthocyanidins in Scots Pine, likely by promoting the expression of 4CL and LAR genes, as well as the biosynthesis of PR1 and PR5 genes in the SA pathway and the relative expression of JA biosynthesis JAZa, JAZb, and MYC genes (Pashkovskiy et al., 2023). The putrescine biosynthesis pathway is an important precursor for the synthesis of tropane alkaloids, while red light enhances nitrogen metabolism and precursor synthesis in Atropa belladonna by regulating the expression of GDHA, At2g42690, and PAO5 genes, thus promoting the accumulation of tropane alkaloids (Gu et al., 2025). Therefore, red light can specifically activate plant photoreceptors and downstream metabolic pathways, directionally increase the content of plant secondary metabolites, and provide sustainable light regulation strategies for medicinal plant cultivation and agricultural development.
2.4 Green light
Green light, as an essential component of the visible spectrum, plays significant regulatory roles in plant physiology despite its low absorption efficiency by chlorophyll and other photosynthetic pigments. Through cryptochrome-mediated signaling pathways and other photoreceptors, green light not only influences photomorphogenesis and developmental processes but also modulates the biosynthesis and accumulation of secondary metabolites, serving crucial functions in environmental adaptation and defense mechanisms. At the molecular level, green light alters metabolic pathway activity by regulating the expression of PAL and CHS enzyme genes, thereby promoting or suppressing specific secondary metabolite production (Liu et al., 2018). Research demonstrates that green light at appropriate intensities can mitigate photo-oxidative damage while enhancing volatile compound accumulation (Lopes et al., 2020). Notably, green light counteracts blue light-induced suppression of HvNCED gene expression, thereby stimulating secondary metabolic processes (Hoang et al., 2014). Mechanistic studies reveal that green light promotes the accumulation of procyanidin B2/B3 and L-ascorbic acid in Camellia sinensis through downregulation of CRY2/3 and PHOT2 expression (Zheng et al., 2019). Furthermore, synergistic effects emerge when green light is combined with UV irradiation, significantly inducing the accumulation of phenolic compounds and phytohormones (Palma et al., 2022). These findings provide novel insights for light-quality regulation in controlled environment agriculture, particularly for enhancing medicinal compound production through optimized spectral combinations. Future research should focus on elucidating the interaction mechanisms between green light signaling and metabolic networks to facilitate its application in precision agriculture.
2.5 Multiple light qualities
Combined light quality application refers to the use of light with different wavelengths in specific ratios to collectively influence plant growth and development. In terms of the mechanism, different light qualities are perceived by plants through their specific photoreceptors, activating downstream signal transduction networks. This composite light environment, through synergistic regulation, can significantly affect the synthesis and accumulation of plant secondary metabolites, often yielding better results than single-light treatments. For example, in Stevia rebaudiana, the synthesis of phenolic compounds such as neochlorogenic acid, chlorogenic acid, and caffeic acid was significantly enhanced under two light combinations: 50% UV + 35% red + 15% blue and 50% far-red + 35% red + 15% blue (Ptak et al., 2024). After 24 days of red and blue light exposure, the levels of total anthocyanins, flavonoids, and phenolics increased in Brassica rapa (Bungala et al., 2024). Similarly, when Cannabis sativa was exposed to a light combination of 90% red, 8% blue, and 1% far-red for 43 days, the contents of 9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol were increased (Carranza-Ramírez et al., 2025). Palma et al. (2022) showed that when Cucumis sativus was grown under green light for 9 days followed by UV supplementation for an additional 14 days, phenolic compounds increased, however, plants exposed to UV under a blue light background exhibited reduced metabolites associated with the hydrocinnamate or flavonoid pathway. Under mixed red-blue light (70% red + 30% blue), the accumulation of total phenolics and rosmarinic acid in Melissa officinalis was increased, which may be due to the up-regulation of genes related to primary metabolism (e.g., DAHPS for aromatic amino acids) and secondary metabolism (e.g., TAT, RAS for phenylpropanoid biosynthesis) (Ahmadi et al., 2022). Therefore, light quality combination technology enables targeted improvement of crop quality, offering new strategies for developing functional plant products and natural medicines. This multi-light synergistic regulation not only enhances the yield of secondary metabolites but also precisely modifies their compositional ratios, demonstrating broad prospects for future applications.
3 Effects of light intensity on plant secondary metabolites
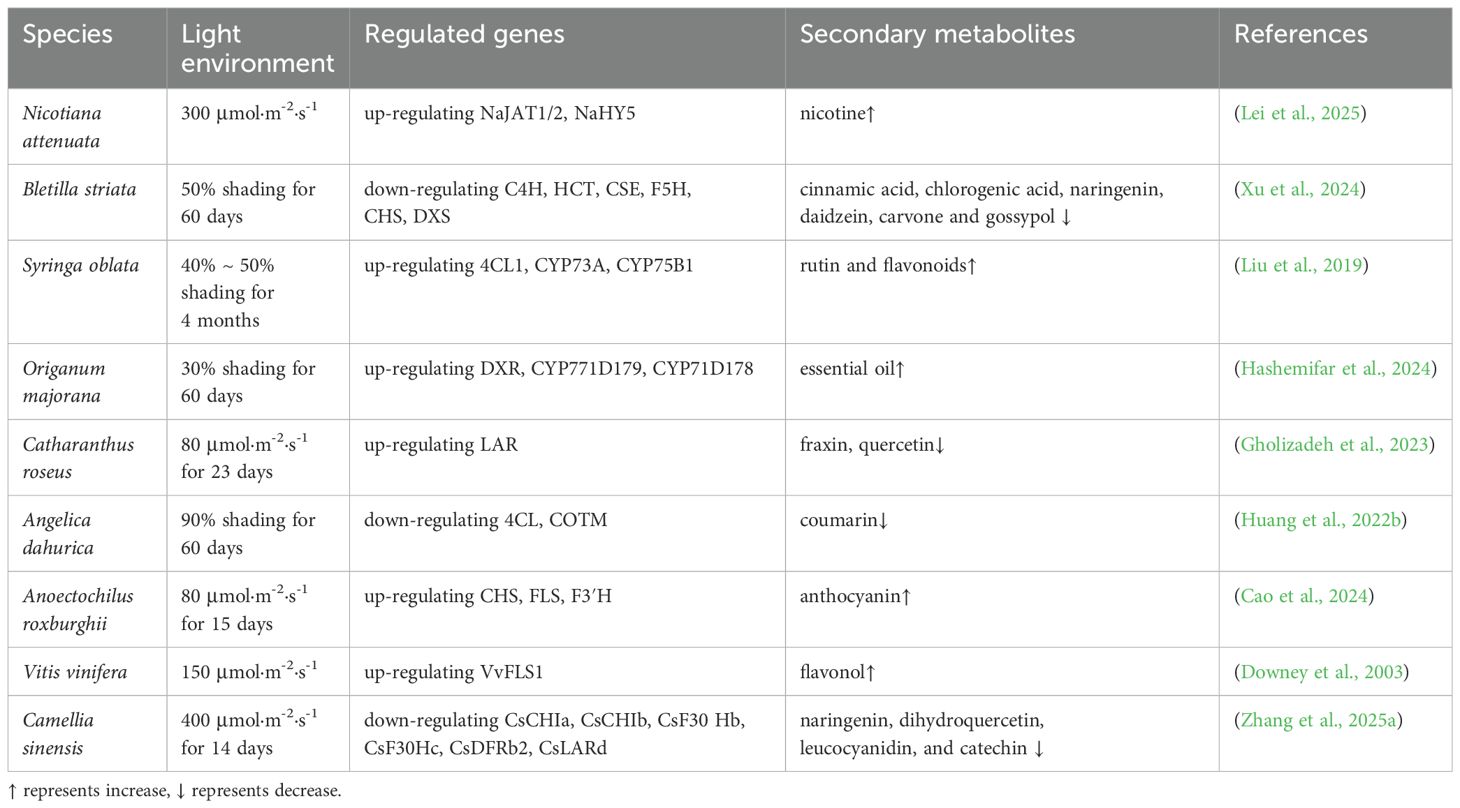
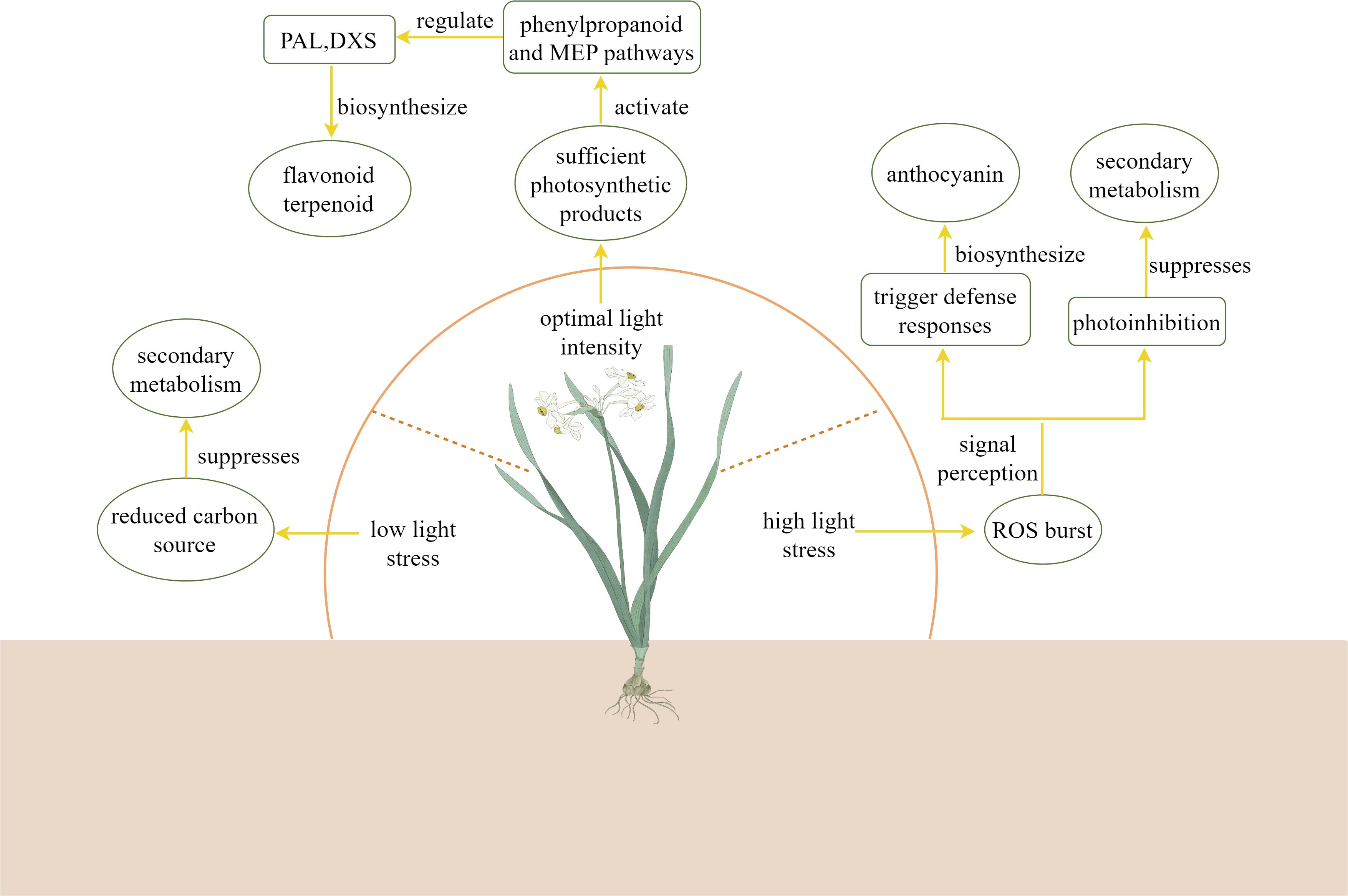
Light intensity is one of the key environmental factors influencing the biosynthesis of plant secondary metabolites. As shown in Table 2, the effects of different light intensity treatments on the secondary metabolites of plants varied. While different light intensities regulate the production and accumulation of various secondary metabolites by altering plant physiological states and metabolic pathways (Formisano et al., 2022). As illustrated in the Figure 5, under low light stress, carbon source accumulation in plants is suppressed, thereby inhibiting secondary metabolite biosynthesis (Shi et al., 2015). Within optimal light ranges, plants achieve peak photosynthetic efficiency, providing sufficient carbon sources and energy to support secondary metabolism (Wang et al., 2020b; An et al., 2022). Under these conditions, plants activate multiple metabolic pathways: they enhance phenylpropanoid metabolism to increase synthesis of antioxidant compounds like flavonoids and phenolics (Liu et al., 2019), while simultaneously stimulating production of terpenoids including volatile monoterpenes and sesquiterpenes (Reichel et al., 2022). However, under high-light stress, the burst of ROS in plants damages the photosynthetic apparatus, reducing ATP/NADPH supply (Borbély et al., 2022). In response to stress signals, plants initiate protective responses (Zhang et al., 2025a). At this time, photosystem II activates defense mechanisms through signal transduction pathways that induce synthesis of protective compounds (Wu et al., 2016). This process leads to significant accumulation of photoprotective pigments such as anthocyanins and carotenoids, along with increased production of defensive secondary metabolites like alkaloids (Zhang et al., 2019). Alternatively, when photoprotection fails, photoinhibition occurs, negatively impacting secondary metabolite biosynthesis (Huang et al., 2022a). Studies demonstrate that high-intensity light stress induces photo-oxidation in etiolated Camellia sinensis, which upregulates the expression of CHI and F3’H genes through the dihydroxy flavonoids and xanthophyll cycle pathways. This metabolic response enhances the accumulation of flavonoid antioxidants such as quercetin, thereby establishing a photoprotective mechanism via ROS scavenging to mitigate light stress tolerance (Zhang et al., 2017). Cao et al. (2024) compared different light intensities in Anoectochilus roxburghii cultivation and measured anthocyanin content. The results demonstrated that under 75% transmittance (80 μmol·m2·s1), the expression levels of CHS, FLS, and F3’H genes were significantly upregulated, leading to increased anthocyanin accumulation. High-intensity light irradiation promotes both a higher net photosynthetic rate and upregulation of PAL, 4CL, and C4H enzyme expression in Asarum heterotropoides, consequently enhancing essential oil biosynthesis (Wang et al., 2020b). Under high light intensity (400 μmol·m2·s1), the gene expression of CsCHIa, CsCHIb, CsF3’Hb, CsF3’Hc, CsDFRb2, and CsLARd in Camellia sinensis was downregulated, leading to reduced accumulation of naringenin, dihydroquercetin, leucocyanidin, and catechin (Zhang et al., 2025a). As a key gene of nicotine biosynthesis in Nicotiana attenuata, NaABI4 activates the gene expression of NaJAT1/2 and NaHY5 under the light intensity of 300 μmol·m-2·s-1, increases the accumulation of nicotine and promotes nicotine biosynthesis (Lei et al., 2025).
Conversely, under low light stress, plants prioritize energy allocation to essential metabolic processes, often reducing synthesis of complex secondary metabolites while maintaining certain specific compounds at elevated levels (Huang et al., 2022b; Kamal et al., 2022). Yamawo and Tomlinson (2023) showed that the total phenolic content in Aralia elata decreased under low light conditions. In Bletilla striata, 50% shading (transmitting 50% natural sunlight) for 60 days downregulates genes involved in phenylpropanoidand and flavonoid(C4H, HCT, CSE, F5H, CHS) biosynthesis, as well as the terpenoid pathway gene DXS, reducing corresponding metabolite levels (Xu et al., 2024). Mangifera indica bagging treatments upregulate LAR expression while suppressing proanthocyanidin accumulation in fruit peel, with additional modulation of flavonoid biosynthesis through MYB, bHLH, ERF, WRKY and bZIP gene regulation (Qian et al., 2023). In Angelica dahurica, Huang et al. (2022b) observed that 90% shading downregulates 4CL and COTM to inhibit coumarin biosynthesis, while 50% shading upregulates PAL to promote coumarin accumulation. Compared to full sunlight (0% shading), 30% shading increased the content of total phenolics, total flavonoids, and chlorogenic acid in Ipomoea batatas (Jing et al., 2023). As a shade-tolerant plant, Glechoma longituba exhibits increased aboveground dry matter yield and enhanced accumulation of ursolic acid and oleanolic acid under appropriate shading, thereby improving its medicinal value (Zhang et al., 2015). Compared to normal light intensity (1000 μmol·m2·s1), low-light stress (250 μmol·m2·s1) suppressed carotenoid and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Brassica campestris, resulting in a phenotypic shift from purple to green leaves (Zhu et al., 2017). Therefore, these findings demonstrate that precise light intensity regulation represents a powerful tool for targeted enrichment of valuable metabolites in medicinal plant cultivation.
4 Effects of photoperiod on plant secondary metabolites
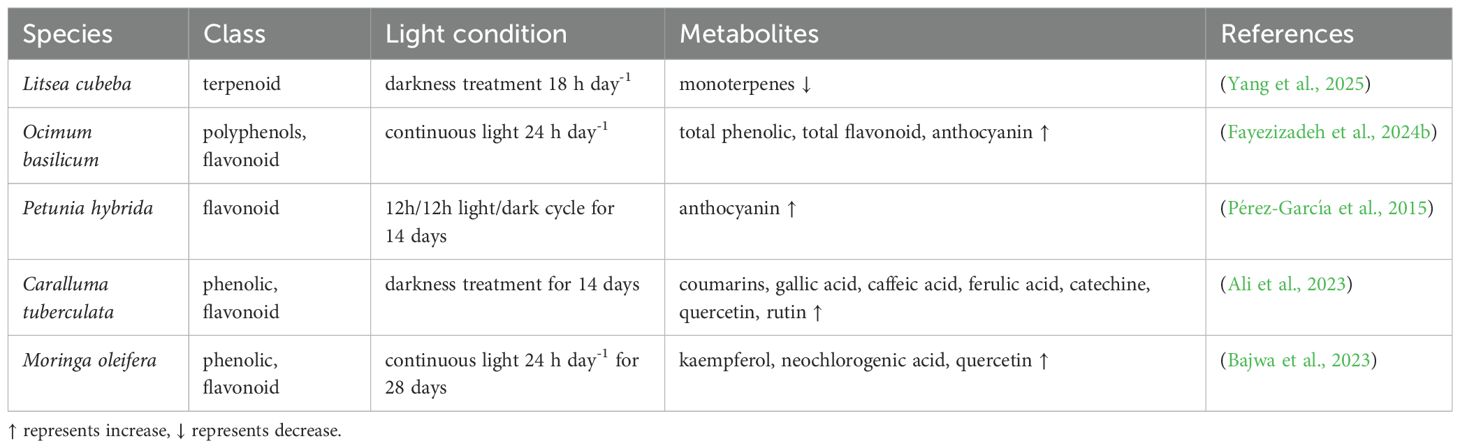
Photoperiod is a crucial environmental signal regulating plant physiological metabolism, which modulates the biosynthesis dynamics of plant secondary metabolites through the circadian clock system and light signal transduction network. The primary mechanism involves plants perceiving changes in day length via specific photoreceptors (e.g., phytochromes, cryptochromes) and transmitting light signals to the central circadian clock, ultimately forming a cascade response system of light signal-circadian rhythm-metabolic network (Flis et al., 2016; Djerrab et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2023; Pérez-Llorca and Müller, 2024). At the metabolic regulation level, the photoperiod effect is mainly reflected in regulating the diurnal expression patterns of key enzymes PAL and TAL in the phenylpropanoid pathway, influencing the synthesis rhythm of flavonoids and phenolic compounds (Vazirifar et al., 2021; Fukuda et al., 2022). Additionally, photoperiod affects the periodic accumulation of terpenoids (Ali et al., 2018; D’aquino et al., 2024) and the synthesis dynamics of nitrogen-containing secondary metabolites (Campos-Tamayo et al., 2008; Akhgari et al., 2015), which may be involved in the plant’s adaptation to light environments. From an ecological perspective, photoperiod-regulated metabolite changes reflect plant adaptation strategies to seasonal environments. As shown in Table 3, photoperiodic changes regulate the accumulation of plant secondary metabolites.
Long-day conditions promote the synthesis of pigments and volatile compounds related to reproduction. In Litsea cubeba, dark treatment significantly reduces monoterpene content in fruits and suppresses gene expression in the MVA and MEP pathways (Yang et al., 2025). Studies have shown that basil exhibits increased levels of total phenolics, flavonoids, and anthocyanins under a 24-hour photoperiod (Fayezizadeh et al., 2024b). Continuous white light (24 hours) for 28 days increases total phenolics and flavonoids (e.g., kaempferol, neochlorogenic acid, quercetin) in Moringa oleifera (Bajwa et al., 2023). Moreover, the accumulation of anthocyanins, carotenoids and flavonoids in plants is regulated by the circadian clock and adapts to photoperiod changes, thereby maintaining circadian clock integrity (Covington et al., 2008; Hildreth et al., 2022; Odgerel et al., 2022). When the photoperiod changes, the regulation of circadian rhythm-related processes affects phenylpropanoid biosynthesis in Populus tremula (Hoffman et al., 2010). In Arabidopsis thaliana, light regulates the interaction between the circadian transcription factors RVE8 and LNK, thereby promoting anthocyanin accumulation (Pérez-García et al., 2015). Studies demonstrate that extended photoperiods enhance the accumulation of volatile compounds in Ocimum basilicum, including linalool, eucalyptol, and eugenol (D’aquino et al., 2024). Many genes in the phenylpropanoid biosynthesis pathway are controlled by the circadian clock and phenylpropanoid-derived secondary metabolites in Arabidopsis thaliana are synthesized to protect cells from photoinhibition (Harmer et al., 2000). In Arabidopsis thaliana, the expression of AtMYB genes is regulated by the circadian clock and promotes anthocyanin biosynthesis in a circadian clock-dependent manner (Nguyen and Lee, 2016). Light promotes glucosinolate biosynthesis in Brassica rapa by modulating the circadian clock gene BrGI (Kim et al., 2021). However, short-day conditions induce the accumulation of stress-resistant metabolites. Ali et al. (2023) cultivated Caralluma tuberculata in complete darkness for 2 weeks with 100 μg/L SeNPs, then transferring them to normal light until day 56, which showed increased contents of coumarin, gallic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, catechin, quercetin, and rutin. Supplementing Solanum lycopersicum with 3-hour morning light boosts phenolics accumulation but reduces flavonoids, whereas 3-hour evening light increases flavonoids without significantly affecting phenolics (Wang et al., 2022). The studies showed that Begonia semperflorens seedlings grown under short days accumulate more carbohydrates and ABA, both of which induce anthocyanin biosynthesis (Zhang et al., 2016). Thus, the core of these “time-dependent metabolic regulation” mechanisms lies in the circadian clock system’s integration and transduction of environmental signals, precisely controlling secondary metabolic pathway activity to optimize plant ecological adaptability (Seaton et al., 2018). This principle holds significant application value in medicinal plant cultivation and specialty agricultural production, providing a theoretical foundation and technical pathway for the temporal precision regulation of metabolites.
5 Light-induced secondary metabolism in plant organs and its technical applications
Light exerts crucial effects on plant growth and development, not only by providing energy for photosynthesis but also by activating multiple signaling pathways to regulate secondary metabolism. Plants perceive light signals through photoreceptors such as phytochromes and cryptochromes, which collaborate with transcription factors (e.g., HY5, PIFs) to form a sophisticated light-signaling network, modulating the synthesis of metabolites in different tissues. Due to structural and functional differentiation among plant organs, leaves, flowers, fruits, and roots exhibit distinct responses to light environments, which determines the distribution patterns of various metabolites. Upon light signal perception by photoreceptors, plants initiate tissue-specific response programs that regulate secondary metabolism through hormonal signaling and transcriptional networks. Taking leaves as an example, their photosynthetic and defensive functions are closely light-dependent. Blue or far-red light activates the leaf photoreceptor system, which modulates MYB transcription factors to alter the phenylpropanoid pathway, thereby enhancing antioxidant production (Zhou et al., 2024). Different light radiation triggers intracellular signaling through specific receptor systems, thereby regulating the synthesis of secondary metabolites such as phenylpropanoids and terpenoids. This process determines the accumulation patterns of defense-related compounds, pigments, or pharmaceutically valuable substances in leaves (Zhu et al., 2017). As crucial reproductive structures in plants, flowers not only facilitate pollination but also serve as biosynthesis sites for diverse secondary metabolites, with their development and metabolic activities being light-regulated. The photoreceptor systems distributed in flowers perceive and transduce light signals, subsequently activating transcription factors (e.g., HY5, MYBs) to modulate phenylpropanoid and terpenoid metabolic pathways (Marzi et al., 2020). Physiologically, light influences the synthesis of anthocyanins and other pigments that determine floral coloration, while simultaneously regulating the accumulation of volatile aromatic compounds and defensive metabolites (Guo et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020). These light-mediated changes carry significant ecological implications: floral pigmentation and fragrance attract pollinators, while defensive compounds enhance reproductive success, thereby optimizing the coordination between developmental processes and metabolic homeostasis. As an essential component of plant reproductive systems, fruits undergo light-regulated physiological processes affecting pigmentation and ripening (Dzakovich et al., 2016). In Solanum lycopersicum, UV-B radiation significantly enhances carotenoid and anthocyanin biosynthesis through the HY5-mediated signaling pathway (Abramova et al., 2023). Furthermore, under 150 µmol·m2·s1 light intensity, upregulated expression of the VvFLS1 gene in Vitis vinifera promotes flavonol production (Downey et al., 2003). Although plant roots do not directly perform photosynthesis, their growth and metabolism remain under photoregulation. This regulation primarily involves light signal perception and response - root tips detect red light signals through phytochromes to trigger negative phototropism, forming characteristic skotomorphogenic growth patterns as demonstrated by inhibited root elongation in Arabidopsis thaliana (Van Gelderen et al., 2018; Spaninks and Offringa, 2023). Furthermore, shoot-to-root communication influences root systems through photosynthetic assimilate allocation, phytohormone network regulation, and systemic signaling transduction three pathways (Valbuena et al., 2018; Leschevin et al., 2024).
The application of light-regulated plant secondary metabolites refers to the targeted induction of functionally specific secondary metabolite biosynthesis in plants through manipulation of light parameters, enabling their industrial utilization in agriculture, medicine, food production, and other fields. In enclosed cultivation systems such as photobioreactors and artificial climate chambers, spectral-tunable LED panels are used to optimize metabolite production by selecting specific wavelength combinations for different metabolites, employing photosensors for real-time monitoring and automatic adjustment of light intensity, and designing photoperiods according to plant circadian rhythms, thereby maximizing the accumulation of secondary metabolites (Hoffman et al., 2010). In vertical farming systems, a stratified lighting strategy with three-dimensional spectral recipes can be implemented: upper layers utilize UV-B to enhance flavonoid production, middle layers employ blue-red light combinations to increase fresh and dry weight, while lower layers apply far-red light to stimulate the accumulation of root bioactive compounds (Larsen et al., 2020; Yoon et al., 2021; Kim et al., 2025). Greenhouse control systems can integrate natural sunlight with LED supplemental lighting to automatically activate specific light wavelengths during low-light seasons, ensuring stable metabolite production. Additionally, stress-induction techniques can be employed, such as short-term high-intensity illumination or UV pulsed irradiation, to activate plant defense metabolic pathways. During the postharvest storage of plants, light treatment technology can effectively preserve and enhance functional components. For example, blue light irradiation during Solanum lycopersicum storage helps delay softening, reduce decay, and better maintain fruit quality (Grzegorzewska et al., 2024). Brief UV-C irradiation applied to postharvest Vigna radiata effectively reduces fresh weight loss, while increasing total phenolics, protein content, and antioxidant capacity (Tripathi et al., 2024). Under 10°C storage conditions, red-blue LED treatment extends the shelf life of Brassica oleracea by 4 days (Liu et al., 2025). Based on these findings, an integrated LED lighting and temperature-controlled storage system was developed to achieve superior plant preservation, enhanced quality, and maintained bioactivity.
6 Discussion
6.1 Light signaling regulates the production of plant secondary metabolites
Light environment is a key ecological factor influencing plant physiological processes, and its regulatory role in secondary metabolites has become a research hotspot in the field of plant science. Studies have shown that light quality, intensity, and photoperiod can regulate the biosynthesis and accumulation of plant secondary metabolites through complex photoreceptor systems, such as phytochromes, cryptochromes, and UVR8 receptor proteins, and signal transduction networks (Ballaré, 2014; Taulavuori et al., 2017; Tossi et al., 2019). This light-mediated regulation not only leads to quantitative changes in end-product content but also affects the expression of key enzyme genes in metabolic pathways (Hideg et al., 2013; Li et al., 2017). In-depth exploration of this regulatory mechanism holds significant value for understanding the evolutionary history of plant photoadaptation and developing light-based strategies for crop quality improvement. From a fundamental research perspective, it provides new insights into the molecular mechanisms of plant environmental adaptation and the regulatory principles of metabolic networks. In practical applications, precise control of light environment parameters can effectively optimize the active compound profiles of medicinal plants and enhance the nutritional and functional properties of agricultural products, which lays a technological foundation for modern facility agriculture and industrialized plant production systems. To leverage the potential of light-regulated plant secondary metabolite accumulation, we can utilize precisely tuned light wavelengths and intensities to achieve targeted biosynthesis of desired metabolites. This integrated approach combines plant photobiology, metabolic pathway characteristics, and engineered control methods, featuring dynamic multi-wavelength switching through tunable LED arrays optimized for different metabolic stages, light intensity gradient optimization with photosensor-enabled real-time adjustment to prevent photoinhibition, and temporal light modulation synchronized with circadian rhythms for enhanced pathway efficiency. Currently, LED-based spectral modulation technology has been widely applied in the commercial cultivation of various medicinal crops, significantly improving the production efficiency of target bioactive compounds (Sankhuan et al., 2022a; Dsouza et al., 2024). These light-regulation technologies exhibit broad application potential, including the production of high-value therapeutics like paclitaxel in optically controlled bioreactor systems (Fernie et al., 2024). LED lighting technology enhances the nutritional quality of Ocimum basilicum and Mentha canadensis plants (Jakubczyk et al., 2024). Developing photo-optimized stress-resistant crops to address climate change challenges in agricultural production (Zhao et al., 2023). Furthermore, light environment regulation has been successfully employed in the targeted cultivation of specialty functional crops, such as glucosinolate-rich Broccoli oleracea (Wang et al., 2021) and high-flavonoid-content Eruca sativa (Veremeichik et al., 2023). Future research must achieve breakthroughs in key technologies including intelligent light-control systems and dynamic metabolic modeling, while evaluating the adaptability between laboratory photic conditions and natural environments, along with potential ecological risks.
6.2 Integration of light signal transduction with metabolic and genetic regulatory networks
Elucidating the integration mechanism between the light signaling system and the plant secondary metabolic network is a core scientific question that urgently needs to be addressed in current research. Although regulatory factors such as HY5 and MYB are involved in light-responsive metabolic processes, the synergistic mechanisms among these core transcriptional regulators and their dynamic response patterns to different light environments still require in-depth exploration (Jiang et al., 2012; Job and Datta, 2021; Chang et al., 2025). In particular, there remain significant research gaps in understanding how the interaction between light signals and abiotic stress factors such as temperature, water, and salinity regulates secondary metabolic pathways. Another key scientific question worthy of further investigation is the species-specific differences in light regulation observed among different plant groups. Studies have shown that due to variations in evolutionary background and ecological adaptation strategies, different plant species may exhibit markedly distinct metabolic responses to the same light conditions (Siatkowska et al., 2021; Jakubczyk et al., 2024). Taking light-adapted plants as an example, sun-loving and shade-tolerant plants may have fundamental differences in the molecular mechanisms of light regulated secondary metabolism, posing challenges for developing precise light regulation strategies in crops (Zhang et al., 2017; Tavridou et al., 2020). From a technological application perspective, integrating light environment control with metabolic engineering is regarded an innovative strategy to improve the production of target metabolites. In addition, by modifying light responsive elements or optimizing key transcriptional regulators, it may be possible to achieve precise regulation of plant secondary metabolic pathways (Riaz et al., 2019; Shi et al., 2024). Current advances in genetic and metabolic engineering focus on wavelength-specific photosensitive promoters (e.g., UV-responsive synthetic elements) to enable spatiotemporal control of metabolic pathways. AI-assisted photoreceptor engineering enhances environmental adaptability, while integrated ROS-sensing systems coordinate antioxidant defenses with secondary metabolite production. Key challenges include:incorporation of extremophile-derived resistance genes for improved stress tolerance, optimization of non-photochemical quenching mechanisms, and dynamic balancing between stress resilience and metabolic yield efficiency. However, such modifications may interfere with normal plant physiological and developmental processes, so it is necessary to find a balance between metabolic regulation and plant growth.
6.3 Intelligent regulation of light environment and multi-omics integrated research
Building an intelligent light environment regulation system may become a key research direction in the future. By leveraging artificial intelligence technology, a real-time monitoring network for plant physiological indicators and environmental parameters can be established to dynamically optimize light parameters and achieve precise regulation of secondary metabolites. This technological framework holds broad application prospects in plant factories and medicinal plant cultivation (Luna-Maldonado et al., 2016; Ren et al., 2023). Additionally, understanding the synergistic regulation mechanisms of multiple environmental factors is of significant research value. Investigating the interactions between light and key environmental variables such as CO2 concentration, temperature, and humidity, and constructing a multi-dimensional environmental regulation model will provide theoretical support for developing new and efficient cultivation methods (Han et al., 2024; Tanigawa et al., 2024). Against the backdrop of increasingly severe global climate change, conducting such multi-factor coupling studies is particularly urgent, offering critical implications for agricultural practices in response to climate challenges.
With advancements in photobiology, metabolomics, and synthetic biology, research on light mediated regulation of plant secondary metabolism is in a rapid development phase, deepening our understanding of complex regulatory systems (Bobrovskikh et al., 2022; Liao et al., 2024; Bechtold et al., 2025). Looking forward to the future, there is an urgent need to integrate multi-omics technologies, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, to systematically elucidate the molecular mechanisms of light-regulated secondary metabolism and translate fundamental research into practical applications, so as to give full unlock the potential of light-regulation technology in agricultural upgrading, drug development, and ecological conservation. In conclusion, light precisely regulates plant secondary metabolism through wavelength specificity, intensity, and duration. The core of these regulatory systems lies in photoreceptor-mediated signal perception, which triggers cascade reactions that activate specific transcription factors, thereby modulating the expression and activity of key metabolic enzymes (Qian et al., 2020). Based on this principle, optimizing crop quality or medicinal components using artificial light sources provides an innovative solution for replacing traditional chemical inducers with optical fertilizers, and also opens up new possibilities for green agriculture and sustainable development.
Author contributions
WW: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Writing – original draft, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Resources, Conceptualization. HW: Investigation, Resources, Writing – review & editing, Validation, Conceptualization. RL: Writing – original draft, Validation, Investigation, Conceptualization. SH: Validation, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Resources. LM: Writing – original draft, Resources, Investigation. MZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. FX: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition. HZ: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Project administration.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82060695); Guangxi Science and Technology Base and Talent Special Project (Gui Ke AD21238031); Guangxi Key Research and Development Program Project (Gui Ke AB21196016).
Acknowledgments
Some cartoon elements were obtained from https://www.figdraw.com for mechanism drawing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Glossary
UV: Ultraviolet light
HY5: hypocotyl 5
UVR8: UV Resistance Locus 8
MYB: myeloblastosis
COP1: constitutive photomorphogenic 1
CRY: cryptochrome
PHOT: phototropin
PHY: phytochrome
MEP: methylerythritol 4-phosphate
MVA: mevalonic acid
JA: jasmonic acid
SA: salicylic acid
ABA: abscisic acid
ROS: reactive oxygen species
LED: light emitting diodes
TL: Tubular Luminescent
FL: fluorescent lamp
CHS: chalcone synthase
PAL: phenylalanine ammonia-lyase
C4H: cinnamate 4-hydroxylase
4CL: 4-coumarate-CoA ligase
CHI: chalcone isomerase
F3’H: flavanone 3’-hydroxylase
FLS: flavonol synthase
GDHA: glutamate dehydrogenase A
PAO5: polyamine oxidase 5
JAZa: jasmonate ZIM-domain protein a
HSF: heat shock factor
C3H: Cys3/His
bHLH: basic Helix-Loop-Helix
CCR: cinnamoyl-CoA reductase
POD: peroxidase
ANR: anthocyanidin reductase
TAT: tyrosine aminotransferase
RAS: rosmarinic acid synthase
DHD: dihydrodipicolinate
SDH: shikimate dehydrogenase
LAR: leucoanthocyanidin reductase
PR1: pathogenesis-related protein 1
PR5: pathogenesis-related protein 5
JAZb: jasmonate ZIM-domain protein b
MYC: myelocytomatosis
COI1: coronatine-insensitive protein 1
JAR1: JA-amino synthetase
DAHPS: 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptolusonate 7-phosphate synthase
DFR: dihydroflavonol 4-reductase
STS: stilbene synthase
ADS: amorpha-4,11-dienesynthase
HMGR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase
DXS: 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate synthase
DXR: 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase
GGPPS: geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase
CPS: copalyl diphosphate synthase
HCT: hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA transferase
CSE: caffeoyl shikimate esterase
F5H: ferulate 5-hydroxylase
COMT: caffeic acid O-methyltransferase.
References
Abramova, A., Vereshchagin, M., Kulkov, L., Kreslavski, V. D., Kuznetsov, V. V., and Pashkovskiy, P. (2023). Potential role of phytochromes A and B and cryptochrome 1 in the adaptation of solanum lycopersicum to UV-B radiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 16. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713142
Ahmadi, T., Shabani, L., and Sabzalian, M. R. (2022). Light emitting diodes improved the metabolism of rosmarinic acid and amino acids at the transcriptional level in two genotypes of Melissa officinalis L. Funct. Plant Biol. 49, 1055–1069. doi: 10.1071/fp21364
Ahmed, S., Jamil, S., and Siddiqui, M. (2024). Secondary metabolites-God gifted arsenal for plants. J. Pharmacogn Phytochem. 13, 38–43. doi: 10.22271/phyto.2024.v13.i1a.14811
Aimvijarn, P., Payuhakrit, W., Charoenchon, N., Okada, S., and Suwannalert, P. (2023). Riceberry rice germination and UVB radiation enhance protocatechuic acid and vanillic acid to reduce cellular oxidative stress and suppress B16F10 melanogenesis relating to F-actin rearrangement. Plants-Basel 12, 12. doi: 10.3390/plants12030484
Akhgari, A., Yrjönen, T., Laakso, I., Vuorela, H., Oksman-Caldentey, K. M., and Rischer, H. (2015). Establishment of transgenic Rhazya stricta hairy roots to modulate terpenoid indole alkaloid production. Plant Cell Rep. 34, 1939–1952. doi: 10.1007/s00299-015-1841-6
Ali, H., Khan, M. A., Ullah, N., and Khan, R. S. (2018). Impacts of hormonal elicitors and photoperiod regimes on elicitation of bioactive secondary volatiles in cell cultures of Ajuga bracteosa. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 183, 242–250. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.044
Ali, A., Mashwani, Z.-U.-R., Raja, N. I., Mohammad, S., Luna-Arias, J. P., Ahmad, A., et al. (2023). Phytomediated selenium nanoparticles and light regimes elicited in vitro callus cultures for biomass accumulation and secondary metabolite production in Caralluma tuberculata. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1253193
Alsharafa, K., Vogel, M. O., Oelze, M. L., Moore, M., Stingl, N., König, K., et al. (2014). Kinetics of retrograde signalling initiation in the high light response of Arabidopsis thaliana. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B-Biological Sci. 369, 9. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0424
An, J., Wei, X. L., and Huo, H. H. (2022). Transcriptome analysis reveals the accelerated expression of genes related to photosynthesis and chlorophyll biosynthesis contribution to shade-tolerant in Phoebe bournei. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 14. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03657-y
Bajwa, M. N., Khanum, M., Zaman, G., Ullah, M. A., Farooq, U., Waqas, M., et al. (2023). Effect of wide-spectrum monochromatic lights on growth, phytochemistry, nutraceuticals, and antioxidant potential of in vitro callus cultures of moringa oleifera. Molecules (Basel Switzerland) 28, 13. doi: 10.3390/molecules28031497
Ballaré, C. L. (2014). ““Light regulation of plant defense,”,” in Annual review of plant biology, vol. 65 . Ed. Merchant, S. S. (Annual Reviews, Palo Alto), 335–363. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-040145
Bechtold, U., Burow, M., and Kangasjärvi, S. (2025). Translational photobiology: towards dynamic lighting in indoor horticulture. Trends Plant Sci. 30, 301–310. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2024.10.006
Bobrovskikh, A. V., Zubairova, U. S., Bondar, E. I., Lavrekha, V. V., and Doroshkov, A. V. (2022). Transcriptomic data meta-analysis sheds light on high light response in arabidopsis thaliana L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms23084455
Borbély, P., Gasperl, A., Pálmai, T., Ahres, M., Asghar, M. A., Galiba, G., et al. (2022). Light intensity- and spectrum-dependent redox regulation of plant metabolism. Antioxidants 11, 37. doi: 10.3390/antiox11071311
Brosset, A. and Blande, J. D. (2022). Volatile-mediated plant-plant interactions: volatile organic compounds as modulators of receiver plant defence, growth, and reproduction. J. Exp. Bot. 73, 511–528. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab487
Bungala, L. T. D., Park, S. U., Nguyen, B. V., Lim, J., Kim, K., Kim, J. K., et al. (2024). Effect of LED lights on secondary metabolites and antioxidant activities in red pakchoi baby leaves. ACS Omega 9, 23420–23430. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10261
Campos-Tamayo, F., Hernández-Domínguez, E., and Vázquez-Flota, F. (2008). Vindoline formation in shoot cultures of Catharanthus roseus is synchronously activated with morphogenesis through the last biosynthetic step. Ann. Bot. 102, 409–415. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcn108
Cao, J. Y., Zeng, J. J., Hu, R. Q., Liang, W. F., Zheng, T., Yang, J. J., et al. (2024). Comparative metabolome and transcriptome analyses of the regulatory mechanism of light intensity in the synthesis of endogenous hormones and anthocyanins in anoectochilus roxburghii (Wall.) lindl. Genes 15, 27. doi: 10.3390/genes15080989
Carranza-Ramírez, J. E., Borda, A. M., and Moreno-Fonseca, L. P. (2025). LED light modifies plant architecture, physiological parameters and cannabinoid content in three varieties of Cannabis sativa L. South Afr. J. Bot. 176, 231–240. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2024.11.023
Chang, Y. K., Shi, M. M., Wang, X., Cheng, H., Zhang, J. L., Liu, H. R., et al. (2025). A CRY1-HY5-MYB signaling cascade fine-tunes guard cell reactive oxygen species levels and triggers stomatal opening. Plant Cell 37, 19. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koaf064
Chen, I. G. J., Lee, M. S., Lin, M. K., Ko, C. Y., and Chang, W. T. (2018). Blue light decreases tanshinone IIA content in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots via genes regulation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 183, 164–171. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.013
Chen, M. Z., Zhong, X. M., Lin, H. S., and Qin, X. M. (2022). Combined transcriptome and metabolome analysis of musa nana laur. Peel treated with UV-C reveals the involvement of key metabolic pathways. Front. Genet. 12. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.792991
Cheng, Y., Xiang, N., Chen, H., Zhao, Y., Wang, L., Cheng, X., et al. (2023). The modulation of light quality on carotenoid and tocochromanol biosynthesis in mung bean (Vigna radiata) sprouts. Food Chem. Mol. Sci. 6, 100170. doi: 10.1016/j.fochms.2023.100170
Contreras-Avilés, W., Heuvelink, E., Marcelis, L. F. M., and Kappers, I. F. (2024). Ménage à trois: light, terpenoids, and quality of plants. Trends Plant Sci. 29, 572–588. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2024.02.007
Covington, M. F., Maloof, J. N., Straume, M., Kay, S. A., and Harmer, S. L. (2008). Global transcriptome analysis reveals circadian regulation of key pathways in plant growth and development. Genome Biol. 9, 18. doi: 10.1186/gb-2008-9-8-r130
D’aquino, L., Cozzolino, R., Malorni, L., Bodhuin, T., Gambale, E., Sighicelli, M., et al. (2024). Light flux density and photoperiod affect growth and secondary metabolism in fully expanded basil plants. Foods 13, 19. doi: 10.3390/foods13142273
Darko, E., Hamow, K. A., Marcek, T., Dernovics, M., Ahres, M., and Galiba, G. (2022). Modulated light dependence of growth, flowering, and the accumulation of secondary metabolites in chilli. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.801656
De Wit, M., Keuskamp, D. H., Bongers, F. J., Hornitschek, P., Gommers, C. M. M., Reinen, E., et al. (2016). Integration of phytochrome and cryptochrome signals determines plant growth during competition for light. Curr. Biol. 26, 3320–3326. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.10.031
Djerrab, D., Bertrand, B., Breitler, J. C., Léran, S., Dechamp, E., Campa, C., et al. (2021). Photoperiod-dependent transcriptional modifications in key metabolic pathways in Coffea arabica. Tree Physiol. 41, 302–316. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpaa130
Downey, M. O., Harvey, J. S., and Robinson, S. P. (2003). Synthesis of flavonols and expression of flavonol synthase genes in the developing grape berries of Shiraz and Chardonnay (Vitis vinifera L.). Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 9, 110–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-0238.2003.tb00261.x
Dsouza, A., Dixon, M., Shukla, M., and Graham, T. (2024). Harnessing controlled-environment systems for enhanced production of medicinal plants. J. Exp. Bot. 76, 76–93. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erae248
Dzakovich, M. P., Ferruzzi, M. G., and Mitchell, C. A. (2016). Manipulating sensory and phytochemical profiles of greenhouse tomatoes using environmentally relevant doses of ultraviolet radiation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 64, 6801–6808. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b02983
Escobar-Bravo, R., Schimmel, B. C. J., Zhang, Y. Q., Wang, L., Robert, C. a. M., Glauser, G., et al. (2024). Far-red light increases maize volatile emissions in response to volatile cues from neighbouring plants. Plant Cell Environ. 47, 3979–3998. doi: 10.1111/pce.14995
Fayezizadeh, M. R., Ansari, N. A., Sourestani, M. M., Fujita, M., and Hasanuzzaman, M. (2024a). Management of secondary metabolite synthesis and biomass in basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) microgreens using different continuous-spectrum LED lights. Plants-Basel 13, 18. doi: 10.3390/plants13101394
Fayezizadeh, M. R., Ansari, N. A., Sourestani, M. M., and Hasanuzzaman, M. (2024b). Variations in photoperiods and their impact on yield, photosynthesis and secondary metabolite production in basil microgreens. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 712. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05448-z
Fernie, A. R., Liu, F., and Zhang, Y. J. (2024). Post-genomic illumination of paclitaxel biosynthesis. Nat. Plants 10, 1875–1885. doi: 10.1038/s41477-024-01869-8
Fitzner, M., Schreiner, M., and Baldermann, S. (2023). Between eustress and distress: UVB induced changes in carotenoid accumulation in halophytic Salicornia europaea. J. Plant Physiol. 291, 10. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2023.154124
Flis, A., Sulpice, R., Seaton, D. D., Ivakov, A. A., Liput, M., Abel, C., et al. (2016). Photoperiod-dependent changes in the phase of core clock transcripts and global transcriptional outputs at dawn and dusk in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Environ. 39, 1955–1981. doi: 10.1111/pce.12754
Formisano, L., Miras-Moreno, B., Ciriello, M., Zhang, L. L., De Pascale, S., Lucini, L., et al. (2022). Between light and shading: morphological, biochemical, and metabolomics insights into the influence of blue photoselective shading on vegetable seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.890830
Fukuda, M. E. N., Yoshida, H., and Kusano, M. (2022). Effects of light quality, photoperiod, CO2 concentration, and air temperature on chlorogenic acid and rutin accumulation in young lettuce plants br. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 186, 290–298. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2022.07.010
Gai, Q. Y., Lu, Y., Jiao, J., Fu, J. X., Xu, X. J., Yao, L., et al. (2022). Application of UV-B radiation for enhancing the accumulation of bioactive phenolic compounds in pigeon pea Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. hairy root cultures. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 228, 11. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2022.112406
Gao, L., Liu, Q., Zhong, M., Zeng, N. N., Deng, W. X., Li, Y. X., et al. (2022). Blue light-induced phosphorylation of Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 is essential for its photosensitivity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 64, 1724–1738. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13331
Gholizadeh, F., Darkó, E., Benczúr, K., Hamow, K. A., Dernovics, M., Nagy, K., et al. (2023). Growth light substantially affects both primary and secondary metabolic processes in Catharanthus roseus plants. Photosynthetica 61, 451–460. doi: 10.32615/ps.2023.037
Grzegorczyk-Karolak, I., Gaweda-Walerych, K., Ejsmont, W., Owczarek-Januszkiewicz, A., Olszewska, M., Grabkowska, R., et al. (2025). Polyphenol production and gene expression in sage shoot cultures exposed to light-emitting diodes. J. Photochem. photobiology. B Biol. 264, 113106. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2025.113106
Grzegorzewska, M., Szwejda-Grzybowska, J., Mieszczakowska-Frac, M., and Matysiak, B. (2024). Postharvest LED treatment of tomatoes harvested at an early stage of coloration. Agronomy-Basel 14, 18. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14112727
Gu, H., Peng, Z., Kuang, X., Hou, L., Peng, X., Song, M., et al. (2024). Enhanced synthesis of volatile compounds by UV-B irradiation in artemisia argyi leaves. Metabolites 14, 14. doi: 10.3390/metabo14120700
Gu, X., Yang, L., Zhang, D., Zhang, S., Zhou, S., Dong, N., et al. (2025). Manipulation of artificial light environment improves tropane alkaloids content in Atropa belladonna L. Plant Physiol. biochemistry: PPB 223, 109828. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109828
Guo, X. L., Yu, C., Luo, L., Wan, H. H., Zhen, N., Li, Y. S., et al. (2018). Developmental transcriptome analysis of floral transition in Rosa odorata var. gigantea. Plant Mol. Biol. 97, 113–130. doi: 10.1007/s11103-018-0727-8
Han, R., Ma, L., Terzaghi, W., Guo, Y., and Li, J. G. (2024). Molecular mechanisms underlying coordinated responses of plants to shade and environmental stresses. Plant J. 117, 1893–1913. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16653
Harmer, S. L., Hogenesch, L. B., Straume, M., Chang, H. S., Han, B., Zhu, T., et al. (2000). Orchestrated transcription of key pathways in Arabidopsis by the circadian clock. Science 290, 2110–2113. doi: 10.1126/science.290.5499.2110
Hashemifar, Z., Sanjarian, F., Badi, H. N., and Mehrafarin, A. (2024). Varying levels of natural light intensity affect the phyto-biochemical compounds, antioxidant indices and genes involved in the monoterpene biosynthetic pathway of Origanum majorana L. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 13. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05739-5
He, R., Li, Y. M., Ou, S. Y., Gao, M. F., Zhang, Y. T., Song, S. W., et al. (2021). Regulation of growth and main health-promoting compounds of chinese kale baby-leaf by UV-A and FR light. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.799376
Hideg, É., Jansen, M., and Strid, Å. (2013). UV-B exposure, ROS, and stress: inseparable companions or loosely linked associates? Trends Plant Sci. 18, 107–115. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2012.09.003
Hildreth, S. B., Littleton, E. S., Clark, L. C., Puller, G. C., Kojima, S., and Winkel, B. S. J. (2022). Mutations that alter Arabidopsis flavonoid metabolism affect the circadian clock. Plant J. 110, 932–945. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15718
Hoang, H. H., Sechet, J., Bailly, C., Leymarie, J., and Corbineau, F. (2014). Inhibition of germination of dormant barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) grains by blue light as related to oxygen and hormonal regulation. Plant Cell Environ. 37, 1393–1403. doi: 10.1111/pce.12239
Hoffman, D. E., Jonsson, P., Bylesjö, M., Trygg, J., Antti, H., Eriksson, M. E., et al. (2010). Changes in diurnal patterns within the Populus transcriptome and metabolome in response to photoperiod variation. Plant Cell Environ. 33, 1298–1313. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2010.02148.x
Holalu, S. V., Reddy, S. K., Blackman, B. K., and Finlayson, S. A. (2020). Phytochrome interacting factors 4 and 5 regulate axillary branching via bud abscisic acid and stem auxin signalling. Plant Cell Environ. 43, 2224–2238. doi: 10.1111/pce.13824
Huang, X., Qin, B., Qin, L., Peng, Z. H., Xia, S. T., Su, Y., et al. (2022a). A comparative study on photosynthetic characteristics and flavonoid metabolism between Camellia petelotii (Merr.) Sealy and Camellia impressinervis Chang &Liang. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1071458
Huang, Y. J., Zhai, Y. N., Huang, Y., Huang, Y. F., Liu, K., Zhang, J., et al. (2022b). Effects of light intensity on physiological characteristics and expression of genes in coumarin biosynthetic pathway of angelica dahurica. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 16. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415912
Jadidi, M., Mumivand, H., Nia, A. E., Shayganfar, A., and Maggi, F. (2023). UV-A and UV-B combined with photosynthetically active radiation change plant growth, antioxidant capacity and essential oil composition of Pelargonium graveolens. BMC Plant Biol. 23, 14. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04556-6
Jahan, T., Huda, M. N., Zhang, K. X., He, Y. Q., Lai, D. L., Dhami, N., et al. (2025). Plant secondary metabolites against biotic stresses for sustainable crop protection. Biotechnol. Adv. 79, 39. doi: 10.1016/j.bioteChadv.2025.108520
Jaiswal, D. and Agrawal, S. B. (2021). Ultraviolet-B induced changes in physiology, phenylpropanoid pathway, and essential oil composition in two Curcuma species (C. caesia Roxb. and C. longa L.). Ecotoxicology Environ. Saf. 208, 12. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111739
Jakubczyk, K., Szymczykowska, K., Melkis, K., Maciejewska-Markiewicz, D., Nowak, A., Muzykiewicz-Szymanska, A., et al. (2024). The role of light in enhancing the nutritional and antioxidant qualities of basil, mint and lemon balm. Foods 13, 29. doi: 10.3390/foods13233954
Jiang, L., Wang, Y., Li, Q. F., Björn, L. O., He, J. X., and Li, S. S. (2012). Arabidopsis STO/BBX24 negatively regulates UV-B signaling by interacting with COP1 and repressing HY5 transcriptional activity. Cell Res. 22, 1046–1057. doi: 10.1038/cr.2012.34
Jing, X. J., Chen, P. R., Jin, X. J., Lei, J., Wang, L. J., Chai, S. S., et al. (2023). Physiological, photosynthetic, and transcriptomics insights into the influence of shading on leafy sweet potato. Genes 14, 15. doi: 10.3390/genes14122112
Job, N. and Datta, S. (2021). PIF3/HY5 module regulates BBX11 to suppress protochlorophyllide levels in dark and promote photomorphogenesis in light. New Phytol. 230, 190–204. doi: 10.1111/nph.17149
Kamal, F., Shen, S. L., Hu, R., Zhang, Q. W., Yin, N. W., Ma, Y. F., et al. (2022). Metabolite characteristics analysis of siliques and effects of lights on the accumulation of glucosinolates in siliques of rapeseed. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.817419
Kang, S. H., Kim, J. E., Zhen, S. Y., and Kim, J. (2022). Mild-intensity UV-A radiation applied over a long duration can improve the growth and phenolic contents of sweet basil. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.858433
Kapoor, S., Raghuvanshi, R., Bhardwaj, P., Sood, H., Saxena, S., and Chaurasia, O. P. (2018). Influence of light quality on growth, secondary metabolites production and antioxidant activity in callus culture of Rhodiola imbricata Edgew. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 183, 258–265. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.018
Khanal, S., Rochfort, S. J., and Steinbauer, M. J. (2025). Ultraviolet-A Radiation (UVA) as a Stress and the Influence of Provenance and Leaf Age on the Expression of Phenolic Compounds by Eucalyptus camaldulensis ssp. camaldulensis. Plants-Basel 14, 16. doi: 10.3390/plants14030493
Kim, N. S., Kim, S. J., Jo, J. S., Lee, J. G., Lee, S. I., Kim, D. H., et al. (2021). The brGI circadian clock gene is involved in the regulation of glucosinolates in chinese cabbage. Genes 12, 16. doi: 10.3390/genes12111664
Kim, Y. L., Sim, H. S., Jang, S. N., Lee, J. H., and Son, K. H. (2025). Changes in the growth and Lancemaside A content of Codonopsis lanceolata (deodeok) sprouts under LED-based lighting at different red/far-red ratios. Front. Plant Sci. 16. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1548781
Kivimäenpä, M., Mofikoya, A., Abd El-Raheem, A. M., Riikonen, J., Julkunen-Tiitto, R., and Holopainen, J. K. (2022). Alteration in light spectra causes opposite responses in volatile phenylpropanoids and terpenoids compared with phenolic acids in sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum) leaves. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 12287–12296. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c03309
Kwon, Y., Kim, C., and Choi, G. (2024). Phytochrome B photobody components. New Phytol. 242, 909–915. doi: 10.1111/nph.19675
Larsen, D. N., Woltering, E. J., Nicole, C. C. S., and Marcelis, L. F. M. (2020). Response of basil growth and morphology to light intensity and spectrum in a vertical farm. Front. Plant Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.597906
Le, A. T., Choi, I. L., Han, G. D., Kang, H. M., Jung, D. H., Park, W. P., et al. (2023). Colored LED lights: use one color alone or with others for growth in hedyotis corymbosa in vitro? Plants-Basel 12, 10. doi: 10.3390/plants12010093
Lee, S., Park, C. H., Kim, J. K., Ahn, K., Kwon, H., Kim, J. K., et al. (2023). LED Lights Influenced Phytochemical Contents and Biological Activities in Kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala) Microgreens. Antioxidants (Basel Switzerland) 12, 14. doi: 10.3390/antiox12091686
Lee, J. H., Tanaka, S., and Goto, E. (2022). Growth and biosynthesis of phenolic compounds of canola (Brassica napus L.) to different ultraviolet (UV)-B wavelengths in a plant factory with artificial light. Plants-Basel 11, 20. doi: 10.3390/plants11131732
Lei, B., Mao, Y., Zhao, H., Yu, J., Wang, B., Li, P., et al. (2025). ABA-INSENSITIVE 4 promotes nicotine biosynthesis under high light in Nicotiana attenuata. Plant science: an Int. J. Exp. Plant Biol. 353, 112416. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2025.112416
Leschevin, M., Ksas, B., Baltenweck, R., Hugueney, P., Caffarri, S., and Havaux, M. (2024). Photosystem rearrangements, photosynthetic efficiency, and plant growth in far red-enriched light. Plant J. 120, 2536–2552. doi: 10.1111/tpj.17127
Li, C. Y., Chen, J., Li, X. Y., Zhang, X., Liu, Y., Zhu, S. R., et al. (2022a). FERONIA is involved in phototropin 1-mediated blue light phototropic growth in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 64, 1901–1915. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13336
Li, T., Jia, K. P., Lian, H. L., Yang, X., Li, L., and Yang, H. Q. (2014). Jasmonic acid enhancement of anthocyanin accumulation is dependent on phytochrome A signaling pathway under far-red light in Arabidopsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 454, 78–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.10.059
Li, Y. H., Liu, S. Z., Shawky, E., Tao, M. L., Liu, A. M., Sulaiman, K., et al. (2022b). SWATH-based quantitative proteomic analysis of Morus alba L. leaves after exposure to ultraviolet-B radiation and incubation in the dark. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 230, 15. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2022.112443
Li, X., Liu, C. C., Zhao, Z. W., Ma, D. B., Zhang, J. Y., Yang, Y., et al. (2020). COR27 and COR28 are novel regulators of the COP1-HY5 regulatory hub and photomorphogenesis in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32, 3139–3154. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00195
Li, C. X., Xu, Z. G., Dong, R. Q., Chang, S. X., Wang, L. Z., Khalil-Ur-Rehman, M., et al. (2017). An RNA-seq analysis of grape plantlets grown in vitro reveals different responses to blue, green, red LED light, and white fluorescent light. Front. Plant Sci. 8. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00078
Liao, R. T., Liu, Z. J., Dongchen, W. H., Deng, X. P., Ma, E. D., Manzoor, N., et al. (2024). Integrated metabolomic and metagenomic strategies shed light on interactions among planting environments, rhizosphere microbiota, and metabolites of tobacco in Yunnan, China. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1386150
Liu, Y. Y., Chen, X. R., Wang, J. P., Cui, W. Q., Xing, X. X., Chen, X. Y., et al. (2019). Transcriptomic analysis reveals flavonoid biosynthesis of Syringa oblata Lindl. in response to different light intensity. BMC Plant Biol. 19, 16. doi: 10.1186/s12870-019-2100-8
Liu, Y., Fang, S. Z., Yang, W. X., Shang, X. L., and Fu, X. X. (2018). Light quality affects flavonoid production and related gene expression in Cyclocarya paliurus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 179, 66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.01.002
Liu, Z., Liu, W. J., Wang, Z. Q., Qi, K. J., Xie, Z. H., Zhang, S. L., et al. (2023). Diurnal transcriptome dynamics reveal the photoperiod response of Pyrus. Physiologia Plantarum 175, 18. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13893
Liu, H., Wang, Q., Zhou, S. W., Xing, Y. G., Xu, Q. L., Zhang, Q., et al. (2025). Effect of light from compound light emitting diodes on nutrient content and storage quality of broccoli plants. J. Food Process Eng. 48, 10. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.70167
Liu, B., Zuo, Z. C., Liu, H. T., Liu, X. M., and Lin, C. T. (2011). Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 interacts with SPA1 to suppress COP1 activity in response to blue light. Genes Dev. 25, 1029–1034. doi: 10.1101/gad.2025011
Lopes, E. M., Guimaraes-Dias, F., Gama, T. D. S., Macedo, A. L., Valverde, A. L., De Moraes, M. C., et al. (2020). Artemisia annua L. and photoresponse: from artemisinin accumulation, volatile profile and anatomical modifications to gene expression. Plant Cell Rep. 39, 101–117. doi: 10.1007/s00299-019-02476-0
Luna-Maldonado, A. I., Vidales-Contreras, J. A., and Rodríguez-Fuentes, H. (2016). Editorial: advances and trends in development of plant factories. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01848
Ma, T. Y., Gao, H., Zhang, D., Shi, Y. H., Zhang, T. Y., Shen, X. F., et al. (2020). Transcriptome analyses revealed the ultraviolet B irradiation and phytohormone gibberellins coordinately promoted the accumulation of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. Chin. Med. 15, 17. doi: 10.1186/s13020-020-00344-8
Ma, J. R., Zhang, J. X., Xie, L. L., Ye, J., Zhou, L., Yu, D. P., et al. (2024). Light quality regulates growth and flavonoid content in a widespread forest understorey medicinal species Scutellaria Baicalensis Georgi. Front. Plant Sci. 15. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1488649
Marzi, D., Brunetti, P., Mele, G., Napoli, N., Calò, L., Spaziani, E., et al. (2020). Light controls stamen elongation via cryptochromes, phytochromes and COP1 through HY5 and HYH. Plant J. 103, 379–394. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14736
Mazhar, M. W., Ishtiaq, M., Maqbool, M., Jafri, F. I., Siddiqui, M. H., Alamri, S., et al. (2024). Synergistic effects of selenium nanoparticles and LED light on enhancement of secondary metabolites in sandalwood (Santalum album) plants through in-vitro callus culturing technique. Peerj 12, 28. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18106
Miao, L. X., Zhao, J. C., Yang, G. Q., Xu, P., Cao, X. L., Du, S. S., et al. (2022). Arabidopsis cryptochrome 1 undergoes COP1 and LRBs-dependent degradation in response to high blue light. New Phytol. 234, 1347–1362. doi: 10.1111/nph.17695
Mokhtari, A., Ebrahimi, M., Azadi, P., Shariatpanahi, M., Amirian, R., Sobhani, A., et al. (2025). Elucidating the regulatory network of valerenic acid biosynthesis in Valeriana officinalis hairy roots under different light qualities: A coexpression perspective. Ind. Crops Products 226, 11. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2025.120625
Morales, L. O., Shapiguzov, A., Rai, N., Aphalo, P. J., and Brosché, M. (2025). Protection of photosynthesis by UVR8 and cryptochromes in arabidopsis under blue and UV radiation. Plant Cell Environ. 48, 6321–6335. doi: 10.1111/pce.15608
Moranska, E., Simlat, M., Warchol, M., Skrzypek, E., Waligórski, P., Laurain-Mattar, D., et al. (2023). Phenolic Acids and Amaryllidaceae Alkaloids Profiles in Leucojum aestivum L. In Vitro Plants Grown under Different Light Conditions. Molecules 28, 17. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041525
Morello, V., Brousseau, V. D., Wu, N., Wu, B. S., Macpherson, S., and Lefsrud, M. (2022). Light quality impacts vertical growth rate, phytochemical yield and cannabinoid production efficiency in cannabis sativa. Plants-Basel 11, 19. doi: 10.3390/plants11212982
Narra, F., Castagna, A., Palai, G., Havlík, J., Bergo, A. M., D’onofrio, C., et al. (2023). Postharvest UV-B exposure drives changes in primary metabolism, phenolic concentration, and volatilome profile in berries of different grape (Vitis vinifera L.) varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 103, 6340–6351. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12708
Nguyen, N. H. and Lee, H. (2016). MYB-related transcription factors function as regulators of the circadian clock and anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Signaling Behav. 11, 3. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2016.1139278
Odgerel, K., Jose, J., Karsai-Rektenwald, F., Ficzek, G., Simon, G., Végvári, G., et al. (2022). Effects of the repression of GIGANTEA gene StGI.04 on the potato leaf transcriptome and the anthocyanin content of tuber skin. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 18. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03636-3
Oh, J., Park, E., Song, K., Bae, G., and Choi, G. (2020). PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR8 inhibits phytochrome A-mediated far-red light responses in arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32, 186–205. doi: 10.1105/tpc.19.00515
Palma, C. F. F., Castro-Alves, V., Morales, L. O., Rosenqvist, E., Ottosen, C. O., Hyötyläinen, T., et al. (2022). Metabolic changes in cucumber leaves are enhanced by blue light but differentially affected by UV interactions with light signalling pathways in the visible spectrum. Plant Sci. 321, 10. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2022.111326
Pashkovskiy, P., Ivanov, Y., Ivanova, A., Kartashov, A., Zlobin, I., Lyubimov, V., et al. (2023). Effect of light of different spectral compositions on pro/antioxidant status, content of some pigments and secondary metabolites and expression of related genes in scots pine. Plants-Basel 12, 16. doi: 10.3390/plants12132552
Pashkovskiy, P., Vereshchagin, M., Kartashov, A., Ivanov, Y., Ivanova, A., Zlobin, I., et al. (2024). Influence of additional white, red and far-red light on growth, secondary metabolites and expression of hormone signaling genes in scots pine under sunlight. Cells 13, 18. doi: 10.3390/cells13020194
Pérez-García, P., Ma, Y., Yanovsky, M. J., and Mas, P. (2015). Time-dependent sequestration of RVE8 by LNK proteins shapes the diurnal oscillation of anthocyanin biosynthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States America 112, 5249–5253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1420792112
Pérez-Llorca, M. and Müller, M. (2024). Unlocking nature’s rhythms: insights into secondary metabolite modulation by the circadian clock. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 19. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137308
Péter, C., Adám, E., Klose, C., Grézal, G., Hajdu, A., Steinbach, G., et al. (2024). Phytochrome C and low temperature promote the protein accumulation and red-light signaling of phytochrome D. Plant Cell Physiol. 65, 1717–1735. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcae089
Pichersky, E. and Raguso, R. A. (2018). Why do plants produce so many terpenoid compounds? New Phytol. 220, 692–702. doi: 10.1111/nph.14178
Ptak, A., Szewczyk, A., Simlat, M., Pawlowska, B., and Warchol, M. (2024). LED light improves shoot multiplication, steviol glycosides and phenolic compounds biosynthesis in Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni in vitro culture. Sci. Rep. 14, 16. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81696-1
Qian, C. Z., Chen, Z. R., Liu, Q., Mao, W. W., Chen, Y. L., Tian, W., et al. (2020). Coordinated transcriptional regulation by the UV-B photoreceptor and multiple transcription factors for plant UV-B responses. Mol. Plant 13, 777–792. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.02.015
Qian, M. J., Wu, H. X., Yang, C. K., Zhu, W. C., Shi, B., Zheng, B., et al. (2023). RNA-Seq reveals the key pathways and genes involved in the light-regulated flavonoids biosynthesis in mango (Mangifera indica L.) peel. Front. Plant Sci. 13. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1119384
Rai, N., Neugart, S., Yan, Y., Wang, F., Siipola, S. M., Lindfors, A. V., et al. (2019). How do cryptochromes and UVR8 interact in natural and simulated sunlight? J. Exp. Bot. 70, 4975–4990. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz236
Reichel, P., Munz, S., Hartung, J., Kotiranta, S., and Graeff-Hönninger, S. (2022). Impacts of different light spectra on CBD, CBDA and terpene concentrations in relation to the flower positions of different cannabis sativa L. Strains. Plants-Basel 11, 19. doi: 10.3390/plants11202695
Ren, G. Q., Wu, H. Y., Bao, A. B., Lin, T., Ting, K. C., and Ying, Y. B. (2023). Mobile robotics platform for strawberry temporal-spatial yield monitoring within precision indoor farming systems. Front. Plant Sci. 14. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1162435
Riaz, B., Chen, H. Q., Wang, J., Du, L., Wang, K., and Ye, X. G. (2019). Overexpression of maize zmC1 and zmR transcription factors in wheat regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in a tissue-specific manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225806
Sankhuan, D., Niramolyanun, G., Kangwanrangsan, N., Nakano, M., and Supaibulwatana, K. (2022a). Variation in terpenoids in leaves of Artemisia annua grown under different LED spectra resulting in diverse antimalarial activities against Plasmodium falciparum. BMC Plant Biol. 22, 13. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03528-6
Sankhuan, D., Roytrakul, S., Nakano, M., and Supaibulwatana, K. (2022b). Proteomic sensing associated with terpenoid biosynthesis of Artemisia annua L. @ in response to different artificial light spectra. J. Plant Interact. 17, 19–32. doi: 10.1080/17429145.2021.2009582
Seaton, D. D., Graf, A., Baerenfaller, K., Stitt, M., Millar, A. J., and Gruissem, W. (2018). Photoperiodic control of the Arabidopsis proteome reveals a translational coincidence mechanism. Mol. Syst. Biol. 14, 19. doi: 10.15252/msb.20177962
Semenova, N. A., Ivanitskikh, A. S., Uyutova, N. I., Smirnov, A. A., Proshkin, Y. A., Burynin, D. A., et al. (2024). Effect of UV stress on the antioxidant capacity, photosynthetic activity, flavonoid and steviol glycoside accumulation of stevia rebaudiana bertoni. Horticulturae 10, 15. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae10030210
Shamala, L. F., Zhou, H. C., Han, Z. X., and Wei, S. (2020). UV-B induces distinct transcriptional re-programing in UVR8-signal transduction, flavonoid, and terpenoids pathways in camellia sinensis. Front. Plant Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00234
Sheteiwy, M. S., El-Sawah, A. M., Kobae, Y., Basit, F., Holford, P., Yang, H. S., et al. (2023). The effects of microbial fertilizers application on growth, yield and some biochemical changes in the leaves and seeds of guar (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba L.). Food Res. Int. 172, 14. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113122
Shi, D. L., Li, W. Y., Hopkinson, B. M., Hong, H. Z., Li, D. M., Kao, S. J., et al. (2015). Interactive effects of light, nitrogen source, and carbon dioxide on energy metabolism in the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. Limnology Oceanography 60, 1805–1822. doi: 10.1002/lno.10134
Shi, M., Zhang, S. W., Zheng, Z. Z., Maoz, I., Zhang, L., and Kai, G. Y. (2024). Molecular regulation of the key specialized metabolism pathways in medicinal plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 66, 510–531. doi: 10.1111/jipb.13634
Siatkowska, K., Chraniuk, M., Bollin, P., and Banasiuk, R. (2021). Light emitting diodes optimisation for secondary metabolites production by Droseraceae plants. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 224, 8. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112308
Singh, P. and Choudhary, K. K. (2025). Mechanistic insights on physiological, biochemical, and metabolite profiling of pearl millet cultivars focusing bioactive compounds under elevated UV-B radiation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 222, 15. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109682
Skowron, E., Trojak, M., and Pacak, I. (2024). Effects of UV-B and UV-C spectrum supplementation on the antioxidant properties and photosynthetic activity of lettuce cultivars. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 24. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179298
Skowron, E., Trojak, M., Pacak, I., Wezigowska, P., and Szymkiewicz, J. (2025). Enhancing the quality of indoor-grown basil microgreens with low-dose UV-B or UV-C light supplementation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 21. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052352
Spaninks, K. and Offringa, R. (2023). Local phytochrome signalling limits root growth in light by repressing auxin biosynthesis. J. Exp. Bot. 74, 4642–4653. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erad163
Su, P. F., Ding, S. S., Wang, D. C., Kan, W. J., Yuan, M., Chen, X., et al. (2024). Plant morphology, secondary metabolites and chlorophyll fluorescence of Artemisia argyi under different LED environments. Photosynthesis Res. 159, 153–164. doi: 10.1007/s11120-023-01026-w
Sun, Q., Li, X. Q., Sun, L., Sun, M. Y., Xu, H. W., and Zhou, X. F. (2024). Plant hormones and phenolic acids response to UV-B stress in Rhododendron chrysanthum pall. Biol. Direct 19, 13. doi: 10.1186/s13062-024-00483-0
Sweere, U., Eichenberg, K., Lohrmann, J., Mira-Rodado, V., Bäurle, I., Kudla, J., et al. (2001). Interaction of the response regulator ARR4 with phytochrome B in modulating red light signaling. Science 294, 1108–1111. doi: 10.1126/science.1065022
Takshak, S. and Agrawal, S. B. (2019). Defense potential of secondary metabolites in medicinal plants under UV-B stress. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 193, 51–88. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2019.02.002
Tanigawa, K., Yuchen, Q., Katsuhama, N., Sakoda, K., Wakabayashi, Y., Tanaka, Y., et al. (2024). C4 monocots and C4 dicots exhibit rapid photosynthetic induction response in contrast to C3 plants. Physiologia Plantarum 176, 13. doi: 10.1111/ppl.14431
Taulavuori, E., Taulavuori, K., Holopainen, J. K., Julkunen-Tiitto, R., Acar, C., and Dincer, I. (2017). Targeted use of LEDs in improvement of production efficiency through phytochemical enrichment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 97, 5059–5064. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8492
Tavridou, E., Schmid-Siegert, E., Fankhauser, C., and Ulm, R. (2020). UVR8-mediated inhibition of shade avoidance involves HFR1 stabilization in Arabidopsis. PloS Genet. 16, 19. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008797
Tossi, V. E., Regalado, J. J., Iannicelli, J., Laino, L. E., Burrieza, H. P., Escandón, A. S., et al. (2019). Beyond arabidopsis: differential UV-B response mediated by UVR8 in diverse species. Front. Plant Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00780
Tripathi, A., Meena, R., Sobhanan, A., Koley, T. K., Meghwal, M., and Giuffre, A. M. (2024). Influence of ultraviolet-C irradiation treatment on quality and shelf life of mung bean sprouts during storage. Ital. J. Food Sci. 36, 180–192. doi: 10.15586/ijfs.v36i4.2619
Valbuena, M. A., Manzano, A., Vandenbrink, J. P., Pereda-Loth, V., Carnero-Diaz, E., Edelmann, R. E., et al. (2018). The combined effects of real or simulated microgravity and red-light photoactivation on plant root meristematic cells. Planta 248, 691–704. doi: 10.1007/s00425-018-2930-x
Van Gelderen, K., Kang, C. K., Paalman, R., Keuskamp, D., Hayes, S., and Pierik, R. (2018). Far-red light detection in the shoot regulates lateral root development through the HY5 transcription factor. Plant Cell 30, 101–116. doi: 10.1105/tpc.17.00771
Vanhaelewyn, L., van der Straeten, D., De Coninck, B., and Vandenbussche, F. (2020). Ultraviolet radiation from a plant perspective: the plant-microorganism context. Front. Plant Sci. 11. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.597642
Vazirifar, S., Samari, E., and Sharifi, M. (2021). Daily dynamics of intermediate metabolite profiles lead to time-dependent phenylethanoid glycosides production in Scrophularia striata during the day/night cycle. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biology 225, 15. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112326
Veremeichik, G. N., Grigorchuk, V. P., Makhazen, D. S., Subbotin, E. P., Kholin, A. S., Subbotina, N. I., et al. (2023). High production of flavonols and anthocyanins in Eruca sativa (Mill) Thell plants at high artificial LED light intensities. Food Chem. 408, 12. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.135216
Viczián, A., Klose, C., Adám, É., and Nagy, F. (2017). New insights of red light-induced development. Plant Cell Environ. 40, 2457–2468. doi: 10.1111/pce.12880
Wang, P. J., Chen, S. R., Gu, M. Y., Chen, X. M., Chen, X. J., Yang, J. F., et al. (2020a). Exploration of the effects of different blue LED light intensities on flavonoid and lipid metabolism in tea plants via transcriptomics and metabolomics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 17. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134606
Wang, S. Y., Jin, N., Jin, L., Xiao, X. M., Hu, L. L., Liu, Z. C., et al. (2022). Response of tomato fruit quality depends on period of LED supplementary light. Front. Nutr. 9. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.833723
Wang, J. W., Mao, S. X., Wu, Q., Yuan, Y. M., Liang, M. T., Wang, S. Z., et al. (2021). Effects of LED illumination spectra on glucosinolate and sulforaphane accumulation in broccoli seedlings. Food Chem. 356, 7. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129550
Wang, X., Wang, Q., Han, Y. J., Liu, Q., Gu, L. F., Yang, Z. H., et al. (2017). A CRY-BIC negative-feedback circuitry regulating blue light sensitivity of Arabidopsis. Plant J. 92, 426–436. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13664
Wang, Z. Q., Xiao, S. Y., Wang, Y. F., Liu, J. Y., Ma, H. Q., Wang, Y. P., et al. (2020b). Effects of light irradiation on essential oil biosynthesis in the medicinal plant Asarum heterotropoides Fr. Schmidt var. mandshuricum (Maxim) Kitag. PloS One 15, 17. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237952
Wu, Q. J., Chen, Z. D., Sun, W. J., Deng, T. T., and Chen, M. J. (2016). De novo Sequencing of the Leaf Transcriptome Reveals Complex Light-Responsive Regulatory Networks in Camellia sinensis cv. Baijiguan. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00332
Xiao, S. Q., Li, D. W., Tang, Z. H., Wei, H. L., Zhang, Y., Yang, J., et al. (2023). Supplementary UV-B radiation effects on photosynthetic characteristics and important secondary metabolites in eucommia ulmoides leaves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 18. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098168
Xie, D. J., Tarin, M. W. K., Chen, L. Y., Ren, K., Yang, D. M., Zhou, C. C., et al. (2021). Consequences of LED lights on root morphological traits and compounds accumulation in sarcandra glabra seedlings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 19. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137179
Xu, S., Zhang, Y., Liang, F., Jiang, S., Niu, S., Wang, X., et al. (2024). Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal the mechanism of polysaccharide and secondary metabolite biosynthesis in Bletilla striata tubers in response to shading. Int. J. Biol. macromolecules 279, 135545. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135545
Yamawo, A. and Tomlinson, K. W. (2023). Defence plasticity in the spiny plant Aralia elata (Miq.) Seem. in response to light and soil fertility. Ann. Bot. 131, 1073–1080. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcac152
Yang, C. K., Wang, X. W., Zhu, W. C., Weng, Z. R., Li, F. L., Zhang, Y. W., et al. (2024). Metabolomic and transcriptomic analyses reveal the regulation mechanism of postharvest light-induced phenolics accumulation in mango peel. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 213, 13. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2024.117050
Yang, J., Zhao, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, Y., and Gao, M. (2025). A comprehensive analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomics reveals key genes involved in terpenes biosynthesis pathway of litsea cubeba under light and darkness treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 20. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072992
Yin, X. J., Fan, H., Chen, Y., Li, L. Z., Song, W., Fan, Y. M., et al. (2020). Integrative omic and transgenic analyses reveal the positive effect of ultraviolet-B irradiation on salvianolic acid biosynthesis through upregulation of SmNAC1. Plant J. 104, 781–799. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14952
Yin, X. J., Singer, S. D., Qiao, H. B., Liu, Y. J., Jiao, C., Wang, H., et al. (2016). Insights into the Mechanisms Underlying Ultraviolet-C Induced Resveratrol Metabolism in Grapevine (V. amurensis Rupr.) cv. “Tonghua-3. Front. Plant Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00503
Yoon, H. I., Kim, H. Y., Kim, J., and Son, J. E. (2021). Quantitative analysis of UV-B radiation interception and bioactive compound contents in kale by leaf position according to growth progress. Front. Plant Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.667456
Zha, L. Y., Wei, S. W., Huang, D. F., and Zhang, J. J. (2024). Multi-omics analyses of lettuce (Lactuca sativa) reveals primary metabolism reorganization supporting distinct features of secondary metabolism induced by supplementing UV-A radiation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 72, 15498–15511. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c00394
Zhang, H., Ge, Y., Hu, J., Wang, Y., Ni, D. J., Wang, P., et al. (2025a). Integrated analyses of metabolome, leaf anatomy, epigenome, and transcriptome under different light intensities reveal dynamic regulation of histone modifications on the high light adaptation in Camellia sinensis. Plant J. 121, 18. doi: 10.1111/tpj.70040
Zhang, L. X., Guo, Q. S., Chang, Q. S., Zhu, Z. B., Liu, L., and Chen, Y. H. (2015). Chloroplast ultrastructure, photosynthesis and accumulation of secondary metabolites in Glechoma longituba in response to irradiance. Photosynthetica 53, 144–153. doi: 10.1007/s11099-015-0092-7
Zhang, Y. J., Li, Y., Li, W. P., Hu, Z. L., Yu, X. H., Tu, Y., et al. (2019). Metabolic and molecular analysis of nonuniform anthocyanin pigmentation in tomato fruit under high light. Horticulture Res. 6, 21. doi: 10.1038/s41438-019-0138-2
Zhang, Q. F., Liu, M. Y., and Ruan, J. Y. (2017). Metabolomics analysis reveals the metabolic and functional roles of flavonoids in light-sensitive tea leaves. BMC Plant Biol. 17, 10. doi: 10.1186/s12870-017-1012-8
Zhang, Y. J., Sun, Y. J., Wang, Y., Zhou, D. D., and Tu, K. (2025c). Effects of blue and red LED treatments on carotenoid and soluble sugar metabolism in postharvest nectarine fruit and their correlation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 224, 11. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2025.109897
Zhang, P., Tang, Y. S., Liu, Y. J., Liu, J. N., Wang, Q. C., Wang, H. X., et al. (2023). Metabolic characteristics of self-pollinated wheat seed under red and blue light during early development. Planta 258, 22. doi: 10.1007/s00425-023-04217-w
Zhang, P., Tang, Y. S., Liu, J. N., Wang, Q. C., Li, L., Li, H. X., et al. (2024b). Multi-omics reveals the metabolic changes and genetic basis of post-flowering rice caryopsis under blue light. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 11, 19. doi: 10.1186/s40538-024-00654-1
Zhang, P., Tang, Y., Zhang, J., Liu, J., Li, L., Li, H., et al. (2025b). Multi-omics analysis of the accumulation mechanism of flavonoids in rice caryopsis under blue light. Plant Cell Rep. 44, 64. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03435-8
Zhang, J., Wang, C., Fang, W., Yang, R., and Yin, Y. (2024a). Production of high-quality wheat sprouts of strong antioxidant capacity: process optimization and regulation mechanism of red light treatment. Foods (Basel Switzerland) 13, 14. doi: 10.3390/foods13172703
Zhang, K. M., Wang, J. W., Guo, M. L., Du, W. L., Wu, R. H., and Wang, X. (2016). Short-day signals are crucial for the induction of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Begonia semperflorens under low temperature condition. J. Plant Physiol. 204, 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2016.06.021
Zhang, Y., Zhu, K., Wang, X., Yan, J., Zhu, H., Zhang, N., et al. (2024c). Manipulation of artificial light environment improves plant biomass and fruit nutritional quality in tomato. J. advanced Res. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.11.030
Zhao, H., Huang, X. Z., Yang, Z. E., Li, F. G., and Ge, X. Y. (2023). Synergistic optimization of crops by combining early maturation with other agronomic traits. Trends Plant Sci. 28, 1178–1191. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2023.04.011
Zheng, C., Ma, J. Q., Ma, C. L., Shen, S. Y., Liu, Y. F., and Chen, L. (2019). Regulation of growth and flavonoid formation of tea plants (Camellia sinensis) by blue and green light. J. Agric. Food Chem. 67, 2408–2419. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b07050
Zhong, W., Tian, X., Zhang, Y., Tang, X., Xiao, S., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Effects of Different Doses of sUV-B Exposure on Taxane Compounds’ Metabolism in Taxus wallichiana var. Mairei. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 13. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126407
Zhou, X. R., Cao, K., Meng, J. H., Xu, H. W., and Zhou, X. F. (2025). Strigolactone modulates phenolic acid accumulation and thereby improves tolerance to UV-B stress in Rhododendron chrysanthum Pall. Plant Cell Rep. 44, 20. doi: 10.1007/s00299-024-03393-7
Zhou, Y., Wu, W. S., Sun, Y., Shen, Y. Y., Mao, L. Z., Dai, Y. H., et al. (2024). Integrated transcriptome and metabolome analysis reveals anthocyanin biosynthesis mechanisms in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) leaves under continuous blue light irradiation. BMC Plant Biol. 24, 18. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04888-x
Zhu, H. F., Li, X. F., Zhai, W., Liu, Y., Gao, Q. Q., Liu, J. P., et al. (2017). Effects of low light on photosynthetic properties, antioxidant enzyme activity, and anthocyanin accumulation in purple pak-choi (Brassica campestris ssp Chinensis Makino). PloS One 12, 17. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179305
Keywords: light, plant, secondary metabolites, light quality, light intensity, photoperiod
Citation: Wu W, Wu H, Liang R, Huang S, Meng L, Zhang M, Xie F and Zhu H (2025) Light regulates the synthesis and accumulation of plant secondary metabolites. Front. Plant Sci. 16:1644472. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1644472
Received: 10 June 2025; Accepted: 17 July 2025;
Published: 04 August 2025.
Edited by:
Michael Moustakas, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceReviewed by:
Salman Ahmed, University of Karachi, PakistanMaria Fitzner, University of Bayreuth, Germany
Copyright © 2025 Wu, Wu, Liang, Huang, Meng, Zhang, Xie and Zhu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hua Zhu, emh1aHVhZ3hAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Fengfeng Xie, MTUxNzcxNDM1NTNAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Miao Zhang, MTc1MzU3NjQ4ODhAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Wenyuan Wu
Wenyuan Wu Huan Wu1
Huan Wu1 Miao Zhang
Miao Zhang Hua Zhu
Hua Zhu